The Neurological Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
|
|
|
- Cornelius Houston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Neurological Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Common or Concerning Symptoms Headache Dizziness Generalized, proximal or distal weakness Numbness Abnormal or loss of sensations Loss of consciousness, syncope or near-syncope Seizures Tremors or involuntary movements Health Promotion and Counseling Preventing stroke or TIA Reducing risk of peripheral neuropathy Detecting the three D s o Delirium o Dementia o depression The Neurological Examination Six Parts of the Neurological Exam o Mental Status o Cranial Nerves o Motor o Coordination o Sensory o Gait Concept of a Screening Exam Screening each of the parts allows one to check on the entire neuroaxis (Cortex, Subcortical White Matter, Basal Ganglia/Thalamus, Brainstem, Cerebellum, Spinal Cord, Peripheral Nerves, NMJ, and Muscles) Expand evaluation of a given part to either o Answer questions generated from the History o Confirm or refute expected or unexpected findings on Exam Mental Status Level of Alertness o Subjective view of Examiner o Definition of Consciousness o Terminology for Depressed Level of Consciousness o Concept of Coma o Delerium
2 Mental Status Level of Alertness o Degree of Orientation To what? o A and O x 4 Concentration o Serial 7 s or 3 s o WORLD backwards o Months of the Year Backwards o Try to quantify degree of impairment A and O and Concentration need to be intact for other aspects of the Mental Status Exam to have localizing value! Mental Status Memory Immediate Recall o A task of concentration Short-Term Memory o 3/3 objects after 5 minutes Long-Term Memory o Last thing to go Mental Status Language Aphasia vs. Dysarthria Receptive Language o Command Following Expressive Language o Fluency o Word Finding Repetition o Screens for Receptive, Expressive, and Conductive Aphasias Language What is Altered Mental Status? What are some symptoms that would make you think your patient has: o Altered Mental Status Altered level of conscious Disorientation Inappropriate behavior Altered cognition What is Level of Consciousness?
3 What Is Altered LOC? Decreased wakefulness Unable to follow commands Decreased awareness Decreased responsiveness Unresponsive Altered Level of Consciousness versus Cognition? Altered Level of Consciousness o Alertness o Wakefulness o Awareness o Responsive o Sedation o Coma o Lethargic Cognition o Orientation o Confusion o Concentration o Comprehension o Logic o Able to follow instructions o Memory long and short term o Appropriate behavior relative to the situation/environment o Age specific o Acute or chronic o Continuum What is Altered Neurologic Status? Altered Level of Consciousness Altered Mental Status Abnormal cranial nerves Abnormal speech Abnormal motor function Abnormal sensory function Alteration in balance/gait What s Normal? Alert and oriented X 3 (Person, Place, Time/Date) consistent with developmental age Follows commands Responds to questions appropriately Speech Clear (?)
4 Specialized Neuro Assessments AVPU (Alert, Verbal, Pain, Unresponsive) NIHSS (National Institute of Health Stroke Scale) Glasgow Coma Scale CAM Confusion Assessment Method Cranial Nerve Assessment CMS Circulation Movement Sensation Withdrawal Alcohol Screening (WAS) Mini mental health Electrolyte (Chvostec, Trousseau) Spinal What can cause alteration in mental status? Neurologic System vs. Other Systems Age Related Genetic/Hereditary Emotional/Psychiatric Acute vs. Chronic Sudden Onset vs. Slow Onset AEIOU TIPS A Alcohol E Electrolytes, Endocrine I Insulin O Oxygenation U Uremia T Trauma, Toxicity, Temperature I Infection P Psych, Pharmacy, Perfusion S Space Occupying lesion, Stroke, Seizure A is for Alcohol E is for Electrolytes or Endocrine I is for Insulin Hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia DKA Hyper Osmolar (HHNK) Renal failure Chronic Changes to brain
5 O is for Oxygenation Hypoxia Hyperventilation (Anxiety vs. Hypoxia) Respiratory Distress o Airway o Upper o Lower o Systemic U is for Uremia Kidney failure-toxins build up Encephalopathy Muscle weakness Mental status changes Seizures Coma T is for Trauma - T is for Toxicity (Poisoning) T is for Temperature Fever Hyperthermia Hypothermia I is for Intracranial Pressure Caused by o Tumor o Bleeding o Infection o Hydrocephalus o Swelling o Hyperosmolar o Seizures I is for Infection Meningitis Encephalitis Brain Abscess P is for Psychiatric Acute psychosis Schizophrenia Bipolar Delirium o Hallucinations o Auditory o Delusional
6 P is for Pharmaceuticals P is for Perfusion Shock-state Hypovolemia Cardiogenic Distributitive o Septis, o Neurogenic o Anaphylatic Obstructive
7 S is for Space Occupying Lesion Tumor Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus Brain Swelling brain injury S is for Stroke S is for Seizures Generalized Tonic-Clonic Complex partial Absence Febrile The Neurological Examination - Cranial Nerves Olfactory Nerve o Distinguish Coffee from Cinnamon o Smelling Salts irritate nasal mucosa and test V2 Trigemminal Sense o Disorders of Smell result from closed head injuries Optic Nerve o Visual Acuity o Visual Fields o Afferent input to Pupillary Light Reflex APD Look at the Nerve (Fundoscopic Exam) Cranial Nerves III, IV, VI o Extra-Ocular Muscles o Efferent limb of pupillary light reflex (III) o Ptosis Oculomotor Nerve Palsy Part of Horner s Syndrome o Cardinal Directions of Gaze Cranial Nerves III, IV, VI o Efferent output for Oculocephalic Reflex o Look for Nystagmus o EOMI without nystagmus Trigeminal Nerve o Motor Component o Opthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), and Mandibular (V3) Distributions o All modes of Primary Sensation Modalities can be tested o Afferent input for the Corneal Blink Reflex Facial sensation intact in all distributions
8 The Neurological Examination - Cranial Nerves Facial Nerve o Motor innervation to facial muscles o UMN versus LMN Facial Weakness o Efferent output to Corneal Blink Reflex o Other Functions Parasympathetic input to lacrimal, sublingual, and submandibular glands, taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue, general sensation to concha of earlobe and small part of scalp, motor input to stapedius muscle o Facial motor intact Vestibulocochlear Nerve o Hearing and Balance Patients will complain of tinnitis, hearing loss, and/or vertigo o Weber and Renee Test Differentiates Conductive vs Sensorineural hearing loss o Afferent input to the Oculocephalic Reflex Doll s Eye Maneuver Cold Calorics Glossopharyngeal and Vagus Nerves o Afferent (IX) and Efferent (X) components for the Gag Reflex o Vagus Nerve also does all parasympathetics from the neck down until the mid-transverse colon Hypoglossal Nerve o Protrudes the tongue to the opposite side o Tongue in cheek (strength) o Hemi-atrophy and fasiculations (LMN) The Motor Examination Strength Tone DTR s Plantar Responses Involuntary Movements Exam of the Motor System Position, movement, muscle bulk and tone o Observe body position and involuntary movements such as tremors, tics, fasiculations o Inspect muscle bulk, note any atrophy o Assess muscle tone flex and extend the arm and lower the leg for residual tension o Tics (sudden, rapid, non-rhytmic)
9 Strength (Medical Research Council Scale) 5/5 = Full Strength 4/5 = Weakness with Resistance 3/5 = Can Overcome Gravity Only 2/5 = Can Move Limb without Gravity 1/5 = Can Activate Muscle without Moving Limb 0/5 = Cannot Activate Muscle The Motor Examination - Weakness Describe the Distribution of Weakness o Upper Motor Neuron Pattern o Peripheral Neuropathy Pattern o Myopathic Pattern The Motor Examination Upper Motor Neuron o Strength - Decreased o Tone - Increased spasticty o DTR - Increased or brisk o Plantar reflexes - Upgoing toes o Atrophy/Fasiculations - None Lower Motor Neuron o Strength - Decreased o Tone - Decreased hypotonia o DTR - Diminished or absent o Plantar reflexes - Downgoing toes o Atrophy/Fasiculations - Positive or negative Muscle Strength Test the following muscle groups and movements o Biceps and triceps wrist flexion & extension o Handgrip, finger abduction, adduction, thumb opposition o Trunk flexion, extension, lateral bending o Thorax expansion, diaphragmatic excursion during respiration o Hip flexion, extension, abduction, adduction o Knee and ankle flexion and extension
10 The Motor Examination Tone o Tone is the resistance appreciated when moving a limb passively o Normal Tone o Hypotonia Central Hypotonia Peripheral Hypotonia o Increased Tone Spasticity (Corticospinal Tract) Rigidity (Basal Ganglia, Parkinson s Disease) Dystonia (Basal Ganglia) DTR s o 0/4 = Absent o 1-2/4 = Normal Range o 3/4 = Pathologically Brisk o 4/4 = Clonus Involuntary Movements o Hyperkinetic Movements Chorea Athetosis Tics Myoclonus o Bradykinetic Movements Parkinsonism (Bradykinesia, Rigidity, Postural Instability, Resting Tremor) Dystonia The Sensory Examination Primary Sensory Modalities o Light Touch (Multiple Pathways) o Pain/Temperature Sensation (Spinothalamic Tract) o Vibration/Position Sensation (Posterior Columns) Cortical Sensory Modalities o Stereognosis o Graphesthesia o Two-Point Discrimination o Double Simultaneous Extinction
11 The Sensory Examination Primary Sensory Modalities o Reflect Input from sensory receptors, sensory nerves, spinal cord, brainstem, through to the level of the Thalamus. Cortical Sensory Modalities o Reflect Processing by the Somatosensory Cortex (post-central gyrus) The Sensory Examination Pain and Temperature o Small-unmyelinated fibers provide pain and temperature input which travels through the dorsal roots o Second-order neurons cross midline at the anterior commissure and travel up the lateral spinothalamic tract Joint Position and Vibration o Larger myelinated fibers bring sensory information concerning vibration and joint position o Second-order neurons cross at the Thalamus Pain and Temperature o Pinprick (One pin per patient!) o Sensation of Cold o Look for Sensory Nerve or o Dermatomal Distribution Vibration Sensation o C-128 Hz Tuning Fork (check great toe) Joint Position Sensation o Check great toe o Romberg Sign Higher Cortical Sensory Function o Graphesthesia o Stereognosis o Two-Point Discrimination o Double Simultaneous Extinction o Gerstmann s Syndrome (acalculia, right-left confusion, finger agnosia, agraphia) Usually seen in Dominant Parietal Lobe lesions Coordination - Coordination Examination Test coordination including o Rapid alternating movements Repeating pronation supination palms Tapping thumbs and fingers Tapping ball of foot with fingers o Point-to-point movements Touching face and nose Moving heel down opposite leg
12 Coordination - Coordination Examination Test coordination including o Gait assess gait as patient o Walks across room o Walks heel-to-toe o Walks on toes and heels o Hops in place Test coordination including o Stance, namely Rhomberg test Patient stands with feet together and arms forward, eyes closed, for seconds without support Loss of balance with eyed closed is + Pronator drift Patient stands for seconds with both arms forward, palms up, eyes closed, tap arms briskly downward Pronation and downward drift is + Sensory Exam General Principles of Exam o Compare symmetric areas on both sides of the body o When testing pain, temperature, and touch, compare distal with proximal areas of extremities o Map out the boundaries of any area of sensory loss or hypersensitivity Test pain using a disposable broken Q-tip or pin and discard after usage o Ask if the prick is sharp or dull or ask the patient to compare two sensations Test light tough using cotton wisp Test vibration with tuning fork Test proprioception hold big toe by its sides between your thumb and index finger, pull it away from other toes, and move it up and down. Ask patient to identify the direction of movement. Assess discriminating sensation to test the ability of the sensory cortex to analyze and interpret sensations o Stereogenesis place a key or familiar object in patient s hand and ask patient to identify o Number identification (graphesthesia) outline a large number in patient s palm and ask them to identify o Two-point discrimination using two ends of an open paper clip, touch the finger pad in two places simultaneously and ask patient to identify 1 touch or 2 Assess discriminating sensation o Point location lightly touch a point on the patient s skin and ask the patient to point to the spot o Extinction touch and area on both sides of the body at the same time and ask if patient feels 1 spot or 2
13 Deep Tendon Reflexes Select a properly weighted hammer Encourage the patient to relax, position the limbs properly and symmetrically Strike the tendon with a brisk direct movement using the minimum force needed to obtain a response Use reinforcement when needed Grade the response o Reflex Grading + 4 Very brisk, hyperactive, with clonus (rhythmic oscillations between flexion and extension) + 3 Brisker than average; possibly, but not necessarily indicative of disease + 2 Average; normal + 1 Somewhat diminished; low normal No response Deep Tendon Reflexes Biceps reflex C5-6 Triceps reflex C6-7 Brachioradialis or supinator C5-6 Knee reflex L2-4 Ankle reflex Mainly S1 Clonus o A hyperactive response required for assigning a reflex grade of 4, usually elicited at the ankle
14 Cutaneous Sensation Reflexes Abdominal reflex o Upper T8-10 o Lower T10-12 Plantar response L5-S1 Anal reflex S2-4 The Gait A normal Gait requires multiple levels of the neuroaxis to be intact o Vision o Strength o Balance/Coordination o Joint Position The Gait Observe Different Aspects of Gait o Arm Swing o Base of Gait o Heel Strike o Time Spent on Each Leg o Posture of Trunk o Toe Walking o Heel Walking o Tandem Walking The Gait Classical Patterns of Abnormal Gait Parkinsonism Gait Hemiparetic Gait Spastic Diplegia Gait Acute Ataxia Gait Chronic Ataxia Gait Waddling Gait (Hip Girdle Weakness) High Stepping Gait
The Neurological System. Neurological Exam 5 Components. Mental Status Examination
 The Neurological System 1 Neurological Exam 5 Components Mental status Cranial nerves Reflexes Motor- includes Cerebellar function Sensory 2 Mental Status Examination Examination - ABCT Appearance Behavior
The Neurological System 1 Neurological Exam 5 Components Mental status Cranial nerves Reflexes Motor- includes Cerebellar function Sensory 2 Mental Status Examination Examination - ABCT Appearance Behavior
Neuro Exam Explained
 Neuro Exam Explained Michael Nelson M.D. Providence Neurological Specialties East Primary Care Conference October 26 rd, 2017 Michael Nelson M.D. Medical School: University of Missouri-Columbia Residency:
Neuro Exam Explained Michael Nelson M.D. Providence Neurological Specialties East Primary Care Conference October 26 rd, 2017 Michael Nelson M.D. Medical School: University of Missouri-Columbia Residency:
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. Vol. 18: Nervous System: Sensory System and Reflexes
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 18: Nervous System: Sensory System and Reflexes Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the sensory system and reflexes are: to assess
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 18: Nervous System: Sensory System and Reflexes Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the sensory system and reflexes are: to assess
Neurological Assessment
 Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Neurological Assessment. Lecture 8
 Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
The High-Yield Neurologic Examination
 The High-Yield Neurologic Examination S. Andrew Josephson MD Carmen Castro Franceschi and Gladyne K. Mitchell Neurohospitalist Distinguished Professor Chair, Department of Neurology Director, Neurohospitalist
The High-Yield Neurologic Examination S. Andrew Josephson MD Carmen Castro Franceschi and Gladyne K. Mitchell Neurohospitalist Distinguished Professor Chair, Department of Neurology Director, Neurohospitalist
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies
 The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies
 The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology Divisions of Neurovascular and Behavioral Neurology University of California San Francisco
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Neurology Divisions of Neurovascular and Behavioral Neurology University of California San Francisco
High Yield Neurological Examination
 High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
High Yield Neurological Examination Vanja Douglas, MD Sara & Evan Williams Foundation Endowed Neurohospitalist Chair Director, Neurohospitalist Division Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology UCSF Department
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam
 A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
A Hypothesis Driven Approach to the Neurological Exam Vanja Douglas, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Department of Neurology Disclosures None 1 Purpose of Neuro Exam Screen asymptomatic patients Screen
Neurological Examination
 Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Cerebrum. Impulses transmitted by:
 Sharon Niggemeier RN MSN Victoria Siegel RN, MSN, EdD Myung-Hee Pak, RN, MSN, CCRN Nervous system- divided into 2 structural parts Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain & spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System
Sharon Niggemeier RN MSN Victoria Siegel RN, MSN, EdD Myung-Hee Pak, RN, MSN, CCRN Nervous system- divided into 2 structural parts Central Nervous System (CNS)- brain & spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System
Anatomy of Nervous System. Neurological Assessment. Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord 03/23/2010. Central. Peripheral
 Anatomy of Nervous System Neurological Assessment Central Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Spinal Nerves Brain Cerebral cortex ( rind ) gray matter Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Wernicke s area receptive
Anatomy of Nervous System Neurological Assessment Central Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Spinal Nerves Brain Cerebral cortex ( rind ) gray matter Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Wernicke s area receptive
Physical Assessment Class 3
 Physical Assessment Class 3 Daily Tasks **Spot Test and assessment 1 (Class materials from1 2)** Goals: Understand significant features of a neurological history Know the complete sequence of cranial nerve
Physical Assessment Class 3 Daily Tasks **Spot Test and assessment 1 (Class materials from1 2)** Goals: Understand significant features of a neurological history Know the complete sequence of cranial nerve
NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES
 NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES Endorsed by the following organizations - October 2000: American Academy of Neurology Association of University Professors of Neurology American Neurological
NEUROLOGY CLERKSHIP CORE CURRICULUM GUIDELINES Endorsed by the following organizations - October 2000: American Academy of Neurology Association of University Professors of Neurology American Neurological
The Neurologic Examination. John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine
 The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
The Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. University of California San Francisco School of Medicine Overview The Neurologic Examination Mental status demonstration/questions Cranial nerves demonstration/questions
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Neurologic Examination
 John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
John W. Engstrom, MD October 16, 2015 Neurologic Examination Overview The Neurologic Examination Neurologic Examination John W. Engstrom, M.D. Dept. of Neurology University of California, San Francisco
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination. Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students
 An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students Prepared by: Dr. Farid Ghalli Clinical Teacher (Hon) November 2016 Before Examination : Wash hands
An Illustrated Guide For Peripheral Nerve Examination Bedside Teaching for 2 nd year medical Students Prepared by: Dr. Farid Ghalli Clinical Teacher (Hon) November 2016 Before Examination : Wash hands
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions. PT Evaluation. PT Evaluation
 Slide 1 Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions PTA 103 Introduction to Clinical Practice 2 Slide 2 Mental status: consciousness, attention, orientation, cognition Communication: speech
Slide 1 Intro to Physical Therapy for Neuromuscular Conditions PTA 103 Introduction to Clinical Practice 2 Slide 2 Mental status: consciousness, attention, orientation, cognition Communication: speech
Neurological examinations made easy. Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 Neurological examinations made easy Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital Introduction The aim of the neurological examination is to delineate the patient
Neurological examinations made easy Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital Introduction The aim of the neurological examination is to delineate the patient
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Cranial Nerves Exam. 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
 Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions
 Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES
 UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES HISTORY Chief Complaint A maximally succinct statement of the patient age, handedness, gender, main problem, and its duration (e.g. 56 year old right-handed
UF NEUROLOGY HISTORY AND PHYSICAL GUIDELINES HISTORY Chief Complaint A maximally succinct statement of the patient age, handedness, gender, main problem, and its duration (e.g. 56 year old right-handed
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
Differences Between Right and Left Patellar Reflexes
 Differences Between Right and Left Patellar Reflexes Background: somatic senses: Miss School, Miss Out! Miss School, Miss Out! 7 1. Receptor region 2. Afferent neuron 3. Interneuron 4. Efferent neuron
Differences Between Right and Left Patellar Reflexes Background: somatic senses: Miss School, Miss Out! Miss School, Miss Out! 7 1. Receptor region 2. Afferent neuron 3. Interneuron 4. Efferent neuron
Name Date Period. Human Reflexes Lab
 Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
Name Date Period Introduction: Human Reflexes Lab Neurons communicate in many ways, but much of what the body must do every day is programmed as reflexes. Reflexes are rapid, predictable, involuntary motor
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis
 Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
Approach to a Neurologic Diagnosis Neurologic Diagnosis History Physical & Neurological Examination Ancillary Procedures 3 Questions Asked Focal neurologic deficits Increased intracranial pressure Signs
what do the numbers really mean? NIHSS Timothy Hehr, RN MA Stroke Program Outreach Coordinator Allina Health
 what do the numbers really mean? NIHSS Timothy Hehr, RN MA Stroke Program Outreach Coordinator Allina Health NIHSS The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a tool used to objectively quantify
what do the numbers really mean? NIHSS Timothy Hehr, RN MA Stroke Program Outreach Coordinator Allina Health NIHSS The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) is a tool used to objectively quantify
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
Reflexes. Dr. Baizer
 Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination
 The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
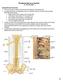 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Cesarean section for breech presentation. Jonathan H. Waters, M.D.
 Cesarean section for breech presentation Jonathan H. Waters, M.D. 1 26 y.o. G1P0 presented to triage in labor at 38 weeks. Patient was a known breech with a failed version 5 days before presentation. PMH
Cesarean section for breech presentation Jonathan H. Waters, M.D. 1 26 y.o. G1P0 presented to triage in labor at 38 weeks. Patient was a known breech with a failed version 5 days before presentation. PMH
The Neurologic Examination
 The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
Neurology. Clerkship. Syllabus
 Neurology Clerkship Syllabus Clerkship Website http://depts.washington.edu/neurolog/education/clerkships/home.html Neurology Clerkship Identifying data Name: Dates of clerkship: / / to / / Location: Contact
Neurology Clerkship Syllabus Clerkship Website http://depts.washington.edu/neurolog/education/clerkships/home.html Neurology Clerkship Identifying data Name: Dates of clerkship: / / to / / Location: Contact
Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination
 Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination K. Jeffrey Miller, DC, DABCO Miller 2002 2002-2012 K Jeffrey Miller DC DABCO Motor Function Neurological Testing Handedness Right or Left Handed
Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination K. Jeffrey Miller, DC, DABCO Miller 2002 2002-2012 K Jeffrey Miller DC DABCO Motor Function Neurological Testing Handedness Right or Left Handed
Examination Approach. Examination Approach. Case 1: Mental Status. The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques 5/8/2015
 The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests and techniques S.
The Neurological Exam In the ICU: High Yield Techniques Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests and techniques S.
Clinical Learning Exercise #1
 Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
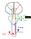 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Emergency Neurology and Management
 Emergency Neurology and Management Nathan Toussaint, NRP Department of Emergency Medicine LIFELINE- Critical Care Transport Team Johns Hopkins Hospital Disclaimer: Anything presented to you in this lecture
Emergency Neurology and Management Nathan Toussaint, NRP Department of Emergency Medicine LIFELINE- Critical Care Transport Team Johns Hopkins Hospital Disclaimer: Anything presented to you in this lecture
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1
 Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Neurocritical Care Basics. Tapan Kavi, MD Christina Fox, RN
 Neurocritical Care Basics Tapan Kavi, MD Christina Fox, RN GOAL 1: DON T LET THE PATIENT DIE Not unique ACLS, ATLS, ENLS, other strategies common to all emergency medical care ABCs MORE not less important
Neurocritical Care Basics Tapan Kavi, MD Christina Fox, RN GOAL 1: DON T LET THE PATIENT DIE Not unique ACLS, ATLS, ENLS, other strategies common to all emergency medical care ABCs MORE not less important
ID # COMPLETED: YES 1 DATE NO 2
 ID # COMPLETED: YES 1 DATE NO 2 NEUROLOGICAL EXAM "Normal, Abnormal, Other, Can't execute or Missing for each question. If you circle "Abnormal" or Other, also check the appropriate reason why or explain
ID # COMPLETED: YES 1 DATE NO 2 NEUROLOGICAL EXAM "Normal, Abnormal, Other, Can't execute or Missing for each question. If you circle "Abnormal" or Other, also check the appropriate reason why or explain
ID # COMPLETED: YES.. 1 DATE NO... 5 NEUROLOGICAL EXAM
 ID # COMPLETED: YES.. 1 DATE NO... 5 NEUROLOGICAL EXAM VIDEOTAPED: YES.. 1 NO... 5 COMMENT: NEUROLOGICAL EXAM "Normal, Abnormal, Other, Can't execute or Missing for each question. Always complete specify
ID # COMPLETED: YES.. 1 DATE NO... 5 NEUROLOGICAL EXAM VIDEOTAPED: YES.. 1 NO... 5 COMMENT: NEUROLOGICAL EXAM "Normal, Abnormal, Other, Can't execute or Missing for each question. Always complete specify
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST
 CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
CRANIAL NERVE TESTING FOR THE PRIMARY CARE OPTOMETRIST Hannah Shinoda, OD Caroline Ooley, OD, FAAO Assistant Professors Pacific University College of Optometry The authors have no financial interest in
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION (1) Dr. Sema Saltık Ass. Prof of Child Neurology
 NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION (1) Dr. Sema Saltık Ass. Prof of Child Neurology Neurological Examınatıon Consciousness level assessment, cooperation Disorders of speech and language Neck stiffness and evidences
NEUROLOGICAL EXAMINATION (1) Dr. Sema Saltık Ass. Prof of Child Neurology Neurological Examınatıon Consciousness level assessment, cooperation Disorders of speech and language Neck stiffness and evidences
University of Manitoba - MPT: Neurological Clinical Skills Checklist
 Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
Name: Site: Assessment Skills Observed Performed Becoming A. Gross motor function i. Describe movement strategies (quality, devices, timeliness, independence): supine sidelying sit stand supine long sitting
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination
 Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination Head Impulse (right- and leftward) Nystagmus type Test of Skew (cover test for skew deviation) Stroke findings: I.N.F.A.R.C.T.
Acute Vestibular Syndrome (VS or Stroke?) Three-step H.I.N.T.S. eye examination Head Impulse (right- and leftward) Nystagmus type Test of Skew (cover test for skew deviation) Stroke findings: I.N.F.A.R.C.T.
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy
 Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
HEAD AND NECK PART 2
 HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
PEDIATRIC BRAIN CARE
 PEDIATRIC BRAIN CARE The brain matters most! OVERVIEW OF NEURO ASSESSMENT 1. Overall responsiveness/activity 2. The eyes 3.? Increased ICP 4. Movements 5.? Seizures 6. Other OVERALL RESPONSIVENESS/ ACTIVITY
PEDIATRIC BRAIN CARE The brain matters most! OVERVIEW OF NEURO ASSESSMENT 1. Overall responsiveness/activity 2. The eyes 3.? Increased ICP 4. Movements 5.? Seizures 6. Other OVERALL RESPONSIVENESS/ ACTIVITY
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems
 NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
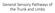 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Lab Activity 19 & 20. Cranial Nerves General Senses. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL. NURSING PROCEDURE NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEALTH STROKE SCALE (neu04) Nursing
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: ISSUED FOR: NURSING PROCEDURE NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEALTH Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: PS1094 7/01 3/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN PURPOSE: OBJECTIVE: DEFINITION:
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: ISSUED FOR: NURSING PROCEDURE NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEALTH Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: PS1094 7/01 3/18 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN PURPOSE: OBJECTIVE: DEFINITION:
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION
 Página 1 de 6 NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION Part of "1 - NEUROPSYCHIATRIC EXAMINATION" The neurologic examination complements the clinical history and mental status examinations that preceded it (3). In the neurologic
Página 1 de 6 NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION Part of "1 - NEUROPSYCHIATRIC EXAMINATION" The neurologic examination complements the clinical history and mental status examinations that preceded it (3). In the neurologic
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System. Chapter 15
 Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
Sensory Pathways & Somatic Nervous System Chapter 15 How Does Brain Differentiate Sensations? Pain impulses make brain aware of injuries and infections. Impulses from eye, ear, nose and tongue make brain
1. Somatosensory Pathways
 1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
1. Somatosensory Pathways Objectives 1. Describe the general characteristics of sensory pathways 2. Understand the general organization and numbered areas of spinal cord gray matter 3. Understand dermatomes
Cancer Rehabilitation New Patient Intake Form
 _ I. Personal Information Date of Birth Age: Home Address: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Office Phone: Fax: E-Mail: II. Chief Complaint Please describe the major problem that brings you in today: Who referred
_ I. Personal Information Date of Birth Age: Home Address: Home Phone: Cell Phone: Office Phone: Fax: E-Mail: II. Chief Complaint Please describe the major problem that brings you in today: Who referred
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses
 Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Nervous system Reflexes and Senses Physiology Lab-4 Wrood Slaim, MSc Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology University of Al-Mustansyria 2017-2018 Nervous System The nervous system is the part of an
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Neurologic Examination
 Neurologic Examination Professor Yasser Metwally www.yassermetwally.com 1 INDEX Click to view my video channel www.yassermetwally.info Equipment Needed Click to view imortanf online video clips General
Neurologic Examination Professor Yasser Metwally www.yassermetwally.com 1 INDEX Click to view my video channel www.yassermetwally.info Equipment Needed Click to view imortanf online video clips General
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CNS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CNS 1 CNS EXAMINATION Take proper history ; then proceed to the following steps in examination of CNS Higher functions Cranial nerves Motor system Reflexes Sensory system Cerebellar
CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF CNS 1 CNS EXAMINATION Take proper history ; then proceed to the following steps in examination of CNS Higher functions Cranial nerves Motor system Reflexes Sensory system Cerebellar
Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination
 Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination K. Jeffrey Miller, DC, FACO, MBA Chiropractic Orthopaedist Miller 2002 Specializing in Spine and Nerve Rehabilitation Motor Function Lower
Motor, Reflex, Coordination and Sensory Screening Examination K. Jeffrey Miller, DC, FACO, MBA Chiropractic Orthopaedist Miller 2002 Specializing in Spine and Nerve Rehabilitation Motor Function Lower
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Spinal nerves. Aygul Shafigullina. Department of Morphology and General Pathology
 Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Spinal nerves Aygul Shafigullina Department of Morphology and General Pathology Spinal nerve a mixed nerve, formed in the vicinity of an intervertebral foramen, where fuse a dorsal root and a ventral root,
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences
 Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
Babak Tamizi Far MD. Assistant professor of internal medicine Al-zahra hospital, Isfahan university of medical sciences ٢ Level of consciousness is depressed Stuporous patients respond only to repeated
Neurologic Exam Evaluation Checklist (NEURO OSCE)
 Neurologic Exam Evaluation Checklist (NEURO OSCE) Student s Name: Date: _ Evaluator s Names: Examiner: Mark A if the step was done correctly Mark B if the step was done but if the technique was unsatisfactory
Neurologic Exam Evaluation Checklist (NEURO OSCE) Student s Name: Date: _ Evaluator s Names: Examiner: Mark A if the step was done correctly Mark B if the step was done but if the technique was unsatisfactory
MOLLOY COLLEGE THE BARBARA H. HAGAN SCHOOL OF NURSING NURSE PRACTITIONER PROGRAMS. Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam
 THE BARBARA H. HAGAN SCHOOL OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2016). (12 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination
THE BARBARA H. HAGAN SCHOOL OF NURSING S Study Guide for the Basic Physical Assessment Exam Questions will be based on following chapters in, Bickley, L.S. (2016). (12 th ed). Bates guide to physical examination
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Academic Resource Center. Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
NERVOUS SYSTEM Academic Resource Center Forskellen mellem oscillator og krystal Overview of the Nervous System Peripheral nervous system-pns cranial nerves spinal nerves ganglia peripheral nerves enteric
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal
 HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
HISTORY TAKING ON NERVOUS SYSTEM Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal General points History of neurological symptoms should also be taken from patient and close relative or friend Memory loss, intoxication, aphasia Patient
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing
 King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
King Saud University College of Nursing Medical-surgical Nursing 1.Obtaining a health history: Ask about chief complain: History of presence of muscle pain (onset, location, Aggravating and alleviating
Infant Reflexes and Stereotypies. Chapter 9
 Infant Reflexes and Stereotypies Chapter 9 Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in the process of development Importance of Infant Reflexes Reflexive movements occur during the last 4 months
Infant Reflexes and Stereotypies Chapter 9 Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in the process of development Importance of Infant Reflexes Reflexive movements occur during the last 4 months
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
