Non-Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis. App.GoSoapbox.com then Join Now. Joel M. Topf, M.D.
|
|
|
- Ada Cornelia Waters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Non-Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis App.GoSoapbox.com then Join Now Joel M. Topf, M.D.
2 App.GoSoapbox.com
3 32 y.o. female with fatigue, weakness and muscle aches App.GoSoapbox.com Answer polls: Uhura: What is the primary acid base Uhura: What is the appropriate pco / 33 / 87 /
4 32 y.o. female with fatigue, weakness and muscle aches / 33 / 87 /
5 Determine the primary disorder 7.34 / 87 / 33 / 16 ph / po2 / pco 2 / HCO 3 1. Acidosis or alkalosis If the ph is is less than it it is is acidosis If the ph is greater than 7.4 it is alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis 2. Determine if it is respiratory or metabolic If the ph, bicarbonate and and pco pco 2 all 2 all move move in the in the same same direction direction (up or (up down) or down) it is it is metabolic If the ph, bicarbonate and pco 2 move in discordant directions (up and down) and down) it is respiratory it is respiratory
6 Predicting pco 2 in metabolic acidosis: Winter s Formula In metabolic acidosis the expected pco 2 can be estimated from the HCO 3 Expected pco 2 = (1.5 x HCO 3 ) + 8 ± 2 If the pco 2 is higher than predicted then there is an addition respiratory acidosis If the pco 2 is lower than predicted there is an additional respiratory alkalosis
7 Is the compensation appropriate? 7.33 / 87 / 33 / 17 ph / po2 / pco 2 / HCO 3 Expected pco 2 = (1.5 x HCO 3 ) + 8 ±2 Appropriately compensated Expected pco 2 = metabolic acidosis Actual pco 2 is 33, which is within the predicted range, indicating appropriate respiratory compensation
8 What anion is associated with the additional acid?
9 Metabolic acidosis is further evaluated by determining the anion associated with the increased H + cation In medicine we categorize the anions into: chloride not chloride Non-Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis and differentiate the two based on the anion gap.
10 Anion gap =
11 Anion gap = Goldmark Mudpiles Plumseeds
12 Calculating the anion gap Anion gap = Na (HCO 3 + Cl) Normal is 12 Varies from lab to lab Average anion gap in healthy controls is 6 ±3 Improving chloride assays have resulted in increased chloride levels and a decreased normal anion gap.
13 Calculating the anion gap Anion gap = Na 139 (HCO ( ) + Cl) Normal Anion gap is 12 = 7 Varies from lab to lab Appropriately compensated Average anion gap in healthy controls is 6 ±3 Improving chloride assays have resulted in increased chloride levels and a decreased normal anion gap. non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
14 Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
15 NAGMA Chloride intoxication Dilutional acidosis HCl intoxication Chloride gas intoxication Early renal failure GI loss of HCO 3 Diarrhea Surgical drains Fistulas Ureterosigmoidostomy Obstructed ureteroileostomy Cholestyramine Renal loss of HCO 3 Renal tubular acidosis Proximal Distal Hypoaldosteronism
16 ph = 5.5 Cl = 154 mmol/l Plasma volume 3 liters Plasma Cl = 105
17
18 Increases in exogenous acid drive the reaction to the right, bicarbonate is consumed Decreases in bicarbonate force the reaction to the left, replacing the bicarbonate and increasing H +
19 in both, the end result is an increase in H + and a decrease in HCO 3, the defining characteristic of metabolic acidosis
20 In NAGMA we will use the loss of HCO 3 model
21 NAGMA Chloride intoxication Dilutional acidosis HCl intoxication Chloride gas intoxication Early renal failure GI loss of HCO 3 Diarrhea Surgical drains Fistulas Ureterosigmoidostomy Obstructed ureteroileostomy Cholestyramine Renal loss of HCO 3 Renal tubular acidosis Proximal Distal Hypoaldosteronism
22
23 Plasma Bile Pancreas Small intestines Large intestines
24
25 Urine ph=5.5 Serum ph= fold difference Ureterosigmoidostomy Ureteroileostomy
26 Urinary diversion Urine NH 4 + is absorbed by the intestinal mucosa and converted to H + and NH 3. Urine Chloride stimulates colonic expression and activation of Cl - /HCO 3 - exchangers exacerbating the loss of bicarbonate. Increased colonic pressures can cause urinary obstruction resulting in a urinary acidification defect Repeated episodes of pyelonephritis may do the same
27 NAGMA Chloride intoxication Dilutional acidosis HCl intoxication Chloride gas intoxication Early renal failure GI loss of HCO 3 Diarrhea Surgical drains Fistulas Ureterosigmoidostomy Obstructed ureteroileostomy Cholestyramine Renal loss of HCO 3 Renal tubular acidosis Proximal Distal Hypoaldosteronism
28 Renal causes of NAGMA: Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA) RTA can be due to a failure of the kidney to 1. Reabsorb all of the filtered bicarbonate 2. Synthesize new bicarbonate to replace bicarbonate lost to metabolism 3. Stow hydrogen ions in ammonia so we can clear the daily acid load
29 The kidney s role in HCO 3 handling is not excretory, rather the kidney needs to reabsorb the thousands of millimoles of filtered bicarbonate and synthesize a few dozen millimoles of bicarbonate to replace the bicarbonate lost to the daily acid load.
30 The kidney s role in HCO 3 handling is not excretory, rather the kidney needs to reabsorb the thousands of millimoles of filtered bicarbonate and synthesize a few dozen millimoles of bicarbonate to replace the bicarbonate lost to the daily acid load.
31 The kidney s role in HCO 3 handling is not excretory, rather the kidney needs to reabsorb the thousands of millimoles of filtered bicarbonate and synthesize a few dozen millimoles of bicarbonate to replace the bicarbonate lost to the daily acid load.
32 Reabsorption How much bicarbonate is filtered everyday? Normal plasma HCO 3 concentration is 24 mmol/l Normal GFR is 100 ml/min, or 0.1 L per minute 1440 minutes in a day = 3,456 mmol of bicarbonate are filtered a day (filtered load)
33 Synthesis How much bicarbonate needs to be replaced? How much bicarbonate is consumed? The daily acid load Protein metabolism consumes bicarbonate 1 mmol/kg 2 mmol/kg in children 4 mmol/kg in infants This bicarbonate must be replaced to maintain homeostasis
34 Two jobs, two locations The proximal tubule needs to reabsorb 3,456 mmol of bicarbonate that is filtered every day. Proximal tubule The kidney must synthesize mmol per day of new HCO 3 to replace HCO 3 lost buffering the daily acid load. Cortical collecting tubule 3456 mmol/day mmol/day
35
36 Proximal tubule: reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate
37 Bicarbonate handling The proximal tubule needs to reabsorb 3,456 mmol of bicarbonate that is filtered every day. Proximal tubule The kidney must synthesize mmol per day of new HCO 3 to replace HCO 3 lost buffering the daily acid load. Cortical collecting tubule 3456 mmol/day mmol/day
38 Distal tubule, completion of reabsorption and replacing bicarbonate lost to the daily acid load. 3 step process: Electrogenic movement of sodium into the tubular cells (enac) H + pumped into the tubular lumen ATPase Maintain the 1000 fold concentration gradient
39 Fate of excreted hydrogen ion The minimal urine ph is 4.5. This is a H+ concentration a 1000 times that of plasma. But It still is only 0.04 mmol/l In order to excrete 50 mmol (to produce enough bicarbonate to account for the daily acid load) one would need 1,250 liters of urine.
40 Fate of excreted hydrogen ion Ammonium Titratable acid
41 Excretion of the daily acid load as free hydrogen is limited by a minimum urinary ph of 4.5 Only 0.1% of the daily acid load is excreted this way Titratable acid is urinary phosphate Titratable acid carries a significant portion of the daily acid load Limited by dietary phosphate Does not respond to changes in the acid load Ammonium carries the bulk of the daily acid load In response to an acid load the kidney will increase production of ammonia (NH 3 ) in order to accept additional protons to carry the load
42 3 steps in renal bicarbonate handling 3456 mmol/day mmol/day
43 Each step can fail which causes RTA and mmol/day NAGMA Proximal RTA mmol/day Distal RTA Hyperkalemic RTA
44 Proximal RTA (Type 2) The Tm is the maximum plasma concentration of any solute at which the proximal tubule is able to completely reabsorb the solute. Beyond the Tm the substance will be incompletely reabsorbed and spill in the urine. Na + H 2 O HCO 3 Amino Acids Glucose In Proximal RTA the Tm for bicarbonate is reduced from 26 to mmol/l.
45 Proximal RTA (Type 2) Damage to the proximal tubule decreases its Tm from 28 to somewhere in the mid-teens 24 mmol/l Tm for HCO 3 at mmol/l Serum HCO 3 is > Tm so HCO 3 spills into the urine ph 8
46 Proximal RTA (Type 2) Serum HCO 3 then falls 15 mmol/l When it falls to the Tm (15 mmol/l) the kidney appears to work normally Homeostasis resumes but at a decreased HCO 3 15 mmol/l ph 5
47 Proximal RTA (Type 2) If the patient encounters an acid load, they synthesize new bicarbonate to return the serum HCO 3 to altered Tm (15) 12 mmol/l 12 mmol/l ph 5
48 Proximal RTA (Type 2) During treatment with exogenous bicarbonate the serum bicarbonate will rise above the Tm and the patient will spill bicarbonate 15 mmol/l 20 mmol/l ph 8
49 Proximal RTA: etiologies Acquired Acetylzolamide Ifosfamide Chronic hypocalcemia Multiple myeloma Cisplatin Lead toxicity Mercury poisoning Streptozocin Expired tetracycline Genetic Cystinosis Galactosemia Hereditary fructose intolerance Wilson s disease Hyperparathyroidism Variable Chronic respiratory alkalosis Intracellular alkalosis
50 Respiratory alkalosis 7.44 / 87 / 22 / 15 ph / po2 / pco 2 / HCO 3 The pco 2 falls due to the primary pathology The bicarbonate falls to compensate The Tm for bicarbonate is lowered
51 Proximal RTA: consequences Loss of potassium (hypokalemia) Bone disease Bone buffering of the acidosis Decreased growth Not typically complicated by stones
52 Each step can fail which causes RTA and mmol/day NAGMA Proximal RTA mmol/day Distal RTA 4 Hyperkalemic RTA
53 Distal RTA, the Murphy s Law of HCO 3 handling
54 Distal RTA, the Murphy s Law of distal HCO 3 handling
55 Distal RTA (Type 1) Failure can happen at any one of the three steps in urinary acidification
56 Distal RTA: Voltage dependent Only variety of distal RTA which is hyperkalemic Differentiate from type 4 by failure to respond to fludrocortisone. Obstructive uropathy Sickle cell anemia Lupus Triameterene Amiloride
57 Distal RTA: H + Secretion Called classic distal RTA Most common cause of distal RTA Congenital Lithium Multiple myeloma Lupus Pyelonephritis Sickle cell anemia Sjögren s syndrome Toluene (Glue sniffing) Wilson s disease
58 Distal RTA: Gradient defect Amphotercin B
59 Distal RTA: consequences Bones Chronic metabolic acidosis results in bone buffering. Bicarbonate Phosphate Calcium Kidney stones Calcium phosphate stones Due to hypercalciuria Increased urine ph Decreased urinary citrate Well Mr. Osborne, it may not be kidney stones after all.
60 Each step can fail which causes RTA and mmol/day NAGMA Proximal RTA mmol/day Distal RTA 4 Hyperkalemic RTA
61 Chronic hyperkalemia of any etiology decreases ammoniagenesis NH 3 is needed to excrete excess H + in the urine
62 Intracellular acidosis stimulates intra-renal ammonia production Intracellular alkalosis suppresses intra-renal ammonia production Intracellular alkalosis With increases in serum potassium, potassium shifts inside the cells To maintain electroneutrality, H + moves out of the cells
63 Hypoaldosteronism: Type 4 Chronic hyperkalemia decreases ammoniagenesis Without ammonia acid excretion is modest Urinary acidification is intact Acidosis is typically mild without significant bone or stone disease Primary problem is high potassium
64 Diagnosing the cause of: non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
65 To look for renal H + clearance look for urinary ammonium NH 4 + Ammonium Titratable acid
66 Urinary anion gap: (Na + + K + ) Cl Urinary ammonium detector In the presence of ammonium the chloride will be larger than the sum of Na and K. So a negative anion gap means ammonium in the urine. Ammonium in the urine = effective renal acid secretion Ammonium in the urine usually rules out RTA
67 Urinary anion gap: (Na + + K + ) Cl Urinary ammonium detector In the absence of ammonium the Na and K will be larger than the chloride. So a positive anion gap means no ammonium in the urine. No ammonium in the urine = no effective renal acid secretion, regardless of the urinary ph A positive urinary anion gap in the presence of metabolic acidosis is consistent with an RTA
68 App.GoSoapbox.com Answer polls: Urinary anion gap and diarrhea Urinary anion gap and proximal RTA Urinary anion gap and distal RTA Urinary anion gap and RTA type 4
69 NAGMA and urinary anion gap Diarrhea Negative Proximal RTA At baseline Negative (variable) During treatment Positive During acid load Negative Distal RTA: Positive Type IV RTA Positive mmol/l mmol/l ph 8 ph 5
70 32 y.o. female with fatigue, weakness and muscle aches / 87 / 33 /
71 / 87 / 33 / 16 U/A ph 6.5 Urine electrolytes Appropriately compensated nonanion gap metabolic acidosis due to distal RTA
72 74 y.o. female with 34 year history of DM c/o weakness App.GoSoapbox.com Answer polls: Dowager Countess: What is the primary acid-base Dowager Countess: What is the appropriate pco2 Dowager Countess: What additional acid-base disorders are present / 87 / 33 / 16 Albumin 1.8
73 74 y.o. female with 34 year history of DM c/o weakness / 38 / 92 / 16 Albumin 1.8
74 Determine the primary disorder 7.28 / 38 / 92 / 16 ph / pco2 / po 2 / HCO 3 1. Acidosis or alkalosis If the ph is is less than it it is is acidosis If the ph is greater than 7.4 it is alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis 2. Determine if it is respiratory or metabolic If the ph, bicarbonate and pco 2 all move in the same direction (up or down) it is metabolic If the ph, bicarbonate and pco 2 move in discordant directions (up and down) it is respiratory
75 Predicting pco 2 in metabolic acidosis: Winter s Formula 7.23 / 38 / 92 / 16 ph / pco 2 / po 2 / HCO 3 Expected pco 2 = (1.5 x HCO 3 ) + 8 ±2 Expected pco 2 = Actual and pco respiratory 2 is 38, which is higher acidosis than predicted, so the patient has an additional respiratory Combined metabolic acidosis
76 Calculating the anion gap Anion gap = Na 139 (HCO ( ) Cl) Anion gap = -1 A negative anion gap! That s got to mean something!
77 Hypoalbuminuria, hypophosphatemia The other anions includes phosphate and albumin Hypoalbuminuria and hypophosphatemia lowers the anion gap If one fails to adjust the upper and lower limit of the normal anion gap, altered albumin and phosphorous can hide a pathologic anion gap Adjusted Normal Anion Gap To estimate the normal anion gap for any individual multiply the albumin by 2.5 and add half the phosphorous
78 Other causes of a low anion gap Increased chloride Hypertriglyceridemia Bromide Iodide Decreased Unmeasured anions Albumin Phosphorous IgA Increased Unmeasured cations Hyperkalemia Hypercalcemia Hypermagnesemia Lithium Increased cationic paraproteins IgG Normal Anion gap Sodium Potassium Calcium Magnesium IgG Chloride Bicarb Albumin Phos IgA
79 Recent lab history Albumin falls 2 g/dl Potassium climbs 2 mmol/l Anion Gap falls 7 from 6 to -1
80 Diagnose the cause of: non-anion gap metabolic acidosis with hyperkalemia 1. Type four RTA, hyporenin-hypoaldo 2. Hyperkalemic Distal (Type 1) RTA, voltage dependent distal RTA
81 A dipstick for aldosterone activity: The trans-tubular potassium gradient The TTKG
82 disclaimer The TTKG is not useful in the diagnosis of hyperkalemia. Persistent hyperkalemia is always associated with an inappropriately low TTKG. The TTKG can be helpful in differentiating renal from extra-renal potassium losses in hypokalemia Recent data on solute handling in the medullary collecting duct calls into question the physiologic assumptions required for the TTKG to be valid.
83 Trans-tubular Potassium Gradient (TTKG) The ratio of tubular to venous K indicates the level of aldosterone activity. In the presence of hyperkalemia the ratio should be > 10. In the presence of hypokalemia the ratio of < 4.
84 Trans-tubular Potassium Gradient (TTKG) The trans-tubular potassium gradient adjusts the urine potassium for water loss in the collecting ducts. This allows the use of urinary potassium to calculate the ratio of potassium from the tubule to the interstitium in the CCD.
85 Trans-tubular Potassium Gradient (TTKG) Pre-requisites to using the TTKG as a measure of aldosterone activity: Urine osmolality > serum osmolality Urine Na > 20 mmol/l Fluid leaving the LoH has an osmolality of 100 mosm/kg In the presence of ADH water leaves the DCT so that the tubular fluid becomes isosmotic
86 Trans-tubular Lets play low, Potassium normal or Gradient high! (TTKG) and Aldo level 1. Type four RTA, hyporenin-hypoaldo Low TTKG Low aldosterone 2. Hyperkalemic Distal (Type 1) RTA, voltage dependent distal RTA Low TTKG High aldosterone
87 74 y.o. female with 34 year history of DM c/o weakness Both the bicarbonate and potassium were normal at admission. This is hospital acquired RTA (type 1 or 4)
88 Lets Hospital play: acquired Name that RTA drug! really means drug induced RTA Answer poll: name that drug 1. Type four RTA, hyporenin-hypoaldo Spironolactone ACEi/ARB Heparin 2. Hyperkalemic Distal (Type 1), voltage dependent distal RTA Amiloride Triamterene Trimethoprim
89 Lets Hospital play: acquired Name that RTA drug! really means drug induced RTA 1. Type four RTA, hyporenin-hypoaldo Spironolactone ACEi/ARB Heparin 2. Hyperkalemic Distal (Type 1), voltage dependent distal RTA Amiloride Triamterene Trimethoprim
90 74 y.o. female with 34 year history of of DM and c/o weakness Patient s TTKG was 2.7 with a K of 5.7 Aldosterone was 22 The patient had been started on a high dose of TMP/SMX for a partially resistant 1. urinary Type four tract RTA, infection 2. Hyperkalemic Distal (Type 1), hyporenin-hypoaldo voltage dependent distal RTA
91 Two women with non-anion gap metabolic acidosis One with hypokalemia One with hyperkalemia Both with distal RTA
92 Lets do some cases App.GoSoapbox.com
93 Lets do some cases
94 25 year old man CC: Recurrent kidney stones serum urine urine ph 6.5 Type 1 classical distal RTA Answer poll: 25 year old recurrent kidney stones
95 36 yr old. Diabetes since age 12, retinopathy, neuropathy. On insulin and ACEi urine ph 6.5 Answer poll: 36 year old diabetic
96 25 year old man CC: Recurrent kidney stones serum urine urine ph 6.5 Type 1 classical distal RTA
97 36 yr old. Diabetes since age 12, retinopathy, neuropathy. On insulin and ACEi urine ph 5.5 Type 4 RTA What do you do?
98 36 yr old. Diabetes since age 12, retinopathy, neuropathy. On insulin but not an ACEi urine ph 5.5 Type 4 RTA
99 36 yr old. Diabetes since age 12, retinopathy, neuropathy. On insulin and ACEi urine ph / 30 / 115 / 15 Answer poll: same 36 year old, 6 months later
100 36 yr old. Diabetes since age 12, retinopathy, neuropathy. On insulin but not an ACEi urine ph / 30 / 115 / 15
101 Type 4 RTA Top left is type 4 RTA Top right is AGMA due to DKA Bottom left is same patient with addition of diuretic Bottom right is NAGMA in the recovery phase of DKA with dilutional acidosis
102 45 year old with alcohol abuse. Also c/o occasional diarrhea Albumin / 28 / 96 / 19 Answer poll: 45 year old alcoholic
103 45 year old with alcohol abuse. Also c/o occasional diarrhea Albumin / 28 / 96 / 19
104 22 y.o. AA female with hyperkalemia and microscopic hematuria Urinalysis ph Blood + WBC RBC 1 RBC cast Systemic Lupus Erethematosus Electrogenic Distal RTA Answer poll: 22 y.o. with microscopic hematuria
105 22 y.o. AA female with hyperkalemia and microscopic hematuria Urinalysis ph Blood + WBC RBC 1 RBC cast Systemic Lupus Erethematosus Electrogenic Distal RTA
106 Most common error in acid-base Personal observation
107 AE 66 yo white male PMHx DM, paraplegia 2 MVA Klebsiella urosepsis induced ARF Blood Cxrs + for Klebsiella
108 8/ / Start bicarbonate gtt 2.8 8/ / / Start oral bicarbonate / 58 / 31 / 25 Respiratory alkalosis
109 Done. Thank-you Please do the post test and answer the discussion question
Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Division of Nephrology Virginia Commonwealth University
 Metabolic Acidosis Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Division of Nephrology Virginia Commonwealth University Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com
Metabolic Acidosis Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Division of Nephrology Virginia Commonwealth University Graphics by permission from The Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Companion, S. Faubel and J. Topf, http://www.pbfluids.com
Renal Tubular Acidosis
 1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
1 Renal Tubular Acidosis Mohammad Tariq Ibrahim 6 th Grade Diyala College Of Medicine supervisor DR. Sabah Almaamoory 2 *Renal Tubular Acidosis:- RTA:- is a disease state characterized by a normal anion
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview
 RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY CLINICAL BIOCHEMISTRY PBL MBBS IV VJ. Temple 1 What is Renal Tubular
3/19/2009. The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load. Buffering of an acid load. A o B - + H + B - A o +OH - C +
 The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
The task of the kidney in acid-base balance Excretion of the daily acid load Buffering of an acid load Oxidation of amino acids, fats and carbohydrates often lead to acid production. On an average American
Acid-Base Tutorial 2/10/2014. Overview. Physiology (2) Physiology (1)
 Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Overview Acid-Base Tutorial Nicola Barlow Physiology Buffering systems Control mechanisms Laboratory assessment of acid-base Disorders of H + ion homeostasis Respiratory acidosis Metabolic acidosis Respiratory
Acid Base Balance. Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih. Clinical Chemistry Professor Dr. Raid M. H. Al-Salih
 Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Acid Base Balance 1 HYDROGEN ION CONCENTRATION and CONCEPT OF ph Blood hydrogen ion concentration (abbreviated [H + ]) is maintained within tight limits in health, with the normal concentration being between
Guidelines for approach to a child with
 Guidelines for approach to a child with Metabolic acidosis (including RTA) Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith
Guidelines for approach to a child with Metabolic acidosis (including RTA) Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings
 Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
Acids and Bases their definitions and meanings Molecules containing hydrogen atoms that can release hydrogen ions in solutions are referred to as acids. (HCl H + Cl ) (H 2 CO 3 H + HCO 3 ) A base is an
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE
 NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
NORMAL POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION AND BALANCE 98% of body potassium is contained within cells, principally muscle cells, and is readily exchangeable. Only 2% is in ECF. Daily intake exceeds the amount in ECF.
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance
 H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
H 2 O, Electrolytes and Acid-Base Balance Body Fluids Intracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid inside the cells 40% of body weight Extracellular Fluid Compartment All fluid outside of cells 20% of body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 27 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Fluid Compartments and Fluid In adults, body fluids make up between 55% and 65% of total body mass. Body
Acid Base Disorders: Key Core Concepts. Thomas DuBose M.D., MACP, FASN ASN Board Review Course Online Resource Material 2014
 Acid Base Disorders: Key Core Concepts Thomas DuBose M.D., MACP, FASN ASN Board Review Course Online Resource Material 2014 Speaker Disclosure I, Thomas DuBose, M.D., have no financial relationships or
Acid Base Disorders: Key Core Concepts Thomas DuBose M.D., MACP, FASN ASN Board Review Course Online Resource Material 2014 Speaker Disclosure I, Thomas DuBose, M.D., have no financial relationships or
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
 Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Chapter 19 The Urinary System Fluid and Electrolyte Balance Chapter Outline The Concept of Balance Water Balance Sodium Balance Potassium Balance Calcium Balance Interactions between Fluid and Electrolyte
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis.
 Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
Potassium regulation. -Kidney is a major regulator for potassium Homeostasis. Normal potassium intake, distribution, and output from the body. Effects of severe hyperkalemia Partial depolarization of cell
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
Acid and Base Balance
 Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
Acid and Base Balance 1 2 The Body and ph Homeostasis of ph is tightly controlled Extracellular fluid = 7.4 Blood = 7.35 7.45 < 7.35: Acidosis (acidemia) > 7.45: Alkalosis (alkalemia) < 6.8 or > 8.0: death
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview
 RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
RENAL FUNCTION An Overview UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL MBBS II SEMINAR VJ. Temple 1 Kidneys
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
The kidney. (Pseudo) Practical questions. The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis. for questions Ella
 The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
The kidney (Pseudo) Practical questions for questions Ella (striemit@gmail.com) The kidneys are all about keeping the body s homeostasis Ingestion Product of metabolism H 2 O Ca ++ Cl - K + Na + H 2 O
There are many buffers in the kidney, but the main one is the phosphate buffer.
 9 Yanal Obada Zalat Renal Control of AcidBase Balance The kidneys play three major roles in the maintenance of normal acidbase balance: 1excretion of H+ (fixed _non volatile H+) 2Reabsorption of filtrated
9 Yanal Obada Zalat Renal Control of AcidBase Balance The kidneys play three major roles in the maintenance of normal acidbase balance: 1excretion of H+ (fixed _non volatile H+) 2Reabsorption of filtrated
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
MS1 Physiology Review of Na+, K+, H + /HCO 3. /Acid-base, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology
 MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
MS1 Physiology Review of,, / /Acidbase, Ca+² and PO 4 physiology I. David Weiner, M.D. Professor of Medicine and Physiology University of Florida College of Medicine Basic principles Proximal tubule Majority
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Acid Base Balance. Chapter 26 Balance. ph Imbalances. Acid Base Balance. CO 2 and ph. Carbonic Acid. Part 2. Acid/Base Balance
 Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Acid Base Balance Chapter 26 Balance Part 2. Acid/Base Balance Precisely balances production and loss of hydrogen ions (ph) The body generates acids during normal metabolism, tends to reduce ph Kidneys:
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
Chapter 27 Water, Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance 1 Body Fluids Intracellular fluid compartment All fluids inside cells of body About 40% of total body weight Extracellular fluid compartment All fluids
1 st JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE
 in association with 1 st JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston Jamaica October 4 th 2014 Demys&fying Renal Tubular Acidosis Rulan S. Parekh Professor of Pediatrics
in association with 1 st JAMAICAN PAEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY CONFERENCE Jamaica Conference Centre Kingston Jamaica October 4 th 2014 Demys&fying Renal Tubular Acidosis Rulan S. Parekh Professor of Pediatrics
Physio 12 -Summer 02 - Renal Physiology - Page 1
 Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
Physiology 12 Kidney and Fluid regulation Guyton Ch 20, 21,22,23 Roles of the Kidney Regulation of body fluid osmolarity and electrolytes Regulation of acid-base balance (ph) Excretion of natural wastes
ACID-BASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR
 ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
ACIDBASE BALANCE URINE BLOOD AIR H 2 PO 4 NH 4 HCO 3 KIDNEY H H HCO 3 CELLS Hb H LUNG H 2 CO 3 HHb CO 2 H 2 O ph = 7.4 [HCO 3 ] = 24 meq/l PCO 2 = 40 mm Hg CO 2 PRIMARY RENAL MECHANISMS INVOLVED IN ACIDBASE
3/17/2017. Acid-Base Disturbances. Goal. Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine
 Acid-Base Disturbances Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders Discuss the approach
Acid-Base Disturbances Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders Discuss the approach
Introduction. Acids, Bases and ph; a review
 0 P a g e Introduction In this sheet, we discuss acidbase balance in our body and the role of kidneys in its establishment. Arrangement of topics is different from that of the lecture, to assure consistency
0 P a g e Introduction In this sheet, we discuss acidbase balance in our body and the role of kidneys in its establishment. Arrangement of topics is different from that of the lecture, to assure consistency
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
Answers and Explanations 1. The answer is D [V B 4 b]. Distal K + secretion is decreased by factors that decrease the driving force for passive diffusion of K + across the luminal membrane. Because spironolactone
9/14/2017. Acid-Base Disturbances. Goal. Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
 Acid-Base Disturbances NCNP October 10, 2017 Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
Acid-Base Disturbances NCNP October 10, 2017 Eric Magaña, M.D. Presbyterian Medical Center Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Goal Provide an approach to determine complex acid-base disorders
11/05/1431. Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Urine Formation by the Kidneys Tubular Processing of the Glomerular Filtrate Chapter 27 pages 327 347 1 OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe: Absorptive Characteristics
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Distal and proximal RTA. Detlef Bockenhauer
 Distal and proximal RTA Detlef Bockenhauer acidosis: Is it real? H + + HCO 3 - > H2 O + CO 2 What do you need to assess an acid-base disorder Blood: blood gas, electrolytes including bicarbonate (measured)
Distal and proximal RTA Detlef Bockenhauer acidosis: Is it real? H + + HCO 3 - > H2 O + CO 2 What do you need to assess an acid-base disorder Blood: blood gas, electrolytes including bicarbonate (measured)
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD
 BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
BUFFERING OF HYDROGEN LOAD 1. Extracellular space minutes 2. Intracellular space minutes to hours 3. Respiratory compensation 6 to 12 hours 4. Renal compensation hours, up to 2-3 days RENAL HYDROGEN SECRETION
** Accordingly GFR can be estimated by using one urine sample and do creatinine testing.
 This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
This sheet includes the lecture and last year s exam. When a patient goes to a clinic, we order 2 tests: 1) kidney function test: in which we measure UREA and CREATININE levels, and electrolytes (Na+,
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
CASE 27. What is the response of the kidney to metabolic acidosis? What is the response of the kidney to a respiratory alkalosis?
 CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
CASE 27 A 21-year-old man with insulin-dependent diabetes presents to the emergency center with mental status changes, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and rapid respirations. On examination, the patient
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
CHAPTER 27 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Body fluid refers to body water and its dissolved substances. B. Regulatory mechanisms insure homeostasis of body fluids since their malfunction may seriously
Total Body Potassium
 Potassium Kate Driver BMLSc MAACB Immunochemistry Product Manager ANZ PI Diasorin Australia kate.driver@diasorin.com.au AACB QLD Branch Education Representative Australasian Association of Clinical Biochemists
Potassium Kate Driver BMLSc MAACB Immunochemistry Product Manager ANZ PI Diasorin Australia kate.driver@diasorin.com.au AACB QLD Branch Education Representative Australasian Association of Clinical Biochemists
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-
 Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-74. (1) Carbon dioxide arrives at the kidney tubule cell in the proximal
Graphics are used with permission of : adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) -42-74. (1) Carbon dioxide arrives at the kidney tubule cell in the proximal
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Acid Base Disorders. ACOI 2017 Board Review Case Studies
 Acid Base Disorders ACOI 2017 Board Review Case Studies Disclosures Nothing to declare High Anion Gap Acidosis Case 1 40 yo gentleman presenting to ER with coma labs : ph 7.14/ pco2 15; Na 138/ K 6.4/
Acid Base Disorders ACOI 2017 Board Review Case Studies Disclosures Nothing to declare High Anion Gap Acidosis Case 1 40 yo gentleman presenting to ER with coma labs : ph 7.14/ pco2 15; Na 138/ K 6.4/
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Patho Instructor Notes Revised: 11/2013 Cells form 4 basic tissue groups: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective
Physiology questions review
 Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Physiology questions review 1- The consumption of O2 by the kidney: a- decrease as blood flow increases b- regulated by erythropoiten c- remains constant as blood flow increase d- direct reflects the level
Biochemistry of acid-base disorders. Alice Skoumalová
 Biochemistry of acid-base disorders Alice Skoumalová Main topics of the lecture: Measurement of acid-base dysbalance Classification of the acid-base disorders 4 basic acid-base disorders and their compensaiton
Biochemistry of acid-base disorders Alice Skoumalová Main topics of the lecture: Measurement of acid-base dysbalance Classification of the acid-base disorders 4 basic acid-base disorders and their compensaiton
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari
![Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics. Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari](/thumbs/90/104323364.jpg) Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
Pharmacology I [PHL 313] Diuretics Dr. Mohammad Nazam Ansari Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Each adult kidney weighs 125-170g in males and 115-155g in females, represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive
A case of DYSELECTROLYTEMIA. Dr. Prathyusha Dr. Lalitha janakiraman s unit
 A case of DYSELECTROLYTEMIA Dr. Prathyusha Dr. Lalitha janakiraman s unit CASE SUMMARY 4 month old, female infant 1 st born to NC parents, term, b.wt: 3.25kg No neonatal hospitalization Attained head control
A case of DYSELECTROLYTEMIA Dr. Prathyusha Dr. Lalitha janakiraman s unit CASE SUMMARY 4 month old, female infant 1 st born to NC parents, term, b.wt: 3.25kg No neonatal hospitalization Attained head control
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance
 25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
25 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid Base Balance Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett Note to the Instructor: For the third edition of Visual Anatomy & Physiology, we have updated our PowerPoints to fully
Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Total body water for 150 lb. male = 40L 65% ICF 35% ECF 25% tissue fluid 8% blood plasma, lymph 2% transcellular fluid (CSF, synovial fluid) Water Movement
Chapter 24 Water, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Total body water for 150 lb. male = 40L 65% ICF 35% ECF 25% tissue fluid 8% blood plasma, lymph 2% transcellular fluid (CSF, synovial fluid) Water Movement
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed
 DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
DIURETICS-4 Dr. Shariq Syed AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 1 Pop Quiz!! Loop diuretics act on which transporter PKCC NKCC2 AIKTCC I Don t know AIKTC - Knowledge Resources & Relay Center 2 Pop
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Acid-Base Disturbance. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Acid-Base Disturbance. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4
 Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Fluid and Electrolytes P A R T 4 Mechanisms that control acid-base homeostasis Acids and bases continually enter and leave body Hydrogen ions also result from metabolic activity Acids Hydrogen ion donors
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Learning Outcomes. Acid base terminology ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION
 Slide 1 ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION David O Neill MSc BSc RN NMP FHEA Associate Lecturer (Non Medical Prescribing) Cardiff University Advanced Nurse Practitioner Respiratory Medicine Slide 2 Learning
Slide 1 ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS INTERPRETATION David O Neill MSc BSc RN NMP FHEA Associate Lecturer (Non Medical Prescribing) Cardiff University Advanced Nurse Practitioner Respiratory Medicine Slide 2 Learning
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT
 Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Managing Acid Base and Electrolyte Disturbances with RRT John R Prowle MA MSc MD MRCP FFICM Consultant in Intensive Care & Renal Medicine RRT for Regulation of Acid-base and Electrolyte Acid base load
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
1. What is the cause and pathophysiology of this patient s metabolic acidosis?
 The Clinical Physiologist Section Editors: John W. Kreit, M.D., and Erik Swenson, M.D. Hypo-Hypo: A Complex Metabolic Disorder Brian L. Block 1, Samuel Bernard 1, and Richard M. Schwartzstein 2 1 Department
The Clinical Physiologist Section Editors: John W. Kreit, M.D., and Erik Swenson, M.D. Hypo-Hypo: A Complex Metabolic Disorder Brian L. Block 1, Samuel Bernard 1, and Richard M. Schwartzstein 2 1 Department
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy AB balance parameters Extracellular ph (plasmatic ph)= 7.35-7.45 < 7.35= acidosis
Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting
 RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
RENAL ANL) ACID-BASE PHYSIOLOGY 213 Case 37 Metabolic Alkalosis: Vomiting Maria Cuervo is a 20-year-old philosophy major at a state university. When the "24-hour" stomach flu went around campus during
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Acid-Base Balance Workshop. Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli
 Acid-Base Balance Workshop Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli Objectives Normal Acid-Base Physiology Simple Acid-Base Disorders Compensations and Disorders The Anion Gap Mixed
Acid-Base Balance Workshop Dr. Najla Al Kuwaiti Dr. Abdullah Al Ameri Dr. Amar Al Shibli Objectives Normal Acid-Base Physiology Simple Acid-Base Disorders Compensations and Disorders The Anion Gap Mixed
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks
 Mayo Clinic O Brien Urology Research Center RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES 2017 Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks John C Lieske, MD July 27, 2017 What types
Mayo Clinic O Brien Urology Research Center RISK FACTORS AND TREATMENT STRATEGIES FOR URINARY STONES 2017 Review of NASA s Evidence Reports on Human Health Risks John C Lieske, MD July 27, 2017 What types
[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum
![[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum [Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut. John A Kellum](/thumbs/85/92127350.jpg) [Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut John A Kellum 25.1 Introduction Throughout this book we have seen that the Stewart formulation can be used to help understand the mechanisms of acid-base equilibrium
[Chapter 25] The Liver and the Gut John A Kellum 25.1 Introduction Throughout this book we have seen that the Stewart formulation can be used to help understand the mechanisms of acid-base equilibrium
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES
 THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
THE HYPERKALEMIC SYNDROMES K + BALANCE Cells (3400 meq) ECF (60 meq) External K Pump insulin catechols Na intake Leak K ph; osmolality membrane integrity distal Na + renal { delivery output aldosterone
Renal Physiology - Lectures
 Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Renal Physiology - Lectures Physiology of Body Fluids PROBLEM SET, RESEARCH ARTICLE Structure & Function of the Kidneys Renal Clearance & Glomerular Filtration PROBLEM SET Regulation of Renal Blood Flow
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis
 Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED. Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics
 Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Diuretics having the quality of exciting excessive excretion of urine. OED Inhibitors of Sodium Reabsorption Saluretics not Aquaretics 1 Sodium Absorption Na Entry into the Cell down an electrochemical
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Normal Renal Function
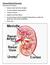 Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Normal Renal Function Functions of the Kidney: balances solute and water transport excretes metabolic waste products conserves nutrient regulates acid-base balance secretes hormones that help regulate
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within normal values. Depends on water and ion balance blood gas homeostasis Blood acidity may be expressed
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within normal values. Depends on water and ion balance blood gas homeostasis Blood acidity may be expressed
URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS. Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-JANUARY 1998 Original Articles URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga From the Departments of
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-JANUARY 1998 Original Articles URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga From the Departments of
Acid-Base disturbances Physiological approach
 AcidBase disturbances Physiological approach Pieter Roel Tuinman, M.D., PhD, intensivist Department of Intensive Care, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands p.tuinman@vumc.nl Content Introduction
AcidBase disturbances Physiological approach Pieter Roel Tuinman, M.D., PhD, intensivist Department of Intensive Care, VU Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands p.tuinman@vumc.nl Content Introduction
D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor
![D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor D fini n tion: p = = -log [H+] ph=7 me m an s 10-7 Mol M H+ + (100 nmol m /l); ) p ; H=8 me m an s 10-8 Mol M H+ + (10 (10 n nmol m /l) Nor](/thumbs/75/72756397.jpg) Definition: ph regulation ph = -log [H + ] ph=7 means 10-7 Mol H + (100 nmol/l); ph=8 means 10 Normal plasma value: 7.35-7.45; 7.45; (H Acidosis: ph7.45 Intracellular ph = 7.1-7.3
Definition: ph regulation ph = -log [H + ] ph=7 means 10-7 Mol H + (100 nmol/l); ph=8 means 10 Normal plasma value: 7.35-7.45; 7.45; (H Acidosis: ph7.45 Intracellular ph = 7.1-7.3
PRINCIPLES OF DIURETIC ACTIONS:
 DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
DIURETIC: A drug that increases excretion of solutes Increased urine volume is secondary All clinically useful diuretics act by blocking Na + reabsorption Has the highest EC to IC ratio = always more sodium
RENAL. 6. Renal acid secretion is affected by all of the following except a. pco 2 b. K c. Carbonic anhydrase d. Aldosterone e. Ca
 RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
RENAL 1. The reabsorption of Na in the proximal tubules a. Reabsorbs 80% of the filtered sodium load b. Causes increased hypertonicity c. Is powered by N/H ATPase d. Shares a common carrier with glucose
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy
 Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within
Dr. Suzana Voiculescu Discipline of Physiology and Fundamental Neurosciences Carol Davila Univ. of Medicine and Pharmacy Definition All the processes inside the body which keep the H+ concentration within
ACID BASE BALANCE AND REGULATION OF ph
 ACID BASE BALANCE AND REGULATION OF ph 4 Chapter objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to: b Define the normal range for plasma ph. c Explain the role of the kidney in the steady state
ACID BASE BALANCE AND REGULATION OF ph 4 Chapter objectives After studying this chapter you should be able to: b Define the normal range for plasma ph. c Explain the role of the kidney in the steady state
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys
 Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
Ch 17 Physiology of the Kidneys Review Anatomy on your own SLOs List and describe the 4 major functions of the kidneys. List and explain the 4 processes of the urinary system. Diagram the filtration barriers
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS AND HYPERKALEMIA. Sheena Surindran, MD 3/22/2011
 CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS AND HYPERKALEMIA Sheena Surindran, MD 3/22/2011 DISTAL TUBULE K SECRETION EFFECTS OF CYCLOSPORINE ON RAS AND POTASSIUM EXCRETION 10 pts on CsA and prednisone / 10 on AZT and prednisone
CALCINEURIN INHIBITORS AND HYPERKALEMIA Sheena Surindran, MD 3/22/2011 DISTAL TUBULE K SECRETION EFFECTS OF CYCLOSPORINE ON RAS AND POTASSIUM EXCRETION 10 pts on CsA and prednisone / 10 on AZT and prednisone
Physiology week 16 Renal 2 (volume/buffers)
 Physiology week 16 Renal 2 (volume/buffers) Defense of Tonicity and Volume Defense of tonicity Tonicity = osmolality of a solution relative to plasma Osmolality measures [ ] all particles in solution,
Physiology week 16 Renal 2 (volume/buffers) Defense of Tonicity and Volume Defense of tonicity Tonicity = osmolality of a solution relative to plasma Osmolality measures [ ] all particles in solution,
S.M. Gorbatkin MD, PhD Emory Board Review in Internal Medicine July Renal Division Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center Atlanta
 S.M. Gorbatkin MD, PhD Emory Board Review in Internal Medicine July 2016 External Industry Relationships * Equity, stock, or options in biomedical industry companies or publishers Board of Directors or
S.M. Gorbatkin MD, PhD Emory Board Review in Internal Medicine July 2016 External Industry Relationships * Equity, stock, or options in biomedical industry companies or publishers Board of Directors or
Low Efficacy Diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Osmotic diuretics. Miscellaneous
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Low Efficacy Diuretics 1. Potassium sparing diuretics 2. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors 3. Osmotic diuretics 4. Miscellaneous
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE
 MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
MODULE 8: URINALYSIS AND ACID BASE BALANCE This lab involves a tutorial that teaches you how to analyze a urine reagent strip. If you are taking the lab on campus, you will be given the opportunity to
Renal Physiology Part II. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
Renal Physiology Part II Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Fluid and Electrolyte balance As we know from our previous studies: Water and ions need to be balanced in order to maintain proper homeostatic
What location in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract has tight, or impermeable, junctions between the epithelial cells?
 CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
CASE 32 A 17-year-old boy presents to his primary care physician with complaints of diarrhea for the last 2 days. The patient states that he just returned to the United States after visiting relatives
BIO132 Chapter 27 Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balance Lecture Outline
 BIO132 Chapter 27 Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balance Lecture Outline Fluid divisions 1. Extracellular fluid (ECF) 2. Intracellular fluid (ICF) Stabilization 1. Fluid balance 2. Electrolyte balance
BIO132 Chapter 27 Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid Base Balance Lecture Outline Fluid divisions 1. Extracellular fluid (ECF) 2. Intracellular fluid (ICF) Stabilization 1. Fluid balance 2. Electrolyte balance
Therapeutics of Diuretics
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Therapeutics of Diuretics Thambi, M. (2017). The Clinical Use of Diuretics. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago.
