Safety Issues in Hockey
|
|
|
- Harvey Hawkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 1 Safety Issues in Hockey Introduction This lesson is an attempt to acquaint you with various injuries associated with hockey and how you should be prepared to deal with these injuries. If you have prepared your first aid kit, brought along the medical records and familiarized yourself with the different types of injuries, you should be able to handle whatever situation arises. Follow the steps that are outlined for you and remember you are not a doctor. If you are in doubt about how to proceed, use the coins in your first aid kit and call for professional help. Do not make decisions about treatments if you are not qualified to make them. Remember, react quickly and with confidence. Most injuries will be minor and the injured players will need only a little reassurance before they can be moved to the bench area. Injuries will always occur in ice hockey. Therefore, you must prepare yourself to deal with whatever happens in a calm, responsible manner. The coach is a teacher, leader and role model for young athletes. The coach is in charge when an emergency occurs, either on or off the ice. 1. The coach is a teacher and a leader. The coach is a role model for young athletes. 2. The coach is in charge when an emergency occurs, either on or off the ice. 3. Emergency care Evaluation of an injured player using the ABC s = Airway, Breathing, Circulation Some points to remember: Don t turn the player Don t move the player Don t remove the player s helmet, it has been shown it is better to leave it on. 4. Injury prevention Warm-up and stretching before and after games and practices. Cooling down after games and practices. Proper practice to game ratio. Importance of hydration during practices and games. 70% - 90% of injuries occur in games. Only 10% - 30% of injuries occur during practice.
3 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 2 Practice to game ratio The recommended practice to game ratio in youth hockey is 2:1 to 4:1 NHL 1:1 (80 to 110 games) College 2:1 (30 to 40 games) Juniors 2:1 (60 to 80 games) High School 2:1 (25 to 30 games) Youth 4:1 to 1:2 (25 to 75 games) Relation of Injuries to Practice to Game Ratio A Premise (as yet unproved) Teams with HIGHER practice to game ratios will have LESS injuries than teams with LOWER practice to game ratios. Dr. Alan Ashare, USA Hockey Some basic ideas in Injury Prevention Injuries are not part of the game. Coaches are our first line of defense against injuries. Coaches are very important in limiting or decreasing the risk for catastrophic injuries. 5. Injuries in Ice Hockey Most common injuries: A. Back or Neck Injury B. Blisters C. Bruise D. Dental Injury E. Dislocation F. Fracture G. Head Injury - Conscious H. Head Injury - Unconscious I. Lacerations J. Loss of Wind K. se Bleed L. Skate Bite M. Sprain N. Strain
4 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 3 A. Back or Neck Injury Any injury to the back or neck area which causes the player to become immobile or unconscious. Pain and tenderness over the spine. Numbness Weakness or heaviness in limbs. Tingling feeling in extremities. Make sure player is breathing. Call for medical assistance. Dependent upon severity of the injury, a bruise may mean no practice for 2-3 days; a fracture may mean the player could never play again. Permission of a physician. B. Blisters Localized collection of fluid in the outer portion of the skin. Redness Inflammation Oozing of fluid Discomfort Clean the site with disinfectant. Use a sterile needle and puncture the blister at the edge; force the fluid out. Put disinfectant on the area. Cover the area with a band-aid. Alter the cause of the problem when possible. (i.e., proper size and/or shape of the skates) Immediately, unless pain is severe
5 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 4 C. Bruise A bruising of the skin caused by a direct blow. Tenderness around the injury. Swelling Localized pain Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation (R.I.C.E.) for the first 3 days. Contrast treatments for days 4-8 Restricted activity, protective padding When there is complete absence of pain and full range of motion D. Dental Injury Any injury to mouth or teeth Pain Bleeding Loss of tooth (partial or total) Clear the airway where necessary. Stop the bleeding with direct pressure. (make sure excess blood does not clog airway) Save any teeth that were knocked free; store them in moist, sterile cloth. They may be reinserted in some cases. Transport to hospital. When pain is gone usually within 2-3 days Permission of a dentist
6 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 5 E. Dislocation Loss of normal anatomical alignment Complaints of joint slipping in and out. (subluxation) Joint out of line. Pain at the joint. Mild - Treat as sprain. (R.I.C.E.) - Obtain medical care. Severe - Immobilize before moving. - Needs to be treated by a physician. - Obtain medical care. (do not attempt to put joint back into place) - R.I.C.E. Subluxation: Go by pain level, range of motion and strength; if no pain, has full range of motion and strength returned to 95% of same joint on opposite side of body, player may return to action. Severe: Surgery may be necessary, six weeks is usually the minimum recovery time; full range of motion must be present, full strength must be present; doctor s permission is required to resume practice.
7 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 6 F. Fracture A crack or complete break in a bone. A simple fracture is a broken bone, but with unbroken skin. A compound fracture is a broken bone and broken skin. Pain at fracture site. Tenderness, swelling. Deformity or unnatural position. Loss of function in injured area. Open wound, bleeding. (compound) A simple fracture may not be evident immediately. If localized pain persists, obtain medical assistance. Full range of motion is present. Strength must be returned to pre-injury levels throughout the entire range of motion of adjoining joints. Permission of a physician. G. Head Injury Conscious Any injury which causes the player to be unable to respond in a coherent fashion to known facts. (names, date, etc.) Dizziness Pupils unequal in size and/or non-responsive to light and dark. Disoriented Unsure of name, date or activity. Unsteady movement of eyeballs when trying to follow a finger moving in front of eyes same symptoms as noted for back or neck injury may be present.
8 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 7 If above symptoms are present, player may be moved carefully when dizziness disappears. Players with head injuries should be removed from further practice or competition that day and should be carefully observed. Obtain medical assistance Permission of a physician. H. Head Injury Unconscious Any injury in which the player is unable to respond to external stimuli by verbal or visual means. Player is unconscious. Cuts or bruises to head area. Any time a player is unconscious, assume an injury to the spinal cord or brain. Remove the mouth piece and clear the airway if necessary. Do not move the player. Call for medical assistance. Do not remove the helmet. Permission of a physician.
9 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 8 I. Lacerations A tearing or cutting of the skin. Bleeding Swelling Direct pressure to the wound for four to five minutes will usually stop bleeding. Clean the wound with disinfectant. R.I.C.E. If stitches are required, send to a doctor within twenty-four hours. As soon as pain is gone, if the wound can be protected from further injury. J. Loss of Wind A forceful blow to mid-abdomen area which causes inability to breathe. Rapid, shallow breathing. Gasping for breath. Make sure no other injuries exist. Place player on back. Get player to relax and breathe slowly. After five minutes of rest to regain composure and breathing has returned to normal rate.
10 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 9 K. se Bleed Bleeding from the nose Bleeding Swelling Pain Deformity of nose Calm the athlete down. Get athlete into a sitting position. Pinch the nostrils together with fingers while the victim breathes through the mouth. If bleeding cannot be controlled, call for medical assistance. Minor nosebleed when bleeding has stopped for several minutes. Serious nosebleed no more competition that day; doctor s permission if a fracture has occurred L. Skate Bite Pain where the skate laces are tied Localized pain. Small, swollen area. Lace skates down one eyelet. Put foam rubber under tongue where laces are tied. Rest if pain continues. Immediately
11 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 10 M. Sprain A stretching or a partial or complete tear of the ligaments surrounding a joint. Pain at the joint. Pain aggravated by motion at the joint. Tenderness and swelling. Looseness at thejoint. Immobilize at time of injury if pain is severe; use hockey stick as splint. R.I.C.E. See physician. Extended rest. Surgery Pain and swelling are gone. Full range of motion reestablished. Strength and stability within 95% of the non-injured limb throughout range of motion. Light formal activity with no favoring of the injury. Moderate to full intensity formal activity with no favoring of the injury. Return to formal practice and competition.
12 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 11 N. Strain Stretching or tearing of the muscle or tendons which attach the muscle to the bone. Commonly referred to as a muscle pull Localized pain brought on by stretching or contracting the muscle in question. Unequal strength between limbs. R.I.C.E. for the first 3 days. Stretching to point of discomfort; no pain, start as soon as player is able. Contrast treatment for days 4-8. Check flexibility can players stretch as far as they could pre-injury? Check strength between limbs; do both sides of the body appear equally strong? Can athlete perform basic hockey tasks (i.e., skating, passing, shooting) without favoring the injury? Mild Strain...1 to 2 days Moderate Strain...4 to 6 days Severe Strain...1 to 2 weeks or more Some t So Common Injuries Dislocated Shoulder Broken Wrist Broken Ankle Concussions Lacerations Three Types of Catastrophic Ice Hockey Injuries Paralysis due to cervical spine injuries. Skateblade neck lacerations. Death due to blunt chest trauma. (commotio cordis)
13 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey Early Treatment R.I.C.E. - Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation 7. Sports Medicine Physicians can be very helpful in evaluating a player s injuries and determining when he/she can return to play. 8. CPR All coaches are strongly urged to take CPR training. Make it a team project to get players and coaches patched in CPR. Take the American Red Cross, USOC Sports Safely Training Course (6 hours) Call your local American Red Cross Chapter to get the schedule for the next course 9. Universal Precautions Hepatitis and HIV Assume that all players have the disease. Cover bleeding wounds and replace bloody uniforms. Use latex gloves and plastic bags. 10. Team First Aid Kit Band-Aids 1-2 rolls of plastic tape 2-4 4x4 sterile gauze pads 3-4 small zip-lock bags (use as ice bags) 1-2 chemical ice bags 2-4 foil covered antiseptic wipes 2-3 pairs of latex gloves List of contents and emergency numbers.
14 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 13 Maintaining Appropriate Records The immediate care you provide to an injured player is important to limit the extent of the injury and set the stage for appropriate rehabilitation and thus a quick recovery. It is not sufficient, however, to terminate your care with these two areas. Two additional brief but valuable tasks should be completed. The first of these is to complete a personal injury report form and the second is to log the injury on your summary of season injuries. Personal Injury Report Form It is important for you to maintain a record of the injuries that occur to your players. This information may be helpful to guide delayed care or medical treatment and may be very important if any legal problems develop in connection with the injury. Summary of Season Injuries A Summary of Season Injuries, lists each type of injury, with a space for you to record when that type of injury occurred. At the end of the season you should total the incidences of each injury to see if there is a trend to the kind of injuries your team has suffered. If a trend exists, evaluate your training methods in all areas of practices and games. Try to alter drills or circumstances that may be causing injuries. Perhaps your practice routine ignores or overemphasizes some area of stretching or conditioning. Decide on a course of action that my be implemented for next season and note the appropriate changes you wish to make on your season or practice plans. Rehabilitation Decisions about the rehabilitation of injuries and re-entry into competition must be made according to a flexible set of guidelines; not hard and fast rules. Every individual on your team and each injury is unique. Therefore, rehabilitation techniques and re-entry criteria will differ for each injured player.
15 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 14 General Procedures Most minor injuries suffered by your players will not be treated by a physician. Therefore, you, the player, and the player s parents will determine when the player returns to action. Players, coaches and parents realize that missing practices will reduce the player s ability to help the team and that the loss of practice time will reuce the opportunity to perfect the skills of the game. Pressure is often exerted on the coach to play injured players before they are fully recovered. However, chances of an injury recurring are greatly increased if a player returns too soon. The following five criteris should be met, in order, before allowing an injured player back into full competition. They are: Absence of Pain Full range of motion at the injured area. rmal size and power (strength throughout the range of motion) at the injured area. rmal speed and agility. rmal level of fitness. If a physician is not overseeing an injured player s rehabilitation, the task of rehabilitation will probably fall upon the coach. Stretching activities, calisthenics and weight training exercises form the basis of a rehabilitation program. Start with simple stretches. Presence of pain during movement is the key to determining if the activity is too stressful. The onset of pain means too much is being attempted too soon. When players can handle the stretching, then calisthenics and weight training can be added to the program. Absence of Pain Most injuries are accompanied by pain, although the pain is not always evident immediately when the injury occurs. Usually, the pain disappears quickly if the injury is a bruise, a strain or a minor sprain. For more serious injuries such as dislocations, tears,,or fractures, the pain may remain for days or weeks. When the pain is gone, the player can start the stretching portion of a rehabilitation program. The main goal of a rehabilitation program is to re-establish range of motion, strength, power and muscular endurance at the point of injury. As long as players remain free of pain, they should proceed with their program. If pain reoccurs they should eliminate pain-producing movements until they are pain-free again. The chance of an injury recurring is greatly increased if a player returns to action too soon. Full Range of Motion Injuries generally reduce the range of motion around a joint. The more sever the injury, the greater the reduction in range of motion, particularly when the injured area has been im mobilized. As soon as they are able, injured players should start moving the injured area in a progressively normal way. For example, if the player has strained a groin muscle, a fairly common injury early in the season, he/she should stretch the muscle as much as possible without causing pain. Initially, the movement may be slight if the injury was severe, but with stretching, the full range of motion will eventually return. When the player can move the injured joint through its normal range, strengthening exercises should begin.
16 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 15 Strength and Size After a body part has been immobilized (cast, splint wrap or disuse), muscles become smaller and weaker then they were prior to the injury. Just because a cast is removed and the injuries have healed does not mean that players are ready to practice or play at full speed. Loss of muscle mass means a loss of strength. Letting the player resume a normal practice schedule before strength has returned to pre-injury levels could lead to re-injury. Strengthening the injured area should be done very conservatively. If weights are used, start with light weights and perform the exercise through the entire range of motion. If the exercise causes pain, then lighter weights should be used. Your goal is to have the players regain full strength through the entire range of motion before allowing them to return to competition. To determine when full strength and size has been regained, compare the injured area to the non-injured area on the opposite side of the body. When both areas are of equal size and strength then the players may progress to the next phase of recovery. rmal Speed and Agility If the lower parts of the body were injured, skating drills which incorporate progressively more intense changes of speed, and/or direction, stopping and accelerating will provide a good indication of the player s recovery. If the upper part of the body was injured, passing and shooting drills should be attempted also. In your observation of injured players, try to detect any favoring of the injury or inability to smoothly perform a skill at increasing intensities. When players can move at pre-injury speed and agility, they are almost ready to play. The main goal of a rehabilitation program is to re-establish range of motion, strength, power and muscular endurance to the injured area. Level of Fitness Every extended layoff reduces the level of muscular fitness. While recovering, the player may be able to exercise other body parts without affecting the injured area. Someone with a sprained ankle may not be able to skate, but may be able to swim. Someone with a broken wrist may be able to jog or ride a bike. Encourage this type of activity, because it helps to maintain portions of their pre-injury levels of fitness. Players who have missed long periods of time due to an injury, should practice for several days after meeting the previous criteria, before being allowed to play in a game. Their cardiovascular system and the endurance of the injured musculature need time to adjust to the demands of the game. The longer the layoff, the more conditioning work they will need. Conclusion When the pain is gone, and the range of motion, strength, agility and conditioning are back to normal, your player is ready to resume play. The entire process may take two days for a bruise to 12 weeks or more for a fracture. In either case, if you have followed the general guidelines of this chapter, you know you have acted in the best long-term interest of the player. Participation is important, but only if the participation is achieved with a healthy body. Resist the pressure and the temptation to rush players into a game before they are ready. Your patience will be rewarded in terms of the long term health and performance of your players.
17 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 16 Addendum A - Medical History Form Name Date Address Birthdate Telephone - Day Evening Who to contact in case of an emergency? Name Telephone Relationship Physician s Name Telephone Hospital of choice (If the answer to any of the following questions is or was yes, please describe the problem and its implications for proper first aid treatment on the back.) Have you had (or do you presently have) any of the following? Circle One Head injury (concussion, skull fracture) Fainting Spells Convulsion/epilepsy Neck or back injury Asthma High blood pressure Kidney problems Hernia Diabetes Heart murmr Allergies Specify Injuries to: Shoulder Knee Ankle Fingers Arm Other Poor Vision Poor Hearing Other Have you had a recent tetanus booster? If so, When? Are you currently taking any medication? What? Why? Has a doctor placed any restrictions on your activity? Explain._ Signed Athlete Parent
18 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 17 Addendum B - Sample 3 x 5 Card Medical Information Player s Name Address Parent s Name Telephone - Home Work Alternate In an emergency, if parents cannot be contacted, notify: Name Telephone - Work Home Doctor s Name Telephone - Day Evening Past Injuries Restrictions/Allergies Hospital Preference
19 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 18 Coaches' Clipboard tes:
20 Safety Issues in Hockey - Presenter: Scott Abbey 19 Coaches' Clipboard tes:
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
First Aid Policy. One member of every coaching staff (competitive) is "required" to be first aid certified.
 First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
Module Summaries: The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program.
 Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Have an Emergency Plan. Injury Prevention. Stretches for All Players
 Have an Emergency Plan It is important to have a well thought out plan for dealing with injuries. It is best to have a written response plan for emergencies. Keep this in your coaching bag where you can
Have an Emergency Plan It is important to have a well thought out plan for dealing with injuries. It is best to have a written response plan for emergencies. Keep this in your coaching bag where you can
Key Words. clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma. Linked Core Abilities
 Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Providing for Players Safety 31. Emergency Plan
 Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Heat Injuries caoches should be aware of...4
 Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide
 SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
First Aid in Agriculture
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
THE GAME IN THE CHILD
 SoccerMaine State Youth Course U8/U10 Youth Module THE GAME IN THE CHILD The mission of the National Youth License and the State Youth Courses is to provide the most current and advanced information on
SoccerMaine State Youth Course U8/U10 Youth Module THE GAME IN THE CHILD The mission of the National Youth License and the State Youth Courses is to provide the most current and advanced information on
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
NOTE If it is necessary to perform abdominal thrusts, expose the abdominal area prior to pressing on the abdomen.
 ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
 UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
OUTLINE SHEET 5.4 PRIMARY SURVEY
 ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
ENABLING OBJECTIVES: 4.7 List the procedures used in a primary survey. 4.8 Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario without injury to personnel or damage to equipment.
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course
 Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
Aviation Rescue Swimmer Course Primary Survey LT 5.4 December 2003 1 Objectives List the procedures used in a primary survey. Demonstrate primary survey procedures used in a mock trauma (moulage) scenario
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared
 Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared EMS #: 9-1-1 Poison Control #: 800.222.1222 Take a first aid course. Learn CPR and first aid for choking. Before you give first aid,
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared EMS #: 9-1-1 Poison Control #: 800.222.1222 Take a first aid course. Learn CPR and first aid for choking. Before you give first aid,
Common types of sports injuries
 Sports injuries Sports injuries are caused by overuse, direct impact, or the application of force that is greater than the body part can structurally withstand. Common injuries include bruises, sprains,
Sports injuries Sports injuries are caused by overuse, direct impact, or the application of force that is greater than the body part can structurally withstand. Common injuries include bruises, sprains,
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES
 BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute)
 Copper Hills Little League P. O. Box 194 Sahuarita, AZ 85629 First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute) Page 1 PREVENTION Following safety rules
Copper Hills Little League P. O. Box 194 Sahuarita, AZ 85629 First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute) Page 1 PREVENTION Following safety rules
LOWER MERION SOCCER CLUB CARE AND PREVENTION OF ATHLETIC INJURIES
 LOWER MERION SOCCER CLUB CARE AND PREVENTION OF ATHLETIC INJURIES Written by William Wardle, MS, ATC, CSCS Head Athletic Trainer / Assistant Director of Athletics The Haverford School, Haverford, PA April,
LOWER MERION SOCCER CLUB CARE AND PREVENTION OF ATHLETIC INJURIES Written by William Wardle, MS, ATC, CSCS Head Athletic Trainer / Assistant Director of Athletics The Haverford School, Haverford, PA April,
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
( PLUM BOROUGH SCHOOL DISTRICT
 No. 209.1 ( PLUM BOROUGH SCHOOL DISTRICT SECTION: PUPILS TITLE: FIRST AID STANDING ORDERS ADOPTED: March 27,1990 REVISED: February 27, 2001 209.1. FIRST AID STANDING ORDERS 1. Guidelines When a student
No. 209.1 ( PLUM BOROUGH SCHOOL DISTRICT SECTION: PUPILS TITLE: FIRST AID STANDING ORDERS ADOPTED: March 27,1990 REVISED: February 27, 2001 209.1. FIRST AID STANDING ORDERS 1. Guidelines When a student
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Be Prepared. Conditions considered to be life or death emergencies: (911 should be called as soon as possible.) Unconscious athlete
 TM Let s Go Team! 800.596.7860 tel 866.255.7135 fax www.nationalcheersafety.com 911 Script This is (caller). The address of my emergency is (address) and the phone number I am calling from is (phone number).
TM Let s Go Team! 800.596.7860 tel 866.255.7135 fax www.nationalcheersafety.com 911 Script This is (caller). The address of my emergency is (address) and the phone number I am calling from is (phone number).
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process
 LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
First Aid Outline. For Minor Injuries: PRICES PEARLS. First Aid Seminar /7/17
 First Aid Outline First Aid Seminar 2017 Presented by: Jeff Lee Bone, bruise, and cut injuries Sprains and strains Fractures Eye injuries Stings Concussions, fainting, heat injuries Tooth loss Nosebleeds
First Aid Outline First Aid Seminar 2017 Presented by: Jeff Lee Bone, bruise, and cut injuries Sprains and strains Fractures Eye injuries Stings Concussions, fainting, heat injuries Tooth loss Nosebleeds
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe
 Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, Page 1
 Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
Hatfield & McCoy Mine Safety Competition First-Aid Contest JULY 15, 2014 Page 1 PROBLEM Billy is a maintenance person that has been conducting clean-up and service duties on the number one conveyor belt
Basic First Aid. Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police
 Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
Basic First Aid Sue Fisher Emergency Management Coordinator CSUF University Police Information given for this lecture is not meant to replace any official training by the American Red Cross, or any other
MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
Disaster Medical Operations-Part 2
 Disaster Medical Operations-Part 2 Community Emergency Response Team Disaster Medical Operations Part 1 Review The killers Airway obstruction Excessive bleeding Shock All immediate receive airway control,
Disaster Medical Operations-Part 2 Community Emergency Response Team Disaster Medical Operations Part 1 Review The killers Airway obstruction Excessive bleeding Shock All immediate receive airway control,
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
Bone Injuries and Treatment. Fractures and Dislocations
 Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH
 STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game
 Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game Print and cut out the playing cards. Divide the class into groups of 3 or 4. Each group will need a set of playing cards. Directions for the Review game 1. Stack all
Unit 7 INJURY MANAGEMENT Review Game Print and cut out the playing cards. Divide the class into groups of 3 or 4. Each group will need a set of playing cards. Directions for the Review game 1. Stack all
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Diagnosis Players, coaches, parents and heath care providers should be able to recognize the symptoms and signs of a concussion:
 USA Hockey Concussion Management Program (as adopted by MAHA, with revisions 12/7/12) 1 Michael Stuart MD Alan Ashare MD A concussion is a traumatic brain injury- there is no such thing as a minor brain
USA Hockey Concussion Management Program (as adopted by MAHA, with revisions 12/7/12) 1 Michael Stuart MD Alan Ashare MD A concussion is a traumatic brain injury- there is no such thing as a minor brain
Ears. Mouth. Jowls 6 Major Bones of the Face Nasal bone Two
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 25 Injuries to the Face, Neck, and Eyes Injuries to the Face and Neck Face and neck are to injury Relatively unprotected positions on body Some injuries are life-threatening. trauma to
INJURIES INJURY PREVENTION. Train Your Way to. A bit about TRAUMATIC CUMULATIVE
 Injuries are not merely accidents. In fact, most injuries are predictable and preventable events - especially when they are caused by activities that play major part in a person s life. A bit about INJURIES
Injuries are not merely accidents. In fact, most injuries are predictable and preventable events - especially when they are caused by activities that play major part in a person s life. A bit about INJURIES
CONCUSSION IN YOUTH SPORTS
 Canada Basketball and our Provincial/ Territorial Sport Organizations understand that having a concussion policy is crucial to the health and wellness of our young athletes. Through the amalgamation of
Canada Basketball and our Provincial/ Territorial Sport Organizations understand that having a concussion policy is crucial to the health and wellness of our young athletes. Through the amalgamation of
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
August 12, Sports Med Critical Question 4.notebook. Critical Question 4. How is injury rehabilitation managed?
 Critical Question 4 How is injury rehabilitation managed? 1 2 Syllabus 3 Big Heading: Critical Questions 4: How is injury rehabilitation managed Heading: Rehabilitation Procedures Rehabilitation after
Critical Question 4 How is injury rehabilitation managed? 1 2 Syllabus 3 Big Heading: Critical Questions 4: How is injury rehabilitation managed Heading: Rehabilitation Procedures Rehabilitation after
Hamilton-Wentworth District School Board. Athletics Concussion Protocol. Part I
 Hamilton-Wentworth District School Board Athletics Concussion Protocol Part I Introduction Concussions are brain injuries caused by excessive, rapid movement of the brain inside the skull. This movement
Hamilton-Wentworth District School Board Athletics Concussion Protocol Part I Introduction Concussions are brain injuries caused by excessive, rapid movement of the brain inside the skull. This movement
Property Latmedical, LLC.
 Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
NFHS BASKETBALL POINTS OF EMPHASIS: sports-medicine related topics for coaches
 2018-19 NFHS BASKETBALL POINTS OF EMPHASIS: sports-medicine related topics for coaches SPORTS MEDICINE CONCUSSION RECOGNITION AND RISK MINIMIZATION Concussions continue to be a focus of attention in contact
2018-19 NFHS BASKETBALL POINTS OF EMPHASIS: sports-medicine related topics for coaches SPORTS MEDICINE CONCUSSION RECOGNITION AND RISK MINIMIZATION Concussions continue to be a focus of attention in contact
Football First Aid: An Overview. Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS
 Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
DOWNLOAD PDF ON-FIELD EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF COMMON ATHLETIC INJURIES
 Chapter 1 : On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Medical Books On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Three of today's leading orthopedic specialists
Chapter 1 : On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Medical Books On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Three of today's leading orthopedic specialists
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Duration of resource: 22 Minutes. Year of Production: Stock code: VEA12046
 ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Accidents and injuries occur without warning. When incidents happen in public places, often the welfare of the victim depends on the level of help they receive before qualified paramedics
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Accidents and injuries occur without warning. When incidents happen in public places, often the welfare of the victim depends on the level of help they receive before qualified paramedics
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
2017 Concussion Management Program
 2017 Concussion Management Program Michael Stuart MD Alan Ashare MD Kevin Margarucci ATC The standard of care for current medical practice and the law in most states requires that any athlete with a suspected
2017 Concussion Management Program Michael Stuart MD Alan Ashare MD Kevin Margarucci ATC The standard of care for current medical practice and the law in most states requires that any athlete with a suspected
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the 4 major ligament stabilizers of the knee. ACL tears are among the most common major knee injuries in active people of
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE IN FEMUR
 Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Disaster Medical Operations Part 2. CERT Basic Training Unit 4
 Disaster Medical Operations Part 2 Unit 4 Unit 3 Review 3 Killers Airway obstruction Excessive bleeding Shock 4-1 CERT Sizeup 1. Gather Facts 2. Assess Damage 3. Consider Probabilities 4. Assess Your Situation
Disaster Medical Operations Part 2 Unit 4 Unit 3 Review 3 Killers Airway obstruction Excessive bleeding Shock 4-1 CERT Sizeup 1. Gather Facts 2. Assess Damage 3. Consider Probabilities 4. Assess Your Situation
Hockey Canada. 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques. 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning
 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT
 UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life
 Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES
 Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture
 Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Middlebury College
 Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Sprain @ Middlebury College ** severe sprains or medial (inner side of ankle) sprains may require a different program Anatomy, Pathology, and Classification of Ankle Sprains
Caring For Your Lateral Ankle Sprain @ Middlebury College ** severe sprains or medial (inner side of ankle) sprains may require a different program Anatomy, Pathology, and Classification of Ankle Sprains
Physical Fitness. Chapter 4
 Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness is the ability to do everyday activities without becoming short of breath, sore, or tired. There are four
Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness is the ability to do everyday activities without becoming short of breath, sore, or tired. There are four
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
B) Sprains cause swelling in the injured area, but strains do not have a tendency to swell
 Lesson U4C2L4 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L4:F1) How many times have you broken a bone? A) none B) one C) two D) more than two 2. (U4C2L4:F2) How many times have you sprained an arm, leg, or other body part?
Lesson U4C2L4 FIT Questions 1. (U4C2L4:F1) How many times have you broken a bone? A) none B) one C) two D) more than two 2. (U4C2L4:F2) How many times have you sprained an arm, leg, or other body part?
Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION
 Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION Major Concepts. Proper planning of an emergency response is essential for appropriate first aid management of an injury. Anything that can be done
Chapter 7 EMERGENCY PLAN AND INITIAL INJURY EVALUATION Major Concepts. Proper planning of an emergency response is essential for appropriate first aid management of an injury. Anything that can be done
Frontline First Aid 2012 Emergency Care Manual Treatments
 Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013
 AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013 Although it is the beautiful game, soccer is one of the leading sports when it comes to its players sustaining concussions. In conjunction with the 2011 Pennsylvania
AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013 Although it is the beautiful game, soccer is one of the leading sports when it comes to its players sustaining concussions. In conjunction with the 2011 Pennsylvania
Physical Activity and Sport Related Concussion
 Appendix C Physical Activity and Sport Related Concussion Common Symptoms and Signs of Concussion It is important to know that an athlete does not need to be knocked out (lose consciousness) to have had
Appendix C Physical Activity and Sport Related Concussion Common Symptoms and Signs of Concussion It is important to know that an athlete does not need to be knocked out (lose consciousness) to have had
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
Face and Throat Injuries. Chapter 26
 Face and Throat Injuries Chapter 26 Anatomy of the Head Landmarks of the Neck Injuries to the Face Injuries around the face can lead to upper airway obstructions. Bleeding from the face can be profuse.
Face and Throat Injuries Chapter 26 Anatomy of the Head Landmarks of the Neck Injuries to the Face Injuries around the face can lead to upper airway obstructions. Bleeding from the face can be profuse.
It s better to miss one game than the whole season. What should I do if I think I have a concussion? Concussion facts:
 Concussion facts: A concussion is a brain injury that affects how your brain works. A concussion is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or body. A concussion can happen even if you haven t been
Concussion facts: A concussion is a brain injury that affects how your brain works. A concussion is caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or body. A concussion can happen even if you haven t been
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I SPRAIN MY ANKLE? HOW SHOULD I REHABILITATE MY ANKLE?
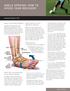 ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
Sports Science Revision Pack. Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow.
 Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
Coach s name: Please print. Coach s signature: Please sign. Today s date: Witness: Print name. Title: Please print. Signature:
 I have been provided the MAHA / USA Hockey Concussion Management educational materials. I have read and understand the information. I agree to comply with the requirement to remove a youth athlete who
I have been provided the MAHA / USA Hockey Concussion Management educational materials. I have read and understand the information. I agree to comply with the requirement to remove a youth athlete who
Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT
 ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
ANTERIOR ANKLE IMPINGEMENT Description Possible Complications Pinching of bone or soft tissue, including scar tissue, at the Frequent recurrence of symptoms, resulting in chronically front of the ankle
Sprains. Initially the ankle is swollen, painful, and may turn eccyhmotic (bruised). The bruising, and the initial swelling, is due to ruptured
 Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Treating the Ankle Sprain
 Treating the Ankle Sprain Ankle 'sprains' are very common injuries. Typically the ankle is rolled either inward (inversion sprain) or outward (eversion sprain). Inversion sprains cause pain along the outside
Treating the Ankle Sprain Ankle 'sprains' are very common injuries. Typically the ankle is rolled either inward (inversion sprain) or outward (eversion sprain). Inversion sprains cause pain along the outside
Extremity Injuries and Splinting
 CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT?
 Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
 Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Table of Contents What is concussion... 2 Causes... 3 Symptoms..3-4 When to get treatment...4-5 Daily activities. 5 Return
Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Concussion or Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Table of Contents What is concussion... 2 Causes... 3 Symptoms..3-4 When to get treatment...4-5 Daily activities. 5 Return
April 2016 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is
 Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
Can We Get Stronger as We Age? The answer to that question is absolutely! After age 40 or so, we all begin to lose muscle strength and bone density, and our hormone production slows. While these factors
Encourage pre-participation physical exams every year. in sports attend school more often, are more community
 Coaches Teaching Kids Safe Ways to Participate in Sports Sports are a great way for kids to exercise, learn about How can I teach a child to play safe? teamwork and discipline all while having fun. Research
Coaches Teaching Kids Safe Ways to Participate in Sports Sports are a great way for kids to exercise, learn about How can I teach a child to play safe? teamwork and discipline all while having fun. Research
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
Dear athletes and parents:
 Dear athletes and parents: I am the head athletic trainer at Tolleson Union High School. I look forward to this season of sports. I would like to give you some information about my job and responsibilities
Dear athletes and parents: I am the head athletic trainer at Tolleson Union High School. I look forward to this season of sports. I would like to give you some information about my job and responsibilities
