Common types of sports injuries
|
|
|
- Dorthy Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sports injuries Sports injuries are caused by overuse, direct impact, or the application of force that is greater than the body part can structurally withstand. Common injuries include bruises, sprains, strains, joint injuries and nose bleeds. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the injury. Sports injuries are commonly caused by overuse, direct impact, or the application of force that is greater than the body part can structurally withstand. An injury that happens suddenly, such as a sprained ankle caused by an awkward footfall, is known as an acute injury. Chronic injuries are caused by overusing the same muscle groups or joints. Poor technique and structural abnormalities can also contribute to the development of chronic injuries. Medical investigation of any sports injury is important, because you may be hurt more severely than you think. For example, what seems like an ankle sprain may actually be a bone fracture. Common types of sports injuries Some of the more common sports injuries include: Ankle sprain symptoms include pain, swelling and stiffness. Bruises a blow can cause small bleeds into the skin. Concussion mild reversible brain injury from a blow to the head, which may be associated with loss of consciousness. Symptoms include headache, dizziness and short term memory loss. Cuts and abrasions are usually caused by falls. The knees and hands are particularly prone. Dehydration losing too much fluid can lead to heat exhaustion and heat stroke. Dental damage a blow to the jaw can crack, break or dislodge teeth. Groin strain symptoms include pain and swelling. Hamstring strain symptoms include pain, swelling and bruising. Knee joint injuries symptoms include pain, swelling and stiffness. The ligaments, tendons or cartilage can be affected. Nose injuries either blood nose or broken nose, are caused by a direct blow. Stress fractures particularly in the lower limbs. The impact of repeated jumping or running on hard surfaces eventually stresses and cracks the bone. First aid for sprains, strains and joint injuries Suggestions on immediate treatment for sprains, strains and joint injuries include: Stop the activity. Rest the injured area.
2 For the first 24 to 48 hours, apply ice packs for 15 minutes every two hours. Bandage the injured area firmly, extending the wrapping above and below the injury. Whenever possible, elevate the injured area above the level of your heart. Avoid heat, alcohol or massage, which can exacerbate the swelling. Seek medical advice. First aid for nose bleeds Suggestions include: Stop the activity. Sit with the head leaning forward. Pinch the nostrils together and breathe through your mouth. Hold the nose for at least 10 minutes. If bleeding continues past 30 minutes, seek medical advice. First aid for dislodged teeth It may be possible to save the tooth with prompt dental treatment. Rinse the tooth in water or milk and see your dentist immediately. Emergency situations Call an ambulance if any of the following injuries are suspected: Prolonged loss of consciousness Neck or spine injuries Broken bones Injuries to the head or face Eye injuries Abdominal injuries. Treatment for sports injuries Treatment depends on the type and severity of the injury. Always see your doctor if pain persists after a couple of days. What you may think is a straightforward sprain may actually be a fractured bone. Physiotherapy can help to rehabilitate the injured site and, depending on the injury, may include
3 exercises to promote strength and flexibility. Returning to sport after injury depends on your doctor s or physiotherapist s assessment. Trying to play before the injury is properly healed will only cause further damage and delay recovery. In the meantime, you can maintain your fitness by choosing forms of exercise that don t involve your injury; for example, ride a stationary bicycle while your sprained wrist is healing. Prevention strategies You can reduce your risk of sports injuries if you: Warm up thoroughly by gently going through the motions of your sport and performing slow, sustained stretches. Wear appropriate footwear. Tape or strap vulnerable joints, if necessary. Use the appropriate safety equipment, such as mouth guards, helmets and pads. Drink plenty of fluids before, during and after the game. Try to avoid exercising in the hottest part of the day, between 11am and 3pm. Maintain a good level of overall fitness. Cross-train with other sports to ensure overall fitness and muscle strength. Don t exert yourself beyond your level of fitness. Use good form and technique. Cool down after sport with gentle, sustained stretches. Allow adequate recovery time between sessions. Have regular medical checkups. Where to get help Your doctor Sports medicine clinic Physiotherapist Hospital emergency department In an emergency, always call 000 for an ambulance Australian Physiotherapy Association Tel. (03) Things to remember Sports injuries are commonly caused by overuse, direct impact, or the application of force that is greater than the body part can structurally withstand. Common injuries include bruises, sprains, strains, joint injuries and nose bleeds. Medical investigation is important, because an injury may be more severe than you think.
4 Injury First Aid Follow the advise of your doctor. These instructions are supplemental. Chronic injuries may require physical therapy after doctor's diagnosis. R.I.C.E. Treatment Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation First aid for strains, sprains, contusions, dislocations, or uncomplicated fractures o Rest Stop using injured part Continued activity could cause further injury, delay healing, increase pain, and stimulate bleeding Use crutches to avoid bearing weight on injuries of the leg, knee, ankle, or foot Use splint for injuries of the arm, elbow, wrist, or hand o Ice Hastens healing time by reducing swelling around injury Sudden cold contracts blood vessels Helps stop internal bleeding from injured capillaries and blood vessels Keep damp or dry cloth between skin and ice pack Do not apply ice for longer than 15 to 20 minutes at a time For 3 days after injury Apply every hour for 10 to 20 minutes Apply ice after 3 days as long as pain or inflammation persist Apply at least 3 times throughout the day for 15 to 20 minutes o Compression Hastens healing time by reducing swelling around injury Decreases seeping of fluid into injured area from adjacent tissue Use elasticized bandage, compression sleeve, or cloth Wrap injured part firmly Do not impair blood supply Too tight of compression may cause more swelling Wrap over ice Loosen the bandage if it gets too tight o Elevation Elevate injured part above level of heart Decreases swelling and pain Use objects and pillows for props o Some texts advocate PRICES (P=Protection, S=Support) Medication Some doctors may recommend the use of a non-steroid anti-inflammatory such as ibuprofen through out the duration of the injury. Check with your physician.
5 Heat Treatment Causes delay in healing if applied too soon after an injury o Wait at least 72 hours (3 days) o Wait until swelling is gone o Some experts recommend going back and forth between cold and heat treatments. Management of Inflammation decrease healing time decrease scare tissue formation o decrease chances of reinjury Recovery There will be a prolonged healing time if usual activities are resumed too soon Proper care and sufficient healing time before resuming activity should prevent permanent disability if it is a first time injury. If it is a repeat injury, complications are more likely to occur. Also see Dealing with Injury. Strain Injury to the muscle or tendon. Pain with moving or stretching the affected muscle or muscle spasms. Acute strains are caused by over stress or direct injury. Chronic strains are caused by overuse. Mild strain (Grade I): o Slightly pulled muscle with no tearing of muscle or tendon. No loss of strength o Ability to produce strong yet painful muscle contractions o Requires self care through rehabilitation after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 2 to 10 days Moderate strain (Grade II): o Tearing of muscle, tendon or at the bone attachment o Weak and painful attempts at muscular contraction o Requires physical therapy after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 10 days to 6 weeks Severe strain (Grade III): o Rupture of muscle-tendon-bone attachment with separation o Extremely weak yet painless attempts at muscular contraction o Requires surgical repair and physical therapy after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 16 to 10 weeks
6 Sprain Violent overstretching of ligament in a joint. Pain, tenderness, swelling or bruising at joint. Mild strain (Grade I): o Tearing of some ligament. No loss of function o Requires self care through rehabilitation after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 2 to 6 weeks Moderate strain (Grade II): o Rupture of portion of ligament resulting in some loss of function o Requires physical therapy after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 6 to 8 weeks Severe strain (Grade III):: o Complete rupture of ligament or complete separation of ligament from bone. A sprainfracture occurs when the ligament pulls loose a fragment of bone 1+ Joint surfaces displaced 3-5 mm 2+ Joint surfaces displaced 6-10 mm 1+ Joint surfaces displaced 10+ mm o Requires surgical repair and physical therapy after doctor's diagnosis o Average healing time: 8 to 10 weeks Injury Information Acute (traumatic injury) Chronic (overuse injury) o Account for more than 50% of injuries in primary care practices o Classification Stages: 1. Pain after activity only 2. Pain during activity. Does not restrict performance 3. Pain during activity. Restricts performance 4. Chronic persistent pain, even at rest See a qualified physician if you have an injury. Only a physician can give diagnosis and prescription for injury. Educate yourself about your injury. See medical links. One starting place on the internet is the Merck Manual's Orthopedic Injuries. A medline or PubMed search can give you ideas about your condition and therapeutic modalities. Several medline links can be found on the ExRx.net. A university library will provide a wealth of information. You may not be able to checkout resources if you are not a student, but you can read and copy materials.
7 First Aid for Athletic Injuries Cuts, Scrapes and Bruises Cuts, scrapes and bruises are everyday occurrences in many sports. Most are obviously minor and can be treated with simple first aid. The objectives in treating t hese minor injuries are to. 1. Stop the bleeding 2. Clean the wound thoroughly; and 3. Protect the wound. The Bloody Nose A bloody nose often can be tough problem. The correct way to stop the bleeding is to have the athlete sit down and firmly pinch his or her nostrils shut for several minutes. Stop the Bleeding First, put on gloves! Cuts and some scrapes may bleed freely. Cuts around the head are often prone to profuse bleeding. Also, athletes with an injured artery can lose a large amount of blood. Arterial bleeding can be recognized by the spurting or pumping of blood from the wound. The proper technique to stop bleeding is to apply direct pressure t o the wound by firmly holding a clean dressing against it. If you are unable to stop the bleeding with direct pressure, seek medical assistance immediately. To stop bleeding from a tongue that has been bitten, gently hold a clean dressing on the cut. Keep the athlete sit ting up so that he or she doesn t choke on the blood or swallow excessive amounts. Strains and Sprains Athletic competition often results in injury to muscles, tendons or ligaments. A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon; a sprain is an injury to a ligament. When athletes sprain an ankle, they have injured the ligaments. When athletes pull a hamstring they have strained t he muscle or tendon. The first goal of treating a strain or sprain is t o limit the swelling in the hours following the injury. The muscle or joint is not recovered until all the swelling is gone. If you can limit t his swelling by proper first aid, the athlete will return to play more quickly. Proper first aid is the immediate application of ice. To help you remember the proper sequence of first aid for athletic injuries, just remember the word ICE: ICE Ice Compression Elevation CE Ice Compression Elevation Ice is one of the most important parts of an athletic first aid kit. Regular cube ice or crushed ice can be placed in plastic bags and easily stored for ready use in a small cooler. (Commercially prepared ice packs are not as good as plain ice and are an unnecessary expense.) The bag of ice should be placed over a couple layers of an elastic bandage and wrapped over the injury. COMPRESSION Compress the injured area by gently wrapping t he ice bag in place with the remainder of the elastic bandage. The wrapping should be gentle and firm but not tight. If the elastic bandage is wrapped too tightly, you may cut off circulation to the underlying skin which, because of the ice, could produce frostbite. ELEVATION Elevate the injury after the ice and elastic wrap have been applied. The injured limb should be propped up so that it rests higher t han the heart. This allows any fluid that is collecting to drain away. After providing first aid, have a doctor see the athlete to evaluate the injury. The sooner the athlete is seen, the bet ter the doctor can
8 Ice, compression and elevation also are good first aid for large bruises, especially on large muscles. Heat Injury Heat injury is a life-threatening condition! If one of the athletes collapses after exertion in a hot environment, you must act quickly. Symptoms the athlete may exhibit prior to collapse are: Dry, hot skin with not sweating (not always) Confusion Dizziness Chills on the chest If you see or an athlete describes any of these symptoms, you must cool him or her immediately. If the athlete is conscious: 1. Remove any head gear and other heavy clothing. 2. Douse with cold water, ice or ice t owels. 3. Give cool liquids by mouth. 4. If improvement is not quick, GET HELP. If the athlete is unconscious: 1. Remove clothes. 2. Cool by packing body with ice, towels, or douse with cold water. 3. Do not give liquids by mouth. 4. Call an ambulance. 5. Give CPR is athlete stops breathing. The Unconscious Player finger. Administer CPR if the athlete stops breathing, Be careful about moving the athlete; besides having a concussion, he or she may also have a neck injury. When t he athlete becomes conscious, keep him or her quiet and in place until seem by a doctor or paramedic. Key points to Remember 1. Have a game plan so you know who to call, how to call, and what to do in case of a serious injury. 2. Remember to bring ice to practice as well as games. 2/3 of injuries occur during practice. 3. The essentials of wound care are: -Stop the bleeding -Cleanse the wound -Protect t he wound 4. Remember and practice the ABC s of ICE. 5. Know and practice CPR. Being knocked unconscious is a serious injury and requires immediate medical assistance. First aid should be limited t o making sure that the athlete is breathing and that his or her mouth and throat are clear of turf, blood or vomit. If the mouth and throat are not clear, clear them out with your What is a Dislocation? A dislocation occurs when the bones that are usually be connected at a joint separate. You can dislocate a variety of different joints in your body, including your knee, hip, ankle, or shoulder.
9 Since a dislocation means your bone is no longer where it should be, you should treat it as an emergency and seek medical attention as soon as possible. An untreated dislocation could cause damage to your ligaments, nerves, or blood vessels. What Causes Dislocations? Dislocations typically result when a joint experiences an unexpected or unbalanced impact. This might happen if you fall or experience a harsh hit to the affected area. Once a joint has been dislocated, it is more at risk for dislocations in the future. Who Is at Risk for Dislocations? Anyone can dislocate joint if he or she has a fall or suffers some other type of trauma. However, elderly people tend to have a higher risk, especially if they lack mobility or are less able to prevent falls. Children can also be at a greater risk for dislocations if they are unsupervised or play in an area that has not been childproofed. Those who practice unsafe behavior during physical activities put themselves at higher risk for accidents, such as dislocations, as well. If you dislocated a joint in the past, the affected area could be more vulnerable to that injury in the future. Recognizing a Dislocation In many scenarios, you will be able easily to see a dislocation when it has occurred. The area may be swollen or look bruised. You may notice that the area is red or discolored. It may also have a strange shape as a result of the dislocation. Some of the other symptoms associated with dislocated joints include: loss of motion pain during movement numbness around the area tingling feeling Diagnosing a Dislocation It may be difficult to determine whether your bone is broken or just dislocated. You should arrange an exam with your doctor as soon as you can. Your doctor may move the affected area around to check your range of motion. If your doctor believes that you have a broken bone, he or she may request an MRI or X-ray to be taken. These imaging tools will enable your doctor to see exactly what is going on in your joint. Treating Dislocations Your doctor s choice of treatment will depend on the joint that you may have dislocated. It may also depend on how severe your dislocation is. According to Johns Hopkins University, initial treatment for any dislocation involves R.I.C.E. Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. In some cases, the dislocated joint might go back into place naturally after this treatment (Johns Hopkins). If the joint does not return to normal naturally, your doctor may use one of the following treatments: manipulation or repositioning immobilization medication rehabilitation Manipulation
10 In this method, your doctor will manipulate or reposition the joint back into place. You will be given a sedative or anesthetic to remain comfortable and also to allow the muscles near your joint to relax, which eases the procedure. Immobilization Once your joint has returned to its proper place, your doctor may ask you to wear a sling or splint for several weeks. This will prevent the joint from moving and allow the area to fully heal. The length of time your joint needs to be immobilized will vary, depending on the location of the injury and how severe it is. Medication Most of your pain should go away once the joint is returned to its proper place. However, your doctor may prescribe a pain reliever or a muscle relaxant if you are still feeling pain. Surgery You will need surgery only if the dislocation has damaged your nerves or blood vessels, or if the doctor is unable to return your bones to the joint. Surgery may also be necessary for those who often dislocate the same joints, such as their shoulders. Rehabilitation Rehabilitation begins after the joint has been properly repositioned or manipulated into the correct position and the sling or splint has been removed (if you needed one). Your doctor will work with you to devise a rehabilitation plan that best works for you. The goal of rehabilitation is to gradually increase the joint s strength and rebuild its range of motion. Remember, it s important to go slowly, so you don t reinjure yourself before the recovery is complete. Typical Recovery Outcomes for Dislocations Every dislocation has its own unique healing time. Most people experience a full recovery in several weeks. For some joints, such as hips, full recovery may take several months. If the dislocation was treated as soon as it occurred, chances are that it will not worsen into a permanent injury. However, it is important to remember that the area will be weakened and is at a greater risk to become dislocated in the future. The healing time will also be longer if blood vessels or nerves were damaged in the dislocation. If the dislocation is severe or is not treated in time, there may be permanent problems such as persistent pain or the cell death of parts of bone around the joint. Preventing Dislocations and Accidental Injury Dislocations can be prevented if people practice safe behavior. Methods for preventing dislocations vary depending on the age you are focusing on. However, general tips to prevent dislocations include: Use handrails when going up and down staircases. Keep a first aid kit in the area. Use nonskid mats in wet areas, such as bathrooms. Move electrical cords off of the floors. To prevent children from possible dislocations, consider practicing the following:
11 Teach children safe behaviors Watch and supervise children as needed. Ensure that your home is childproof and safe. Put gates on stairways to prevent falls. If you are an adult and want to protect yourself from dislocations, you should: Wear protective gear or clothing when doing physical activities, such as sports. Remove throw rugs from your floor, or replace them with nonskid rugs. Avoid standing on unstable items, such as chairs
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
First Aid Policy. One member of every coaching staff (competitive) is "required" to be first aid certified.
 First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture
 Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
 UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
Arm Injuries and Disorders
 Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Arm Injuries and Disorders Introduction Your arms are made up of muscles, joints, tendons and other connective tissue. There are many injuries and disorders that can affect the arm. Some arm injuries and
Providing for Players Safety 31. Emergency Plan
 Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Providing for Players Safety 31 Emergency Plan An emergency plan is the final step in preparing to take appropriate action for severe or serious injuries. The plan calls for three steps: 1. Survey the
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
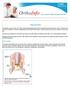 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Key Words. clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma. Linked Core Abilities
 Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Module Summaries: The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program.
 Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Dr. Berkson offers a list of some of the most common exercise-related injuries:
 AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
AS we get older, we become more vulnerable to injuries, in part because we are less agile than we used to be, and we have also lost some of our former bone and muscle mass, says the October 2013 issue
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
DOWNLOAD PDF ON-FIELD EVALUATION AND TREATMENT OF COMMON ATHLETIC INJURIES
 Chapter 1 : On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Medical Books On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Three of today's leading orthopedic specialists
Chapter 1 : On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Medical Books On Field Evaluation And Treatment Of Common Athletic Injuries, 1e Three of today's leading orthopedic specialists
What Are Sports Injuries?
 What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
CAST CARE. Helping Broken Bones Heal
 CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
CAST CARE Helping Broken Bones Heal When You Need a Cast Are you injured and in need of a cast? Don t worry, you ll get through it. Wearing a cast will help your injured body part heal. Healing takes time,
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide
 SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
Heat Injuries caoches should be aware of...4
 Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
First Aid in Agriculture
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
Have an Emergency Plan. Injury Prevention. Stretches for All Players
 Have an Emergency Plan It is important to have a well thought out plan for dealing with injuries. It is best to have a written response plan for emergencies. Keep this in your coaching bag where you can
Have an Emergency Plan It is important to have a well thought out plan for dealing with injuries. It is best to have a written response plan for emergencies. Keep this in your coaching bag where you can
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life
 Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH
 STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
Mr. Siva Chandrasekaran Orthopaedic Surgeon MBBS MSpMed MPhil (surg) FRACS
 Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Sprained Ankle An ankle sprain occurs when the strong ligaments that support the ankle stretch beyond their limits and tear. Ankle sprains are common injuries that occur among people of all ages. They
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared
 Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared EMS #: 9-1-1 Poison Control #: 800.222.1222 Take a first aid course. Learn CPR and first aid for choking. Before you give first aid,
Note: This CareKit does not replace expert medical care. Be Prepared EMS #: 9-1-1 Poison Control #: 800.222.1222 Take a first aid course. Learn CPR and first aid for choking. Before you give first aid,
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures)
 METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
METATARSAL FRACTURE (Including Jones and Dancer s Fractures) Description Possible Complications Metatarsal fracture is a broken bone (fracture) in the middle Nonunion (fracture does not heal, particularly
First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute)
 Copper Hills Little League P. O. Box 194 Sahuarita, AZ 85629 First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute) Page 1 PREVENTION Following safety rules
Copper Hills Little League P. O. Box 194 Sahuarita, AZ 85629 First Aid Training (Materials provided by the MAYO Clinic and the American Safety & Health institute) Page 1 PREVENTION Following safety rules
Reynella Football Club Medical Advice
 Reynella Football Club Medical Advice Trainer Recommendations: Implement RICER, NO HARM after Injury / Soreness Advise trainers of injury recovery progress Strap injuries for remainder of season o It takes
Reynella Football Club Medical Advice Trainer Recommendations: Implement RICER, NO HARM after Injury / Soreness Advise trainers of injury recovery progress Strap injuries for remainder of season o It takes
Bone Injuries and Treatment. Fractures and Dislocations
 Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
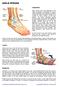 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
RIB FRACTURE. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms. Diagnosis
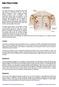 RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Functional Well-Being. Neck, Shoulders and Wrist
 Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain
 What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
What is lateral collateral ligament sprain? Lateral Collateral Ligament Sprain A sprain is a joint injury that causes a stretch or tear in a ligament, a strong band of tissue connecting one bone to another.
MENISCUS TEAR. Description
 MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MENISCUS TEAR Description Expected Outcome The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage structure in the knee that sits on top of the leg bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci, an inner and outer meniscus. The
MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT?
 Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Back Protection. Training Guide
 Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I SPRAIN MY ANKLE? HOW SHOULD I REHABILITATE MY ANKLE?
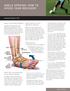 ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
ANKLE SPRAINS: HOW TO SPEED YOUR RECOVERY AOSSM SPORTS TIPS WHAT IS AN ANKLE SPRAIN? A sprain is a stretch injury of the ligaments that support the ankle. About 25,000 ankle sprains occur in the United
PAIN. Headache. enstrual Pain. Low Back Pain. Osteoarthritis. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Sprains and Strains. Taking Care of. Pain of
 Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Low Back Pain Sprains and Strains Taking Care of PAIN TIPS FOR UNDERSTANDING, AVOIDING, AND CARING FOR COMMON TYPES OF PAIN Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pain of Osteoarthritis enstrual Pain Headache BROUGHT
Facial Sports Injuries
 Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Facial Sports Injuries Playing catch, shooting hoops, bicycling on a scenic path or just kicking around a soccer ball have more in common than you may think. On the up side, these activities are good exercise
Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Health and Safety
 Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Health and Safety People suffer heat-related illness when their bodies are unable to compensate and properly cool themselves. The body normally cools itself
Extreme Heat: A Prevention Guide to Promote Health and Safety People suffer heat-related illness when their bodies are unable to compensate and properly cool themselves. The body normally cools itself
Injury Recovery and Prevention. ~Joshua Bowen
 Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
NEW PATIENT HOME CARE PACKET
 NEW PATIENT HOME CARE PACKET CORRECT POSTURE Correct posture is a very important component to your TMJ treatment and overall health. Poor posture can throw your head and spine off balance in relation to
NEW PATIENT HOME CARE PACKET CORRECT POSTURE Correct posture is a very important component to your TMJ treatment and overall health. Poor posture can throw your head and spine off balance in relation to
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Tuscola High School Athletic Guidelines
 2016-17 Tuscola High School Athletic Guidelines Necessary Forms: Pre-Participation Form (signed & dated) Consent to treat (signed & dated) Concussion Form (Checked, Initialed, Signed & Dated) Physical
2016-17 Tuscola High School Athletic Guidelines Necessary Forms: Pre-Participation Form (signed & dated) Consent to treat (signed & dated) Concussion Form (Checked, Initialed, Signed & Dated) Physical
Sports Science Revision Pack. Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow.
 Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS
 SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
SEMIMEMBRANOSUS TENDINITIS Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: Semimembranosus tendinitis is characterized by inflammation and pain at the knee joint on the back part of the inner side of the
Vibration (i.e., driving a Lack of exercise
 What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
RIB INJURIES. Contents What are rib injuries?...3
 Contents What are rib injuries?.............................................3 What are the symptoms and how is it diagnosed?.....................4 YOUR GUIDE TO RIB INJURIES Are there any complications
Contents What are rib injuries?.............................................3 What are the symptoms and how is it diagnosed?.....................4 YOUR GUIDE TO RIB INJURIES Are there any complications
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
DISCOID MENISCUS Description For participation in jumping (basketball, volleyball) or The meniscus is a cartilage structure in the knee that sits on contact sports, protect the knee joint with supportive
MODULE 5 THE EMERGENCY
 HEALTH EDUCATION II MODULE 5 THE EMERGENCY What this Module is all about You and your friends are biking when suddenly you hear car tires screeching behind you. You turn around and see your friend hit
HEALTH EDUCATION II MODULE 5 THE EMERGENCY What this Module is all about You and your friends are biking when suddenly you hear car tires screeching behind you. You turn around and see your friend hit
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe
 Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
What Are Shoulder Problems?
 What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
What Are the Parts of the Shoulder? The shoulder joint is made up of bones held in place by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Tendons are tough cords of tissue that hold the shoulder muscles to bones. They
ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An IPRS Guide to provide you with exercises and advice to ease your condition
 Contents What causes an A/C joint sprain?..................................3 What treatment can I receive?.....................................4 YOUR GUIDE TO ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An
Contents What causes an A/C joint sprain?..................................3 What treatment can I receive?.....................................4 YOUR GUIDE TO ACROMIO- CLAVICULAR (A/C) JOINT SPRAIN An
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries
 Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries Maintaining an active lifestyle offers a number of benefits for your physical and mental health. While exercise and sports-related activities often have a positive
Guide to Prevention of Sports Injuries Maintaining an active lifestyle offers a number of benefits for your physical and mental health. While exercise and sports-related activities often have a positive
Sprains. Initially the ankle is swollen, painful, and may turn eccyhmotic (bruised). The bruising, and the initial swelling, is due to ruptured
 Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Medical & Safety. Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011
 Medical & Safety Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011 Seizures Seizures are very misunderstood and may be caused by many different types of conditions, such as: Insulin shock High fevers Viral infections of
Medical & Safety Stay safe at Kamp Dovetail 2011 Seizures Seizures are very misunderstood and may be caused by many different types of conditions, such as: Insulin shock High fevers Viral infections of
Anterior Shoulder Instability
 Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Anterior Shoulder Instability Anterior shoulder instability typically results from a dislocation injury to the shoulder joint when the humeral head (ball) of the humerus (upper arm bone) is displaced from
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES
 BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
 SPORTS MEDICINE CONCEPT Sports medicinespecializes in preventing, diagnosing and treating injuries related to participation in sports and/or exercise, specifically the rotation or deformation of joints
SPORTS MEDICINE CONCEPT Sports medicinespecializes in preventing, diagnosing and treating injuries related to participation in sports and/or exercise, specifically the rotation or deformation of joints
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
For patients going home after surgery You have had an anesthetic or narcotic medicine.
 Form: D-2896 Knee Arthroscopy For patients going home after surgery Read this pamphlet to learn about: How to take care of yourself at home How to cope with pain What activities are safe What to do in
Form: D-2896 Knee Arthroscopy For patients going home after surgery Read this pamphlet to learn about: How to take care of yourself at home How to cope with pain What activities are safe What to do in
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in How to Prevent and Treat Aches and Pains. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO
 neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
Extremity Injuries and Splinting
 CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
CHAPTER 15 Extremity Injuries and Splinting Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the 3 general types of splints and how to improvise splints with common materials. 2. List the general guidelines for splinting
DISCOID MENISCUS. Description
 Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
Montefiore Pediatric Orthopedic and Scoliosis Center Children s Hospital at Montefiore Norman Otsuka MD Eric Fornari MD Jacob Schulz MD Jaime Gomez MD Christine Moloney PA 3400 Bainbridge Avenue, 6 th
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION
 PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
PATELLAR DISLOCATION AND SUBLUXATION Description For jumping (basketball, volleyball) or contact sports, Patellar dislocation and subluxation are injuries to the protect the patella with supportive devices,
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
Frontline First Aid 2012 Emergency Care Manual Treatments
 Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
Heart Attack/Angina (p. 132) 1. Recognize signals of a heart attack 2. Assist with Nitroglycerin 3. Assist with ASA 4. Rest and Comfort 6. More advanced medical care Breathing Emergencies (p. 105) Anaphylaxis
Exercises and advice following your breast reconstruction surgery
 Exercises and advice following your breast reconstruction surgery This leaflet gives information to people who have had breast reconstructive surgery. It contains exercises that your physiotherapist would
Exercises and advice following your breast reconstruction surgery This leaflet gives information to people who have had breast reconstructive surgery. It contains exercises that your physiotherapist would
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Inner side of knee. Outer side of knee. PCL - Posterior cruciate ligament. Femur Articular cartilage. ACL - Anterior cruciate ligament
 ACL surgery Outer side of knee Inner side of knee PCL - Posterior cruciate ligament Femur Articular cartilage LCL - Lateral collateral ligament Lateral meniscus Tibia ACL - Anterior cruciate ligament MCL
ACL surgery Outer side of knee Inner side of knee PCL - Posterior cruciate ligament Femur Articular cartilage LCL - Lateral collateral ligament Lateral meniscus Tibia ACL - Anterior cruciate ligament MCL
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 42 Caring for Clients with Musculoskeletal Trauma Musculoskeletal Trauma Tissue is subjected to more
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process
 LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? How Are Shoulder Problems Treated? What Are the Most Common Shoulder Problems? What Are Shoulder Problems?
 How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
How Are Shoulder Problems Diagnosed? Doctors diagnose shoulder problems by using: Medical history. Physical examination. Tests such as x rays, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) How Are Shoulder
Information for patients preparing for recovery at home. You have had an anesthetic or narcotic medicine.
 Hip Arthroscopy Information for patients preparing for recovery at home Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of yourself at home How to cope with pain Problems to watch for When to get medical
Hip Arthroscopy Information for patients preparing for recovery at home Read this brochure to learn about: How to take care of yourself at home How to cope with pain Problems to watch for When to get medical
Football First Aid: An Overview. Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS
 Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
Hemophilia. Staff Training Module 2016/2017
 MISSION The Hemophilia Federation of America (HFA) is a national nonprofit organization that assists and advocates for the bleeding disorders community. Hemophilia Staff Training Module 2016/2017 Developed
MISSION The Hemophilia Federation of America (HFA) is a national nonprofit organization that assists and advocates for the bleeding disorders community. Hemophilia Staff Training Module 2016/2017 Developed
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE
 ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
ACHILLES TENDON RUPTURE Description Expected Outcome Achilles tendon rupture is a complete tear of the Achilles tendon. This tendon, sometimes called the heel cord, is the tendon attachment of the calf
NECK OWNER S MANUAL. A Guide to the Care of the Neck
 NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
What is arthroscopy? Normal knee anatomy
 What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
What is arthroscopy? Arthroscopy is a common surgical procedure for examining and repairing the inside of your knee. It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure which uses an Arthroscope and other specialized
Duration of resource: 22 Minutes. Year of Production: Stock code: VEA12046
 ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Accidents and injuries occur without warning. When incidents happen in public places, often the welfare of the victim depends on the level of help they receive before qualified paramedics
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Accidents and injuries occur without warning. When incidents happen in public places, often the welfare of the victim depends on the level of help they receive before qualified paramedics
INJURIES: Treatment and Prevention Dave Mansfield MA, MSPT, HFI, CSCS
 INJURIES: Treatment and Prevention Dave Mansfield MA, MSPT, HFI, CSCS It goes without saying that if you sustain a serious injury or feel significant and/or unusual pain and symptoms you should seek medical
INJURIES: Treatment and Prevention Dave Mansfield MA, MSPT, HFI, CSCS It goes without saying that if you sustain a serious injury or feel significant and/or unusual pain and symptoms you should seek medical
Handout on Health: Sports Injuries
 R EADING: SPORTS I NJURIES Handout on Health: Sports Injuries In recent years, increasing numbers of people of all ages have been heeding their health professionals advice to get active for all of the
R EADING: SPORTS I NJURIES Handout on Health: Sports Injuries In recent years, increasing numbers of people of all ages have been heeding their health professionals advice to get active for all of the
Soccer Injuries. Dr. John Greco 927 Franklin Street, Huntsville, AL /
 Soccer Injuries Soccer is one of the most popular sports in the world and the fastest-growing team sport in the United States. Although soccer provides an enjoyable form of aerobic exercise and helps develop
Soccer Injuries Soccer is one of the most popular sports in the world and the fastest-growing team sport in the United States. Although soccer provides an enjoyable form of aerobic exercise and helps develop
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY
 KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY SUMMARY OF PROCEDURE Arthroscopy involves looking at the inside of the knee joint with a small telescope and camera (arthroscope). The image is projected onto a television monitor
KNEE ARTHROSCOPY SURGERY SUMMARY OF PROCEDURE Arthroscopy involves looking at the inside of the knee joint with a small telescope and camera (arthroscope). The image is projected onto a television monitor
