A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report
|
|
|
- Augustus Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2018; 12: Online September 11, 2017 DOI: /jnet.cr A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Accompanying a Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Case Report Rie Aoki, Kittipong Srivatanakul, Takahiro Osada, Takatoshi Sorimachi, and Mitsunori Matsumae Objective: In cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula (CSdAVF), multiple shunt points are often demonstrated on the angiogram. In some cases, shunt points may be located not only at the CS itself but at the part surrounding the CS. We report a rare case of CSdAVF with a shunt at the diploic vein of the orbital roof (DVOR). Case Presentation: A 64-year-old man presented with exophthalmos, conjunctival injection, and abducens nerve palsy. The shunt points were suspected to be located at the anterior lateral part and posterior medial part of the left CS on the angiogram and the drainage route was the left superior ophthalmic vein (SOV) and the veins of the posterior fossa via the left petrosal vein. We embolized the suspected shunt points in the CS transvenously. Another shunt point was identified anterior to the CS by superselective angiography. By meticulous review of the angioarchitecture, using 3D rotational angiography and multi-planar reconstruction (MPR) images, another shunt point was found at the DVOR fed by branches of the ophthalmic artery and sphenopalatine artery branches. Conclusion: We report a case of CSdAVF with multiple shunt points including a shunt located at the DVOR. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report with CSdAVF with a shunt point at the DVOR. In cases of CSdAVFs, careful analysis of the angioarchitecture using 3D rotational angiography, MPR images, and superselective angiography is necessary to elucidate the presence of shunts in rare locations. Keywords diploic vein of the orbital roof, cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, endovascular treatment Introduction Cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula (CSdAVF) is the most common type of davf in Japan. 1) Embolization of the whole sinus has been recommended. 2) However, a large amount of coils and longer procedure time are required to obtain complete obliteration of the shunt with transvenous sinus packing. Recently, superselective embolization of the shunted parts of the CS has been introduced. 3) The shunt points in CSdAVF are often multiple. 4) Department of Neurosurgery, Tokai University, Isehara, Kanagawa, Japan Received: May 4, 2017; Accepted: August 5, 2017 Corresponding author: Rie Aoki. Department of Neurosurgery, Tokai University, 143 Shimokasuya, Isehara, Kanagawa , Japan s9021@nms.ac.jp This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives International License The Japanese Society for Neuroendovascular Therapy In rare cases, the shunt is not located on CS itself but outside of the CS. 5,6) We report a rare case of CSdAVF with one of the shunts localized at the diploic vein of the orbital roof (DVOR). Case Presentation A 64-year-old man presented with left exophthalmos, conjunctival injection, and abducens nerve palsy. Time of flight MRI demonstrated a high-intensity lesion around the left CS and dilation of the left superior ophthalmic vein (SOV). Angiography showed two shunt points, at the anterolateral and at the posteromedial wall of the left CS. The shunt drained through the left SOV and the veins of the posterior fossa via a bridging vein (Fig. 1). A 4 Fr intermediate catheter was positioned into the inferior petrosal sinus through a 6 Fr Roadmaster guiding catheter (Goodman Co., LTD., Aichi, Japan). An Excelsior SL-10 (Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) microcatheter, through the 4 Fr catheter, was introduced into the anterior shunt point which was causing the reflux to the SOV. 38
2 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Fig. 1 Angiograms demonstrating the CSdAVF. (A) The left internal carotid angiogram shows the reflux to the SOV (arrow) and the veins of the posterior fossa (arrowhead) via a bridging vein (lateral view). (B) The left external carotid angiogram shows the feeders from the middle meningeal artery, the accessory meningeal artery, the ascending pharyngeal artery, and the sphenopalatine artery (lateral view). The anterolateral shunt point (dotted circle) and posterolateral shunt point (arrowhead) are demonstrated. (C) Fusion of the 3D rotational angiogram volume rendering image of the left internal carotid artery and external carotid artery showing the same structures as in (B). CSdAVF: cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistula; SOV: superior ophthalmic vein We embolized this part of the CS with coils. After embolization of the anterior part, another shunt point anterior to that became apparent by a superselective angiography of the left sphenopalatine artery. This newly discovered shunt point was later on identified to be at the DVOR. Although we tried to embolize the DVOR, it was not reachable transvenously due to the previously placed coil mass. We alternatively embolized the distal branches of the left sphenopalatine artery with coils and injected pieces of Gelfoam (Upjohn, Kalamazoo, MI, USA) at the third portion of the internal maxillary artery to obliterate the feeding arteries supplying the shunt. Subsequently, additional coil embolization to the posterior part of the CS including the posterior shunt point was done. However, a faint early venous filling of the SOV remained on the control left internal carotid artery angiogram done immediately after the embolization, which, after being retrospectively analyzed, is suggestive of a small residual shunt at the DVOR (Fig. 2). The symptoms improved completely 3 days after the procedure. A cerebral angiography performed 3 months after the procedure demonstrated complete disappearance of the shunt. Meticulous re-evaluation of 3D rotational angiogram and multi-planar reconstruction (MPR) images led to the discovery of the shunt point at the DVOR (Fig. 3). MPR revealed transosseous feeders from the left external carotid artery converging to the shunt point at the DVOR (Fig. 4). 3D rotational angiogram demonstrated that the DVOR had a connection to the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing and the anterolateral part of the CS (Fig. 3). The DVOR had no direct communication to the SOV. The SOV joined the CS at the anteroinferior aspect. In other words, the CS is the only connection between the DVOR and the SOV. The persistent reflux to the SOV at the end of the procedure was assumed to be caused by not having enough coil density in the part of the CS between the DVOR and the SOV. However, as there was no other drainage route, the coils promoted further thrombosis and led to the complete disappearance of the shunt. Discussion In CSdAVF, shunt points located outside the CS are rare. Watanabe et al. 7) reported a case of CSdAVF with multiple shunts involving the CS and the sphenoparietal sinus treated in separate sessions. In a case series of CSdAVF reported by Satow et al., 3) 7 of 14 shunt points were mentioned to be located outside the CS, at the paracavernous sinus but these shunts can be considered to be adjacent to the CS wall. Remote shunts mimicking CSdAVF have been reported. Hwang et al. 6) reported two cases of a shunt located at the ophthalmic sheath. Kobkitsuksakul et al. 5) reported 10 cases of extra-cs shunts in 350 patients initially diagnosed as CSdAVF, two of these extra-cs shunts were located close to the CS, one intraorbital and another at the lesser sphenoid wing. In patients with CSdAVF, multiple shunt points are frequently observed. 4) In planning the embolization for patients with davf, in principle, we analyze the angioarchitecture of davf meticulously using rotational angiography to clarify the exact shunt points. Based on the preprocedural analysis of the present patient, we expected the shunt points to be at the anterior and posterior part of the CS. Immediately after 39
3 Aoki R, et al. Fig. 2 (A) A left external carotid angiogram performed after the embolization of the shunt point located at the anterior part of the CS. The angiogram shows a separate shunt point located at the DVOR (arrow) (lateral view). (B) Superselective angiogram of the left sphenopalatine artery (left oblique view). The tip of the microcatheter (arrow) was introduced into the left sphenopalatine artery. This angiogram shows a shunt point (arrowhead) at the DVOR. (C) After transarterial embolization of the sphenopalatine artery branches, a left external carotid angiogram shows the disappearance of the blood supply from the external carotid artery (lateral view). (D) A left internal carotid angiogram shows that the reflux to the SOV (arrow) still remains in the late arterial phase (lateral view). DVOR: diploic vein of the orbital roof; CS: cavernous sinus; SOV: superior ophthalmic vein Fig. 3 (A) Left superior oblique view of the fusion of the ECA and ICA 3D rotational angiogram showing the shunt point (arrowhead) located at the anterior part of the DVOR (asterisk) and the reflux to the SOV (double arrowheads). The shunt at the DVOR drains through a venous connection at the tip of the anterior clinoid process (dotted line) directly into the lateral part of the CS (arrow) dorsal to the entrance of the SOV (double arrow). (B) Left superior oblique view of the fusion of the ECA, ICA, and coils (light blue) 3D rotational angiogram showing the location of the coils after embolization. Coils were placed into the entrance of the SOV, the lower part, the medial part and the posterolateral part of the CS. No coils were placed into the DVOR nor into the connection of the DVOR to the CS. (C) MPR (2.3-mm thick) oblique image shows transosseous feeders (arrow) converging to the shunt point (arrowhead) located at the DVOR (asterisk). This image clearly demonstrates that this vein is completely surrounded by the bone. (D) MPR (6-mm thick) axial image demonstrates the feeders (arrow), the shunt point (arrowhead), the DVOR (asterisk), and the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (double arrowheads). The outlet to the CS (not seen here) through the tip of the anterior clinoid process is at the point of the curved arrow. (E) The left posterior oblique view of the fusion of the ECA with the bone 3D rotational angiogram shows that the DVOR (asterisk) has a connection to the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (arrow). ECA: external carotid artery; ICA: internal carotid artery; DVOR: diploic vein of the orbital roof; CS: cavernous sinus; MPR: multi-planar reconstruction; SOV: superior ophthalmic vein 40
4 A Shunt of the Diploic Vein of the Orbital Roof Fig. 4 The schema showing the angioarchitecture of the shunt point located at the DVOR (arrow), the shunt points at the CS (arrowheads), the CS, the SOV and the DVOR (asterisk). The DVOR may connect to the FDV and the SoV. The FDV and the SoV were not seen in this case. The DVOR connects to the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (SLSW) and drains into the CS. CS: cavernous sinus; DVOR: diploic vein of the orbital roof; FDV: frontal diploic vein; FO: foramen ovale; FR: foramen rotundum; FS: foramen spinosum; IPS: inferior petrosal sinus; OA: ophthalmic artery; PV: petrosal vein; SPS: superior petrosal sinus; SOV: superior ophthalmic vein; SoV: supraorbital vein embolization of the anterior part of the CS including the shunt already identified, another shunt, which was presumably located more anterior to the known embolized shunt, became apparent. The exact position of this shunt point could not be confirmed during the procedure. Meticulous retrospective review of the 3D rotational angiogram and MPR images revealed another additional shunt point at a diploic vein running inside the bone of the orbital roof (Fig. 3). This vein fits the description of the DVOR reported by Ruíz et al. He demonstrated that this vein was one of the tributaries of the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing. The DVOR can connect with frontal diploic veins and supraorbital veins (Fig. 4). 8) Feeders supplying the shunt originated from the ipsilateral ophthalmic artery and bilateral sphenopalatine artery branches. The shunt at the DVOR drains through a venous connection at the tip of the anterior clinoid process directly into the lateral part of the cavernous sinus dorsal to the entrance of the SOV. In this case, the DVOR also has a connection to the sinus of the lesser sphenoid wing (Figs. 3 and 4). In some cases of CSdAVF, the shunt points are not always located in the CS itself. In this case, the shunt point was located at the DVOR. We were not able to locate the exact shunt point because we were not aware of the possibility of shunts in this area. Inappropriate embolization of CSdAVF could obstruct venous outflows, which may increase cortical venous reflux leading to the risk of cerebral hemorrhage. Furthermore, the deployed coil mass could block the catheterization to the residual shunt point. Therefore, appropriate embolization strategy should be developed prior to the embolization procedure by preprocedural meticulous evaluation of davf angioarchitecture. In our experience, careful analysis of the 3D rotational angiogram and its MPR images is useful in identifying the precise location of the shunt points in davfs. In this specific case, fusion of bilateral external carotid arteries and the left internal carotid artery 3D rotational angiograms demonstrated precise angioarchitecture of the CS and the DVOR. The DVOR was not recognized until we made fusion MPR images of the shunt with the bone. Adding the spatial information of the shunt related to the bone led to the final diagnosis of the shunt located inside the orbital roof, in other words, the DVOR. Superselective angiography of the feeders is also helpful in obtaining precise information on the angioarchitecture of CSdAVF during the procedure (Fig. 2). In addition to meticulous analysis of the 3D images and intraprocedural superselective angiography, one must keep in mind the existence of unexpected shunt points outside the CS. Conclusion We report a case of CSdAVF with an additional shunt located at the DVOR. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case report on a CSdAVF associated with an extra-cs shunt at the DVOR. In treating the patients with CSdAVF, careful analysis of 3D rotational angiography and MPR images prior to the procedure is essential to elucidate the precise angioarchitecture and one must be aware of unusual additional shunt points outside the CS. Disclosure Statement The authors declare no conflict of interest. 41
5 Aoki R, et al. References 1) Hiramatsu M, Sugiu K, Hishikawa T, et al: Epidemiology of dural arteriovenous fistula in Japan: analysis of Japanese registry of neuroendovascular therapy (JR-NET2). Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 2014; 54: ) Kirsch M, Henkes H, Liebig T, et al: Endovascular management of dural carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas in 141 patients. Neuroradiology 2006; 48: ) Satow T, Murao K, Matsushige T, et al: Superselective shunt occlusion for the treatment of cavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulae. Neurosurgery 2013; 73: ons100 ons105. 4) Kiyosue H, Tanoue S, Hori Y, et al: Shunted pouches of cavernous sinus dural AVFs: evaluation by 3D rotational angiography. Neuroradiology 2015; 57: ) Kobkitsuksakul C, Jiarakongmun P, Chanthanaphak E, et al: Noncavernous arteriovenous shunts mimicking carotid cavernous fistulae. Diagn Interv Radiol 2016; 22: ) Hwang J, Jo KI, Yeon JY, et al: Transvenous coil embolization for dural arteriovenous fistulas of the ophthalmic sheath: report of two cases and review of the literature. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg 2016; 18: ) Watanabe T, Matsumaru Y, Sonobe M, et al: Multiple dural arteriovenous fistulae involving the cavernous and sphenoparietal sinuses. Neuroradiology 2000; 42: ) San Millán Ruíz D, Fasel JH, Rüfenacht DA, et al: The sphenoparietal sinus of breschet: does it exist? An anatomic study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004; 25:
Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving the Laterocavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 1 7 Online November 9, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0062 Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Shunts Involving
A Case of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Transfacial Vein Placement of a Distal Access Catheter in the Cavernous Sinus
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 431 436 Online April 21, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0127 A Case of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Transfacial Vein Placement of
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 431 436 Online April 21, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0127 A Case of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Transfacial Vein Placement of
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations and Fistulae (DAVM S DAVF S)
 Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Jorge Guedes Campos NEUROIMAGING DEPARTMENT HOSPITAL SANTA MARIA UNIVERSITY OF LISBON PORTUGAL DEFINITION region of arteriovenous shunting confined to a leaflet of packymeninges often adjacent to a major
Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after Surgery for Maxillary Cancer
 Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
Case Report J Korean Neurosurg Soc 60 (1) : 89-93, 2017 https://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.1206.001 pissn 2005-3711 eissn 1598-7876 Cerebellar Hemorrhage due to a Direct Carotid Cavernous Fistula after
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula
 169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
169 Case Report Endovascular treatment with transvenous approach for embolization of carotid cavernous fistula Benny Young, Agusmanan Bojeng Department of Radiology, University Malaysia Sarawak, Faculty
Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
 Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Pan et al. Chinese Neurosurgical Journal (2018) 4:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41016-018-0121-z CHINESE MEDICAL ASSOCIATION COMMENTARY Differences between CS-DAVF and TCCF to reveal and redefine CS-DAVF
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience
 230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
230 Chiriac et al - Superior ophthalmic vein approach The superior ophthalmic vein approach for the treatment of carotid-cavernous fistulas: our first experience A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin 1, Georgiana Ion
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment.
 Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Borden type3 superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula, angiographic features and endovascular treatment. Poster No.: C-1939 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Dotsu 1, H.
Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0136 Treatment of Superior Sagittal Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula by Transarterial Multiple Balloon-assisted Onyx Embolization: A Case Report Shunsuke Yamashita, 1 Atsushi
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment
 166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
166 Chiriac et al Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the cavernous sinus - clinical case and treatment A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*, St.M. Iencean, I. Poeata
point of dural arteriovenous fistul
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Efficacy of DynaCT digital angiogra point of dural arteriovenous fistul Hiu, Takeshi; Kitagawa, Naoki; Mori Horie, Nobutaka; Morofuji, Yoichi;
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 371 375 Online March 3, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0114 Posterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysms with Common Carotid Artery Occlusion: A Report of Two Cases
Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center Cohort of 12 Patients
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2017.19.4.284 Original Article Tentorial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-Center
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils
 High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
High-Flow, Small-Hole Arteriovenous Fistulas: Treatment with Electrodetachable Coils Guido Guglielmi, Fernando Viñuela, Gary Duckwiler, Jacques Dion, and Alfredo Stocker Summary: We present one case of
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1715 1722, August 2005 Dural Sinus Compartment in Dural Arteriovenous Shunts: A New Angioarchitectural Feature Allowing Superselective Transvenous Dural Sinus Occlusion Treatment
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
Untangling Cerebral Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Bradley A. Gross, MD Assistant Professor, Dept of Neurosurgery, University of Pittsburgh September 2017 davfs Definition Clinical Presentation Natural History
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY
 Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Yamaguchi, Susumu; Morikawa, Minoru
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Quadruple coaxial catheter system o arteriovenous fistula Hayashi, Kentaro; Horie, Nobutaka; Yamaguchi, Susumu; Morikawa, Minoru Neurological
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Quadruple coaxial catheter system o arteriovenous fistula Hayashi, Kentaro; Horie, Nobutaka; Yamaguchi, Susumu; Morikawa, Minoru Neurological
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus
 TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
TECHNICAL NOTE J Neurosurg 129:922 927, 2018 An Onyx tunnel: reconstructive transvenous balloon-assisted Onyx embolization for dural arteriovenous fistula of the transverse-sigmoid sinus *Mena G. Kerolus,
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Usefulness of Coil-assisted Technique in Treating Wide-neck Intracranial Aneurysms: Neck-bridge Procedure Using the Coil Mass as a Support
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 220 225 Online December 14, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0081 Usefulness of Coil-assisted Technique in Treating Wide-neck Intracranial Aneurysms: Neck-bridge
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 220 225 Online December 14, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0081 Usefulness of Coil-assisted Technique in Treating Wide-neck Intracranial Aneurysms: Neck-bridge
Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma
 ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1507-6164 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.889610 Received: 2013.07.25 Accepted: 2013.08.08 Published: 2013.10.28 Dural arteriovenous fistula discovered in patient presenting with recent head trauma Authors Contribution:
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
The Sphenoparietal Sinus of Breschet: Does It Exist? An Anatomic Study
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:112 120, January 2004 The Sphenoparietal Sinus of Breschet: Does It Exist? An Anatomic Study Diego San Millán Ruíz, Jean H. D. Fasel, Daniel A. Rüfenacht, and Philippe Gailloud
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:112 120, January 2004 The Sphenoparietal Sinus of Breschet: Does It Exist? An Anatomic Study Diego San Millán Ruíz, Jean H. D. Fasel, Daniel A. Rüfenacht, and Philippe Gailloud
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
The orbit-1. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
The orbit-1 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Orbital plate of frontal bone Orbital plate of ethmoid bone Lesser wing of sphenoid Greater wing of sphenoid Lacrimal bone Orbital
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
MAXILLA, ORBIT & PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine Maxilla MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal
Angiographic Anatomy of the Laterocavernous Sinus
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1923 1929, November/December 2000 Angiographic Anatomy of the Laterocavernous Philippe Gailloud, Diego San Millán Ruíz, Michel Muster, Kieran J. Murphy, Jean H. D. Fasel, and Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1923 1929, November/December 2000 Angiographic Anatomy of the Laterocavernous Philippe Gailloud, Diego San Millán Ruíz, Michel Muster, Kieran J. Murphy, Jean H. D. Fasel, and Daniel
Recurrence of the Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at Adjacent Sinuses
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Recurrence of the cavernous sinus d sinuses following repeated transven literature review. Hiu, Takeshi; Horie, Nobutaka; Haya Morikawa, Minoru;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Recurrence of the cavernous sinus d sinuses following repeated transven literature review. Hiu, Takeshi; Horie, Nobutaka; Haya Morikawa, Minoru;
Transarterial access through arteriotomy of the femoral artery
 TECHNICAL NOTE C.-H. Yeh Y.-M. Wu C.-H. Toh Y.-L. Chen H.-F. Wong A Safe and Efficacious Alternative: Sonographically Guided Internal Jugular Vein Puncture for Intracranial Endovascular Intervention SUMMARY:
TECHNICAL NOTE C.-H. Yeh Y.-M. Wu C.-H. Toh Y.-L. Chen H.-F. Wong A Safe and Efficacious Alternative: Sonographically Guided Internal Jugular Vein Puncture for Intracranial Endovascular Intervention SUMMARY:
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are acquired abnormal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
ORIGINAL RESEARCH R.G. Nogueira G. Dabus J.D. Rabinov C.J. Eskey C.S. Ogilvy J.A. Hirsch J.C. Pryor Preliminary Experience with Onyx Embolization for the Treatment of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
SDAVFs are rare acquired vascular lesions predominantly
 CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
Occlusion of Arteriovenous Malformations of the Cavernous Sinus via the Superior Ophthalmic Vein
 539 Occlusion of Arteriovenous Malformations of the Cavernous Sinus via the Superior Ophthalmic Vein Michael Mu Huo Teng' 2 Wan-Yuo Guo' Chun-I Huang 3 Chih-Chiau Wu 4 Tsuen Chang' The treatment of five
539 Occlusion of Arteriovenous Malformations of the Cavernous Sinus via the Superior Ophthalmic Vein Michael Mu Huo Teng' 2 Wan-Yuo Guo' Chun-I Huang 3 Chih-Chiau Wu 4 Tsuen Chang' The treatment of five
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: Therapeutic Strategy and Follow-Up Outcomes
 Original Article Neurointervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.334 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):334-341 Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural
Original Article Neurointervention https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.334 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):334-341 Endovascular Treatment of Bilateral Cavernous Sinus Dural
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage Patterns
 New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
New Concept in Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Correlation With Presenting Symptom and Venous Drainage s Dae Chul Suh, MD; Jeong Hyun Lee, MD; Sang Joon Kim, MD; Sun Ju Chung, MD; Choong Gon
DAVFs are defined as abnormal communications between
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Lekkhong S. Pongpech K. ter Brugge P. Jiarakongmun R. Willinsky S. Geibprasert T. Krings Transvenous Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Shunts through Occluded Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Lekkhong S. Pongpech K. ter Brugge P. Jiarakongmun R. Willinsky S. Geibprasert T. Krings Transvenous Embolization of Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Shunts through Occluded Venous
A Case of Traumatic Vertebral Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Coil Embolization Using Braided-stent for Preservation of Parental Artery
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2018-0025 A Case of Traumatic Vertebral Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Coil Embolization Using Braided-stent for Preservation of Parental Artery Koji Shimonaga, 1 Toshinori Matsushige,
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2018-0025 A Case of Traumatic Vertebral Arteriovenous Fistula Treated by Coil Embolization Using Braided-stent for Preservation of Parental Artery Koji Shimonaga, 1 Toshinori Matsushige,
Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature
 . 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
. 252. Post-traumatic persistent trigeminal artery-cavernous fistula: a case report and review of literature HU Wei-peng 胡伟鹏 *, HUANG Tian-zao 黄天造, GAO Hong-zhi 高宏志, YU Mao-qing 余茂清 and XU Chao-yang 徐朝阳
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture of Spinal Artery Aneurysm
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 230, 205-209 Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with SAH 205 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 230, 205-209 Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with SAH 205 Bilateral Carotid and Vertebral Rete Mirabile Presenting with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Caused by the Rupture
Variations of the Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein: Classification Using Three-dimensional CT Angiography
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:932 938, May 2000 Variations of the Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein: Classification Using Three-dimensional CT Angiography Yasuhiro Suzuki and Kiyoshi Matsumoto BACKGROUND AND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:932 938, May 2000 Variations of the Superficial Middle Cerebral Vein: Classification Using Three-dimensional CT Angiography Yasuhiro Suzuki and Kiyoshi Matsumoto BACKGROUND AND
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Pterygopalatine fossa: The pterygopalatine fossa is a cone-shaped depression, It is located between the maxilla,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are relatively
 case report J Neurosurg 122:1208 1213, 2015 Torcular dural arteriovenous fistula treated via stent placement and angioplasty in the affected straight and transverse sinuses: case report Shigeki Takada,
case report J Neurosurg 122:1208 1213, 2015 Torcular dural arteriovenous fistula treated via stent placement and angioplasty in the affected straight and transverse sinuses: case report Shigeki Takada,
Vascular supply with angio-ct for superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy in advanced maxillary sinus cancer
 The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), 171 178 PICTORIAL REVIEW Vascular supply with angio-ct for superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy in advanced maxillary sinus cancer 1 N KASHIWAGI, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 83 (2010), 171 178 PICTORIAL REVIEW Vascular supply with angio-ct for superselective intra-arterial chemotherapy in advanced maxillary sinus cancer 1 N KASHIWAGI, MD,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Traumatic Carotid-Cavernous Fistula Identified by Three-dimensional Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 369 373, 2003 Traumatic Carotid-Cavernous Fistula Identified by Three-dimensional Digital Subtraction Angiography Technical Note Fujimaro ISHIDA, Tadashi KOJIMA, KenjiKAWAGUCHI*,
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43, 369 373, 2003 Traumatic Carotid-Cavernous Fistula Identified by Three-dimensional Digital Subtraction Angiography Technical Note Fujimaro ISHIDA, Tadashi KOJIMA, KenjiKAWAGUCHI*,
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the hypoglossal canal: systematic review on imaging anatomy, clinical findings, and endovascular management
 literature review J Neurosurg 122:883 903, 2015 Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the hypoglossal canal: systematic review on imaging anatomy, clinical findings, and endovascular management Björn Spittau,
literature review J Neurosurg 122:883 903, 2015 Dural arteriovenous fistulas of the hypoglossal canal: systematic review on imaging anatomy, clinical findings, and endovascular management Björn Spittau,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are abnormal arteriovenous
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.J. Kim D.I. Kim S.H. Suh J. Kim S.K. Lee E.Y. Kim T.S. Chung Results of Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Single-Center Experience with Emphasis on
ORIGINAL RESEARCH D.J. Kim D.I. Kim S.H. Suh J. Kim S.K. Lee E.Y. Kim T.S. Chung Results of Transvenous Embolization of Cavernous Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: A Single-Center Experience with Emphasis on
OBJECTIVES. At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries.
 DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
DR JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: List the cerebral arteries. Describe the cerebral arterial supply regarding the origin, distribution and branches.
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit
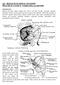 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 12 Cranial cavity, eye and orbit OSTEOLOGY Identify the bones which comprise the walls of the orbit: maxilla, zygomatic, ethmoid, lachrymal, frontal, and
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology
 Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology 3 (2013) 168e172 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology journal homepage: www.e-tjo.com Case report Central retinal vein occlusion
Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology 3 (2013) 168e172 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Taiwan Journal of Ophthalmology journal homepage: www.e-tjo.com Case report Central retinal vein occlusion
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
The inferior petrosal sinus (IPS) is a dural venous sinus running
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Mitsuhashi A. Nishio S. Kawahara T. Ichinose S. Yamauchi H. Naruse Y. Matsuoka K. Ohata M. Hara Morphologic Evaluation of the Caudal End of the Inferior Petrosal Sinus Using 3D Rotational
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Mitsuhashi A. Nishio S. Kawahara T. Ichinose S. Yamauchi H. Naruse Y. Matsuoka K. Ohata M. Hara Morphologic Evaluation of the Caudal End of the Inferior Petrosal Sinus Using 3D Rotational
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
A Novel Technique of Microcatheter Shaping with Cerebral Aneurysmal Coil Embolization: In Vivo Printing Method
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 48 52 Online November 28, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0051 A Novel Technique of Microcatheter Shaping with Cerebral Aneurysmal Coil Embolization: In Vivo
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 48 52 Online November 28, 2016 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2016-0051 A Novel Technique of Microcatheter Shaping with Cerebral Aneurysmal Coil Embolization: In Vivo
Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:630 634, March 2005 Technical Note Dynamic 3D MR Angiography of Intra- and Extracranial Vascular Malformations at 3T: A Technical Note S. Ziyeh, R. Strecker, A. Berlis, J. Weber,
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
The Endovascular Treatment of Traumatic Cavernous Sinus Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-center Experience
 Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 450 456 Online June 7, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0139 The Endovascular Treatment of Traumatic Cavernous Sinus Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-center
Journal of Neuroendovascular Therapy 2017; 11: 450 456 Online June 7, 2017 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.oa.2016-0139 The Endovascular Treatment of Traumatic Cavernous Sinus Arteriovenous Fistulas: A Single-center
Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines
 Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Carotid-Cavernous Fistulas (CCF s): Imaging Features and Endovascular Treatment
 Carotid-Cavernous Fistulas (CCF s): Imaging Features and Endovascular Treatment Poster No.: C-2141 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Rodriguez, L. Aja Rodriguez, P. Mora Montoya,
Carotid-Cavernous Fistulas (CCF s): Imaging Features and Endovascular Treatment Poster No.: C-2141 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Rodriguez, L. Aja Rodriguez, P. Mora Montoya,
Ruptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report
 Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
Case eport JNET 7:312-316, 2013 uptured aberrant internal carotid artery pseudoaneurysm presenting with spontaneous massive ear bleeding following a single sneeze: a case report Seiichiro HIONO 1) Eiichi
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
2014. Middle Meningeal Artery Arising from the Basilar Artery.
 Middle Meningeal rtery rising from the asilar rtery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Salem, Mohamed M.,
Middle Meningeal rtery rising from the asilar rtery The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Salem, Mohamed M.,
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Am Coll Radiol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 24.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Am Coll Radiol. 2010 January ; 7(1): 73 76. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2009.06.015. Cerebral Aneurysms Janet C. Miller, DPhil, Joshua A.
The orbit-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
Carotid Cavernous Fistula
 Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
Chief Complaint: Double vision. Carotid Cavernous Fistula Alex W. Cohen, MD, PhD; Richard Allen, MD, PhD May 14, 2010 History of Present Illness: A 46 year old female patient presented to the Oculoplastics
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
A Case of Curable Dementia Treated by Effective Endovascular Embolization for Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Published online: April 16, 2014 1662 680X/14/0061 0116$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
Published online: April 16, 2014 1662 680X/14/0061 0116$39.50/0 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported license (CC BY-NC)
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
