HYDROCEPHALUS ASSOCIATED WITH OBLITERATION OF THE LONGITUDINAL SINUS
|
|
|
- Amanda Spencer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HYDROCEPHALUS ASSOCIATED WITH OBLITERATION OF THE LONGITUDINAL SINUS BY J. L. EMERY and R. B. ZACHARY From The Children's Hospital, Sheffield (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 16, 1956) There are theoretically three possible causes of hydrocephalus; first, an excessive production of cerebrospinal fluid, secondly a block in its circulation and thirdly a defect in reabsorption of the fluid. The majority of cases belong to the second group, that is obstruction to the circulation, and examples of hydrocephalus due to a defect in reabsorption from the subarachnoid space via the pia-arachnoid villi are extremely rare (Potter, 1952; Russell, 1949). The purpose of this communication is to report two cases, one of a child dying at the age of 2 years in whom hydrocephalus was due apparently to complete organization of the longitudinal sinus over more than 400 mm. Three millilitres of phenol red was introduced into the ventricular fluid and appeared in a short time in the lumbar fluid, and the hydrocephalus was thus shown to be communicating. Following these investigations there was some infection of the cerebrospinal fluid with coagulasenegative Staphylococcus albus, which cleared up with antibiotics. After an unsuccessful attempt to drain the cerebrospinal fluid into the gall bladder an anastomosis was made between the lumbar theca and the left ureter after removal of the left kidney. This procedure was well tolerated and the child went home two weeks after operation, very well and with an obvious depression of the peculiar fontanelle on each side of the midline. The which a bony ridge had developed, and a second child died quite suddenly a week later. child with a history suggesting a cerebral sinus NECROPSY. The body was that of a male child, with thrombosis, and in whom the development of a gross hydrocephalus, but no other external anatomical similar bony ridge suggested the same aetiology. deformities. The serous cavities and the abdominal viscera showed Case Reports no notable abnormality. The appearance of the polythene catheter in the left ureter suggested that there had Case 1. This child was three weeks premature. Three weeks after birth he became ill with a temperature of been some obstruction to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid F. and was very sleepy and lethargic. He was given The surface of the brain was quite moist, and the convolutions were not abnormally flattened, as is usual in medicine by the family doctor, and appeared to recover from the acute illness, but he still remained for long obstructive hydrocephalus. The cortex was approximately 4 mm. thick at the vertex, gradually becoming periods of the day staring in front of him, and the mother thought his eyesight was very poor. At 6 months of age the mother thought his head was large and he was noticed to have a convergent squint. He did make a little progress in general development, but was far below the normal development for the age of 2 at which time he was admitted to hospital. The head circumference was 241 in. and an anterior fontanelle was felt to the right of the midline. Further examination revealed another depression to the left of the midline. He was able to follow a light with his eyes, and would smile and move objects from one hand to the other, but did not say any words with m,eaning and was not able to drink from a cup. General physical examination revealed nothing unusual apart from the hydrocephalus. There was no spina bifida. Ventricular studies showed a symmetrical gross hydrocephalus. The ventricular pressure was more than FiG. y.vew of the falx, longitudinal sinus and attached dura 400 mm. and the pressure in the lumbar fluid was also sho%ing the apparent complete obliteration of the sinus. (
2 H YDROCEPHALUS AND OBLITERATION OF LONGITUDINAL SINUS Fi;. 2.-View of the outside of the skull at the site of the antcrior footanele showing the longitudinal bony ridge dividing the normally demnd-shaped spac. ( x L2.) thicker in the lateral direction and in the region of the occipital poles. There was a fine granularity over the inner surface of both ventricles, but no brown staining or other evidence of haemorrhage. The third ventricle was enlarged, and the choroid plexus throughout the lateral ventricles appeared normal. The aqueduct between the third and fourth ventncles was probably within normal limits. The fourth ventricle appeared to be slightly enlarged. The cerebellum and medulla showed no Arnold Chiari defonnity, and the spinal cord and column were normal. There was no meningocoele or spina bifida. The longitudinal sinus appeared at first sight to be completely converted into a firm, fibrous mass (Fig. 1), but on closer inspection there were a few small blood vessels within this. The vessels leading into the longitudinal sinus were remarkably small, and there was no evidence of scar tissue or altered blood around them. The organization of the longitudinal sinus ended abruptly at the tentorium where the sinus was joined by a fairly large blood vessel running in the falx. The straight sinus and lateral sinuses were normal. The skull showed a remarkable thickened, dark, bony ridge immediately over the longitudinal sinus throughout the 289 whole length of the vault. This bony ridge completely divided the anterior fontanelle into two triangular lateral fontaneues (Figs. 2 and 4). No notable abnormalities were found in the sections from al of the abdominal or thoracic viscera, with the exception of the lungs which had small, long-standing areas of collapse. The longitudinal sinus (Fig. 3) consisted of a dense mass of collagenous material containing several small, thin, strand-like channels of blood vessels lined by a single layer of endothelium. No altered blood pigment was found to suggest thrombosis with canalization. Sections taken from different parts of the longitudinal canal showed a similar picture. The choroid plexuses appeared normal, and the irregularity of the lining of the ventricles was due to a general undulation of surface, and not to any local disease. No inflammatory changes were seen throughout the ependyfma. The child apparently died as the result of excessive salt loss due to unrestricted drainage of C.S.F. into the urinary tract; we have seen other children who have died in this way. No gross developmental deformities were found in any of its systems, and the brain, the falx.
3 290 FIG. 3.-Low-power view of the central area of the longitudinal sinus showing dense conncetive tissue and a few small blood spaces. (Haematoxylin and eosion x 50.) tentorium and foramen magnum suggested that there were no congenital deformities in the brain at the time of birth. The hydrocephalus was clinically of the communicating type, and no obstructive ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD cause for hydrocephalus was found at necropsy; in fact the external appearance of the brain suggested that the brain had been subjected to pressure on both sides instead of the usual inner side only. figure.i,mcdian ridge fig.2 FiG. 4.-Diagram showing the bone ridge and location of the previous figures. The longitudinal sinus was almost completely replaced by fibrous tissue of very long standing. While the cause of this fibrous replacement was not obvious, if there had been a gross neonatal longitudinal sinus thrombosis it is likely that all of the blood pigments would have been resorbed by this time. Attempts were made to cut sections of vessels from the meninges over the upper surface of the brain, but no pia-arachnoid villi were found. We feel justified in suggesting that the hydrocephalus in this child was due to a removal of the absorptive mechanism over the cerebral hemispheres by way of the longitudinal sinus. Since the vascularity of the membrane overlying the longitudinal sinus is bound to be intimately related to the sinus, it is difficult to dissociate the overlying bony ridge in the child from the abnormal underlying sinus. It would seem most probable that this abnormal bone production was a direct result of the obliteration of the sinus. The entire clinical picture could well be due to thrombosis preceding the obliteration of the sinus. Case 2. This baby was a first child, and, apart from toxaemia of pregnancy from about five months, the mother was quite well. The baby was born somewhat postmaturely by forceps delivery. At 1 week of age, he had meningitis due to Bact. coli. This responded well to streptomycin and chloramphenicol, and he appeared to make a complete recovery. At 3 months of age it was noticed that his head was increasing rapidly in size and at that time was 17 in. He was admitted to the Children's Hospital, Sheffield, in December, 1953, and was found to have a communicating hydrocephalus in which the ventricles were enormous. The head circumference was 20-7 in. An anastomosis was made between the spinal theca and the left ureter after removal of the left kidney. Drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid appeared to be perfectly satisfactory, and the child was given an additional 3 g. of salt per day to compensate for the loss of electrolytes into the bladder. He was discharged home after 11 days, and appeared to be quite well. He was again seen three and a half months after the operation. The shunt appeared to be working quite well. The anterior fontanelle was felt to be divided by a bony ridge into two lateral fontanelles. These fontanelles were depressed. The last time the baby was seen at the Children's Hospital was nine months after operation, when he was 14 months of age and appeared to be making quite good progress. He was still not able to sit up because of the weight of the head, but had started to say words. The head circumference at that time was 231 in. The baby was admitted to another hospital 11 months after operation with a temperature of 103- F. due to an acute tonsillitis. There was no sign of meningism at that time, but he died within 24 hours.
4 HYDROCEPHALUS AND OBLITERATION OF LONGITUDINAL SINUS The cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal theca was found to be infected, and the cause of death was given as meningits superimposed upon hydrocephalus. The pathologist who carried out the necropsy observed the abnormal bony ridge dividing the anterior fontanelle, but did not deliberately examine the cerebral sinuses, or attempt to determine a cause of the hydrocephalus. The general condition of the child was satisfactory up to the time that he had a severe infection. Following this, hydrocephalus developed, and later the bony ridge overlying the longitudinal sinus in the skull was observed. The child had a communicating type of hydrocephalus which was apparently temporarily relieved by the theca-ureter shunt. Discussion The earliest description of hydrocephalus associated with obstruction of the central venous return known to us is by Browning (1887), who described a child aged 6 years who died with hydrocephalus following an illness lasting six months. In this child there was thrombosis of the straight sinus, and perisinusitis of the longitudinal sinus with apparent obliteration of the smallr vessels leading to the longitudinal sinus. Ellis (1937) recorded a child who developed hydrocephalus following a phase of semi-consciousness. He was able to demonstrate by means of a venogram that there was a complete obstruction to the posterior half of the longitudinal sinus. Bailey and Hass (1937) described two children, both of whom, after a period of normal growth, had convulsions, one at the age of 6 months and the other at 1 month. These children died, and at necropsy both showed longstanding thrombotic occlusion of the longitudinal sinus. Symonds (1937) and Russell (1949) refer to other suggestive, but not conclusive cases. Byers and Hass (1933) in a survey of 50 cases of intracranial venous thrombosis in children found hydrocephalus in eight of these. They state that the hydrocephalus had apparently preceded the thrombosis in five infants, but made no definite statements concerning the other three. Discussion on the role of thrombosis in the production of hydrocephalus has largely centred around the conditions called 'otitic hydrocephalus'. Whereas some (Symonds, 1937) consider this condition to be a manifestation of cerebral sinus thrombosis, others (McAlpine, 1952) consider the condition to be due to an increased production of cerebrospinal fluid. Thrombosis of the dural sinuses can produce bizarre features in adults. Ray and Dunbar (1951) describe four cases of 'pseudotumour cerebri', in 291 which a block was demonstrated by venogram, and in one case they removed the clot in the posterior third of the longitudinal sinus, with apparent complete recovery of the patient. Martin (1941) and Martin and Sheehan (1941) reported a series of cases of cerebral sinus thrombosis occurring during the puerpenum and causing increased intracranial pressure. Barr and Daws (1956) reported a tumour that apparently produced an increase in intracranial pressure due to obstructing the saggital sinus. It has not been possible to produce hydrocephalus in experimental animals by occluding the cerebral sinuses. Bedford (1934) tied the great vein of Galen in the dog and found that there was rapid formation of collateral circulation, and Beck and Russell (1946) failed similarly with ligatures of the longitudinal sinus. However, the venous drainage in experimental animals is not identical with that in man, and the evidence obtained from animals is not conclusive. Surgical approach to the brain occasionally necessitates ligature of the longitudinal sinus. When the sinus is already partly occluded by tumour ligature apparently produces no ill effects (Dandy, 1940), but when no previous occlusion has taken place it seems that the sinus can only be ligatured with impunity anterior to the anastomotic Rolandic veins. If the whole vein is occluded, and the occlusion spreads to the cortical veins, extensive degeneration of the brain ensues (Jaeger, 1942). We have ourselves observed a very great variation in the anastomotic veins in infants' skulls. There are often large vessels running in the falx from the longitudinal sinus to the straight sinus, so that it is to be expected that the effects of occlusion of the longitudinal sinus are bound to vary much between individuals. In our present Case 1, the whole of the length of the longitudinal sinus was occluded, but not the lateral sinuses or straight sinus. Anastomotic vessels were not seen, and the superficial vessels over the vertex of the brain appeared to be bloodless. No evidence of recent reaction was seen in the sinus nor evidence of old haemorrhage, and the sinus occlusion must have occurred in the distant past, possibly even in utero. In Case 2, we have considerably less evidence than in the other. There is a history of a cerebral incident with clinical meningitis during the newborn period. Cerebral venous thrombosis is frequent in such infants, and occlusion of the sinus could well have occurred at that time. We have never seen the longitudinal bony ridge over the anterior fontanelle in infants in whom hydrocephalus was due to inflammatory scarring around the base of the brain.
5 Two children with hydrocephalus of the communicating type are described. In both, an abnormal bony ridge was present, covering the longitudinal sinus and dividing the anterior fontanelle into two parts. At necropsy, the longitudinal sinus in one case was almost completely occluded by dense con- 292 ARCHIVES OF DISEASE IN CHILDHOOD The presence of the longitudinal ridge dividing nective tissue. It is suggested that the hydrocephalus the anterior fontanelle (Fig. 2) was a striking feature in these children was due to a defect in resorption of these cases, and we have not found any record as a consequence of longitudinal sinus thrombosis, of its occurrence with or without sinus occlusion. and that the bony ridge in the skull was also Since the venous blood from the dura and periosteal secondary to the sinus thrombosis. layers overlying the longitudinal sinus flow into the lateral sinus, it would seem justifiable to assume that the calcification is a direct result of the local diminution in the blood flow, due to the obstruction of the sinus. Sumxmary REFEJtEs Bailey, 0. T. and Hass, G. M. (1937). Brain, 60, 293. Barr, J. and Daws, A. (1956). Brit. J. Surg., Beck, D. J. K. and Russell, D. S. (1946). J. Neurosurg., 3, 377. Bedford, T. H. B. (1934). Brain, Browning, W. (1887). J. Nerr. ment. Dis., 14, 260. Byers, R. K. and Hass, G. M. (1933). Amer. J. Dis. Child., 45, Dandy, W. E. (1940). Arch. Surg. (Chicago), Ellis, R. W. B. (1937). Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 30, 768. Jaeger, J. R. (1942). Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chicago) Martin, J. P. (1941). Brit. med. J., and Sheehan. H. L. (1941). Ibid., McAlpine, D. (1952). Arch. Middx. Hosp., Potter, E. L. (1952). Pathology of the Fetus and the Newborn. p Chicago. Ray, B. S. and Dunbar, H. S. (1951). Ann. Surg Russell. D. S. (1949). Observations on the Pathology of Hydrocephalus. Med. Res. Coun. Spec. Rep. Ser. (Lond.). No p. 86. Symonds, C. P. (1937). Brain Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 August Downloaded from on 13 July 2018 by guest. Protected by
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Ventricles, CSF & Meninges Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Thursday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop by for a minute or an
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves. Chapter 14 Part A
 Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Central Nervous System - Brain & Cranial Nerves Chapter 14 Part A Central Nervous System Central nervous system (CNS) is responsible for: Receiving impulses from receptors Integrating information Sending
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Chapter 14. The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid
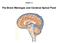 Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
Chapter 14 The Brain Meninges and Cerebral Spinal Fluid Meninges of the Brain Skull Brain: Blood vessel Pia mater Gray matter White matter Dura mater: Periosteal layer Meningeal layer Arachnoid villus
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-DURA MATER 2-ARACHNOID MATER 3-PIA MATER
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE*
 SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
congenital hydrocephalus
 J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 348 Fibrin and thrombosis in the central nervous system in children with particular reference to congenital hydrocephalus JOHN L. EMERY From the Department of Pathology, The
J. clin. Path. (1964), 17, 348 Fibrin and thrombosis in the central nervous system in children with particular reference to congenital hydrocephalus JOHN L. EMERY From the Department of Pathology, The
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Chiari malformations. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Chiari Malformations. Google. Objectives Seventh Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/22/13. Kerry R. Crone, M.D.
 Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Cranial cavity. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
Cranial cavity Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Cerebrum Cerebral hemispheres The Meninges The brain in the skull is surrounded by three membranes or meninges: 1-THE DURA
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
PARA210 SUMMARY Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology Degenerative Neurological Disorders
 PARA210 SUMMARY Page Topic 01-03 Diabetes Mellitus 04-05 Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) 06-13 Toxicology 14-18 12 Lead ECG 19-21 Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology 22-24 Degenerative Neurological
PARA210 SUMMARY Page Topic 01-03 Diabetes Mellitus 04-05 Hyperglycaemia (DKA & HHS) 06-13 Toxicology 14-18 12 Lead ECG 19-21 Brain & Nervous System Anatomy & Physiology 22-24 Degenerative Neurological
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR
 CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR Sankar K 1, Shankar N 2, Anushya 3, ShymalaDevi 4, Purvaja 5 3,4,5 III Biomedical Student, Alpha college of Engineering, Chennai. kssankar10@yahoo.co.in 1,
CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID ANALYSIS IN BRAIN TUMOUR Sankar K 1, Shankar N 2, Anushya 3, ShymalaDevi 4, Purvaja 5 3,4,5 III Biomedical Student, Alpha college of Engineering, Chennai. kssankar10@yahoo.co.in 1,
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE
 Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
Superior View of the Skull (Norma Verticalis) Anteriorly the frontal bone articulates with the two parietal bones AT THE CORONAL SUTURE 1 The two parietal bones articulate in the midline AT THE SAGITTAL
MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU
 If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
If you have low self-esteem, please hang up. Our operators are too busy to talk with you. MENTAL HOSPITAL PHONE MENU Hello and thank you for calling The State Mental Hospital. Please select from the following
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
M555 Medical Neuroscience Blood Flow in CNS Meninges Blood Brain Barrier CSF Arterial Blood Flow to CNS approximately % of what goes wrong within the skull that produces neurological deficits is vascular
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts. Information for patients
 Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
CYANOTIC ATTACKS IN NEWBORN INFANTS
 BY R. S. ILLINGWORTH From the Jessop Hospital for Women and the Children's Hospital, the United Sheffield Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MARCH 10, 1957) By the term 'cyanotic attacks in newborn infants'
BY R. S. ILLINGWORTH From the Jessop Hospital for Women and the Children's Hospital, the United Sheffield Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MARCH 10, 1957) By the term 'cyanotic attacks in newborn infants'
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
longitudinal sinus. A decrease in blood flow was observed when the pressure
 362 J. Physiol. (I942) IOI, 362-368 6I2.I44:6I2.824 THE EFFECT OF VARIATIONS IN THE SU.BARACHNOID PRESSURE ON THE VENOUS PRESSURE IN THE SUPERIOR LONGITUDINAL SINUS AND IN THE TORCULAR OF THE DOG BY T.
362 J. Physiol. (I942) IOI, 362-368 6I2.I44:6I2.824 THE EFFECT OF VARIATIONS IN THE SU.BARACHNOID PRESSURE ON THE VENOUS PRESSURE IN THE SUPERIOR LONGITUDINAL SINUS AND IN THE TORCULAR OF THE DOG BY T.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Cranio-cervical decompression. Information for patients Neurosurgery
 Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Cranio-cervical decompression Information for patients Neurosurgery page 2 of 12 What is a cranio-cervical decompression? A cranio-cervical decompression is an operation involving the back of the head
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان مادة التشريح املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Sample page. Radiology. Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS
 Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
2/20/2019 BRAIN DISSECTION CODING AND DOCUMENTATION OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
 BRAIN DISSECTION CODING AND DOCUMENTATION Diana R. Phelps, CPC, CPC-I, CEMC OBJECTIVES Identify general structure of the human brain Describe how the different parts work Recognized the two hemispheres
BRAIN DISSECTION CODING AND DOCUMENTATION Diana R. Phelps, CPC, CPC-I, CEMC OBJECTIVES Identify general structure of the human brain Describe how the different parts work Recognized the two hemispheres
Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts
 Acta Radiologica: Diagnosis ISSN: 0567-8056 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard19 Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts To cite this article: (1966)
Acta Radiologica: Diagnosis ISSN: 0567-8056 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard19 Chapter IV: Percutaneous Puncture of Spinal Cord Cysts To cite this article: (1966)
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
Hydrocephalus in the Newborn
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 44. Incidence and Treatment of Post-meningitic Hydrocephalus in the Newborn JOHN LORBER and DOUGLAS PICKERING From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 44. Incidence and Treatment of Post-meningitic Hydrocephalus in the Newborn JOHN LORBER and DOUGLAS PICKERING From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield,
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy Examination 1 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your scantron answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet ID
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide - Lab Exercises Please make sure you read the entire set of instructions on Dissection the Sheep Brain before beginning to cut. Also, please do not forget to go over
Vascular Malformations of the Brain. William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist. September 8, 2014
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
Vascular Malformations of the Brain William A. Cox, M.D. Forensic Pathologist/Neuropathologist September 8, 2014 Vascular malformations of the brain are classified into four principal groups: arteriovenous
GUIDELINES. Module 2 Content module 11. brain. The formation and ways of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Medical1,2,3,4, military.
 Bogomolets National Medical University Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject Matter HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Content module 11 Theme of the lesson The meninges of spinal cord and brain.
Bogomolets National Medical University Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject Matter HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Content module 11 Theme of the lesson The meninges of spinal cord and brain.
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
OF INTRA-UTERINE LIFE
 THE WEIGHT OF THE VENTRICLES IN THE LATER WEEKS OF INTRA-UTERINE LIFE BY JOHN L. EMERY AND M. S. MACDONALD From the Department ofpathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield Received December 17, 1959
THE WEIGHT OF THE VENTRICLES IN THE LATER WEEKS OF INTRA-UTERINE LIFE BY JOHN L. EMERY AND M. S. MACDONALD From the Department ofpathology, The Children's Hospital, Sheffield Received December 17, 1959
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Fistula between three main cerebral arteries and a large occipital vein
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 308-312 Fistula between three main cerebral arteries and a large occipital vein J. BRET AND Z. KUNC From the Neurosurgical Clinic of the Charles University, Prague,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1969, 32, 308-312 Fistula between three main cerebral arteries and a large occipital vein J. BRET AND Z. KUNC From the Neurosurgical Clinic of the Charles University, Prague,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS
 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
QUADRIGEMINAL CISTERN
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1961, 24, 374. RADIOLOGICAL AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF AN ARACHNOID CYST OF THE QUADRIGEMINAL CISTERN BY HERBERT LOURIE and ALFRED S. BERNE From the Division of Neurological
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1961, 24, 374. RADIOLOGICAL AND CLINICAL FEATURES OF AN ARACHNOID CYST OF THE QUADRIGEMINAL CISTERN BY HERBERT LOURIE and ALFRED S. BERNE From the Division of Neurological
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Nervous system. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Nervous system Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed Central nervous system (CNS) CNS consists of the brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem) and spinal cord CNS is covered by connective tissue layers, the meninges
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
T HIS paper presents an experimental
 CIRCULATION OF THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID DEMONSTRATION OF THE CHOROID PLEXUSES AS THE GENERATOR OF THE FORCE FOR FLOW OF FLUID AND VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT* EDGAR A. BERING, JR., M.D. Neurosurgical Research
CIRCULATION OF THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID DEMONSTRATION OF THE CHOROID PLEXUSES AS THE GENERATOR OF THE FORCE FOR FLOW OF FLUID AND VENTRICULAR ENLARGEMENT* EDGAR A. BERING, JR., M.D. Neurosurgical Research
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES)
 HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
T HE coexistence of hydrocephalus and
 J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / November, 1969 Venous Factors in Infantile Hydrocephalus* HORAE NORRELL, M.D., HARLES WILSON, M.D., JOHN HOWIESON, M.D., LOYD MEGISON, M.D., AND VURAL BERTAN, M.D. Division
J. Neurosurg. / Volume 31 / November, 1969 Venous Factors in Infantile Hydrocephalus* HORAE NORRELL, M.D., HARLES WILSON, M.D., JOHN HOWIESON, M.D., LOYD MEGISON, M.D., AND VURAL BERTAN, M.D. Division
Recurrent haemorrhage from cerebral aneurysms
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 164 haemorrhage from cerebral aneurysms and its prevention by surgeryt M. R. CROMPTON From the Neurosurgical Department of St. George's Hospital at Atkinson Morley's
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1966, 29, 164 haemorrhage from cerebral aneurysms and its prevention by surgeryt M. R. CROMPTON From the Neurosurgical Department of St. George's Hospital at Atkinson Morley's
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
