Inpatient Treatment of Refractory Headache
|
|
|
- Austen Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Inpatient Treatment of Refractory Headache MaryAnn Mays, MD Headache Center Center for Neurological Restoration Neurological Institute Cleveland Clinic
3 Disclosures Speakers Bureau for Allergan, Teva, and Avanir
4 Headache is best managed in the outpatient department
5 1-3 million visits to ED annually (US)
6 ED Chief Complaint 4 th most common reason adults Approximately two-thirds of these visits were for primary headache disorders, most commonly migraine headaches 3rd leading common reason pediatrics
7 Problem with ED Care of Migraine Medications: Variability of treatment ~20 parenteral medications Lack of evidence for therapeutic benefit Opioids: Less effective than other medications Carry the risk of adverse CNS side effects, habituation, and addiction Headache relief: High frequency of headache recurrence
8 1.4.1 Status migrainosus ICHD-3 May occur in migraine with or without aura Migraine is typical of previous attacks except for its duration and severity Characteristics: unremitting for >72 hours pain and/or associated symptoms are debilitating Cephalgia. 2013; 33:
9 Chronic daily headache (CDH) A group of headache disorders, in which headaches occur daily or near-daily (>15 days per month) and last for more than 3 months. CDH subtypes: Chronic migraine Chronic tension-type headache Hemicrania continua New daily persistent headache.
10 General Principles of Treating HA in the ED (1) Adequately IV hydration (2) Treat head pain with nonopioid medications (3) Provide rapid relief with IV medications (4) Establish the correct expectations - CDH for years: pain reduction - Episodic migraineur: pain free
11 Goals of ED Treatment Headache free upon discharge Sustained pain freedom 48 hours postdischarge Pain free: 20% to 25% of patients 24 hour recurrence: 30% Predictors of poor outcomes: severe pain at baseline presence of nausea longer duration of headache. Friedman BW, et al. Ann Emerg Med 2008;52(6):696Y704.
12 Factors that Influence Rx Comorbid medical illnesses Vascular Disease GI Bleed Hypotension: Dopamine receptor antagonist and magnesium can BP Past response to treatment(ed, headache infusions) t. Current medication list What has the pt has already taken prior to the ED visit? Try to get contract treating physician Past responses to meds in ED or infusion centers
13 Medication Choices for Acute Treatment of Status Migrainosus Glutamate effect must be blocked GABA levels enhanced Dopamine and histamine effect blocked Serotonin levels raised CNS inflammation blocked The patient must be hydrated
14 Intravenous Fluids Rehydrate patient with uncontrolled vomiting Hydrate all migraineurs? Harden et al.: IM ketorolac 60 mg, meperidine 50 mg + promethazine 25 mg, and normal saline:all treatments equally produced a significant reduction in head pain Headache 1996;36(6):
15 Outcomes Balbin et al. (2) Post hoc analysis of 570 patients No evidence of short-term or sustained efficacy among pts who were administered IVF in addition to IV metoclopramide Babin JEB. American Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2016; 34:(4)
16 Dopamine Receptor Antagonist Effective: antiemetic effects relief of both pain and aura symptoms sedative 3 subclasses Metoclopramide Phenothiazines (prochlorperazine, promethazine, and chlorpromazine) Butyrophenones (droperidol and haloperidol)
17 Dopamine Receptor Antagonist Efficacy Adverse Events Haloperidol Chlorpromazine* Droperidol Prochlorperazine Promethazine** Metoclopramide** ** strong recommendavon * weak recommendavon Orr S. Cephalalgia 2015;35(3):271Y284.
18 Dopamine Receptor Antagonist Risks Hypotension Prolong QT interval ( butyrophenes and chlorpromazine) Extrapyramidal effects: akathisia or dystonia Pretreatment with IV benztropine or diphenhydramine (25-50 mg) Post: PO Inderal 10 mg
19 Dopamine Receptor Antagonists Dosing Metoclopramide 10 mg IV Promethazine mg IM or IV (possible tissue injury) * Prochlorperazine 10 mg IV (repeat 30 min- max 40 mg /day) Droperidol mg IV (ICU restricted) Chlorpromazine mg IV
20 IV Promethazine Black Box Warning Risks of severe tissue injury/gangrene associated with IV/SQ administration of this drug Preferred route of administration is deep IM SQ is contraindicated.
21 Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Ketorolac mg IV or IM Contraindications: GI bleed Systematic review ( 34 studies, including 8 trials) Effective: 55% (combined with prochlorperazine ~93%) Similar pain relief to meperidine More efficacious than sumatriptan Not as effective as phenothiazines and metoclopramide. 24 hr recurrence ~30% Taggart E, et al. Ketorolac in the treatment of acute migraine: a systemavc review. Headache 2013;53(2):
22 Magnesium Sulfate mg (up to 5 g) Effect: antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, or blockade of cortical spreading depression SE: Hypotension Caution use with other medication Lamictal: rash Topirimate: hyperammonemia Evidence: conflicting, probably better in migraine with aura
23 Additional Anti-nausea Ondansetron- 4 to 8 Hydroxyzine: 25 to 50 mg IM
24 Parenteral NSAIDS Diclofenac mg Ibuprofen mg Lysine acetylsalicylate 1 gm
25 Corticosteroids Meta-analysis (25 studies/ 3989 pts) does not support the use of dexamethasone for acute treatment but may delay recurrence by 72 hours with fewer repeat physician visits 2 nd line therapy Contraindications: DM, infection Risk: Avascular necrosis Dosing Methylprednisolone mg Dexamathasone mg Woldeamanuel YW, et.al.. Cephalalgia Oct;35(11):
26 Opioids in Headache Rx Consensus guidelines: advise against the use of for migraine 70% increase in the use of hydromorphone, morphine, and oxycodone in US emergency departments from 2001 to 2010 Opioids are typically less effective or, at most, equally effective as multiple nonopioid acute migraine treatments (ketorolac, DHE, corticosteroids, and multiple dopamine receptor antagonist compounds) Mazer-Amirshahi M, et al. Trends in opioid analgesic use for headaches in US emergency departments.am J Emerg Med 2014;32(9):
27 Antiepileptic Drugs Valproate sodium (Depacon) mg May be efficacious Well tolerated: sedation, dizziness Avoid if pregnant, liver failure or taking lamotrigine
28 Opioids More side effects More likely to need rescue medication Increased risk of relapse and need for return to the ED May also render acute migraine medications, such as triptans, less effective May impair the effectiveness of migraine preventives. Have the potential to promote chronic migraine Promote medication overuse Migraine patients with opioid dependence have more disability, depression, and anxiety issues when compared to those who had not with similar headache frequencies Use should be used for rare occasions Colman I, et al. Neurology 2004;62(10): Tornabene SV, et al.. J Emerg Med 2009;36(4):333Y3
29 Vasoconstrictors Sumatriptan (Imitrex)- 6 mg SQ Effective 70% in ED DHE (dihydroergotamine)- 1 mg IV (Raskin protocol) Effective 60% -70 %at 1 hour Contraindications uncontrolled hypertension stroke or myocardial infarction peripheral vascular disease hemiplegic aura and prolonged aura (> 1 hour)
30 Triptan Sumatriptan SQ Peak concentration (Tmax): 12 minutes Bioavailability: 97% Migraine relief: 6 mg SQ: 63% at 30 min; 75% at one hour 100 mg oral: ~60% 2 hr; 78% 4hr) Pain free at 2 hr: 65%
31 Diphenhydramine as Adjuvant Therapy IV diphenhydramine 50 mg +IV metoclopramide 10 mg 208 patients Conclusion: Adjuvant therapy did not improve migraine outcomes Also did not decrease the rate of akathisia No reason to co-administer Friedman BW et al. Diphenhydramine as Adjuvant Therapy for Acute Migraine: An Emergency Department-Based Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann Emerg Med Jan;67(1):32-39.
32 Outcomes
33 Opioids
34
35
36
37 Nerve Blockade Greater occipital nerve blocks Cervical facet blocks Cervical epidural steroid injections Suriculotemporal blocks Supraorbital nerve blocks Supratrochlear nerve blocks
38 Canadian HA Society Guidelines for Headache Treatment in the ED Strongly recommended: Sumatriptan Prochlorperazine Metoclopramide Ketorolac Strongly not recommended: IV haloperidol IV dexamathasone. Orr SL, et al. Canadian Headache Society systemavc review and recommendavons on the treatment of migraine pain in emergency sedngs. Cephalalgia 2015;35(3):
39 AHS Guidelines Level B- Should be offered as first line Metoclopramide Prochlorperazine Sumatriptan SQ Dexamethasone- to prevent recurrence of HA Level C- Best to be avoided as first line Parenteral morphine Parenteral hydromorphone Orr SL, et al. Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies. Headache Jun;56(6):
40 AHS Guidelines Level C May offer IV acetaminophen IV acetylsalicylic acid Parenteral chlorpromazine Intravenous dexketoprofen Intravenous diclofenac Parenteral droperidol Parenteral haloperidol Intravenous ketorolac Intravenous valproate
41 AHS Guidelines Level C- May avoid IV Diphenhydramine IV Hydromorphone IV Morphine IV Lidocaine IV Octreotide
42 AHS Guidelines No Recommendation (Level U) IV Dexamethasone (acute) IV DHE Parenteral ergotamine IV Ketamine IV Lysine clonixinate IV Magnesium (except migraine with aura) IV Meperidine IV Nalbuphine IV Propofol IV Promethazine IV Tramadol IM Trimethobenzamide
43 Emergency Department Treatment Strategy IVF (2-3 L bolus or cc/hr) IV diphenhydramine mg IV Metoclopramide 10 mg or prochlorperazine 10 mg IV Magnesium Sulfate 1 gm IV Ketorolac 30 mg IV Sodium Valproate mg Or Methylprednisolone mg Rozen TD. ConVnuum (Minneap Minn) Aug;21(4 Headache): (modified) IV DHE mg
44 Problem with Guidelines Some drugs are studied poorly- Class III (highest risk of bias) Older drugs- fewer studies Lack of evidence does not mean lack of efficacy
45 Strategies at ED Discharge
46 ED Success? 22% of patients were pain free on discharge 64% of patients discharged with improvement had a return of severe headache within 24 hours Gupta MX, Silberstein SD, Young WB, Hopkins M, Lopez BL, Samsa GP. Less is not more: underuvlizavon of headache medicavons in a university hospital emergency department. Headache 2007; 47 (8)
47 Strategies at ED Discharge Headache free: At home treatment triptan, naproxen, antiemetic Residual pain Reassurance Encourage sleep Additional DHE or phenothiazine prior to d/c NSAID bridge
48 Why Admit? Patient doing poorly with OP withdrawal Emergency (suicidal, dehydrated) Failed outpatient therapy Patient desperate Family desperate Doctor desperate Not getting better
49 Hospital Admissions 50,000 patients were hospitalized for migraine in the USA (2008) $375 million, roughly $7500 per patient Insinga RP, Ng-Mak DS, Hanson ME. Costs associated with outpavent, emergency room and inpavent care for migraine in the USA. Cephalalgia. 2011;31(15):
50 Hospital Admission Daily use of opioids or butalbital-containing compounds (Caution 3 tabs/day) Daily use of triptans, simple analgesics, or ergotamines with a failed trial of outpatient discontinuation (rare) Failed 3 days of OP infusion therapy Patient continues with intractable daily head pain after a single or multiple visits to the ED Home rescue therapies failed with no access to outpatient infusion therapy
51 Inpatient Treatment 2004 meta-analysis:>50 % headache improvement (mean LOS 4-14 days) CDH (<6 months): 81% CDH (>6 months): 60.5% 2009 retrospective study: 78 % of patients had moderate to significant pain reduction + improvement in mood, function, and behavior Factors associated with a good outcome Dx MOH (84 vs. 69 %) Absence of personality disorder (81 vs.68%) Freitag FG, et al.. InpaVent treatment of headache: an evidence-based assessment. Headache. 2004;44: Lake AE, et al. Comprehensive inpavent treatment of refractory chronic daily headache. Headache. 2009;49:
52 Goals for Inpatient Treatment Chronic Migraine Multidisciplinary program Reduce daily pain intensity and possibly introduce pain-free time Detoxify acute medication overuse Identify response to IV medications so an outpatient treatment program can be established Educate about chronic pain and MOH Psychiatric/psychological eval/ behavioral Rx
53 Overall all Goals Decreasing disability Reducing the use of rescue medications Reduce the numbers of office and ED visits Improving quality of life
54 Typical Inpatient Protocol IVF: 80 cc/h IV diphenhydramine 25 mg every 8 hours IV metoclopramide 10 mg every 8 hours IV magnesium sulfate 500 mg every 8 hours IV DHE: mg every 8 hours IV ketorolac 30 mg q 8 hours IV Depacon 1 gram daily If no response: IV levetiracetam, IV methylprednisolone, other dopamine receptor antagonists such as prochlorperazine or droperidol.
55 DHE Raskin protocol Repetitive IV DHE titrated to the effective sub-nauseating dose (1 mg IV tid) Typically 3 days Antiemetic 25 minutes prior: Metoclopramide 10mg or prochlorperazine 10 mg or ondansetron 8 mg Can precede with diphenhydramine 25mg IV or po Stop other analgesics Side effects respond to dose reduction: leg cramps, diarrhea SQ: patients can inject DHE1 mg SQ q 8 hours until headache free 24 hours Avoid in CAD, pregnancy Raskin NH.. Neurology 1986; 36: Ford RG, Ford KT. Headache 1997; 37:
56 Other IV IV Propofol 20- to 30-mg IV push, which is repeated every 5 minutes until light sedation is induced Close monitoring of respirations and airway protection is essential. IV Lidocaine 2 to 4 mg/min in D5W, starting at 1 cardiac telemetry and blood pressure monitoring aiming to keep systolic blood pressure between 90 to160 mm Hg, diastolic between 45 to 95 mm Hg, and pulse 50 to 120 bpm. Side effects include nausea, hypotension, arrhythmias, and occasional hallucinations 6 to 14 days.
57 MOH Treatment 1 st Step: Withdrawal of medication Education- habituated inadvertently Cognitive behavioral therapy increasing problem-solving skills changing the functional approach to pain in order to cope more effectively with disability, discomfort and distress A willingness to experience continuing pain without needing to reduce, avoid or otherwise change it Effective preventative migraine medications
58 Withdrawal What to expect Main withdrawal symptoms: worsening of the headache, nausea, vomiting, arterial hypotension, tachycardia, sleep disturbances, restlessness, anxiety, and nervousness Duration: typically 2 and 10 days (up to 4 weeks) Duration of withdrawal headache: triptans (mean 1-4 days) ergotamine (mean 6-7 days) NSAIDs (mean 5-9 days)
59 Butalbital Withdrawal Oral clonazepam: 0.25 mg mg bid-tid Phenobarbital orally or IV 60 mg to 120 mg per dose 100mg butalbital = 30 mg phenobarbital
60 Management of Opioid Withdrawal Slow taper over a few days Opioid substitution: methadone or buprenorphine, followed by a gradual taper Abrupt opioid discontinuation with the use of clonidine (0.1 mg q8 hrs prn) Clonidine-naltrexone detoxification
61 Posthospital Planning Realistic expectations Improvement in pain might only be apparent following hospitalization Prophylactic and acute medication with instructions Follow-up appointment within 2-4 weeks
62 Posthospital Planning Nonpharmacologic strategies Relaxation techniques Exercise Meal and sleep regulation Avoidance of sedatives and other substances Good psychological support Support systems (family and friends)
63 Outpatient Alternative? Yes! Address medical, psychological, social and physical problems Alternative to more expensive inpatient treatment and is associated with: Significant reductions in pain Improved functional activity over the period of followup Diminished depression Diminished reactivity to stress
64 IMATCH (Interdisciplinary Method for the Assessment and Treatment of Chronic Headache) CDH Nursing CoordinaVon and EducaVon Medical Therapy Psychological Treatment Physical Therapy
65 IMATCH is an Outpatient Program Physician visits 1 initial IMATCH evaluation 6 established visits Psychological visits 1 new evaluation 37 group sessions 2 team feedback mtgs 2 individual established visits 2 biofeedback session Nurse Visits 5 RN visits Infusion Room 4 days of 4-6 hours each day Physical Therapy visits 1 new evaluation 6 individual visits 14 group sessions
66 Standard of Care vs IMATCH
67 Conclusion Acute and chronic headache are frequent causes of ED visits Inpatient admission may be necessary to effectively treat headache and associated disability Utilize evidence based guidelines to support clinical judgment Success depends on continued OP successful treatment program
68 References 1. Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D. Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies. Headache Jun;56(6): Kabbouche M, Khoury CK. Management of Primary Headache in the Emergency Department and Inpatient Headache Unit. Semin Pediatr Neurol Feb;23(1): Levin M. Approach to the Workup and Management of Headache in the Emergency Department and Inpatient Settings. Semin Neurol Dec;35(6): Rozen TD. Emergency Department and Inpatient Management of Status Migrainosus and Intractable Headache. Continuum (Minneap Minn) Aug;21(4 Headache): Pari E, Rinaldi F, Gipponi S, Venturelli E, Liberini P, Rao R, Padovani A. Management of headache disorders in the Emergency Department setting.neurol Sci Jul;36(7): Marmura MJ, Goldberg SW. Inpatient management of migraine. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep Apr;15(4): Lai TH, Wang SJ. Update of Inpatient Treatment for Refractory Chronic Daily Headache. Curr Pain Headache Rep Jan;20(1):5. 8. Chiang CC, Schwedt TJ, Wang SJ, Dodick DW. Treatment of medication-overuse headache: A systematic review. Cephalalgia 2015.
Treatment of Headache in the ED
 Treatment of Headache in the ED Benjamin W. Friedman, MD, MS, FAAEM Associate professor of Emergency Medicine Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore Medical Center Disclosure Topics of Discussion
Treatment of Headache in the ED Benjamin W. Friedman, MD, MS, FAAEM Associate professor of Emergency Medicine Albert Einstein College of Medicine Montefiore Medical Center Disclosure Topics of Discussion
Inpatient Treatment of Status Migraine With Dihydroergotamine in Children and Adolescents
 Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
The best defense is a good offense. Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine. Disclosures 11/10/2017
 Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine Brian M. Plato, DO, FAHS Norton Neuroscience Institute Louisville, KY Disclosures Speakers Bureau (personal): Allergan, Depomed, Avanir Research Funding (paid
Optimizing the Acute Treatment of Migraine Brian M. Plato, DO, FAHS Norton Neuroscience Institute Louisville, KY Disclosures Speakers Bureau (personal): Allergan, Depomed, Avanir Research Funding (paid
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Faculty Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Acute Treatment Strategies
 WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
WWW.AMERICANHEADACHESOCIETY.ORG Acute Treatment Strategies Content developed by: Lawrence C. Newman, MD, FAHS Donna Gutterman, PharmD Faculty Disclosures LAWRENCE C. NEWMAN, MD, FAHS Dr. Newman has received
Treatment Of Medication. Overuse Headache
 7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
7 November 2012 BASH GPwSI Meeting Lecture title... Treatment Of Medication Dr... Overuse Headache Dr Marcus Lewis Dr... The National Migraine Centre International Headache Society Diagnostic criteria
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
IV Pharmacological Approaches to Treating Migraine & Pain in the Clinic
 IV Pharmacological Approaches to Treating Migraine & Pain in the Clinic John Claude Krusz, PhD, MD Medical Director Anodyne Headache and Pain Care, Dallas & Grapevine, Texas 1-877-4PAIN44 www.anodynehheadachepain.com
IV Pharmacological Approaches to Treating Migraine & Pain in the Clinic John Claude Krusz, PhD, MD Medical Director Anodyne Headache and Pain Care, Dallas & Grapevine, Texas 1-877-4PAIN44 www.anodynehheadachepain.com
ISSN doi: /head VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012
 What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012 Objectives Describe the EM relevance of headaches and migraines Discuss the rationale for steroid therapy Review the evidence Conclusions My inspiration
What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012 Objectives Describe the EM relevance of headaches and migraines Discuss the rationale for steroid therapy Review the evidence Conclusions My inspiration
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
BJF Acute Pain Team Formulary Group
 Title Analgesia Guidelines for Acute Pain Management (Adults) in BGH Document Type Issue no Clinical guideline Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date April 2013 Review date April 2015 Distribution
Title Analgesia Guidelines for Acute Pain Management (Adults) in BGH Document Type Issue no Clinical guideline Clinical Governance Support Team Use Issue date April 2013 Review date April 2015 Distribution
Migraine is a common recurrent neurological disorder with
 Review Article Department Part 1: Diagnosis, General Management, and Role of Dopamine Antagonists and NSAIDs Vongvaivanich K, MD Kiratikorn Vongvaivanich, MD 1 Keywords: treatment for migraine headache,
Review Article Department Part 1: Diagnosis, General Management, and Role of Dopamine Antagonists and NSAIDs Vongvaivanich K, MD Kiratikorn Vongvaivanich, MD 1 Keywords: treatment for migraine headache,
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Approach to the Workup and Management of Headache in the Emergency Department and Inpatient Settings
 667 Approach to the Workup and Management of Headache in the Emergency Department and Inpatient Settings Morris Levin, MD 1 1 Division of Headache Medicine, Department of Neurology, University of California,
667 Approach to the Workup and Management of Headache in the Emergency Department and Inpatient Settings Morris Levin, MD 1 1 Division of Headache Medicine, Department of Neurology, University of California,
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
Dose: Metoclopramide -0.1 mg/kg (max 10 mg) IV, over 15 minutes
 Metoclopramide for Refractory Migraine in the ED Specific Care Question : In the pediatric patient diagnosed with refractory migraine, is metoclopramide an effective treatment? Question Originator: Migraine
Metoclopramide for Refractory Migraine in the ED Specific Care Question : In the pediatric patient diagnosed with refractory migraine, is metoclopramide an effective treatment? Question Originator: Migraine
Management options for Migraine. Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM
 Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Management options for Migraine Prof. Dr. Khwaja Nazimuddin Head Dept. of Internal Medicine BIRDEM Assessment The Migraine Disability Assessment Score MIDAS Complete loss of work Partial loss of work Off
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics. Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute
 Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
Risk Factors, Clinical Course, and Barriers to Care in Adults and Pediatrics Rebecca R. Buttaccio, PA-C Dent Neurologic Institute Speaker for Avanir Disclosures Learning Objectives 1. Review the risk factors
Aleksandra Radojičić. Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia
 European Headache School Belgrade 2012 MEDICATION OVERUSE HEADACHE Aleksandra Radojičić Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia Historical data First cases were described in XVII century
European Headache School Belgrade 2012 MEDICATION OVERUSE HEADACHE Aleksandra Radojičić Headache Center, Neurology Clinic, Clinical Center of Serbia Historical data First cases were described in XVII century
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Specific Care Question : Question Originator: Plain Language Summary from The Office of Evidence Based Practice: Conditional Recommendation
 Ketorolac for Refractory Migraine in the ED Specific Care Question : In the pediatric patient diagnosed with refractory migraine is ketorolac an effective treatment? Question Originator: Migraine Therapy
Ketorolac for Refractory Migraine in the ED Specific Care Question : In the pediatric patient diagnosed with refractory migraine is ketorolac an effective treatment? Question Originator: Migraine Therapy
Migraine Acute treatment
 Migraine Acute treatment Elizabeth Loder, MD, MPH Professor of Neurology, Harvard Medical School Chief, Division of Headache, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, MA Disclosures
Migraine Acute treatment Elizabeth Loder, MD, MPH Professor of Neurology, Harvard Medical School Chief, Division of Headache, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, MA Disclosures
Screening - inclusion criteria
 A Date of data collection: B Time of data collection: C Ward where data is collected: 2 0 1 Y M M D D H H M M D Research assistant Code: Patient code (local): Room number: Screening - inclusion criteria
A Date of data collection: B Time of data collection: C Ward where data is collected: 2 0 1 Y M M D D H H M M D Research assistant Code: Patient code (local): Room number: Screening - inclusion criteria
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
EMERGENCY AND INPATIENT MANAGEMENT OF MIGRIANE AND OTHER HEADACHE DISORDERS
 EMERGENCY AND INPATIENT MANAGEMENT OF MIGRIANE AND OTHER HEADACHE DISORDERS Stephanie J. Nahas, MD, MSEd, FAHS, FAAN William B. Young, MD, FAHS, FAAN Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA In this
EMERGENCY AND INPATIENT MANAGEMENT OF MIGRIANE AND OTHER HEADACHE DISORDERS Stephanie J. Nahas, MD, MSEd, FAHS, FAAN William B. Young, MD, FAHS, FAAN Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA In this
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Prevention of Antineoplastic Medication induced Nausea and Vomiting in Pediatric Cancer Patients
 Prevention of Antineoplastic Medication induced Nausea and Vomiting in Pediatric Cancer Patients Done by :Meznah Zaid Al-Mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU University College of Pharmacy Introduction Nausea
Prevention of Antineoplastic Medication induced Nausea and Vomiting in Pediatric Cancer Patients Done by :Meznah Zaid Al-Mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU University College of Pharmacy Introduction Nausea
Building a Headache Infusion Program
 Building a Headache Infusion Program Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO UCNS Board Certified Headache Specialist Headache Clinic Director Assistant Professor in Pediatric Neurology Associate Residency Director,
Building a Headache Infusion Program Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO UCNS Board Certified Headache Specialist Headache Clinic Director Assistant Professor in Pediatric Neurology Associate Residency Director,
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Opioid Initiative Wave I Treating Opioid-Use Disorder in the ED Part 1
 Opioid Initiative Wave I Treating Opioid-Use Disorder in the ED Part 1 Presenter Eric Ketcham, MD, MBA Reuben J. Strayer, MD emergency department management of the patient with opioid withdrawal OD is
Opioid Initiative Wave I Treating Opioid-Use Disorder in the ED Part 1 Presenter Eric Ketcham, MD, MBA Reuben J. Strayer, MD emergency department management of the patient with opioid withdrawal OD is
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Learning Objectives. Perioperative goals. Acute Pain in the Chronic Pain Patient for Ambulatory Surgery 9/8/16
 Acute Pain in the Chronic Pain Patient for Ambulatory Surgery Danielle Ludwin, MD Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Division of Regional and Orthopedic Anesthesia Columbia University Medical Center
Acute Pain in the Chronic Pain Patient for Ambulatory Surgery Danielle Ludwin, MD Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Division of Regional and Orthopedic Anesthesia Columbia University Medical Center
disease or in clients who consume alcohol on a regular basis. bilirubin
 NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
NON-OPIOID Acetaminophen(Tylenol) Therapeutic class: Analgesic, antipyretic Aspirin (ASA, Acetylsalicylic Acid) Analgesic, NSAID, antipyretic Non-Opioid Analgesics COMMON USES WHAT I NEED TO KNOW AS A
Delirium. Assessment and Management
 Delirium Assessment and Management Goals and Objectives Participants will: 1. be able to recognize and diagnose the syndrome of delirium. 2. understand the causes of delirium. 3. become knowledgeable about
Delirium Assessment and Management Goals and Objectives Participants will: 1. be able to recognize and diagnose the syndrome of delirium. 2. understand the causes of delirium. 3. become knowledgeable about
Screening - inclusion criteria
 PAIN OUT Community research EU ROP EAN COMMISSION A Date of data collection: B Time of data collection: C Ward where data is collected: 2 0 1 Y M M D D H H M M D Research assistant Code: Room number: Screening
PAIN OUT Community research EU ROP EAN COMMISSION A Date of data collection: B Time of data collection: C Ward where data is collected: 2 0 1 Y M M D D H H M M D Research assistant Code: Room number: Screening
10/13/17. Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD
 Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor
 Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
Acute Migraine Treatment: What you and your family should know to help you make the best choices with your doctor TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR MIGRAINES! ABOUT THIS PATIENT GUIDE: Migraine attacks are often debilitating
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention
 Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description
 Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
An Overview of MOH. ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California
 An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
An Overview of MOH IHS ASIAN HA MASTERS SCHOOL MARCH 24, 2013 ALAN M. Rapoport, M.D. Clinical Professor of Neurology The David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA Los Angeles, California President-Elect
Palliative Care and the Critical Role of the Pharmacist. Arti Thakerar Education/ Palliative Care Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
 Palliative Care and the Critical Role of the Pharmacist Arti Thakerar Education/ Palliative Care Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview What is palliative care Role of a pharmacist in palliative care Issues
Palliative Care and the Critical Role of the Pharmacist Arti Thakerar Education/ Palliative Care Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Overview What is palliative care Role of a pharmacist in palliative care Issues
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D.
 Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Prevention and Treatment of Migraines CAITLIN BARNES, PHARM.D. CANDIDATE AMBULATORY CARE JOE CAMMILLERI, PHARM.D. NATOHYA MALLORY, PHARM.D. Objectives Present patient case Review epidemiology/pathophysiology
Goals for sedation during mechanical ventilation
 New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
New Uses of Old Medications Gina Riggi, PharmD, BCCCP, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Trauma ICU Jackson Memorial Hospital Disclosure I do not have anything to disclose Objectives Describe the use of ketamine
Opioid dependence: Detoxification
 Opioid dependence: Detoxification What is detoxification? A. Process of removal of toxins from the body? B. Admitting a drug dependent person in a hospital and giving him nutrition? C. Stopping drug use
Opioid dependence: Detoxification What is detoxification? A. Process of removal of toxins from the body? B. Admitting a drug dependent person in a hospital and giving him nutrition? C. Stopping drug use
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation. Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital
 Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
ANESTHESIA DRUG REVIEW
 ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
ANESTHESIA REVIEW CAPA S 39 TH ANNUAL CONFERENCE PALM SPRINGS OCTOBER 10, 2015 ROBERT F. KOPEL, MD, FACP, FCCP HOAG HOSPITAL CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGIST ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR UCLA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
NEUROPATHIC CANCER PAIN STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES
 NEUROPATHIC CANCER PAIN STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES GENERAL PRINCIPLES Neuropathic pain may be relieved in the majority of patients by multimodal management A careful history and examination are essential.
NEUROPATHIC CANCER PAIN STANDARDS AND GUIDELINES GENERAL PRINCIPLES Neuropathic pain may be relieved in the majority of patients by multimodal management A careful history and examination are essential.
Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone
 Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone Methadone/Buprenorphine 101 Workshop, December 10, 2016 Leslie Lappalainen, MD, CCFP, dip ABAM Prepared by Mandy Manak, MD, ABAM, CCSAM
Substitution Therapy for Opioid Use Disorder The Role of Suboxone Methadone/Buprenorphine 101 Workshop, December 10, 2016 Leslie Lappalainen, MD, CCFP, dip ABAM Prepared by Mandy Manak, MD, ABAM, CCSAM
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Lumbar Fusion. Reference Guide for PACU CLINICAL PATHWAY. All patient variances to the pathway are to be circled and addressed in the progress notes.
 Reference Guide for PACU Lumbar Fusion CLINICAL PATHWAY All patient variances to the pathway are to be circled and addressed in the progress notes. This Clinical Pathway is intended to assist in clinical
Reference Guide for PACU Lumbar Fusion CLINICAL PATHWAY All patient variances to the pathway are to be circled and addressed in the progress notes. This Clinical Pathway is intended to assist in clinical
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
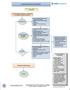 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox ) in Reducing the Number of Chronic Migraines (CM) in Patients Years Old?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Eric P. Baron, DO Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute Center for Neurological Restoration Headache and Chronic Pain Medicine barone2@ccf.org @Neuralgroover Disclosures
UPDATE IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Eric P. Baron, DO Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute Center for Neurological Restoration Headache and Chronic Pain Medicine barone2@ccf.org @Neuralgroover Disclosures
Agenda. Case Discussions. Managing Acute & Chronic Pain (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients on MAT. Daniel Alford, MD Disclosures
 Managing Acute & Chronic Pain (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients on MAT Case Discussions August 26, 2014 PCSS MAT Webinar Sponsored by the American Psychiatric Association Daniel P. Alford, MD,
Managing Acute & Chronic Pain (requiring opioid analgesics) in Patients on MAT Case Discussions August 26, 2014 PCSS MAT Webinar Sponsored by the American Psychiatric Association Daniel P. Alford, MD,
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME. C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis
 CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
CYCLIC VOMITING SYNDROME C. Prakash Gyawali, MD Professor of Medicine Washington University in St. Louis Case 26 year old male Symptoms began at age 19 yr 5-6 day episodes of recurrent, severe vomiting
Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
MEDICATIONS IN PREGNANCY
 MEDICATIONS IN PREGNANCY If patient presents with significant past history of drug addiction pain control should be closely monitored due to increased tolerance to narcotics. Consult Pain Specialist and
MEDICATIONS IN PREGNANCY If patient presents with significant past history of drug addiction pain control should be closely monitored due to increased tolerance to narcotics. Consult Pain Specialist and
Complicated Withdrawal
 Complicated Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Director, Adult Burns & Trauma Psychiatry Division of Psychiatry and Medicine Medical Director, Addiction Consultation Team MGH Center for Addiction Medicine Massachusetts
Complicated Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Director, Adult Burns & Trauma Psychiatry Division of Psychiatry and Medicine Medical Director, Addiction Consultation Team MGH Center for Addiction Medicine Massachusetts
Overview of Essentials of Pain Management. Updated 11/2016
 0 Overview of Essentials of Pain Management Updated 11/2016 1 Overview of Essentials of Pain Management 1. Assess pain intensity on a 0 10 scale in which 0 = no pain at all and 10 = the worst pain imaginable.
0 Overview of Essentials of Pain Management Updated 11/2016 1 Overview of Essentials of Pain Management 1. Assess pain intensity on a 0 10 scale in which 0 = no pain at all and 10 = the worst pain imaginable.
H-A-L-D-O-L Spells Relief
 No Relevant Financial Disclosures H-A-L-D-O-L Spells Relief Novel Pain Management Strategies Bill Soares MD, MS Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UMMS-Baystate Put another way Decreased opioid
No Relevant Financial Disclosures H-A-L-D-O-L Spells Relief Novel Pain Management Strategies Bill Soares MD, MS Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine UMMS-Baystate Put another way Decreased opioid
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Short Clinical Guidelines: Headache, Key Points for Diagnosis and Treatment
 Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Clinical Highlights 1. Headache is diagnosed by history and physical examination with limited need for imaging or laboratory tests. 2. Warning signs of possible disorder other than primary headache are:
Acute Pain Management in the Hospital Setting. Alexandra Phan, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Medical Center Hospital Odessa, TX
 Acute Pain Management in the Hospital Setting Alexandra Phan, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Medical Center Hospital Odessa, TX 2 What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated
Acute Pain Management in the Hospital Setting Alexandra Phan, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Medical Center Hospital Odessa, TX 2 What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated
The Fifth Vital Sign.
 Recognizing And Monitoring The Painful Patient Susan Clark, LVT, VTS(ECC) The Fifth Vital Sign. Pain control is part of the accepted standard of care in veterinary medicine. The ability to recognize the
Recognizing And Monitoring The Painful Patient Susan Clark, LVT, VTS(ECC) The Fifth Vital Sign. Pain control is part of the accepted standard of care in veterinary medicine. The ability to recognize the
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
North Wales Critical Care Network
 North Wales Critical Care Network SEDATION GUIDELINES FOR ADULTS IN CRITICAL CARE Approved 6.9.12 1 Sedation guidelines for intensive care Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board (Adapted from guidelines
North Wales Critical Care Network SEDATION GUIDELINES FOR ADULTS IN CRITICAL CARE Approved 6.9.12 1 Sedation guidelines for intensive care Betsi Cadwaladr University Health Board (Adapted from guidelines
SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine
 GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
COMBINATION THERAPIES PREVENTATIVE THERAPIES BETA BLOCKERS
 ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
PAIN. TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics. NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose
 NON-OPIOID SHORT-ACTING LONG-ACTING **** O PAIN TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose Tramadol 50 mg Ultram Every 4 hours 1-2 tabs,
NON-OPIOID SHORT-ACTING LONG-ACTING **** O PAIN TREATMENT TABLES Analgesics NON-OPIOID ANALGESICS Generic Name Trade Names (Examples) Duration Initial Dose Tramadol 50 mg Ultram Every 4 hours 1-2 tabs,
Acute Migraine Treatment in Adults
 PL Detail-Document #301104 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER November 2014 Acute Migraine Treatment
PL Detail-Document #301104 This PL Detail-Document gives subscribers additional insight related the Recommendations published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER November 2014 Acute Migraine Treatment
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists. Lesson 6.1. Lesson 6.1. Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists
 Slide 1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists Chapter 6 1 Slide 2 Lesson 6.1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists 1. Explain the classification, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetics
Slide 1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists Chapter 6 1 Slide 2 Lesson 6.1 Opioid (Narcotic) Analgesics and Antagonists 1. Explain the classification, mechanism of action, and pharmacokinetics
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
First a caution. Processes we might NOT try to treat with medications. Processes we might try to treat. Main drug categories.
 Pharmacological Interventions for dizziness Timothy C. Hain, MD Northwestern University Medical School Chicago, Illinois, USA First a caution Torok N. Old and new in Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope 87:1870-1877,
Pharmacological Interventions for dizziness Timothy C. Hain, MD Northwestern University Medical School Chicago, Illinois, USA First a caution Torok N. Old and new in Meniere's disease. Laryngoscope 87:1870-1877,
Measure Components Numerator Statement
 MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After
 Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
Complicated Withdrawal
 Complicated Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Medical Director, Psycho-Oncology Services Swedish Cancer Institute Swedish Medical Center Seattle, Washington Shamim.Nejad@Swedish.org Disclosures: Shamim Nejad,
Complicated Withdrawal Shamim Nejad, MD Medical Director, Psycho-Oncology Services Swedish Cancer Institute Swedish Medical Center Seattle, Washington Shamim.Nejad@Swedish.org Disclosures: Shamim Nejad,
Addressing Emergency Neuro- Pharmacologic Controversies Head-On. What dose of IV benzodiazepine makes you uncomfortable?
 Addressing Emergency Neuro- Pharmacologic Controversies Head-On 38 y/o 136 bpm Bryan D. Hayes @PharmERToxGuy Sz, tremor, hallucinations Which benzodiazepine would you administer first? Why? Diazepam Lorazepam
Addressing Emergency Neuro- Pharmacologic Controversies Head-On 38 y/o 136 bpm Bryan D. Hayes @PharmERToxGuy Sz, tremor, hallucinations Which benzodiazepine would you administer first? Why? Diazepam Lorazepam
BACKGROUND Measuring renal function :
 A GUIDE TO USE OF COMMON PALLIATIVE CARE DRUGS IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT These guidelines bring together information and recommendations from the Palliative Care formulary (PCF5 ) BACKGROUND Measuring renal
A GUIDE TO USE OF COMMON PALLIATIVE CARE DRUGS IN RENAL IMPAIRMENT These guidelines bring together information and recommendations from the Palliative Care formulary (PCF5 ) BACKGROUND Measuring renal
Knock Out Opioid Abuse in New Jersey:
 Knock Out Opioid Abuse in New Jersey: A Resource for Safer Prescribing GUIDELINE FOR PRESCRIBING OPIOIDS FOR CHRONIC PAIN IMPROVING PRACTICE THROUGH RECOMMENDATIONS CDC s Guideline for Prescribing Opioids
Knock Out Opioid Abuse in New Jersey: A Resource for Safer Prescribing GUIDELINE FOR PRESCRIBING OPIOIDS FOR CHRONIC PAIN IMPROVING PRACTICE THROUGH RECOMMENDATIONS CDC s Guideline for Prescribing Opioids
Iroquois Healthcare Association (IHA) Opioid Alternative Project. Clinician Training Materials
 Iroquois Healthcare Association (IHA) Opioid Alternative Project Clinician Training Materials Introduction IHA Opioid Alternative Project Clinician Toolkit Course Overview Thank you for participating
Iroquois Healthcare Association (IHA) Opioid Alternative Project Clinician Training Materials Introduction IHA Opioid Alternative Project Clinician Toolkit Course Overview Thank you for participating
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
