III./ Cerebral embolism
|
|
|
- Annabella Ellen French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
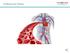
1 III./11.3 Neurological consequences of cardiac disorders Epidemiology Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of death in Western countries, thus the prevention, pathology and treatment of these disorders is of paramount importance. Cardiac disorders lead to neurological complications via two mechanisms: cardiac embolisation and a hemodynamic mechanism (the acute or chronic reduction of cardiac output results in the decrease of cerebral perfusion). These are discussed in more detail below. III./ Cerebral embolism Cerebral emboli may originate from the heart or the calcified arterial wall of the aorta and supra aortic vessels. The role of ultrasound in the clarification of the origin of cerebral emboli. Cardiac sources of cerebral emboli in order of frequency: 1. Atrial fibrillation 2. Post-myocardial infarction 3. Rheumatic and other valvular disorders, artificial heart valves About cerebral embolism: 62% of embolisation of cardiac origin and 46% of embolisation of atherothrombotic origin occurs between 6-12 hours a.m. (it is suggested that platelet aggregation is increased in the morning) % of all ischemic strokes are caused by cardiac embolism in the age group of years, and 15% above the age of 60 years. In 82% of patients, neurological symptoms develop suddenly, and symptoms are usually severe initially. Gradually increasing symptoms are typical in atherothrombotic stroke, while progressive symptoms are characteristic for cerebral bleeding. Symptoms are mainly cortical; cardiac emboli cause territorial infarcts an ischemic lesion in the territory of a vessel, with specific neurological symptoms. These symptoms reflect the function of the territory supplied by the occluded vessel. Disorder of consciousness may occur in 20% of patients. Cardiac emboli are rarely the cause of transient ischemic attacks (TIA). Cardiac emboli lead to large wedge-shaped cortical or multiple bilateral cerebral infarcts. Over 10% of infarcts show spontaneous internal hemorrhage. In the acute phase, the frequency of hemorrhagic transformation may reach 20% when anticoagulant therapy is used. In cases of cardiac emboli, cerebral edema is more pronounced than in ischemic stroke of other origin. Carotid ultrasound is normal, or shows non-relevant findings. If plaque ulceration is found on the symptomatic side of the internal carotid artery, it is considered as a potential source of emboli.
2 Transthoracal echocardiography shows a direct source of emboli in 10% of patients. The sensitivity of transesophageal echocardiography is higher. History of myocardial infarction, congenital heart disease, endocarditis, or artificial heart valve. 12% of lacunar encephalopathies are caused by embolisation from artery-to-artery. III./ : Heart disease as a potential source of emboli; sudden decrease of cardiac output associated with heart disease as a cause of neurological symptoms III./ : Atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias Atrial fibrillation is the most common form of supraventricular tachyarrhythmia (0.5% of the population over the age of 18 years, 4% above the age of 60 years). Causes: idiopathic (appr. 15%), mitral valve disease, coronary artery disease (angina pectoris, acute myocardial infarction), cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, pericarditis. Extracardiac causes: hypertension of long duration, hyperthyroidism, pulmonary embolism, alcohol intoxication. Cardiac output may be reduced by 20% because of the absence of normal atrial contraction. Clinical symptoms Anticoagulant therapy Definition Clinical symptoms Neurological consequences Clinical symptoms: palpitation, weakness because of reduced cardiac output, dizziness, syncope (the differential diagnosis of syncope includes atrial fibrillation; in addition to atrial fibrillation, other arrhythmias may also lead to loss of consciousness because of a sudden decrease of cardiac output, such as sick sinus syndrome, sinoatrial block, Adams-Stokes syndrome, atrioventricular block, and ventricular tachyarrhythmias.) Atrial fibrillation can be a paroxysmal or a chronic disorder. Chronic atrial fibrillation is one of the most important risk factors of cerebral embolisation. Cardiac embolisation often recurs during the first two weeks, which underlines the importance of early diagnosis and therapy. If not contraindicated, anticoagulant therapy should be administered: LMWH should be given simultaneously with coumarin derivatives for five days. When INR reaches the therapeutic range (INR: 2-3), LMWH can be discontinued. When indicating anticoagulant therapy, many circumstances should be considered: co-morbidities with high risk of bleeding, concomitant medications affecting the serum level of coumarin, and compliance (anticoagulant therapy is contraindicated in demented patients). III./ Acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
3 Ischemic necrosis of the myocardium, which occurs because of the significant stenosis of coronary arteries. Plaques, which have been present and slowly growing for a long time, become unstable and suddenly rupture. This is followed by the formation of a red thrombus on the ulcerated plaque, leading to the occlusion of the vessel. Clinical symptoms: strong gripping chest pain, unrelated to breathing. It may irradiate to the left arm or the jaw. Weakness, fear of death, and autonomic signs may be associated. Acute arrhythmias are typical, and often hypotension develops. ECG signs and laboratory findings are characteristic. In the acute phase, a sudden decrease of cardiac output may cause syncope - when blood pressure decreases below the cerebral autoregulation threshold. If it lasts for minutes, watershed cerebral infarcts may develop. Watershed or borderzone infarcts are cortical and subcortical ischemic lesions at the junction of brain areas supplied by different major cerebral vessels. In the chronic phase, mural dyskinesis-hypokinesis or in severe cases akinesis develops due to myocardium necrosis. Intracardiac thrombi can develop on the hypokinetic heart wall, which is a source of emboli. An intracardiac aneurysm developing at the site of the necrotic wall may also be a source of emboli. When these are seen on echocardiography, permanent anticoagulant therapy is required! III./ Cardiomyopathies Forms Dilatative cardiomyopathy (DCM): enlarged heart, and a decrease of systolic pump function and ejection fraction. Etiology is unknown in most cases, although some causes are known. Ischemic CM (severe coronary artery disease, or remodeling of intact myocardium after AMI, which overloads the myocardium); Valvular CM (severe valve insufficiency); Hypertensive CM (diastolic, later systolic impairment - hypertonic heart ); Alcoholic CM, Toxic CM (progressive left ventricular failure, dyspnea, followed by global heart failure and mainly ventricular arrhythmias). Therapy: supportive, and treatment of heart failure. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM): left ventricular idiopathic hypertrophy; the thick septum obstructs the outflow of blood (the most frequent cause of sudden cardiac death in sportsmen). Restrictive-obliterate cardiomyopathy (RCM): rare left ventricular diastolic dysfunction with unknown etiology. Therapy: heart transplantation. Arrhythmic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVCM): rare disorder. Lipomatous degeneration and dilation of the myocardium of the right ventricle. Therapy is supportive, or heart transplantation. Neurological consequences: cardiomyopathies can be the cause of arrhythmias, or heart failure with decreased cardiac output.
4 III./ Bacterial endocarditis Definition: Most common pathogens Complications: Infection of the endocardium or heart valves Streptococcus, staphylococcus, enterococcus Congenital or secondary valvular diseases predispose for endocarditis Acute phase: sepsis, septico-toxic state of many organs, acute heart failure fatal without treatment. Chronic complications include severe valvular diseases, which may later necessitate the implantation of an artificial heart valve. Latent thrombi containing bacteria may remain on heart valves for decades. Septic emboli from these may cause stroke, or solitary or multiple cerebral abscesses. If a cerebral abscess is diagnosed and there is no history of head trauma or operation, mastoiditis or otitis media, sinus thrombosis, and meningitis, septic emboli from endocarditis should be considered. III./ Secondary valvular diseases Treatment: antibiotics! Mitral and aortic valvular diseases may have neurological complications. Calcified thrombi may form on the damaged mitral or aortic valves, which are sources of emboli. In end-stage valvular diseases, artificial heart valve implantation is indicated (mechanical in young people, and biological when expected survival time is less than 10 years). The artificial heart valve may be a source of emboli, thus permanent anticoagulant therapy is necessary (INR ). III./ Congenital heart diseases Foramen ovale apertum is important in adults, because a right to left shunt may cause paradox embolism from the venous system. Surgery is sometimes indicated. Recommended references Vascularis Neurologia Dr Nagy Zoltán, B+V Kiadó A Vascularis neurológiai kórállapotok kialakulásának mechanizmusai: 9-75 old.,; A cerebrovascularis betegségek diagnosztikája: old.,; Cerebrovascularis kórképek: old. Stroke kézikönyv Nagy Zoltán, Springer kiadó Az agyérbetegségek epidemiológiája old,; Az agyi vérkeringés élettana és kórélettana: old. Korszerű Orvosi Diagnosztika és Terápia A Szív old. MSD Orvosi Kézikönyv The Merck Manual Cerebrovascularis betegségek old; Cardiovascularis betegségek old. A Hypertonia kézikönyve Farsang Csaba, Medintel Kiadó VI/3. Hypertonia és a szív: old. Belgyógyászat G. Harold II/Kardiológia old.
5 Neurology, 4th Edition Mark Mumenthaler, Thieme Clinical Syndromes in Neurology 2-11 old.,; Diseases Mainly Affecting the Brain and its Coverings: old. Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology, Ninth Edition, McGraw-Hill kiadó Part 4 Major Categories of Neurologic Disease: Section 34.- Cerebrovascular Diseases. /stroke_guideline_2008_europai.pdf?web_id type=file&id=49
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic
 Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiothoracic and Cardiothoracic Surgery ICD-10-CM 2014: Reference Mapping Card
 2014: Reference Mapping Card 162.3 Malignant neoplasm upper lobe lung 162.5 Malignant neoplasm lower lobe lung 162.9 lung/bronchus 396.2 396.3 Mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis Mitral aortic valve
2014: Reference Mapping Card 162.3 Malignant neoplasm upper lobe lung 162.5 Malignant neoplasm lower lobe lung 162.9 lung/bronchus 396.2 396.3 Mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis Mitral aortic valve
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United
 Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
 CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
CLINICAL FEATURES THAT SUPPORT ATHEROSCLEROTIC STROKE 1. cerebral cortical impairment (aphasia, neglect, restricted motor involvement, etc.) or brain stem or cerebellar dysfunction 2. lacunar clinical
ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography
 ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function 1 2 Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE Symptoms or conditions potentially
ASE 2011 Appropriate Use Criteria for Echocardiography Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function 1 2 Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE Symptoms or conditions potentially
7. Echocardiography Appropriate Use Criteria (by Indication)
 Criteria for Echocardiography 1133 7. Echocardiography Criteria (by ) Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE 1. Symptoms or conditions
Criteria for Echocardiography 1133 7. Echocardiography Criteria (by ) Table 1. TTE for General Evaluation of Cardiac Structure and Function Suspected Cardiac Etiology General With TTE 1. Symptoms or conditions
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
ACUTE CENTRAL PERIFERALEMBOLISM
 EAE TEACHING COURSE 2010 Belgrade, Serbia October 22-23, 2010 ACUTE CENTRAL and PERIFERALEMBOLISM Maria João Andrade Lisbon, PT BACKGROUND Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and long-term disability
EAE TEACHING COURSE 2010 Belgrade, Serbia October 22-23, 2010 ACUTE CENTRAL and PERIFERALEMBOLISM Maria João Andrade Lisbon, PT BACKGROUND Stroke is a leading cause of mortality and long-term disability
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Invasive and Medical Treatments for Atrial Fibrillation. Thomas J Dresing, MD Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing Cleveland Clinic
 Invasive and Medical Treatments for Thomas J Dresing, MD Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Fellow s advisory panel for St Jude Medical Speaking honoraria from: Boston
Invasive and Medical Treatments for Thomas J Dresing, MD Section of Electrophysiology and Pacing Cleveland Clinic Disclosures Fellow s advisory panel for St Jude Medical Speaking honoraria from: Boston
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Cardiovascular Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology
 Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Heart failure congestive heart failure, or CHF
 Heart failure Heart failure (also called congestive heart failure, or CHF) is a frequent end point of many of the conditions In the United States alone, CHF affects nearly 5 million individuals annually,
Heart failure Heart failure (also called congestive heart failure, or CHF) is a frequent end point of many of the conditions In the United States alone, CHF affects nearly 5 million individuals annually,
Ischemic Heart Diseases. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Ischemic Heart Diseases Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast the different types of angina regarding their pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and evolution. Discuss myocardial infarct,
Ischemic Heart Diseases Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast the different types of angina regarding their pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and evolution. Discuss myocardial infarct,
Atrial fibrillation Etiology and complications - A descriptive study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-081.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. I (Sep. 2015), PP 115-119 www.iosrjournals.org Atrial fibrillation Etiology and complications
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-081.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. I (Sep. 2015), PP 115-119 www.iosrjournals.org Atrial fibrillation Etiology and complications
EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism. Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC
 EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC Background Stroke is the 3 cause of death in several industrial countries; Embolism accounts for 15-30%
EAE RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHO. Cardiac Sources of Embolism Luigi P. Badano, MD, FESC Background Stroke is the 3 cause of death in several industrial countries; Embolism accounts for 15-30%
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise. Cardiac Conditions in Sport. USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) Dr Anita Green. Sudden Cardiac Death
 Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Recommended Evaluation Data Excerpt from NVIC 04-08
 Recommended Evaluation Data Excerpt from NVIC 04-08 Purpose: This document is an excerpt from the Medical and Physical Evaluations Guidelines for Merchant Mariner Credentials, contained in enclosure 3
Recommended Evaluation Data Excerpt from NVIC 04-08 Purpose: This document is an excerpt from the Medical and Physical Evaluations Guidelines for Merchant Mariner Credentials, contained in enclosure 3
Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease???
 Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease??? Is mitral regurg. Is complication of CHF??? Cardiomyopathy Definition The term cardiomyopathy is purely descriptive, meaning disease of the heart muscle
Is it HF secondary to rheumatic heart disease??? Is mitral regurg. Is complication of CHF??? Cardiomyopathy Definition The term cardiomyopathy is purely descriptive, meaning disease of the heart muscle
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Cardiomyopathy Consequences. function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease in which the heart muscle
 Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
Chest Pain. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal. Department of Medicine
 Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography
 Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
WHI Form Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver (For items 1-11, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.
 WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
Aerobic Exercise Screening Stratification Tool
 Aerobic Screening Stratification Tool Disclaimer: The Aerobics Screening Stratification Tool is a working document currently used within the Stroke Rehabilitation Service of St. Joseph s Care Group- Thunder
Aerobic Screening Stratification Tool Disclaimer: The Aerobics Screening Stratification Tool is a working document currently used within the Stroke Rehabilitation Service of St. Joseph s Care Group- Thunder
SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CARDIO-VASCULAR SYSTEM
 1. Myocardia lischemia is mainly a result of: 1.Coronary hypoxemia. 2. Coronary artery disease (CAD). 3. Acute coronaritis. 4. Coronary anemia. 5. Heart remodelling. SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CARDIO-VASCULAR
1. Myocardia lischemia is mainly a result of: 1.Coronary hypoxemia. 2. Coronary artery disease (CAD). 3. Acute coronaritis. 4. Coronary anemia. 5. Heart remodelling. SPECIAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CARDIO-VASCULAR
Chapter 21: Clinical Exercise Testing Procedures
 Publisher link: thepoint http://thepoint.lww.com/book/show/2930 Chapter 21: Clinical Exercise Testing Procedures American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise
Publisher link: thepoint http://thepoint.lww.com/book/show/2930 Chapter 21: Clinical Exercise Testing Procedures American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating)
 Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Appropriate Use Criteria for Initial Transthoracic Echocardiography in Outpatient Pediatric Cardiology (scores listed by Appropriate Use rating) Table 1: Appropriate indications (median score 7-9) Indication
Lnformation Coverage Guidance
 Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Lnformation Coverage Guidance Coverage Indications, Limitations, and/or Medical Necessity Abstract: B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) is a cardiac neurohormone produced mainly in the left ventricle. It
Review of Cardiac Mechanics & Pharmacology 10/23/2016. Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA 1. Learning Objectives
 Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA Associate Director of Advanced Practice Division Chief, Nurse Anesthesia Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee Learning Objectives Review the principles
Brent Dunworth, CRNA, MSN, MBA Associate Director of Advanced Practice Division Chief, Nurse Anesthesia Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, Tennessee Learning Objectives Review the principles
CARDIOMYOPATHY IN CT. Hans- Christoph Becker Professor of Radiology
 CARDIOMYOPATHY IN CT Hans- Christoph Becker Professor of Radiology 1 Cardiomyopathy Heart muscle disease Deterioration of the heart function, heart failure Dyspnea, peripheral edema Risk of arrhythmia,
CARDIOMYOPATHY IN CT Hans- Christoph Becker Professor of Radiology 1 Cardiomyopathy Heart muscle disease Deterioration of the heart function, heart failure Dyspnea, peripheral edema Risk of arrhythmia,
Index. K Knobology, TTE artifact, image resolution, ultrasound, 14
 A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
A Acute aortic regurgitation (AR), 124 128 Acute aortic syndrome (AAS) classic aortic dissection diagnosis, 251 263 evolutive patterns, 253 255 pathology, 250 251 classifications, 247 248 incomplete aortic
Acute Coronary Syndrome
 ACUTE CORONOARY SYNDROME, ANGINA & ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Administrative Consultant Service 3/17 Acute Coronary Syndrome Acute Coronary Syndrome has evolved as a useful operational term to refer to
ACUTE CORONOARY SYNDROME, ANGINA & ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Administrative Consultant Service 3/17 Acute Coronary Syndrome Acute Coronary Syndrome has evolved as a useful operational term to refer to
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Blueprints Blueprint for the Full-Day, Multiple-Choice Questions Component of the Exam: Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge,
Cardiovascular Disease Certification Examination Blueprints Blueprint for the Full-Day, Multiple-Choice Questions Component of the Exam: Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge,
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Cardiovascular Disease MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that
CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Cardiovascular Disease MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that
Valvular defects. Lectures from Pathological Physiology. Study materials from Pathological Physiology, 2017/2018 Oliver Rácz, Eva Sedláková
 Valvular defects Lectures from Pathological Physiology Study materials from Pathological Physiology, 2017/2018 Oliver Rácz, Eva Sedláková 1 2 3 1 Valvular dysfunction - introduction Stenosis block of flow;
Valvular defects Lectures from Pathological Physiology Study materials from Pathological Physiology, 2017/2018 Oliver Rácz, Eva Sedláková 1 2 3 1 Valvular dysfunction - introduction Stenosis block of flow;
Ejection across stenotic aortic valve requires a systolic pressure gradient between the LV and aorta. This places a pressure load on the LV.
 Valvular Heart Disease Etiology General Principles Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Valvular Heart Disease Etiology General Principles Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT
 HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS. 1. Cardiovascular Disease
 THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
THE FRAMINGHAM STUDY Protocol for data set vr_soe_2009_m_0522 CRITERIA FOR EVENTS 1. Cardiovascular Disease Cardiovascular disease is considered to have developed if there was a definite manifestation
Cardiac Pathology 2: Heart Failure, Ischemic Heart Disease and other assorted stuff. Kris=ne Kra>s, M.D.
 Cardiac Pathology 2: Heart Failure, Ischemic Heart Disease and other assorted stuff Kris=ne Kra>s, M.D. Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Heart I Heart II Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels
Cardiac Pathology 2: Heart Failure, Ischemic Heart Disease and other assorted stuff Kris=ne Kra>s, M.D. Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels Heart I Heart II Cardiac Pathology Outline Blood Vessels
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors:
 Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
Heart murmurs The production of murmurs is due to 3 main factors: high blood flow rate through normal or abnormal orifices forward flow through a narrowed or irregular orifice into a dilated vessel or
University of Florida Department of Surgery. CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives
 University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
University of Florida Department of Surgery CardioThoracic Surgery VA Learning Objectives This service performs coronary revascularization, valve replacement and lung cancer resections. There are 2 faculty
ADVANCED CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Adult Cardiac Surgery
 Adult Cardiac Surgery Mahmoud ABU-ABEELEH Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery School of Medicine University Of Jordan Adult Cardiac Surgery: Ischemic Heart Disease
Adult Cardiac Surgery Mahmoud ABU-ABEELEH Associate Professor Department of Surgery Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery School of Medicine University Of Jordan Adult Cardiac Surgery: Ischemic Heart Disease
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
CMS Limitations Guide - Radiology Services Starting October 1, 2015, CMS will update their existing medical necessity limitations on tests and procedures to correspond to ICD-10 codes. This limitations
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Bhakta N, Liu Q, Yeo F, et al. Cumulative burden
Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with (acute) exacerbation J45.22 Mild, with status asthmaticus
 A Fib & Flutter I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation I48.1 Persistent atrial fibrillation I48.2 Chronic atrial fibrillation I48.3 Typical atrial flutter Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with
A Fib & Flutter I48.0 Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation I48.1 Persistent atrial fibrillation I48.2 Chronic atrial fibrillation I48.3 Typical atrial flutter Asthma J45.20 Mild, uncomplicated J45.21 Mild, with
Ejection across stenotic aortic valve requires a systolic pressure gradient between the LV and aorta. This places a pressure load on the LV.
 Valvular Heart Disease General Principles Etiology Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
Valvular Heart Disease General Principles Etiology Cellular and molecular mechanism of valve damage Structural pathology Functional pathology - stenosis/regurgitation Loading conditions - pressure/volume
ARRHYTHMIAS AND DEVICE THERAPY
 Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Objectives. Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2
 10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention
 Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Diseases. Cardiovascular System
 Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care AF symptoms Tachycardia
 Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Supplementary Table S1 International Classification of Disease 10 (ICD-10) codes Comorbidity or medical history Existing diagnoses between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2011 AF management care I48 AF
Index. interventional.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alagille syndrome, pulmonary artery stenosis in, 143 145, 148 149 Amplatz devices for atrial septal defect closure, 42 46 for coronary
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept
 Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram
 When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram Updates in Cardiology 2015 March 7, 2015 Donald L. Lappé, MD, FAHA, FACC Chairman, Cardiovascular Department Medical Director, Intermountain Cardiovascular
When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram Updates in Cardiology 2015 March 7, 2015 Donald L. Lappé, MD, FAHA, FACC Chairman, Cardiovascular Department Medical Director, Intermountain Cardiovascular
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)
 Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
