Grade Description of injury ICD-9 AIS-90
|
|
|
- Jeremy Walker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scaling system for organ specific injuries Ernest E. Moore, MD, Thomas H. Cogbill, MD, Mark Malangoni, MD, Gregory J. Jurkovich, MD, and Howard R. Champion, MD Table Cervical vascular organ injury scale Grade Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Thyroid vein Common facial vein External jugular vein Non-named arterial/venous branches External carotid arterial branches (ascending pharyngeal, superior thyroid, ngual, facial maxillary, occipital, posterior auricular) Thyrocervical trunk or primary branches nternal jugular vein External carotid artery Subclavian vein ertebral artery Common carotid artery Subclavian artery nternal carotid artery (extracranial) *ncrease one grade for multiple grade or injuries involving more than 0% vessel circumference. Decrease one grade for less than % vessel circumference disruption for grade or. From Moore et al. []; with permission. Table Chest wall injury scale* Grade njury Type Description of njury CD-9 AS-90 Fracture Fracture Fracture Fracture Fracture Any size Skin & subcutaneous < ribs, closed; nondisplaced clavicle closed Skin, subcutaneous and muscle > adjacent ribs, closed Open or displaced clavicle Nondisplaced sternum, closed Scapular body, open or closed Full thickness including pleural penetration Open or displaced sternum Flail sternum Unilateral flail segment (< ribs) Avulsion of chest wall tissues with underlying rib fractures Unilateral flail chest (> ribs) Bilateral flail chest (> ribs on both sides) 9.0/ / / / / / / *This scale is confined to the chest wall alone and does not reflect associated internal or abdominal injuries. Therefore, further delineation of upper versus lower or anterior versus posterior chest wall was not considered, and a grade was warranted. Specifically, thoracic crush was not used as a descriptive term; instead, the geography and extent of fractures and soft tissue injury were used to define the grade. From Moore et al. []; with permission.
2 Table Heart injury scale Grade Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Blunt cardiac injury with minor ECG abnormality (nonspecific ST or T wave changes, premature arterial or ventricular contraction or persistent sinus tachycardia) Blunt or penetrating pericardial wound with out cardiac injury, cardiac tamponade, or cardiac herniation Blunt cardiac injury with heart block (right or left bundle branch, left anterior fascicular, or atrioventricular) or ischemic changes (ST depression or T wave inversion) without cardiac failure Penetrating tangential myocardial wound up to, but not extending through endocardium, without tamponade Blunt cardiac injury with sustained (>6 beats/min) or multilocal ventricular contractions Blunt or penetrating cardiac injury with septal rupture, pulmonary or tricuspid valvular incompetence, papillary muscle dysfunction, or distal coronary arterial occlusion without cardiac failure Blunt pericardial laceration with cardiac herniation Blunt cardiac injury with cardiac failure Penetrating tangential myocardial wound up to, but extending through, endocardium, with tamponade Blunt or penetrating cardiac injury with septal rupture, pulmonary or tricuspid valvular incompetence, papillary muscle dysfunction, or distal coronary arterial occlusion producing cardiac failure Blunt or penetrating cardiac injury with aortic mitral valve incompetence Blunt or penetrating cardiac injury of the right ventricle, right atrium, or left atrium Blunt or penetrating cardiac injury with proximal coronary arterial occlusion Blunt or penetrating left ventricular perforation Stellate wound with < 0% tissue loss of the right ventricle, right atrium, or of left atrium Blunt avulsion of the heart; penetrating wound producing > 0% tissue loss of a chamber *Advance one grade for multiple wounds to a single chamber or multiple chamber involvement. From Moore et al. []; with permission.
3 Table Lung njury Scale Grade* njury Type Description of njury CD-9 AS-90 ascular Unilateral, < lobe Unilateral, single lobe Simple pneumothorax Unilateral, > lobe Persistent (> 7 hrs) air leak from distal airway Nonexpanding intraparenchymal Major (segmental or lobar) air leak Expanding intraparenchymal Primary branch intrapulmonary vessel disruption / / 860./ ascular ascular Hilar vessel disruption Total uncontained transection of pulmonary hilum *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade. Hemothorax is scored under thoracic vascular injury scale. From Moore et al. []; with permission. Table Thoracic ascular njury Scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 ntercostal artery/vein nternal mammary artery/vein Bronchial artery/vein Esophageal artery/vein Hemizygous vein Unnamed artery/vein Azygos vein nternal jugular vein Subclavian vein nnominate vein Carotid artery nnominate artery Subclavian artery Thoracic aorta, descending nferior vena cava (intrathoracic) Pulmonary artery, primary intraparenchymal branch Pulmonary vein, primary intraparenchymal branch Thoracic aorta, ascending and arch Superior vena cava Pulmonary artery, main trunk Pulmonary vein, main trunk Uncontained total transection of thoracic aorta or pulmonary hilum *ncrease one grade for multiple grade or injuries if more than 0% circumference; decrease one grade for grade injuries if less than % circumference. From Moore et al []; with permission
4 Table 6 Diaphragm injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 <cm -0cm >0 cm with tissue loss < cm with tissue loss > cm *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade. From Moore et al. []; with permission Table 7 Spleen injury scale (99 revision) Grade* njury type Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Subcapsular, <0% surface area Capsular tear, <cm parenchymal depth Subcapsular, 0%-0% surface area; intraparenchymal, < cm in diameter Capsular tear, -cm parenchymal depth that does not involve a trabecular vessel Subcapsular, >0% surface area or expanding; ruptured subcapsular or parecymal hematoma; intraparenchymal hematoma > cm or expanding > cm parenchymal depth or involving trabecular vessels involving segmental or hilar vessels producing major devascularization (>% of spleen) ascular Completely shattered spleen Hilar vascular injury with devascularizes spleen *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. From Moore et al. []; with permission
5 Table 8 Liver injury scale (99 revision) Grade* Type of njury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Subcapsular, <0% surface area Capsular tear, <cm parenchymal depth Subcapsular, 0% to 0% surface area: intraparenchymal <0 cm in diameter Capsular tear - parenchymal depth, <0 cm in length Subcapsular, >0% surface area of ruptured subcapsular or parenchymal hematoma; intraparenchymal hematoma > 0 cm or expanding > cm parenchymal depth Parenchymal disruption involving % to 7% hepatic lobe or - Couinaud s segments Parenchymal disruption involving >7% of hepatic lobe or > Couinaud s segments within a single lobe ascular ascular Juxtahepatic venous injuries; ie, retrohepatic vena cava/central major hepatic veins Hepatic avulsion 6 *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table 9 Extrahepatic billiary tree injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Gallbladder contusion/hematoma Portal triad contusion Partial gallbladder avulsion from liver bed; cystic duct intact or perforation of the gallbladder Complete gallbladder avulsion from liver bed Cystic duct laceration Partial or complete right hepatic duct laceration Partial or complete left hepatic duct laceration Partial common hepatic duct laceration (<0%) Partial common bile duct laceration (<0%) >0% transection of common hepatic duct >0% transection of common bile duct Combined right and left hepatic duct injuries ntraduodenal or intrapancreatic bile duct injuries *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. From Moore et al. []; with permission
6 Table 0 Pancreas njury Scale Grade* Type of njury Description of njury CD-9 AS-90 Minor contusion without duct injury Superficial laceration without duct injury Major contusion without duct injury or tissue loss Major laceration without duct injury or tissue loss Distal transection or parenchymal injury with duct injury 86.9/86.9 Proximal а transection or parenchymal injury involving ampulla Massive disruption of pancreatic head *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. *86., head; 86.99,86.9-body;86.8,86.9-tail. a Proximal pancreas is to the patients right of the superior mesenteric vein. From Moore et al. [6]: with permission. Table Esophagus injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 /hematoma Partial thickness laceration <0% circumference >0% circumference Segmental loss or devascularization <cm Segmental loss or devascularization >cm 86./. 86./. 86./. 86./. 86./. 86./. *Advance one grade for multiple lesions up to grade. From Moore et al []; with permission Table Stomach injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 /hematoma Partial thickness laceration <cm in GE junction or pylorus <cm in proximal / stomach <0cm in distal / stomach >cm in GE junction or pylorus >cm in proximal / stomach >0cm in distal / stomach Tissue loss or devascularization </ stomach Tissue loss or devascularization >/ stomach 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. 86.0/. *Advance one grade for multiple lesions up to grade. GE-gastroesophageal. From Moore et al.[]; with permission
7 Table Duodenum injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 nvolving single portion of duodenum Partial thickness, no perforation nvolving more than one portion Disruption <0% of circumference Disruption 0%-7% of circumference of D Disruption 0%-00% of circumference of D,D,D ascular Disruption >7% of circumference of D nvolving ampulla or distal common bile duct Massive disruption of duodenopancreatic complex Devascularization of duodenum *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. D-first position of duodenum; D-second portion of duodenum; D-third portion of duodenum; D-fourth portion of duodenum From Moore et al. [6]; with permission. Table Small bowel injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma without devascularization 86.0 Partial thickness, no perforation <0% of circumference > 0% of circumference without transection Transection of the small bowel Transection of the small bowel with segmental tissue loss ascular Devascularized segment 86.0 *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. From Moore et al. [6]; with permission Table Colon injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma without devascularization Partial thickness, no perforation <0% of circumference > 0% of circumference without transection ascular Transection of the colon Transection of the colon with segmental tissue loss Devascularized segment *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. *86.,86.-ascending;86., 86.-transverse;86.,86.-descending; 86.,86.-rectum. From Moore et al. [6]; with permission
8 Table 6 Rectum injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma without devascularization 86. Partial-thickness laceration < 0% of circumference > 0% of circumference Full-thickness laceration with extension into the perineum ascular Devascularized segment 86. *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade. From Moore et al. [6]; with permission Table 7 Abdominal vascular injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Non-named superior mesenteric artery or superior mesenteric vein branches Non-named inferior mesenteric artery or inferior mesenteric vein branches Phrenic artery or vein Lumbar artery or vein Gonadal artery or vein Ovarian artery or vein Other non-named small arterial or venous structures requiring ligation Right, left, or common hepatic artery Splenic artery or vein Right or left gastric arteries Gastroduodenal artery nferior mesenteric artery, or inferior mesenteric vein, trunk Primary named branches of messenteric artery (e.g., ileocolic artery) or messenteric vein Other names abdominal vessels requiring ligation or repair Superior mesenteric vein, trunk Renal artery or vein lliac artery or vein Hypogastric artery or vein ena cava, infrarenal Superior mesenteric artery, trunk Celiac axis proper ena cava, suprarenal and infrahepatic Aorta, infrarenal Portal vein Extraparenchymal hepatic vein ena cava, retrohepatic or suprahepatic Aorta suprarenal, subdiaphragmatic 90.0/ / / / /. 90.6/ /. 90./. 90./ NS NS NS NS NS NS NS (hepatic vein) (liver + veins) *This classification system is applicable to extraparenchymal vascular injuries. f the vessel injury is within cm of the organ parenchyma, refer to specific organ injury scale. ncrease one grade for multiple grade or injuries involving > 0% vessel circumference. Downgrade one grade if <% vessel circumference laceration for grades or. NS-not scored. From Moore et al []; with permission
9 Table 8 Adrenal organ injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 involving only cortex (< cm) extending into medulla (> cm) >0% parenchymal destruction Total parenchymal destruction (including massive intraparenchymal hemorrhage) Avulsion from blood supply 868.0/ / / / /. *Advance one grade for bilateral lesions up to grade From Moore et al []; with permission Table 9 Kidney injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Microscopic or gross hematuria, urologic studies normal Subcapsular, nonexpanding without parenchymal laceration Nonexpanding perirenal hematoma confirmed to renal retroperitoneum <.0 cm parenchymal depth of renal cortex without urinary extravagation <.0 cm parenchymal depth of renal cortex without collecting system rupture or urinary extravagation Parenchymal laceration exteding through renal cortex, medulla, and collecting system 866. ascular Main renal artery or vein injury with contained hemorrhage ascular Completely shattered kidney Avulsion of renal hilum which devascularizes kidney *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade From Moore et al. [7]; with permission
10 Table 0 Ureter injury scale Grade* Type of injury Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma without devascularization 867./867. < 0% transection 867./867. > 0% transection 867./867. Complete transection with < cm devascularization 867./867. Avulsion with > cm of devascularization 867./867. *Advance one grade for bilateral up to grade. From Moore et al. []; with permission Table Bladder injury scale Grade* njury type Description of injury CD-9 AS-90, intramural hematoma Partial thickness 867.0/867. Extraperitoneal bladder wall laceration < cm 867.0/867. Extraperitoneal (>cm) or intraperitoneal (<cm) bladder wall laceration ntraperitoneal bladder wall laceration >cm 867.0/ /867. ntraperitoneal or extraperitoneal bladder wall laceration extending into the bladder neck or ureteral orifice (trigone) 867.0/867. *Advance one grade for multiple lesions up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission
11 Table Urethra injury scale Grade* njury type Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Blood at urethral meatus; retrography normal 867.0/867. Stretch injury Partial disruption Complete disruption Complete disruption Elongation of urethra without extravasation on urethrography Extravasation of urethrography contrast at injury site with visualization in the bladder Extravasation of urethrography contrast at injury site without visualization in the bladder; <cm of urethra seperation Complete transaction with > cm urethral separation, or extension into the prostate or vagina 867.0/ / / /867. *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table Uterus (nonpregnant) injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 /hematoma Superficial laceration (< cm) Deep laceration (> cm) involving uterine artery Avulsion/devascularization 867./. 867./. 867./ /. *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table Uterus (pregnant) injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma (without placental abruption) Superficial laceration (<cm) or partial placental abruption <% Deep laceration (>cm) occurring in second trimester or placental abruption >% but <0% Deep laceration (>cm) in third trimester involving uterine artery Deep laceration (>cm) with >0% placental abruption Uterine rupture Second trimester Third trimester Complete placental abruption 867./. 867./. 867./. 867./ /. 867./. 867./. 867./. - *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission
12 Table Fallopian tube injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or contusion <0% circumference >0% circumference Transection ascular injury; devascularized segment 867.6/ / / / *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table 6 Ovary injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma Superficial laceration (depth <0. cm) Deep laceration (depth > 0. cm) Partial disruption or blood supply Avulsion or complete parenchymal destruction 867.6/ / / *Advance one grade for bilateral injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table 7 agina injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma, superficial (mucosa only), deep into fat or muscle, complex, into cervix or peritoneum njury into adjacent organs (anus, rectum, urethra, bladder) *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission Table 8 ulva injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 or hematoma, superficial (skin only), deep (into fat or muscle) Avulsion; skin, fat or muscle njury into adjacent organs (anus, rectum, urethra, bladder) *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission
13 Table 9 Testis injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 /hematoma Subclinical laceration of tunica albuginea of tunica albuginea with <0% parenchymal loss Major laceration of tunica albuginea with >0% parenchymal loss Total testicular destruction or avulsion 9.0/ *Advance one grade for bilateral lesions up to grade From Moore et al []; with permission Table 0 Scrotum injury scale Grade Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 <% of scortal diameter >% of scrotal diameter Avulsion <0% Avulsion >0% From Moore et al []; with permission Table Penis injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Cutaneous laceration/contusion Buck s fascia (cavernosum) laceration without tissue loss Cutaneous avulsion through glans/meatus Cavemosal or urethral defect <cm Partial penectomy Cavarnosal or urethral defect > cm Total penectomy *Advance one grade for multiple injuries up to grade From Moore et al. []; with permission
14 Table Peripheral vascular organ injury scale Grade* Description of injury CD-9 AS-90 Digital artery/vein Palmar artery/vein Deep palmar artery/vein Dorsalla pedia artery Plantar artery/vein Non-named arterial/venous branches Basilic/cephalic vein Saphenous vein Radial artery Ulnar artery Axillary vein Superficial/deep femoral vein Popliteal vein Brachial artery Anterior tibial artery Posterior tibial artery Peroneal artery Tibioperoneal trunk Superficial/deep femoral artery Popliteal artery Axillary artery Common femoral artery / / / / *ncrease one grade for multiple grade or injuries involving >0% vessel circumference. Decrease one grade for < % vessel circumference disruption for grades or From Moore et al []; with permission
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Internal Injury Documentation Guidelines
 Internal Injury Documentation Guidelines General Open Wound of Thorax Injury to Heart Identify episode of care Initial Subsequent Sequela Laterality Sequela of injury Place of occurrence of injury Activity
Internal Injury Documentation Guidelines General Open Wound of Thorax Injury to Heart Identify episode of care Initial Subsequent Sequela Laterality Sequela of injury Place of occurrence of injury Activity
PROTOCOLS. Lap-belt syndrome. Principal investigator. Background
 Lap-belt syndrome Principal investigator Claude Cyr, MD, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke, 3001 12 e Avenue Nord, Sherbrooke QC J1H 5N4; tel.: (819) 346-1110, ext. 14634; fax: (819) 564-5398;
Lap-belt syndrome Principal investigator Claude Cyr, MD, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke, 3001 12 e Avenue Nord, Sherbrooke QC J1H 5N4; tel.: (819) 346-1110, ext. 14634; fax: (819) 564-5398;
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma. Last reviewed June 2014
 Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
Canadian Undergraduate Urology Curriculum (CanUUC): Genitourinary Trauma Last reviewed June 2014 Session Objectives 1. Recognize hematuria as the cardinal symptom of urinary tract trauma. 1. Outline the
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
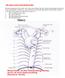 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
cast specimens Showing the branches of arteries, with the skull reserved. C005 Head veins and skull
 cast specimens Art-No. Name Description C001 Brain arteries Whole arteries of brain. C002 Arteries of head Arterial branches in head, without skull C003 Veins of head Venous tributaries in head, without
cast specimens Art-No. Name Description C001 Brain arteries Whole arteries of brain. C002 Arteries of head Arterial branches in head, without skull C003 Veins of head Venous tributaries in head, without
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Contents. Pig Dissection. Contents. External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index
 Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
Pig Dissection External Features Sex Determination Mouth and Maxillary Nerve Muscles Index Internal Systems Index External features Sex determination Male Female Male to External anatomy 1. Pinna 2. External
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
Role of imaging in evaluation of genitourinary i trauma Spectrum of GU injuries Relevance of imaging findings in determining management Focus on MDCT
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
PRACTICE GUIDELINE TITLE: NON-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF LIVER / SPLENIC INJURIES
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 6-18-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: N-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF LIVER / SPLENIC INJURIES PURPOSE: To define when non-operative management of liver
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 6-18-04 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: N-OPERATIVE MANAGEMENT OF LIVER / SPLENIC INJURIES PURPOSE: To define when non-operative management of liver
1. Distinguish among the types of blood vessels on the basis of their structure and function.
 Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
Blood Vessels and Circulation Objectives This chapter describes the structure and functions of the blood vessels Additional subjects contained in Chapter 13 include cardiovascular physiology, regulation,
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology
 Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
Urogenital Injuries The role of radiology NORDTER 7 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course Helsinki, Finland May 21-24, 2012 Johann Baptist Dormagen, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital, Norway Kidney injuries
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Penetrating abdominal trauma clinical view. Ari Leppäniemi, MD Department of Abdominal Surgery Meilahti hospital University of Helsinki Finland
 Penetrating abdominal trauma clinical view Ari Leppäniemi, MD Department of Abdominal Surgery Meilahti hospital University of Helsinki Finland Meilahti hospital - one of Helsinki University hospitals -
Penetrating abdominal trauma clinical view Ari Leppäniemi, MD Department of Abdominal Surgery Meilahti hospital University of Helsinki Finland Meilahti hospital - one of Helsinki University hospitals -
ANATOMY - II. FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX
 ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
ANATOMY - II FOR 2 MARKS QUESTIONS(for Anatomy II Q.NO 1 ) THORAX 1. Total no. of true ribs. 2. Total no. of false ribs. 3. Total no. of floating ribs. 4. Total no. of typical ribs. 5. Total no. of vertebra.
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Anatomy II ANAT 302. Course Description
 Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Anatomy II ANAT 302 Course Description This course provides the students with lectures and comprehensive overview of the gross anatomy of the components of the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive and
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked
 Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
Genitourinary Trauma Introduction GU Trauma overlooked 10-20% of all injured patients Long term morbidity Impotence Incontinence Life-threatening injuries first Urethral Injury Plan Bladder Injury Kidney
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green
 Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
Group B: Organ systems (digestive, respiratory, urinary, genital system, heart, glands and skin) green Digestive system 1. Teeth Main points: external and internal structure of a tooth, fixation of a tooth
UROLOGIC TRAUMA. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 UROLOGIC TRAUMA Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara UROLOGIC TRAUMA Renal trauma Ureteral injury Bladder injury Urethral injury Injury to external genitalia
UROLOGIC TRAUMA Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara UROLOGIC TRAUMA Renal trauma Ureteral injury Bladder injury Urethral injury Injury to external genitalia
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE. There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood
 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS AND CYCLE 2 LAB EXAM TEMPLATE There are two main mechanisms that work in conjunction to return the blood THE CARDIAC PUMP 1) The forward pull(vis a fronte) This
MINK DISSECTION LAB DAY 1 NECK
 MINK DISSECTION LAB PURPOSE: This lab dissection is designed to give you first hand experience with the organs (or their mink counterparts) that we have learned about all year long. After seeing the organs,
MINK DISSECTION LAB PURPOSE: This lab dissection is designed to give you first hand experience with the organs (or their mink counterparts) that we have learned about all year long. After seeing the organs,
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
NBME Anatomy Review. Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015
 NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
Fig Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata. Integrating center. Receptor. Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
 Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Fig. 5. Integrating center Glossopharyngeal nerve transmits signals to medulla oblongata Receptor 3 Vagus nerve transmits inhibitory signals to cardiac pacemaker Baroreceptors sense increased blood pressure
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
A Z OF ABDOMINAL RADIOLOGY
 Z OF BDOMINL RDIOLOGY bdominal trauma to Z of bdominal Radiology Clinical characteristics general discussion, followed by organ-specific summaries, is given below. bdominal trauma is managed as part of
Z OF BDOMINL RDIOLOGY bdominal trauma to Z of bdominal Radiology Clinical characteristics general discussion, followed by organ-specific summaries, is given below. bdominal trauma is managed as part of
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 23 : Vessels and Circulation 23-1 Blood Vessels An efficient style of transport for oxygen, nutrients, and waste products to and from body tissues.
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
IMAGING OF BLUNT ABDOMINAL TRAUMA, PART I
 IMAGING OF BLUNT ABDOMINAL TRAUMA, PART I QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ruedi F. Thoeni, M. D. D University of California, San Francisco SCBT-MR Summer
IMAGING OF BLUNT ABDOMINAL TRAUMA, PART I QuickTime and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Ruedi F. Thoeni, M. D. D University of California, San Francisco SCBT-MR Summer
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
HBA 531 THE BODY. Trunk Examination September 30, What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5)
 HBA 531 THE BODY Trunk Examination September 30, 2013 Name: 1. What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5) a) Heart rate b) Male reproductive function c) Pylorus d) Internal anal
HBA 531 THE BODY Trunk Examination September 30, 2013 Name: 1. What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5) a) Heart rate b) Male reproductive function c) Pylorus d) Internal anal
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Anatomy of the renal system. Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi
 Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
BILLING BULLETIN. Re: Interventional Cardiology. Bulletin #: 1. Date Issued: November 10, Background
 BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
Sample page. POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com.
 2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
ICD-10-PCS The Complete Official Code Set. Sample
 ICD-10-PCS The Complete Official Code Set 2017 021 021 Heart and Great Vessels 021 021 Heart and Great Vessels ICD-10-PCS 2017 2 Heart and Great Vessels 021 1 Bypass Definition: Altering the route of passage
ICD-10-PCS The Complete Official Code Set 2017 021 021 Heart and Great Vessels 021 021 Heart and Great Vessels ICD-10-PCS 2017 2 Heart and Great Vessels 021 1 Bypass Definition: Altering the route of passage
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet
 Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
Interventional Radiology for Solid Organ Trauma. Case Study 8/17/2017. Diagnosis? Case Study (cont d)
 Interventional Radiology for Solid Organ Trauma Jamie Gallivan RN, BSN Interventional Radiology Case Study 6 y/o boy fell out of 2 nd story window onto concrete Hemodynamically stable at scene Arrival
Interventional Radiology for Solid Organ Trauma Jamie Gallivan RN, BSN Interventional Radiology Case Study 6 y/o boy fell out of 2 nd story window onto concrete Hemodynamically stable at scene Arrival
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
