Electrocardiographic T wave abnormalities
|
|
|
- Gertrude Greer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
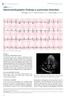
1 Singapore Med J 2013; 54(11): doi: /smedj CMEArticle Electrocardiographic T wave abnormalities Weiqin Lin 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee Guan Teo 2, MBBS (Hons), MRCP, Kian Keong Poh 1,3, FRCP, FACC Fig. 1 ECG of patient shows T wave inversions. CASE 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION A 61-year-old man was admitted for intermittent chest pain, which lasted for over one week. It worsened on exertion and was associated with diaphoresis. The pain was described as a central squeezing sensation that lasted for about ten minutes and was relieved with rest. Cardiovascular examination of the patient was unremarkable, and he was normotensive at rest. What are the electrocardiographic (ECG) abnormalities seen in Fig. 1? 1 Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre, National University Health System, 2 Raffles Heart Centre, Raffles Hospital, Singapore, 3 Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore Correspondence: A/Prof Poh Kian Keong, Senior Consultant and Associate Professor, Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre, 1E Kent Ridge Road, NUHS Tower Block, Level 9, Singapore kian_keong_poh@nuhs.edu.sg 606
2 E lectrocardiography S eries 2a 2b 2c Fig. 2 Coronar y angiography in the (a) right anterior oblique caudal and (b) anterior-posterior cranial views of the left coronar y ar ter y show 9 0% stenosis of the mid segment (arrows). (c) Coronar y angiography in the right anterior oblique cranial view of the left coronar y ar ter y post angioplasty shows good flow with no residual stenosis. EC G I N T E R PR E TAT I O N The ECG in Fig. 1 shows sinus rhythm with normal PR and QRS durations. There are deep T waves in the chest leads (V2 to V6), as well as biphasic T waves in the inferior leads. There were no ST changes and the ECG findings did not meet the criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy.(1) CLI N I CA L CO U R S E The patient was treated for ischaemic heart disease. Serial cardiac enzyme studies and ECG examinations performed revealed elevation of cardiac troponins and no change in ECG findings. The patient was then managed for non-st-elevation myocardial infarction. On coronary angiography, single vessel coronary artery disease with the culprit being a 90% stenosis of the mid-left anterior descending artery (Figs. 2a & b) was shown. The patient underwent coronary angioplasty with subsequent stenting of the culprit lesion (Fig. 2c). Subsequent echocardiography showed preser ved lef t ventricular ejection fraction. Fig. 3 ECG shows T wave inversions and left ventricular hyper trophy. CASE 2 C L I N I C A L PR E S E N TAT I O N An 80-year-old man presented to the cardiology service for evaluation of a cardiac murmur. He was otherwise asymptomatic, with no exertion chest pain or dyspnoea. Physical examination revealed a grade 2 ejection systolic murmur, as well as a grade 2 early diastolic murmur at the lower left sternal edge. The patient was normotensive. What does the patient s ECG (Fig. 3) show? 607
3 ECG INTERPRETATION The ECG in Fig. 3 shows sinus rhythm in the patient. Both the PR interval and QRS duration were within normal limits. There was also evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy, fulfilling Sokolow-Lyon criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy (i.e. S wave in V1 + R wave in V5 or V6 35 mm). (2) In this case, the sum was 43 mm. It also fulfilled the Cornell criteria for left ventricular hypertrophy in male patients (i.e. R wave in avl + S wave in V3 > 28 mm). (3) There was also widespread T wave inversion in the anterolateral leads (V2 to V6, I and avl), as well as downward ST depression in the chest leads (V3 to V6), representing a strain pattern. LV LA Ao CLINICAL COURSE Transthoracic echocardiography was performed with an intravenous contrast agent to better delineate the left ventricular borders. Asymmetrical left ventricular hypertrophy at the septum was observed (Fig. 4). However, the gradient across the left ventricular outflow tract was not elevated. These features were consistent with nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. There was also mild aortic, mitral and tricuspid valve regurgitation. The pulmonary artery and aortic root were dilated. In addition to his hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the patient also had several cardiovascular risk factors, for which he is currently under follow-up. DISCUSSION On ECG, the T wave represents rapid ventricular repolarisation (i.e. phase 3) of the ventricular action potential. During phase 3, there is closure of the calcium channels, while the potassium channels remain open, resulting in rapid loss of positive charge from the cardiomyocytes and restoration of the resting membrane potential. As such, the configuration of the T wave is dependent on the spatial-temporal characteristics of ventricular repolarisation. In normal adults, the T wave amplitude is usually upright in all leads, except the avr, avl, III and V1 leads, with maximal amplitudes in precordial leads V2 and V3. (4) It is usually asymmetrical with a smooth peak. T wave inversions in the right precordial leads (V1 up to V4) are common in children. In normal adults, T wave inversions may be present, although rare, in up to lead V3. In addition, T waves should not exceed 5 mm in the limb leads and 10 mm in the precordial leads. Any deviation from this normal pattern can thus provide much information about many disease states. Abnormalities in T waves can present as inverted, biphasic, flattened or tall T waves. The T wave is considered inverted if the inversion is deeper than 1.0 mm, and flattened if it is between 1 mm and 1.0 mm. (5) In both the illustrated cases, the identification of an abnormal T wave provided clues that enabled the cardiac diagnoses to be eventually established. Causes of T wave abnormalities are varied and include functional/physiological variants (e.g. postprandial state), Fig. 4 Contrast echocardiogram in the parasternal long axis view shows asymmetrical ventricular septal wall thickening (white arrows). The septum (indicated by white arrows) measures 19 mm. Ao: aorta; LA: left atrium; LV: left ventricle endocrine/electrolyte abnormality, myocardial ischaemia, myocarditis/pericarditis/cardiomyopathy, postcardiac surgery state, pulmonary embolism, fever/infection, anaemia, acidosis/ alkalosis, drugs, endogenous catecholamine, metabolic changes, acute abdominal process, intracranial pathology, and systemic disease/amyloidosis/lung diseases. (6) As mentioned earlier, T wave inversion is commonly seen in normal children, but rarely in normal adults. In a Finnish study of 10,899 asymptomatic middle-aged subjects, T wave inversions in the right precordial leads (i.e. V1 to V3) were seen in 54 subjects and T wave inversions in leads other than V1 to V3 in 76 subjects. After an average follow-up period of 30 years, it was noted that right precordial T wave inversions did not predict increased mortality, whereas inverted T waves in leads other than V1 to V3 were associated with increased risks of cardiac and arrhythmia deaths. (7) In the two cases discussed in this article, there was either a positive physical finding of a cardiac murmur or a presentation of chest pain. As such, the T wave inversions on their ECG are likely to represent underlying cardiac diseases. For instance, the ECG in Case 1 showed deep T wave inversions, which suggest underlying ischaemic heart disease; together with the clinical scenario, a diagnosis of non-st-elevation myocardial infarction was made. Common ECG patterns seen in ischaemic heart disease include: (a) ST segment depression or T wave inversion during myocardial ischaemia directed in the opposite direction as the QRS complex; (b) ST segment depression with upright T wave; (c) a positive-negative biphasic T wave pattern; (d) T wave symmetrically inverted with a pointed configuration, while the ST segment is either upwardly bowed (i.e. coved) or horizontally depressed, or not deviated; and (e) ST segment depression progressing to T wave abnormality during ischaemia free intervals. (4) T wave changes in patients with severe ischaemia or injury in the distribution of the left anterior descending artery, 608
4 known as Wellens syndrome, has also been observed by de Zwaan et al. (8) This syndrome is characterised by two patterns of T wave changes. de Zwaan et al found that in 75% of the cases, T waves were symmetrically inverted > 5 mm from leads V2 to V4, while 25% of cases had positive-negative T wave morphology in leads V2 through V4. In both patterns, the ST segments were either isoelectric or minimally deviated (< 1 mm). It also noted that 75% of the cohort with such T wave abnormalities, who were treated medically without angiographic investigation, subsequently developed extensive anterior wall myocardial infarction within a mean period of 8.5 days. (8) Another important cause of deep T wave inversions is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a disease characterised by excessive thickening of the left, and occasionally the right, ventricular myocardium. The prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is estimated to be 1 in 500 patients. It can be associated with either left ventricular outflow tract obstruction or no significant resting outflow tract gradient (in 75% of cases). (9) The 12-lead ECG is abnormal in 75% 95% of patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Common ECG patterns include evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy, large QRS voltages with giant negative T waves, as well as deep and narrow Q waves. (10) Giant negative T waves are, however, more characteristic of patients with nonobstructive apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. (11) In Case 2, the ECG showed evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy according to both the Sokolow-Lyon and Cornell criteria. (2,3) It also showed widespread ST depressions in the anterolateral precordial leads, representing the strain pattern. Echocardiogram subsequently confirmed the diagnosis of nonobstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The patient also underwent a contrast echocardiogram, which enabled better delineation of the left ventricular endocardial borders (Fig. 4). The administration of ultrasonography contrast agent is a safe and noninvasive method of enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of echocardiography. In contrast echocardiography, microbubble contrast agents are injected intravenously while echocardiographic images are being acquired. The microbubbles show up as echodense particles within the cardiac chambers and great vessels, allowing for better delineation of cardiac anatomy, (12) as seen in Case 2. In summary, there are a multitude of causes for T wave inversions on ECG. Correlation of the ECG with careful history taking and physical examination, together with directed cardiac investigations, will often reveal the underlying cardiac pathology. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We acknowledge Professor Chia Boon Lock for his advice and help in the writing of this article. ABSTRACT The causes of abnormal T waves on electrocardiography are multiple and varied. Careful clinical history taking and physical examination are necessary for accurate identification of the cause of such abnormalities. Subsequent targeted specialised cardiac investigations, such as echocardiography or coronary angiography, may be of importance in the diagnosis of the underlying cardiac pathology. We present two cases of T wave inversions with markedly different aetiologies. Keywords: ECG, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ischaemic heart disease, T wave abnormalities REFERENCES 1. Poh KK, Teo SG, Tay EL, Yip JW. Electrocardiography Series. ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 1. Singapore Med J 2011; 52:855-8; quiz Sokolow M, Lyon TP. The ventricular complex in left ventricular hypertrophy as obtained by unipolar precordial and limb leads. Am Heart J 1949; 37: Casale PN, Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Campo E, Kligfield P. Improved sexspecific criteria of left ventricular hypertrophy for clinical and computer interpretation of electrocardiograms: validation with autopsy findings. Circulation 1987; 75: Hanna EB, Glancy DL. ST-segment depression and T-wave inversion: classification, differential diagnosis, and caveats. Cleve Clin J Med 2011; 78: Rautahraju PM, Surawicz B, Gettes LS, et al. AHA/ ACCF/ HRS recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part IV: the ST segment, T and U waves, and the QT interval: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society. Endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 53: Prutkin JM. ECG tutorial: ST and T wave changes. In: UpToDate Inc [online]. Available at: Accessed October 14, Aro AL, Anttonen O, Tikkanen JT, et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of T-wave inversions in right precordial leads of a 12- lead electrocardiogram in the middle-aged subjects. Circulation 2012; 125: de Zwaan C, Bär FW, Wellens HJ. Characteristic electrocardiographic pattern indicating a critical stenosis high in left anterior descending coronary artery in patients admitted because of impending myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 1982; 103(4 Pt 2): Maron BJ. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: a systematic review. JAMA 2002; 287: Prinz C, Farr M, Hering D, Horstkotte D, Faber L. The diagnosis and treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2011; 108: Yamaguchi H, Ishimura T, Nishiyama S, et al. Hypertrophic nonobstructive cardiomyopathy with giant negative T waves (apical hypertrophy): ventriculographic and echocardiographic features in 30 patients. Am J Cardiol 1979; 44: Mulvagh SL, Rakowski H, Vannan MA, et al. American Society of Echocardiography Consensus Statement on the Clinical Applications of Ultrasonic Contrast Agents in Echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2008; 21:
5 SINGAPORE MEDICAL COUNCIL CATEGORY 3B CME PROGRAMME (Code SMJ A) Question 1. In the interpretation of T waves on an electrocardiogram (ECG): (a) T wave represents rapid ventricular depolarisation. (b) T wave amplitude should not exceed 5 mm in the limb leads. (c) T wave should not exceed 15 mm in the precordial leads. (d) T wave is usually upright in lead avr. True False Question 2. T wave abnormalities on an ECG can be caused by: (a) Acute myocardial infarction. (b) Recent cardiac surgery. (c) Acute intracranial haemorrhage. (d) Severe sepsis with metabolic acidosis. Question 3. Regarding T wave inversions in ischaemic heart disease: (a) T inversions are always seen with depressed ST segments. (b) Inverted T waves are usually symmetrical with pointed configuration. (c) Wellens syndrome describes T wave changes in the precordial leads associated with myocardial ischaemia in the left anterior descending artery territory. (d) T wave inversions can only be seen during acute ischaemic periods. Question 4. Regarding hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: (a) It can be classified by the presence or absence of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction. (b) ECG is normal in the majority of patients. (c) Left ventricular hypertrophy pattern can be seen on ECG. (d) Large QRS complexes and giant negative T waves can be seen on ECG. Question 5. Regarding the approach to patients with significant T wave inversions on ECG: (a) To diagnose any underlying cardiac pathology, thorough history taking and physical examination is key. (b) Family history of sudden cardiac death is significant. (c) T wave inversion in the precordial leads is common in prepubertal children. (d) Right precordial leads (V1 to V3) T wave inversions on ECG in asymptomatic adults have been shown to be associated with higher cardiovascular mortality. Doctor s particulars: Name in full : MCR number : Specialty:_ address : SUBMISSION INSTRUCTIONS: (1) Log on at the SMJ website: and select the appropriate set of questions. (2) Provide your name, address and MCR number. (3) Select your answers and click Submit. RESULTS: (1) Answers will be published in the SMJ January 2014 issue. (2) The MCR numbers of successful candidates will be posted online at the SMJ website by 23 December (3) Passing mark is 60%. No mark will be deducted for incorrect answers. (4) The SMJ editorial office will submit the list of successful candidates to the Singapore Medical Council. (5) One CME point is awarded for successful candidates. Deadline for submission: (November 2013 SMJ 3B CME programme): 12 noon, 16 December
ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(9) : 647 CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction Seow S C, Omar A R, Hong E C T Cardiology Department, National University
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(9) : 647 CME Article Brugada pattern masking anterior myocardial infarction Seow S C, Omar A R, Hong E C T Cardiology Department, National University
15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New Electrocardiographic Insights in 2014
 DOI 10.7603/s40602-016-0006-3 ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.globalsciencejournals.com/journal/40602 Vol. 24, no.1, 98 105 (2016) ISSN: 2315-4551 15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New
DOI 10.7603/s40602-016-0006-3 ASEAN Heart Journal http://www.globalsciencejournals.com/journal/40602 Vol. 24, no.1, 98 105 (2016) ISSN: 2315-4551 15 th Sukaman Memorial Lecture ST Segment Elevation: New
1 Fq-ii I - I I...L w. husband on the morning of her admission. Her symptoms
 . ', ir Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 202;53(6) 367 CM EARTCLE Nonischaemic causes of ST segment elevation vandito Kuntjorol, MD, Swee Guan Teo'2, MBBS, MRCP, Kian Keong Poh'2, FRCP, FACC
. ', ir Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 202;53(6) 367 CM EARTCLE Nonischaemic causes of ST segment elevation vandito Kuntjorol, MD, Swee Guan Teo'2, MBBS, MRCP, Kian Keong Poh'2, FRCP, FACC
CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 77 CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2 Ayyachamy SS 1, MRCP, Teo SG 1, MBBS, MRCP, Tay ELW 1, MRCP, FACC, Yip JWL 1, MBBS, MRCP, Poh KK 1,2, FRCP, FACC Fig.
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(2) : 77 CMEArticle ECGs of structural heart disease: Part 2 Ayyachamy SS 1, MRCP, Teo SG 1, MBBS, MRCP, Tay ELW 1, MRCP, FACC, Yip JWL 1, MBBS, MRCP, Poh KK 1,2, FRCP, FACC Fig.
the ECG, 6 mg of intravenous adenosine was administered as a fast bolus through a large bore intravenous cannula in
 (arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
(arrows). Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med.1 2011, 52(3) 146 CME Article Regular narrow complex tachycardia Singh D, Teo S G, Poh K K V Hr JL1 11 VL VF WA, Fig. I ECG shows regular narrow complex
12 Lead ECG Interpretation
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
12 Lead ECG Interpretation Julie Zimmerman, MSN, RN, CNS, CCRN Significant increase in mortality for every 15 minutes of delay! N Engl J Med 2007;357:1631-1638 Who should get a 12-lead ECG? Also include
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG
 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
_FT 4. _Ci4 - ;,..., r. _ L.1_4±J-1 +.1_77 di _-_,..i , lt.! -7H :-,-...i-2 Litt drri "94. _Ia. :7...-t. ' ; r., r - .J...
 rr 7 :,Liir 6 E I it i, r i s : al, r I Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med 20, 52() 3 C M E Article ECG ST segment elevation in patients with chest pain Poh K K, Tan H C, Teo S G Cardiac Department,
rr 7 :,Liir 6 E I it i, r i s : al, r I Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med 20, 52() 3 C M E Article ECG ST segment elevation in patients with chest pain Poh K K, Tan H C, Teo S G Cardiac Department,
Case 1. Case 2. Case 3
 Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
Case 1 The correct answer is D. Occasionally, the Brugada syndrome can present similar morphologies to A and also change depending on the lead position but in the Brugada pattern the r is wider and ST
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto
 How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
How NOT to miss Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy? Adaya Weissler-Snir, MD University Health Network, University of Toronto Introduction Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is the most common genetic cardiomyopathy,
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI
 Case Report Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI Melissa Lyle 1, Ryan C. Van Woerkom 2,
Case Report Conus artery occlusion causing isolated right ventricular outflow tract infarction: novel application of cardiac magnetic resonance in anterior STEMI Melissa Lyle 1, Ryan C. Van Woerkom 2,
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
Introduction to Electrocardiography
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
About T waves
 About T waves - 2014 Dr. Andres R. Pérez Riera The T waves is a positive deflection after each QRS complex. It represents ventricular repolarization The T wave represents the unconcealed potential differences
About T waves - 2014 Dr. Andres R. Pérez Riera The T waves is a positive deflection after each QRS complex. It represents ventricular repolarization The T wave represents the unconcealed potential differences
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals. Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
Basic electrocardiography reading. R3 lee wei-chieh
 Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
 Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
Case Reports Inspiratory Right Ventricular Outflow Obstruction in a Patient with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Kazufumi TSUCHIHASHI, M.D., Akihito TSUCHIDA, M.D., Nobuichi HIKITA, M.D., Shuji YONEKURA, M.D.,
ECG Workshop. Nezar Amir
 ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
ECG Workshop Nezar Amir Myocardial Ischemia ECG Infarct ECG in STEMI is dynamic & evolving Common causes of ST shift Infarct Localisation Left main artery occlusion: o diffuse ST-depression with ST elevation
Electrocardiogram ECG. Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University
 Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(9): 516-520 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017088 CMEArticle Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis Yi-Ting Laureen Wang 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Chong Seow 1,2, MRCP, FACC,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(9): 516-520 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017088 CMEArticle Rhythmic chaos: irregularities of computer ECG diagnosis Yi-Ting Laureen Wang 1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Chong Seow 1,2, MRCP, FACC,
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes
 Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
Normal ECG And ECHO Findings in Athletes Dr.Yahya Kiwan Consultant Interventional Cardiologist Head Of Departement Of Cardiology Canadian Specialist Hospital Sinus Bradycardia The normal heartbeat is initiated
December 2018 Tracings
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Cardiovascular Images
 Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
Cardiovascular Images Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosed From Right Heart Changes Seen After Exercise Stress Echocardiography Brian C. Case, MD; Micheas Zemedkun, MD; Amarin Sangkharat, MD; Allen J. Taylor,
PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY
 PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY ANDRÉS RICARDO PÉREZ RIERA MD Chief of the Sector of Electro-Vectocardiography of the
PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY ANDRÉS RICARDO PÉREZ RIERA MD Chief of the Sector of Electro-Vectocardiography of the
Preface: Wang s Viewpoints
 AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
AHA/ACCF/HRS Recommendations for the Standardization and Interpretation of the Electrocardiogram: Part IV, Ischemia and Infarction Presented by: WANG, TZONG LUEN, MD, PhD, JM, FACC, FESC, FCAPSC Professor,
Biventricular Enlargement/ Hypertrophy
 Biventricular Enlargement/ Hypertrophy Keywords congenital heart disease left ventricular hypertrophy right ventricular hypertrophy SR MITTAL Abstract Electrocardiographic diagnosis of early biventricular
Biventricular Enlargement/ Hypertrophy Keywords congenital heart disease left ventricular hypertrophy right ventricular hypertrophy SR MITTAL Abstract Electrocardiographic diagnosis of early biventricular
Myocardial Infarction. Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline )
 Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D.
 Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Biphasic T-wave in patient with chest pain (Wellens syndrome)
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Biphasic T-wave in patient with chest pain (Wellens syndrome) Ahmed Zedan, Osama Mukarram, Umer Malik, Raja Naidu ABSTRACT Abstract is
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Biphasic T-wave in patient with chest pain (Wellens syndrome) Ahmed Zedan, Osama Mukarram, Umer Malik, Raja Naidu ABSTRACT Abstract is
Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 301e307 Cardiac hypertrophy and how it may break an athlete s heart e the Cypriot case C.E. Chee a,1, C.P. Anastassiades a,1, A.G. Antonopoulos b, A.A. Petsas b, L.C. Anastassiades
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) PRESENTED AS UNSTABLE ANGINA COMPLICATED BY SERIOUS VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS CASE REPORT AND REVIEW LITERATURE Lusyun Kumar Yadav * and Jin li Jun Department of Cardiology,
HISTORY. Question: What type of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance.
 HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
HISTORY 15-year-old male. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance. PRESENT ILLNESS: A heart murmur was noted in childhood, but subsequent medical care was sporadic. Easy fatigability and slight
ECG pre-reading manual. Created for the North West Regional EMET training program
 ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
ECG pre-reading manual Created for the North West Regional EMET training program Author:- Dr Juan Carlos Ascencio-Lane juan.ascencio-lane@ths.tas.gov.au 1 Disclaimer This handbook has been created for
12 LEAD EKG BASICS. By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC
 12 LEAD EKG BASICS By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC ECG Review Waves and Intervals P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria QRS complex: right and left ventricular
12 LEAD EKG BASICS By: Steven Jones, NREMT P CLEMC ECG Review Waves and Intervals P wave: the sequential activation (depolarization) of the right and left atria QRS complex: right and left ventricular
The T wave represents the period of ventricular repolarization
 Rare Giant T-Wave Inversions Associated With Myocardial Stunning: Report of 2 Cases Li Yue-Chun, MD and Jia-Feng Lin, MD Abstract: Prominent T-wave inversions are well recognized electrocardiographic signs
Rare Giant T-Wave Inversions Associated With Myocardial Stunning: Report of 2 Cases Li Yue-Chun, MD and Jia-Feng Lin, MD Abstract: Prominent T-wave inversions are well recognized electrocardiographic signs
Dr Navin Chandra Clinical Research Fellow in Cardiology St George s University of London
 Dr Navin Chandra Clinical Research Fellow in Cardiology St George s University of London Cardiac Adaptation in Athletes Athletic training for prolonged periods may result in physiological adaptations of
Dr Navin Chandra Clinical Research Fellow in Cardiology St George s University of London Cardiac Adaptation in Athletes Athletic training for prolonged periods may result in physiological adaptations of
DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES
 PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
PRACTICAL ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY DR QAZI IMTIAZ RASOOL OBJECTIVES Recording of electrical events in heart Established electrode pattern results in specific tracing pattern Health of heart i. e. Anatomical
Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes
 REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
REVIEW ARTICLE 7 How to differentiate physiological adaptation to intensive physical exercise from pathologies Current ECG interpretation guidelines in the screening of athletes Gemma Parry-Williams, Sanjay
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know. Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series
 ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
Historical Notes: Clinical Exercise Testing in the Athlete. An Efficient Heart. Structural Changes, Cont. Coronary Arteries
 Clinical Exercise Testing in the Athlete The athlete s heart Sudden cardiac death in athletes Screening athletes for cardiovascular disease Historical Notes: Giovanni Lancisi (father of cardiology), 17
Clinical Exercise Testing in the Athlete The athlete s heart Sudden cardiac death in athletes Screening athletes for cardiovascular disease Historical Notes: Giovanni Lancisi (father of cardiology), 17
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO)
 Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Anaesthesia for non-cardiac surgery in patients left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) Dr. Siân Jaggar Consultant Anaesthetist Royal Brompton Hospital London UK Congenital Cardiac Services
Paediatric ECG Interpretation
 Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
15 16 September Seminar W10O. ECG for General Practice
 15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT
 HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
HEART CONDITIONS IN SPORT Dr. Anita Green CHD Risk Factors Smoking Hyperlipidaemia Hypertension Obesity Physical Inactivity Diabetes Risks are cumulative (multiplicative) Lifestyles predispose to RF One
All About STEMIs. Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC. Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager.
 All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
All About STEMIs Presented By: Brittney Urvand, RN, BSN, CCCC Essentia Health Fargo Cardiovascular Program Manager Updated 10/2/2018 None Disclosures Objectives Identify signs and symptoms of a heart attack
Electrocardiographic abnormalities encountered in acute myocardial infarction
 40 J Accid Emerg Med 2000;17:40 45 ECG NTERPRETATON FOR THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA W J Brady Department
40 J Accid Emerg Med 2000;17:40 45 ECG NTERPRETATON FOR THE EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, Virginia, USA W J Brady Department
12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice. Presented By: Cynthia Webner, BSN, RN, CCRN-CMC. Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC
 12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice NTI 2009 Preconference Session 803 Presented By: Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC 1 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals: The Starting Place for Linking
12 Lead ECG Skills: Building Confidence for Clinical Practice NTI 2009 Preconference Session 803 Presented By: Karen Marzlin, BSN, RN,CCRN-CMC 1 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals: The Starting Place for Linking
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
ECG Cases and Questions. Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology
 ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG. Jakub Dorożyński
 Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH. General. Heart Rate. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
Left posterior hemiblock (LPH)/
 ECG OF THE MONTH Left Postero-inferior Depolarization Delay Keywords Electrocardiography Intraventricular conduction delay, Inferoposterior hemiblock, Left posterior fascicular block, Left posterior hemiblock
ECG OF THE MONTH Left Postero-inferior Depolarization Delay Keywords Electrocardiography Intraventricular conduction delay, Inferoposterior hemiblock, Left posterior fascicular block, Left posterior hemiblock
INTRODUCTION TO ECG. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
 INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series
 ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
5- The normal electrocardiogram (ECG)
 5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging. Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology
 Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
Managing Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy with Imaging Gisela C. Mueller University of Michigan Department of Radiology Disclosures Gadolinium contrast material for cardiac MRI Acronyms Afib CAD Atrial fibrillation
E CG Challenges. The ST segment on an electrocardiogram (ECG) correlates to the plateau. Wellens Syndrome
 AACN Advanced Critical Care Volume 29, Number 3, pp 360-364 2018 AACN E CG Challenges Karen M. Marzlin, DNP, RN, CCNS, ACNPC-AG, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Department Editor Wellens Syndrome Karen M. Marzlin, DNP,
AACN Advanced Critical Care Volume 29, Number 3, pp 360-364 2018 AACN E CG Challenges Karen M. Marzlin, DNP, RN, CCNS, ACNPC-AG, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Department Editor Wellens Syndrome Karen M. Marzlin, DNP,
also aid the clinician in recognizing both the obvious and subtle abnormalities that may help guide therapy.
 Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
Karen Lieberman, MS, CRNP f the many diagnostic tools used to screen for and evaluate cardiac abnormalities, the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) is among the most basic. This inexpensive and noninvasive
Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism
 Singapore Med J 2015; 56(10): 533-537 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015147 Electrocardiography Series CMEArticle Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism Elaine Boey1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Guan Teo2, MRCP,
Singapore Med J 2015; 56(10): 533-537 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2015147 Electrocardiography Series CMEArticle Electrocardiographic findings in pulmonary embolism Elaine Boey1, MBBS, MRCP, Swee-Guan Teo2, MRCP,
ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES
 Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
Ministry of Health of Ukraine Kharkiv National Medical University ECG SIGNS OF HYPERTROPHY OF HEART ATRIUMS AND VENTRICLES Methodical instructions for students Рекомендовано Ученым советом ХНМУ Протокол
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p
 Title A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction Author(s) Ng, W; Wong, CK; Lau, CP Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p. 199-202 ssued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45037
Title A patient with non-q wave acute inferior myocardial infarction Author(s) Ng, W; Wong, CK; Lau, CP Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1997, v. 19 n. 4, p. 199-202 ssued Date 1997 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/45037
12 Lead ECG. Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept.
 12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
12 Lead ECG Presented by Rebecca Sevigny BSN, RN Professional Practice & Development Dept. Two Main Coronary Arteries RCA LCA which branches into Left Anterior Descending Circumflex Artery Two Main Coronary
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react
 TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
TGA atrial vs arterial switch what do we need to look for and how to react Folkert Meijboom, MD, PhD, FES Dept ardiology University Medical entre Utrecht The Netherlands TGA + atrial switch: Follow-up
Understanding basics of EKG
 Understanding basics of EKG By Alula A.(R III) www.le.ac.uk Topic for discussion Understanding of cellular electrophysiology Basics Rate Rhythm Axis Intervals P wave QRS ST/T wave Abnormal EKGs Understanding
Understanding basics of EKG By Alula A.(R III) www.le.ac.uk Topic for discussion Understanding of cellular electrophysiology Basics Rate Rhythm Axis Intervals P wave QRS ST/T wave Abnormal EKGs Understanding
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Little is known about the degree and time course of
 Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Differential Changes in Regional Right Ventricular Function Before and After a Bilateral Lung Transplantation: An Ultrasonic Strain and Strain Rate Study Virginija Dambrauskaite, MD, Lieven Herbots, MD,
Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012
 Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012 Session 2: 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals 101 Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Though for Today Mastery is not something that strikes in an instant, like a thunderbolt,
Relax and Learn At the Farm 2012 Session 2: 12 Lead ECG Fundamentals 101 Cynthia Webner DNP, RN, CCNS, CCRN-CMC, CHFN Though for Today Mastery is not something that strikes in an instant, like a thunderbolt,
Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis
 CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis Martin J. Nathan, M.D., Roman W. DeSanctis, M.D., Mortimer J. Buckley, M.D., Charles A. Sanders, M.D., and W. Gerald Austen,
CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis and Mitral Stenosis Martin J. Nathan, M.D., Roman W. DeSanctis, M.D., Mortimer J. Buckley, M.D., Charles A. Sanders, M.D., and W. Gerald Austen,
Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular Obstruction
 CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
CSE REPORT DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.1.37 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Tako-Tsubo Cardiomyopathy by Transient Dynamic Left Midventricular
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
How to Assess Dyssynchrony
 How to Assess Dyssynchrony Otto A. Smiseth, Professor, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital None Conflicts of interest Cardiac resynchronization therapy effect on mortality Cleland JG et al, N Engl J Med
How to Assess Dyssynchrony Otto A. Smiseth, Professor, MD, PhD Oslo University Hospital None Conflicts of interest Cardiac resynchronization therapy effect on mortality Cleland JG et al, N Engl J Med
Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina Non ST segment Elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST segment Elevation MI (STEMI)
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
ECG CONVENTIONS AND INTERVALS
 1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
1 ECG Waveforms and Intervals ECG waveforms labeled alphabetically P wave== represents atrial depolarization QRS complex=ventricular depolarization ST-T-U complex (ST segment, T wave, and U wave)== V repolarization.
Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy With Hemodynamically Unstable Ventricular Arrhythmia Atypical Presentation
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hemant Chaturvedi* Department of Cardiology, Non-Invasive Cardiology, Eternal Heart Care Center & research Institute, Rajasthan, India Received: September 15, 2015; Published: October
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Hemant Chaturvedi* Department of Cardiology, Non-Invasive Cardiology, Eternal Heart Care Center & research Institute, Rajasthan, India Received: September 15, 2015; Published: October
Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
ECG Interpretation. Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction
 ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECG. Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13
 ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
Syncope Due to Intracavitary Left Ventricular Obstruction Secondary to Giant Esophageal Hiatus Hernia
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise. Cardiac Conditions in Sport. USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD) Dr Anita Green. Sudden Cardiac Death
 Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Cardiac Conditions in Sport & Exercise Dr Anita Green Cardiac Conditions in Sport Sudden Cardiac Death USA - Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
F or a long time the 12-lead electrocardiogram
 490 REVIEW The electrocardiogram in ST elevation acute myocardial infarction: correlation with coronary anatomy and prognosis Y Birnbaum, B J Drew... The electrocardiogram is considered an essential part
490 REVIEW The electrocardiogram in ST elevation acute myocardial infarction: correlation with coronary anatomy and prognosis Y Birnbaum, B J Drew... The electrocardiogram is considered an essential part
