Specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus
|
|
|
- Winifred Cunningham
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
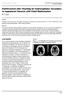
1 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987, 62, Specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus A E O'HARE, J K BROWN, AND R A MINNS Department of Paediatric Neurology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh SUMMARY Disproportionate enlargement or isolation of the fourth ventricle are rare complications of ventriculo-peritoneal shunt for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Obvious features such as ataxia may indicate raised intracranial pressure in the posterior fossa. The child may, however, present with less specific signs of vomiting, anorexia, and lethargy and these symptoms may be misinterpreted as secondary to dilation of the lateral ventricular system due to malfunction of the ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. Two children with disproportionate enlargement of the fourth ventricle and two children with isolation of the fourth ventricle are described to illustrate the wide variations in clinical presentation. These rare complications can be diagnosed by real time ultrasound examination of the brain or computed tomography of the head. They should be considered in the differential diagnosis of a child who deteriorates after lateral ventriculo-peritoneal shunting for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus, and dealt with specifically to avoid the risk of upward herniation of the enlarged fourth ventricle. Intracranial haemorrhage is a common problem in the premature neonate and occurs in up to 70% of infants who are born at less than 35 weeks' gestation, weigh less than 1500 g, and require assisted ventilation.' Post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus may result from inflammatory ependymitis; basilar arachnoiditis; obstruction of the foramen of Munro, aqueduct of Sylvius, or fourth ventricular outflow foramina;2 or occlusion and scarring of surface absorptive mechanisms.3 Many infants require ventricular cerebrospinal fluid shunting to control the dilatation of the ventricles4 and there is substantial morbidity associated with progressive posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus.5 Intraventricular haemorrhage may also occur in the infant born at term; 35% subsequently require ventricular shunting.6 We described three premature infants and one infant born at term who required lateral ventricular shunting for control of post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus and who subsequently developed the rare complication of specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle. They illustrate a breadth of presentation and management and are discussed in the context of published experience. Case reports CASE 1 This infant was delivered at 30 weeks by caesarean section because of severe maternal pre-eclampsia. He did not breathe spontaneously at birth and required immediate intermittent positive pressure ventilation. His need for respiratory support increased and at 28 hours his condition deteriorated sharply; ultrasonographic examination showed a grade four intraventricular haemorrhage. He needed artificial ventilation for some weeks and at the age of 2 months he was referred for further management of post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Three days later he had a ventriculoperitoneal shunt inserted. At first his postoperative course was uncomplicated, but three weeks later he developed paroxysmal episodes of cyanosis with respiratory irregularities; ultrasound examination of the ventricular system showed no increase in enlargement of the lateral and third ventricles but a disproportionate increase in the size of the fourth ventricle (fig 1). Intracranial pressure was measured from the right lateral ventricle and was 1*07 kpa. A small amount 1025
2 1026 O'Hare, Brown, and Minns Fig. 1 a & b (:N\ K1-) Case 1: disproportionate enlargement offourth ventricle on real time ultrasonography. of ventricular fluid was withdrawn. Thereafter his respiratory abnormalities resolved, and follow up ultrasonographic examination showed resolution of the enlargement of the fourth ventricle. Subsequently the infant made good progress, and at the age of 18 months showed normal development apart from slight delay in motor development with a degree of ataxia. CASE 2 This infant was delivered at term by spontaneous vertex delivery. There was no asphyxia at birth, she was breast fed, and given vitamin K supplements. She was admitted at the age of 3 weeks with an acute history of irritability, vomiting, and opisthotonus and was shown to have bilateral haemorrhages into the ventricular system. Two weeks later a Rickham reservoir was inserted into the right lateral ventricle, but daily removal of cerebrospinal fluid failed to control her intracranial pressure and she had a theco-peritoneal shunt inserted. At the age of 41/2 months computed tomography of the head showed marked ventricular enlargement and her theco-peritoneal shunt was replaced with a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. After operation she developed ventriculitis, and Escherichia coli was isolated from the lumbar and ventricular cerebrospinal fluid. She required seven shunt revisions over the next four years. When she was 41/2 years old, she was admitted with acute pain down the left side of her neck associated with torticollis and vomiting. It was impossible to measure intracranial pressure because of the occluded Rickham reservoir. Computed tomography showed enlargement of the right lateral ventricle with obvious enlargement of the fourth ventricle. (fig 2a). Revision of the right ventriculoperitoneal shunt was performed with subsequent decrease in the size of the fourth ventricle and resolution of her symptoms. (fig 2b). rb;) Fig. 2a Case 2: disproportionate enlargement offourth ventrirle. Fig. 2b Case 2: disproportionate enlargement offourth ventricle less marked after revision oflateral ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
3 Specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt 1027 CASE 3 This baby boy was delivered by emergency caesarian section at 34 weeks after a concealed placental haemorrhage. He was asphyxiated at birth and received full intensive care to minimise secondary brain swelling. During his early course he was hypoglycaemic and had tonic convulsions. On the fifth day he sustained a bowel perforation caused by necrotising enterocolitis. On day 13 he was noted to have post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Ventricular taps and removal of cerebrospinal fluid had no effect and initially he had a theco-peritoneal shunt inserted; this blocked after 38 hours and he then had a lateral ventriculo-peritoneal shunt performed. Follow up ultrasonography showed good control of his hydrocephalus. At the age of 8 months he was admitted with ventriculitis due to Staphylococcus albus, for which he was treated with intravenous and intrathecal gentamicin and flucloxacillin and shunt revision. At this time he had cerebral palsy with a diplegia and a right hemiplegia and microcephaly. At the age of 3 years 4 months he was readmitted with a one week history of anorexia and drowsiness. There was no change in his neurological condition but intracranial pressure monitoring carried out through his left Rickham reservoir showed intermittent high pressure readings of 2-67 kpa. There was a history of a minor head injury one month before his admission. Computed tomography showed obvious enlargement of the fourth ventricle with small lateral ventricles and a small third ventricle (fig 3a). He underwent posterior fossa craniectomy with exploration of the large fourth ventricle and insertion of a cysto-peritoneal shunt. Postoperatively computed tomography showed considerable reduction in the size of the fourth ventricle (fig 3b) and his symptoms resolved. CASE 4 This baby girl was delivered by spontaneous vertex delivery at 28 weeks; no asphyxia or respiratory distress was noted at birth. Her occipitofrontal circumference increased abnormally suggesting the development of hydrocephalus, and an ultrasound examination at 2 months of age showed gross enlargement of both lateral ventricles and a left porencephalic cyst. At the age of 2 months a ventriculo-peritoneal shunt was inserted. A month later isolated enlargement of the fourth ventricle was detected on ultrasound examination. At the age of 6 months she had a left hemiparesis. When she was 9 months old she presented with paroxysmal episodes of right sided weakness associated with fever, and computed tomography showed that the lateral ventricles were not grossly enlarged and the third ventricle was small and displaced. There was a large cystic area in the posterior fossa comprising the grossly distended Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 October Downloaded from Fig. 3a Case 3: isolated enlargement offourth ventricle. Fig. 3b Case 3: resolution of enlargement offourth ventricle after cysto-peritoneal shunt diversion. on 29 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
4 1028 O'Hare, Brown, and Minns t cl I Fig. 4a Case 4: isolated enlargement offourth ventricle. Fig. 4b Case 4: reduction in size offourth ventricle after cysto-peritoneal shunt diversion. fourth ventricle, and there appeared to be no obvious communication between the fourth ventricle and the supratentorial ventricular system. Her right hemiparesis resolved completely on conservative management. Four months later she was admitted with an acute attack of anorexia and vomiting. Clinical examination revealed neck retraction, hypertension, and bradycardia. Intracranial pressure measured through a right lateral ventricle Rickham reservoir was *60 kpa. Computed tomography showed persisting enlargement of an isolated fourth ventricle (fig 4a) and a cysto-peritoneal shunt was inserted. Follow up computed tomography (fig 4b) showed an improvement in the size of the ventricle and the raised intracranial pressure in the posterior fossa had resolved. Discussion Specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle can take the form of a disproportionate enlargement or a complete isolated encystment, and although the presentation of the two conditions may be similar in children who have had shunts inserted for posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus the management is quite different. In disproportionate enlargement of the fourth ventricle the aqueductal canal is patent and this can be shown using air contrast studies or Conray ventriculography, whereas the foramina of Luschka and Megendi are occluded.7 The abnormality arises when this type of occlusion occurs at the same time as abnormal weakness of the brain stem parenchyma around the fourth ventricle. Collision of cerebrospinal fluid against the obstruction produces a j 'water hammer' effect and results in enlargement of the fourth ventricle. This disproportionate enlargement can be detected by real time ultrasonography of the posterior fossa8 or computed tomography of the head. The presenting symptoms of both the cases with this condition suggested raised pressure in the posterior fossa with bradycradia and respiratory irregularities prominant in case 1, and neck pain and torticollis in case 2. Although the intracranial pressure was not raised in case 1 when measured through a Rickman reservoir in his right lateral ventricle, his symptoms resolved when cerebrospinal fluid was removed from the lateral ventricle. In case 2 the disproportionate enlargement of the fourth ventricle improved and she became asymptomatic after revision of her lateral ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Presumably these forms of management are effective because the enlarged fourth ventricle remains in communication with the rest of the ventricular system. The fourth ventricle may, however, become completely isolated from the rest of the ventricular system when both the aqueduct of Sylvius and the exit foramina of Lushka and Magendi are occluded.9 This acquired condition must be distinguished from other cystic malformations of the posterior fossa.1' It is never a primary disease in that it occurs only after shunting of the lateral ventricular system for communicating hydrocephalus, aqueduct stenosis, or obstruction to the outlets of the fourth ventricle'1 and only in the presence of the foreign body of the shunt. The initial reports of the condition were in patients who had communicating hydrocephalus after infections of the central nervous system.'2 13 Even in the children who develop the condition after shunting for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus the likelihood of isolation of the fourth ventricle developing is greater if they have had episodes of ventriculitis and many children have had multiple shunt revisions.14 Isolation of the fourth ventricle may be associated with clinical signs of an expanding lesion in the posterior fossa and ataxia, neck retraction, torticollis, nystagmus, diplopia, and dysarthria should alert a clinician to the condition in children who have previously had a shunt inserted for post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Not only might the symptoms be of a non-localising nature, for example, anorexia and lethargy,9 but a subtle deterioration may be difficult to detect in these children, who often have several handicaps, and therefore a high index of suspicion is required. Measurement of the intracranial pressure through a reservoir in the lateral ventricle does not always
5 Specific enlargement of the fourth ventricle after ventriculo-peritoneal shunt 1029 help: it was raised in one of our cases and normal in another. If the intracranial pressure is measured directly from the fourth ventricle, however, it is raised in symptomatic cases. 15 As the fourth ventricle is completely isolated from the rest of the ventricular system, a mistaken diagnosis of malfunction of the lateral ventriculoperitoneal shunt leading to subsequent revision of the shunt may lead to upward herniation of the enlarged fourth ventricle, whereas independent shunting of the cystic ventricle results in control of the condition.9 References Bowerman RA, Donn SM, Silvers TM, Jaffe MH. Review. Natural history of periventricular-intraventricular haemorrhage and its complications: sonographic observations. American Journal of Neuroradiology 1984;143: Levene NI, Williams JL, Fawer CL. Ultrasound of the infants brain. Spastics International Medical Publications, Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications Ltd, Ellington JL, Zachary RB. Block of arachnoid villus by subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurosurg 1969;30: Hill AE, Morgan MEI. Post haemorrhagic hydrocephalus in the newborn term infants. Arch Dis Child 1985;60: Cook RWI. Early prognosis of low birthweight infants treated for progressive post haemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 1983;58: Scher MS, Wright FS, Lockman LA, Thomson TR. Intraventricular haemorrhage in the full term neonate. Child Neurology 1982;39: Matsumoto M, Kushida Y, Shibata I, Seiki Y, Terao H. Disproportionately large communicating fourth ventricle. Report of two cases. No Shinkei Geka 1983;11: Grant EG, Schellinger D, Richardson JD. Real time ultrasonography of the posterior fossa. J Ultrasound Med 1983;2: Scotti G, Musgrave MA, Fitz CR, Harwood-Nash DC. The isolated fourth ventricle in children: CT and clinical review of sixteen cases. American Journal of Neuroradiology 1980;135: Rayband C. Cystic malformation of the posterior fossa. J Neuroradiol 1982;9: Hawkins JC, Hoffman HJ, Humphries RP. Isolated fourth ventricle as a complication of ventricular shunting. Report of three cases. J Neurosurg 1978;49: Defeo DR, Foltz EL, Hamilton AE. Double compartment hydrocephalus in a patient with cysticercosis meningitis. Surg Neurol 1975;4: Kalsbeck JE, Desousa AL, Kleiman MB, Goodman JM, Franken EA. Compartmentalisation of the cerebral ventricles as a sequelae of neonatal meningitis. J Neurosurg 1980;52: Mickle JP, Friedman WAE. Cysted fourth ventricle. Surg Neurol 1981;16: Foltz EL, Defeo DR. Double compartment hydrocephalus-a new clinical entity. Neurosurgery 1980;7: Correspondence to Dr A E O'Hare, Department of Paediatric Neurology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Sciennes Road, Edinburgh. Received 22 April 1987 Arch Dis Child: first published as /adc on 1 October Downloaded from on 29 June 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
The "Keyhole": A Sign of
 473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
473 The "Keyhole": A Sign of Herniation of a Trapped Fourth Ventricle and Other Posterior Fossa Cysts Barbara J. Wolfson' Eric N. Faerber' Raymond C. Truex, Jr. 2 When a cystic structure in the posterior
The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children
 J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
J Neurosurg 61:752-756, 1984 The arrest of treated hydrocephalus in children A radionuclide study IAN H. JOHNSTON, F.R.C.S., ROBERT HOWMAN-GILES, F.R.A.C.P., AND IAN R. WHITTLE, M.B., B.S. T. Y. Nelson
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Neonate Angela Forbes, RN, MN, ARNP Seattle Children s Hospital Division of Pediatric Neurosurgery Seattle, Washington, U.S.A. Intraventricular Hemorrhage Who Premature
and management in four cases
 1216 16ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:1216-1220 Department of Paediatrics, University of Aachen, Pauwelsstrasse 30, D-52057 Aachen, Germany V Th Ramaekers Department of Neuroradiology,
1216 16ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:1216-1220 Department of Paediatrics, University of Aachen, Pauwelsstrasse 30, D-52057 Aachen, Germany V Th Ramaekers Department of Neuroradiology,
ultrasonography in preterm infants: association with outcome
 Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
Archives ofdisease in Childhood 1990; 65: 1033-1037 nstitut de la Sante et de la Recherche Medicale (NSERM), Unite 316, Tours, France Philippe Bertrand Francis Gold Sophie Marchand Department of Paediatric
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Severe apnea and bradycardia in a term infant October 2014 2 Walker JH, Arlettaz Mieth R, Däster C, Division of Neonatology, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Swiss Society
Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42 cases
 Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Child s Nerv Syst (2001) 17:348 352 DOI 10.1007/s003810000425 ORIGINAL PAPER Raj Kumar Manoj Kumar Jain Devendra Kumar Chhabra Dandy-Walker syndrome: different modalities of treatment and outcome in 42
Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation
 Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation Benedetta Pettorini Consultant Paediatric Neurosurgeon Alder Hey Childrens Hospital Liverpool, UK Risk Factors for IVH 1. Prematurity: Occurs
Surgical Options in Post Haemorrhagic Ventricular Dilation Benedetta Pettorini Consultant Paediatric Neurosurgeon Alder Hey Childrens Hospital Liverpool, UK Risk Factors for IVH 1. Prematurity: Occurs
CYANOTIC ATTACKS IN NEWBORN INFANTS
 BY R. S. ILLINGWORTH From the Jessop Hospital for Women and the Children's Hospital, the United Sheffield Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MARCH 10, 1957) By the term 'cyanotic attacks in newborn infants'
BY R. S. ILLINGWORTH From the Jessop Hospital for Women and the Children's Hospital, the United Sheffield Hospitals (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION MARCH 10, 1957) By the term 'cyanotic attacks in newborn infants'
GEORGE E. PERRET, M.D., AND CARL J. GRAF, M.D.
 J Neurosurg 47:590-595, 1977 Subgaleal shunt for temporary ventricle decompression and subdural drainage GEORGE E. PERRET, M.D., AND CARL J. GRAF, M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, University of Iowa
J Neurosurg 47:590-595, 1977 Subgaleal shunt for temporary ventricle decompression and subdural drainage GEORGE E. PERRET, M.D., AND CARL J. GRAF, M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, University of Iowa
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele
 Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Two-Stage Management of Mega Occipito Encephalocele CASE REPORT A I Mardzuki*, J Abdullah**, G Ghazaime*, A R Ariff!'*, M Ghazali* *Department of Neurosciences, **Department of Radiology, Hospital Universiti
Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip
 197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
 RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Elham BIDABADI MD Assistant Professor of Pediatric Neurology, Guilan University of Medical Sciences,Guilan,Iran Corresponding
RESEARCH ARTICLE RELATIVE FREQUENCY OF HYDROCEPHALUS IN RASHT PEDIATRIC PATIENTS Elham BIDABADI MD Assistant Professor of Pediatric Neurology, Guilan University of Medical Sciences,Guilan,Iran Corresponding
The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1
 9 The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1 periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). These lesions are more common in the smallest and most
9 The two most common forms of brain injury noted in preterm neonates are intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) and 1 periventricular leukomalacia (PVL). These lesions are more common in the smallest and most
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE*
 SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
SYSTEMATIC VENTRICULOGRAPHIC STUDIES IN INFANTS BORN WITH MENINGOMYELOCELE AND ENCEPHALOCELE* THE INCIDENCE AND DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROCEPHALUS BY JOHN LORBER From the Department of Child Health, University
Treatment of Acute Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture
 19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
M ULTIPLE causes of hydrocephalus
 Conversion of Communicating Hydrocephalus to Stenosis or Occlusion of the Aqueduct during Ventricular Shunt* ELDON L. FOLTZ, M.D., AND DAVID B. SHURTLEFF, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery and Department
Conversion of Communicating Hydrocephalus to Stenosis or Occlusion of the Aqueduct during Ventricular Shunt* ELDON L. FOLTZ, M.D., AND DAVID B. SHURTLEFF, M.D. Department of Neurological Surgery and Department
Prevalence of "Compressed" and Asymmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic
 Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
obstructive hydrocephalus
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1986;49:238-242 Entrapment of the temporal horn: a form of focal obstructive hydrocephalus RS MAURICE-WILLIAMS, M CHOKSEY From the Royal Free Hospital
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1986;49:238-242 Entrapment of the temporal horn: a form of focal obstructive hydrocephalus RS MAURICE-WILLIAMS, M CHOKSEY From the Royal Free Hospital
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form
 National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
National follow-up program CPUP Pediatric Neurology paper form 110206 1 National Follow-Up program- CPUP Pediatric Neurology Personal nr (unique identifier): Last name: First name: Region child belongs
IMPLICATIONS OF NEURO-DEVELOPMENTAL DEVIATIONS IN LOW BIRTHWEIGHT AND MECHANICALLY VENTILATED INFANTS
 IMPLICATIONS OF NEURO-DEVELOPMENTAL DEVIATIONS IN LOW BIRTHWEIGHT AND MECHANICALLY VENTILATED INFANTS A condition described as transient dystonia which may have long term effects on the development of
IMPLICATIONS OF NEURO-DEVELOPMENTAL DEVIATIONS IN LOW BIRTHWEIGHT AND MECHANICALLY VENTILATED INFANTS A condition described as transient dystonia which may have long term effects on the development of
Hydrocephalus in the Newborn
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 44. Incidence and Treatment of Post-meningitic Hydrocephalus in the Newborn JOHN LORBER and DOUGLAS PICKERING From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield,
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1966, 41, 44. Incidence and Treatment of Post-meningitic Hydrocephalus in the Newborn JOHN LORBER and DOUGLAS PICKERING From the Department of Child Health, University of Sheffield,
Chronic abscess of the brain stem
 J. A. RUSSELL AND M. D. M. SHAW Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 625--629 From the Institute of Neurological Sciences, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, Scotland S U M M
J. A. RUSSELL AND M. D. M. SHAW Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 625--629 From the Institute of Neurological Sciences, Southern General Hospital, Glasgow, Scotland S U M M
Chiari Malformations. Google. Objectives Seventh Annual NKY TBI Conference 3/22/13. Kerry R. Crone, M.D.
 Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
Chiari Malformations Kerry R. Crone, M.D. Professor of Neurosurgery and Pediatrics University of Cincinnati College of Medicine University of Cincinnati Medical Center Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical
What Are We Going to Do? Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy. Hydrocephalus and Effects of Interruption of CSF Flow. Tube Blockage Doctrine
 Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia
 Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia Intraventricular Hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is bleeding inside the lateral ventricles. Bleeding frequently occurs in areas
Intraventricular Hemorrhage and Periventricular Leukomalacia Intraventricular Hemorrhage Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) is bleeding inside the lateral ventricles. Bleeding frequently occurs in areas
Surgical management of the fourth ventricle arachnoid cysts
 Annals of Medical Research DOI: 10.5455/annalsmedres.2018.09.199 2019;26(1):42-6 Original Article Surgical management of the fourth ventricle arachnoid cysts Sukru Oral 1, Hanifi Bayarogullari 2, Atilla
Annals of Medical Research DOI: 10.5455/annalsmedres.2018.09.199 2019;26(1):42-6 Original Article Surgical management of the fourth ventricle arachnoid cysts Sukru Oral 1, Hanifi Bayarogullari 2, Atilla
Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Extensive cystic periventricular leukomalacia following early-onset group B streptococcal sepsis in a very low birth weight infant July 2012 2 Berger TM, Caduff JC, Neonatal
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES)
 HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
HYDROCEPHALUS OF THE INFANT (ABOUT 86 CASES) K.EL KHOU;R.ANDALOUSSI;L.OUZIDANE Pediatric radiology department-chu Ibn Rochd Casablanca-Morroco Morroco. Introduction Hydrocephalus of infant is a progressive
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Periventricular/Intraventricular Hemorrhage in the Newborn
 Khalid N. Haque, FRCP(Ed), FRCP(I), FAAP, FICP, DCH, DTM&H; Omar B. A. Basit, MRCP(UK), DCH; Meeralebbae M. Shaheed, MD, MRCP(UK), DCH From the Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, College
Khalid N. Haque, FRCP(Ed), FRCP(I), FAAP, FICP, DCH, DTM&H; Omar B. A. Basit, MRCP(UK), DCH; Meeralebbae M. Shaheed, MD, MRCP(UK), DCH From the Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics, College
Influence of Aetiology on Prognosis in Surgically
 Arch. Dis. ChildA., 1969, 44, 29. Influence of Aetiology on Prognosis in Surgically Treated Infantile Hydrocephalus A. N. GUTHKELCH* and N. A. RILEY From Hull Royal Infirmary, and Royal Manchester Children's
Arch. Dis. ChildA., 1969, 44, 29. Influence of Aetiology on Prognosis in Surgically Treated Infantile Hydrocephalus A. N. GUTHKELCH* and N. A. RILEY From Hull Royal Infirmary, and Royal Manchester Children's
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool.
 Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Neonatal Intracranial Ultrasound Imaging - A Pictorial Review from The Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Alder Hey, Liverpool. Poster No.: C-1115 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
386 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL July 2000
 386 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL July 2000 East African Medical Journal Vol. 77 No. 7 July 2000 VENTRICULOPERITONEAL SHUNT SURGERY AND SHUNT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN WITH NON-TUMOUR HYDROCEPHALUS AT THE
386 EAST AFRICAN MEDICAL JOURNAL July 2000 East African Medical Journal Vol. 77 No. 7 July 2000 VENTRICULOPERITONEAL SHUNT SURGERY AND SHUNT INFECTIONS IN CHILDREN WITH NON-TUMOUR HYDROCEPHALUS AT THE
I mprovements in perinatal and neonatal care have contributed
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posthaemorrhagic ventricular in the premature infant: natural history and predictors of outcome B P Murphy, T E Inder, V Rooks, G A Taylor, N J Anderson, N Mogridge, L J Horwood, J J Volpe...
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posthaemorrhagic ventricular in the premature infant: natural history and predictors of outcome B P Murphy, T E Inder, V Rooks, G A Taylor, N J Anderson, N Mogridge, L J Horwood, J J Volpe...
ventriculography compared, those with mass lesions involving the cerebral hemispheres were excluded.
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 203-211 Computerized tomography (the EMAI Scanner): a comparison with pneumoencephalography and ventriculography J. GAWLER, G. H. DU BOULAY,
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
(Received for publication February ~7, 1956)
 PAPILLOMA OF THE CHOROID PLEXUS OF THE LATERAL VENTRICLES CAUSING HYDROCEPHALUS IN AN INFANT BnONSON S. RAY, M.D., AND FREMONT C. PECK, JR., M.D. Department of Surgery, New York Hospital-Cornell Medical
PAPILLOMA OF THE CHOROID PLEXUS OF THE LATERAL VENTRICLES CAUSING HYDROCEPHALUS IN AN INFANT BnONSON S. RAY, M.D., AND FREMONT C. PECK, JR., M.D. Department of Surgery, New York Hospital-Cornell Medical
Visual defects in children of low birthweight
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 818-822 Visual defects in children of low birthweight EVA ALBERMAN, JULIA BENSON, AND STEPHEN EVANS Department of Clinical Epidemiology, London Hospital Medical
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 818-822 Visual defects in children of low birthweight EVA ALBERMAN, JULIA BENSON, AND STEPHEN EVANS Department of Clinical Epidemiology, London Hospital Medical
Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1985, 60, 349-355 Developmental sequence of periventricular leukomalacia Correlation of ultrasound, clinical, and nuclear magnetic resonance functions L M S DUBOWITZ,
Death after late failure of third ventriculostomy in children
 J Neurosurg 97:211 215, 2002 Death after late failure of third ventriculostomy in children Report of three cases WALTER J. HADER, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), JAMES DRAKE, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), DOUGLAS COCHRANE, M.D.,
J Neurosurg 97:211 215, 2002 Death after late failure of third ventriculostomy in children Report of three cases WALTER J. HADER, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), JAMES DRAKE, M.D., F.R.C.S.(C), DOUGLAS COCHRANE, M.D.,
Developmental and neurological progress of preterm infants with intraventricular haemorrhage and
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 748-753 Developmental and neurological progress of preterm infants with intraventricular haemorrhage and ventricular dilatation PENELOPE PALMER, LLLY M S DUBOWTZ,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1982, 57, 748-753 Developmental and neurological progress of preterm infants with intraventricular haemorrhage and ventricular dilatation PENELOPE PALMER, LLLY M S DUBOWTZ,
Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November March 2014
 Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November 1996- March 2014 March 2014 A 5-year-old patient presents for a myringotomy and grommet insertion as a day case. During your pre-operative assessment
Final FRCA Written PAEDIATRICS Past Paper Questions November 1996- March 2014 March 2014 A 5-year-old patient presents for a myringotomy and grommet insertion as a day case. During your pre-operative assessment
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Progressive cranial nerve palsy following shunt placement in an isolated fourth ventricle
 J Neurosurg (Pediatrics 3) 102:326 331, 2005 Progressive cranial nerve palsy following shunt placement in an isolated fourth ventricle Case report DACHLING PANG, M.D., F.R.C.S(C)., MARIKE ZWIENENBERG-LEE,
J Neurosurg (Pediatrics 3) 102:326 331, 2005 Progressive cranial nerve palsy following shunt placement in an isolated fourth ventricle Case report DACHLING PANG, M.D., F.R.C.S(C)., MARIKE ZWIENENBERG-LEE,
Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari Malformation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
Upward spinal coning: impaction of occult spinal tumours following relief of hydrocephalus
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47: 386-390 Upward spinal coning: impaction of occult spinal tumours following relief of hydrocephalus RASHID JOOMA, RICHARD D HAYWARD From the Departments
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1984;47: 386-390 Upward spinal coning: impaction of occult spinal tumours following relief of hydrocephalus RASHID JOOMA, RICHARD D HAYWARD From the Departments
CHAPTER 11 Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas
 Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas Foolishly, I waited 7 months before I joined this (or any) group. By that time, my son had radiation, chemo, and a recurrence of
Tumors Originating in the Brain Medulloblastomas, PNETs and Ependymomas Foolishly, I waited 7 months before I joined this (or any) group. By that time, my son had radiation, chemo, and a recurrence of
Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1196-1202 Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate J Q TROUNCE, N RUTTER, AND M LEVENE Department of Child Health,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1196-1202 Periventricular leucomalacia and intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm neonate J Q TROUNCE, N RUTTER, AND M LEVENE Department of Child Health,
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
Chiari malformations. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors April 2010 2 Pronzini F, Fontijn J, Fauchère JC, Bucher HU, Clinic of Neonatology,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Vein of Galen aneurysm: Aneurysmal characteristics and clinical features as predictive factors April 2010 2 Pronzini F, Fontijn J, Fauchère JC, Bucher HU, Clinic of Neonatology,
Slit ventricle syndrome and early-onset secondary craniosynostosis in an infant
 ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890590 Received: 2014.02.25 Accepted: 2014.03.01 Published: 2014.06.10 Slit ventricle syndrome and early-onset secondary craniosynostosis in an infant Authors Contribution:
ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.890590 Received: 2014.02.25 Accepted: 2014.03.01 Published: 2014.06.10 Slit ventricle syndrome and early-onset secondary craniosynostosis in an infant Authors Contribution:
Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15921-15927 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022273 Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage Xielin Tang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15921-15927 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022273 Original Article CT grouping and microsurgical treatment strategies of hypertensive cerebellar hemorrhage Xielin Tang
Two RAMs and Half a Brain
 Two RAMs and Half a Brain J. Ron Allen, MD, MPH Lt Col, USAF, MC, SFS W. Javier Nieves, MD, MPH Lt Col, USAF, MC, FS USAF School of Aerospace Medicine WPAFB, OH RAM 2013 Distribution A: Approved for public
Two RAMs and Half a Brain J. Ron Allen, MD, MPH Lt Col, USAF, MC, SFS W. Javier Nieves, MD, MPH Lt Col, USAF, MC, FS USAF School of Aerospace Medicine WPAFB, OH RAM 2013 Distribution A: Approved for public
Infusion studies in clinical practice. Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London
 Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Neuro. Development. Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC. ! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation. ! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months!
 Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Neuro Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Microsoft clip art Development! Primary neurulation! Prosencepahlic! Neuronal proliferation! Neuronal migration! Organization! Myelination! 3-4 weeks! 2-3 months! 3-4 months!
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors
 Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
neurodevelopmental outcome in
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987, 62, 3-36 Periventricular leucomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome in C L FAWER, P DIEBOLD, AND A CALAME preterm infants Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1987, 62, 3-36 Periventricular leucomalacia and neurodevelopmental outcome in C L FAWER, P DIEBOLD, AND A CALAME preterm infants Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois,
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations
 Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Pediatric Neurointervention: Vein of Galen Malformations Johanna T. Fifi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai November 9 th, 2014
Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital
 Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital Please complete in black ballpoint pen Hospital name: Form 6: Baby Outcomes Please complete this form when a Baby-OSCAR participant is transferred to another
Form 6: Baby Outcomes Outcomes at THIS hospital Please complete in black ballpoint pen Hospital name: Form 6: Baby Outcomes Please complete this form when a Baby-OSCAR participant is transferred to another
NYEIS Version 4.3 (ICD) ICD - 10 Codes Available in NYEIS at time of version launch (9/23/2015)
 D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
D82.1 Di George's syndrome E63.9 Nutritional deficiency, unspecified E70.21 Tyrosinemia E70.29 Other disorders of tyrosine metabolism E70.30 Albinism, unspecified E70.5 Disorders of tryptophan metabolism
Sample page. Radiology. Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS
 Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS
 PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS 1. A patient presents with muscle weakness. To assess his condition, you test his knee-jerk reflex by tapping his patella tendon with your hammer. Next you examine the jaw-jerk
PRACTICE EXAM QUESTIONS 1. A patient presents with muscle weakness. To assess his condition, you test his knee-jerk reflex by tapping his patella tendon with your hammer. Next you examine the jaw-jerk
A few Neurosurgical Emergencies. Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015
 A few Neurosurgical Emergencies Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015 Outline Neuroanatomy and physiology (85 slides ) Raised
A few Neurosurgical Emergencies Cathrin Parsch Lyell Mc Ewin Hospital SA Ambulance Service SAAS medstar Spring Seminar on Emergency Medicine 2015 Outline Neuroanatomy and physiology (85 slides ) Raised
Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms
 33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
33 Treatment of Unruptured Vertebral Artery Dissecting Aneurysms Isao NAITO, M.D., Shin TAKATAMA, M.D., Naoko MIYAMOTO, M.D., Hidetoshi SHIMAGUCHI, M.D., and Tomoyuki IWAI, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
 INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE Sheba Medical Center, Acute Medicine Department Irene Frantzis P-Year student SGUL 2013 Normal Values Normal intracranial volume: 1700 ml Volume of brain: 1200-1400 ml CSF:
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine
 Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
Stroke - Intracranial hemorrhage Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Associate Professor Department of Medicine Etiology and pathogenesis ICH accounts for ~10% of all strokes 30 day mortality - 35 45% Incidence rates
The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 64, No. 3, pp. 194 198 Copyright 2005 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl The choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle and its arteries Mansoor
ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection. Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017
 ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017 Monro-Kellie doctrine Intracranial volume = brain volume (85%) + blood volume (10%) + CSF volume (5%) Brain parenchyma Skull
ICP CSF Spinal Cord Anatomy Cord Transection Alicia A C Waite March 2nd, 2017 Monro-Kellie doctrine Intracranial volume = brain volume (85%) + blood volume (10%) + CSF volume (5%) Brain parenchyma Skull
Nature and Science 2017;15(7) Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus
 Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
Surgical Options for Treatment of Posterior Fossa Tumors with Hydrocephalus Mohamed Mahmoud Abohashima; Ahmed Mohamed Hasan Salem; Magdy Asaad El-Hawary Neurosurgery department, Faculty of Medicine, Al-azhar
A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection
 74 Original Article THIEME A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection T. P. Jeyaselvasenthilkumar 1 V. G. Ramesh 1 C. Sekar 1 S. Sundaram 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery,
74 Original Article THIEME A Study to Formulate a Strategy to Prevent Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Infection T. P. Jeyaselvasenthilkumar 1 V. G. Ramesh 1 C. Sekar 1 S. Sundaram 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery,
Aneurysms of the vein of Galen
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 1612-1617 Aneurysms of the vein of Galen D O'DONNABHAIN AND D F DUFF Our Lady's Hospital for Sick Children, Dublin SUMMARY Six neonates with aneurysms of the
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 1612-1617 Aneurysms of the vein of Galen D O'DONNABHAIN AND D F DUFF Our Lady's Hospital for Sick Children, Dublin SUMMARY Six neonates with aneurysms of the
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with
 Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
Anesthetic Management of Laparoscopic Surgery for a Patient with a Ventriculoperitoneal shunt Abstract With the advances in the management of hydrocephalus, patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunt are
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM
 TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
TUMOURS IN THE REGION OF FORAMEN MAGNUM Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 119 To 122 Naim-ur-Rahman ( Department of Neurosurgery, Rawalpindi Medical College, Rawalpindi. ) A very unusual case
Adult - Cerebrovascular. Adult - Cranio-Cervical Junction. Adult - Epilepsy. Adult - Hydrocephalus
 list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
Cranial ultrasound abnormalities in full term infants in a postnatal ward: outcome at 12 and 18 months
 F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
F128 Department of Paediatrics and Neonatal Medicine, Imperial College School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W12 0HS, UK L Haataja E Mercuri FCowan L Dubowitz Correspondence to:
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov Dandy-Walker Malformation
 REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
REVIEW ARTICLE Egypt. J. Hum. Genet. Vol. 8, No. 2, Nov. 2007 Medical Genetics Center, Ain Shams University INTRODUCTION Dandy-Walker malformation is a rare congenital malformation and involves the cerebellum
Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature
 Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature Mohamad Bakhaidar Division of Neurological Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz
Viscus Perforation in Children caused by Peritoneal Shunt Catheters : Case series of 10 patients and review of literature Mohamad Bakhaidar Division of Neurological Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz
leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1203-1207 Intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation J Q TROUNCE, D FAGAN, AND M I LEVENE Department of
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1986, 61, 1203-1207 Intraventricular haemorrhage and periventricular leucomalacia: ultrasound and autopsy correlation J Q TROUNCE, D FAGAN, AND M I LEVENE Department of
Appendix 1. Causes of Neonatal Deaths. Interval between. Gestation at birth. birth and death. Allocation. (weeks +days ) Cause of death.
 Appendix 1. Causes of Neonatal Deaths Interval between Gestation at birth birth and death Allocation (weeks +days ) (days) Cause of death Amnioinfusion 25 +1/7 20 Respiratory and circulatory insufficiency
Appendix 1. Causes of Neonatal Deaths Interval between Gestation at birth birth and death Allocation (weeks +days ) (days) Cause of death Amnioinfusion 25 +1/7 20 Respiratory and circulatory insufficiency
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Stroke in the ED. Dr. William Whiteley. Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian
 Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report
 Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt
 Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
Bangladesh Medical Journal 2011 Vol. 0 No. 1 Orginal Article Clinical Outcome of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery Without Preoperative Ventriculo-peritoneal Shunt MR Islam 1, KMT Islam 2, M Hossain, MH Rashid,
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
HYDROCEPHALUS ASSOCIATED WITH OBLITERATION OF THE LONGITUDINAL SINUS
 HYDROCEPHALUS ASSOCIATED WITH OBLITERATION OF THE LONGITUDINAL SINUS BY J. L. EMERY and R. B. ZACHARY From The Children's Hospital, Sheffield (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 16, 1956) There are theoretically
HYDROCEPHALUS ASSOCIATED WITH OBLITERATION OF THE LONGITUDINAL SINUS BY J. L. EMERY and R. B. ZACHARY From The Children's Hospital, Sheffield (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION APRIL 16, 1956) There are theoretically
