Conduction System of the Heart
|
|
|
- Mercy Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Conduction System of the Heart -Conduction system is very important; without it we will not have impulses or action potentials and there will be NO contraction of the heart muscle. -It consists of modified cardiac muscle cells which are able to produce automatic and rhythmic impulses. Functional modification by leakiness to Na+ (these cells are leaky to Na+) Structural modification by presence of actin and myosin (contractile cells) -Leakiness differs from one part to another: SA-node is the most leaky one to Na+ AV-node is less leaky Purkinje fibers are the least leaky to Na+ That s why they have different rates (highest rate in SA-node, lowest rate in Purkinje) SA-node >AV-node > Purkinje Leakage to Na+/ rate decreases -SA-node produces impulses, they spread through the atrial muscle to the AV-node (which is emerged in the atrial muscle), so AV-node picks the impulse and conducts it to the AV-bundle (bundle of His), then through right & left bundle branches, to Purkinje fibers to the ventricular muscle cells. There is NO direct connection between SA-node & AV-node; AVnode receives the impulses from the atrial muscle (since it is part of it). -Approximately 1% of cardiac muscle cells are autorhythmic rather than contractile, despite that, they are very important; because they are able to produce intrinsic impulses that spread all through the heart and cause contraction. SA-node : AV-node : Purkinje : (highest rate) (lowest rate) P a g e 1
2 -Normally, the SA-node produces (70-80) action potential/min, which is conducted through AV-node to AV-bundle to Purkinje, so the heart is working with that rate also (70-80) beats per minute. -As a result, intrinsic rates of AV-node and Purkinje fibers have been suppressed by the higher intrinsic rate from SA-node (they are not working with their own rates), this is called Overdrived suppression. By removing SA-node working by the rate of AV-node (40-60) If AV-node is blocked no direct connection between the atrium and the ventricle, therefore, ventricles beat by the rate of Purkinje (15-40), whereas atria beat by the rate of SA-node (70-80), this is called AV block or Heart block. Conduction speed (how fast they conduct the impulse or action potential) AV-node has the slowest conduction speed Purkinje fibers have the fastest conduction speed (4-5 m/sec) Ventricular & atrial muscle cells have moderate speeds -As we took before, conducting rate of nerve fiber depends on the myelination and diameter. The AV-node conducts the impulse very slowly, why? Normally, the atria and the ventricles should NOT contract together (the atria should contract and finish their contraction then the ventricles start to contract), to assure this, there should be a delay in the impulse so they will not overlap. Purkinje fiber conducts with the highest rate, why? In order to conduct the impulses to all ventricular muscle cells almost at the same time, so that they can contract simultaneously as one unit. (Purkinje is wider) P a g e 2
3 Slow Response Action Potential (pacemaker potential) Because these cells are leaky to Na+, the resting membrane potential will never reach -90mV (it reaches -60mV) Slow depolarization due to Na+ influx (because it is slowly depolarized, the inactivation gate of Na+ channels close before the activation gate opens so Na+ gated channels are closed), and then Ca++ channels open causing Ca++ influx (depolarization) phase zero Slow Depolarization due to Na+ influx through leakage channels phase 4 Repolarization due to K+ efflux phase 3 There is NO ( 1 or 2) phases no Plateau P a g e 3
4 Fast Response Action Potential Resting membrane potential is much more negative Fast depolarization due to Na+ influx phase zero There are phases 1 & 2 (Plateau) -Ectopic pacemaker: abnormal site of pacemaker (ex: AV-node). Extrinsic Innervation of the Heart -The heart is supplied by Autonomic nerves (sympathetic & parasympathetic) -They are working for regulation of the impulse not initiation -Chronotropic effect: change in the rate -Inotropic effect: change in force of contraction in atria and ventricles (contractility) -Dromotropic effect: change in rate (speed) of conduction P a g e 4
5 Sympathetic Extrinsic Innervation of the Heart - From the cardiac plexus - Supplies all parts of the heart (atria, ventricles, SA & AV nodes, AV bundle and Purkinje) - Affects either directly or indirectly through its neurotransmitters which are epinephrine and norepinephrine (AKA: adrenaline and noradrenaline) - Causes increase in permeability of cardiac cells to Na+ & Ca++ - Positive Chronotropic, positive Inotropic, positive Dromotropic Increasing permeability to Na+ -The resting membrane potential will not reach (-60mV) less negative (ex. - 55mV) due to Na+ influx (more positive charges enter these cells) -Faster depolarization we reach the threshold earlier, so that we have higher rate -Positive Chronotropic effect (increase in the rate) Increasing permeability to Ca++ -This will affect the contractile cells _especially the ventricles_ (Ca++ does not affect conductor cells) -Increasing in the force of contracting (due to Ca++ influx, so more Ca++ would be inside) more contractility -Positive Inotropic effect (increasing contractility) -Positive Dromotropic effect (faster rate (speed) of conduction of the impulse) Parasympathetic Extrinsic Innervation of the Heart - From Vagus nerves - Supplies only the SA & AV nodes and the atria (does not supply the ventricles) - Affects either directly or indirectly through its neurotransmitter which is acetylcholine - Causes increase in permeability of these cells to K+ and decrease of permeability to Na+ & Ca++ - Negative Chronotropic, negative Drpmotropic, NO Inotropic effect P a g e 5
6 Increasing permeability to K+ -The resting membrane potential will be more negative due to K+ outflux Decreasing permeability to Na+ -Slower depolarization longer time to reach the threshold, so that we have slower rate -Negative Chronotropic effect (decrease in the rate) Decreasing permeability to Ca++ -Has almost NO effect on contractility; because the ventricles are not supplied by parasympathetic Vagus nerve -Almost NO Inotropic effect To summarize: **sympathetic increase in rate, resting membrane potential is less negative **parasympathetic decrease in rate, resting membrane potential is more negative (hyperpolarization) **the maximum rate is not affected **the heart rate we measure is the ventricular rate NOT the atrial rate P a g e 6
7 If you stimulate the vagal nerves, the heart will stop for a while (not forever), and the patient falls down, after a while (15-30 sec) the heart pumps again but with a slower rate,which is Purkinje rate (15-40), this is called Ventricular escape. (Firstly, Purkinje was suppressed by Overdrive suppression from SAnode. However, the ventricles are not supplied by the vagus nerve,so when the vagus nerve is stimulated, the ventricles won t be affected,and thus escape from the parasympathetic effect.) Receptors functions and Signal Transduction - Transduction: conversion of one type of energy into another - Signal molecules (hormones) need specific receptors on their target cells (without receptors, hormones do not act and there will be NO response) - First messenger is the signal molecule which is the hormone. Second messenger is something inside the cell - Hormones act on the cell, specifically the cell membrane (which consists of phospholipid bilayer,and has a lot of proteins which work as receptors) Intercellular Communication - Hormones are secreted by glands or cells then they diffuse into the blood for circulation and bind to specific receptors on target cells elsewhere in the body - If the target cell (which has the receptors) is far from hormone-secreting cell Endocrine - When the receptors are on cells nearby (very close) to the hormone-secreting cells Paracrine - When the receptors are on the secreting cell itself Autocrine - When specialized neurons secrete chemicals (neurohormones) into the blood to a distant target cell Neuroendocrine P a g e 7
8 **Sometimes the signal molecule is gas (ex- nitric oxide); it will permeate to all cells around; passing through the membrane; because membranes are highly permeable to gases. **Cells that do not have receptors to a specific hormone cannot respond Hormones of the endocrine system usually affect the metabolism, growth and reproduction of the cell. On the other hand, neurohormones of the nervous system affect the contraction and relaxation of the muscle. To see the importance of the receptors. - A person with a (44 + XY) chromosome should be a male - When we come on a female -at age of years- with (44 + XY) chromosome, she looks like a lady from all aspects. Her parents thought that she is a girl from the start, they discover that there is abnormality after puberty because she does not have menstrual cycle (menstruation), by taking the genotype cells they discover the (44 + XY), this is called Testicular Feminizing syndrome. - Reason: genetic absence of testosterone receptor, so there will be NO action for testosterone. Therefore, there will be no development for male sexual characteristics and this leads to a female. (phenotype=female, genotype=male) The hormone can be substituted, but we can`t substitute the receptors P a g e 8
9 Classes of Hormones: 1) Peptide and protein hormones - They differ in the amino acid chain ( <100 amino acids peptide, >100 amino acids protein) - They are water soluble hormones 2) Steroid hormones - Derived from cholesterol - They are lipid soluble hormone - Examples: estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, cortisone and aldosterone 3) Amine hormones - Derived from amino acids - Could be lipid or water soluble - Two kinds: Thyroid hormones T3,T4 (tri-iodothyronine, tetra-iodothyronine, respectively.) and they are lipid soluble Catechol hormones (ex. Epinephrine and norepinephrine) and they are water soluble 4) Gas (ex. Nitric oxide NO) *** The difference between lipid soluble and water soluble hormones is in their receptors. Receptors for lipid soluble hormones are found inside the cell; either in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus. Whereas receptors for water soluble hormones are found on the target cell membrane. Good luck :) : P a g e 9
Conduction System of the Heart. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Conduction System of the Heart Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives l List the parts that comprise the conduction system l Explain the mechanism of slow response action potential (pacemaker potential)
Conduction System of the Heart Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives l List the parts that comprise the conduction system l Explain the mechanism of slow response action potential (pacemaker potential)
Conduction System of the Heart 4. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Conduction System of the Heart 4 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives List the parts that comprise the conduction system Explain the mechanism of slow response action potential (pacemaker potential)
Conduction System of the Heart 4 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives List the parts that comprise the conduction system Explain the mechanism of slow response action potential (pacemaker potential)
The conduction system
 The conduction system In today s lecture we will discuss the conducting system of the heart. If we placed the heart in a special solution that contains Ca+ it will keep on contracting, keep in mind that
The conduction system In today s lecture we will discuss the conducting system of the heart. If we placed the heart in a special solution that contains Ca+ it will keep on contracting, keep in mind that
Conduction system of the heart
 Conduction system of the heart -For skeletal muscle to contract, it has to be innervated by spinal nerves (there must be a neuromuscular junction). *The heart is innervated by autonomic nervous system
Conduction system of the heart -For skeletal muscle to contract, it has to be innervated by spinal nerves (there must be a neuromuscular junction). *The heart is innervated by autonomic nervous system
Rhythmical Excitation of the Heart
 Rhythmical Excitation of the Heart KALEB HOOD AND JIMMY JOHNSON Special Excitory and Conductive System of the Heart Sinus Node (or sinoatrial node or S-A): A small node with almost no contractile muscle,
Rhythmical Excitation of the Heart KALEB HOOD AND JIMMY JOHNSON Special Excitory and Conductive System of the Heart Sinus Node (or sinoatrial node or S-A): A small node with almost no contractile muscle,
Introduction. Circulation
 Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
Introduction Circulation 1- Systemic (general) circulation 2- Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood to all parts of the body carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs From Lt. ventricle aorta From
CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY. Amelyn U. Ramos-Rafael,M.D. Functional Anatomy of the Heart
 CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY Amelyn U. Ramos-Rafael,M.D. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1 Functional Anatomy of The Heart The Atria relatively thin walled The Ventricles ventricular walls thicker than atrial walls
CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGY Amelyn U. Ramos-Rafael,M.D. Functional Anatomy of the Heart 1 Functional Anatomy of The Heart The Atria relatively thin walled The Ventricles ventricular walls thicker than atrial walls
آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر. Faisal Muhammad
 16 آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions: 1. During phase 0: changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
16 آالء العجرمي أسامة الخضر Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions: 1. During phase 0: changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition
 TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
Where are the normal pacemaker and the backup pacemakers of the heart located?
 CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
CASE 9 A 68-year-old woman presents to the emergency center with shortness of breath, light-headedness, and chest pain described as being like an elephant sitting on her chest. She is diagnosed with a
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
االء العجرمي. Not corrected. Faisal Muhammad
 61 االء العجرمي Not corrected Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions : 1. During phase 0 : changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
61 االء العجرمي Not corrected Faisal Muhammad 1. Summary for what taken : *changes in permeability of ions : 1. During phase 0 : changes happen due to the influx of Na+, the permeability of Na ions increase
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY]](/thumbs/96/126998162.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 CARDIAC MYOCYTE PHYSIOLOGY [CARDIOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Describe the ionic basis of action potentials in cardiac contractile and autorhythmic cells Explain the relationship
During exercise the heart rate is 190 bpm and the stroke volume is 115 ml/beat. What is the cardiac output?
 The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
PART I. Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles
 PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Anatomy of the Heart (See lab handout for terms list) A. Describe the size, shape and location of the heart B. Describe the structure and function of the pericardium
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions
 Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
 V.O.D https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rum4xxhx32u How does the heart work? Learning Intentions I can explain the steps in the cardiac cycle including diastole and systole stages. I know the parts of the
V.O.D https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rum4xxhx32u How does the heart work? Learning Intentions I can explain the steps in the cardiac cycle including diastole and systole stages. I know the parts of the
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System
 Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Chp. 17 FUNCTIONAL ORG. Char.of the Endocrine System Glands that secrete chemical signals (hormones) into circulatory system Hormone characteristics Produced in small quantities Secreted into intercellular
Homeostasis. Endocrine System Nervous System
 Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Homeostasis Endocrine System Nervous System 2004-2005 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation
Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week
 Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week Semester: winter Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology Faculty of Medicine PJŠU Cardiovascular
Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week Semester: winter Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology Faculty of Medicine PJŠU Cardiovascular
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
Cardiac muscle is different from other types of muscle in that cardiac muscle
 6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Control of Heart Rate
 Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
Control of Heart Rate Control of Heart Rate The beating of your heart is an involuntary movement one that is beyond your direct control. The nerve impulse that causes the heart to beat originates within
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiac physiology. b. myocardium -- cardiac muscle and fibrous skeleton of heart
 I. Heart anatomy -- general gross. A. Size/orientation - base/apex B. Coverings D. Chambers 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral pericardium 3. Layers of heart wall a. epicardium Cardiac physiology b. myocardium
I. Heart anatomy -- general gross. A. Size/orientation - base/apex B. Coverings D. Chambers 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral pericardium 3. Layers of heart wall a. epicardium Cardiac physiology b. myocardium
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
The Electrocardiogram
 The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Nervous System 1. Draw a neuron, label 3 parts and give the function of those parts. Dendrite: carry signals to the cell body Cell
Cardiac Properties MCQ
 Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Properties MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 1- Cardiac Valves: a- Prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria during
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011
 Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
Dr David Begley Papworth Hospital, Cambridge HRUK Certificate of Accreditation Course: Core Heart Rhythm Congress 2011 The AV node is the soul of the heart, and whoever understands its anatomy and electrophysiology
Close to site of release (at synapse); binds to receptors in
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Chemical Messengers 1. Neural 2. Endocrine 3. Neuroendocrine 4. Paracrine 5. Autocrine Endocrine System --Endocrine and nervous systems work together --Endocrine vs. Nervous
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Neurons & Impulses
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Neurons & Impulses Organization of the Nervous System: Two Major Portions: The central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). CNS = Brain/Spinal Cord PNS = Nerves-provide
Collin County Community College. ! BIOL Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5. The Heart
 Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
By the name of Allah
 By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
By the name of Allah Receptors function and signal transduction ( Hormones and receptors Types) We were talking about receptors of the neurotransmitters; we have 2 types of receptors: 1- Ionotropic receptors
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Physiology - A. 1. Sympathetic reflexes are geared more for maintaining than for maintaining.
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Physiology - A 1. Sympathetic reflexes are geared more for maintaining than for maintaining. A. cardiac output; arterial pressure B. arterial pressure; cardiac output C. venous
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Physiology - A 1. Sympathetic reflexes are geared more for maintaining than for maintaining. A. cardiac output; arterial pressure B. arterial pressure; cardiac output C. venous
Omar Sami. Muhammad Abid. Muhammad khatatbeh
 10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
10 Omar Sami Muhammad Abid Muhammad khatatbeh Let s shock the world In this lecture we are going to cover topics said in previous lectures and then start with the nerve cells (neurons) and the synapses
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology I (Kristan) Problem set #5 p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology I (Kristan) Problem set #5 p. 1 1. Dantrolene has the same effect on smooth muscles as it has on skeletal muscle: it relaxes them by blocking the release of Ca ++ from the
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiology I (Kristan) Problem set #5 p. 1 1. Dantrolene has the same effect on smooth muscles as it has on skeletal muscle: it relaxes them by blocking the release of Ca ++ from the
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the
 Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography-
 *questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
*questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling The Neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are composed of a cell body, which contains the nucleus and organelles; Dendrites which are extensions
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
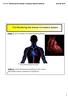 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
Investigation of human cardiovascular physiology is very interesting, but many
 6 E X E R C I S E Frog Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To list the properties of cardiac muscle as automaticity and rhythmicity, and to define each. 2. To explain the statement, Cardiac
6 E X E R C I S E Frog Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To list the properties of cardiac muscle as automaticity and rhythmicity, and to define each. 2. To explain the statement, Cardiac
Branches of the Nervous System
 The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
The Nervous System Branches of the Nervous System There are 2 main branches of the nervous system Central Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System All nerves leading to rest of body Anatomy
Axon Nerve impulse. Axoplasm Receptor. Axomembrane Stimuli. Schwann cell Effector. Myelin Cell body
 Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
Nervous System Review 1. Explain a reflex arc. 2. Know the structure, function and location of a sensory neuron, interneuron, and motor neuron 3. What is (a) Neuron Axon Nerve impulse Axoplasm Receptor
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
The Nervous System. Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output
 The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
The Nervous System Nervous System Functions 1. gather sensory input 2. integration- process and interpret sensory input 3. cause motor output The Nervous System 2 Parts of the Nervous System 1. central
Lab 2. The Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System. 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1
 Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Exam 3. Short Answer/Terminology (1 pt each except where noted, 35 pts total) Version B. Zoology 250, Fall 2003
 Exam 3 Version B Zoology 250, Fall 2003 5 pages, 50 points total please check to see that your copy is complete. Please SIGN your name here if you would like me to post your grade by the last five digits
Exam 3 Version B Zoology 250, Fall 2003 5 pages, 50 points total please check to see that your copy is complete. Please SIGN your name here if you would like me to post your grade by the last five digits
Mohammad Tarek. Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat. Faisal Mohammad
 15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
15 Mohammad Tarek Wahab Al-tekreeti Tamer Barakat Faisal Mohammad Things to remember Types of synapse: Neuron types and neurotransmitters When it happens between an axon and dendrites it is called axodendritic
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems
 SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems Part I: Multiple Choice 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and starting transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching
SBI4U PRACTICE QUIZ Endocrine and Nervous Systems Part I: Multiple Choice 1. Steroid hormones operate by: A. crossing the cell membrane and starting transcription for the appropriate protein B. attaching
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Marah karablieh. Osama khader. Muhammad khatatbeh. 0 P a g e
 15 Marah karablieh Osama khader 0 P a g e Muhammad khatatbeh Cardiac Muscle Physiology Introduction The heart has two ventricles and two atriums. The heart wall is composed primarily of spirally arranged
15 Marah karablieh Osama khader 0 P a g e Muhammad khatatbeh Cardiac Muscle Physiology Introduction The heart has two ventricles and two atriums. The heart wall is composed primarily of spirally arranged
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System
 Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Practice Exercises for the Cardiovascular System On the diagram below, color the oxygen-rich blood red and the oxygen-poor blood blue. Label the parts: Continued on the next page... Label the parts on
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Nervous System. 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands. 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data
 Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
Nervous System 1. Relays messages, processes info, analyzes data 2. Receives information from the environment from CNS to organs and glands 3. Transmits impulses from CNS to muscles and glands 4. Transmits
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
The Nervous System AP Biology
 The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
The Nervous System 2005-2006 Neuron (nerve cell) signal direction dendrites cell body Structure fits function, it have many entry points for signal one path out transmits signal Nodes of Ranvier axon signal
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction L1- L2 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 Introduction to Physiology (0501110) Spring 2013 Subject Receptors: types and adaptation - Membrane
Cell communication. S Cellbiosystems Olli-Pekka Koistinen
 Cell communication S-114.2500 Cellbiosystems Olli-Pekka Koistinen 28.11.2007 Cell communication Cellbiosystems? What does it mean? Large groups of cells interacting with each other? Complex cell communication
Cell communication S-114.2500 Cellbiosystems Olli-Pekka Koistinen 28.11.2007 Cell communication Cellbiosystems? What does it mean? Large groups of cells interacting with each other? Complex cell communication
Omar Ismail. Dana Almanzalji. Faisal Mohammad
 11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
11 Omar Ismail Dana Almanzalji Faisal Mohammad Neuronal classification: Neurons are responsible for transmitting the action potential to the brain. The speed at which the action potential is transmitted
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9)
 NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
NOTES: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (CH 9) Endocrine System *The endocrine system consists of a range of glands and tissues throughout the body Functions of the Endocrine System: 1) Maintain balance within body (homeostasis)
PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE. Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y
 PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE Value: 50 marks Suggested Time: 75 minutes Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y 1. Name structures X and Y and explain how each functions in protein synthesis. (4
PART B: WRITTEN RESPONSE Value: 50 marks Suggested Time: 75 minutes Use the following diagram to answer question 1. X Y 1. Name structures X and Y and explain how each functions in protein synthesis. (4
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45. Intercellular communication. Paracrine and Autocrine Signaling. Signaling by local regulators 11/26/2017
 Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Hormones and the Endocrine System Chapter 45 Intercellular communication Endocrine signaling Local regulators Paracrine and autocrine signaling Neuron signaling Synaptic and neuroendocrine signaling Paracrine
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue I. Functions of the Nervous System A. List and describe the five major nervous system functions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. II. Divisions of the Nervous System
Neural Tissue. Chapter 12 Part B
 Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
Neural Tissue Chapter 12 Part B CNS Tumors - Neurons stop dividing at age 4 but glial cells retain the capacity to divide. - Primary CNS tumors in adults- division of abnormal neuroglia rather than from
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Muscles general information. Smooth Muscle - introduction. Smooth muscles - introduction
 Slide 1 Muscles general information Vertebrates and many invertebrates have three main classes of muscle Skeletal muscle Smooth muscles surround internal organs such as the large and small intestines,
Slide 1 Muscles general information Vertebrates and many invertebrates have three main classes of muscle Skeletal muscle Smooth muscles surround internal organs such as the large and small intestines,
Laith Abu Shekha. Omar Sami. Ebaa Alzayadneh
 24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
24 Laith Abu Shekha Omar Sami Ebaa Alzayadneh Signal Transduction Please note that it s very important to refer to the slides. Introduction: Through these five lectures, we should know the basics of signal
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
NEURONS Chapter Neurons: specialized cells of the nervous system 2. Nerves: bundles of neuron axons 3. Nervous systems
 NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
NEURONS Chapter 12 Figure 12.1 Neuronal and hormonal signaling both convey information over long distances 1. Nervous system A. nervous tissue B. conducts electrical impulses C. rapid communication 2.
Electrical and Mechanical Properties of the Frog Heart. Carmen Lee. Nina Cung, Yuen Ki Ip, Lauren Nolen. Section 6 Phung Thai
 Electrical and Mechanical Properties of the Frog Heart Carmen Lee Nina Cung, Yuen Ki Ip, Lauren Nolen Section 6 Phung Thai May 16, 2012 Introduction: The heart is one of three components that make up the
Electrical and Mechanical Properties of the Frog Heart Carmen Lee Nina Cung, Yuen Ki Ip, Lauren Nolen Section 6 Phung Thai May 16, 2012 Introduction: The heart is one of three components that make up the
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination
 Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Biology 12 August 2003 Provincial Examination ANSWER KEY / SCORING GUIDE CURRICULUM: Organizers 1. Cell Biology 2. Cell Processes and Applications 3. Human Biology Sub-Organizers A, B, C, D E, F, G, H
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Cardiac Muscle Physiology. Physiology Sheet # 8
 15 8 1 We have three types of muscles in our body: 1. Skeletal muscles. 2. Cardiac muscle. 3. Smooth muscles. The cardiovascular system consists of : Heart, cardiac vessels. The wall of the Heart has three
15 8 1 We have three types of muscles in our body: 1. Skeletal muscles. 2. Cardiac muscle. 3. Smooth muscles. The cardiovascular system consists of : Heart, cardiac vessels. The wall of the Heart has three
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Neurogenic and Myogenic hearts
 Neurogenic and Myogenic hearts In animals with open circulatory system the heart is usually sac-like or tubular. It has ostia or lateral openings which get closed when heart contracts and opens when heart
Neurogenic and Myogenic hearts In animals with open circulatory system the heart is usually sac-like or tubular. It has ostia or lateral openings which get closed when heart contracts and opens when heart
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Homeostasis Strand
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Homeostasis Strand Introduction In general, a nervous system has three overlapping functions : 1. Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors to integration centres 2.
