Cardiorespiratory changes in progressive
|
|
|
- Rosa Houston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Heart Journal, 197I, 33, Cardiorespiratory changes in progressive muscular dystrophy P. L. Wahi, K. C. Bhargava, and S. Mohindra From the Department of Medicine, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India Incipient cardiac failure was detected in 56 per cent of cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy, 50per cent oflimb girdle type ofmyopathies, and 2 ofthe 3 cases with 'unclassifled' variety. 'Myopathic pattern' in the electrocardiogram was seen in 82 per cent of the cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy who showed abnormal haemodynamics. This suggests that this pattern is due to myocardial damage. Thus the electrocardiogram can be used as a simple and safe procedure for the detection of dystrophic heart disease. Though 'myopathic pattern' is seen only in pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy the haemodynamic evidence of dystrophic heart disease is seen in other myopathies as well. Pulmonary ventilatory function tests revealed restrictive changes in 57 per cent of cases of myopathy when muscles of the chest wall were involved. This abnormality in pulmonary function tests had no apparent haemodynamic effect. Cardiopulmonary complications are well known in muscular dystrophy (Globus, I923; Nothacker and Netsky, I950; Hurwitz, I936). They occur in the form of cardiac arrhythmias, congestive cardiac failure, electrocardiographic changes, pulmonary infections, and pulmonary insufficiency (Rubin and Buchberg, I952; Weisenfeld and Messinger, I952; Manning and Cropp, 1958; Gilroy et al., I963; Arce-Gomez et al., 1964). A specific 'myopathic pattern' in the electrocardiogram in cases with pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy has been described by us. This pattern consists of sinus tachycardia, short PR interval, R/S in Vi more than I5, high amplitude R wave and deep Q wave in V4-6 and other left praecordial leads, and prolonged QTc (Fig. I). It was suggested that these electrocardiographic changes were probably due to myocardial damage (Wahi, I96I, I963). Detailed pulmonary and haemodynamic studies in progressive muscular dystrophy are few (Gailani, Danowaki, and Fisher, I958; Storstein, 1964; Perloff, de Leon, and O'Doherty I966; Perloff et ar ; Gilroy et al., 1963; Wahi et al., I968; Arce-Gomez et al., I964). The incidence of pulmonary infections, mostly pneumonias, is high in advanced cases of myopathy. Ventilatory function studies in these cases have shown Received 3 June restrictive changes with limitation of all lung volumes. In our total experience of I8o cases of myopathy we have encountered bronchiectasis in two cases, bronchopneumonia in one, and congestive cardiac failure in two cases. Pulmonary insufficiency and cardiac failure do not manifest early owing to restricted physical activity because of disability. Pulmonary function tests and cardiac catheterization can be useful means of detecting early changes and latent heart failure. Material and methods The present study is of 41 cases of progressive muscular dystrophy. Out of a large series of i8o cases of myopathy 32 were studied haemodynamically in the Nehru Hospital of the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, and 9 were studied for us by Professor S. B. Roy at All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, before our own laboratories were set up. There were 30 cases with pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy (sex-linked, Duchenne type), 8 cases of limb girdle myopathy, and another 3 cases were atypical and were grouped as 'unclassified'. Muscle biopsy was done in all cases where the clinical picture was even slightly atypical (14 cases). After detailed clinical examination a radiograph of the chest for heart size and lung fields was done at a standard distance. A i2-lead electrocardiogram was taken in all these cases.
2 534 Wahi, Bhargava, and Mohindra FIG. I Showing typical myopathic pattern in electrocardiogram - RIS in Vi, IN5, and deep Q waves in lead I, avl, and V4-6. Ventilatory pulmonary functions were studied in 29 cases. These included tidal volume, minute ventilation, vital capacity, maximum breathing capacity, and forced expiratory volume. In 8 cases functional residual capacity and total lung capacity were also done. All the ventilatory pulmonary functions were done in basal condition, and a repeat study was done where co-operation was inadequate. The pulmonary functions were done by Goddard Pulmotest except functional residual capacity, which was done by open circuit nitrogen wash-out method. Standard right heart catheterization was done in all these cases. Pressures were recorded at rest, and in suitable cases records were taken after exercise or right hypochondriac compression, or both, to bring out findings of incipient right heart failure. Cardiac output was calculated by the Fick principle. Findings The clinical examination found associated atrial septal defect in one patient and another had mild hypertension. None of these patients u * showed frank congestive cardiac failure or any physical signs in the chest. Radiography showed cardiac enlargement in 4 cases. There was no pulmonary pathology. Twenty out of 30 patients (66%) with pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy showed a 'myopathic pattern' in the electrocardiogram (Wahi, I963). Haemodynamic studies Twenty-seven patients had normal values for resting pressures. Twelve had abnormal right ventricular end-diastolic pressure and in another two cases the pressures were on higher limits of normal (6 mm.) (Fig. 2). Leg-raising exercise for three minutes could be given in 6 patients, and only one of these showed distinct elevation of right ventricular end-diastolic pressure (Fig. 3). Right hypochondriac compression was applied in 32 patients. Eleven patients with normal or borderline resting pressure showed elevation of right ventricular enddiastolic pressure after right hypochondriac compression (Fig. 4). Generally the patients having abnormal right ventricular enddiastolic pressure at rest also had abnormal mean right atrial pressure. Right atrial mean pressure showed an increase corresponding to changes in right ventricular end-diastolic pressure after right hypochondriac compres- "'VIV 25 t,- restinrst 25/8 20i I ~5,\. 4/ >/g djv II ff -L.li r FIG. 2 Showing abnormal right ventricular end-diastolic pressure at rest. FIG. 3 Showing normal right ventricular end-diastolic pressure at rest and its abnormal increase after 2 min exercise. MMHq 20~ 15 ofter 1 min exerctse after 2min. exercise _tt 0W5, 9," ORV resting 12/3
3 Cardiorespiratory changes in progressive muscular dystrophy L-1, ajla-lau.a.a IL. I w-mw.iww resting RT hypochondriac pressure pressure released t FIG. 4 Showing normal right ventricular pressures at rest and abnormal increase of right ventricular end-diastolic pressure after right hypochondriac compression and return to normal after release of pressure. sion except in two cases (Fig. 5). In total, 23 out of 4I patients (56%) showed abnormal haemodynamic findings suggestive of cardiac failure. This was noticed in I7 out of 30 cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy (56%), 4 out of 8 cases of limb girdle myopathy (50%), while 2 out of 3 cases of unclassified variety had abnormal haemodynamics. Pulmonary artery pressure was normal in all, and there was no systolic gradient across the pulmonary valve. Pulmonary capillary pressure was found to be normal in all except one case with mild hypertension. Cardiac output was measured in 36 cases. It varied from l./min. Cardiac index was normal in 28 cases (3-5 1./minim2), 2 cases showed a rise (5 5, /min/m2), and 5 showed decreased values (less than /min/m2). Considerable irritability of the myocardium was noticed in the form of arrhythmias during catheterization as compared to the other patients studied in the same laboratory during the same period. One patient with a high right FI G. 5 Showing normal resting mean right atrial pressure, its increase after right hypochondriac compression, and return to normal after release of pressure. RA restinq RT hypochondriac pressure pressure released mm.hq (2-5) (95) (20) 0] _ ventricular end-diastolic and mean right atrial pressure developed ventricular tachycardia during catheterization but was successfully revived. Pulmonary function studies The details of the ventilatory pulmonary function tests are described in different groups separately (TablesI, 2, 3). Vital capacity and maximum breathing capacity were reduced in two-thirds TABLE I dystrophy Pseudohypertrophic muscular Case Vital % of predicted Maximum % of predicted FEVy 2 o I I * go I i*I I o I II8-8 I I I I5 I * o-8io I I8* i*o I9* I * o i-o8o IOO I ioo 89 * Co-operation was not adequate. TABLE 2 Limb girdle type Case Vital % of predicted Maximum % of predicted FEVy I II I22-78 I o I I IOI TABLE 3 Unclassified variety Case Vital % of predicted Maximum % of predicted FEV, I I I
4 536 Wahi, Bhargava, and Mohindra of the cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy. Similar changes were seen in 44.4 per cent of limb girdle type of myopathy, but the cases with 'unclassified' variety of myopathy had normal values. Timed vital capacity (FEV1) did not suggest any obstructive airway disease. Functional residual capacity and total lung capacity were done in 8 cases and were found to be normal in 4 cases which showed other function to be normal. Four cases had reduced values, and they also showed restrictive airway disease as judged from vital capacity and maximum breathing capacity. Discussion Fifty-six per cent of cases of myopathy studied by us showed raised right ventricular enddiastolic or mean right atrial pressure, or both, at rest or when challenged with exercise or right hypochrondriac compression, though none of them had shown clinical evidence of right heart failure. A rise of right ventricular end-diastolic pressure or mean right atrial pressure, or both, after abdominal compression may reflect reduced distensibility of the right ventricle and its inability to handle augmented volume overloading. Out of I7 cases of Duchenne type of muscular dystrophy who showed abnormal haemodynamics, I4 (82%) showed typical 'myopathic pattern' in the electrocardiogram. This supports our contention that this pattern is an evidence of dystrophic heart disease and not a conduction defect. Similar studies by Perloff et al. (I966) also support this hypothesis. However, 'myopathic pattern' was seen in 20 cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy, while haemodynamic abnormalities were seen in I7 only. Besides, some patients with abnormal haemodynamics did not show the characteristic electrocardiographic changes. It is possible that the electrocardiographic pattern is suggestive of predominantly localized dystrophic changes in the myocardium in the region of the posterolateral wall of the left ventricle which may occur earlier than the disturbed haemodynamics. The cases with more diffuse damage may not show characteristic electrocardiographic changes but depict abnormal haemodynamics. Such a view is supported by the observation of Perloff et al. (i966, i967). Our study suggests that, though 'myopathic pattern' in the electrocardiogram was limited to the cases of pseudohypertrophic muscular dystrophy, abnormal haemodynamics and thus the 'dystrophic heart disease' is equally common in limb girdle and unclassified varieties. The ventilatory pulmonary function tests showed that 57 per cent of cases had changes suggestive of restrictive airway disease, which were present in Duchenne and limb girdle type of myopathies. These changes were not seen in the unclassified variety because of the predominantly distal muscular involvement. The ventilatory function abnormality is due to inadequate expansion of lungs because of weakness of the respiratory muscles. In spite of these restrictive changes there were no symptoms of respiratory insufficiency, most probably because of limited physical activity due to generalized muscular weakness. None of the cases showed any evidence of obstructive airway disease. The changes in the pulmonary functions had no apparent haemodynamic effect, as pulmonary artery pressure and peripheral oxygen saturation were normal in all these cases. We are grateful to Professor J. N. Berry and his team for doing some of the haemodynamic studies. References Arce-Gomez, E., Palma-Garcia, S., Yanez, J. L., Lopez-Portillo, M., Lombardo, L., Brandt, H., and Marquez, M. H. (1964). Study of cardiorespiratory function in patients with progressive muscular dystrophy. Angiology, 15, 407. Gailani, S., Danowaki, T. S., and Fisher, D. S. (I958). Muscular dystrophy. Catheterization studies indicating latent congestive heart failure. Circulation, 17, 583. Gilroy, J., Cahalan, J. L., Berman, R., and Newman, M. (I963). Cardiac and pulmonary complications in Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy. Circulation, 27, 484. Globus, J. H. (I923). The pathologic findings in the heart muscle in progressive muscular dystrophy. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry, 9, 59. Hurwitz, S. (1936). Primary myopathies, report of 36 cases and review of the literature. Archives of Neurology and Psychiatry, 36, Manning, G. W., and Cropp, G. J. (I958). The electrocardiogram in progressive muscular dystrophy. British Heart Journal, 20, 416. Nothacker, W. G., and Netsky, M. G. (1950). Myocardial lesions in progressive muscular dystrophy. Archives of Pathology, 50, 578. Perloff, J. K., de Leon, A. C., and O'Doherty, D. (1966). The cardiomyopathy of progressive muscular dystrophy. Circulation, 33, 625. Perloff, J. K., Roberts, W. C., de Leon, A. C., and O'Doherty, D. (I967). The distinctive ECG of Duchenne's progressive muscular dystrophy (an ECG-pathologic correlative study). American Jrournal of Medicine, 42, I79. Rubin, I. L., and Buchberg, A. S. (I952). The heart in progressive muscular dystrophy. American Heart Journal, 43, i6i. Storstein, 0. (x964). The heart in progressive muscular dystrophy. Experimental Medicine and Surgery, 22, I3.
5 Cardiorespiratory changes in progressive muscular dystrophy 537 Wahi, P. L. (I96I). Electrocardiographic changes in progressive muscular dystrophy. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 9, 662. Wahi, P. L. (I963). Cardiac changes in myopathy. American Heart Journal, 66, 748. Wahi, P. L., Manchanda, S. S., Thind, M. S., and Akhtar, M. (I968). Cardiopathy in muscular dystrophy. Diseases of the Chest, 53, 79. Weisenfeld, S., and Messinger, W. J. (I952). Cardiac involvement in progressive muscular dystrophy. American Heart3journal, 43, I70. Br Heart J: first published as /hrt on 1 July Downloaded from on 13 July 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Electrocardiographic Studies in the Patients of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
 Abstract Electrocardiographic Studies in the Patients of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Pages with reference to book, From 117 To 121 Naeema Ansari, P.Q.R. Siddiqui ( Department of Physiology, University
Abstract Electrocardiographic Studies in the Patients of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Pages with reference to book, From 117 To 121 Naeema Ansari, P.Q.R. Siddiqui ( Department of Physiology, University
Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris
 British Heart Journal, I974, 36, I0-I09I Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris From the Department of Clinical Physiology, Malmo General Hospital, S-214 OI Malmo, Sweden. Central pressures
British Heart Journal, I974, 36, I0-I09I Central haemodynamics during spontaneous angina pectoris From the Department of Clinical Physiology, Malmo General Hospital, S-214 OI Malmo, Sweden. Central pressures
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY. Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR
 -SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0099111 -Session-1989-90 -Superclass- PB -Title- PRINCIPLES
-SQA-SCOTTISH QUALIFICATIONS AUTHORITY Hanover House 24 Douglas Street GLASGOW G2 7NQ NATIONAL CERTIFICATE MODULE DESCRIPTOR -Module Number- 0099111 -Session-1989-90 -Superclass- PB -Title- PRINCIPLES
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM AND RESPONSES TO EXERCISE Mr. S. Kelly PSK 4U North Grenville DHS THE HEART: A REVIEW Cardiac muscle = myocardium Heart divided into two sides, 4 chambers (L & R) RS: pulmonary
Lecture Notes. Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure
 Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Exercise Testing Interpretation in the Congenital Heart.
 Interpretation in the Congenital Heart. Stephen M. Paridon, MD Medical Director, Exercise Physiology Laboratory The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Professor of Pediatrics The University of Pennsylvania
Interpretation in the Congenital Heart. Stephen M. Paridon, MD Medical Director, Exercise Physiology Laboratory The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Professor of Pediatrics The University of Pennsylvania
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE
 Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Brit. Heart J., 1963, 25, 583. RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY AND THE SMALL PULMONARY ARTERIES IN CHRONIC LUNG DISEASE BY W. R. L. JAMES AND A. J. THOMAS From Llandough Hospital (United Cardiff Hospitals)
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
STUDY OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN RESPIRATORY DISORDERS
 STUDY OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN RESPIRATORY DISORDERS *Hegde R.R., Bharambe R.S., Phadtare J.M. and Ramraje N.N. Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Grant Government Medical College, Mumbai-8
STUDY OF PULMONARY ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION IN RESPIRATORY DISORDERS *Hegde R.R., Bharambe R.S., Phadtare J.M. and Ramraje N.N. Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Grant Government Medical College, Mumbai-8
Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease
 British Heart Journal, I975, 37, 74-78. Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease Natural history and results of surgery C. Ward and B. W. Hancock From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Northern
British Heart Journal, I975, 37, 74-78. Extreme pulmonary hypertension caused by mitral valve disease Natural history and results of surgery C. Ward and B. W. Hancock From the Cardio-Thoracic Unit, Northern
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments. Medical Provider:
 Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
Cardiac Output MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
PERICARDIAL DIAESE. Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University
 PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
PERICARDIAL DIAESE Kaijun Cui Associated professor Sichuan University CLASSIFICATION acute pericarditis pericardial effusion cardiac tamponade constrictive pericarditis congenitally absent pericardium
Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle
 British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
British Heart Journal, 1978, 40, 1040-1045 Anomalous muscle bundle of the right ventricle Its recognition and surgical treatment M. D. LI, J. C. COLES, AND A. C. McDONALD From the Department of Paediatrics,
cardiograms is arbitrary to some degree unless the changes are large. Quantitative information about intraindividual
 British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 66o-664. Repeat variation of electrocardiogram, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol within one hour and six months' Ernst Simonson and Ancel Keys From Laboratory of Physiological
British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 66o-664. Repeat variation of electrocardiogram, blood pressure, and blood cholesterol within one hour and six months' Ernst Simonson and Ancel Keys From Laboratory of Physiological
Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial
 British Heart Journal, I972, 34, I176-iI80. Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial infarction T. G. Feest,' G. C. Sutton,2 R. J. Vecht, and R. V. Gibson
British Heart Journal, I972, 34, I176-iI80. Signs of pericardial constriction in rupture of ventricular septum complicating myocardial infarction T. G. Feest,' G. C. Sutton,2 R. J. Vecht, and R. V. Gibson
Pulmonary blood flow and left ventricular volumes
 British Heart Journal, I973, 35, 52I-526. Pulmonary blood flow and left ventricular volumes in transposition of the great arteries and intact ventricular septum' John F. Keane, R. Curtis llison, Michael
British Heart Journal, I973, 35, 52I-526. Pulmonary blood flow and left ventricular volumes in transposition of the great arteries and intact ventricular septum' John F. Keane, R. Curtis llison, Michael
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings
 Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Other 12-Lead ECG Findings Left Atrial Enlargement Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom
Pulmonary artery and left heart end-diastolic pressure relations'
 British Heart journal, I970, 32, 774-778. Pulmonary artery and left heart end-diastolic pressure relations' Walter H. Herbert From Cardiopulmonary Laboratory, Grasslands Hospital, Valhalla, New York, U.S.A.
British Heart journal, I970, 32, 774-778. Pulmonary artery and left heart end-diastolic pressure relations' Walter H. Herbert From Cardiopulmonary Laboratory, Grasslands Hospital, Valhalla, New York, U.S.A.
Reversible electrocardiographic changes in severe
 Thorax, 1977, 32, 328-332 Reversible electrocardiographic changes in severe acute asthma DAVD SEGLER From Bromnpton Hospital, London Siegler, D. (1977). Thorax, 32, 328-332. Reversible electrocardiographic
Thorax, 1977, 32, 328-332 Reversible electrocardiographic changes in severe acute asthma DAVD SEGLER From Bromnpton Hospital, London Siegler, D. (1977). Thorax, 32, 328-332. Reversible electrocardiographic
Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion
 British Heart journal, 974, 36, 155-59. Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion Michael Tynan, D. Behrendt, W. Urquhart, and G.
British Heart journal, 974, 36, 155-59. Portal vein catheterization and selective angiography in diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connexion Michael Tynan, D. Behrendt, W. Urquhart, and G.
Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in
 Br Heart J 1981; 45: 522-26 Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in emphysema with poor R wave progression in anterior chest leads GRAHAM J HART, PETER A BARRETT, PETER F BARNABY, ELIZABETH
Br Heart J 1981; 45: 522-26 Diagnosis of old anterior myocardial infarction in emphysema with poor R wave progression in anterior chest leads GRAHAM J HART, PETER A BARRETT, PETER F BARNABY, ELIZABETH
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG. Jakub Dorożyński
 Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Aorticopulmonary septal defect
 British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 630-635. Aorticopulmonary septal defect An experience with I7 patients Leonard C. Blieden' and James H. Moller From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota,
British HeartJournal, I974, 36, 630-635. Aorticopulmonary septal defect An experience with I7 patients Leonard C. Blieden' and James H. Moller From the Department of Pediatrics, University of Minnesota,
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT
 THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT BY KNUD H. OLESEN Fi om the Medical Department B, Rigshospitalet, (Chief: Professor Erik Warburg) University of Copenhagen,
THE NATURAL HISTORY OF 271 PATIENTS WITH MITRAL STENOSIS UNDER MEDICAL TREATMENT BY KNUD H. OLESEN Fi om the Medical Department B, Rigshospitalet, (Chief: Professor Erik Warburg) University of Copenhagen,
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Myocardial lactate metabolism during isometric hand grip test
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, 79-84. Myocardial lactate metabolism during isometric hand grip test Comparison with pacing tachycardia F. Khan Nakhjavan, Gangaiah Natarajan, Allan M. Smith, Michael Dratch,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, 79-84. Myocardial lactate metabolism during isometric hand grip test Comparison with pacing tachycardia F. Khan Nakhjavan, Gangaiah Natarajan, Allan M. Smith, Michael Dratch,
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO
 OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Subject Index ACE inhibitors, see Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Aging
OOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOOO Subject Index ACE inhibitors, see Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Aging
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases. Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis Kazuaki SERA, M.D. Pulmonary function studies have been undertaken on the pulmonary fibrosis as diagnosed
Ventilatory Mechanics in Patients with Cardio-Pulmonary Diseases Part III. On Pulmonary Fibrosis Kazuaki SERA, M.D. Pulmonary function studies have been undertaken on the pulmonary fibrosis as diagnosed
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE
 A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE BY PAUL WOOD AND A. SELZER t (From the National Hospital.for Diseases of the Heart and the British Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith, London) The prominent
A NEW SIGN OF LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE BY PAUL WOOD AND A. SELZER t (From the National Hospital.for Diseases of the Heart and the British Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith, London) The prominent
Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity'
 British Heart journal, I972, 34, 34I-346. Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity' Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University
British Heart journal, I972, 34, 34I-346. Aberrant atrial conduction Unrecognized electrocardiographic entity' Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency
 Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Application of ICG in Intensive Care and Emergency Aim of haemodynamic monitoring in ICU and ED Detection and therapy of insufficient organ perfusion Answers to common cardiovascular
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
The Cardiomyopathy of Progressive Muscular Dystrophy
 The Cardiomyopathy of Progressive Muscular Dystrophy By JOSEPH K. PERLOFF, M.D., ANTONIO C. DE LEON, JR., M.D., AND DESMOND O'DOHERTY, M.D. Downloaded from http://circ.ahajournals.org/ by guest on July,
The Cardiomyopathy of Progressive Muscular Dystrophy By JOSEPH K. PERLOFF, M.D., ANTONIO C. DE LEON, JR., M.D., AND DESMOND O'DOHERTY, M.D. Downloaded from http://circ.ahajournals.org/ by guest on July,
Abstract Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog
 Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Myocardial Infarction. Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline )
 Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Myocardial Infarction Reading Assignment (p66-78 in Outline ) Objectives 1. Why do ST segments go up or down in ischemia? 2. STEMI locations and culprit vessels 3. Why 15-lead ECGs? 4. What s up with avr?
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Coronary arteriographic study of mild angina
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, 752-756. Coronary arteriographic study of mild angina W. Walsh, A. F. Rickards, R. Balcon From the National Heart Chest Hospitals, London Chest Hospital, London The results
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, 752-756. Coronary arteriographic study of mild angina W. Walsh, A. F. Rickards, R. Balcon From the National Heart Chest Hospitals, London Chest Hospital, London The results
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary
 British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
British HeartJournal, I975, 37, ii84-ii90. Pulmonary valve echo motion in pulmonary regurgitation' Arthur E. Weyman, James C. Dillon, Harvey Feigenbaum, and Sonia Chang From the Department of Medicine,
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090)
 Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD
Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Cardiac Catheterization (L29090) Contractor Information Contractor Name First Coast Service Options, Inc. Contractor Number 09102 Contractor Type MAC - Part B LCD
a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical pulse Apical-radial pulse a complete absence of respirations Apnea
 Afebrile absence of a fever Apical pulse a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical-radial pulse measurement of the apical beat and the radial pulse at the same time Apnea a complete absence
Afebrile absence of a fever Apical pulse a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical-radial pulse measurement of the apical beat and the radial pulse at the same time Apnea a complete absence
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right ventricular sinusoids
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 1990 Doppler-echocardiographic findings in a patient with persisting right
Syncope Due to Intracavitary Left Ventricular Obstruction Secondary to Giant Esophageal Hiatus Hernia
 American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
American Journal of Medical Case Reports, 2017, Vol. 5, No. 4, 89-93 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajmcr/5/4/4 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajmcr-5-4-4 Syncope Due to Intracavitary
Vectorcardiogram of Combined Ventricular Hypertrophy: Posterior Counterclockwise Loop
 Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 457. Vectorcardiogram of Combined Ventricular Hypertrophy: Posterior Loop (Frank System) PHILIP VARRIALE, RICHARD J. KENNEDY, AND JOSEPH C. ALFENITO From the Department of Medicine,
Brit. Heart J., 1969, 31, 457. Vectorcardiogram of Combined Ventricular Hypertrophy: Posterior Loop (Frank System) PHILIP VARRIALE, RICHARD J. KENNEDY, AND JOSEPH C. ALFENITO From the Department of Medicine,
Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person. Describe the major functions of the bronchial circulation
 OBJECTIVES Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person Define zones I, II, and III in the lung, with respect to pulmonary vascular pressure and alveolar pressure Describe
OBJECTIVES Describe regional differences in pulmonary blood flow in an upright person Define zones I, II, and III in the lung, with respect to pulmonary vascular pressure and alveolar pressure Describe
ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I
 Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
Electrocardiography Series Singapore Med J 2011; 52(12) 855 CME Article ECGs of structural heart disease: Part I Poh K K, Teo S G, Tay E L W, Yip J WL Cardiac Department, National University Heart Centre,
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
Mitral valve replacement
 Mitral valve replacement Long-term results, with particular reference to changes in pulmonary vascular resistance Thorax (1968), 23, 1. J. HAMER, T. BOULTON, J. FLEMING, G. W. HAYWARD, I. M. HILL, I. MONRO,
Mitral valve replacement Long-term results, with particular reference to changes in pulmonary vascular resistance Thorax (1968), 23, 1. J. HAMER, T. BOULTON, J. FLEMING, G. W. HAYWARD, I. M. HILL, I. MONRO,
What s New in IV Conduction? (Quadrafascicular, not Trifascicular)
 What s New in IV Conduction? (Quadrafascicular, not Trifascicular) Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor, University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services (Urban Central Region) http://ecg.utah.edu
What s New in IV Conduction? (Quadrafascicular, not Trifascicular) Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor, University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services (Urban Central Region) http://ecg.utah.edu
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
 Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Competency Title: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Trainee Name: ------------------------------------------------------------- Title: ---------------------------------------------------------------
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
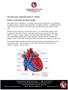 Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL
 Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
Lancashire & South Cumbria Cardiac Network ECG INTERPRETATION MANUAL THE NORMAL ECG Lancashire And South Cumbria Cardiac Physiologist Training Manual THE NORMAL ECG E.C.G CHECKLIST 1) Name, Paper Speed,
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Capnography Connections Guide
 Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Haemodynamic factors influencing opening snap interval in mltral stenosis
 British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 350-354. Haemodynamic factors influencing opening snap interval in mltral stenosis Roland Ebringer, Aubrey Pitt, and S. T. Anderson From Cardiovascular Diagnostic Service,
British Heart Journal, I970, 32, 350-354. Haemodynamic factors influencing opening snap interval in mltral stenosis Roland Ebringer, Aubrey Pitt, and S. T. Anderson From Cardiovascular Diagnostic Service,
CARDIAC OUTPUT,VENOUS RETURN AND THEIR REGULATION. DR.HAROON RASHID. OBJECTIVES
 CARDIAC OUTPUT,VENOUS RETURN AND THEIR REGULATION. DR.HAROON RASHID. OBJECTIVES Define Stroke volume, Cardiac output Venous return,& identity their normal values. Describe control (intrinsic & extrinsic)
CARDIAC OUTPUT,VENOUS RETURN AND THEIR REGULATION. DR.HAROON RASHID. OBJECTIVES Define Stroke volume, Cardiac output Venous return,& identity their normal values. Describe control (intrinsic & extrinsic)
Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation
 Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation Lou Irving Director Respiratory and Sleep Medicine, RMH louis.irving@mh.org.au Capacity of the Respiratory System At rest During
Causes and Consequences of Respiratory Centre Depression and Hypoventilation Lou Irving Director Respiratory and Sleep Medicine, RMH louis.irving@mh.org.au Capacity of the Respiratory System At rest During
A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation
 1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό
 Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
Μαρία Μπόνου Διευθύντρια ΕΣΥ, ΓΝΑ Λαϊκό Diastolic HF DD: Diastolic Dysfunction DHF: Diastolic HF HFpEF: HF with preserved EF DD Pathophysiologic condition: impaired relaxation, LV compliance, LV filling
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer Turquoise team
 15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
15 physiology 6 Mohammed Jaafer 22-3-2016 Turquoise team Cardiac Arrhythmias and Their Electrocardiographic Interpretation Today, we are going to talk about the abnormal excitation. As we said before,
Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension. Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London
 Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, January 2012 ACC/AHA 2008 Guidelines ASD closure Closure is indicated for right atrial
Closing ASDs with pulmonary hypertension Shakeel A Qureshi Evelina Children s Hospital London Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam, January 2012 ACC/AHA 2008 Guidelines ASD closure Closure is indicated for right atrial
Comparison of formulae used to estimate oxygen
 British Heart Journal, I974, 36 446-45i. Comparison of formulae used to estimate oxygen saturation of mixed venous blood from caval samples H. C. Miller', D. J. Brown, and G. A. H. Miller From the Cardiac
British Heart Journal, I974, 36 446-45i. Comparison of formulae used to estimate oxygen saturation of mixed venous blood from caval samples H. C. Miller', D. J. Brown, and G. A. H. Miller From the Cardiac
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
PFIZER INC. Study Center(s): A total of 6 centers took part in the study, including 2 in France and 4 in the United States.
 PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
PFIZER INC. These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert. For publications based on this study, see associated bibliography.
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
Mechanical Support in the Failing Fontan-Kreutzer
 Mechanical Support in the Failing Fontan-Kreutzer Stephanie Fuller MD, MS Thomas L. Spray Endowed Chair in Congenital Heart Surgery Associate Professor, The Perelman School of Medicine at the University
Mechanical Support in the Failing Fontan-Kreutzer Stephanie Fuller MD, MS Thomas L. Spray Endowed Chair in Congenital Heart Surgery Associate Professor, The Perelman School of Medicine at the University
AORTIC COARCTATION. Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta
 AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
AORTIC COARCTATION Synonyms: - Coarctation of the aorta Definition: Aortic coarctation is a congenital narrowing of the aorta, usually located after the left subclavian artery, near the ductus or the ligamentum
Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Physician Assistant Studies Faculty Research and Publications Health Sciences, College of 7-15-2010 Determining Axis and Axis Deviation on an ECG Patrick Loftis
Coronary arteriography in complicated acute myocardial infarction; clinical and angiographic correlates
 Coronary arteriography in complicated acute myocardial ; clinical and angiographic correlates Luis M. de la Fuente, M.D. Buenos Aires, Argentina From January 1979 to June 30, 1979, we performed coronary
Coronary arteriography in complicated acute myocardial ; clinical and angiographic correlates Luis M. de la Fuente, M.D. Buenos Aires, Argentina From January 1979 to June 30, 1979, we performed coronary
