Review Article ABSTRACT HOW TO EXAMINE THE FETAL HEART DURING ROUTINE ANOMALY SCAN INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Bryan Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
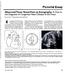
1 Review Article Prenatal Detection /jp-journals of Critical Congenital Heart Disease 1 Lina W Irshaid, 2 Najwa Elfky, 3 Badreldeen Ahmed ABSTRACT Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a leading cause of infant mortality and 30% fetuses born with CHDs have other associated malformations and chromosomal abnormalities. Prenatal diagnosis also allows parents to opt for termination of the pregnancy. Keywords: Critical congenital heart disease, Fetal echocardiography, Prenatal diagnosis. How to cite this article: Irshaid LW, Elfky N, Ahmed B. Prenatal Detection of Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Donald School J Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2016;10(2): Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None INTRODUCTION When discussing congenital heart disease (CHD), consideration of certain points is critical. The first consideration is that CHD is a leading cause of infant mortality, with an estimated incidence of about 4 to 13 per 1000 live births. 1,2 Moreover, between 1950 and 1994, 42% of infant deaths reported to the World Health Organization were attributable to cardiac defects. 3 The second consideration is that 30% of fetuses born with CHDs have other associated malformations or chromosomal abnormalities. The third consideration is that the vast majority of CHDs affect pregnancies with no previously known risk factors. The fourth consideration is that prenatal diagnosis of CHDs improves the outcome in certain cardiac conditions, which include hypoplastic left heart, transposition of the great arteries, and coarctation of the aorta. 4,5 In special situations, prenatal diagnosis of CHDs gives parents the choice of the place of delivery. Prenatal diagnosis may also allow parents the option of termination of the pregnancy. Antenatal diagnosis of cardiac defects did not witness a great improvement over the last few years. 6,7 Furthermore, prenatal detection rates of CHD vary 1-3 Medical Student 1 Weill Cornell Medical School, Qatar 2 Weill Cornell Medicine, Al Luqta St, Ar-Rayyan, Qatar 3 Feto maternal Centre, Doha, Qatar Corresponding Author: Badreldeen Ahmed, Feto maternal Centre, Weill Cornell Medical School, Qatar, Phone: , profbadreldeen@hotmail.com widely. 8 Some of this variation can be attributed to differences in examiner experience, maternal obesity, transducer frequency, abdominal scars, gestational age at the time of ultrasound examination, amniotic fluid volume, and fetal position. 9,10 Because of the above, efforts are being made to try to improve the detection rates and diagnosis of CHD. These efforts include classroom courses, online courses, training in referred centers, and introduction of guidelines and protocols to diagnose CHD by professional bodies, such as the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG). HOW TO EXAMINE THE FETAL HEART DURING ROUTINE ANOMALY SCAN A strict protocol should be followed, which should include the subsequent points. Firstly, examination of all fetuses should be done at gestational age between 18 and 22 weeks. Secondly, the abdominal probe should be done using high-resolution ultrasound. The zoom and cine loop facilities should be used when needed. Thirdly, in all fetuses, a four-chamber view of the heart, with comments on situs, atrial chambers, ventricular chambers, and atrioventricular junction and valves (Figs 1 and 2) should be viewed. The left and right ventricular outflow tracts should be examined. Fourthly, outflow tracts are imaged by tilting the probe toward the fetal head. The great arteries should be of equal size and should cross at approximately 90 (Figs 3 and 4). Fifthly, all fetuses should have a three-vessel view, which enabled diagnosis of conditions such as coarctation of the aorta, right aortic arch, double aortic arch, and vascular rings (Fig. 5). Sixthly, all fetuses had a three-vessel and trachea view. Using this view, the transverse aortic arch and its relationship to the trachea could be demonstrated. Seventhly, color Doppler mapping should be used to examine the various cardiac structures and to improve the detection of abnormal blood flow. Many congenital heart defects can be seen on the standard four-chamber view (Table 1). However, four-chamber views are not enough to diagnose all cardiac malformations because of many factors, such as the anomaly could be far away from the four-chamber view, the anomaly evolved in utero, routine checklist may be overlooked, and inadequate examination. Examination of the outflow and outflow trachea tract is essential to diagnose other congenital cardiac defects (Table 2). Donald School Journal of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, April-June 2016;10(2):
2 Lina W Irshaid et al Fig. 1: Four-chamber view, showing both atria of similar size, ventricles of similar size, foramen ovale flap in the left atrium Fig. 2: Four-chamber view showing both ventricles on equal size, intact septum, moderator band seen in the right ventricle, and different levels of attachment of atrioventricular valve Fig. 3: Left outflow tract. The anterior aortic wall is continuous with the intact interventricular septum Fig. 4: Right outflow tract. The pulmonary artery bifurcates immediately. The pulmonary valve moves freely Table 1: Congenital cardiac defects detected on four-chamber view Hypoplastic right and left ventricle Atrioventricular canal defect Double inlet ventricle Ebstein s anomaly Single ventricle Cardiac tumors Large ventricular septal defect Fig. 5: The three-vessel view. This view demonstrates the relationship between superior vena cava, aorta, and pulmonary artery. Note the correct position and the size of the three vessels as well as correct alignment Table 2: Congenital cardiac defects missed on four-chamber view Transposition of the great vessels Tetralogy of Fallot Double outlet right ventricle Truncus arteriosus Small/moderate ventricular septal defect Atrial septal defect Coarctation of the aorta Total anomalous pulmonary venous return Aortic stenosis Pulmonary stenosis 132
3 DISCUSSION When we examine the fetal heart during anomaly scan, we aim to screen for any critical congenital heart defect which may affect the life of the newborn. Detection and diagnosis are distinct terms. Detection is the process of discovering a finding, while diagnosis is the process of identifying a disease by examination. In many fetomaternal centers, such as our center in Doha, detection rate is very high, as we were able to discover 10 out of 11 cases of CHD. The accuracy of our diagnosis of CHD is 100%, as all those who were referred to the pediatric cardiologist had their diagnosis confirmed postnatally via echocardiography. This result demonstrates that a high detection rate and accurate diagnosis of CHD is possible. Such result is very encouraging as only a few years ago the detection rate of CHD was suboptimal. A European study between 2000 and 2005 involving 16 countries and including live births showed the prenatal detection rate of CHD is only 20%. Many other studies done in European countries showed that the detection rate varies dramatically, between 20 and 80%, emphasizing the need for additional studies and an improvement in detection rate Another study by Galindo et al 14 involving 33 centers in Spain, and including 1,060 major CHDs between 2004 and 2006, reported that the prenatal detection rate of CHD in routine second-trimester scans was as low as 52.6% (95% confidence interval (CI) ). The study identified two important predictors of an increased detection rate by center: firstly, a systematic approach to the examination of the heart, showing at least the fourchamber view and the outflow tracts (prevalence ratio 1.3, 95% CI ) and secondly, the availability of specialists in fetal echocardiography to perform the examination (prevalence ratio 1.4, 95% CI ). 15 The study advised that prenatal detection of CHD should be globally strengthened by way of a uniform approach to the cardiac examination along with improving examiner training and skills. Moreover, authors of the study recommended close collaboration with fetal heart specialists to help accomplish this aim. 15 A prospective observational study at a London teaching hospital reported similar conclusions. Authors encouraged continuous feedback-based training of health care professionals, a low threshold for echocardiography referrals, and convenient access to fetal heart specialists as techniques to improve the effectiveness of a screening for CHDs. 11 A study by Marek et al, 16 including all pediatric and fetal patients with CHD over a 21-year period in the Czech Republic, reported a discrepancy in the detection rate of various cardiac defects. For example, the prenatal Fig. 6: Hypoplastic heart. This condition may be present at the time of anomaly scan at 20 weeks or may evolve as the result of atrioventricular valve stenosis detection rate for hypoplastic left heart was 95.8% (Fig. 6), whereas detection of transposition of the great arteries was only 25.6%. Prenatal detection of CHD is essential because it has a large impact on the appropriate management of affected infants during labor and delivery. For example, some babies may need to be delivered in a cardiac operation room for quick intervention. When the fetus is delivered, there are critical changes in the fetal circulation which include initiation of breathing, conversion of the fetal circulation from a parallel circuit to a series circuit, increase in the systemic vascular resistance, decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance, and closure of fetal shunt pathways. Detection of CHD during the antenatal period allows parents and physicians to choose the place of delivery and prepare a multidisciplinary team for the baby s arrival, which includes a fetal medicine specialist, pediatric cardiologist, neonatologist, anesthesiologist, and pediatric cardiac surgeon. These preparations improve the prognosis of the infant. The accepted gestational age for performing fetal echocardiography is between 18 and 22 weeks. However, a small proportion of CHDs become evident or more obvious as pregnancy progresses. Thus, the cardiac evaluation can be normal at 18 weeks, although a significant malformation is diagnosed later on in the pregnancy or after birth. This is true of some cases of aortic or pulmonary stenosis, cardiac tumors, and cardiomyopathies (Fig. 7). Fortunately, it is rare for a life-threatening malformation to arise after 20 weeks gestation. In addition, minor lesions, such as small ventricular septal defects can be overlooked because of the limitation of ultrasound resolution (Fig. 8). Other defects, such as persistent arterial duct and atrial septal defect cannot be predicted prenatally as these communications are always present Donald School Journal of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, April-June 2016;10(2):
4 Lina W Irshaid et al Fig. 7: A case of rhabdomyoma which is a benign cardiac tumor; however, it could be associated with tuberous sclerosis which is autosomal dominant condition Fig. 8: Ventricular septal defect can occur in any part of the interventricular septum and is often associated with other cardiac defects prenatally. Thus, there are confidence limits with even detailed fetal heart scanning. These confidence limits may be much wider with poor image quality. For this reason, it is crucial to counsel the parents on these limitations of antenatal scanning and to ensure that they are aware that while prenatal screening presents a huge benefit to their fetus, the detection is not 100%. WHAT IS NEW? The New 3D/4D-based Spatiotemporal Imaging Correlation in Fetal Echocardiography Spatiotemporal imaging correlation is an automated device incorporated into the ultrasound probe and has the capacity to perform slow sweep to acquire a single three-dimensional (3D) volume. This acquired volume is composed of a great number of two-dimension (2D) frames. 17,18 This volume can be analyzed and reanalyzed as required to demonstrate all the required cardiac views. It also provides the examiner with the ability to review all images in a looped cine sequence. Spatiotemporal imaging correlation has the potential to improve our ability to diagnose CHD. This potential becomes possible because of unlimited number of images available for viewing, additional information not available in the standard 2D ultrasound images, information can be shared with other colleagues remote from the site of examination for second opinion, and the patient can be counseled in great detail in light of new information. In conclusion, the majority of prenatally detectable cases of CHD occur in patients without any risk factors or extracardiac anomalies. Several studies have reported the detection rate of CHD; however, these figures vary widely. Regardless, these studies all came down to the general agreement that an improvement in detection rate is necessary, as it can greatly improve the prognosis of the infant. It also allows hospital systems to prepare for the arrival of the infant by making sure a multidisciplinary team is available. Detection rate can be improved by implementing a uniform, systematic approach to the fetal cardiac examination and by ensuring that fetal echocardiography is performed by specialists who are familiar with the prenatal diagnosis of CHD. REFERENCES 1. Ferencz C, Rubin JD, McCarter RJ, Brenner JI, Neill CA, Perry LW, Hepner SI, Downing JW. Congenital heart disease: prevalence at livebirth. The Baltimore-Washington Infant Study. Am J Epidemiol 1985 Jan;121(1): Cuneo BF, Curran LF, Davis N, Elrad H. Trends in prenatal diagnosis of critical cardiac defects in an integrated obstetric and pediatric cardiac imaging center. J Perinatol 2004 Nov; 24(11): Rosano A, Botto LD, Botting B, Mastroiacovo P. Infant mortality and congenital anomalies from 1950 to 1994: an international perspective. J Epidemiol Community Health 2000 Sep;54(9): Crane JP, Lefevre ML, Winborn RC, Evans JK, Ewigman BG, Bain RP, Frigoletto FD, McNellis D. A randomized trial of prenatal ultrasonographic screening: impact on the detection, management, and outcome of anomalous fetuses. The RADIUS Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994 Aug;171(2): Abu-Harb M, Hey E, Wren C. Death in infancy from unrecognized congenital heart disease. Arch Dis Child 1994 Jul;71(1): Bonnet D, Coltri A, Butera G, Fermont L, Le Bidois J, Kachaner J, Sidi D. Detection of transposition of the great arteries in Fetuses reduces neonatal morbidity and mortality. Circulation 1999 Feb 23;99(7): Tworetzky W, Wilkins-Haug L, Jennings RW, Van Der Velde ME, Marshall AC, Marx GR, Colan SD, Benson CB, Lock JE, Perry SB. Balloon dilation of severe aortic stenosis in the fetus: potential for prevention of hypoplastic left heart syndrome: candidate selection, technique, and results of successful intervention. Circulation 2004 Oct 12;110(15): Simpson LL. Screening for congenital heart disease. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2004 Mar;31(1):
5 9. Devore GR, Medearis AL, Bear MB, Horenstein J, Platt LD. Fetal echocardiography: factors that influence imaging of the fetal heart during the second trimester of pregnancy. J Ultrasound Med 1993 Nov;12(11): Sharland GK, Allan LD. Screening for congenital heart disease prenatally. Results of a 2 1/2-year study in the South East Thames region. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1992 Mar;99(3): Carvalho JS, Mavrides E, Shinebourne EA, Campbell S, Thilaganathan B. Improving the effectiveness of routine prenatal screening for major congenital heart defects. Heart 2002 Oct;88(4): Yagel S, Weissman A, Rotstein Z, Manor M, Hegesh J, Anteby E, Lipitz S, Achiron R. Congenital heart defects. Natural course and in utero development. Circulation 1997 Jul 15;96(2): Stumpflen I, Stumpflen A, Wimmer M, Bernaschek G. Effect of detailed fetal echocardiography as part of routine prenatal ultrasonographic screening on detection of congenital heart disease. Lancet 1996 Sep 28;348(9031): Galindo A, Herraiz I, Escribano D, Lora D, Melchor JC, de la Cruz J. Prenatal detection of congenital heart defects: a survey on clinical practice in Spain. Fetal Diagn Ther 2011;29(4): Dolk H, Loane M, Garne E; European Surveillance of Congenital Anomalies Working Group. Congenital heart defects in Europe: prevalence and perinatal mortality, 2000 to Circulation 2011 Mar 1;123(8): Marek J, Tomek V, Skovránek J, Povysilová V, Samánek M. Prenatal ultrasound screening of congenital heart disease in an unselected national population: a 21-year experience. Heart 2011 Jan;97(2): DeVore GR, Falkensammer P, Sklansky MS, Platt LD. Spatiotemporal image correlation: new technology for evaluation of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003 Oct;22(4): DeVore GR, Polanko B. Tomographic ultrasound imaging of the fetal heart: a new technique for identifying normal and abnormal cardiac anatomy. J Ultrasound Med 2005 Dec;24(12): Donald School Journal of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology, April-June 2016;10(2):
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Fetal echocardiography. Ahmeabad. to neonatal series due to high SB rate. Prenatal detection can improve the fetal outcome. (4, 5) 60% 40% 20%
 Guidelines for Fetal Echocardiography 1 Fetal echocardiography Introduction Dr Jayprakash Shah MD; FICOG Chairman Imaging science committee FOGSI Fetal Medicine expert Rajni Hospital, Ahmedabad, Ex sonologist
Guidelines for Fetal Echocardiography 1 Fetal echocardiography Introduction Dr Jayprakash Shah MD; FICOG Chairman Imaging science committee FOGSI Fetal Medicine expert Rajni Hospital, Ahmedabad, Ex sonologist
Summary. HVRA s Cardio Vascular Genetic Detailed L2 Obstetrical Ultrasound. CPT 76811, 76825, _ 90% CHD detection. _ 90% DS detection.
 What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Disclosures. Outline. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Introduction. Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart
 Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram
 JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Objectives. Introduction 11/2/2015
 Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
The sonographic approach to the detection of fetal cardiac
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 19: 360 365 The sonographic approach to the detection of fetal cardiac Blackwell Science Ltd anomalies in early pregnancy M. BRONSHTEIN* and E. Z. ZIMMER* *Department of
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 19: 360 365 The sonographic approach to the detection of fetal cardiac Blackwell Science Ltd anomalies in early pregnancy M. BRONSHTEIN* and E. Z. ZIMMER* *Department of
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
Case Report by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2004; 23: /04/$3.50
 Case Report A Systematic Approach to Prenatal Diagnosis of Transposition of the Great Arteries Using 4-Dimensional Ultrasonography With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza,
Case Report A Systematic Approach to Prenatal Diagnosis of Transposition of the Great Arteries Using 4-Dimensional Ultrasonography With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza,
Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural congenital heart diseases
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 21: 19 25 Published online 12 December 2002 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7 Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 21: 19 25 Published online 12 December 2002 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7 Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
C ongenital heart disease accounts for the majority of
 387 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Improving the effectiveness of routine prenatal screening for major congenital heart defects J S Carvalho, E Mavrides, E A Shinebourne, S Campbell, B Thilaganathan... See end
387 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Improving the effectiveness of routine prenatal screening for major congenital heart defects J S Carvalho, E Mavrides, E A Shinebourne, S Campbell, B Thilaganathan... See end
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 340 345 The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac Blackwell Science, Ltd scanning S. YAGEL*, R. ARBEL, E. Y. ANTEBY*, D. RAVEH and R. ACHIRON *Department
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 340 345 The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac Blackwell Science, Ltd scanning S. YAGEL*, R. ARBEL, E. Y. ANTEBY*, D. RAVEH and R. ACHIRON *Department
Introduction to Fetal Medicine. Lloyd R. Feit M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics Warren Alpert Medical School Brown University
 Associate Professor of Pediatrics Warren Alpert Medical School Brown University Fetal Cardiology Important in evaluation of high risk pregnancies. Information obtainable in > 95% of patients attempted.
Associate Professor of Pediatrics Warren Alpert Medical School Brown University Fetal Cardiology Important in evaluation of high risk pregnancies. Information obtainable in > 95% of patients attempted.
Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation
 Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation Ivan Romero Rivera, Maria Alayde Mendonça da Silva, José Maria Gonçalves Fernandes, Ana Claire
Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation Ivan Romero Rivera, Maria Alayde Mendonça da Silva, José Maria Gonçalves Fernandes, Ana Claire
Opinion. Isolated major congenital heart disease
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 370 379 Opinion Blackwell Science, Ltd Isolated major congenital heart disease The principal theme of this issue of the Journal is the prenatal detection of fetal cardiac
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: 370 379 Opinion Blackwell Science, Ltd Isolated major congenital heart disease The principal theme of this issue of the Journal is the prenatal detection of fetal cardiac
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program
 DOI: 10.1002/pd.4372 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program Jodi I. Pike, Anita
DOI: 10.1002/pd.4372 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program Jodi I. Pike, Anita
UPDATE FETAL ECHO REVIEW
 UPDATE 1 FETAL ECHO REVIEW Study Alert for RDCS Candidates D A V I E S P U B L I S H I N G I N C. Fetal Echo Review Study Alert U P D A T E D A U G U S T 1, 2 0 1 2 Nikki Stahl, RT(R)(M)(CT), RDMS, RVT
UPDATE 1 FETAL ECHO REVIEW Study Alert for RDCS Candidates D A V I E S P U B L I S H I N G I N C. Fetal Echo Review Study Alert U P D A T E D A U G U S T 1, 2 0 1 2 Nikki Stahl, RT(R)(M)(CT), RDMS, RVT
Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease
 Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Mohamed Sulaiman, MD Pediatric cardiologist Kidsheart: American Fetal & Children's Heart Center Dubai Healthcare City, Dubai-UAE First Pediatric
Before we are Born: Fetal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease Mohamed Sulaiman, MD Pediatric cardiologist Kidsheart: American Fetal & Children's Heart Center Dubai Healthcare City, Dubai-UAE First Pediatric
Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus*
 Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
 Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Outcomes of Infants with Prenatally Diagnosed Congenital Heart Disease Delivered in a Tertiary-care Pediatric Cardiac Facility METHODS
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Outcomes of Infants with Prenatally Diagnosed Congenital Heart Disease Delivered in a Tertiary-care Pediatric Cardiac Facility TRUPTI DEEPAK CHANGLANI, ANNU JOSE, ABISH SUDHAKAR,
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Outcomes of Infants with Prenatally Diagnosed Congenital Heart Disease Delivered in a Tertiary-care Pediatric Cardiac Facility TRUPTI DEEPAK CHANGLANI, ANNU JOSE, ABISH SUDHAKAR,
Accuracy of the Fetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right Ventricle
 Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USACHDCongenital Heart Disease 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing, Inc.? 200723237Original ArticleFetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right
Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USACHDCongenital Heart Disease 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing, Inc.? 200723237Original ArticleFetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
Impact of audit of routine second-trimester cardiac images using a novel image-scoring method
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 29; 33: 545 551 Published online 9 April 29 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.6323 Impact of audit of routine second-trimester cardiac images using
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 29; 33: 545 551 Published online 9 April 29 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.6323 Impact of audit of routine second-trimester cardiac images using
Editorial. The four-chamber view: four reasons why it seems to fail in screening for cardiac abnormalities and suggestions to improve detection rate
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 22: 3 10 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.187 Editorial The four-chamber view: four reasons why it seems to fail in
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 22: 3 10 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.187 Editorial The four-chamber view: four reasons why it seems to fail in
Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley Lee, MD, Fernando Viñals, MD, Josep Maria Martinez, MD, PhD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley Lee, MD, Fernando Viñals, MD, Josep Maria Martinez, MD, PhD,
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Methods PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
Coarctation of the aorta: difficulties in prenatal
 7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems. Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven
 Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Evolution of Foetal echocardiography as a screening tool for prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease
 Review Article Evolution of Foetal echocardiography as a screening tool for prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease Nuruddin Badruddin. Mohammed, 1 Anandakumar Chinnaiya 2 Maternal and Foetal Medicine
Review Article Evolution of Foetal echocardiography as a screening tool for prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease Nuruddin Badruddin. Mohammed, 1 Anandakumar Chinnaiya 2 Maternal and Foetal Medicine
Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 964-968 Personal practice Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities L D ALLAN Guy's Hospital, London The feasibility of cross sectional imaging of the structure
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 964-968 Personal practice Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities L D ALLAN Guy's Hospital, London The feasibility of cross sectional imaging of the structure
Congenital Cardiac Anomalies
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Congenital Cardiac Anomalies Prenatal Readings Versus Neonatal Outcomes Neha Trivedi, MD, Denis Levy, MD, Maryam Tarsa, MD, Tracy Anton, RDMS, Caitlin Hartney, Tanya Wolfson, MS, Dolores
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Congenital Cardiac Anomalies Prenatal Readings Versus Neonatal Outcomes Neha Trivedi, MD, Denis Levy, MD, Maryam Tarsa, MD, Tracy Anton, RDMS, Caitlin Hartney, Tanya Wolfson, MS, Dolores
CIC EDIZIONI INTERNAZIONALI. Two-dimensional fetal echocardiography: where we are
 Two-dimensional fetal echocardiography: where we are Luigi Caserta 1 Zaira Ruggeri 2 Laura D Emidio 3 Claudio Coco 3 Pietro Cignini 3 Alessandra Girgenti 3 Lucia Mangiafico 3 Claudio Giorlandino 3 1 Department
Two-dimensional fetal echocardiography: where we are Luigi Caserta 1 Zaira Ruggeri 2 Laura D Emidio 3 Claudio Coco 3 Pietro Cignini 3 Alessandra Girgenti 3 Lucia Mangiafico 3 Claudio Giorlandino 3 1 Department
Relationship Between Isolated Mild Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation in Second-Trimester Fetuses and Postnatal Congenital Cardiac Disorders
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Relationship Between Isolated Mild Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation in Second-Trimester Fetuses and Postnatal Congenital Cardiac Disorders Jizi Zhou, MD, PhD, Yun Zhang, MD, Yonghao Gui,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Relationship Between Isolated Mild Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation in Second-Trimester Fetuses and Postnatal Congenital Cardiac Disorders Jizi Zhou, MD, PhD, Yun Zhang, MD, Yonghao Gui,
Variation in Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in Infants
 Variation in Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in Infants Michael D. Quartermain, MD a, Sara K. Pasquali, MD b, Kevin D. Hill, MD c, David J. Goldberg, MD d, James C. Huhta, MD e, Jeffrey
Variation in Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in Infants Michael D. Quartermain, MD a, Sara K. Pasquali, MD b, Kevin D. Hill, MD c, David J. Goldberg, MD d, James C. Huhta, MD e, Jeffrey
Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different
 Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different methods with echocardiography Ying Zhang 1* * Corresponding author Email: baogoubei@hotmail.com Ai-Lu Cai 1 Email: caial_us@hotmail.com
Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different methods with echocardiography Ying Zhang 1* * Corresponding author Email: baogoubei@hotmail.com Ai-Lu Cai 1 Email: caial_us@hotmail.com
Presentation of congenital heart disease in infancy: implications for routine examination
 Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 999;80:F49 F5 F49 Presentation of congenital heart disease in infancy: implications for routine examination Christopher Wren, Sam Richmond, Liam Donaldson Department of
Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 999;80:F49 F5 F49 Presentation of congenital heart disease in infancy: implications for routine examination Christopher Wren, Sam Richmond, Liam Donaldson Department of
Improvement in the antenatal detection rate of CHD and its effect on survival in Wales: How can we improve our results further?
 Improvement in the antenatal detection rate of CHD and its effect on survival in Wales: How can we improve our results further? Dr Orhan Uzun Consultant Paediatric Cardiologist UHW Welcome Improvement!
Improvement in the antenatal detection rate of CHD and its effect on survival in Wales: How can we improve our results further? Dr Orhan Uzun Consultant Paediatric Cardiologist UHW Welcome Improvement!
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
 Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15 weeks gestation with later cardiac evaluation
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 679 686 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12517 Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 679 686 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12517 Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15
Disclosures 5/2/17. None
 Joshua A. Copel, MD Professor, Ob-Gyn & Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT None Disclosures 1 Infant mortality, USA, 2006 # Rate* % Congenital anomalies 5,769 133.3 19.7 Premat,
Joshua A. Copel, MD Professor, Ob-Gyn & Pediatrics Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT None Disclosures 1 Infant mortality, USA, 2006 # Rate* % Congenital anomalies 5,769 133.3 19.7 Premat,
Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
Congenital heart defects are frequent and serious. Racial and Temporal Variations in the Prevalence of Heart Defects
 Racial and Temporal Variations in the Prevalence of Heart Defects Lorenzo D. Botto, MD; Adolfo Correa, MD, PhD; and J. David Erickson, DDS, PhD ABSTRACT. Background. Documenting the prevalence and trends
Racial and Temporal Variations in the Prevalence of Heart Defects Lorenzo D. Botto, MD; Adolfo Correa, MD, PhD; and J. David Erickson, DDS, PhD ABSTRACT. Background. Documenting the prevalence and trends
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal
 Br Heart J 1984; 52: 542-8 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal congenital heart disease LINDSEY D ALLAN, DIANE C CRAWFORD, ROBERT H ANDERSON,* MICHAEL J TYNAN From Guy's Hospital, London;
Br Heart J 1984; 52: 542-8 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal congenital heart disease LINDSEY D ALLAN, DIANE C CRAWFORD, ROBERT H ANDERSON,* MICHAEL J TYNAN From Guy's Hospital, London;
AbnormalThree-VesselView on Sonography: A Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus
 rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
Outflow Tracts Anomalies
 Diagnosis of Outflow Tract Anomalies in the Fetus General Framing D.Paladini Fetal Medicine & Surgery Unit Gasllini Children s Hospital - Genoa dariopaladini@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Outflow Tracts Anomalies
Diagnosis of Outflow Tract Anomalies in the Fetus General Framing D.Paladini Fetal Medicine & Surgery Unit Gasllini Children s Hospital - Genoa dariopaladini@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Outflow Tracts Anomalies
Transient malformations like PDA and PDA of prematurity were not considered. We have divided cardiac malformations in 2 groups:
 CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
CARDIAC MALFORMATIONS DETECTED AT BIRTH Anwar Dudin-MD, Annie Rambaud-Cousson-MD, Mahmoud Nashashibi-MD Pediatric Department Makassed Hospital Jerusalem Diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the neonatal
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus*
 Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Lori Erickson MSN, RN, CPNP-PC Ward Family Heart Center
 Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Lori Erickson MSN, RN, CPNP-PC Ward Family Heart Center The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 05/14 Objectives Evaluate our regional prenatal
Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Lori Erickson MSN, RN, CPNP-PC Ward Family Heart Center The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 05/14 Objectives Evaluate our regional prenatal
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Congenital Heart Disease. Morphological and Physiological Predictors of Fetal Aortic Coarctation
 Congenital Heart Disease Morphological and Physiological Predictors of Fetal Aortic Coarctation Hikoro Matsui, MD; Mats Mellander, PhD, MD; Michael Roughton, PhD; Hana Jicinska, MD; Helena M. Gardiner,
Congenital Heart Disease Morphological and Physiological Predictors of Fetal Aortic Coarctation Hikoro Matsui, MD; Mats Mellander, PhD, MD; Michael Roughton, PhD; Hana Jicinska, MD; Helena M. Gardiner,
Research article. Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic
 Research article Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic Irina A. Akhmedova, Gulzada A. Imanalieva, Damir A.Abibillaev, Taalaibek Z. Kudaiberdiev Scientific Research Institute
Research article Primary detection of congenital heart diseases in the Kyrgyz Republic Irina A. Akhmedova, Gulzada A. Imanalieva, Damir A.Abibillaev, Taalaibek Z. Kudaiberdiev Scientific Research Institute
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Barriers to prenatal detection of congenital heart disease: a population-based study
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 40: 418 425 Published online 17 September 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10116 Barriers to prenatal detection of congenital heart
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2012; 40: 418 425 Published online 17 September 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.10116 Barriers to prenatal detection of congenital heart
2019 Fetal Echocardiography:
 AVAILABLE NOW ON-DEMAND, USB, OR DVD A CME Teaching Activity 2019 Fetal Echocardiography: Normal and Abnormal Hearts Designated for SA-CME 17.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Release Date: February 1,
AVAILABLE NOW ON-DEMAND, USB, OR DVD A CME Teaching Activity 2019 Fetal Echocardiography: Normal and Abnormal Hearts Designated for SA-CME 17.0 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Release Date: February 1,
Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Sonographic Features and Techniques for Prenatal Detection
 650434JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316650434Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyScott et al. research-article2016 Literature Review Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Sonographic Features and Techniques
650434JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316650434Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyScott et al. research-article2016 Literature Review Screening for Congenital Heart Disease: Sonographic Features and Techniques
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation
 Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Jenny Ecord, APRN Ward Family Heart Center Wichita
 Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Jenny Ecord, APRN Ward Family Heart Center Wichita The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 05/14 Objectives Review current local and regional
Regional Prenatal Congenital Heart Disease Detection and Practices Jenny Ecord, APRN Ward Family Heart Center Wichita The Children's Mercy Hospital, 2014. 05/14 Objectives Review current local and regional
Three and four dimensional ultrasound: a novel method for evaluating fetal cardiac anomalies
 PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2009; 29: 645 653. Published online 1 April 2009 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2257 Three and four dimensional ultrasound: a novel method for evaluating
PRENATAL DIAGNOSIS Prenat Diagn 2009; 29: 645 653. Published online 1 April 2009 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).2257 Three and four dimensional ultrasound: a novel method for evaluating
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding at various stages of pregnancy
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
2018 Fetal Echocardiography:
 AVAILABLE NOW ON-DEMAND, USB, OR DVD A CME Teaching Activity 2018 Fetal Echocardiography: Designated for SA-CME 16.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Release Date: February 1, 2018 Educational Symposia
AVAILABLE NOW ON-DEMAND, USB, OR DVD A CME Teaching Activity 2018 Fetal Echocardiography: Designated for SA-CME 16.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM Release Date: February 1, 2018 Educational Symposia
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital heart disease in the northern region of England: benefits of a training programme for obstetric ultrasonographers
 294 Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne NE7 7DN, UK S Hunter A Heads J Wyllie S Robson Correspondence to: Dr Hunter Accepted 2 June 2000 Prenatal diagnosis of congenital
294 Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne NE7 7DN, UK S Hunter A Heads J Wyllie S Robson Correspondence to: Dr Hunter Accepted 2 June 2000 Prenatal diagnosis of congenital
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4,
 Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4, 475-481 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.174.rvd The role of ventricular disproportion, aortic, and ductal isthmus ultrasound measurements for the diagnosis
Original papers Med Ultrason 2015, Vol. 17, no. 4, 475-481 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.174.rvd The role of ventricular disproportion, aortic, and ductal isthmus ultrasound measurements for the diagnosis
Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography using spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC)
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 535 545 Published online 6 May 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1075 Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 535 545 Published online 6 May 2004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1075 Three-dimensional (3D) and 4D color Doppler fetal echocardiography
Data Collected: June 17, Reported: June 30, Survey Dates 05/24/ /07/2010
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
The Polish National Registry for Fetal Cardiac Pathology: organization, diagnoses, management, educational aspects and telemedicine endeavors
 DOI: 10.1002/pd.3838 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Polish National Registry for Fetal Cardiac Pathology: organization, diagnoses, management, educational aspects and telemedicine endeavors Maciej Slodki 1 *, Joanna
DOI: 10.1002/pd.3838 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Polish National Registry for Fetal Cardiac Pathology: organization, diagnoses, management, educational aspects and telemedicine endeavors Maciej Slodki 1 *, Joanna
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
Rendering in fetal cardiac scanning: the intracardiac septa and the coronal atrioventricular valve planes
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: 266 274 Published online 3 August 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2843 Rendering in fetal cardiac scanning: the intracardiac
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: 266 274 Published online 3 August 2006 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2843 Rendering in fetal cardiac scanning: the intracardiac
Transposition of the great arteries in the fetus: assessment of the spatial relationships of the arterial trunks by four-dimensional echocardiography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 271 276 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5276 Transposition of the great arteries in the fetus: assessment of the
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2008; 31: 271 276 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.5276 Transposition of the great arteries in the fetus: assessment of the
The role of tissue harmonic imaging in fetal echocardiography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 159 164 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.962 The role of tissue harmonic imaging in fetal echocardiography D. PALADINI,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 23: 159 164 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.962 The role of tissue harmonic imaging in fetal echocardiography D. PALADINI,
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations. John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK
 Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Transposition of the Great Arteries Preoperative Diagnostic Considerations John Simpson Evelina Children s Hospital London, UK Areas to be covered Definitions Scope of occurrence of transposition of the
Epidemiology of congenital heart diseases
 Epidemiology of congenital heart diseases Damien Bonnet Unité médico-chirurgicale de Cardiologie Congénitale et Pédiatrique Hôpital Universitaire Necker Enfants malades APHP, Université Paris Descartes,
Epidemiology of congenital heart diseases Damien Bonnet Unité médico-chirurgicale de Cardiologie Congénitale et Pédiatrique Hôpital Universitaire Necker Enfants malades APHP, Université Paris Descartes,
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
T wo dimensional and Doppler echocardiography is being
 F287 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of echocardiography on the neonatal unit S Moss, D J Kitchiner, C W Yoxall, N V Subhedar... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Subhedar,
F287 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of echocardiography on the neonatal unit S Moss, D J Kitchiner, C W Yoxall, N V Subhedar... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Subhedar,
A New Approach to Fetal Echocardiography
 Article A New Approach to Fetal Echocardiography Digital Casts of the Fetal Cardiac Chambers and Great Vessels for Detection of Congenital Heart Disease Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley
Article A New Approach to Fetal Echocardiography Digital Casts of the Fetal Cardiac Chambers and Great Vessels for Detection of Congenital Heart Disease Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view.
 An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study
 J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic venous anomaly
 World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
World Database for Pediatric and Congenital Heart Surgery Appendix B: Diagnosis (International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Codes (IPCCC) and definitions) Anomalous Systemic Venous Connection Systemic
D. PALADINI, M. VASSALLO, G. SGLAVO, C. LAPADULA and P. MARTINELLI
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 555 561 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2749 The role of spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) with tomographic
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: 555 561 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.2749 The role of spatio-temporal image correlation (STIC) with tomographic
Echocardiography of Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography of Congenital Heart Disease Sunday, April 15 Tuesday, April 17, 2018 Ruth and Tristram Colket, Jr. Translational Research Building on the Raymond G. Perelman Campus Learn more: chop.cloud-cme.com
Echocardiography of Congenital Heart Disease Sunday, April 15 Tuesday, April 17, 2018 Ruth and Tristram Colket, Jr. Translational Research Building on the Raymond G. Perelman Campus Learn more: chop.cloud-cme.com
Potential Data Sources
 Potential Data Sources Addressing Congenital Heart Defects: Occurrence, Populations and Risk Factors Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Birth Defects Data and Statistics http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/data.html
Potential Data Sources Addressing Congenital Heart Defects: Occurrence, Populations and Risk Factors Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Birth Defects Data and Statistics http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/data.html
