ECG Success Exercises in ECG Interpretation
|
|
|
- Marlene Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECG Success Exercises in ECG Interpretation Shirley A. Jones, MS Ed, MHA, EMT-P Emergency Medical Services Educator Arrhythmia Instructor Riverview Hospital Noblesville, Indiana Basic Life Support Instructor American Heart Association Advanced Cardiac Life Support Instructor American Heart Association
2 F. A. Davis Company 1915 Arch Street Philadelphia, PA Copyright 2008 by F. A. Davis Company Copyright 2008 by F. A. Davis Company. All rights reserved. This product is protected by copyright. No part of it may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without written permission from the publisher. Printed in the United States of America Last digit indicates print number: Acquisitions Editor: Lisa B. Deitch Project Editor: Ilysa Richman, Padraic J. Maroney Director of Content Development: Darlene D. Pedersen Art and Design Manager: Carolyn O Brien As new scientific information becomes available through basic and clinical research, recommended treatments and drug therapies undergo changes. The author(s) and publisher have done everything possible to make this book accurate, up to date, and in accord with accepted standards at the time of publication. The author(s), editors, and publisher are not responsible for errors or omissions or for consequences from application of the book, and make no warranty, expressed or implied, in regard to the contents of the book. Any practice described in this book should be applied by the reader in accordance with professional standards of care used in regard to the unique circumstances that may apply in each situation. The reader is advised always to check product information (package inserts) for changes and new information regarding dose and contraindications before administering any drug. Caution is especially urged when using new or infrequently ordered drugs. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Jones, Shirley A. ECG success : exercises in ECG interpretation / Shirley A. Jones. p. ; cm. ISBN-13: ISBN-10: Electrocardiography Interpretation Problems, exercises, etc. I. Title. [DNLM: 1. Electrocardiography methods Problems and Exercises. 2. Arrhythmia diagnosis Problems and Exercises. WG 18.2 J76e 2007] RC683.5.E5J dc Authorization to photocopy items for internal or personal use, or the internal or personal use of specific clients, is granted by F. A. Davis Company for users registered with the Copyright Clearance Center (CCC) Transactional Reporting Service, provided that the fee of $.10 per copy is paid directly to CCC, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA For those organizations that have been granted a photocopy license by CCC, a separate system of payment has been arranged. The fee code for users of the Transactional Reporting Service is: $.10.
3 Preface No one is born knowing how to read ECG strips. We learn to do many things in a lifetime, and nearly all of them get better with practice. If you re planning to use this book, ECG isn t completely new to you you have a good idea of what s involved in generating and interpreting a tracing. ECG Success covers all the information you will need anatomy and physiology, practice, and case scenarios, and relevant emergency care to help you feel competent and in control, whether the situation involves an emergency or just a nonthreatening ECG. This book has staying power. You will find its content useful across a spectrum of situations, from classroom study through clinical experience and later in actual practice. Pattern recognition lies at the heart of ECG interpretation. This skill develops with experience, gained through repetition and variety. You need to see the same patterns over and over again, but you also need to see as great a diversity as possible. In ECG Success you ll find more than 550 ECG tracings. The book is organized into four units. First, two introductory chapters review the background information you need for working with ECG. Chapter One discusses heart anatomy and physiology, including biomechanics and electrophysiology. Chapter Two gives you the basics of ECG: limb and chest leads, electrode placement, cable connections, components of a tracing, rhythm strip analysis, and more. In Unit Two, seven chapters explain and illustrate the different types of rhythm, some dangerous, others merely troublesome, and a few even normal. Each of these chapters gives you a group of nine practice strips to analyze, with the answers given at the end of the chapter. All types of arrhythmias are discussed and illustrated: sinus, atrial, junctional, and ventricular; atrioventricular and bundle branch blocks; artifact; and artificial pacemaker rhythm. The section ends with a chapter on myocardial infarction and the 12-lead ECG. The chapter practice strips will warm you up for Unit Three, the working core of the book. You ll find four test chapters with a total of 300 strips and the answers given at the end of each chapter so you can check your work. In case you re hungry for more, the two chapters in Unit Four comprise eleven real-life case studies, followed by multiple-choice questions and illustrated by more ECG strips. Four appendices round out the book: Healthcare Provider Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, Advanced Cardiac Life Support Protocols, Emergency Medications, and Emergency Medical Skills. As you page through this book you ll find some special features to guide you. In Units One and Two, frequent Clinical Tips provide valuable information on how an arrhythmia can affect the patient. Hints on rhythm interpretation appear throughout the first practice strip chapter. I couldn t have written this book without building up a track record of my own ECG successes. The secret: I had a good instructor who was patient and explained everything in detail. She kept emphasizing that we had to follow every step when analyzing a rhythm; shortcuts are dangerous because you can miss critical details on the rhythm strip. Then we had to practice, practice, practice. That repetition, combined with careful attention to every step, was the real key to my success. Take your time now, and use ECG Success to improve your skills. Once you run into a genuine emergency you will have only minutes, or less, to interpret the ECG correctly and ensure the right treatment for the patient. Shirley A. Jones vii
4 Consultants Dawn McKay, RN, MSN, CCRN Critical Care Instructor Assistant Professor of Nursing Liberty University Lynchburg, Virginia Basic Life Support Instructor, American Heart Association Advanced Cardiac Life Support Instructor, American Heart Association Trauma Nursing Core Course Instructor, Emergency Nurses Association Fundamental Critical Care Support Instructor, Society of Critical Care Medicine Carmen J. Petrin, MS, APRN, BC Nurse Practioner New England Heart Institute at Catholic Medical Center Manchester, New Hampshire Former Critical Care Educator Catholic Medical Center Manchester, New Hampshire Basic Life Support Instructor, American Heart Association Advanced Cardiac Life Support Instructor, American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support Instructor, American Heart Association National Advanced Cardiac Life Support Faculty, American Heart Association Pediatric Advanced Life Support Training Center Faculty, American Heart Association Basic Life Support Training Center Faculty, American Heart Association Shirley A. Jones has worked in the field of emergency medical services for more than 30 years. She received her Master of Science in Education and her Master of Health Administration degrees from Indiana University. She has been awarded five first-place honors in tri-state and state-wide advanced life support competitions, served on the faculty of national conferences, and won honors from the Medical Writers Association for two textbooks. She is an accomplished writer and educator in the fields of electrocardiology and pharmacological and mechanical therapy. She welcomes the comments, criticisms, and ideas of readers for the improvement of future editions. ix
5 Reviewers Lori Baker, RN Surgical Nurse Educator Lions Gate Hospital North Vancouver, Canada Carole Berube, MA, MSN, RN Professor Emerita in Nursing Bristol Community College Fall River, Massachusetts Daryl Boucher, MSN, RN Flight Nurse/Nursing and Allied Health Faculty Aroustook Medical Center/Northern Maine Community College Presque Isle, Maine Carmen Carpenter, RN, MS, CMA Department Chair, Allied Health Sciences and Medical Assisting South University West Palm Beach, Florida Barbara Chamberlain, MSN, APRN, BC Critical Care Clinical Nurse Specialist Kennedy Health System Turnersville, New Jersey Pam Chambers, MPH, PA-C Associate Professor, Physician Assistant Program Des Moines University Des Moines, Iowa Julie Chew, RN, MS, PhD Clinical Educator Sacred Heart Medical Center Eugene, Oregon Jeff Chianfagna, BS, MA, PA Clinical Physician Assistant and Academic Instructor/Faculty Pace Lenox Hill Hospital Physician Assistant Program New York, New York Nancy Edge, RN, BSN Clinical Educator, Cardiac Surgery Vancouver General Hospital Vancouver, Canada Linda Latham, RN, BSN, MA Lead Instructor Forsyth Technical Community College Winston-Salem, North Carolina Cindy Light, RN, MSN, CEN Nursing Instructor Baker University School of Nursing Topeka, Kansas Dawn McKay, RN, MSN, CCRN Assistant Professor Liberty University Lynchburg, Virginia Susan Moore, PhD, RN Professor of Nursing New Hampshire Community Technical College Manchester, New Hampshire Deborah Opacic, EdD, PA-C Professor, Clinical Educator Duquesne University Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Patricia Richards, RN, MSN, CCRN Faculty, Nursing Department Central Maine Community College Auburn, Maine Catherine Richmond, RN, BSN, MSN Professor, Nursing SUNY Alfred State College Alfred, New York Robert Spears, MPAS, PA-C Assistant Professor The University of Findlay Findlay, Ohio Walt Stoy, PhD Director of Education Center for Emergency Medicine Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Debbie Sullivan, PhD, PA-C Assistant Professor/PA Program Faculty/Interim Director Midwestern University Glendale, Arizona Rita Tomasewski, MSN, ARCNP Cardiovascular Clinical Nurse Specialist St. Francis Health Center Topeka, Kansas Marilyn Turner, RN, CMA Medical Assisting Program Director Ogeechee Technical College Statesboro, Georgia xi
6 Contents UNIT ONE Heart Structure and Electrical Activity Chapter 1: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HEART 2 Overview 2 Anatomy of the Heart 2 Layers of the Heart 2 Heart Valves 2 Heart Chambers and Great Vessels 3 Coronary Vessel Circulation 3 Anatomy of the Cardiovascular System 4 Blood Vessel Structures 4 Arterial Circulation 4 Venous Circulation 5 Physiology of the Heart 5 Mechanical Physiology 5 Electrophysiology 6 Chapter 2: THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM 9 Overview 9 Limb Leads 10 Standard Chest Leads 10 Cable Connections 11 Electrode Placement Using a Three-wire Cable 11 Electrode Placement Using a Five-wire Cable 12 Modified Chest Leads 12 The Right-sided 12-Lead ECG 12 The 15-Lead ECG 13 Recording of the ECG 13 Components of an ECG Tracing 14 Methods for Calculating Heart Rate 14 Rhythm Strip Analysis 16 Instructions for Analyzing ECG Practice and Test Strips 16 UNIT TWO Rhythms and Their Analysis Chapter 3: SINOATRIAL NODE ARRHYTHMIAS 20 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) 20 Sinus Bradycardia 21 Sinus Tachycardia 21 Sinus Arrhythmia 22 Sinus Pause (Sinus Arrest) 22 Sinoatrial (SA) Block 23 ECG Practice Strips 23 Answers to Chapter 3 ECG Practice Strips 26 Chapter 4: ATRIAL ARRHYTHMIAS 28 Wandering Atrial Pacemaker (WAP) 28 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) 29 Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) 29 Atrial Tachycardia 30 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) 30 Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia (PSVT) 31 Atrial Flutter 31 Atrial Fibrillation 32 Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome 32 ECG Practice Strips 33 Answers to Chapter 4 ECG Practice Strips 36 Chapter 5: JUNCTIONAL ARRHYTHMIAS 37 Junctional Rhythm 37 Accelerated Junctional Rhythm 38 Junctional Tachycardia 38 Junctional Escape Beat 38 xiii
7 xiv Contents Premature Junctional Contraction (PJC) 39 ECG Practice Strips 39 Answers to Chapter 5 ECG Practice Strips 42 Chapter 6: VENTRICULAR ARRHYTHMIAS 44 Idioventricular Rhythm 44 Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm 45 Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC) 45 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Uniform 46 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Multiform 46 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Ventricular Bigeminy 46 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Ventricular Trigeminy 46 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Ventricular Quadrigeminy 47 Premature Ventricular Contraction: Couplets 47 Premature Ventricular Contraction: R on T Phenomenon 47 Premature Contraction: Interpolated PVC 48 Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Monomorphic 48 Ventricular Tachycardia (VT): Polymorphic 49 Torsade de Pointes 49 Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) 50 Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) 50 Asystole 51 ECG Practice Strips 51 Answers to Chapter 6 ECG Practice Strips 54 Chapter 7: ATRIOVENTRICULAR AND BUNDLE BRANCH BLOCKS 56 First-degree AV Block 56 Second-degree AV Block: Type I (Mobitz I or Wenckebach) 57 Second-degree AV Block: Type II (Mobitz II) 57 Third-degree AV Block 58 Bundle Branch Block (BBB) 58 ECG Practice Strips 59 Answers to Chapter 7 ECG Practice Strips 62 Chapter 8: ARTIFICIAL CARDIAC PACEMAKERS 63 Artificial Pacemaker 63 Pacemaker Modes 64 Understanding Pacemaker Codes 64 Artificial Pacemaker Rhythm 64 Single-chamber Pacemaker Rhythm Atrial 65 Single-chamber Pacemaker Rhythm Ventricular 65 Dual-chamber Pacemaker Rhythm Atrial and Ventricular 65 Pacemaker Malfunctions 65 Failure to Capture 66 Failure to Sense 66 Oversensing 66 ECG Practice Strips 67 Answers to Chapter 8 ECG Practice Strips 70 Chapter 9: ARTIFACT 71 Loose Electrical Connection 71 Variation with Respiration cycle Interference 72 Muscle Artifact 72 ECG Practice Strips 72 Answers to Chapter 9 ECG Practice Strips 75 Chapter 10: THE 12-LEAD ECG AND ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION 77 Troubleshooting ECG Problems 77 R Wave Progression 78 Electrical Axis Deviation 78 Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction 78 Progression of an Acute Myocardial Infarction 79 ST Segment Elevation and Depression 79 The Normal 12-lead ECG 80 Anterior Myocardial Infarction 80 Inferior Myocardial Infarction 80 Lateral Myocardial Infarction 81 Septal Myocardial Infarction 81 Posterior Myocardial Infarction 82 Left Bundle Branch Block 82 Right Bundle Branch Block 82 ECG Practice Tests UNIT THREE Chapter 11: ECG PRACTICE TEST ONE 86 Test Strip Section One 86 Answers to Practice Test One 115 Chapter 12: ECG PRACTICE TEST TWO 122 Test Strip Section Two 122 Answers to Practice Test Two 147 Chapter 13: ECG PRACTICE TEST THREE 154 Test Strip Section Three 154 Answers to Practice Test Three 179
8 Contents xv Chapter 14: ECG PRACTICE TEST FOUR 186 Test Strip Section Four 186 Answers to Practice Test Four 211 Case Studies UNIT FOUR Chapter 15: ECG CASE STUDIES ONE 220 Case Study One 220 Case Study Two 222 Case Study Three 223 Case Study Four 226 Case Study Five 228 Answers to Case Study One 229 Answers to Case Study Two 229 Answers to Case Study Three 230 Answers to Case Study Four 231 Answers to Case Study Five 231 Chapter 16: ECG CASE STUDIES TWO 232 Case Study One 232 Case Study Two 233 Case Study Three 235 Case Study Four 237 Case Study Five 239 Case Study Six 241 Answers to Case Study One 242 Answers to Case Study Two 243 Answers to Case Study Three 243 Answers to Case Study Four 244 Answers to Case Study Five 244 Answers to Case Study Six 244 APPENDICES Appendix A: HEALTHCARE PROVIDER GUIDELINES FOR CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION (CPR) 247 CPR Healthcare Provider Skill Performance 247 CPR: Adult 247 CPR: Child 248 CPR: Infant 249 OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY: Conscious Adult or Child 249 OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY: Conscious Infant 250 OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY: Unconscious Adult 250 OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY: Unconscious Child 251 OBSTRUCTED AIRWAY: Unconscious Infant 251 CPR and Obstructed Airway Positions 252 Appendix B: ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS 253 Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) 253 Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA) 254 Asystole 254 Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) 255 Bradycardia 255 Tachycardia Unstable 256 Narrow-complex Tachycardia Stable Regular Rhythm 257 Narrow-complex Tachycardia Stable Irregular Rhythm 257 Wide-complex Tachycardia Stable Regular Rhythm 258 Wide-complex Tachycardia Stable Irregular Rhythm 258 Appendix C: EMERGENCY MEDICATIONS 259 Appendix D: EMERGENCY MEDICAL SKILLS 265 Defibrillation 265 Cardioversion (Synchronized) 266 Transcutaneous Pacing 267 Carotid Sinus Massage (Vagal Maneuver) 267 Abbreviations Used in Text 269 Selected References 271 Index 273
9 Chapter 4 Atrial Arrhythmias Atrial rhythms originate in the atria. Their common ECG features are P waves that differ in appearance from sinus P waves, and normal-duration QRS complexes if no ventricular conduction disturbances are present. Atrial rhythms to be described here are wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP), multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT), premature atrial contractions (PAC), atrial tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), atrial flutter (A-flutter), atrial fibrillation (A-fib), and Wolff- Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome. All ECG strips, including the practice strips, were recorded in lead II. WANDERING ATRIAL PACEMAKER (WAP) The pacemaker site transfers from the SA node to other latent pacemaker sites in the atria and the AV junction and then moves back to the SA node. Normal ( bpm) Irregular P Waves: At least three different PR Interval: Variable; determined QRS: Normal ( sec) forms, determined by focus in atria by focus Wandering atrial pacemaker may occur in normal hearts as a result of fluctuations in vagal tone. It may also be seen in patients with heart disease or COPD. 28
10 Chapter 4 Atrial Arrhythmias 29 MULTIFOCAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA (MAT) This form of WAP is associated with a ventricular response of 100 bpm. MAT may be confused with atrial fibrillation (A-fib); however, MAT has a visible P wave. Fast ( 100 bpm) Irregular P Wave: At least three different PR Interval: Variable; determined QRS: Normal ( sec) forms, determined by focus in atria by focus MAT is commonly seen in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease but may also occur in acute MI. PREMATURE ATRIAL CONTRACTION (PAC) A single contraction occurs earlier than the next expected sinus contraction. After the PAC, sinus rhythm usually resumes. Depends on rate of underlying rhythm Irregular whenever a PAC occurs P Waves: Present; in the PAC, PR Interval: Varies in the PAC; QRS: Normal ( sec) may have a different shape otherwise normal ( sec) In patients with heart disease, frequent PACs may precede PSVT, A-fib, or A-flutter.
11 30 ECG Success ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA A rapid atrial rate overrides the SA node and becomes the dominant pacemaker. Some ST wave and T wave abnormalities may be present bpm Regular P Waves: Normal (upright and PR Interval: May be short QRS: Normal ( sec) uniform) but differ in shape from ( 0.12 sec) in rapid rates but can be aberrant at times sinus P waves SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (SVT) This arrhythmia has such a fast rate that the P waves may not be seen bpm Regular P Waves: Frequently buried in PR Interval: Usually not possible QRS: Normal ( sec) preceding T waves and difficult to measure but may be wide if abnormally to see conducted through ventricles SVT may be related to caffeine intake, nicotine, stress, or anxiety in healthy adults. Some patients may experience angina, hypotension, light headedness, palpitations, and intense anxiety.
12 PAROXYSMAL SUPRAVENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (PSVT) PSVT is a rapid rhythm that starts and stops suddenly. For accurate interpretation, the beginning or end of the PSVT must be seen. PSVT is sometimes called paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) bpm Irregular P Waves: Frequently buried in PR Interval: Usually not possible QRS: Normal ( sec) preceding T waves and difficult to measure but may be wide if abnormally to see conducted through ventricles The patient may feel palpitations, dizziness, lightheadedness, or anxiety. ATRIAL FLUTTER The AV node conducts impulses to the ventricles at a 2:1, 3:1, 4:1, or greater ratio (rarely 1:1). The degree of AV block may be consistent or variable. Atrial: bpm; ventricular: variable. Atrial: regular; ventricular: variable P Waves: Flutter waves have a PR Interval: Variable QRS: Usually normal (0.06 saw-toothed appearance; some 0.10 sec), but may appear may not be visible, being widened if flutter waves are buried in the QRS buried in QRS The presence of A-flutter may be the first indication of cardiac disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the ventricular response rate. 31
13 32 ECG Success ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Rapid, erratic electrical discharge comes from multiple atrial ectopic foci. No organized atrial depolarization are detectable. Atrial: 350 bpm; ventricular: variable Irregular P Waves: No true P waves; chaotic PR Interval: None QRS: Normal ( sec) atrial activity Atrial fibrillation is often a chronic arrhythmia associated with underlying heart disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the ventricular response rate. WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE (WPW) SYNDROME In WPW an accessory conduction pathway is present between the atria and the ventricles. Electrical impulses may be rapidly conducted to the ventricles. These rapid impulses create a slurring of the initial portion of the QRS; the slurred effect is called a delta wave. Depends on rate of underlying rhythm Regular unless associated with A-fib P Waves: Normal (upright and PR Interval: Short ( 0.12 sec) QRS: Wide ( 0.10 sec); delta uniform) unless A fib is present wave present WPW is associated with narrow-complex tachycardias, including A-flutter and A-fib.
14 Chapter 4 Atrial Arrhythmias 33 ECG PRACTICE STRIPS For instructions on analyzing these practice strips, please see the guidelines given at the end of Chapter 2. ECG 4 1 ECG 4 2 ECG 4 3
15 34 ECG Success ECG 4 4 ECG 4 5 ECG 4 6
16 Chapter 4 Atrial Arrhythmias 35 ECG 4 7 ECG 4 8 ECG 4 9
17 36 ECG Success Answers to Chapter 4 ECG PRACTICE STRIPS ECG bpm Regular P Waves: Buried in T waves PR Interval: Not possible to measure QRS: 0.08 sec Supraventricular tachycardia ECG bpm Regular P Waves: Flutter waves PR Interval: Not possible to measure QRS: 0.10 sec Atrial flutter with 3:1 block (every third flutter wave is buried in the QRS) ECG bpm Regular P Waves: Not clearly visible PR Interval: Not measurable QRS: 0.08 sec Supraventricular tachycardia with ST segment depression ECG bpm Irregular P Waves: Buried in T waves in beats 1 through 10, normal in beats 11 through 14 PR Interval: None in beats 1 through 10, 0.16 sec in beats 11 through 14 QRS: 0.10 sec Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (supraventricular tachycardia converting to normal sinus rhythm) ECG bpm Irregular P Waves: None PR Interval: None QRS: 0.10 sec Atrial fibrillation ECG bpm Irregular P Waves: Normal PR Interval: 0.20 sec QRS: 0.08 sec Sinus bradycardia with two PACs at beats 2 and 4 ECG bpm Regular P Waves: Flutter waves PR Interval: Not possible to measure QRS: 0.20 sec with notched appearance Atrial flutter with a bundle branch block ECG bpm Irregular P Waves: None PR Interval: None QRS: 0.08 sec Atrial fibrillation ECG bpm Irregular P Waves: Normal in first three beats PR Interval: 0.16 sec in first three beats QRS: 0.10 sec Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (sinus bradycardia converting to supraventricular tachycardia)
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University. OBHG Education Subcommittee
 -RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation
 Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Basic Dysrhythmia Interpretation Objectives 2 To understand the Basic ECG To understand the meaning of Dysrhythmia To describe the normal heart conduction system. To describe the normal impulse pathways.
Course Objectives. Proper Lead Placements. Review the ECG print paper. Review the mechanics of the Myocardium. Review basics of ECG Rhythms
 ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
ECG Interpretations Course Objectives Proper Lead Placements Review the ECG print paper Review the mechanics of the Myocardium Review basics of ECG Rhythms How Leads Work The ECG Leads we use are Bipolar
CORONARY ARTERIES. LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral wall of left vent Anterior 2/3 of interventricluar septum R & L bundle branches
 CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
CORONARY ARTERIES RCA Right atrium Right ventricle SA node 55% AV node 90% Posterior wall of left ventricle in 90% Posterior third of interventricular septum 90% LAD Anterior wall of the left vent Lateral
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
ECG Interpretation. Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry. Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services
 ECG Interpretation Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the electrical conduction pathway in
ECG Interpretation Introduction to Cardiac Telemetry Michael Peters, RN, CCRN, CFRN CALSTAR Air Medical Services Disclosures Nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the electrical conduction pathway in
CRC 431 ECG Basics. Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C
 CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
CRC 431 ECG Basics Bill Pruitt, MBA, RRT, CPFT, AE-C Resources White s 5 th ed. Ch 6 Electrocardiography Einthoven s Triangle Chest leads and limb leads Egan s 10 th ed. Ch 17 Interpreting the Electrocardiogram
EKG Competency for Agency
 EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
EKG Competency for Agency Name: Date: Agency: 1. The upper chambers of the heart are known as the: a. Atria b. Ventricles c. Mitral Valve d. Aortic Valve 2. The lower chambers of the heart are known as
Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is greater than 100 bpm (usually between bpm).
 Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
Sinus Bradycardia Regularity: The R-R intervals are constant; the rhythm is regular. Rate: The atrial and ventricular rates are equal; heart rate is less than 60 bpm. P wave: There is a uniform P wave
COURSE DESCRIPTION. Rev 2.0 7/2013. Page 1 of 26
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Ventricular dysrhythmias (arrhythmias) are unique and potentially dangerous cardiac rhythms. They are often associated with Code Blue calls, and life and death situations. The only two
COURSE DESCRIPTION Ventricular dysrhythmias (arrhythmias) are unique and potentially dangerous cardiac rhythms. They are often associated with Code Blue calls, and life and death situations. The only two
2017 BDKA Review. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation 1/1/2017
 1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation
 PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation Introduction Activity Summary Target Audience Educational Objectives Nursing Educational Objective Faculty Physician Continuing Medical Education Nursing
PACIFIC MEDICAL TRAINING Arrhythmia Interpretation Introduction Activity Summary Target Audience Educational Objectives Nursing Educational Objective Faculty Physician Continuing Medical Education Nursing
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms
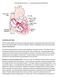 Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
Arrhythmia Study Guide 3 Junctional and Ventricular Rhythms JUNCTIONAL RHYTHMS The AV Junction (Bundle of His and surrounding cells) only acts as pacemaker of the heart when the SA Node is not firing normally
Basic EKG Interpretation. Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT
 Basic EKG Interpretation Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT Electrocardiogram (EKG) Using surface electrodes record the electrical activity of the heart electrical activity (usually) correlates to mechanical function
Basic EKG Interpretation Nirja Parikh, PT, DPT Electrocardiogram (EKG) Using surface electrodes record the electrical activity of the heart electrical activity (usually) correlates to mechanical function
TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT
 Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-ecgs-made-easy-5thedition-by-aehlert/ TEST BANK FOR ECGS MADE EASY 5TH EDITION BY AEHLERT Chapter 5 TRUE/FALSE 1. The AV junction consists
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance
 Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
Confirming Pages ECG Interpretation and Clinical Significance Chapter Outline 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 5.8 5.9 5.10 Learning Outcomes Key Terms Introduction (p. 114) Identifying the Components of the
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2
8/20/2012. Learning Outcomes (Cont d)
 1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
1 2 3 4 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 7: Junctional Dysrhythmias Learning Outcomes 7.1 Describe the various junctional dysrhythmias 7.2 Identify premature junctional complexes
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด
 Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Ambulatory Electrocardiography. Holter Monitor Electrocardiography
 Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography Edward K. Chung Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography With 152 Electrocardiograms Springer-Verlag New York
Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography Edward K. Chung Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography With 152 Electrocardiograms Springer-Verlag New York
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 9.1 Describe the various ventricular dysrhythmias 9.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 9: Ventricular Dysrhythmias 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 9.1 Describe the various ventricular dysrhythmias 9.2
EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Intermediate Tips, tricks, tools Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION
 BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
BEDSIDE ECG INTERPRETATION Presented by: Ryan Dean, RN, MSN, CCRN, CCNS, CFRN Flight Nurse 2017 Based on presentations originally by Gennifer DePaoli, RN Objectives Hospital policies Electrical conduction
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep
 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
MA-1600: EKG - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM FUNDAMENTALS
 MA-1600: EKG - Electrocardiogram Fundamentals 1 MA-1600: EKG - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM FUNDAMENTALS Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:MA-1600 : EKG - Electrocardiogram Fundamentals Board of Trustees: May 2018
MA-1600: EKG - Electrocardiogram Fundamentals 1 MA-1600: EKG - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM FUNDAMENTALS Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:MA-1600 : EKG - Electrocardiogram Fundamentals Board of Trustees: May 2018
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction
 How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Lake EMS Basic EKG Review: Atrial Rhythms. The Lake EMS Quality Development Team
 Lake EMS Basic EKG Review: Atrial Rhythms The Lake EMS Quality Development Team This program is the Intellectual Property of Lake Emergency Medical Services Use of this program is limited to training and
Lake EMS Basic EKG Review: Atrial Rhythms The Lake EMS Quality Development Team This program is the Intellectual Property of Lake Emergency Medical Services Use of this program is limited to training and
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE. Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology
 PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
ABCs of ECGs. Shelby L. Durler
 ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
ABCs of ECGs Shelby L. Durler Objectives Review the A&P of the cardiac conduction system Placement and obtaining 4-lead and 12-lead ECGs Overview of the basics of ECG rhythm interpretation Intrinsic
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture.
 PATHWAYS AROUND THE PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM INTERPRETATION Donald D. Brown, MD April 4, 2019 I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture. OBJECTIVES FOR PATHWAYS AROUND PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM
PATHWAYS AROUND THE PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM INTERPRETATION Donald D. Brown, MD April 4, 2019 I have no conflicts of interest relative to this lecture. OBJECTIVES FOR PATHWAYS AROUND PITFALLS OF EKG RHYTHM
EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam
 as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
as EKG Rhythm Interpretation Exam Name: Date: ID# Unit Assume each strip is a 6 second strip. Passing is 80%. 1. Identify the following rhythm: a. Asystole b. Ventricular fibrillation c. Atrial fibrillation
CSI Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment
 CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
CSI 202 - Skills Lab #5: Arrhythmia Interpretation and Treatment Origins of the ACLS Approach: CSI 202 - Skills Lab 5 Notes ACLS training originated in Nebraska in the early 1970 s. Its purpose was to
PA-1350: ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
 PA-1350: Electrocardiography 1 PA-1350: ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:PA-1350 : Electrocardiography Board of Trustees: 2015-05-28 Academic Term: 2015-08-24 Subject Code PA - Physician
PA-1350: Electrocardiography 1 PA-1350: ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY Cuyahoga Community College Viewing:PA-1350 : Electrocardiography Board of Trustees: 2015-05-28 Academic Term: 2015-08-24 Subject Code PA - Physician
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD
 KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD 1. DISCIPLINE AND COURSE NUMBER: HCRS C255 2. COURSE TITLE: Basic Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation 3. SHORT BANWEB TITLE:
KERN COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT CERRO COSO COLLEGE HCRS C255 COURSE OUTLINE OF RECORD 1. DISCIPLINE AND COURSE NUMBER: HCRS C255 2. COURSE TITLE: Basic Cardiac Rhythm Interpretation 3. SHORT BANWEB TITLE:
4/14/15 HTEC 91. Topics for Today. Guess That Rhythm. Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms
 4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 10: Pacemaker Rhythms and Bundle Branch Block Learning Outcomes 10.1 Describe the various pacemaker rhythms. 10.2
Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Reading Assignment. Chapter 5 (p17-30)
 Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/AV Blocks Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P
 Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Northwest Community Healthcare Paramedic Education Program AV Conduction Defects/ Connie J. Mattera, M.S., R.N., EMT-P Reading assignments: Bledsoe Vol. 3: pp. 88-93; 120-121 (atropine, norepinephrine,
Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP
 What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6,
 ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
Ronald J. Kanter, MD Director, Electrophysiology Miami Children s Hospital Professor Emeritus, Duke University Miami, Florida
 S306- Pediatric Electrocardiography: A Potpourri Ronald J. Kanter, MD Director, Electrophysiology Miami Children s Hospital Professor Emeritus, Duke University Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
S306- Pediatric Electrocardiography: A Potpourri Ronald J. Kanter, MD Director, Electrophysiology Miami Children s Hospital Professor Emeritus, Duke University Miami, Florida Disclosure of Relevant Relationship
a lecture series by SWESEMJR
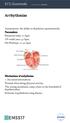 Arrhythmias Automaticity- the ability to depolarize spontaneously. Pacemakers: Sinoatrial node: 70 bpm AV-nodal area: 40 bpm His-Purkinje: 20-40 bpm it Mechanisms of arrhythmias 1. Increased automaticity
Arrhythmias Automaticity- the ability to depolarize spontaneously. Pacemakers: Sinoatrial node: 70 bpm AV-nodal area: 40 bpm His-Purkinje: 20-40 bpm it Mechanisms of arrhythmias 1. Increased automaticity
Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook
 Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook ECG_Notebook_04.27.05 Page 1 of 142 Basic ECG Interpretation Table of Contents Module Objectives... 3 Module Outline... 6 Lesson I... 6 Lesson II... 8 Lesson III...
Basic ECG Interpretation Module Notebook ECG_Notebook_04.27.05 Page 1 of 142 Basic ECG Interpretation Table of Contents Module Objectives... 3 Module Outline... 6 Lesson I... 6 Lesson II... 8 Lesson III...
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
ACLS Study Guide for Precourse Self-Assessment
 20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
20 rhythm strips on Precourse Self-Assessment with the following matching choices: Agonal Rhythm/Asystole Atrial Fibrillation Flutter Ventricular Fibrillation Monomorphic Ventricular Normal Sinus Rhythm
CORONARY ARTERIES HEART
 CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
CARDIAC/ECG MODULE THE HEART CORONARY ARTERIES FIBRILLATING HEART CORONARY ARTERIES HEART PRACTICE RHYTHMS PRACTICE RHYTHMS ELECTRICAL CONDUCTION SA Node (60 100) Primary pacemaker AV Node (40 60) ***Creates
15 16 September Seminar W10O. ECG for General Practice
 15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70. Sinus bradycardia with one ventricular escape (*)
 1? HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70 1 Sinus P waves? 2 sinus cycles The pause (2 sinus cycles) suggests that the sinus fired (?) but did not conduct to the atria (i.e., missing
1? HR: 50 bpm (Sinus) PR: 280 ms QRS: 120 ms QT: 490 ms Axis: -70 1 Sinus P waves? 2 sinus cycles The pause (2 sinus cycles) suggests that the sinus fired (?) but did not conduct to the atria (i.e., missing
CASE 10. What would the ST segment of this ECG look like? On which leads would you see this ST segment change? What does the T wave represent?
 CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
12 Lead ECG Interpretation: The Basics and Beyond
 12 Lead ECG Interpretation: The Basics and Beyond Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS-CC, FNP-BC Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College of Nursing cweston@tamhsc.edu Objectives Review the basics
12 Lead ECG Interpretation: The Basics and Beyond Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS-CC, FNP-BC Assistant Professor Texas A&M University College of Nursing cweston@tamhsc.edu Objectives Review the basics
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8)
 Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs. Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions
 The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
The ABCs of EKGs/ECGs for HCPs Al Heuer, PhD, MBA, RRT, RPFT Professor, Rutgers School of Health Related Professions Learning Objectives Review the basic anatomy of the heart Describe the cardiac conducting
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Cardiac Telemetry Self Study: Part One Cardiovascular Review 2017 THINGS TO REMEMBER
 Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias. Conduction
 Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Complex Arrhythmias: Self Assessment
 Complex Arrhythmias: Self Assessment Edward K. Chung Complex Αrrhéthmiαs: Self Assessment 157 figures, 1985 KARGER Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney Edward K. Chung
Complex Arrhythmias: Self Assessment Edward K. Chung Complex Αrrhéthmiαs: Self Assessment 157 figures, 1985 KARGER Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney Edward K. Chung
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: WPW Revised: 11/2013 Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) is a syndrome of pre-excitation of the
Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology. Cardiac Physiology. Cardiovascular Anatomy
 Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology Part 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia Analysis 1 2 Cardiovascular Anatomy Coronary Circulation Cardiac Physiology The cardiac cycle
Chapter 28, Part 1 Cardiology Part 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy & Physiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia Analysis 1 2 Cardiovascular Anatomy Coronary Circulation Cardiac Physiology The cardiac cycle
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD
 Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Nathan Cade, MD Brandon Fainstad, MD Andrew Prouse, MD OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the basic electrophysiology of the four causes of wide complex tachycardia. 2. Develop a simple framework for acute management
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced. Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA
 2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to disclose
 Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
3. AV Block 1. First-degree AV block 1. Delay in AV node 2. Long PR interval 3. QRS complex follows each P wave 4. Benign, no tx
 1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
1. Rhythms & arrhythmias SA nodal rhythms Sinus rhythm Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Sinus arrhythmia Sick sinus syndrome SA block Sinus arrest AV blocks First-degree Second-degree Mobitz Type I
Basic electrocardiography reading. R3 lee wei-chieh
 Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series
 ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies
 Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
Cardiac Arrhythmias & Drugs used in Advanced Life Support and Cardiac Emergencies CNHE Ballarat Health Services Valid from 1 st March 2016 to 31 st June 2018 1 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) An atrial
RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
PhD FRCP MESC MEAPCI. Consultant Cardiologist SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia. Coronary Arteries
 SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
SVT - Supra Ventricular Tachycardia Coronary Arteries Overview LMS Supraventricular tachycardia is defined as an abnormally fast heartbeat. It's a describes a group of arrhythmias which all originate from
Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner. Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries
 Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner The Rapid Reference Series Books
Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner The Rapid Reference Series Books
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company
 Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks
 Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
Emerg Med Clin N Am 24 (2006) 1 9 Bradydysrhythmias and Atrioventricular Conduction Blocks Jacob W. Ufberg, MD*, Jennifer S. Clark, MD Department of Emergency Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine,
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc.
 Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Cardiac Implanted Electronic Devices Pacemakers, Defibrillators, Cardiac Resynchronization Devices, Loop Recorders, etc. The Miracle of Living February 21, 2018 Matthew Ostrom MD,FACC,FHRS Division of
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology
 Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Conduction disorders
 Conduction disorders L.V. Bogun, N.I. Yabluchansky, F.M. Abdueva, O.Y. Bichkova, A.N. Fomich, P.A. Garkavyi, A.L. Kulik, N.V. Lysenko, N.V. Makienko, L.A. Martimyanova, I.V. Soldatenko, E.E. Tomina Department
Conduction disorders L.V. Bogun, N.I. Yabluchansky, F.M. Abdueva, O.Y. Bichkova, A.N. Fomich, P.A. Garkavyi, A.L. Kulik, N.V. Lysenko, N.V. Makienko, L.A. Martimyanova, I.V. Soldatenko, E.E. Tomina Department
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
