Complex Arrhythmias: Self Assessment
|
|
|
- Amice Silvia Sanders
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Arrhythmias: Self Assessment
2
3 Edward K. Chung Complex Αrrhéthmiαs: Self Assessment 157 figures, 1985 KARGER Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney
4 Edward K. Chung MD, FRCP, FACC, Professor of Medicine, Thomas Jefferson University; Director of the Heart Station, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia, Pa., USA National Library of Medicine, Cataloging in Publication Chung, Edward K. Complex arrhythmias: self assessment/ Edward K. Chung. Basel; New York: Karger, Bibliography: p. includes index. 1. Arrhythmia case studies 2. Electrocardiography case studies I. Title WG 330 C559c ISBN Drug Dosage The author and the publishers have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any change in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be translated into other languages, reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, microcopying, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Copyright 1985 by S. Karger AG, P.O. Box, CH-4009 Basel (Switzerland) Typeset in Hong Kong by Asco Trade Typesetting Limited Printed in Switzerland by Thür AG Offsetdruck, Pratteln ISBN
5 Το my wife, Lisa and my children, Linda and Christopher
6
7 Contents Abbreviations Preface XII XIII Case 1 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block in recent diaphragmatic MI 1 Case 2 Mobitz type II A-V block with intermittent demand pacemaker beats and bifascicular block (RBBB with left anterior hemiblock) 3 Case 3 Sinus rhythm with frequent blocked A-V JPCs or RBs 5 Case 4 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block with a blocked APC 7 Case 5 Sinus rhythm and frequent APCs with aberrant ventricular conduction 9 Case 6 Atrial impure flutter with frequent aberrant ventricular conduction as a result of Ashman's phenomenon 11 Case 7 AF with LBBB 13 Case 8 AF with anomalous A-V conduction in WPW syndrome, type-β 15 Case 9 AF with rapid ventricular response and intermittent LBBB 19 Case 10 Bradycardie-dependent RBBB with partial BFB and possible partial TFB (discussion of ΒΒΒΒ) 21 Case 11 Sinus rhythm with intermittent non-paroxysmal A-V JT producing incomplete A-V dissociation (digitalis-induced) 25 Case 12 Atrial flutter-fibrillation with occasional aberrant ventricular conduction as a result of Ashman's phenomenon 27 Case 13 WPW syndrome, type-a 29 Case 14 Interpolated VPCs with an APC 31 Case 15 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block and blocked reciprocal beats associated with intermittent left anterior hemiblock and Chung's phenomenon (aberrant atrial conduction) 33 Case 16 Sinus tachycardia with 2 : 1 A-V block and a VPC associated with recent diaphragmatic MI 35 Case 17 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm with atrial capture 37 Case 18 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm (over-driving) with Wenckebach ventriculoatńal block 39 Case 19 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm with Wenckebach ventriculoatríal block and frequent reciprocal beats 41 Case 20 Sinus rhythm with frequent VPCs causing ventricular trigeminy and LBBB 43 Case 21 Sinus rhythm with 2 : 1 A-V block (intra-his block) 45 Case 22 Sinus rhythm with frequent blocked APCs 47 Case 23 AF with A-V JER due to complete A-V block as a result of digitalis intoxication 49 Case 24 Atrial flutter with 2 :1 A-V response 51 Case 25 Sinus rhythm with paroxysmal atrial tachycardia 53 Case 26 Atrial flutter with 2 : 1 A-V conduction and RBBB associated with pulmonary embolism 55 Case 27 Atrial flutter with 3 :1 A-V block 57 Case 28 Atrial tachycardia with non-paroxysmal A-V JT producing complete A-V dissociation in DI. 59 Case 29 Sinus bradycardie with intermittent A-V JER producing incomplete A-V dissociation due to SSS 61 Case 30 A-V JT or reciprocating tachycardia 63 Case 31 Atrial flutter with 2 : 1 A-V conduction associated with recent diaphragmatic and posterior MI 65 VII
8 Contents Case 32 Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MΑT) associated with COPD 67 Case 33 Left atrial rhythm 69 Case 34 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm with 2 : 1 electrical alternans 71 Case 35 Two to one ventricular electrical altemans associated with uremic pericardial effusion 73 Case 36 Sinus rhythm with intermittent RBBB and fixed left anterior hemiblock 75 Case 37 Sinus rhythm with atńal bigeminy and demand ventricular pacemaker escape-bigeminy 77 Case 38 BFB (combination of RBBB and left posterior hemiblock) in cardiomyopathy 79 Case 39 Multifocal atńal tachycardia with a VPC 81 Case 40 Sinus rhythm and atrial bigeminy with tachycardia-dependent RBBB 83 Case 41 Paroxysmal Α-V junctional tachycardia or reciprocating tachycardia with Wenckebach Α-V block in recent diaphragmatic MI 85 Case 42 Sinus rhythm with an APC and intermittent demand pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm associated with BFB (RBBB with LAHB) 87 Case 43 WPW syndrome, type-a 89 Case 44 Atńal flutter-fibrillation with rapid ventricular response associated with diaphragmatic postern-lateral MI 91 Case 45 Sinus tachycardia with BFB (incomplete RΒΒΒ with LAHB) associated with recent posterolateral MI 93 Case 46 Atrial flutter with 2:1 Α-V conduction and recent postern-lateral MI associated with BFB (RBBB with LAHB) 95 Case 47 Sinus bradycardia with intermittent non-paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia associated with recent anteńor MI 97 Case 48 Non-paroxysmal Α-V junctional tachycardia in DI 99 Case 49 Sinus rhythm with LBBB associated with acute diaphragmatic MI 101 Case 50 Sinus rhythm and an interpolated WC with concealed ventriculoatríal conduction 103 Case 51 AF with anomalous A-V conduction in WPW syndrome, type-a 105 Case 52 Sinus rhythm with first degree A-V block and LBBB associated with 2 : 1 electrical alternans. 107 Case 53 Left atrial rhythm associated with BFB (RBBB with LAHB) 109 Case 54 Sinus bradycardia with intermittent demand ventricular pacemaker rhythm and RBBB 111 Case 55 Sinus rhythm with bilateral bundle branch block (RΒΒΒ on one occasion and LBBB on another occasion) 113 Case 56 Sinus tachycardia with 2 : 1 Α-V block associated with acute diaphragmatic MI and old anterior MI 115 Case 57 Sinus rhythm with 4 : 3 Wenckebach A-V block 117 Case 58 Sinus tachycardia and frequent APCs with aberrant ventricular conduction 119 Case 59 LBBB with primary T wave change suggestive of acute anterior MI 121 Case 60 WPW syndrome, type-a, associated with RBBB 123 Case 61 Sinus bradycardia with ventricular parasystole and RBBB 125 Case 62 Sinus bradycardia with A-V junctional parasystole 127 Case 63 Sinus bradycardia with Wenckebach A-V block and occasional A-V junctional escape beats associated with recent diaphragmatic MI 129 Case 64 Ventricular flutter associated with acute anterior MI 131 Case 65 AF with intermittent bidirectional ventricular tachycardia 133 Case 66 SSS manifested by sinus arrest and intermittent A-V junctional escape rhythm 135 Case 67 Sinus rhythm and frequent APCs producing atrial bigeminy with aberrant ventricular conduction associated with BFB (RBBB with left anterior hemiblock) 137 Case 68 Sinus bradycardia and interpolated APCs with aberrant ventricular conduction 139 Case 69 Pulmonary embolism manifested by marked sinus tachycardia with P-pulmonale and right axis deviation as well as posterior axis deviation of the QRS complexes 141 Case 70 Advanced hyperkalemia-induced ECG abnormalities including tall and peaked T waves and RBBB with diffuse intraventricular block along with flat P waves and first degree Α-V block 143 Case 71 Pulmonary embolism manifested by marked sinus tachycardia, APCs, P-pulmonale, RBBB, VIII
9 Contents right axis deviation of the ORS complexes and marked S-T segment depression involving many leads 145 Case 72 WPW syndrome, type-b 147 Case 73 Artifacts due to muscle tremors resembling atrial flutter or runaway artificial pacemaker 149 Case 74 Atrial flutter with Wenckebach A-V response (4 : 1 and 2 : 1 alternating conduction ratios) and RBBB associated with antero-septal MI 151 Case 75 Multifocal atnal tachycardia (MAT) 153 Case 76 AF with BFB (combination of RBBB and left anterior hemiblock) 155 Case 77 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block and frequent reciprocal (echo) beats 157 Case 78 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block and reciprocal beats initiating reciprocating (reentrant) tachycardia 159 Case 79 AF with advanced A-V block causing frequent ventricular escape beats suggestive of SSS 161 Case 80 Sinus rhythm with frequent VPCs producing ventricular bigeminy (descriptions of malignant ventricular arrhythmias) 163 Case 81 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm with dual ventriculoatrial conduction 165 Case 82 Digitalis-induced atrial tachycardia with 6 :1 A-V block and frequent VPCs causing ventricular group beats 167 Case 83 Sinus tachycardia with intermittent LBBB 169 Case 84 Sinus rhythm with intermittent non-paroxysmal A-V junctional tachycardia producing incomplete A-V dissociation in digitalis toxicity 171 Case 85 Non-paroxysmal A-V junctional tachycardia or reciprocating tachycardia 173 Case 86 Sinus rhythm and frequent A-V junctional premature contractions (some aberrantly conducted and some blocked) 175 Case 87 Sinus rhythm and intermittent non-paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia with 3 : 2 Wenckebach exit block 177 Case 88 Sinus rhythm and intermittent reciprocating tachycardia with occasional aberrant ventricular conduction and occasional artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular beats 179 Case 89 Sinus bradycardia with sinus arrest leading to ventricular escape-bígemíny and atrial parasystole in a patient with SSS 181 Case 90 Sinus bradycardia with sinus arrest due to SSS 183 Case 91 A-V junctional escape rhythm 185 Case 92 Sinus rhythm and frequent APCs, some interpolated and some aberrantly conducted 187 Case 93 AF with intermittent accelerated ventricular escape rhythm (intermittent non-paroxysmal ventricular tachycardia) 189 Case 94 Sinus tachycardia with Wenckebach A-V block associated with acute diaphragmatic-lateral MI 191 Case 95 Sinus tachycardia with 4: 3 Wenckebach S-A block 193 Case 96 Sinus tachycardia with advanced Mobitz type II A-V block and LBBB associated with frequent accelerated ventricular escape beats 195 Case 97 WPW syndrome, type A 197 Case 98 WPW syndrome, type A associated with RBBB 199 Case 99 Sinus rhythm with atypical Wenckebach (Mobitz type I) A-V block 201 Case 100 Sinus tachycardia with complete A-V block 203 Case 101 Sinus rhythm with congenital complete A-V block 205 Case 102 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm and intermittent atrial 'capture with Wenckebach ventriculoatrial block and frequent reciprocal beats 207 Case 103 A-V junctional parasystole 209 Case 104 Digitalis-induced atrial tachycardia with 2 :1 A-V block 211 Case 105 Sinus rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block and intermittent reciprocating tachycardia associated with intermittent RBBB 213 Case 106 Sinus rhythm with intermittent fascicular tachycardia producing incomplete A-V dissociation 215 Case 107 Sinus tachycardia with 3 : 2 Wenckebach A-V block and RBBB and aberrant ventricular conduction due to Ashman's phenomenon 217 IX
10 Contents Case 108 Sinus bradycardia with diaphragmatic-postern-lateral MI and RBBB 219 Case 109 Acute extensive anterior MI associated with RBBB and low voltage 221 Case 110 Bifascicular block (RBBB with left posterior hemiblock), tall and peaked T waves, diffuse intraventricular block and flat P waves due to advanced hyperkalemia 223 Case 111 Prolonged Q-T interval due to broad and tall T wave as a result of central nervous system disorder 225 Case 112 Sinus tachycardia with diaphragmatic-postern-lateral MI associated with RBBB and low voltage 227 Case 113 RBBB with left posterior hemiblock in a patient with tetralogy of Fallot 229 Case 114 Sinus tachycardia with 6: 5 Wenckebach A-V block and a ventricular escape beat 231 Case 115 Sinus tachycardia with varying degree A-V block and intermittent non-paroxysmal A-V junctional tachycardia leading to ventricular standstill 233 Case 116 Torsade de pointes (multiformed ventricular tachycardia) in a patient with acute extensive anterior MI 235 Case 117 Chaotic ventricular rhythm (possible ventricular dissociation) 237 Case 118 AF with A-V junctional escape rhythm due to complete A-V block and frequent VPCs in a patient with digitalis intoxication 239 Case 119 Sinus rhythm and A-V junctional escape rhythm with LBBB associated with ventricular bigeminy 241 Case 120 Sinus rhythm with frequent blocked (non-conducted) APCs 243 Case 121 Sinus tachycardia with frequent VPCs producing ventricular bigeminy 245 Case 122 Atrial flutter-fibrillation with occasional aberrant ventricular conduction as a result of Ashman's phenomenon 247 Case 123 Atrial pacing rhythm and RBBB with diaphragmatic and extensive anterior MI associated with post-cardiotomy syndrome 249 Case 124 Sinus rhythm with intermittent RBBB 251 Case 125 RBBB associated with recent diaphragmatic and extensive anterior MI 253 Case 126 AF with very rapid ventricular response 255 Case 127 Supraventńculartachycardia 257 Case 128 Recent diaphragmatic MI associated with LBBB 259 Case 129 Artificial pacemaker-induced ventricular rhythm 3 : 2 Wenckebach ventriculoatńal block and reciprocal beats 261 Case 130 Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) 263 Case 131 Sinus bradycardia with A-V JER producing incomplete A-V dissociation and occasional aberrant ventricular conduction in a patient with DI 265 Case 132 SSS manifested by sinus bradycardia with occasional ventricular escape beats and VPCs 267 Case 133 SSS manifested by marked sinus bradycardia, A-V junctional escape beats as well as ventricular escape beats, and areas of sinus arrest with AF and VPCs leading to brady-tachyarrhythmia 269 Case 134 SSS manifested by sinus bradycardia, with first degree A-V block, and frequent VPCs with ventricular tachycardia leading to brady-tachyarrhythmia 271 Case 135 SSS manifested by type II S-A block 273 Case 136 SSS manifested by marked sinus bradycardia, S-A block (type II), and frequent ventricular escape beats associated with LBBB 275 Case 137 Sinus rhythm with intermittent LBBB and occasional APCs 277 Case 138 Sinus rhythm with frequent VPCs leading to ventricular trígeminy and intermittent LBBB 279 Case 139 Sinus arrhythmia with intermittent WPW syndrome 281 Case 140 Sinus rhythm with intermittent LBBB 283 Case 141 Sinus rhythm with intermittent non-paroxysmal A-V junctional tachycardia producing incomplete A-V dissociation and occasional aberrant ventricular conduction in a patient with DI 285 Case 142 A-V junctional escape rhythm with Wenckebach A-V block and frequent reciprocal beats 287 Case 143 Sinus tachycardia with 5 : 4 Wenckebach A-V block associated with acute diaphragmatic MI 289 Case 144 Sinus bradycardia with A-V junctional escape-bigeminy and BFB consisting of RBBB and left anteńor hemiblock 291 Χ
11 Contents Case 145 Digitalis-induced AF with bidirectional ventricular tachycardia 293 Case 146 Digitalis-induced double A-V junctional escape rhythms and a reciprocal beat producing incomplete A-V dissociation 295 Case 147 Malfunctioning pacemaker manifested by runaway pacemaker 297 Case 148 Malfunctioning pacemaker manifested by extremely rapid pacing rate (runaway pacemaker) with pre-existing complete A-V block 299 Case 149 Malfunctioning pacemaker manifested by slow and irregular pacing 301 Case 150 Atrial flutter with A-V junctional escape rhythm due to complete A-V block 303 Suggested Readings 305 Subject Index 307 XI
12 Abbreviations AF Atrial fibrillation LAHB Left anterior hemibiock AMI Anterior myocardial infarction LBBB Left bundle branch block APC Atrial premature contraction LPHB Left posterior hemfibluck AT Atrial tachycardia LVH Left ventricular hypertrophy A-V Atrioventrícular MI Myocardial infarction ΒΒΒΒ Bilateral bundle branch block MVPS Mitral valve prolapse syndrome BFB Bifascicular block PAT Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia BTS Brady-tachyarrhythmia syndrome RB Reciprocal beat CAD Coronary artery disease RBBB Right bundle branch block CCU Coronary care unit RVH Right ventricular hypertrophy CHF Congestive heart failure S-A Sino-atrial CNS disorder Central nervous system disorder SSS Sick sinus syndrome COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease TFB Trifascicular block DC shock Direct current shock VΕΒ Ventricular escape beat ER Emergency room VER Ventricular escape rhythm JEB Junctional escape beat VF Ventricular fibrillation JER Junctional escape rhythm VPC Ventricular premature contraction JPC Junctional premature contraction VT Ventricular tachycardia JT Junctional tachycardia WPW syndrome Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome XII
13 Preface It is not my intention to describe every aspect of ECG abnormalities and cardiac arrhythmias. Rather, the primary intention is to include all ECG tracings showing relatively common ECG abnormalities and somewhat complex cardiac arrhythmias which are frequently encountered in our medical practice. Thus, the book is written primarily for busy practicing physicians including family physicians, internists, cardiologists, emergency room physicians and medical house officers as well as cardiology fellows. In addition, medical students, cardiac care nurses and anesthesiologists will obtain great benefit by reading this book. The secretarial activity was carried out cheerfully by Ms. Michele Harvey, the personal secretary to the author. Her able assistance and efforts have been most valuable in the completion of this book. It has been my pleasure to share the work to complete this valuable book with the staff of S. Karger Publishers. Lastly, I will always owe deep gratitude and appreciation to my father, Dr. Il-Chun Chung, who has always provided guidance and inspiration for me. Bryn Mawr, Pa. Edward K. Chung, MD XIII
14
Ambulatory Electrocardiography. Holter Monitor Electrocardiography
 Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography Edward K. Chung Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography With 152 Electrocardiograms Springer-Verlag New York
Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography Edward K. Chung Ambulatory Electrocardiography Holter Monitor Electrocardiography With 152 Electrocardiograms Springer-Verlag New York
Please check your answers with correct statements in answer pages after the ECG cases.
 ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
ECG Cases ECG Case 1 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature 2018 S. Okutucu, A. Oto, Interpreting ECGs in Clinical Practice, In Clinical Practice, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-90557-0
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis
 Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
Appendix D Output Code and Interpretation of Analysis 8 Arrhythmia Code No. Description 8002 Marked rhythm irregularity 8110 Sinus rhythm 8102 Sinus arrhythmia 8108 Marked sinus arrhythmia 8120 Sinus tachycardia
402 Index. B β-blockers, 4, 5 Bradyarrhythmias, 76 77
 Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), 126, 163 Action potentials, 1, 5, 27 Acute coronary syndromes, 123t, 129 Adenosine, intravenous, 277 Alcohol abuse, as T wave inversion cause, 199 Aneurysm,
Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), 126, 163 Action potentials, 1, 5, 27 Acute coronary syndromes, 123t, 129 Adenosine, intravenous, 277 Alcohol abuse, as T wave inversion cause, 199 Aneurysm,
Electrical System Overview Electrocardiograms Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning Values To Memorize Calculating Rates
 Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
Electrocardiograms Electrical System Overview James Lamberg 2/ 74 Action Potentials 12-Lead Positioning 3/ 74 4/ 74 Values To Memorize Inherent Rates SA: 60 to 100 AV: 40 to 60 Ventricles: 20 to 40 Normal
Cardiology Flash Cards
 Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Cardiology Flash Cards EKG in a nut shell www.brain101.info Conduction System www.brain101.info 2 Analyzing EKG Step by step Steps in Analyzing ECG'S 1. Rhythm: - Regular _ Sinus, Junctional or Ventricular.
Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC
 Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC Consultant Interventional Cardiology & Structural Heart Disease Department of Medicine Sultan Qaboos University Hospital hatim.al.lawati@gmail.com April 2017
Hatim Al Lawati. MD, FRCPC, DABIM(CV), FACC Consultant Interventional Cardiology & Structural Heart Disease Department of Medicine Sultan Qaboos University Hospital hatim.al.lawati@gmail.com April 2017
Arrhythmic Complications of MI. Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine
 Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Arrhythmic Complications of MI Teferi Mitiku, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California Irvine Objectives Brief overview -Pathophysiology of Arrhythmia ECG review of typical
Supraventricular Arrhythmias. Reading Assignment. Chapter 5 (p17-30)
 Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
Supraventricular Arrhythmias Reading Assignment Chapter 5 (p17-30) The Supraventricular Rhythms In Our Lives Site of Origin Single Events Slow Rates Intermediate Rates Fast Rates (>100 bpm) Sinus Sinus
12-Lead ECG Interpretation. Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP
 12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
12-Lead ECG Interpretation Kathy Kuznar, RN, ANP The 12-Lead ECG Objectives Identify the normal morphology and features of the 12- lead ECG. Perform systematic analysis of the 12-lead ECG. Recognize abnormalities
15 16 September Seminar W10O. ECG for General Practice
 15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
15 16 September 2012 Seminar W10O ECG for General Practice Speaker: Ms Natasha Eaton ECG for General Practice Speaker: Natasha Eaton Cardiac CNC Executive Representative Electrocardiography The graphic
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University. OBHG Education Subcommittee
 -RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
-RHYTHM PRACTICE- By Dr.moanes Msc.cardiology Assistant Lecturer of Cardiology Al Azhar University The Normal Conduction System Sinus Node Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia
ECG Interpretation Made Easy
 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG Interpretation Made Easy Dr. A Tageldien Abdellah, MSc MD EBSC Lecturer of Cardiology- Hull University Hull York Medical School 2007-2008 ECG Interpretation Made Easy Synopsis Benefits Objectives Process
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH
 ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
ECG ABNORMALITIES D R. T AM A R A AL Q U D AH When we interpret an ECG we compare it instantaneously with the normal ECG and normal variants stored in our memory; these memories are stored visually in
REtrive. REpeat. RElearn Design by. Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book
 Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning Test-Enhanced Learning based ECG practice E-book REtrive REpeat RElearn Design by S I T T I N U N T H A N G J U I P E E R I Y A W A
Chapter 2 Practical Approach
 Chapter 2 Practical Approach There are beginners in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis who are fascinated by a special pattern (e.g., a bundle-branch block or a striking Q wave) and thereby overlook other
Chapter 2 Practical Approach There are beginners in electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis who are fascinated by a special pattern (e.g., a bundle-branch block or a striking Q wave) and thereby overlook other
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction
 How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
How To Think About Rhythms and Conduction Frank Yanowitz, MD Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) University of Utah School of Medicine Medical Director, IHC ECG Services Intermountain Healthcare http://ecg.utah.edu
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias. Conduction
 Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Conduction Problems / Arrhythmias Conduction Wolf-Parkinson White Syndrome (WPW) and Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL): Atrial impulses bypass the AV node through an accessory pathway or bypass tract (bundle of
Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG?
 Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG? The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic
Reading Assignment (p1-91 in Outline ) Objectives What s in an ECG? The 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic
Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner. Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries
 Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner The Rapid Reference Series Books
Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner Maureen McMichael Ryan Fries Life-Threatening Cardiac Emergencies for the Small Animal Practitioner The Rapid Reference Series Books
Blocks & Dissociations. Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline )
 Blocks & Dissociations Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline ) Objectives Who are Wenckebach and Mobitz? Review SA and AV Blocks AV Dissociations: learning who s the boss and why 2 nd degree SA Block:
Blocks & Dissociations Reading Assignment (p47-52 in Outline ) Objectives Who are Wenckebach and Mobitz? Review SA and AV Blocks AV Dissociations: learning who s the boss and why 2 nd degree SA Block:
Karger Basel München Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore -Tokyo Sydney
 22 Progress in Respiration Research Editor: H. Herzog A. Zapletal, M. Šamánek, T. Paul Lung Function in Children and Adolescents Lung Function in Children and Adolescents Progress in Respiration Research
22 Progress in Respiration Research Editor: H. Herzog A. Zapletal, M. Šamánek, T. Paul Lung Function in Children and Adolescents Lung Function in Children and Adolescents Progress in Respiration Research
, David Stultz, MD.
 http://www.dilbert.com EKG Rounds Handouts available at http://www.drstultz.com January 5, 2004 David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 Overview of Topics How to read an EKG Normal EKG Determination
http://www.dilbert.com EKG Rounds Handouts available at http://www.drstultz.com January 5, 2004 David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY 4 Overview of Topics How to read an EKG Normal EKG Determination
Diploma in Electrocardiography
 The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
The Society for Cardiological Science and Technology Diploma in Electrocardiography The Society makes this award to candidates who can demonstrate the ability to accurately record a resting 12-lead electrocardiogram
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
1 st Degree Block Prolonged P-R interval caused by first degree heart block (lead II)
 AV Heart Blocks 1 st degree A condition of a rhythm, not a true rhythm Need to always state underlying rhythm 2 nd degree Type I - Wenckebach Type II Classic dangerous to the patient Can be variable (periodic)
AV Heart Blocks 1 st degree A condition of a rhythm, not a true rhythm Need to always state underlying rhythm 2 nd degree Type I - Wenckebach Type II Classic dangerous to the patient Can be variable (periodic)
ECG Interactive Session
 SA HEART 2018 PRE-CONGRESS WORKSHOP 4 OCTOBER 2018 ECG Interactive Session Ashley Chin Cardiologist/Electrophysiologist University of Cape Town Groote Schuur Hospital ECG 1 Which ONE of the following is
SA HEART 2018 PRE-CONGRESS WORKSHOP 4 OCTOBER 2018 ECG Interactive Session Ashley Chin Cardiologist/Electrophysiologist University of Cape Town Groote Schuur Hospital ECG 1 Which ONE of the following is
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know. Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series
 ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
ECGs: Everything a finalist needs to know Dr Amy Coulden As part of the Simply Finals series Aims and objectives To be able to interpret basic ECG abnormalities To be able to recognise commonly tested
1/22/2007 Fernald Medical Monitoring Program Sort Code EKG coding
 1/22/2007 Fernald Medical Monitoring Program Sort Code EKG coding PLEASE NOTE THAT ALL EKG CODES MUST RANGE FROM 500-599 OR FROM 900-999. PLEASE DO NOT ASSIGN NUMBERS OUTSIDE THAT RANGE FOR EKG CODES.
1/22/2007 Fernald Medical Monitoring Program Sort Code EKG coding PLEASE NOTE THAT ALL EKG CODES MUST RANGE FROM 500-599 OR FROM 900-999. PLEASE DO NOT ASSIGN NUMBERS OUTSIDE THAT RANGE FOR EKG CODES.
Rhythm ECG Characteristics Example. Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR)
 Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Rate: 60-100 per minute Rhythm: R- R = P waves: Upright, similar P-R: 0.12-0.20 second & consistent P:qRs: 1P:1qRs Sinus Tachycardia Exercise Hypovolemia Medications Fever Substances
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley Content Basic ECG interpretation pattern Some common (examined) abnormalities Presenting ECGs in context Setting up an ECG Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space
December 2018 Tracings
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline
 Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
Miscellaneous Stuff Keep reading the Outline Welcome to the 5-Step Method ECG #: Mearurements: Rhythm (s): Conduction: Waveform: Interpretation: A= V= PR= QRS= QT= Axis= 1. Compute the 5 basic measurements:
17w Dandy Walker Syndrome
 17w Dandy Walker Syndrome Anthony J. Raimondi Kiyoshi Sato Takeyoshi Shimoji The JJrnidy-W«lλ er Sωίdrοme 13 figures and 6 tables, 1984 KARGER S. Karger Basel München Paris London New York Tokyo Sydney
17w Dandy Walker Syndrome Anthony J. Raimondi Kiyoshi Sato Takeyoshi Shimoji The JJrnidy-W«lλ er Sωίdrοme 13 figures and 6 tables, 1984 KARGER S. Karger Basel München Paris London New York Tokyo Sydney
ECG Cases and Questions. Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology
 ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
ECG Cases and Questions Ashish Sadhu, MD, FHRS, FACC Electrophysiology/Cardiology 32 yo female Life Insurance Physical 56 yo male with chest pain Terminology Injury ST elevation Ischemia T wave inversion
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016
 Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation & UPMC 43rd Refresher Course in Family Medicine CME Conference March 10-13, 2016 Disclosures: EKG Workshop Louis Mancano, MD Speaker has no disclosures
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology
 Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Huseng Vefali MD St. Luke s University Health Network Department of Cardiology Learning Objectives Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Review Essential Cases for Paramedics and first responders
Section V. Objectives
 Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
Section V Landscape of an MI Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation Demonstrate the process for determining
The Electrocardiogram part II. Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD
 The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
The Electrocardiogram part II Dr. Adelina Vlad, MD PhD Basic Interpretation of the ECG 1) Evaluate calibration 2) Calculate rate 3) Determine rhythm 4) Determine QRS axis 5) Measure intervals 6) Analyze
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced. Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA
 2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
2017 EKG Workshop Advanced Family Medicine Review Course Lou Mancano, MD, FAAFP Reading Health System Family and Community Medicine Reading, PA Part II - Objective Describe a useful approach to interpreting
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด
 Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Cardiac Arrhythmia How to approach นพ.พ น จ แกวส วรรณะ หน วยโรคห วใจและหลอดเล อด EKG paper is a grid where time is measured along the horizontal axis. Each small square is 1 mm in length and represents
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director
 December 2018 ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director To obtain best results Select Slide Show from the ribbon at the top of your PowerPoint screen Select From Beginning on the
December 2018 ECG Underwriting Puzzler Dr. Regina Rosace AVP & Medical Director To obtain best results Select Slide Show from the ribbon at the top of your PowerPoint screen Select From Beginning on the
SIMPLY ECGs. Dr William Dooley
 SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
SIMPLY ECGs Dr William Dooley 1 No anatomy just interpretation 2 Setting up an ECG 3 Setting up an ECG 1 V1-4 th Right intercostal space at sternal border 2 V2-4 th Left intercostal space at sternal border
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series
 ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECG Basics Sonia Samtani 7/2017 UCI Resident Lecture Series Agenda I. Introduction II.The Conduction System III.ECG Basics IV.Cardiac Emergencies V.Summary The Conduction System Lead Placement avf Precordial
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009
 Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
Rate Rhythm Intervals Hypertrophy ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2009 Axis Jess (Fogler) Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Ischemia Overview
ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1:
 ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1: The first 20 strips are for teaching various abnormalities of the morphology of the waves of the ECG. Strips 21 and following are for teaching some abnormalities
ECG Practice Strips Discussion part 1: The first 20 strips are for teaching various abnormalities of the morphology of the waves of the ECG. Strips 21 and following are for teaching some abnormalities
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1
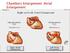 If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
If the P wave > 0.12 sec( 3 mm) usually in any lead. Notched P wave usually in lead I,aVl may be lead II Negative terminal portion of P wave in V1, 1 mm depth and 3 mm width( most specific) Since Mitral
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW
 UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
UNDERSTANDING YOUR ECG: A REVIEW Health professionals use the electrocardiograph (ECG) rhythm strip to systematically analyse the cardiac rhythm. Before the systematic process of ECG analysis is described
Acute Coronary Syndromes Unstable Angina Non ST segment Elevation MI (NSTEMI) ST segment Elevation MI (STEMI)
 Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CSC, PCCN-CMC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Objectives Evaluate common abnormalities that mimic myocardial infarction. Identify
Intermediate ECG Course - Part 4. Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STVAHCS
 Intermediate ECG Course - Part 4 Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STVAHCS Topics in Intermediate ECG Consolidation of prior information with additional details Not advanced, but feel free to ask advanced
Intermediate ECG Course - Part 4 Joe M. Moody, Jr, MD UTHSCSA and STVAHCS Topics in Intermediate ECG Consolidation of prior information with additional details Not advanced, but feel free to ask advanced
Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II
 Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Bundle-branch blocks Understanding the 12-lead ECG, part II Most common electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormality Appears as a wider than normal S complex Occurs when one of the two bundle branches can t conduct
Step by step approach to EKG rhythm interpretation:
 Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
Sinus Rhythms Normal sinus arrhythmia Small, slow variation of the R-R interval i.e. variation of the normal sinus heart rate with respiration, etc. Sinus Tachycardia Defined as sinus rhythm with a rate
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6,
 ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
ECG S: A CASE-BASED APPROACH December 6, 2018 1 Faculty Disclosure Faculty: Lorne Gula MD, FRCPC Professor, Western University Cardiologist, Hearth Rhythm Specialist Director, Electrophysiology Laboratory,
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE. Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology
 PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
PATIENT WITH ARRHYTHMIA IN DENTIST S OFFICE Małgorzata Kurpesa, MD., PhD. Chair&Department of Cardiology Medical University of Łódź The heart is made up of four chambers Left Atrium Right Atrium Left Ventricle
at least 4 8 hours per week
 ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
ECG IN ATHLETS An athlete is defined as an individual who engages in regular exercise or training for sport or general fitness, typically with a premium on performance, and often engaged in individual
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse
 Neurobiology of Drug Abuse Monographs in Neural Sciences Vol. 13 Series Editor Maynard M. Cohen, Chicago, Ill. KARGER Basel Miinchen. Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney Neurobiology
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse Monographs in Neural Sciences Vol. 13 Series Editor Maynard M. Cohen, Chicago, Ill. KARGER Basel Miinchen. Paris London New York New Delhi Singapore Tokyo Sydney Neurobiology
ΔΙΑΤΑΡΑΧΕΣ ΕΝΔΟΚΟΙΛΙΑΚΗΣ ΑΓΩΓΙΜΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Δ. ΜΑΝΩΛΑΤΟΣ Β ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Γ.Ν.Α.
 ΔΙΑΤΑΡΑΧΕΣ ΕΝΔΟΚΟΙΛΙΑΚΗΣ ΑΓΩΓΙΜΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Δ. ΜΑΝΩΛΑΤΟΣ Β ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Γ.Ν.Α. «ΕΥΑΓΓΕΛΙΣΜΟΣ» Intraventricular conduction delay and Blocks Right Bundle Branch
ΔΙΑΤΑΡΑΧΕΣ ΕΝΔΟΚΟΙΛΙΑΚΗΣ ΑΓΩΓΙΜΟΤΗΤΑΣ ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Δ. ΜΑΝΩΛΑΤΟΣ Β ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΙΚΗ ΚΛΙΝΙΚΗ ΕΡΓΑΣΤΗΡΙΟ ΗΛΕΚΤΡΟΦΥΣΙΟΛΟΓΙΑΣ Γ.Ν.Α. «ΕΥΑΓΓΕΛΙΣΜΟΣ» Intraventricular conduction delay and Blocks Right Bundle Branch
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep
 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Only 53 Slides! Gauresh H Kashyap, MD, FACP, FCCP, FAASM 1 2 Cardiac Arrhythmias in Sleep Out of 400 Patients with OSA, 48% had some Arrhythmias 20% - 2 PVCs/min 7% - Bradycardia
National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8)
 Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
Page 1 of 12 Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services National Coverage Determination (NCD) for Cardiac Pacemakers (20.8) Tracking Information Publication Number 100-3 Manual Section Number 20.8 Manual
General Introduction to ECG. Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline )
 General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
General Introduction to ECG Reading Assignment (p2-16 in PDF Outline ) Objectives 1. Practice the 5-step Method 2. Differential Diagnosis: R & L axis deviation 3. Differential Diagnosis: Poor R-wave progression
4/14/15 HTEC 91. Topics for Today. Guess That Rhythm. Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) Ventricular Rhythms
 4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
4/14/15 Topics for Today HTEC 91 Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 5 Ventricular Rhythms PVCs: Premature Ventricular Contractions VT: Ventricular Tachycardia VF: Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole Study
Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to disclose
 Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
Valerie A Schroeder MD MS Assistant Professor University of Kansas Medical Center READING THE WAVES- THE HEART S ELECTRICAL MESSAGE FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE Dr. Schroeder has no financial relationships to
Return to Basics. ECG Rate and Rhythm. Management of the Hospitalized Patient September 25, 2009
 Management of the Hospitalized Patient September 25, 2009 ECG Refresher and Update 2009 Return to Basics Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare with
Management of the Hospitalized Patient September 25, 2009 ECG Refresher and Update 2009 Return to Basics Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare with
Basic electrocardiography reading. R3 lee wei-chieh
 Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Basic electrocardiography reading R3 lee wei-chieh The Normal Conduction System Lead Placement avf Limb Leads Precordial Leads Interpretation Rate Rhythm Interval Axis Chamber abnormality QRST change What
Section 3 and 4. Objectives. Bundle Branches 10/9/2018. LBBB, RBBB Bifascicular, Trifascicular Block
 Section 3 and 4 LBBB, RBBB Bifascicular, Trifascicular Block Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation
Section 3 and 4 LBBB, RBBB Bifascicular, Trifascicular Block Objectives At the conclusion of this presentation the participant will be able to Outline a systematic approach to 12 lead ECG interpretation
Return to Basics. Normal Intervals & Axes. ECG Rate and Rhythm
 Return to Basics Management of the Hospitalized Patient October 15, 2010 ECG Refresher and Update 2010 Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare with
Return to Basics Management of the Hospitalized Patient October 15, 2010 ECG Refresher and Update 2010 Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare with
Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2018) 15: 193 198 2018 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Case Report Open Access Repetitive narrow QRS tachycardia in a 61-year-old female patient with recent palpitations
Return to Basics. ECG Rate and Rhythm. Management of the Hospitalized Patient October 4, 2007
 Management of the Hospitalized Patient October 4, 2007 ECG Refresher for the Hospitalists Return to Basics Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare
Management of the Hospitalized Patient October 4, 2007 ECG Refresher for the Hospitalists Return to Basics Determine rate and rhythm Determine intervals and axes Define morphology of P-QRS-T-U Compare
China's Sports Medicine
 China's Sports Medicine Medicine and Sport Science Founder and Editor from 1969 to 1984 E. Jokl, Lexington, Ky. Vol. 28 Series Editors M. Hebbelinck, Brussels R.J. Shephard, Toronto, Ont. KARGDER ΈΜΗ Basel
China's Sports Medicine Medicine and Sport Science Founder and Editor from 1969 to 1984 E. Jokl, Lexington, Ky. Vol. 28 Series Editors M. Hebbelinck, Brussels R.J. Shephard, Toronto, Ont. KARGDER ΈΜΗ Basel
Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk
 1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
1. Periodical Evaluations: each 2 years. Study methodology for screening candidates to athletes risk 2. Personal history: Personal history of murmur in childhood; dizziness, syncope, palpitations, intolerance
PATIENT S NAME, DATE/TIME,
 ECG and Arrhythmias Dec, 1 st 2014 Doctor Mohammad Jarrah References: - Lecture and Slides - ECG Made Easy - Davidson Principles of Medicine - First Aid Cases for the USMLE Step 1 - Mini-OSCE Archive ECG
ECG and Arrhythmias Dec, 1 st 2014 Doctor Mohammad Jarrah References: - Lecture and Slides - ECG Made Easy - Davidson Principles of Medicine - First Aid Cases for the USMLE Step 1 - Mini-OSCE Archive ECG
April 2018 Tracings. Tracing 1 Tracing 4. Tracing 6 Answer. Tracing 4 Answer. Tracing 2 Tracing 5. Tracing 5 Answer.
 Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Tracings Tracing 1 Tracing 4 Tracing 1 Answer Tracing 4 Answer Tracing 2 Tracing 5 Tracing 2 Answer Tracing 5 Answer Tracing 3 Tracing 6 Tracing 3 Answer Tracing 6 Answer Questions? Contact Dr. Nelson
Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia
 British Heart Journal, 197I, 33, 500-504. Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia Uuiversity School of Medicine, Morgantown,
British Heart Journal, 197I, 33, 500-504. Appraisal of mulfifocal atrial tachycardia Edward K. Chung From Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia Uuiversity School of Medicine, Morgantown,
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012
 Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
Overview ECGs and Arrhythmias: Family Medicine Board Review 2012 Jess Waldura, MD University of California, San Francisco walduraj@nccc.ucsf.edu Bundle branch blocks Quick review of ischemia Arrhythmias
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT
 ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
ARRHYTHMIAS IN THE ICU: DIAGNOSIS AND PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT Nora Goldschlager, M.D. MACP, FACC, FAHA, FHRS SFGH Division of Cardiogy UCSF CLINICAL VARIABLES IN ARRHYTHMOGENESIS Ischemia/infarction (scar)
Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances
 Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Complete the following. Chapter 16: Arrhythmias and Conduction Disturbances 1. Cardiac arrhythmias result from abnormal impulse, abnormal impulse, or both mechanisms together. 2. is the ability of certain
Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD
 EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
EKG Conference Ventricular tachycardia Ventricular fibrillation and ICD Samsung Medical Center CCU D.I. Hur Ji Won 2006.05.20 Ventricular tachyarrhythmia ventricular tachycardia ventricular fibrillation
Appendix. Table 1: Causes for abnormal axis deviation Left axis deviation
 Appendix Table 1: Causes for abnormal axis deviation Left axis deviation Normal variant (2 5%) Left anterior fascicular block Left ventricular hypertrophy Inferior wall myocardial infarction Primum atrial
Appendix Table 1: Causes for abnormal axis deviation Left axis deviation Normal variant (2 5%) Left anterior fascicular block Left ventricular hypertrophy Inferior wall myocardial infarction Primum atrial
2017 BDKA Review. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation. Regularity Rate P waves PRI QRS Interpretation 1/1/2017
 1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
1. 2017 BDKA Review 2. 3. 4. Interpretation 5. QT 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. QT 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. QT 19. 20. QT 21. 22. QT 23. 24. Where are pacer spikes? Before the P wave or before the QRS complex?
Ekg pra pr c a tice D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Ekg practice D.HAMMOUDI.MD Anatomy Revisited RCA (Right Coronary Artery) Right ventricle Inferior wall of LV Posterior wall of LV (75%) SA Node (60%) AV Node (>80%) LCA (Left Coronary Artery) Septal wall
Ekg practice D.HAMMOUDI.MD Anatomy Revisited RCA (Right Coronary Artery) Right ventricle Inferior wall of LV Posterior wall of LV (75%) SA Node (60%) AV Node (>80%) LCA (Left Coronary Artery) Septal wall
Paediatric ECG Interpretation
 Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
Paediatric ECG Interpretation Dr Sanj Fernando (thanks to http://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/paediatric-ecginterpretation/) 3 yo boy complaining of abdominal pain and chest pain Child ECG vs Adult
ECG Interpretation. Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction
 ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
ECG to save Babies ECG Interpretation Best to have a system to methodically evaluate ECG (from Dubin) * Rate * Rhythm * Axis * Intervals * Hypertrophy * Infarction Electrical Activity in the heart 5 events
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals. Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Chapter 14 Basic 12-Lead ECG Interpretation 2012 The Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Outcomes 14.1 Discuss the anatomic views seen on a 12-lead
12 Lead ECG Workshop. Virginia Hass, DNP, FNP-C, PA-C Kim Newlin, CNS, ANP-C, FPCNA. California Association of Nurse Practitioners March 18, 2016
 12 Lead ECG Workshop Virginia Hass, DNP, FNP-C, PA-C Kim Newlin, CNS, ANP-C, FPCNA California Association of Nurse Practitioners March 18, 2016 Learning Objectives Identify key changes on the ECG which
12 Lead ECG Workshop Virginia Hass, DNP, FNP-C, PA-C Kim Newlin, CNS, ANP-C, FPCNA California Association of Nurse Practitioners March 18, 2016 Learning Objectives Identify key changes on the ECG which
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH. General. Heart Rate. Starship Children s Health Clinical Guideline
 General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
General Heart Rate QRS Axis T Wave Axis PR Interval according to Heart Rate & Age P Wave Duration and Amplitude QRS Duration according to Age QT Interval R & S voltages according to Lead & Age R/S ratio
RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! 1 A. Atropine
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss. Objectives
 10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
10 ECGs No Practitioner Can Afford to Miss Mary L. Dohrmann, MD Professor of Clinical Medicine Division of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Missouri School of Medicine No disclosures Objectives 1.
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
Anti arrhythmic drugs. Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University
 Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
Anti arrhythmic drugs Hilal Al Saffar College of medicine Baghdad University Mechanism of Arrhythmia Abnormal heart pulse formation Abnormal heart pulse conduction Classification of Arrhythmia Abnormal
Schizophrenia: Positive and Negative Symptoms and Syndromes
 Schizophrenia: Positive and Negative Symptoms and Syndromes Modern Problems of Pharmacopsychiatry Founded 1968 by F.A. Freyhant, N. Petrilowitscht, and P. Pichot Vol. 24 Series Editors T.A. Ban, Nashville,
Schizophrenia: Positive and Negative Symptoms and Syndromes Modern Problems of Pharmacopsychiatry Founded 1968 by F.A. Freyhant, N. Petrilowitscht, and P. Pichot Vol. 24 Series Editors T.A. Ban, Nashville,
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM A UBIQUITOUS AND COST-EFFECTIVE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL FOR THE FAMILY MEDICINE REFRESHER COURSE MARCH 8, 2019
 THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM A UBIQUITOUS AND COST-EFFECTIVE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL FOR THE FAMILY MEDICINE REFRESHER COURSE MARCH 8, 2019 Major Clinical Disorders Pulmonary Embolism 69 y/o woman with dyspnea and an
THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM A UBIQUITOUS AND COST-EFFECTIVE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL FOR THE FAMILY MEDICINE REFRESHER COURSE MARCH 8, 2019 Major Clinical Disorders Pulmonary Embolism 69 y/o woman with dyspnea and an
Advances in Nutrition and Top Sport
 Advances in Nutrition and Top Sport Medicine and Sport Science Vol. 32 Series Editors M. Hebbelinck, Brussels R.J. Shephard, Toronto Founder and Editor from 1969 to 1984 E. Jokl, Lexington, Ky. KARG E
Advances in Nutrition and Top Sport Medicine and Sport Science Vol. 32 Series Editors M. Hebbelinck, Brussels R.J. Shephard, Toronto Founder and Editor from 1969 to 1984 E. Jokl, Lexington, Ky. KARG E
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material
 1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
1 Cardiology Acute Care Day 22 April 2013 Arrhythmia Tutorial Course Material Arrhythmia recognition This tutorial builds on the ECG lecture and provides a framework for approaching any ECG to allow the
KNOW YOUR ECG. G. Somasekhar MD DM FEp Consultant Electro physiologist, Aayush Hospital, Vijayawada
 KNOW YOUR ECG G. Somasekhar MD DM FEp Consultant Electro physiologist, Aayush Hospital, Vijayawada CASE DETAILS A 48-year-old female non hypertensive, non diabetic presented with history of shortness of
KNOW YOUR ECG G. Somasekhar MD DM FEp Consultant Electro physiologist, Aayush Hospital, Vijayawada CASE DETAILS A 48-year-old female non hypertensive, non diabetic presented with history of shortness of
Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC)
 Where s the PAC? Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC) A junctional premature contraction (JPC) is a beat that originates prematurely in the AV node. It can occur sporadically or in a grouped pattern.
Where s the PAC? Junctional Premature Contraction (JPC) A junctional premature contraction (JPC) is a beat that originates prematurely in the AV node. It can occur sporadically or in a grouped pattern.
Antiplatelet Therapy in ACS and A-Fib
 Antiplatelet Therapy in ACS and A-Fib Advances in Cardiology Vol. 47 Series Editor Jeffrey S. Borer New York, N.Y. Antiplatelet Therapy in ACS and A-Fib Volume Editors Victor L. Serebruany Towson, Md.
Antiplatelet Therapy in ACS and A-Fib Advances in Cardiology Vol. 47 Series Editor Jeffrey S. Borer New York, N.Y. Antiplatelet Therapy in ACS and A-Fib Volume Editors Victor L. Serebruany Towson, Md.
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO
 Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
Presented By: Barbara Furry, RN-BC, MS, CCRN, FAHA Director The Center of Excellence in Education Director of HERO Follow me on Twitter! CEE Med Updates@BarbaraFurryRN Like me on Facebook! What is a
Electrocardiogram A valuable diagnostic tool. Jean Vorster Netcare Unitas Hospital STEMI Early Reperfusion Initiative 2015
 Electrocardiogram A valuable diagnostic tool Jean Vorster Netcare Unitas Hospital STEMI Early Reperfusion Initiative 2015 Overview 1. Arrhythmias 2. Structural heart disease 3. Ischaemia Arrhythmias Sinus
Electrocardiogram A valuable diagnostic tool Jean Vorster Netcare Unitas Hospital STEMI Early Reperfusion Initiative 2015 Overview 1. Arrhythmias 2. Structural heart disease 3. Ischaemia Arrhythmias Sinus
