Association Between Hypertension and Coronary Artery Disease as Assessed by Coronary Computed Tomography
|
|
|
- Adrian Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Paper Association Between Hypertension and Coronary Artery Disease as Assessed by Coronary Computed Tomography Ryoko Mitsutake, MD, PhD; Shin-ichiro Miura, MD, PhD; Yuhei Shiga, MD; Yoshinari Uehara, MD, PhD; Keijiro Saku, MD, PhD Multidetector row computed tomography (MDCT) enables the accurate noninvasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis and plaque imaging. The characteristics of patients who have coronary artery disease (CAD) as assessed by MDCT coronary computed tomography (CT) are not well known. Participants consisted of 13 consecutive patients with suspected CAD who underwent coronary CT. The authors quantified patient characteristics, including the prevalence of hypertension (HTN), hyperlipidemia and diabetes mellitus (DM), visceral fat area (VFA) and subcutaneous fat area using CT, and plasma levels of metabolic factors, including adiponectin and leptin. Although plasma levels of adiponectin in men and leptin in women were significantly associated with chronic kidney disease, there were no differences in these levels between patients with and without CAD. HTN was most significantly associated with the presence of CAD by multivariate logistic regression analysis (men, P=.2; women, P=.48). Finally, the percentage From the Department of Cardiology, Fukuoka University School of Medicine, Fukuoka, Japan Address for correspondence: Shin-ichiro Miura, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Department of Cardiology, Fukuoka University School of Medicine 7-4-1, Nanakuma, Jonan-ku, Fukuoka , Japan Manuscript received July 13, 1; revised October 24, 1; accepted October 28, 1 doi: /j x of CAD significantly increased as systolic blood pressure increased (trend, P=.2) in men but not women. In conclusion, hypertension was significantly associated with CAD as assessed by coronary CT. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 11;13: ª 1 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Multidetector row computed tomography (MDCT) has become more widely available in many general hospitals and enables the accurate noninvasive assessment of coronary artery stenosis 1 and calcification 2,3 and plaque imaging. 4 Invasive coronary angiography (CAG) is performed for patients who are strongly suspected to have coronary artery disease (CAD) based on the judgment of a specialized cardiologist. On the other hand, since noncardiologists care for patients with the metabolic syndrome (MetS), which is the cluster of abdominal obesity, hyperlipidemia (HL), hypertension (HTN), and glucose intolerance, and since MetS is induced by the dysregulation of adipocytokines, such as adiponectin and is associated with increased CAD, 6 8 they often have to judge whether patients should undergo MDCT coronary angiography (coronary CT). The characteristics of patients who should receive coronary CT as screening for CAD are unknown, and there are no criteria for patient selection. Therefore, we analyzed the backgrounds of patients who underwent coronary CT at Fukuoka University Hospital and identified the characteristics, including cardiac risk factors, of those with CAD. 198 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11
2 METHODS A total of 13 consecutive patients who were clinically suspected of having CAD according to abnormal electrocardiography and or chest symptoms (such as chest pain or chest discomfort) or who had at least one cardiac risk factor (smoking, abdominal obesity, HL, HTN, and or diabetes mellitus [DM]) were enrolled in this study. All patients underwent coronary CT between July 6 and August 8. The protocol in this study was approved by the ethics committee of Fukuoka University Hospital, and all participants gave their informed consent to participate. We evaluated coronary stenosis using MDCT as previously described. 9 Briefly, all patients were scanned by 64-MDCT on an Aquilion 64 (Toshiba, Tokyo, Japan). The use of b-blockers and nitroglycerin before scanning was left to the physician s discretion. A 7-mL bolus of contrast media (Omnipaque, 3 mg iodine ml; Daiichi Sankyo Co, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was injected at a flow rate of 3.6 ml s and was followed by 3 ml of contrast agent and 3 ml of saline solution, each at a flow rate of 1.8 ml s, with a dual injector. The region of interest was placed within the ascending aorta, and the scan was started when the CT density reached 1 HU higher than the baseline CT density. The scan was performed between the tracheal bifurcation and diaphragm with the following parameters: collimation width,. mm; rotation speed.4 s rotation; tube voltage, 13 kv; and effective tube current, 36 ma. Any narrowing of the normal contrast-enhanced lumen to <% that could be identified in multiplanar reconstructions or cross-sectional images was defined as significant coronary stenosis in CAD. Body mass index (BMI), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), serum levels of triglycerides (TGs), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), uric acid (UA), fasting plasma glucose, hemoglobin A 1c (HbA 1c ), smoking status (current vs nonsmokers), family history (myocardial infarction [MI], angina pectoris, or sudden death), and medication use were collected as cardiovascular risk factors in all patients. BP was determined as the mean of two measurements obtained in an office setting by the conventional cuff method using a mercury sphygmomanometer after at least minutes of rest. All blood samples were drawn in the morning after the patients had fasted overnight. Concentrations of TGs, HDL-C, LDL-C, and UA were measured by enzymatic methods, as described previously. 1 Plasma levels of adiponectin and leptin were determined with adiponectin 11 and leptin 12 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits, respectively. The characteristics of patients, including the history of HTN, HL, DM, and history of smoking, were obtained from medical records. Patients who had a current SBP DBP 14 9 mm Hg or were receiving antihypertensive therapy were considered to have HTN. Patients with LDL-C 14 mg dl and or TGs 1 mg dl or who were receiving lipid-lowering therapy were defined as having hyperlipidemia. DM was defined using the American Diabetes Association criteria. BMI was calculated as weight (kg) height (m) 2. Hyperuricemia was defined as a serum UA level of 7. mg dl or the administration of UA-lowering drugs. MetS was diagnosed by the criteria published by the Examination Committee of Criteria for Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome in Japan in : visceral fat area (VFA) 1 cm 2 and the presence of >2 of the following: high BP (SBP 13 mm Hg or DBP 8 mm Hg or taking an antihypertensive drug) or dyslipidemia (TGs 1 mg dl or 4 mg dl HDL-C or taking a lipid-lowering drug) or high fasting glucose (fasting glucose 11 mg dl or taking a glucose-lowering drug). Patients were classified according to the number of components of the MetS. For the measurement of VFA, subcutaneous fat area (SFA) and waist circumference was performed. These values were measured from CT cross-sectional scans at the level of the umbilicus using software (Fat Scan; N2 System, Hyogo, Japan). The National Kidney Foundation 13 has defined CKD as a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of <6 ml min 1.73 m 2. Estimated GFR (egfr) was determined using the abbreviated equation as modified for Japanese by the Japanese Society of Nephrology based on the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease study 14 ; (age [years]) ).3 (serum Cr [mg dl]) )1.14 [.742 if female]. 14 Statistical analysis was performed using the Stat View statistical software package (Stat View ; SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC) at Fukuoka University (Fukuoka, Japan). Data are shown as the mean standard deviation (SD). Categoric and continuous variables were compared between the groups by a chi-square analysis and analysis of variance followed by Fisher PLSD, respectively. A value of P<. was considered significant. Multivariate analysis was performed by a logistic regression analysis for independent variables that were related to the presence or absence of CAD. VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 199
3 Table I. Patients Clinical Characteristics All HTN()) HTN(+) Age, y a Men, % Family history, % Smoking, % BMI, kg m a Hypertension, % 69 1 SBP DBP, mm Hg a 8112 a Hyperlipidemia, % TG, mg dl HDL-C, mg dl LDL-C, mg dl DM, % HbA1c, % Fasting glucose, mg dl HU, % a Uric acid, mg dl a Medication use, % ARB or ACEI 39 2 a CCB a Statin a Leptin, ng ml a Adiponectin, mg ml SFA VFA, cm a a WC, cm a CKD, % a egfr, ml min 1.73 m a MetS, % a CKD, % a Abbreviations: ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; BMI, body mass index; CAD, coronary artery disease; CCB, calcium channel blocker; CKD, chronic kidney disease; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; DM, diabetes mellitus; egfr; estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HTN, hypertension; HU, hyperuricemia; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; MetS, metabolic syndrome; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SFA, subcutaneous fat area; TG, triglycerides; VFA, visceral fat area; WC, waist circumference. Continuous variables are expressed as mean standard deviation. a P <. vs HT ()). RESULTS Table I shows the clinical characteristics of the 13 patients, who consisted of 277 (4%) men and 236 (46%) women. The percentages of HTN, HL, DM, and MetS were 68%, 8%, 4%, and 41%, respectively. The mean age was 6411 years, BMI was 244 kg m 2,andVFAwas12263 cm 2.In addition, the percentages of the use of angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), calcium channel blockers (CCBs), and statins were 39%, 4%, and 3%, respectively. Patients in the HTN (+) group were older; had higher BMI, BP, HU, and uric acid levels; more ARB or ACEI, CCB, and statin use; and increased liptin, SFA, VFA, WC, CKD, egfr, MetS, and CAD presence compared with the HTN ()) group. On the other hand, percentage of sex, family history, smoking hyperlipidemia, and DM were similar between HTN ()) and HTN (+) groups. As shown in Figure 1, percentage of CAD in men significantly increased as the number of metabolic factors increased (trend, P<.), while there was no similar relation in women (P=.12). In addition, although plasma levels of adiponectin in men andleptininwomenweresignificantlyassociated with CKD, there were no differences in these levels between patients with and without CAD (Figure 2). Next, we examined the associations between the presence of CAD as assessed by coronary CT and (model 1) or 8 (model 2) possible factors by logistic regression analysis (Table II). Since MetS is associated with DM, HTN, hyperlipidemia, and VFA, and since leptin and adiponectin are also associated THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11
4 Patients With CAD, % Men (Trend, P<.) Women (Trend, P=.12) Metabolic Factors, No. the presence of CAD in model 2, we analyzed percentage of CAD according to SBP levels (<1 mm Hg, mm Hg, mm Hg, and 16 mm Hg) (Figure 3) and DBP levels (<8 mm Hg, 8 84 mm Hg, 8 89 mm Hg, and 9 mm Hg). Percentage of CAD significantly increased as SBP increased (trend, P=.2) in men, while there was no similar association in women (trend, P=.21). Percentage of CAD according to DBP did not show significant changes in men (trend, P=.133) or women (trend, P=.38). Figure 1. The prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) according to the number of metabolic factors ( 4) in men and women. with MetS, we excluded these factors from the analysis. In model 1, CAD was significantly associated with MetS (P=.13) and age (P=.14) in men and age in women (P=.6). In addition, CAD was significantly associated with HTN in men (P=.2) and in women (P=.48) in model 2. Since HTN was most significantly associated with DISCUSSION In the present study, we demonstrated a significant association between HTN and CAD as assessed by coronary CT. The 8 factors in Table II are independent risk factors for CAD. 1 Although plasma leptin might also be a risk factor for CAD, there is no consensus regarding this point. 16,17 In this study, HTN was the most important factor associated with the presence or absence of CAD among the 8 factors considered, although it is well known that the A. Plasma Adiponectin, μg/ml 1 1 * (-) ( + ) (-) ( + ) Plasma Leptin, ng/ml * (-) ( + ) (-) (+) B. Male Female Male Female CKD CKD Plasma Adiponectin, μg/ml 1 1 (-) (+) (-) (+) Plasma Leptin, ng/ml NS (-) (+) (-) (+) Male Female Male Female CAD CAD Figure 2. Plasma levels of adiponectin and leptin in the presence (+) or absence ()) of chronic kidney disease (CKD) (A) and coronary artery disease (CAD) (B) in men and women. *P<. vs CKD ()) group. NS indicates not significant. VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 1
5 Table II. Factors that Contribute to Coronary Artery Disease Men Women OR (9% CI) P Value OR (9% CI) P Value Model 1 Age 1.3 ( ) ( ).6 Smoking.87 (. 1.) (.92.63).77 Family history 1.37 ( ).41.9 (.4 2.6).89 CKD 1. ( ) ( ).268 MetS 1.97 ( ) (.4 1.6).61 Model 2 Age 1.3 (1. 1.6) ( ).234 Smoking.82 ( ) (.81.38).128 Family history 1.36 ( ) ( ).86 HTN 2.94 (1.4.89) (1.1.3).48 HL 1.16 ( ) ( ).261 DM.77 ( ) ( ).619 CKD 1.4 ( ).99.8 ( ).69 VFA 1. (.99 1.) ( ).6 Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; CKD, chronic kidney disease; DM, diabetes mellitus; HL, hyperlipidemia; HTN, hypertension; MetS, metabolic syndrome; OR, odds ratio; VFA, visceral fat area. Patients with CAD (%) Mal e (Tren d, P<. 2) Female (Trend, P=.21) < SBP, mmhg 16 Figure 3. The prevalence of coronary artery disease (CAD) according to the systolic blood pressure level in men and women. clustering of metabolic disorders induces CAD. In a meta-analysis of individual data for 1 million adults in 61 prospective studies, 18 cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risk were shown to increase with an increase in BP. In Japan, NIPPON DATA8 reported that elevated SBP is an independent risk factor for CAD mortality for men of all ages. 19 Although HTN is an independent risk factor for CAD, there are several possible reasons why HTN was the most important independent risk factor for the presence of CAD in this study. First, the percentages of medication use (ARB ACEI, 39%; CCB, 4%) were relatively low, although 68% of all patients had HTN, and the levels were relatively high (SBP, 136 mm Hg; DBP, 7912 mm Hg). In fact, percentage of CAD in men significantly increased as SBP increased: 48% of men with SBP 14 mm Hg showed CAD (Figure 3). Thus, there is a problem associated with the control of BP in patients with HTN among our study patients. Second, although CKD is an independent risk factor for all-cause death or CAD in the general population and CKD may contribute to the severity of CAD associated with the progression of coronary artery calcification, 21 CKD did not show a stronger association than HTN in this study. Cardiac and renal dysfunction frequently coexist. Although the cardio-renal syndrome represents the sum total of an adversarial relation and clinically manifests as worsening renal function, the average egfr was 6818 ml min 1.73 m 2 and there were no patients with severe renal dysfunction because patients with 1. mg dl Cr underwent coronary CT in this study. Third, we do not know why HTN is a more important risk factor than DM and HL. Since the blood levels of LDL-C and HbA 1c are mg dl and 6.7%2.%, respectively, there is not so good control for preventing CAD. Nonetheless, HL and DM are less important factors for the presence of CAD than HTN. It takes a long time for coronary atherosclerosis to progress. Although we analyzed the prevalence of and attempts to control HTN, DM, and HL, we do not have data about the duration of these diseases. Adiponectin and leptin are produced by adipose tissue and are known to play an important role in 2 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11
6 the development of MetS. 22 There have been several reports about the relationship between adiponectin or leptin and BP. For example, there is a strong correlation between leptin plasma concentrations and renal sympathetic activation, as shown in men with widely differing degrees of adiposity. 23 Patients with hypertension appear to have significantly lower plasma adiponectin levels than normotensive patients. 24 Since plasma levels of leptin may be associated with HTN in this study, dysfunction of this adipocytokine-induced visceral fat accumulation may also interact with HTN. LIMITATIONS There are several limitations in this study. First, although the patients in this study were clinically suspected of having CAD or had at least one cardiac risk factor, more than half of the patients were considered to not have CAD by coronary CT. The possibility of a patient selection bias would change the results. Second, although this is the cross-sectional nature of the study design, we can observe an association between clinical parameters. Third, the evaluation of coronary stenosis with severe coronary calcification was not performed using coronary CT. In this study, all segments were assessed according to the 1-segment American Heart Association coronary artery model. 2 Since 88 (17.2%) patients had at least one unevaluable segment on MDCT because of severe calcification and motion artifacts, they could not be evaluated by MDCT. Overall, 1 coronary artery segments of 13 patients (total 769) were assessed. Of the total 769 segments, 118 (1.%) and 243 (3.2%) segments could not be evaluated by MDCT because of severe calcification and motion artifacts, respectively. Thus, we used 7334 segments (9.3%) for further analysis. Fourth, although we understand that the newer 12-slice CT should give superior results, 64-slice MDCT is still more widely available in many general hospitals. Our results may be useful for doctors who are working at these hospitals. CONCLUSIONS HTN is significantly associated with CAD as assessed by coronary CT. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES 1 Rumberger JA, Sheedy PF 3rd, Breen JF, et al. Coronary calcium, as determined by electron beam computed tomography, and coronary disease on arteriogram. Effect of patient s sex on diagnosis. Circulation. 199;91: Nitta K, Akiba T, Suzuki K, et al. Assessment of coronary artery calcification in hemodialysis patients using multidetector spiral CT scan. Hypertens Res. 4;27: Mikami S, Hamano T, Fujii N, et al. Serum osteoprotegerin as a screening tool for coronary artery calcification score in diabetic pre-dialysis patients. Hypertens Res. 8;31: Achenbach S, Ropers D, Hoffmann U, et al. Assessment of coronary remodeling in stenotic and nonstenotic coronary atherosclerotic lesions by multidetector spiral computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 4;43: Nakamura Y, Shimada K, Fukuda D, et al. Implications of plasma concentrations of adiponectin in patients with coronary artery disease. Heart. 4;9: Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, et al. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2;288: Takeuchi H, Saitoh S, Takagi S, et al. Metabolic syndrome and cardiac disease in Japanese men: applicability of the concept of metabolic syndrome defined by the National Cholesterol Education Program-Adult Treatment Panel III to Japanese men the Tanno and Sobetsu Study. Hypertens Res. ;28: Koji Y, Tomiyama H, Yamada J, et al. Relationship between arterial stiffness and the risk of coronary artery disease in subjects with and without metabolic syndrome. Hypertens Res. 7;3: Mitsutake R, Niimura H, Miura S, et al. Clinical significance of the coronary calcification score by multidetector row computed tomography for the evaluation of coronary stenosis in Japanese patients. Circ J. 6;7: Mitsutake R, Miura S, Kawamura A, et al. Are metabolic factors associated with coronary artery stenosis on MDCT? Circ J. 9;73: Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;27: Schwartz MW, Peskind E, Raskind M, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leptin levels: relationship to plasma levels and to adiposity in humans. Nat Med. 1996;2: National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative (K DOQI) clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2;39(suppl 1):S1 S Imai E, Horio M, Iseki K, et al. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in the Japanese general population predicted by the MDRD equation modified by a Japanese coefficient. Clin Exp Nephrol. 7;11: The Japanese Society of Hypertension Committee for Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. Chapter 2. Measurement and clinical evaluation of blood pressure. Hypertens Res. 9;32: Kim SK, Kim HJ, Ahn CW, et al. Hyperleptinemia as a robust risk factor of coronary artery disease and metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. Endocr J. 8;: Wolk R, Berger P, Lennon RJ, et al. Body mass index: a risk factor for unstable angina and myocardial infarction in patients with angiographically confirmed coronary artery disease. Circulation. 3;18: Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, et al. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2;36: Okayama A, Kadowaki T, Okamura T, et al. Age-specific effects of systolic and diastolic blood pressures on mortality due to cardiovascular diseases among Japanese men (NIPPON DATA8). J Hypertens. 6;24: Al Suwaidi J, Reddan DN, Williams K, et al. Prognostic implications of abnormalities in renal function in patients VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11 THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION 3
7 with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation. 2;16: Mitsutake R, Miura S, Shiga Y, et al. Is chronic kidney disease associated with coronary artery stenosis or calcification as assessed by multi-detector row computed tomography? Intern Med. 8;47: Katagiri H, Yamada T, Oka Y. Adiposity and cardiovascular disorders: disturbance of the regulatory system consisting of humoral and neuronal signals. Circ Res. 7; 11: Eikelis N, Schlaich M, Aggarwal A, et al. Interactions between leptin and the human sympathetic nervous system. Hypertension. 3;41: Adamczak M, Wiecek A, Funahashi T, et al. Decreased plasma adiponectin concentration in patients with essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 3;16: Dodge JT, Brown BG, Bolson EL, et al. Intrathoracic spatial location of coronary segments on the normal human heart. Circulation. 1988;78: THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL HYPERTENSION VOL. 13 NO. 3 MARCH 11
Impact of Body Mass Index and Metabolic Syndrome on the Characteristics of Coronary Plaques Using Computed Tomography Angiography
 Impact of Body Mass Index and Metabolic Syndrome on the Characteristics of Coronary Plaques Using Computed Tomography Angiography Cardiovascular Division, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba Akira
Impact of Body Mass Index and Metabolic Syndrome on the Characteristics of Coronary Plaques Using Computed Tomography Angiography Cardiovascular Division, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tsukuba Akira
MDCT による冠動脈狭窄や石灰化スコアの評価と PWV の関連性
 Online publication May 27, 2010 総 説 第 49 回総会シンポジウム 2 血管病スクリーニングのための画像診断 MDCT による冠動脈狭窄や石灰化スコアの評価と PWV の関連性 要旨 : CT MDCT MDCT MDCT PWV J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2010, 50: 163 167 Key words: coronary artery disease,
Online publication May 27, 2010 総 説 第 49 回総会シンポジウム 2 血管病スクリーニングのための画像診断 MDCT による冠動脈狭窄や石灰化スコアの評価と PWV の関連性 要旨 : CT MDCT MDCT MDCT PWV J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2010, 50: 163 167 Key words: coronary artery disease,
Keywords: Blood pressure; Heart rate; Hypotension; Adverse events. Introduction
 Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(1):22-26 Safety of Landiolol Hydrochloride as a Premedication for Producing an Appropriate Heart Rate for Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography
Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(1):22-26 Safety of Landiolol Hydrochloride as a Premedication for Producing an Appropriate Heart Rate for Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography
Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Fixed-Dose Combination of Azilsartan and Amlodipine
 Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(12):888-892 Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Fixed-Dose Combination of Azilsartan and Amlodipine Kota Motozato a, b, Shin-ichiro Miura a, c, d, Yuhei
Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2016;8(12):888-892 Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Fixed-Dose Combination of Azilsartan and Amlodipine Kota Motozato a, b, Shin-ichiro Miura a, c, d, Yuhei
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography
 Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
Statin therapy in patients with Mild to Moderate Coronary Stenosis by 64-slice Multidetector Coronary Computed Tomography Hyo Eun Park 1, Eun-Ju Chun 2, Sang-Il Choi 2, Soyeon Ahn 2, Hyung-Kwan Kim 3,
Characteristics of Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients without Known Coronary Artery Disease
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research in Diabetes http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/diab/diab.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 322292, 12 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014.322292 Research Article Characteristics
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research in Diabetes http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/diab/diab.html Vol. 2014 (2014), Article ID 322292, 12 pages DOI: 10.5171/2014.322292 Research Article Characteristics
Methods. Study design
 Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2017;9(2):98-103 Efficacy and Safety of Combination Therapy Consisting of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blocker, Calcium Channel Blocker and Hydrochlorothiazide
Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2017;9(2):98-103 Efficacy and Safety of Combination Therapy Consisting of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Blocker, Calcium Channel Blocker and Hydrochlorothiazide
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
The relation between estimated glomerular filtration rate and proteinuria in Okayama Prefecture, Japan
 Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:191 195 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0183-9 SHORT COMMUNICATION The relation between estimated glomerular filtration rate and proteinuria in Okayama Prefecture, Japan Nobuyuki
Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:191 195 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0183-9 SHORT COMMUNICATION The relation between estimated glomerular filtration rate and proteinuria in Okayama Prefecture, Japan Nobuyuki
2 Furthermore, quantitative coronary angiography
 ORIGINAL PAPER Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Reversal by Blood Pressure Lowering in Chronic Kidney Disease: Japan Multicenter Investigation for Cardiovascular DiseaseB CKD Study Yoshiki Yui, MD;
ORIGINAL PAPER Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Reversal by Blood Pressure Lowering in Chronic Kidney Disease: Japan Multicenter Investigation for Cardiovascular DiseaseB CKD Study Yoshiki Yui, MD;
Methods. 2 Ueda, ET AL
 CLINICAL STUDY Association Between the Presence or Severity of Coronary Artery Disease and Pericardial Fat, Paracardial Fat, Epicardial Fat, Visceral Fat, and Subcutaneous Fat as Assessed by Multi-Detector
CLINICAL STUDY Association Between the Presence or Severity of Coronary Artery Disease and Pericardial Fat, Paracardial Fat, Epicardial Fat, Visceral Fat, and Subcutaneous Fat as Assessed by Multi-Detector
Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome
 243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
RAMA-EGAT Risk Score for Predicting Coronary Artery Disease Evaluated by 64- Slice CT Angiography
 RAMA-EGAT Risk Score for Predicting Coronary Artery Disease Evaluated by 64- Slice CT Angiography Supalerk Pattanaprichakul, MD 1, Sutipong Jongjirasiri, MD 2, Sukit Yamwong, MD 1, Jiraporn Laothammatas,
RAMA-EGAT Risk Score for Predicting Coronary Artery Disease Evaluated by 64- Slice CT Angiography Supalerk Pattanaprichakul, MD 1, Sutipong Jongjirasiri, MD 2, Sukit Yamwong, MD 1, Jiraporn Laothammatas,
Epicardial fat volume as a predictor of coronary vulnerable plaques using cardiac computed tomography in the patients with zero calcium score
 ESC Congress 2011 Epicardial fat volume as a predictor of coronary vulnerable plaques using cardiac computed tomography in the patients with zero calcium score K. Harada, N. Terada, A. Okada, M. Shigekiyo,
ESC Congress 2011 Epicardial fat volume as a predictor of coronary vulnerable plaques using cardiac computed tomography in the patients with zero calcium score K. Harada, N. Terada, A. Okada, M. Shigekiyo,
JNC Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults
 JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
JNC 8 2014 Evidence-Based Guidelines for the Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults Table of Contents Why Do We Treat Hypertension? Blood Pressure Treatment Goals Initial Therapy Strength of Recommendation
Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD
 1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines
 Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Todd S. Perlstein, MD FIFTH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM
 Todd S. Perlstein, MD FIFTH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM Faculty Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose No off-label use of medications will be discussed FIFTH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM Recognize changes between
Todd S. Perlstein, MD FIFTH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM Faculty Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose No off-label use of medications will be discussed FIFTH ANNUAL SYMPOSIUM Recognize changes between
Total risk management of Cardiovascular diseases Nobuhiro Yamada
 Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
Nobuhiro Yamada The worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases (WHO) To prevent cardiovascular diseases Beyond LDL Multiple risk factors With common molecular basis The Current Burden of CVD CVD is responsible
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. Nothing to disclose
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to disclose Four-Year Clinical Outcomes of the OLIVUS (Impact of OLmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis; evaluation by IntraVascular UltraSound
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to disclose Four-Year Clinical Outcomes of the OLIVUS (Impact of OLmesartan on progression of coronary atherosclerosis; evaluation by IntraVascular UltraSound
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease
 Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Metabolic Syndrome and Chronic Kidney Disease Definition of Metabolic Syndrome National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference
Fat Accumulation and Obesity-related Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Middle-aged Japanese Men and Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fat Accumulation and Obesity-related Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Middle-aged Japanese Men and Women Miwa Ryo 1, Tohru Funahashi 1, Tadashi Nakamura 1, Shinji Kihara 1, Kazuaki Kotani
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fat Accumulation and Obesity-related Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Middle-aged Japanese Men and Women Miwa Ryo 1, Tohru Funahashi 1, Tadashi Nakamura 1, Shinji Kihara 1, Kazuaki Kotani
Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents
 Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents Stella Stabouli Ass. Professor Pediatrics 1 st Department of Pediatrics Hippocratio Hospital Evaluation of
Hypertension with Comorbidities Treatment of Metabolic Risk Factors in Children and Adolescents Stella Stabouli Ass. Professor Pediatrics 1 st Department of Pediatrics Hippocratio Hospital Evaluation of
Module 2. Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension
 Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
Module 2 Global Cardiovascular Risk Assessment and Reduction in Women with Hypertension 1 Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored,
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Low fractional diastolic pressure in the ascending aorta increased the risk of coronary heart disease
 (2002) 16, 837 841 & 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low fractional diastolic pressure in the ascending aorta increased the risk
(2002) 16, 837 841 & 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low fractional diastolic pressure in the ascending aorta increased the risk
Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome
 Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome Helder Dores, Luís Bronze Carvalho, Ingrid Rosário, Sílvio Leal, Maria João
Relationship between body mass index, coronary disease extension and clinical outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome Helder Dores, Luís Bronze Carvalho, Ingrid Rosário, Sílvio Leal, Maria João
Development of the Automated Diagnosis CT Screening System for Visceral Obesity
 Review Asian Pacific Journal of Disease Management 2008; 2(2), 31-38 Development of the Automated Diagnosis CT Screening System for Visceral Obesity Toru Nakagawa 1), Syuichiro Yamamoto 1), Masataka Irokawa
Review Asian Pacific Journal of Disease Management 2008; 2(2), 31-38 Development of the Automated Diagnosis CT Screening System for Visceral Obesity Toru Nakagawa 1), Syuichiro Yamamoto 1), Masataka Irokawa
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication
 Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
Scientific Exhibit. Authors: D. Takenaka, Y. Ohno, Y. Onishi, K. Matsumoto, T.
 The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
Risk Assessment of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus in patient on antihypertensive medication
 41 Research Article Risk Assessment of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus in patient on antihypertensive medication Amarjeet Singh*, Sudeep bhardwaj, Ashutosh aggarwal Department of Pharmacology, Seth
41 Research Article Risk Assessment of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus in patient on antihypertensive medication Amarjeet Singh*, Sudeep bhardwaj, Ashutosh aggarwal Department of Pharmacology, Seth
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease. albuminuria
 1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
1. Albuminuria an early sign of glomerular damage and renal disease albuminuria Cardio-renal continuum REGRESS Target organ damage Asymptomatic CKD New risk factors Atherosclerosis Target organ damage
Cedars Sinai Diabetes. Michael A. Weber
 Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Evidence-Based Management of CAD: Last Decade Trials and Updated Guidelines
 Evidence-Based Management of CAD: Last Decade Trials and Updated Guidelines Enrico Ferrari, MD Cardiac Surgery Unit Cardiocentro Ticino Foundation Lugano, Switzerland Conflict of Interests No conflict
Evidence-Based Management of CAD: Last Decade Trials and Updated Guidelines Enrico Ferrari, MD Cardiac Surgery Unit Cardiocentro Ticino Foundation Lugano, Switzerland Conflict of Interests No conflict
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi Medical University Saitama Medical Center, Japan
 Association between continuously elevated C-reactive protein and restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention using drug-eluting stent in angina patients Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi
Association between continuously elevated C-reactive protein and restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention using drug-eluting stent in angina patients Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Jichi
Hypertension and obesity. Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital
 Hypertension and obesity Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital No conflict of interests to declare Obesity Definition: excessive weight that may impair health BMI Categories Underweight BMI
Hypertension and obesity Dr Wilson Sugut Moi teaching and referral hospital No conflict of interests to declare Obesity Definition: excessive weight that may impair health BMI Categories Underweight BMI
Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome. Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group
 Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group Conflict of interest regarding this presentation: I have no conflict of interest to
Establishment of Efficacy of Intervention in those with Metabolic Syndrome Dr Wendy Russell - ILSI Europe Expert Group Conflict of interest regarding this presentation: I have no conflict of interest to
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes
 VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
VBWG Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes Nicola Abate, M.D., F.N.L.A. Professor and Chief Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism The University of Texas Medical Branch Galveston, Texas Coronary
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology
 Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:313 319 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0201-y REGULAR ARTICLE Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology Hirokuni Hashikata Kouji H. Harada
Environ Health Prev Med (2011) 16:313 319 DOI 10.1007/s12199-010-0201-y REGULAR ARTICLE Usefulness of a large automated health records database in pharmacoepidemiology Hirokuni Hashikata Kouji H. Harada
Protecting the heart and kidney: implications from the SHARP trial
 Cardiology Update, Davos, 2013: Satellite Symposium Protecting the heart and kidney: implications from the SHARP trial Colin Baigent Professor of Epidemiology CTSU, University of Oxford S1 First CTT cycle:
Cardiology Update, Davos, 2013: Satellite Symposium Protecting the heart and kidney: implications from the SHARP trial Colin Baigent Professor of Epidemiology CTSU, University of Oxford S1 First CTT cycle:
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Kavousi M, Leening MJG, Nanchen D, et al. Comparison of application of the ACC/AHA guidelines, Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines, and European Society of Cardiology guidelines
Supplementary Online Content Kavousi M, Leening MJG, Nanchen D, et al. Comparison of application of the ACC/AHA guidelines, Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines, and European Society of Cardiology guidelines
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease
 The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
The Diabetes Link to Heart Disease Anthony Abe DeSantis, MD September 18, 2015 University of WA Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology and Nutrition Oswald Toosweet Case #1 68 yo M with T2DM Diagnosed DM
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Xu X, Qin X, Li Y, et al. Efficacy of folic acid therapy on the progression of chronic kidney disease: the Renal Substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Xu X, Qin X, Li Y, et al. Efficacy of folic acid therapy on the progression of chronic kidney disease: the Renal Substudy of the China Stroke Primary Prevention Trial. JAMA
Serum Creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Serum Creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease MAK Akanda 1, KN Choudhury 2, MZ Ali 1, MK Kabir 3, LN Begum 4, LA Sayami 1 1 National Institute of Cardiovascular
Serum Creatinine and Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease MAK Akanda 1, KN Choudhury 2, MZ Ali 1, MK Kabir 3, LN Begum 4, LA Sayami 1 1 National Institute of Cardiovascular
THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS Daisuke MAEBUCHI, Yasuyuki SHIRAISHI, Hiroaki TANAKA, Yumiko INUI, Makoto TAKEI,
THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS Daisuke MAEBUCHI, Yasuyuki SHIRAISHI, Hiroaki TANAKA, Yumiko INUI, Makoto TAKEI,
ALLHAT. Major Outcomes in High Risk Hypertensive Patients Randomized to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Calcium Channel Blocker vs Diuretic
 1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health Major Outcomes in High Risk Hypertensive Patients Randomized to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Calcium Channel Blocker
1 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health Major Outcomes in High Risk Hypertensive Patients Randomized to Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor or Calcium Channel Blocker
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS & TARGET ORGAN DAMAGE IN GREEK HYPERTENSIVES
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS & TARGET ORGAN DAMAGE IN GREEK HYPERTENSIVES C. Liakos, 1 G. Vyssoulis, 1 E. Karpanou, 2 S-M. Kyvelou, 1 V. Tzamou, 1 A. Michaelides, 1 A. Triantafyllou, 1 P. Spanos, 1 C. Stefanadis
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS & TARGET ORGAN DAMAGE IN GREEK HYPERTENSIVES C. Liakos, 1 G. Vyssoulis, 1 E. Karpanou, 2 S-M. Kyvelou, 1 V. Tzamou, 1 A. Michaelides, 1 A. Triantafyllou, 1 P. Spanos, 1 C. Stefanadis
Cardiovascular Health Practice Guideline Outpatient Management of Coronary Artery Disease 2003
 Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient
 Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July 7, :45-9:30am
 Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Advances in Cardiovascular Disease 30 th Annual Convention and Reunion UERM-CMAA, Inc. Annual Convention and Scientific Meeting July 5-8, 2018 New Hypertension Guideline Recommendations for Adults July
Update on Current Trends in Hypertension Management
 Friday General Session Update on Current Trends in Hypertension Management Shawna Nesbitt, MD Associate Dean, Minority Student Affairs Associate Professor, Department of Internal Medicine Office of Student
Friday General Session Update on Current Trends in Hypertension Management Shawna Nesbitt, MD Associate Dean, Minority Student Affairs Associate Professor, Department of Internal Medicine Office of Student
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention
 CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
CVD risk assessment using risk scores in primary and secondary prevention Raul D. Santos MD, PhD Heart Institute-InCor University of Sao Paulo Brazil Disclosure Honoraria for consulting and speaker activities
The Final 10-Year Follow-up Results from the Bari Randomized Trial J Am Coll Cardiol (2007) 49;1600-6
 The Final 10-Year Follow-up Results from the Bari Randomized Trial J Am Coll Cardiol (2007) 49;1600-6 n&list_uids=17433949 64-Multislice Detector Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography as Potential Alternative
The Final 10-Year Follow-up Results from the Bari Randomized Trial J Am Coll Cardiol (2007) 49;1600-6 n&list_uids=17433949 64-Multislice Detector Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography as Potential Alternative
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Education Hokenshido Program Reduced Metabolic Syndrome in the Amagasaki Visceral Fat Study. Three-Year Follow-up Study of 3,174 Japanese Employees Miwa Ryo 1, Tadashi Nakamura
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Education Hokenshido Program Reduced Metabolic Syndrome in the Amagasaki Visceral Fat Study. Three-Year Follow-up Study of 3,174 Japanese Employees Miwa Ryo 1, Tadashi Nakamura
HDL-C. J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart
 Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Online publication March 25, 2009 48 6 2007 2007 HDL-C LDL-C HDL-C J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2008, 48: 463 470 NIPPON DATA80, MEGA study, JELIS, dyslipidemia, risk assessment chart 1987 NIPPON DATA80 Iso 10 MRFIT
Effective Date: TBD Version: 1.0 (Revised: 6/11/2014)
 Protocol Title: Hypertension Effective Date: TBD Version: 1.0 (Revised: 6/11/2014) Approval By: TBD Planned Review Date: TBD 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based care recommendations
Protocol Title: Hypertension Effective Date: TBD Version: 1.0 (Revised: 6/11/2014) Approval By: TBD Planned Review Date: TBD 1 Purpose & Objective This protocol provides evidence-based care recommendations
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ. Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH
 ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
ΑΡΥΙΚΗ ΠΡΟΔΓΓΙΗ ΤΠΔΡΣΑΙΚΟΤ ΑΘΔΝΟΤ Μ.Β.Παπαβαζιλείοσ Καρδιολόγος FESC - Γιεσθύνηρια ιζμανόγλειον ΓΝΑ Clinical Hypertension Specialist ESH Hypertension Co-Morbidities HTN Commonly Clusters with Other Risk
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula
 T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
T. Suithichaiyakul Cardiomed Chula The cardiovascular (CV) continuum: role of risk factors Endothelial Dysfunction Atherosclerosis and left ventricular hypertrophy Myocardial infarction & stroke Endothelial
hypertension Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath
 hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
hypertension t. Samavat MD,Cadiologist,MPH Head of prevention and control of CVD disease office Ministry of heath RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HYPERTENSION DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT, AND TREATMENT Definition of hypertension
Management of Hypertension. M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine
 Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
Management of Hypertension M Misra MD MRCP (UK) Division of Nephrology University of Missouri School of Medicine Disturbing Trends in Hypertension HTN awareness, treatment and control rates are decreasing
What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines?
 American College of Physicians Ohio/Air Force Chapters 2018 Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 5, 2018 What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines? Max C. Reif, MD, FACP Objectives: At the end of the
American College of Physicians Ohio/Air Force Chapters 2018 Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 5, 2018 What s In the New Hypertension Guidelines? Max C. Reif, MD, FACP Objectives: At the end of the
DISCLOSURE PHARMACIST OBJECTIVES 9/30/2014 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES. I have nothing to disclose.
 JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
JNC 8: A REVIEW OF THE LONG-AWAITED/MUCH-ANTICIPATED HYPERTENSION GUIDELINES Tiffany Dickey, PharmD Assistant Professor, UAMS COP Clinical Pharmacy Specialist, Mercy Hospital Northwest AR DISCLOSURE I
Significance of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Visit-to-Visit Variability of Blood Pressure in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease in a 12-Month Follow-Up
 Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2017;9(4):345-352 Significance of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Visit-to-Visit Variability of Blood Pressure in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease in a 12-Month
Elmer ress Original Article J Clin Med Res. 2017;9(4):345-352 Significance of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Visit-to-Visit Variability of Blood Pressure in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease in a 12-Month
A: Epidemiology update. Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups
 A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
A: Epidemiology update Evidence that LDL-C and CRP identify different high-risk groups Women (n = 27,939; mean age 54.7 years) who were free of symptomatic cardiovascular (CV) disease at baseline were
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
Appendix This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. Appendix to: Banks E, Crouch SR, Korda RJ, et al. Absolute risk of cardiovascular
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. Nothing to disclose
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to disclose Prognostic value of multidetector computed tomography coronary angiography in a large population of patients with unknown cardiac disease but suspected
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST Nothing to disclose Prognostic value of multidetector computed tomography coronary angiography in a large population of patients with unknown cardiac disease but suspected
Characteristics and Future Cardiovascular Risk of Patients With Not-At- Goal Hypertension in General Practice in France: The AVANT AGE Study
 ORIGINAL PAPER Characteristics and Future Cardiovascular Risk of Patients With Not-At- Goal Hypertension in General Practice in France: The AVANT AGE Study Yi Zhang, MD, PhD; 1 Helene Lelong, MD; 2 Sandrine
ORIGINAL PAPER Characteristics and Future Cardiovascular Risk of Patients With Not-At- Goal Hypertension in General Practice in France: The AVANT AGE Study Yi Zhang, MD, PhD; 1 Helene Lelong, MD; 2 Sandrine
Calcium is a chemical element that is essential for living organisms.
 1 of 8 9/28/2015 9:04 AM Home About me Health and Nutrition Diet General Health Heart Disease August 19, 2014 By Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 259 Comments Like Share 82 Calcium is a chemical element that is essential
1 of 8 9/28/2015 9:04 AM Home About me Health and Nutrition Diet General Health Heart Disease August 19, 2014 By Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 259 Comments Like Share 82 Calcium is a chemical element that is essential
Abstract Background: Methods: Results: Conclusions:
 Two-Year Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Overlapping Sirolimusversus Paclitaxel- Eluting Stents in the Treatment of Diffuse Long Coronary Lesions Kang-Yin Chen 1,2, Seung-Woon Rha 1, Yong-Jian Li
Two-Year Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Overlapping Sirolimusversus Paclitaxel- Eluting Stents in the Treatment of Diffuse Long Coronary Lesions Kang-Yin Chen 1,2, Seung-Woon Rha 1, Yong-Jian Li
The Latest Generation of Clinical
 The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
The Latest Generation of Clinical Guidelines: HTN and HLD Dave Brackett Clinical Guideline Purpose Uniform approach Awareness of key details Diagnosis Treatment Monitoring Evidence based approach Inform
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension.
 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
Echocardiography analysis in renal transplant recipients
 Original Research Article Echocardiography analysis in renal transplant recipients S.A.K. Noor Mohamed 1*, Edwin Fernando 2, 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Professor Department of Nephrology, Govt. Stanley Medical
Original Research Article Echocardiography analysis in renal transplant recipients S.A.K. Noor Mohamed 1*, Edwin Fernando 2, 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Professor Department of Nephrology, Govt. Stanley Medical
Patient is healthy with no chronic disease or significant risk factors [16%].
![Patient is healthy with no chronic disease or significant risk factors [16%]. Patient is healthy with no chronic disease or significant risk factors [16%].](/thumbs/96/129036215.jpg) AAFP Risk Level 1 Patient is healthy with no chronic disease or significant risk factors [16%]. Exclude the following chronic problems from active patient list o Depression o Diabetes Type I or Type II
AAFP Risk Level 1 Patient is healthy with no chronic disease or significant risk factors [16%]. Exclude the following chronic problems from active patient list o Depression o Diabetes Type I or Type II
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4):
 300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
Metabolic Syndrome Is A Key Determinant Of Coronary Microvascular Function In Patients With Stable Coronary Disease Undergoing PCI
 Metabolic Syndrome Is A Key Determinant Of Coronary Microvascular Function In Patients With Stable Coronary Disease Undergoing PCI Narbeh Melikian*, Ajay M Shah*, Martyn R Thomas, Roy Sherwood, Mark T
Metabolic Syndrome Is A Key Determinant Of Coronary Microvascular Function In Patients With Stable Coronary Disease Undergoing PCI Narbeh Melikian*, Ajay M Shah*, Martyn R Thomas, Roy Sherwood, Mark T
An Epidemiological Overview
 An Epidemiological Overview Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. In 2005 CVD accounted for approximately 38 percent of all deaths CVD has been the number one killer in
An Epidemiological Overview Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. In 2005 CVD accounted for approximately 38 percent of all deaths CVD has been the number one killer in
Renal function had an independent relationship with coronary artery calcification in Chinese elderly men
 Fu et al. BMC Geriatrics (2017) 17:80 DOI 10.1186/s12877-017-0470-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Renal function had an independent relationship with coronary artery calcification in Chinese elderly men Shihui Fu 1,2,
Fu et al. BMC Geriatrics (2017) 17:80 DOI 10.1186/s12877-017-0470-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Renal function had an independent relationship with coronary artery calcification in Chinese elderly men Shihui Fu 1,2,
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Supplementary Table 1. Baseline Characteristics by Quintiles of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressures
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Table 1. Baseline Characteristics by Quintiles of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressures Quintiles of Systolic Blood Pressure Quintiles of Diastolic Blood Pressure Q1 Q2
Supplementary Data Supplementary Table 1. Baseline Characteristics by Quintiles of Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressures Quintiles of Systolic Blood Pressure Quintiles of Diastolic Blood Pressure Q1 Q2
Cardiovascular Disease in CKD. Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center
 Cardiovascular Disease in CKD Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center Objectives Describe prevalence for cardiovascular disease in CKD
Cardiovascular Disease in CKD Parham Eftekhari, D.O., M.Sc. Assistant Clinical Professor Medicine NSUCOM / Broward General Medical Center Objectives Describe prevalence for cardiovascular disease in CKD
How Low Do We Go? Update on Hypertension
 How Low Do We Go? Update on Beth L. Abramson, MD, FRCPC, FACC As presented at the University of Toronto s Saturday at the University Session (September 2003) Arecent World Health Organization report states
How Low Do We Go? Update on Beth L. Abramson, MD, FRCPC, FACC As presented at the University of Toronto s Saturday at the University Session (September 2003) Arecent World Health Organization report states
Mandana Nikpour 1,2, Murray B Urowitz 1*, Dominique Ibanez 1, Paula J Harvey 3 and Dafna D Gladman 1. Abstract
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Importance of cumulative exposure to elevated cholesterol and blood pressure in development of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: a prospective
Blood Pressure Monitoring in Chronic Kidney Disease
 Blood Pressure Monitoring in Chronic Kidney Disease Aldo J. Peixoto, MD FASN FASH Associate Professor of Medicine (Nephrology), YSM Associate Chief of Medicine, VACT Director of Hypertension, VACT American
Blood Pressure Monitoring in Chronic Kidney Disease Aldo J. Peixoto, MD FASN FASH Associate Professor of Medicine (Nephrology), YSM Associate Chief of Medicine, VACT Director of Hypertension, VACT American
Central pressures and prediction of cardiovascular events in erectile dysfunction patients
 Central pressures and prediction of cardiovascular events in erectile dysfunction patients N. Ioakeimidis, K. Rokkas, A. Angelis, Z. Kratiras, M. Abdelrasoul, C. Georgakopoulos, D. Terentes-Printzios,
Central pressures and prediction of cardiovascular events in erectile dysfunction patients N. Ioakeimidis, K. Rokkas, A. Angelis, Z. Kratiras, M. Abdelrasoul, C. Georgakopoulos, D. Terentes-Printzios,
Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital
 Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
Original Research Article A study of waist hip ratio in identifying cardiovascular risk factors at Government Dharmapuri College Hospital M. Arivumani * Assistant Professor of General Medicine, Government
Coronary Artery Calcium Score
 Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
The role of coronary artery calcium score on the detection of subclinical atherosclerosis in metabolic diseases
 The role of coronary artery calcium score on the detection of subclinical atherosclerosis in metabolic diseases Eun-Jung Rhee Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Kangbuk Samsung Hospital Sungkyunkwan
The role of coronary artery calcium score on the detection of subclinical atherosclerosis in metabolic diseases Eun-Jung Rhee Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Kangbuk Samsung Hospital Sungkyunkwan
DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES
 DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES 1 Dr.Mohamed Omar Shariff, 2 nd Year Post Graduate, Department of General Medicine. DR.B.R.Ambedkar Medical College & Hospital. 2 INTRODUCTION Leading cause of global
DEPARTMENT OF GENERAL MEDICINE WELCOMES 1 Dr.Mohamed Omar Shariff, 2 nd Year Post Graduate, Department of General Medicine. DR.B.R.Ambedkar Medical College & Hospital. 2 INTRODUCTION Leading cause of global
Hypertension Update Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital
 Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
 Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Hypoinsulinemia is strongly associated with coronary artery calcification (CAC) assessed by multislice computed tomography
 Hypoinsulinemia is strongly associated with coronary artery calcification (CAC) assessed by multislice computed tomography Yohei Oda 1, Muhei Tanaka 2, Michiaki Fukui 2, Sei Tsunoda 1, Satoshi Akabame
Hypoinsulinemia is strongly associated with coronary artery calcification (CAC) assessed by multislice computed tomography Yohei Oda 1, Muhei Tanaka 2, Michiaki Fukui 2, Sei Tsunoda 1, Satoshi Akabame
Causes of death in Diabetes
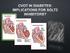 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
