Endometriosis. Second edition. by Botros Rizk and Hossam Abdalla. Epidemiology and pathogenesis 9. Endometriosis and infertility 32
|
|
|
- Angel Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endometriosis Second edition by Botros Rizk and Hossam Abdalla Epidemiology and pathogenesis 9 Endometriosis and infertility 32 Diagnosis of endometriosis 41 Medical treatment of endometriosis 55 Surgical treatment of endometriosis 71 Treatment of infertility associated with endometriosis 81 Assisted reproductive technology and endometriosis 92 Extrapelvic endometriosis 103 Recurrent endometriosis 110 Adenomyosis 117 The doctor patient partnership 125 HEALTH PRESS
2 Endometriosis Second edition Botros Rizk Professor and Chief Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of South Alabama, Alabama, USA Hossam Abdalla Director of the Lister Fertility Clinic The Lister Hospital, London, UK HEALTH PRESS Oxford
3 Fast Facts Endometriosis First published 1998 Second edition September 2003 Text 2003 Botros Rizk, Hossam Abdalla 2003 in this edition Health Press Limited Health Press Limited, Elizabeth House, Queen Street, Abingdon, Oxford OX14 3JR, UK Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0) Fast Facts is a trademark of Health Press Limited All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the express permission of the publisher. The rights of Botros Rizk and Hossam Abdalla to be identified as the authors of this work have been asserted in accordance with the Copyright, Designs & Patents Act 1988 Sections 77 and 78. The publisher and the authors have made every effort to ensure the accuracy of this book, but cannot accept responsibility for any errors or omissions. Registered names, trademarks, etc. used in this book, even when not marked as such, are not to be considered unprotected by law. A CIP catalogue record for this title is available from the British Library. ISBN Rizk, B (Botros) Fast Facts Endometriosis/ Botros Rizk, Hossam Abdalla Medical illustrations by Dee McLean and Jane Fallows, London, UK. Typesetting and page layout by Zed, Oxford, UK. Printed by Fine Print (Services) Ltd, Oxford, UK. Printed with vegetable inks on fully biodegradable and recyclable paper manufactured from sustainable forests. Low chlorine Sustainable forests
4 Glossary 4 Introduction 7 Epidemiology and pathogenesis 9 Endometriosis and infertility 32 Diagnosis of endometriosis 41 Medical treatment of endometriosis 55 Surgical treatment of endometriosis 71 Treatment of infertility associated with endometriosis 81 Assisted reproductive technology and endometriosis 92 Extrapelvic endometriosis 103 Recurrent endometriosis 110 Adenomyosis 117 The doctor patient partnership 125 Useful addresses 127 Index 129
5 Glossary 4 adhesiolysis: separation/removal of adhesions adnexal masses: enlarged parts of the Fallopian tubes or ovaries AFS: American Fertility Society, now known as the ASRM amenorrhea: absence of menstruation anovulation: lack of ovulation ASRM: American Society for Reproductive Medicine blastocyst stage: stage at which an embryo implants in the uterus blebs: blister-like lumps filled with fluid catechol estrogens: hormones derived from amino acids cervical atresia: closure of the neck of the womb COH: controlled ovarian hyperstimulation dyschezia: painful defecation dysmenorrhea: pain before and during menstruation dyspareunia: painful sexual intercourse dysuria: pain on passing urine endometrial atrophy: pseudopregnancy endometrioma: tumor of abnormally placed endometrium estradiol: natural estrogen used to control menopausal symptoms fecundity rate: fertility ability rating FSH: follicle-stimulating hormone GIFT: gamete intrafallopian transfer glandular epithelia: outer cell layer of glands GnRH: gonadotropin-releasing hormone GnRH analogs: drugs which initially superstimulate the pituitary gland to make more GnRH and then shut down GnRH production GnRH antagonists: drugs which stop the production of GnRH hematuria: blood in the urine hirsutism: excessive growth of hair on face and body humoral immune response: antibody response hypermenorrhea: heavy menstrual bleeding hyperplasia: abnormal growth in number of tissue cells, increasing the size of the organ hyperprolactinemia: abnormally high production of the hormone prolactin ICSI: intracytoplasmic sperm injection implantation: penetration of and attachment to lining of womb by fertilized ovum IUI: intrauterine insemination IVF: in-vitro fertilization LH: luteinizing hormone lysis: destruction of living cells through rupture of membranes macrophages: scavenging cells of the immune system
6 Glossary mesothelium: lining cells of the peritoneum, pleura and other body parts metaplasia: abnormal change in tissue as a result of change in cells uterine fibroids: benign tumors growing in the uterus wall VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor occlusion: closing of an opening, or obstruction of a hollow part oligomenorrhea: abnormally infrequent periods oophorectomy: surgical removal of ovaries parenchyma: the functional tissue of an organ pathognomonic: uniquely characteristic of a disease periovarian adhesions: adhesions around the ovaries peritoneal fluid: lubricant secreted by the peritoneum phagocytosis: destruction of foreign bodies by phagocytes prostaglandins: hormone-like substances involved in many body processes (e.g. influencing blood clotting, inducing abortion, causing muscle contraction) retrograde menstruation: retention of menstrual blood in the body serum immunoassays: method of testing concentration of antibodies sperm motility: swimming action of sperm in seminal fluid stroma: the tissue forming the supporting framework of an organ superovulation: production of more than one or two eggs (ova) at one time synthetic progestogens: drugs chemically and pharmacologically similar to natural hormone progesterone 5
7 Introduction Endometriosis, the presence of tissue histologically similar to endometrium outside the uterine cavity and the myometrium, is one of the most common gynecologic conditions in women of reproductive age, but it remains one of the most complicated and baffling. It is estimated that over 5 million women in the USA have endometriosis, and it is thought to affect 10 25% of all women attending gynecologic clinics in the USA and the UK. Sufferers make up a sizeable proportion of those attending gynecologic practices, whether seeking help for infertility or because the condition has become chronic with disabling effects. Although it is not easy to determine how prevalent the disease is among the general population (at present, it can only be confirmed by laparoscopy or laparotomy), there are indications that it is increasing. One factor in this could be the considerable delay between the onset of pain and the surgical diagnosis in the UK it is 8 years, in the USA it is about 10 years. In addition to the physical effects of the disease, the psychological impact of endometriosis is also a cause for concern. Every practicing primary care provider and gynecologist should be aware of the feelings of frustration and consequent depression experienced by women with endometriosis. On numerous occasions women have been referred to psychiatrists as mental cases, a psychologizing of endometriosis that represents the failure of gynecologists to diagnose the condition. In one clinic, out of 850 laparoscopies performed in patients with pain of 6 months duration or longer, histologically proven endometriosis or adhesions were found in 92%. After this treatment, their psychological profiles returned to near-normal, because when endometriosis was removed, pelvic pain improved. We must stop the psychologizing of endometriosis. Gynecologists must not allow frustrated or ill-informed colleagues to dismiss patients as cranks rather than diagnose and treat them or refer them to specialists who can do so. 7
8 Fast Facts Endometriosis Though the disease has been known for more than a century, it remains a challenge to gynecologists and primary care physicians. Fast Facts Endometriosis presents healthcare professionals with the latest information to enable the patient to be treated with consideration and speed. 8
9 1 Epidemiology and pathogenesis Epidemiology The incidence of endometriosis remains unknown, because the disease is usually recorded as part of another investigation, for example into infertility or chronic pain in the abdomen or pelvis, or during another procedure such as sterilization. Many factors could account for the variations in the estimates of prevalence of endometriosis drawn from different investigations. Prevalence of endometriosis On the basis of hospital and surgical records. In the USA in 1980, among women aged years, 6.3% of first diagnosis and 6.9% of all diagnoses for genitourinary problems were linked to endometriosis (National Center for Health Statistics). Between 1988 and 1990 the US National Hospital Discharge Survey, covering over 5 million gynecologic diagnoses, put endometriosis as first diagnosis at 11.2%. US Army records ( ) show that endometriosis was diagnosed in 6.2% of women undergoing gynecologic surgery. Another review from Houston, Texas, put the prevalence of endometriosis at 10.3%. Smaller surgical case reports show a range of findings: when laparoscopy was performed for pelvic pain, a prevalence rate of 4 80% was reported for endometriosis compared with 2 80% for infertility. Endometriosis was reported in 4% of over women undergoing tubal ligation. In the UK, endometriosis was noted in 21% of women being investigated for infertility and in 6% being sterilized. For those with chronic abdominal pain, the incidence of endometriosis was 15%; among those having abdominal hysterectomy it was 25%. On the basis of population studies. In the UK and the USA, three general epidemiological studies of endometriosis have been reported. In the UK, the Oxford Family Planning Association studied a cohort of British women between 1968 and The authors reviewed the women s medical records up until the end of 1990 for a diagnosis of 9
10 Fast Facts Endometriosis 10 endometriosis at laparoscopy or laparotomy, identifying 142 in which endometriosis was the first diagnosis. One limitation of this study is that controls did not undergo laparoscopy and therefore some could have undiagnosed endometriosis. Houston and co-authors reviewed the medical records of white residents of Rochester, Minnesota, USA, from 1970 to 1979, to find newly diagnosed cases of endometriosis. They had four diagnostic groups: histologically confirmed disease visualization of disease during surgery clinically probable diagnosis based on pain and positive examination clinically possible diagnosis based on examination alone. From these data, the authors concluded a prevalence of between 2.5% and 3.3% assuming that the endometriosis had an average duration of 10 years. However, should the duration be 25 years, the prevalence rate would be %. As there is known to be considerable delay in the diagnosis between the onset of pain symptoms and the surgical confirmation, prevalence rates should take this into account. Kjerulff and colleagues used the self-reporting method (US Health Interview Survey, ), asking a random sample aged years about their gynecologic problems of the previous year. Of women surveyed, 211 had been diagnosed with endometriosis and 1666 reported having menstrual disorders. The authors acknowledged that the reported prevalence rates of 6.9/1000 for endometriosis and 53/1000 for menstrual disorders could be underestimates because many respondents were embarrassed to answer personal questions. Others had not reported their symptoms to a physician; some had forgotten about them. Changes in prevalence. The available data show that gynecologic surgery for endometriosis has been on the rise. In 1965, approximately hysterectomies were performed for endometriosis in the USA, compared with in 1984 (the proportions are shown in Figure 1.1). Although the general trend was to an increase in the number of hysterectomies performed during this period (Figure 1.2), the proportion carried out for endometriosis rose from 9% to 19%, an
11 Epidemiology and pathogenesis 20 Hysterectomies performed for endometriosis (%) Years Figure 1.1 Proportion of hysterectomies performed in the USA for endometriosis. Source: US National Center for Health Statistics, Hyattsville, MD Increase or decrease (%) Prolapse Fibroids Cancer Hyperplasia Other Endometriosis Diagnoses Figure 1.2 Changes in the indications for hysterectomy in the USA between 1965 and Source: Nezhat et al increase of 120%, which is unmatched by any other condition. It seems likely, given the dramatically increased frequency of surgical intervention for endometriosis, that the prevalence of the disease has increased. 11
12 4 Medical treatment of endometriosis Medical treatment remains the cornerstone of the management of symptoms associated with endometriosis. In adolescents repeated courses of medical therapy will be needed to achieve symptom regression and avoid repeated surgery. Hormonal therapy This has been the main medical treatment for endometriosis for half a century. In the 1940s and 1950s, diethylstilbestrol and methyltestosterone were used, but were abandoned because the side effects were too great. In the 1960s, progestogen alone or combined estrogen/progestogen preparations were used in an attempt to produce a state of pseudopregnancy (see below), but again significant side effects rendered the treatment unpopular. The modern era of hormonal therapy began with the description of danazol by Dmowski et al. in By 1987, the aggregate pregnancy rate was 40% in 16 studies involving 511 patients with mild endometriosis. However, Evers found the pregnancy rates to be similar to placebo-treated patients in randomized clinical trials, as verified by Collins. The concept of downregulation with GnRH agonist in endometriosis was introduced in 1984 from Quebec City in a pivotal paper by Lemay. More recently, GnRH antagonists and antiprogesterones have been used, with favorable reports. Aromatase inhibitors are the newest class of medication with the greatest promise for the treatment of endometriosis. In the future, the development of antiangiogenesis therapy and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors will have a marked impact on the treatment of endometriosis. Pseudopregnancy. In 1959, Kistner reported the use of Enovid (norethynodrel and mestranol) in 58 women with pelvic endometriosis. It was a landmark in the history of pharmacological treatment of endometriosis, but it lost popularity because of both estrogenic and progestational side effects. 55
13 Fast Facts Endometriosis Danazol is a synthetic by-product of testosterone with a half-life of 4.5 hours. Peak levels are reached 2 hours after oral ingestion, and after 8 hours it is no longer detectable. It is metabolized in the liver, and the principal metabolite methylethisterone exhibits mild progestational and androgenic activity. Danazol has a direct effect on steroidogenesis, including cholesterol cleavage enzymes, and on intracellular steroid receptors. It has an indirect action by decreasing GnRH pulse frequency, which may suppress ovulation. Side effects. The most common are related to the hyperandrogenic state weight gain, oily skin and hair, nausea, acne, muscle cramps, hot flashes and hirsutism. Deepening of the voice, though uncommon, is irreversible. Danazol has multiple metabolic side effects, the most important of which relate to blood cholesterol. It decreases HDL and increases LDL levels, which must be taken into account as the drug is given for long periods (6 9 months). Its use should be avoided in women with a history of liver disease. Gestrinone is a progesterone agonist/antagonist that has been used in Europe for treatment of endometriosis, but is unavailable in the USA. Gestrinone causes amenorrhea and endometrial atrophy, as do other androgen steroid analogs (e.g. danazol). It acts both centrally and peripherally to reduce estradiol and obliterate the mid-cycle luteinizing hormone (LH) surge. Gestrinone has a long half-life, allowing oral administration 2 3 times weekly. In randomized clinical trials, gestrinone was effective in reducing the painful symptoms of endometriosis. Side effects. Gestrinone has similar androgenic symptomatic and metabolic effects to danazol, but fewer hypoestrogenic side effects. 56 Progestogens. The effect of progestogens on endometrial tissue depends on the dosage, length of treatment and activity of the individual progestogen (Table 4.1). Side effects include irregular vaginal bleeding, weight gain, fluid retention, breast tenderness and mood changes.
Endometriosis. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Endometriosis A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications Committee.
Endometriosis A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications Committee.
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Endometriosis. A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES
 Endometriosis A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications Committee.
Endometriosis A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the Patient Education Committee and the Publications Committee.
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S. Congress Avenue, Lake Worth, FL 33461 561.434.0111 4631 N. Congress Avenue, Suite 102, West Palm Beach, FL 33407 Endometriosis The lining of the uterus is
Reproductive System. Testes. Accessory reproductive organs. gametogenesis hormones. Reproductive tract & Glands
 Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Reproductive System Testes gametogenesis hormones Accessory reproductive organs Reproductive tract & Glands transport gametes provide nourishment for gametes Hormonal regulation in men Hypothalamus - puberty
Infertility. Review and Update Clifford C. Hayslip MD Intrauterine Inseminations
 Infertility Review and Update Clifford C. Hayslip MD Intrauterine Inseminations Beneficial effects of IUI not consistently documented in studies No deleterious effects on fertility 3-4 cycles of IUI should
Infertility Review and Update Clifford C. Hayslip MD Intrauterine Inseminations Beneficial effects of IUI not consistently documented in studies No deleterious effects on fertility 3-4 cycles of IUI should
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones
 10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
10.7 The Reproductive Hormones December 10, 2013. Website survey?? QUESTION: Who is more complicated: men or women? The Female Reproductive System ovaries: produce gametes (eggs) produce estrogen (steroid
5/5/2010. Infertility FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. Infertility Definition. Objectives. Normal Human Fertility. Normal Menstrual Cycle
 Infertility FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE I HAVE NO FINANCIAL INTEREST IN ANY OF THE PRODUCTS MENTIONED IN MY PRESENTATION Bryan K. Rone, M.D. University of Kentucky Obstetrics and Gynecology I AM RECEIVING COMPENSATION
Infertility FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE I HAVE NO FINANCIAL INTEREST IN ANY OF THE PRODUCTS MENTIONED IN MY PRESENTATION Bryan K. Rone, M.D. University of Kentucky Obstetrics and Gynecology I AM RECEIVING COMPENSATION
Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary
 Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Subfertility Infertility: failure to conceive within one year of unprotected regular sexual intercourse. Primary secondary Infertility affects about 15 % of couples. age of the female. Other factors that
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Endometriosis. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Endometriosis What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition whereby the lining
Endometriosis What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis is a condition whereby the lining
Endometriosis Treatment & Management Medscape
 Endometriosis Treatment & Management Medscape Updated: Apr 25, 2016 Author: G Willy Davila, MD; Chief Editor: Michel E Rivlin, MD more... Approach Considerations The dependence of endometriosis on the
Endometriosis Treatment & Management Medscape Updated: Apr 25, 2016 Author: G Willy Davila, MD; Chief Editor: Michel E Rivlin, MD more... Approach Considerations The dependence of endometriosis on the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Formerly The American Fertility Society OVULATION DETECTION A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Formerly The American Fertility Society OVULATION DETECTION A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive
Androgens Hormones that are produced by the testes of the male and in small amounts by the ovaries and adrenal glands of the female.
 http://www.myfertility.ca/glossary.xhtml (February 27, 2015) Glossary Acrosome This is a membrane-bound cap-like structure found at the head of the sperm. It contains enzymes that are thought to help the
http://www.myfertility.ca/glossary.xhtml (February 27, 2015) Glossary Acrosome This is a membrane-bound cap-like structure found at the head of the sperm. It contains enzymes that are thought to help the
Phases of the Ovarian Cycle
 OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
INFERTILITY CAUSES. Basic evaluation of the female
 INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability to conceive after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. There are multiple causes of infertility and a systematic way to evaluate the condition. Let s look at some
INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability to conceive after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. There are multiple causes of infertility and a systematic way to evaluate the condition. Let s look at some
Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis
 Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference PCOS vs Endometriosis Ovaries play an important role in the reproduction and the maintenance of the female body. They
Difference Between PCOS and Endometriosis www.differencebetween.com Key Difference PCOS vs Endometriosis Ovaries play an important role in the reproduction and the maintenance of the female body. They
EVALUATING THE INFERTILE PATIENT-COUPLES. Stephen Thorn, MD
 EVALUATING THE INFERTILE PATIENT-COUPLES Stephen Thorn, MD Overview The field of reproductive medicine continues to evolve rapidly by offering newer diagnostic testing and therapeutic options to improve
EVALUATING THE INFERTILE PATIENT-COUPLES Stephen Thorn, MD Overview The field of reproductive medicine continues to evolve rapidly by offering newer diagnostic testing and therapeutic options to improve
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
CASE 41. What is the pathophysiologic cause of her amenorrhea? Which cells in the ovary secrete estrogen?
 CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
CASE 41 A 19-year-old woman presents to her gynecologist with complaints of not having had a period for 6 months. She reports having normal periods since menarche at age 12. She denies sexual activity,
Endometriosis. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary
 Endometriosis What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a common condition in young women. It's chronic, painful, and it often progressively gets worse over the time. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary Normally,
Endometriosis What is endometriosis? Endometriosis is a common condition in young women. It's chronic, painful, and it often progressively gets worse over the time. *Chocolate cyst in the ovary Normally,
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Gynaecological oncology
 PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Endometriosis. Assoc.Prof.Pawin Puapornpong, Faculty of Medicine, Srinakharinwirot University.
 Endometriosis Assoc.Prof.Pawin Puapornpong, Faculty of Medicine, Srinakharinwirot University. Endometriosis Definition: Ectopic Endometrial Tissue True Incidence Unknown:? 1-5% Does NOT Discriminate by
Endometriosis Assoc.Prof.Pawin Puapornpong, Faculty of Medicine, Srinakharinwirot University. Endometriosis Definition: Ectopic Endometrial Tissue True Incidence Unknown:? 1-5% Does NOT Discriminate by
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Glossary
 Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Glossary The following is a glossary of terms you may hear during your association with the University of Mississippi Health Care's reproductive endocrinology and
Reproductive Endocrinology & Infertility Glossary The following is a glossary of terms you may hear during your association with the University of Mississippi Health Care's reproductive endocrinology and
GLOSSARY OF INFERTILITY TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF INFERTILITY TERMS Adapted from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM). A nonprofit,professional medical organization of more than 9,000 health care specialistsinterested in reproductive
GLOSSARY OF INFERTILITY TERMS Adapted from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM). A nonprofit,professional medical organization of more than 9,000 health care specialistsinterested in reproductive
Causes of Infertility and Treatment Options
 Causes of Infertility and Treatment Options Dr Mrs.Kiran D. Sekhar Former vice President-FOGSI Former Chairperson- Genetics and Foetal medicine-fogsi Founder and Medical Director-Kiran Infertility centre
Causes of Infertility and Treatment Options Dr Mrs.Kiran D. Sekhar Former vice President-FOGSI Former Chairperson- Genetics and Foetal medicine-fogsi Founder and Medical Director-Kiran Infertility centre
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Reproductive Testing: Less is More G. Wright Bates, Jr., M.D. Professor and Director Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Objectives
 Reproductive Testing: Less is More G. Wright Bates, Jr., M.D. Professor and Director Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Objectives 1. Review definition of infertility and impact of age 2. Stress
Reproductive Testing: Less is More G. Wright Bates, Jr., M.D. Professor and Director Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Objectives 1. Review definition of infertility and impact of age 2. Stress
FERTILITY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE INFERTILITY: AN OVERVIEW A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE INFERTILITY: AN OVERVIEW A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine
 1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
Gastroenterology Second edition
 Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Clinical drawings for your patients Patient Pictures books are: PATI ENT PICTU RES Patient Pictures time-saving books for doctors and nurses. Use them when describing medical conditions and treatments
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد
 Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
Endometriosis د. نجمه محمود كلية الطب جامعة بغداد فرع النسائية والتوليد Objectives:- To know what is endometriosis The sites where it occur To explain its itiology & pathogenesis To know the clinical features
Saint Mary s Hospital. Gynaecology Unit. Saint Mary s Hospital. Endometriosis. Information For Patients
 Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Unit Saint Mary s Hospital Endometriosis Information For Patients Contents What is endometriosis?... 3 What happens?... 3 Who is affected?... 3 Outlook... 3 What are the
Saint Mary s Hospital Gynaecology Unit Saint Mary s Hospital Endometriosis Information For Patients Contents What is endometriosis?... 3 What happens?... 3 Who is affected?... 3 Outlook... 3 What are the
Clinical evaluation of infertility
 Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Clinical evaluation of infertility DR. FARIBA KHANIPOUYANI OBSTETRICIAN & GYNECOLOGIST PRENATOLOGIST Definition: inability to achieve conception despite one year of frequent unprotected intercourse. Male
Obstetrics and Gynecology. Infertility. Dr. Layla Zaghal. Definition
 Obstetrics and Gynecology Infertility Dr. Layla Zaghal Definition The term infertility is no more used and has been replaced by the term subfertility ; when you tell a couple that they are infertile, it
Obstetrics and Gynecology Infertility Dr. Layla Zaghal Definition The term infertility is no more used and has been replaced by the term subfertility ; when you tell a couple that they are infertile, it
Infertility. Thomas Lloyd and Samera Dean
 Infertility Thomas Lloyd and Samera Dean Infertility Definition Causes Referral criteria Assisted reproductive techniques Complications Ethics What is infertility? Woman Reproductive age Has not conceived
Infertility Thomas Lloyd and Samera Dean Infertility Definition Causes Referral criteria Assisted reproductive techniques Complications Ethics What is infertility? Woman Reproductive age Has not conceived
Infertility F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS. Q: Is infertility a common problem?
 Infertility (female factors). In another one third of cases, infertility is due to the man (male factors). The remaining cases are caused by a mixture of male and female factors or by unknown factors.
Infertility (female factors). In another one third of cases, infertility is due to the man (male factors). The remaining cases are caused by a mixture of male and female factors or by unknown factors.
Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis George D Perkin and Jerry S Wolinsky Second edition 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis Second edition George D
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis George D Perkin and Jerry S Wolinsky Second edition 2006 Health Press Ltd. www.fastfacts.com Fast Facts Fast Facts: Multiple Sclerosis Second edition George D
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE. Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract
 POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS Detailed syllabus: Part 1 Basic Sciences: Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract Physiology Endocrinology
POST - DOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP PROGRAMME IN REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS Detailed syllabus: Part 1 Basic Sciences: Anatomy : Male and Female genital tract Physiology Endocrinology
Fertility assessment and assisted conception
 Fertility assessment and assisted conception Dr Geetha Venkat MD FRCOG Director Pulse Learning Women s health 14 September 2016 Disclosure statement Dr Venkat is a director of Harley Street Fertility Clinic.
Fertility assessment and assisted conception Dr Geetha Venkat MD FRCOG Director Pulse Learning Women s health 14 September 2016 Disclosure statement Dr Venkat is a director of Harley Street Fertility Clinic.
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Endometriosis and Infertility - FAQs Introduction The inner lining of the uterus is called the endometrium and it responds to changes that take place during a woman's monthly menstrual
LOW RESPONDERS. Poor Ovarian Response, Por
 LOW RESPONDERS Poor Ovarian Response, Por Patients with a low number of retrieved oocytes despite adequate ovarian stimulation during fertility treatment. Diagnosis Female About Low responders In patients
LOW RESPONDERS Poor Ovarian Response, Por Patients with a low number of retrieved oocytes despite adequate ovarian stimulation during fertility treatment. Diagnosis Female About Low responders In patients
ORILISSA (elagolix) oral tablet
 ORILISSA (elagolix) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
ORILISSA (elagolix) oral tablet Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy Coverage
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
Biology of fertility control. Higher Human Biology
 Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Biology of fertility control Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Compare fertile periods in females and males What is infertility? Infertility is the inability of a sexually active, non-contracepting
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Reproductive Hormones
 Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive Hormones Male gonads: testes produce male sex cells! sperm Female gonads: ovaries produce female sex cells! ovum The union of male and female sex cells during fertilization produces a zygote
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Understanding Infertility, Evaluations, and Treatment Options
 Understanding Infertility, Evaluations, and Treatment Options Arlene J. Morales, M.D., F.A.C.O.G. Fertility Specialists Medical Group, Inc. What We Will Cover Introduction What is infertility? Briefly
Understanding Infertility, Evaluations, and Treatment Options Arlene J. Morales, M.D., F.A.C.O.G. Fertility Specialists Medical Group, Inc. What We Will Cover Introduction What is infertility? Briefly
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY
 WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY Intrauterine Insemination 1 About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and
WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY Intrauterine Insemination 1 About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Patient Past Medical History
 Patient Past Medical History A. Identifying Data Date this form when completed Your name Partner's name Age Birth date Height Weight Length of marriage (or relationship) How long have you been trying unsuccessfully
Patient Past Medical History A. Identifying Data Date this form when completed Your name Partner's name Age Birth date Height Weight Length of marriage (or relationship) How long have you been trying unsuccessfully
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy Number: PA.018.MH Last Review Date: 08/04/2016 Effective Date: 01/01/2017
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL PA.018.MH Infertility- Treatment This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP (Not Covered) MedStar
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL PA.018.MH Infertility- Treatment This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP (Not Covered) MedStar
Subfertility B Y A L I S O N, B E N A N D J O H N
 Subfertility B Y A L I S O N, B E N A N D J O H N Contents Definition Causes Male Female Hx & Ex Investigations Treatment Definition Failure to conceive after a year of frequent, unprotected communion.
Subfertility B Y A L I S O N, B E N A N D J O H N Contents Definition Causes Male Female Hx & Ex Investigations Treatment Definition Failure to conceive after a year of frequent, unprotected communion.
Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur?
 Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
Published on: 8 Apr 2013 Intrauterine Insemination - FAQs Q. How Does Pregnancy Occur? A. The female reproductive system involves the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina. The female hormones,
Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer Christina Fotopoulou MD PhD Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital London, UK Thomas J Herzog MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Ovarian Cancer Christina Fotopoulou MD PhD Consultant Gynaecological Oncologist Queen Charlotte s and Chelsea Hospital London, UK Thomas J Herzog MD Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Estrogens and progestogens
 Estrogens and progestogens Estradiol and Progesterone hormones produced by the gonads are necessary for: conception embryonic maturation development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Estrogens and progestogens Estradiol and Progesterone hormones produced by the gonads are necessary for: conception embryonic maturation development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Infertility: An Overview
 AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE Infertility: An Overview A Guide for Patients PATIENT INFORMATION SERIES Published by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine under the direction of the
Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms
 WELCOME Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad,
WELCOME Stage 4 - Ovarian Cancer Symptoms University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad,
Reproductive Health and Pituitary Disease
 Reproductive Health and Pituitary Disease Janet F. McLaren, MD Assistant Professor Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology jmclaren@uabmc.edu Objectives
Reproductive Health and Pituitary Disease Janet F. McLaren, MD Assistant Professor Division of Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology jmclaren@uabmc.edu Objectives
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Frequency of menses. Duration of menses 3 days to 7 days. Flow/amount of menses Average blood loss with menstruation is 60-80cc.
 Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
Frequency of menses 24 days (0.5%) to 35 days (0.9%) Age 25, 40% are between 25 and 28 days Age 25-35, 60% are between 25 and 28 days Teens and women over 40 s cycles may be longer apart Duration of menses
Infertility treatment
 In the name of God Infertility treatment Treatment options The optimal treatment is one that provide an acceptable success rate, has minimal risk and is costeffective. The treatment options are: 1- Ovulation
In the name of God Infertility treatment Treatment options The optimal treatment is one that provide an acceptable success rate, has minimal risk and is costeffective. The treatment options are: 1- Ovulation
Female Reproductive Physiology. Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF
 Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
Human Reproduction. Human Reproductive System. Scrotum. Male Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
Human Reproductive System Human Reproduction Chapter 41 Contraceptives Scrotum Testes Epididymus Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicles Prostate Gland Bulbourethral Gland Penis Scrotum Sac of smooth muscle tissue
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
Female Consultation Questionnaire
 Female Consultation Questionnaire In order to schedule a consultation with the doctor, an overview of your medical history along with a copy of your medical records are requested. Dr. Zouves will review
Female Consultation Questionnaire In order to schedule a consultation with the doctor, an overview of your medical history along with a copy of your medical records are requested. Dr. Zouves will review
The reproductive lifespan
 The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
The reproductive lifespan Reproductive potential Ovarian cycles Pregnancy Lactation Male Female Puberty Menopause Age Menstruation is an external indicator of ovarian events controlled by the hypothalamicpituitary
Infertility for the Primary Care Provider
 Infertility for the Primary Care Provider David A. Forstein, DO FACOOG Clinical Associate Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville Disclosure I have
Infertility for the Primary Care Provider David A. Forstein, DO FACOOG Clinical Associate Professor Obstetrics and Gynecology University of South Carolina School of Medicine Greenville Disclosure I have
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Infertility DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 Infertility DR. RAHUL BEVARA Definitions Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of unprotected coitus. Affects 10-15% of couples Primary Infertility, that is inability to conceive
Infertility DR. RAHUL BEVARA Definitions Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of unprotected coitus. Affects 10-15% of couples Primary Infertility, that is inability to conceive
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health. Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital
 Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
Ovaries: In Sickness and Health Mr N Pisal Consultant Gynaecologist The Portland Hospital Topics for discussion How to assess ovarian function? AMH PCOS Ovarian pain Ovarian cysts Ovarian screening Menopause
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Assisted Reproduction. By Dr. Afraa Mahjoob Al-Naddawi
 Assisted Reproduction By Dr. Afraa Mahjoob Al-Naddawi Learning Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1) Define assisted reproductive techniques (ART). 2) List indications for various
Assisted Reproduction By Dr. Afraa Mahjoob Al-Naddawi Learning Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: 1) Define assisted reproductive techniques (ART). 2) List indications for various
Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE. result graph based on Luteal Phase. result graph based on Luteal Phase
 Patient Name: Patient DOB: Gender: Physician: Test Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE Grote, Mary Jane Batch Number: B6437 2/16/1954 Accession Number: N52281 F Date Received: 2/3/2015 Any Lab Test
Patient Name: Patient DOB: Gender: Physician: Test Hormone Balance - Female Report SAMPLE Grote, Mary Jane Batch Number: B6437 2/16/1954 Accession Number: N52281 F Date Received: 2/3/2015 Any Lab Test
MANAGEMENT OF REFRACTORY ENDOMETRIOSIS
 (339) MANAGEMENT OF REFRACTORY ENDOMETRIOSIS Serdar Bulun, MD JJ Sciarra Professor and Chair Department of Ob/Gyn Northwestern University ENDOMETRIOSIS OCs Teenager: severe dysmenorrhea often starting
(339) MANAGEMENT OF REFRACTORY ENDOMETRIOSIS Serdar Bulun, MD JJ Sciarra Professor and Chair Department of Ob/Gyn Northwestern University ENDOMETRIOSIS OCs Teenager: severe dysmenorrhea often starting
Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) / Infertility / Synarel (nafarelin)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.03 Subject: Synarel Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Synarel Description Assisted
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.03 Subject: Synarel Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Synarel Description Assisted
UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA. About Uterine leiomyosarcoma
 UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA Uterine Lms, Ulms Or Just Lms Rare uterine malignant tumour that arises from the smooth muscular part of the uterine wall. Diagnosis Female About Uterine leiomyosarcoma Uterine LMS
UTERINE LEIOMYOSARCOMA Uterine Lms, Ulms Or Just Lms Rare uterine malignant tumour that arises from the smooth muscular part of the uterine wall. Diagnosis Female About Uterine leiomyosarcoma Uterine LMS
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Realizing dreams booklet.indd 1 5/20/ :26:52 AM
 Realizing dreams. 18891booklet.indd 1 5/20/2010 11:26:52 AM The Journey To Parenthood The first Gator Baby was born in 1988 through the in vitro fertilization program at the University of Florida. Since
Realizing dreams. 18891booklet.indd 1 5/20/2010 11:26:52 AM The Journey To Parenthood The first Gator Baby was born in 1988 through the in vitro fertilization program at the University of Florida. Since
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
ACT TRYING TO HAVE A BABY? YOUR STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO ASSISTED CONCEPTION THE ACT PATHWAY
 ACT TRYING TO HAVE A BABY? YOUR STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO CONCEPTION THE ACT PATHWAY ACT HOW TO USE THE ACT PATHWAY BOOKLET Firstly: You are not alone. Up to 1 in 6 couples around the world will experience
ACT TRYING TO HAVE A BABY? YOUR STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE TO CONCEPTION THE ACT PATHWAY ACT HOW TO USE THE ACT PATHWAY BOOKLET Firstly: You are not alone. Up to 1 in 6 couples around the world will experience
- Linzagolix overall efficacy and safety maintained or improved at week 24
 Final results of ObsEva SA Phase 2b EDELWEISS trial of Linzagolix show sustained efficacy and Bone Mineral Density safety, for the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain - Linzagolix overall efficacy
Final results of ObsEva SA Phase 2b EDELWEISS trial of Linzagolix show sustained efficacy and Bone Mineral Density safety, for the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain - Linzagolix overall efficacy
Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis
 Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: Know the clinicopathologic features of endometriosis with special emphasis on: definition,
Polycystic ovarian disease and Endometriosis Objectives: At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to: Know the clinicopathologic features of endometriosis with special emphasis on: definition,
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Endometriosis BRADEN COLEMAN, MD PGY-3
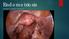 Endometriosis BRADEN COLEMAN, MD PGY-3 Case 1: 30 y/o F PMH Borderline personality disorder, anxiety, depression, presents with complaints of LLQ abdominal pain and palpable abdominal nodules. She reports
Endometriosis BRADEN COLEMAN, MD PGY-3 Case 1: 30 y/o F PMH Borderline personality disorder, anxiety, depression, presents with complaints of LLQ abdominal pain and palpable abdominal nodules. She reports
Pelvic Pain. What you need to know. 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone Fax
 Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
Pelvic Pain What you need to know 139 Dumaresq Street Campbelltown Phone 4628 5292 Fax 4628 0349 www.nureva.com.au September 2015 PELVIC PAIN This is a common problem and most women experience some form
