Evaluating the toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on the dominant bacteria in the sludge of wastewater treatment facilities
|
|
|
- Bruce O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Environmental Biology, 7(4): , 213 ISSN This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluating the toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on the dominant bacteria in the sludge of wastewater treatment facilities 1 Ali Toolabi and 2 Narges Khanjani 1 Master of Environmental Health Engineering, Faculty of Public Health, Bam Medical University, Bam, Iran. 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Kerman Medical University, Kerman, Iran Ali Toolabi and Narges Khanjani; Evaluating the toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on the dominant bacteria in the sludge of wastewater treatment facilities ABSTRACT We intended to assess the toxicity and evaluate the toxicity of the ZnO nanoparticles by examining them on bacteria of wastewater sludge. The results of this study can justify the use of nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents.the stock solution of 1 g/l of these nanoparticles were diluted by the Mueller Hinton Agar culture and 5 to 6 mg/l concentrations were created. and purified bacteria were cultivated on them. Then the percentage of growth prohibiting was determined by comparing the samples including nanoparticles and control samples. Half maximal effective concentration (EC 5 ), NOEC and the concentration with 1% growth prohibition was determined.the EC 5 of ZnO nanoparticles for, Bacillus Subtilis, Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa were respectively 181.7, 656.4, 93.9 and mg/l. Staphylococcus Aureus had a high sensitivity to ZnO nanoparticles and can be used as a parameter in the biological tests for the effect of nanoparticles on bacteria. Also the ZnO nanoparticles had a high toxicity and even the least amount (at 2813 mg/l ) could stop the growth of all bacteria.this nanoparticle can probably be used for hygienic and water treatment purposes and for protecting food from contamination. Key words: nanoparticles, toxicity, ZnO, wastewater treatment. Introduction Different organisms and species can be used to determine the toxicity of chemicals. However researchers have always tried to determine the most sensitive organism and use it in these studies. By using these sensitive organisms we can generalize the results by means of a certainty score to other organisms such as human beings. Among the different organisms, bacteria are distributed widely and their culture is easy which makes them appropriate organisms to study. Their wide spread in the environment, makes the results of these studies more practical in real environments. On the side, these organisms in contrary to algaes, nematodes and crustaceans which are among the most used organisms in determining toxicity [8,1,2,19], do not need a aqueous environment and can grow in solid environments and with low humidity. Therefore they are appropriate organism to determine toxicity. On the other side, the ZnO nanoparticles are among the most used nanoparticles which are produced at industrial scale. The ZnO nanoparticles are used in antisolar creams, pigments, electricity cables, tiles and etc [1]. Although the benefits of nanoparticles are undeniable, we should keep in mind that the wide use of these chemicals leads to the entry of millions of tons of nanoparticles to the environment, water reservoirs and the food chain [9]. Therefore, in order to prevent the negative consequences, it is necessary to evaluate all aspects including the toxicity of chemicals entering the environment. Studies About the toxicity of nanoparticles have been conducted that illuminate the possible danger of these particles for humans and the environment [12,3,4,13]. However, most of the studies that have evaluated the toxicity of metal oxide nanoparicles have been conducted on eukaryotes and multicellular organisms and especially cancer cells and few studies have evaluated their effects on bacteria. In this regard Block et al who have studied the anti bacterial effects of UV and TiO 2 nanoparticles in aqueous environments, reported that the 1% TiO 2 nanoparticle solution was the best concentration for eliminating bacteria and concentrations 1 times this amount had less effect [5]. In another study conducted in 27 by Brayner et al the toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles was evaluated by bacteria [6]. in this study the nanoparticles had a significant prohibiting effect on the growth of E.coli in 3 mmol concentrations. Also it was found that the ZnO nanoparticles had more antibacterial effect on Bacillus Subtilis in comparison Corresponding Author Ali Toolabi, Master of Environmental Health Engineering, Faculty of Public Health, Bam Medical University, Bam, Iran. n_khanjani@kmu.ac.ir
2 to E. coli [16]. In this study the minimum growth prohibiting effect for Bacillus Subtilis was 2 to 125 ppm and for it was 5 to 1 ppm according to the size of nanoparticles. Limited studies have been done about the effect of nanoparticles on bacteria in aqueous environments. However, according to previous research it has been shown that the diameter of the nanoparticle in aqueous environment increases due to their absorbing characteristics and their contact with each other [4,14]. On the other side the diameters of nanoparticles is effective in the penetration rate of the particles into the bacteria and therefore are effective on their toxicity [4,17]. Therefore one of the problems encountered in nanoparticle studies evaluating their toxicity characteristics is that they accumulate and sediment and this leads to little confrontation of the bacteria with nanoparticles and therefore decreased toxicity. According to this, it is necessary to determine the toxicity of these materials in solid environments as well. On the other side, comparing previous research about the toxicity of nanoparticles that have been done on one bacteria show that the results of these studies are very different from each other and this difference is mainly due to the experimental condition and the genetic difference in the bacteria under study and also the characteristics of the chemicals and the culture environments [1,13]. Therefore in order to better compare and determine the best organism for evaluating the toxicity of nanoparticles it is better to evaluate all of the organisms simultaneously in one study, to minimize the effect of these parameters. Meanwhile most of the studies have been alone on one bacterium or in aqueous environments [6,15,11]. Also in previous research the EC 5 (the concentration of chemicals that kills 5% of the population under experiment) has not been clearly determined and this fact has led to difficult comparisons. Therefore this research is the first comprehensive study that evaluates the effect of ZnO on four types of bacteria which are E. coli,, and Bacillus Subtilis, in order to determine the most appropriate organism for using in these experiments and to evaluate the toxicity of these nanoparticles. Also determining the 1% growth prohibiting effect of the ZnO nanoparticle in this study can led to more illimination on the anti bacterial effect of these nanoparticles, which has been shown that in comparison to organic material and minerals have more stability in high pressure and temperature [11]. Therefore the results of this research can help justify the wide use of these nanoparticles as antibacterial, hygienic and therapeutic agents. Materials and Methods The ZnO nanoparticles had a diameter of 2 nm, a purity of 99% and specific surface of 9 m 2 /g and were supplied by the Merck Company, Germany. 813 Stock solutions (1 g/l) of the nanoparticles were prepared and then in order to prevent accumulation and create an even solution, they were left for 3 minutes in a sonicator machine. According to the Book of Standard Methods [2], for determining the EC 5 at least 5 concentrations of the solutions underexpriment is needed, but in this study according to the results of previous studies and in order to increase accuracy, the growth prohibition rate was evaluated in 14 concentrations and in the range of 5 to 6 mg/l. In order to prepare these concentrations the stock nanoparticle concentrations were diluted using the Mueller Hinton Agar culture. Then after preparing these concentrations in lidded experimented tubes and before pouring them into petri dishes, the culture environment was autoclaved. After putting them in petri dishes, bacteria were cultured on them and the percent of growth prohibition was compared with the control dishes. In order to create more practical results, and evaluate the anti bacterial effects of these nanoparticles in solid environments and waste water sludge, samples of bacteria from the sludge of the Kerman Wastewater Plant were taken. For this experiment samples of sludge were cultivated on the Nutrient Agar environment. This culture was incubated for 24 to 48 hours in 37 C to allow bacteria to breed and create colonies. The type of bacteria grown was isolated and determined by biochemical tests at the Microbiology Lab of the School of Public Health at Kerman Medical University. After the isolated bacteria were re-cultivated, they were used in toxicity experiments. The number of inoculated bacteria in each plate was 2 CFU. The test was done 3 times in each concentration and the average was taken as the growth prohibition rate in each concentration. The results were analyzed by Probit analysis and in SPSS16 Software. Probit analysis is a type of regression used to analyze binomial response variables which transforms the sigmoid doseresponse curve to a straight line that can then be analyzed by regression [19]. The results of this analysis were used to draw the dose response figures. The NOEC concentration was also determined by Probit analysis. According to this, the concentration in which the growth prohibition effect of the bacteria was less than 1% was determined as NOEC. Results: The results of determining the frequent species of bacteria in Kerman's wastewater sludge showed that 4 species of bacteria including, S. Aureus,, are prevalent in wastewater sludge. Therefore the experiments were conducted using these bacteria. The summary of Probit analysis has been shown in table 1-3 and figure 1.
3 814 Fig. 1: The dose - response diagram of different bacteria in different concentrations of the ZnO nanoparticles. Table 1: The EC 5 of ZnO Nanoparticles by Using Different Bacteria. Bacteria EC 5 (mg/l) Lower limit of EC 5 Upper limit of EC Table 2: The NOEC of ZnO Nanoparticles by Using Different Bacteria. Bacteria NOEC (mg/l) Lower limit of NOEC Upper limit of NOEC According to table 3 the amount of 1% growth prohibition of the ZnO nanoparticles by using P. Aeruginosa,,, was 2813., 244., 536.4, These results show that the maximums concentration of ZnO for 1% growth elimination is required for and the minimum is required for. Table 3: The 1% Growth Prohibition Effect of ZnO for Different Bacteria. Bacteria 1% Growth prohibition (mg/l) Lower limit of 1% growth prohibition(mg/l) Upper limit of 1% growth prohibition(mg/l) Discussion: According to the results, the minimum amount of EC 5 (93.9 mg/l) for ZnO nanoparticles was for Staphylococcus Aureus and the maximum (935.8 mg/l) was determined by. The two other bacteria (181.7 mg/l) and Bacillus Subtilis (656.4 mg/l) had a EC 5 that was in between. The NOEC was zero for all four bacteria. However the maximum and minimum NOEC for each species was specific and different from other species. According to figure 1, there is a significant relation between the concentration of ZnO nanoparticles and the toxicity of these chemicals, and as their concentration increases, the toxicity of these chemicals also increases. In this case the Pearson's correlation was always more than.98 and the P- value was less than.5. In order to determine bio-indicators it is necessary to choose organisms among species which are prevalent in the environment and their cultivation and growth is feasible. This study showed that 4 bacterial species including E coli,, P. Aeroginosa and are prevalent in wastewater sludge and their growth and cultivation is easy. Therefore they are appropriate bio-indicators for determining the toxicity of nanoparticles. According to our results different bacteria respond differently to a specific nanoparticle in similar concentrations and conditions. By determining EC 5 we found out that is the most sensitive and P. Aeroginosa is the most resistant bacteria to ZnO
4 nanoparticles. Therefore in sensitivity determining experiments, among the four bacteria under study S. Aureus was the most appropriate bacteria. Since in these experiments the data generated by an organism is appropriate which has a high sensitivity and therefore a high certainty score. According to this it is obvious that the 3 other bacteria species should not be recommended. Of course for practical antibacterial experiments of nanoparticles, the P. Aeroginosa bacteria is an appropriate biological indicator, because it has high resistancy and total elimination of this bacteria means that the weaker and more sensitive bacteria will already be eliminated. According to this, the results from 1% elimination showed that in solid environments when the 4 species E coli,, P. Aeroginosa and B. Subtilis are present, 244 mg/l of the ZnO nanoparticle can eliminate all 4 species completely. In this regard, there has not been a comprehension study for determining EC 5 by several bacteria and in solid environment, but a study Adams et al [1] showed that the growth prohibiting concentration of 48% of the species was 1 ppm of ZnO nanoparticles. However in the present study this amount was calculated to be mg/l. This big different in the results of these two studies was mainly because of difference in the kind of nanoparticles and the experimental methods. In a study done by Adams et al, in addition to the fact that the diameter of the nanoparticle used was much more than the nanoparticles used in our study, the experiments were done in a mixed liquid environment. In experiments done in liquid environments on bacteria, in order to prevent the sediment of nanoparticles, solutions are mixed, but this mixing leads to the accumulation of nanoparticles and therefore increase in their diameter [18]. Increase in diameter on the other side leads to less penetration of these chemicals into the cells and organisms, and therefore the real toxicity of these chemicals will be underestimated. This fact can be the main reason for the wide growth prohibiting concentrations in Adams et al's experiments in comparison to our research. In Adams et al's study the concentrations were 1 ppm with 14% prohibiting to 1 ppm with 5% prohibiting. Meanwhile, in the present study using E. coli showed that the concentration range for 5% elimination and NOEC is between zero to mg/l. As it was shown before in the different methods for determining the toxicity of a chemical, the test that shows more toxicity has a higher confidence score, therefore we suggest that for nanoparticle experiments a simultaneous experiment in which a non-aqueous solution is used be conducted (as was done in this study) to better illuminate the potential toxic effects of nanoparticles. In this study, the NOEC rate for all four bacteria was zero and this means that the least concentration of ZnO nanoparticles is toxic for all four species of E coli, S. 815 Aureus, P. Aeroginosa and. It is worth mentioning that the concentrations under experiment which were less than.5 mg/l did not cause any growth reduction in any of the bacterial species (the results have not been shown), but according to the Probit analysis this rate was estimated zero and because NOEC results are mainly used for toxicity determination (and not anti bacterial use), this difference in the results of real concentration and the Probit analysis results show increase in the confidence score of Probit analysis for analysis of the results related to chemical toxicity. In other words this different shows that Probit analysis estimates NOEC with a higher confidence score in comparison to the real situation and this is one of the pros of using this test in the analysis of the results. Conclusion: This study showed that the four species of E coli,, P. Aeroginosa and have a high prevalence in wastewater sludge, and can act as appropriate biomarkers. is appropriate in determining the toxicity of nanoparticles and P. Aeroginosa is appropriate in determining the antibacterial characteristics. However, it is obviously necessary to examine other bacteria species which might be prevalent in other environments in order to complete the results of this study in determining biological markers. Although the results showed that ZnO nanoparticles can be used potentially in wastewater sludge as antibacterial agents, but the practical application of these chemicals and their isolation after use in sludge and preventing the entry these chemical into the environment has to be evaluated. The resulted showed that different bacteria respond differently to similar concentrations of ZnO. By more accurately determining these concentrations for each bacteria species, we can use them extensively for hygienic. therapeutic and experimental purposes. References 1. Adams, L.K., D. Lyon, 26. Comparative ecotoxicity of anoscale TiO2, SiO2, and ZnO water suspensions. J Water Research, 4: APHA-AWWA-WEF, 25. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 2th ed., American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation, New York, USA 3. Barbu, E., R. Moln, 29. The potential for nanoparticle-based drug delivery to the brain: overcoming the blood-brain barrier. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery, 6(6): Baveye, P., M. Laba, 28. Aggregation and toxicology of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J Environal Health Perspectives, 116(4): A152.
5 5. Block, S., V. Seng, Chemically enhanced sunlight for killing bacteria SolEnergy Eng, 119: Brayner, R., I. Ferrari, 26. Toxicological impact studies based on Escherichia coli bacteria in ultrafine ZnO nanoparticles colloidal medium. Nano Lett., 6: Bystrzejewska, G., J. Golimowski, 29. Their potential toxicity waste and environmental management. Waste Management, 35: Heinlaan, M., 28. Toxicity of nanosized and bulk ZnO, CuO and TiO2 to bacteria Vibrio fischeri and crustaceans Daphnia magna and Thamnocephalus platyurus, 71: Jones, C., D. Grainger, 29. In vitro assessments of nanomaterial toxicity Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 61: Kahru, A., H. Dubourguier, 28. Biotests and Biosensors for Ecotoxicology of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. J A Minireview Sensors, 8: Liu, Y., L. He, 29. Antibacterial activities of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Applied Microbiology, 17: Lockman, P., M. Oyewumi, 23. Brain uptake of thiamine-coated nanoparticles. J of Controlled Release, 93(3): Naddafi, K., M. Zare, 211. Investigating potential toxicity of phenanthrene adsorbed to nano-zno using Daphnia magna. J Toxicological & Environmental Chemistry, 93(4): Navarro, E., A. Baun, 28. Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. J Ecotoxicology, 17(5): Reddy, K., K. Feris, 27. Selective toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles to prokaryotic and eukaryotic systems. J Applied Physics Letters, 9: Sawai, J., H. Igarashi, Effect of ceramic powders on spores of Bacillus subtilis. J Chem. Eng. Japan, 28: Sawai, J., H. Igarashi, Effect of particle size and heating temperature of ceramic powders on antibacterial activity of their slurries. J Chem Eng. Japan, 29: Sovova, T., V. Koci, 29. Ecotoxicity of nano and bulk forms of metal oxides. J Nanocon, 1: Vincent K. (3/1/212). "Probit Analysis. bit/probit Analysis.pdf Access Date." 2. Wang, H., R.L. Wick, 29. Toxicity of nanoparticulate and bulk ZnO, Al2O3 and TiO2 to the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Environmental Pollution, 157(4): Wang, X., B. Xing, 28. Sorption of Pyrene by Regular and Nanoscaled Metal Oxide Particles Influence of Adsorbed Organic Matter. J Environmental Science & Technology, 42:
Antibacterial activity of Zinc Oxide and Ag doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against E.coli
 Research Article Antibacterial activity of Zinc Oxide and Ag doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against E.coli Karthiga Venkatasubramanian, Selvakumar Sundaraj* Department of Natural Resources and Waste Recycling,
Research Article Antibacterial activity of Zinc Oxide and Ag doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles against E.coli Karthiga Venkatasubramanian, Selvakumar Sundaraj* Department of Natural Resources and Waste Recycling,
Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles Coated on Ceramic Tiles Prepared by Sol-Gel Method
 Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol. 27 No. 2 pp. 1-5, 2017 Sumalee CHANRAWANGYOT 1, Sirirat T.RATTANACHAN 1,*, Apichon WATCHARENWONG 2, and Thipwan FANGSUWANNARAK 1 School of Ceramic Engineering,
Journal of Metals, Materials and Minerals, Vol. 27 No. 2 pp. 1-5, 2017 Sumalee CHANRAWANGYOT 1, Sirirat T.RATTANACHAN 1,*, Apichon WATCHARENWONG 2, and Thipwan FANGSUWANNARAK 1 School of Ceramic Engineering,
Antibacterial activity and mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles on C. jejuni
 Antibacterial activity and mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles on C. jejuni Yiping He Yanping Xie Molecular Characterization of Foodborne Pathogens Research Unit, USDA-ARS ZnO It is stable under high temperatures
Antibacterial activity and mechanism of ZnO nanoparticles on C. jejuni Yiping He Yanping Xie Molecular Characterization of Foodborne Pathogens Research Unit, USDA-ARS ZnO It is stable under high temperatures
Developing a Yeast Cell Assay for Measuring the Toxicity of Inorganic Oxide Nanoparticles
 Developing a Yeast Cell Assay for Measuring the Toxicity of Inorganic Oxide Nanoparticles Citlali Garcia Saucedo Chemical & Environmental Engineering Department University of Arizona May 6 th, 2010 1 Outline
Developing a Yeast Cell Assay for Measuring the Toxicity of Inorganic Oxide Nanoparticles Citlali Garcia Saucedo Chemical & Environmental Engineering Department University of Arizona May 6 th, 2010 1 Outline
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds
 Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
Evaluation of Antibacterial Effect of Odor Eliminating Compounds Yuan Zeng, Bingyu Li, Anwar Kalalah, Sang-Jin Suh, and S.S. Ditchkoff Summary Antibiotic activity of ten commercially available odor eliminating
FIT TECHNICAL DATA. Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials
 FIT TECHNICAL DATA Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials Fit Efficacy vs. Bacteria Pathogens Bacteria Pathogen Staphylococcus Aureus (ATCC 8) Listeria Monocytogenes (ATCC 9) Escherichia Coli
FIT TECHNICAL DATA Summary of Research Studies and Production Trials Fit Efficacy vs. Bacteria Pathogens Bacteria Pathogen Staphylococcus Aureus (ATCC 8) Listeria Monocytogenes (ATCC 9) Escherichia Coli
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety
 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety, 2012, 1(2): 54-59 International Journal of Food Nutrition and Safety Journal homepage: www.modernscientificpress.com/journals/ijfns.aspx ISSN: 2165-896X
Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle on grampositive and gram-negative bacteria
 African Journal of Microbiology Research Vol. 5(12), pp. 1368-1373, 18 June, 2011 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/ajmr DOI: 10.5897/AJMR10.159 ISSN 1996-0808 2011 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Microbiology Research Vol. 5(12), pp. 1368-1373, 18 June, 2011 Available online http://www.academicjournals.org/ajmr DOI: 10.5897/AJMR10.159 ISSN 1996-0808 2011 Academic Journals Full
AgriTitan TM. Effective, Safe, & Smart. Harvest the Power of Light To Control Bacterial Plant Disease. EcoActive Surfaces, Inc.
 AgriTitan TM Effective, Safe, & Smart Harvest the Power of Light To Control Bacterial Plant Disease 1 What is AgriTitan TM? AgriTitan TM is a proprietary water-based formulation of extremely small particles
AgriTitan TM Effective, Safe, & Smart Harvest the Power of Light To Control Bacterial Plant Disease 1 What is AgriTitan TM? AgriTitan TM is a proprietary water-based formulation of extremely small particles
EFFECT OF ZNO NANO PARTICLES AGAINST STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI
 Vol 7, Issue 5, 2014 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article EFFECT OF ZNO NANO PARTICLES AGAINST STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI ANJU THANGAM*, PRITAM, SAKTHI RAMLAKSHMI Department of Biotechnology, SRM University,
Vol 7, Issue 5, 2014 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article EFFECT OF ZNO NANO PARTICLES AGAINST STRAINS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI ANJU THANGAM*, PRITAM, SAKTHI RAMLAKSHMI Department of Biotechnology, SRM University,
Active properties of foam coated paper by functionalised nanofibrillated
 Active properties of foam coated paper by functionalised nanofibrillated cellulose Final Conference 20.6.2012 Patrizia Sadocco, Jessica Causio - INNOVHUB Giovanni Baldi - Centro Ricerche Colorobbia Italia
Active properties of foam coated paper by functionalised nanofibrillated cellulose Final Conference 20.6.2012 Patrizia Sadocco, Jessica Causio - INNOVHUB Giovanni Baldi - Centro Ricerche Colorobbia Italia
Mechanochemical Doping of a Non-Metal Element into Zinc Oxide
 Chemistry for Sustainable Development 15 (2007) 249 253 249 Mechanochemical Doping of a Non-Metal Element into Zinc Oxide J. WANG, J. F. LU, Q. W. ZHANG, S. YIN, T. SATO and F. SAITO Institute of Multidisciplinary
Chemistry for Sustainable Development 15 (2007) 249 253 249 Mechanochemical Doping of a Non-Metal Element into Zinc Oxide J. WANG, J. F. LU, Q. W. ZHANG, S. YIN, T. SATO and F. SAITO Institute of Multidisciplinary
314 Bystrzejewska-Piotrowska G., et al.
 Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 21, No. 2 (212), 313-319 Original Research Influence of Earthworms on Extractability of Metals from Soils Contaminated with Al 2 O 3, TiO 2, Zn, and ZnO Nanoparticles and Microparticles
Pol. J. Environ. Stud. Vol. 21, No. 2 (212), 313-319 Original Research Influence of Earthworms on Extractability of Metals from Soils Contaminated with Al 2 O 3, TiO 2, Zn, and ZnO Nanoparticles and Microparticles
BACTERIAL PLATING INSTRUCTIONS AND INTERPRETATION. SHELLFISH BACTERIAL WORKSHOP APRIL 26, 2017 SUSAN LARAMORE
 BACTERIAL PLATING INSTRUCTIONS AND INTERPRETATION SHELLFISH BACTERIAL WORKSHOP APRIL 26, 2017 SUSAN LARAMORE slaramo1@fau.edu 772 242 2525 Spread Plate Method This is the easiest and most common plating
BACTERIAL PLATING INSTRUCTIONS AND INTERPRETATION SHELLFISH BACTERIAL WORKSHOP APRIL 26, 2017 SUSAN LARAMORE slaramo1@fau.edu 772 242 2525 Spread Plate Method This is the easiest and most common plating
Chapter 4. Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata. 4.1 Introduction
 Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
Anti-bacterial studies of PUFA extracts from Sardinella longiceps and Sardinella fimbriata C o n t e n t s 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Materials and Methods 4.2.1 Extract Preparation and Determination of PUFA
Formulation of alternative culture media for bacterial and fungal growth
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (1):431-436 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2016, 8 (1):431-436 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Biological Consulting Services
 Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Biological Consulting Services of North Florida/ Inc. May 13, 2009 Aphex BioCleanse Systems, Inc. Dear Sirs, We have completed antimicrobial efficacy study on the supplied Multi-Purpose Solution. The testing
Determination of MIC & MBC
 1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
1 Determination of MIC & MBC Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial that will inhibit the visible growth of a microorganism after overnight
AN EVALUATION OF COMMERCIAL TEXTILE TANNINS BASED ON THEIR INERT COD CONTENT AND TOXICITY
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 16, No 1, pp 52-58, 2014 Copyright 2014 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AN EVALUATION OF COMMERCIAL TEXTILE TANNINS BASED ON THEIR INERT COD CONTENT AND TOXICITY
Global NEST Journal, Vol 16, No 1, pp 52-58, 2014 Copyright 2014 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AN EVALUATION OF COMMERCIAL TEXTILE TANNINS BASED ON THEIR INERT COD CONTENT AND TOXICITY
Environment Protection Engineering. EFFECTS OF ZnO, CuO, Au, AND TiO 2 NANOPARTICLES ON DAPHNIA MAGNA AND EARLY LIFE STAGES OF ZEBRAFISH DANIO RERIO
 Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 40 2014 No. 1 DOI: 10.5277/epe140111 JINING LIU 1, 2, DELING FAN 1, LEI WANG 2, LILI SHI 2, JIE DING 1,YINGWEN CHEN 1, SHUBAO SHEN 1 EFFECTS OF ZnO, CuO, Au, AND
Environment Protection Engineering Vol. 40 2014 No. 1 DOI: 10.5277/epe140111 JINING LIU 1, 2, DELING FAN 1, LEI WANG 2, LILI SHI 2, JIE DING 1,YINGWEN CHEN 1, SHUBAO SHEN 1 EFFECTS OF ZnO, CuO, Au, AND
Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment
 United States Patent 4,882,059 Wong, et al. November 21, 1989 Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment Abstract A method for solubilizing particulate or colloidal materials in wastewater
United States Patent 4,882,059 Wong, et al. November 21, 1989 Solubilization of organic materials in wastewater treatment Abstract A method for solubilizing particulate or colloidal materials in wastewater
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Extracellular Saccharide-Mediated Reduction of Au 3+ to Gold Nanoparticles: New Insights for Heavy Metals Biomineralization on Microbial Surfaces Fuxing Kang,, Xiaolei Qu, Pedro
Supporting Information Extracellular Saccharide-Mediated Reduction of Au 3+ to Gold Nanoparticles: New Insights for Heavy Metals Biomineralization on Microbial Surfaces Fuxing Kang,, Xiaolei Qu, Pedro
Effect of ph on the production of protease by Fusarium oxysporum using agroindustrial waste
 Biotechnological Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 8(1): 78-83 (2015) Effect of ph on the production of protease by Fusarium oxysporum using agroindustrial waste Rupali R. Deshmukh and N. N. Vidhale*
Biotechnological Communication Biosci. Biotech. Res. Comm. 8(1): 78-83 (2015) Effect of ph on the production of protease by Fusarium oxysporum using agroindustrial waste Rupali R. Deshmukh and N. N. Vidhale*
ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 5, 2013, 989 993 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) ANTIBACTERIAL EFFECTS OF CRUDE EXTRACT OF Azadirachta indica AGAINST Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page:
 Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
Research Article CODEN: AJPAD7 ISSN: 2321-0923 Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis and Medicinal Chemistry Journal home page: www.ajpamc.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF HERBAL WASH FOR NASAL HEALTH
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 8, August-2016 105 Antimicrobial activity of Andrographis paniculata stem extracts. S.Gurupriya 1 and Dr.L.Cathrine 2 1 M.phil
International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences 2018; 2(4): Dr. Skandhan S Kumar and Dr. Shivaprasad K
 2018; 2(4): 23-27 E-ISSN: 2616-4493 P-ISSN: 2616-4485 IJHS 2018; 2(4): 23-27 Received: 14-08-2018 Accepted: 18-09-2018 Dr. Skandhan S Kumar Assistant Professor Homoeopathic Medical College, Mangaluru,
2018; 2(4): 23-27 E-ISSN: 2616-4493 P-ISSN: 2616-4485 IJHS 2018; 2(4): 23-27 Received: 14-08-2018 Accepted: 18-09-2018 Dr. Skandhan S Kumar Assistant Professor Homoeopathic Medical College, Mangaluru,
Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet
 Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet Introduction Bunsen Burner is the most frequently used apparatus in the laboratory as a source of heat. Typically used inside
Increased Microbiological Challenge Test with Bunsen Burner Inside the Cabinet Introduction Bunsen Burner is the most frequently used apparatus in the laboratory as a source of heat. Typically used inside
Hong-qi Sun, Xue-mei Lu, Pei-ji Gao* State Key Laboratory of Microbial Technology, Shandong University, Jinan , China.
 Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2011) 42: 410-414 ISSN 1517-8382 THE EXPLORATION OF THE ANTIBACTERIAL MECHANISM OF FE 3+ AGAINST BACTERIA Hong-qi Sun, Xue-mei Lu, Pei-ji Gao* State Key Laboratory of
Brazilian Journal of Microbiology (2011) 42: 410-414 ISSN 1517-8382 THE EXPLORATION OF THE ANTIBACTERIAL MECHANISM OF FE 3+ AGAINST BACTERIA Hong-qi Sun, Xue-mei Lu, Pei-ji Gao* State Key Laboratory of
Genotoxic Effects Of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
 Genotoxic Effects Of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Genotoxic Effects Of Zinc Oxide Summary. This scientific review report is limited to the review of safety concerns surrounding zinc oxide
Genotoxic Effects Of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles 1 / 7 2 / 7 3 / 7 Genotoxic Effects Of Zinc Oxide Summary. This scientific review report is limited to the review of safety concerns surrounding zinc oxide
Jl. Perintis Kemerdekaan KM.5 Makassar 90231, South Sulawesi Indonesia.
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com ANTIMICROBIAL POTENCY OF PASSIFLORA FOETIDA LINN FROM SOUTH SULAWESI INDONESIA AGAINST BACTERIA IN VITRO Andi
In the future, Sharp intends to further its efforts for improving the effectiveness of Plasmacluster technology to create a healthy environment.
 November 13, 2009 Sharp s Plasmacluster *1 Technology Proven Effective in Inhibiting the Activity of Adherent and Airborne Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus *3 (MRSA), a Typical Bacterial Cause
November 13, 2009 Sharp s Plasmacluster *1 Technology Proven Effective in Inhibiting the Activity of Adherent and Airborne Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus *3 (MRSA), a Typical Bacterial Cause
EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ZnO NANOPARTICLES COATED SONOCHEMICALLY ONTO TEXTILE FABRICS
 Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Singh et al. 2012 : 2 (1) 106-120 Food Sciences REGULAR ARTICLE EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ZnO NANOPARTICLES COATED SONOCHEMICALLY ONTO TEXTILE FABRICS
Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Singh et al. 2012 : 2 (1) 106-120 Food Sciences REGULAR ARTICLE EVALUATION OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ZnO NANOPARTICLES COATED SONOCHEMICALLY ONTO TEXTILE FABRICS
The University of Queensland, National Research Centre for Environmental Toxicology (Entox), Brisbane QLD 4108 Australia
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information: Behaviour of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information: Behaviour of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles
Higher plants produced hundreds to thousands of diverse chemical compounds with different biological activities (Hamburger and Hostettmann, 1991).
 4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella dysenteriae, and Salmonella typhi
 292 AMJ June 2016 Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Sim Chee Fong, 1 Yanti Mulyana, 2 Dolvy Girawan 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department of Microbiology Faculty
292 AMJ June 2016 Antibacterial Effect of Pulsatilla chinensis towards Sim Chee Fong, 1 Yanti Mulyana, 2 Dolvy Girawan 3 1 Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjadjaran, 2 Department of Microbiology Faculty
STUDIES ON THE PHOTO DEGRADATION OF MALACHITE GREEN DYE BY THE SYNTHESIZED ZnO NANO PARTICLES WITH DIFFERENT SOURCES OF ENERGY
 IJRPC 214, 4(3), 571-576 Shanthi et al. ISSN: 22312781 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article STUDIES ON THE PHOTO DEGRADATION OF
IJRPC 214, 4(3), 571-576 Shanthi et al. ISSN: 22312781 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article STUDIES ON THE PHOTO DEGRADATION OF
ANNEX III ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES
 Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) ANNEX III ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES Disclaimer: This document is provided for information purpose only and subject
Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) ANNEX III ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES Disclaimer: This document is provided for information purpose only and subject
ADEKA NOL NHG. Product Properties. Antibacterial Properties. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for each bacterial strain. E.
 TECHNICAL INFORMATION ADEKA NOL NHG ADEKA NOL NHG is a product that has an excellent balance of antibacterial effects, low skin irritation and water solubility, with bacteriostatic and moisturizing effects.
TECHNICAL INFORMATION ADEKA NOL NHG ADEKA NOL NHG is a product that has an excellent balance of antibacterial effects, low skin irritation and water solubility, with bacteriostatic and moisturizing effects.
BY ZACHARY MODISPACHER 11 TH GRADE CENTRAL CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL
 BY ZACHARY MODISPACHER 11 TH GRADE CENTRAL CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL INTRODUCTION Chicken is one of the most consumed meats in the world, though can pose health risks (salmonella). Salmonella was thought only
BY ZACHARY MODISPACHER 11 TH GRADE CENTRAL CATHOLIC HIGH SCHOOL INTRODUCTION Chicken is one of the most consumed meats in the world, though can pose health risks (salmonella). Salmonella was thought only
Vimta Labs Ltd., Life Sciences Facility, Plot No. 5, Alexandria Knowledge Park, Genome Valley, Shameerpet, Hyderabad, Telangana
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. DRUGS & PHARMACEUTICALS 1. Biological Assays Antibiotics And Other Drugs Bulk Drugs & Their Formulations: Erythromycin, Gentamicin, Nystatin IP Appendix 9.1 2.2.10 BP
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. DRUGS & PHARMACEUTICALS 1. Biological Assays Antibiotics And Other Drugs Bulk Drugs & Their Formulations: Erythromycin, Gentamicin, Nystatin IP Appendix 9.1 2.2.10 BP
Antimicrobial activity of fabrics treated with Quercus Infectoria extract for foot odour control. V.Yamuna, S.Sudha*
 ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 7 Issue 6 Antimicrobial activity of fabrics treated with Quercus Infectoria extract for foot odour control V.Yamuna, S.Sudha* Department of Fashion Technology, PSG College of Technology,
ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 7 Issue 6 Antimicrobial activity of fabrics treated with Quercus Infectoria extract for foot odour control V.Yamuna, S.Sudha* Department of Fashion Technology, PSG College of Technology,
ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES (TM) AND HEALTH SUPPLEMENTS (HS)
 Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES (TM) AND HEALTH SUPPLEMENTS (HS) Version 3.0 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...2 2. Objective...
Association of South East Asian Nations (ASEAN) ASEAN GUIDELINES ON LIMITS OF CONTAMINANTS FOR TRADITIONAL MEDICINES (TM) AND HEALTH SUPPLEMENTS (HS) Version 3.0 CONTENTS 1. Introduction...2 2. Objective...
Antibacterial activity of nitric oxide (NO) releasing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)
 Antibacterial activity of nitric oxide (NO) releasing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) Dr Amedea B. Seabra amedea.seabra@ufabc.edu.br Universidade Federal do ABC, Brazil 1 Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) 2 Silver
Antibacterial activity of nitric oxide (NO) releasing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) Dr Amedea B. Seabra amedea.seabra@ufabc.edu.br Universidade Federal do ABC, Brazil 1 Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) 2 Silver
A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide. Nanofibers Gas Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Summary and Conclusion
 Summary and Conclusion Milk and milk products are consumed daily by Indian citizens. This type of food is easily perishable and support growth of foodborne pathogens keeping this view in mind the investigation
Summary and Conclusion Milk and milk products are consumed daily by Indian citizens. This type of food is easily perishable and support growth of foodborne pathogens keeping this view in mind the investigation
Puducherry. Antimicrobial activity, Crude drug extraction, Zone of Inhibition, Culture Media, RVSPHF567.
 ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE DRUGS AND THE POLYHERBAL FORMULATION (RVSPHF567) BY STANDARDIZED CUP AND PLATE METHOD C.S. Kandasamy 1,2*, Suman Nath 2, P. Arulraj 1,2, V. Gopal 3, P. Muthusamy 4,
ANTI-MICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE DRUGS AND THE POLYHERBAL FORMULATION (RVSPHF567) BY STANDARDIZED CUP AND PLATE METHOD C.S. Kandasamy 1,2*, Suman Nath 2, P. Arulraj 1,2, V. Gopal 3, P. Muthusamy 4,
Laboratorios CONDA, S.A. Distributed by Separations
 Culture Media as on Pharmacopoeia 7.3, Harmonized Method for Microbiological Examination of non sterile products -FORMULATIONS Buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution ph 7.0 Cat. Nº 1401 Potassium dihydrogen
Culture Media as on Pharmacopoeia 7.3, Harmonized Method for Microbiological Examination of non sterile products -FORMULATIONS Buffered sodium chloride-peptone solution ph 7.0 Cat. Nº 1401 Potassium dihydrogen
Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles against ESBL and Amp-C Producing Gram Negative Isolates from Superficial Wound Infections
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-1 (2015) pp. 38-47 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-1 (2015) pp. 38-47 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Antibacterial Activity of ZnO Nanoparticles
SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO. Iyyanuchamy, S.K and A. Periyanayagasamy*
 Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
Research Paper: Iyyanuchamy and Periyanayagasamy., 2011: Pp.6-10 SCREENING THE BIOACTIVE POTENTIAL OF PROTEIN ISOLATED FROM CYPRINUS CARPIO Iyyanuchamy, K and A. Periyanayagasamy* Department of Microbiology,
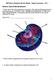
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Norovirus Report. Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report
 Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Microbiology Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials T Wadhwani, K Desai, D Patel, D Lawani,
Nanopigments For Broad Spectrum Sun Protection. Patricia Aikens NAFTA Technical Services
 Nanopigments For Broad Spectrum Sun Protection Patricia Aikens NAFTA Technical Services UV radiation and the skin UV absorbers Nanopigments Titanium dioxide Zinc Oxide Electromagnetic Radiation Longer
Nanopigments For Broad Spectrum Sun Protection Patricia Aikens NAFTA Technical Services UV radiation and the skin UV absorbers Nanopigments Titanium dioxide Zinc Oxide Electromagnetic Radiation Longer
COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA Dr. Nisha Kumari.P. R *Dr. Dinesh Nayak J **, Dr. Sathyanarayana
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 COMPARATIVE ANTI MICROBIAL STUDY OF SHUDDHA KASISA AND KASISA BHASMA Dr. Nisha Kumari.P. R *Dr. Dinesh Nayak J **, Dr. Sathyanarayana
PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY
 18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
18/8/2016 SOURCES OF MICROBIAL CONTAMINANTS IN BIOSAFETY LABORATORIES IN KENYA PRESENTER: DENNIS NYACHAE MOSE KENYATTA UNIVERSITY 1 INTRODUCTION Contamination occurs through avoidable procedural errors
Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials
 The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
The Internet Journal of Microbiology 2009 : Volume 7 Number 1 Effect of various solvents on bacterial growth in context of determining MIC of various antimicrobials Teena Wadhwani M.Sc.(semester IV) Nirma
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
Q1. (a) (i) Some diseases can be tackled by using antibiotics and vaccination. Explain fully why antibiotics cannot be used to cure viral diseases.
 Q. (a) (i) Some diseases can be tackled by using antibiotics and vaccination. Explain fully why antibiotics cannot be used to cure viral diseases......... (ii) A recent study found that babies in 90 %
Q. (a) (i) Some diseases can be tackled by using antibiotics and vaccination. Explain fully why antibiotics cannot be used to cure viral diseases......... (ii) A recent study found that babies in 90 %
Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes
 ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
ISSN: 2454-132X Impact factor: 4.295 (Volume3, Issue1) Available online at: www.ijariit.com Bioprospecting of Neem for Antimicrobial Activity against Soil Microbes R. Prasanna PRIST University, Tamilnadu
Transgenerational impact on nutrients and enzymatic activity of beans grown in soil with coated/uncoated ZnO nanomaterials
 THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT EL PASO Transgenerational impact on nutrients and enzymatic activity of beans grown in soil with coated/uncoated ZnO nanomaterials Illya Aideé Medina Velo The University of Texas
THE UNIVERSITY OF TEXAS AT EL PASO Transgenerational impact on nutrients and enzymatic activity of beans grown in soil with coated/uncoated ZnO nanomaterials Illya Aideé Medina Velo The University of Texas
Supplementary information on Colourless agar for enhancing colour contrast between microbial colonies and agar
 Supplementary information on Colourless agar for enhancing colour contrast between microbial colonies and agar Wenfa Ng Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore
Supplementary information on Colourless agar for enhancing colour contrast between microbial colonies and agar Wenfa Ng Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, National University of Singapore
Risk Assessment for coating applications
 Facutly of Mechanical Engineering Institute of Process Engineering and Environmental Technology, Research Group Mechanical Process Engineering Experimental Study Risk Assessment for coating applications
Facutly of Mechanical Engineering Institute of Process Engineering and Environmental Technology, Research Group Mechanical Process Engineering Experimental Study Risk Assessment for coating applications
Current Opinions on the Human Safety of Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide
 Current Opinions on the Human Safety of Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide J F. Nash, Ph.D. Central Product Safety The Procter & Gamble Company Cincinnati, OH 45241 nash.jf@pg.com Human Safety: Objective
Current Opinions on the Human Safety of Titanium Dioxide and Zinc Oxide J F. Nash, Ph.D. Central Product Safety The Procter & Gamble Company Cincinnati, OH 45241 nash.jf@pg.com Human Safety: Objective
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Silverzanit antibacterial ceramics for a healthy foundation.
 Silverzanit antibacterial ceramics for a healthy foundation. Die Fliesen der Sonderklasse. Silver for health, tiles of a class of its own for architecture. Silverzanit antibacterial ceramics is active
Silverzanit antibacterial ceramics for a healthy foundation. Die Fliesen der Sonderklasse. Silver for health, tiles of a class of its own for architecture. Silverzanit antibacterial ceramics is active
Nanoparticles against Radiation
 Nanoparticles against Radiation Abstract With cancer being one of the top diagnosed disease in the United States of America, it makes sense that many doctors across the world are trying to find the cure
Nanoparticles against Radiation Abstract With cancer being one of the top diagnosed disease in the United States of America, it makes sense that many doctors across the world are trying to find the cure
Available online at Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Zoological Research, 2013, 2 (4):76-81 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 7356 Investigate the antibacterial
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Zoological Research, 2013, 2 (4):76-81 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN: 2278 7356 Investigate the antibacterial
1. Effect of Temperature on Antibacterial Activity of Honey
 ~'} ~" The Antimicrobial Action of Honey Original Article 1. Effect of Temperature on Antibacterial Activity of Honey Nongluksna Sriubolmas M.Sc. (Pharm)* Areerat Laorpaksa M.Sc. (Pharm)* Saree Virunhaphol
~'} ~" The Antimicrobial Action of Honey Original Article 1. Effect of Temperature on Antibacterial Activity of Honey Nongluksna Sriubolmas M.Sc. (Pharm)* Areerat Laorpaksa M.Sc. (Pharm)* Saree Virunhaphol
bacteria (burst size). It consists in diluting a suspension of infected2 Only a small fraction of the samples will then contain more than one infected
 THE BURST SIZE DISTRIBUTION IN THE GROWTH OF BACTERIAL VIRUSES (BACTERIOPHAGES)l M. DELBRtrCK Departments of Physics and Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee Received for publication January
THE BURST SIZE DISTRIBUTION IN THE GROWTH OF BACTERIAL VIRUSES (BACTERIOPHAGES)l M. DELBRtrCK Departments of Physics and Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee Received for publication January
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COMPOSITES BASED ON THE ZINC OXIDE CAPTURED ON THE SURFACE OF KAOLINITE
 PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COMPOSITES BASED ON THE ZINC OXIDE CAPTURED ON THE SURFACE OF KAOLINITE Barbora JANÍKOVÁ, Lucie NEUWIRTHOVÁ, Lenka MATĚJOVÁ, Vlastimil MATĚJKA VŠB Technical University
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF THE COMPOSITES BASED ON THE ZINC OXIDE CAPTURED ON THE SURFACE OF KAOLINITE Barbora JANÍKOVÁ, Lucie NEUWIRTHOVÁ, Lenka MATĚJOVÁ, Vlastimil MATĚJKA VŠB Technical University
A Study of Consumer Storage of Commercially Available Peanut Butter with Analysis of Variance
 A Study of Consumer Storage of Commercially Available Peanut Butter with Analysis of Variance Abstract Outbreaks of Salmonella contamination of peanut butter have become a serious food safety concern for
A Study of Consumer Storage of Commercially Available Peanut Butter with Analysis of Variance Abstract Outbreaks of Salmonella contamination of peanut butter have become a serious food safety concern for
Cellular and Ecotoxicological Analysis of Nanofunctionalized Textiles (Project TECHNOTOX)
 Cellular and Ecotoxicological Analysis of Nanofunctionalized Textiles (Project TECHNOTOX) Prof. Dr. Dirk Höfer BfR, Berlin, February 9 th 2012 COMPETENCE IN TEXTILES No. 2 Hohenstein Institute Department
Cellular and Ecotoxicological Analysis of Nanofunctionalized Textiles (Project TECHNOTOX) Prof. Dr. Dirk Höfer BfR, Berlin, February 9 th 2012 COMPETENCE IN TEXTILES No. 2 Hohenstein Institute Department
4-3 Infection and Response Biology
 4-3 Infection and Response Biology. Pathogens are disease causing microorganisms. Draw one line from each disease to the correct disease-causing microorganism. [3 marks] Disease Measles Microorganism Virus
4-3 Infection and Response Biology. Pathogens are disease causing microorganisms. Draw one line from each disease to the correct disease-causing microorganism. [3 marks] Disease Measles Microorganism Virus
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS
 CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
CHAPTER 8 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THE CRUDE ETHANOLIC EXTRACT AND THE ISOLATED COMPOUNDS FROM THE STEM OF COSTUS IGNEUS 8.1 INTRODUCTION Medicinal plants are the backbone of traditional medicine and
Year 9 Cells, Tissues and Organs, Microbiology Revision Questions January 2018
 Year 9 Cells, Tissues and Organs, Microbiology Revision Questions January 2018 Cell Structure Q1. The diagrams show a cheek cell from a human and a leaf cell from a plant. (a) The two cells have a number
Year 9 Cells, Tissues and Organs, Microbiology Revision Questions January 2018 Cell Structure Q1. The diagrams show a cheek cell from a human and a leaf cell from a plant. (a) The two cells have a number
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples
 Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
Evaluation of the feasibility of the VACUETTE Urine CCM tube for microbial testing of urine samples Background The VACUETTE Urine CCM tube is for the collection, transport and storage of urine samples
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college
 A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
A.Kavitha Assistant professor Department of Botany RBVRR Womens college The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell The Bacterial Cell This is a diagram of a typical bacterial cell, displaying all of
Volume 2, ISSN (Online), Published at:
 INFLUENCE OF PROTECTORS ON PRESERVATION OF LAСTIC ACID MICROORGANISMS Karlygash M. Kebekbaeva (RSE "Institute of Microbiology and Virology" KH MES RK, Kazakhstan, Almaty) Abstract In this paper we studied
INFLUENCE OF PROTECTORS ON PRESERVATION OF LAСTIC ACID MICROORGANISMS Karlygash M. Kebekbaeva (RSE "Institute of Microbiology and Virology" KH MES RK, Kazakhstan, Almaty) Abstract In this paper we studied
THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN
 THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN BY FRANKLIN A. STEVENS, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, and the
THE BACTERICIDAL PROPERTIES OF ULTRAVIOLET IRRADIATED LIPIDS OF THE SKIN BY FRANKLIN A. STEVENS, M.D. (From the Department of Medicine, College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University, and the
Antimicrobial effect of Silver nanoparticle on pathogenic organisms isolated from East Kolkata Wetland
 2015; 1(12): 745-752 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(12): 745-752 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 17-09-2015 Accepted: 19-10-2015 Rini Roy Department of
2015; 1(12): 745-752 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(12): 745-752 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 17-09-2015 Accepted: 19-10-2015 Rini Roy Department of
Calcium chloride produced from eggshell for vegetable washing
 ISSN 1513-7805 Printed in Thailand Research Article Calcium chloride produced from eggshell for vegetable washing Vichai Domrongpokkaphan 1 * and Maneerat Khemkhao 2 1 Department of Agro-Industrial, Food
ISSN 1513-7805 Printed in Thailand Research Article Calcium chloride produced from eggshell for vegetable washing Vichai Domrongpokkaphan 1 * and Maneerat Khemkhao 2 1 Department of Agro-Industrial, Food
People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production.
 Q1. Read the passage about antibiotics. People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production. If we put low doses of antibiotics in feed for animals such as cattle and sheep, it helps
Q1. Read the passage about antibiotics. People do not always agree about the use of antibiotics in food production. If we put low doses of antibiotics in feed for animals such as cattle and sheep, it helps
Commercial in Confidence
 Determination of Bactericidal Activity of Zwiteck Sanitizer using the European Standard Method BS EN 1276:2009 ~ Project Report Prepared for Zwiteck BV Inspiring tomorrow s professionals Determination
Determination of Bactericidal Activity of Zwiteck Sanitizer using the European Standard Method BS EN 1276:2009 ~ Project Report Prepared for Zwiteck BV Inspiring tomorrow s professionals Determination
Auriga Research Ltd., Vill. Bagbania, The-Nalagarh, Distt-Solan, Himachal Pradesh. Discipline Biological Testing Issue Date
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. FOOD & AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS 1. Dairy Products Condensed milk/ partly skimmed/ skimmed condensed milk, Dairy whitener, Dahi, Cheese, hard/processed, spread, Ice cream/
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 14 I. FOOD & AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS 1. Dairy Products Condensed milk/ partly skimmed/ skimmed condensed milk, Dairy whitener, Dahi, Cheese, hard/processed, spread, Ice cream/
HOW TO SOLVE PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF MICROBIOLOGY
 HOW TO SOLVE PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF MICROBIOLOGY PROPOSAL: NEW EXERCISES PART 2 Inés Arana, Maite Orruño & Isabel Barcina Department of Immunology, Microbiology and Parasitology University of Basque Country
HOW TO SOLVE PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF MICROBIOLOGY PROPOSAL: NEW EXERCISES PART 2 Inés Arana, Maite Orruño & Isabel Barcina Department of Immunology, Microbiology and Parasitology University of Basque Country
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/Thurs. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Tues/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 27 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations March 1 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/Weds. Split Lab Sections ONLY
 Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
Mt. San Antonio College Microbiology 22 Lab Schedule for Spring 2018 Mon/ Split Lab Sections ONLY Wk 1 Feb. 26 Orientation with Introductions & Safety Rules/Regulations Feb. 28 Orientation with Pathogen
RAPID REDUCTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS POPULATIONS ON STAINLESS STEEL SURFACES BY ZEOLITE CERAMIC COATINGS CONTAINING SILVER AND ZINC IONS
 RAPID REDUCTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS POPULATIONS ON STAINLESS STEEL SURFACES BY ZEOLITE CERAMIC COATINGS CONTAINING SILVER AND ZINC IONS INE 2 (CAR HEADLINE 2) By: K. R. Bright C. P. Gerba P. A. Rusin
RAPID REDUCTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS POPULATIONS ON STAINLESS STEEL SURFACES BY ZEOLITE CERAMIC COATINGS CONTAINING SILVER AND ZINC IONS INE 2 (CAR HEADLINE 2) By: K. R. Bright C. P. Gerba P. A. Rusin
FACTORS AFFECTING WATER QUALITY
 TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
International Journal of Nano Dimension
 ISSN: 2008-8868 Contents list available at IJND International Journal of Nano Dimension Journal homepage: www.ijnd.ir Synthesis, characterization and investigation photocatalytic degradation of Nitro Phenol
ISSN: 2008-8868 Contents list available at IJND International Journal of Nano Dimension Journal homepage: www.ijnd.ir Synthesis, characterization and investigation photocatalytic degradation of Nitro Phenol
The Effects of Reiki on Bacteria Survivorship. Jordan Ciccone Central Catholic High School
 The Effects of Reiki on Bacteria Survivorship Jordan Ciccone Central Catholic High School Reiki Japanese spiritual healing practice meaning universal life energy. Training is done by a Reiki Master. Either
The Effects of Reiki on Bacteria Survivorship Jordan Ciccone Central Catholic High School Reiki Japanese spiritual healing practice meaning universal life energy. Training is done by a Reiki Master. Either
Microbial load and prevalence of pathogens on surface of fresh vegetables in local market yards across Junagadh district of Gujarat
 International Journal of Plant Protection Volume 5 Issue 1 April, 2012 84-88 Research Article IJPP Microbial load and prevalence of pathogens on surface of fresh vegetables in local market yards across
International Journal of Plant Protection Volume 5 Issue 1 April, 2012 84-88 Research Article IJPP Microbial load and prevalence of pathogens on surface of fresh vegetables in local market yards across
In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa carandas leaf extracts
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Asian Journal of Plant Science and Research, 2012, 2 (1):36-40 ISSN : 2249-7412 CODEN (USA): AJPSKY In vitro study of antibacterial activity of Carissa
Product Information PREVENTOL CMK 40
 Product Information PREVENTOL CMK 40 1/8 Uses For the preservation of concrete additives, metalworking fluids, textile auxiliaries, thickener solutions, adhesives (including protein-based formulations)
Product Information PREVENTOL CMK 40 1/8 Uses For the preservation of concrete additives, metalworking fluids, textile auxiliaries, thickener solutions, adhesives (including protein-based formulations)
The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora. Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School
 The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Shampoo Hair care product used to clean hair of unwanted build up Combined soap, water, and herbs to make hair
The Effects of Shampoo on Microbial Flora Andrew Walker Grade 9 Central Catholic High School Shampoo Hair care product used to clean hair of unwanted build up Combined soap, water, and herbs to make hair
THE MOUTHWASH CHALLENGE
 THE MOUTHWASH CHALLENGE Ginny Brown Churchill HS / Montgomery Co. MD Abstract A problem assignment to design a new mouthwash that will combat the growth of bacteria that is frequently blamed for gum disease.
THE MOUTHWASH CHALLENGE Ginny Brown Churchill HS / Montgomery Co. MD Abstract A problem assignment to design a new mouthwash that will combat the growth of bacteria that is frequently blamed for gum disease.
Nanoparticles: -health hazards and risks. Nano-1. Kaarle Hämeri University of Helsinki/ Finnish Institute of Occupational Health
 Nanoparticles Health hazards and risks, Kaarle Hämeri 8.11.2010 Nano-1 Nanoparticles: -health hazards and risks Kaarle Hämeri University of Helsinki/ Finnish Institute of Occupational Health Conclusions
Nanoparticles Health hazards and risks, Kaarle Hämeri 8.11.2010 Nano-1 Nanoparticles: -health hazards and risks Kaarle Hämeri University of Helsinki/ Finnish Institute of Occupational Health Conclusions
Nano EHS Impact Globally: Predictive Approach Assists nano EHS Decision Making and Risk Identification
 Nano EHS Impact Globally: Predictive Approach Assists nano EHS Decision Making and Risk Identification Nanomaterial libraries High throughput screening In silico decisions, in vitro ranking Compositional
Nano EHS Impact Globally: Predictive Approach Assists nano EHS Decision Making and Risk Identification Nanomaterial libraries High throughput screening In silico decisions, in vitro ranking Compositional
