Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610)
|
|
|
- Theodore Chandler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scheme of work Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) Unit 2: Animal nutrition Recommended prior knowledge Students can come into this unit with very little biological knowledge. However, they do need to understand some basic chemistry such as atoms, elements and compounds. An understanding of bonding and the role of ions in simple chemical reactions is an advantage. Context The molecules that make up the bodies of living things are introduced here, and will be referred to in all of the subsequent units. Outline This unit considers the molecules from which living organisms are made, and then looks in detail at how animals acquire the materials that they need to form the structure of their bodies, and also to supply energy. The way in which small molecules can be used to make larger ones is briefly considered, before thinking about how such large molecules need to be broken down again before they can be absorbed through the wall of the alimentary canal. The functions of the main digestive enzymes are considered, linking back to the work on enzymes in Unit 1. The use of food to supply energy will be covered in more detail in Unit 4, and the functions of the liver in glucose and amino acid metabolism, touched on very briefly here, will be treated in more depth in Unit 5. (Please note: (S) in bold denotes material in the Supplement (Extended syllabus) only) Syllabus ref Learning objectives Suggested teaching activities Learning resources II Nutrition Define nutrition as taking in of nutrients which are organic substances and mineral ions, containing raw materials or energy for growth and tissue repair, absorbing and assimilating them Discuss the need for materials for growth and repair and for energy to maintain their activities such as movement and sensitivity. A simple definition of an organic substance is one whose molecules contain carbon and hydrogen. Cross link with plant nutrition in Unit p44 45 Unit revision: evise-it/nutrition Unit revision: stage4/biology/pc/lessons/uk_ks4 _digestion/h-frame-ie.htm v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 1
2 II Nutrients List the chemical elements which make up: - carbohydrates - fats - proteins Describe the synthesis of large molecules from smaller basic units: - simple sugars to starch and glycogen - amino acids to proteins - fatty acids and glycerol to fats and oils Ensure that students have some understanding of the terms: element, atom, molecule. Beads that string together, or simple chemical modelling kits, can be used to illustrate the idea of small molecules joining together to make larger ones. A table or flash cards can identify the classes of foods. Headings: class of food; source of food; uses of food in body; Once Unit 1.11 is completed, the enzymes and products of digestion could also be added to the summary table. Students should understand that starch is the carbohydrate stored only in plants. Animals store carbohydrate as glycogen. For detail on carbohydrates, fats and proteins: ex.php?info_center=11&tax_level =2&tax_subject=388&topic_id=16 65&placement_default=0 PowerPoint presentation The Chemicals of Living Things: II 6.1 Describe tests for: - starch (iodine solution) - reducing sugars (Benedict's solution) - protein (biuret test) - fats (ethanol) List the principal sources of, and describe the importance of: - carbohydrates - fats - proteins - vitamins (C and D only) - mineral salts (calcium and iron only), fibre (roughage) - water Describe the deficiency symptoms for: - vitamins (C and D only) - mineral salts (calcium and iron only) Students should have the opportunity to carry out each of these tests on a range of foods. It is a good practical lab in which students should realize the importance of safety when using a water bath. As an extension exercise, students can be given a solution containing a mixture of unknowns such as a reducing sugar and a protein. This can also give useful practice in recording qualitative results in a clearly presented results chart. Conclusions can also be written from the observed results. Food tests also enhance the students' understanding of the main classes of foods. The information on multivitamin tablet packets lists the vitamin contents and their requirements in the human body. Extension students could carry out research into food composition using the site Nutrition.gov p46 47 Food tests: Revision Food tests: 4/biology/pc/modules/digestion/fo od_tests/index.html Nutrition.gov: What s in food: ex.php?info_center=11&tax_level =1&tax_subject=388 v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 2
3 A summary table could be produced with vitamins and minerals, their source, function in the body and details of deficiencies. II 6.1 (S) 2.2 Describe the use of microorganisms in the food industry, with reference to yoghurt and single cell protein Describe uses, benefits and health hazards associated with food additives, including colourings May/June 2011 Paper 0610/22 question 6b Oct/Nov 2009 Paper 0610/02 question 3 Students can make yoghurt in the lab and should discuss the importance of sterile apparatus and of the constant temperature necessary for the process. The use of yeast for bread making can be linked to anaerobic respiration: Unit 4.3 Students can vary the mass of yeast in a given volume of water that is added to a constant mass of flour to measure the increase in height of flour in a large test tube or plastic cup over time. Temperature or sugar can also be used as a variable. A good source of ideas for this is the booklet 'Practical Biotechnology'. May/June 2010 Paper 0610/31 question 5 Oct/Nov 2008 Paper 0610/32 question 3 The health benefits of preservatives, in terms of greatly reduced risk of food poisoning, should be emphasised. Antioxidants also increase storage times for many foods. Flavourings and flavour enhancers increase palatability. A few artificial colourings, such as tartrazine, have been associated with problems such as hyperactivity. This website has some suggestions on fermentation: tocols/pracbiotech.html and tocols/juice.html Revision Fermentation: stage4/biology/pc/modules/breathi ng_respiration/fermentation/index. html Practical Biology Preserving food: roductory/health-anddisease/preservingfood/preserving-food,96,exp.html Nelson Thornes 2009 p50 51 Oct/Nov 2009 Paper 0610/31 question 2c II Diet State what is meant by the term balanced diet and describe a balanced diet related to: Diets in most countries depend on a staple food such as bread, potatoes or rice, which is usually the main source of carbohydrate. Students should be aware of the main sources of each type of nutrient in their own country, but also be Nelson Thornes 2009 p72 73 v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 3
4 - age - sex - activity of an individual Describe the effects of malnutrition in relation to: - starvation - coronary heart disease - constipation - obesity prepared to consider how diets differ in other parts of the world. Extension the Association for Science Education has a project called Science Across the World, which includes a unit on diet, and encourages schools in different parts of the world to share information. Students can keep a record of the food that they eat during a short period of time and then consider whether they are obtaining the nutrients that they need. Their diet could be analysed using standard food tables or by accessing the nutrient data laboratory. Alternatively students could use the interactive Balanced Diet activity. Show video clips Balanced diet: Malnutrition should be considered as the result of eating an unbalanced diet, not just the lack of a particular type of nutrient. Controlled discussion on malnutrition can be useful and the problems associated with starvation can be linked to Unit 10.1 The long term problems associated with obesity like onset diabetes should be discussed. Students could take part in the Science Across the World Keeping Healthy. May/June 2011 Paper 0610/21 question 2 May/June 2011 Paper 0610/22 question 2 Oct/Nov 2008 Paper 0610/32 question 2 Science Across the World Talking about food: brary/resource/1727/talkingabout-food-food-nutrition-andhealth Revision: 4/biology/pc/modules/digestion/ba lanced_diet/index.html National nutrient database: search/ Interactive Balanced diet: dules/balanceddiet/index.cfm Practical Biology Energy in food: roductory/energy/energy-infood/how-much-energy-is-therein-food,42,exp.html Nelson Thornes 2009 p76 77 Science Across the World Keeping Healthy: brary/resource/1741/keepinghealthy Revision Malnutrition: 4/biology/pc/modules/digestion/m v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 4
5 II Food supply Discuss the ways in which the use of modern technology has resulted in increased food production to include: - modern agriculture machinery - chemical fertilisers - pesticides - herbicides - artificial selection II (S) 2.4 Discuss the problems of world food supplies Discuss the problems which contribute to famine: - unequal distribution of food - drought - flooding - increasing population II Human alimentary canal Define ingestion as taking substances e.g. food and drink into the body through the mouth Define egestion as passing out of food that has not been digested as faeces, through the anus Identify the main regions of the alimentary canal and associated organs including: - mouth - salivary glands - oesophagus - stomach Material to illustrate this topic, and to form the basis of discussion, can be collected from newspaper and television reports. Students may like to consider whether new technologies, such as the development of genetically modified varieties of crops, are likely to improve the situation or exacerbate it. Extension students could consider food miles. May/June 2009 Paper 0610/02 question 9 Drought and flooding can be linked to Unit May/June 2010 Paper 0610/31 question 6 Oct/Nov 2008 Paper 0610/31 question 2 Students often do not understand that the alimentary canal is a long tube - albeit a coiled one - through which food passes. A long flexible rubber tube can demonstrate the idea. A schematic diagram on A3 paper can clarify the main events that take place from ingestion by the mouth to egestion from the anus. Arrows in different colours can show which enzymes are involved along the canal. Students should understand that food cannot be considered to have entered the body until it crosses the wall of the canal. The need for digestion to take place before absorption occurs is shown by using Visking tubing (to represent the alimentary alnutrition/index.html Science Across the World How Plants Grow: brary/resource/1725/how-plantsgrow Food miles: ing-resources/138--how-scienceworks-food-miles-and-changinglevels-of-co2 Links with Unit 10 Human influences on the environment Technology to Feed the World: xtra/crops/ A discussion of the problems of feeding the world's growing population, with excellent links to many other websites. Nelson Thornes 2009 p78 83 Digestion: sourceimport/resources04/digesti on/index.cfm v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 5
6 - small intestine: duodenum and ileum - pancreas - liver - gall bladder - large intestine: colon and rectum - anus Describe the functions of the regions of the alimentary canal listed above, in relation to: - ingestion - digestion - absorption - assimilation - egestion of food Cross reference to inclusive. canal) containing a mixture of glucose, starch and water. The visking tubing is placed in a beaker or a large test tube of water (to represent the blood), and left for several hours to allow the glucose to diffuse across the tubing. The contents of the tubing and of the beaker can be tested for starch and for glucose. Extension the importance of active uptake could be considered. This is particularly important for students studying Supplement. II Mechanical and physical digestion Define digestion as the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water soluble molecules using mechanical and chemical processes Identify the types of human teeth and describe their structure and functions State the causes of dental decay and describe the proper care of teeth Describe the process of chewing Describe the role of longitudinal and circular muscles in peristalsis Outline the role of bile in emulsifying fats, to increase the surface area for the action of enzymes May/June 2010 Paper 0610/21 question 7 Extension different types of teeth could be studied and related to different diets. Revision: 4/biology/pc/modules/digestion/di gestion_part_1/index.html Video clips Digestion: /the-digestive-system/4180.html /the-human-alimentarycanal/103.html v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 6
7 II (S) 2.6 Describe how fluoride reduces tooth decay and explain arguments for and against the addition of fluoride to public water supplies Although most health professionals strongly support the addition of fluoride to water supplies, there are also some arguments against this. May/June 2011 Paper 0610/32 question 5 Fluorides and fluoridation: The American Dental Association's site dealing with the fluoride issue. II II Chemical Digestion State the significance of chemical digestion in the alimentary canal, in producing small, soluble molecules that can be absorbed State where, in the alimentary canal: - amylase - protease - lipase enzymes are secreted State the functions of a typical: - amylase - protease - lipase listing the substrate and end products 2.8 Absorption Define absorption as the movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine into the blood or lymph Identify the small intestine as the region for absorption of digested food Describe the significance of villi in increasing the internal surface area of the small intestine II (S) 2.8 Describe the structure of the villus, including the role of This topic should be linked with earlier work on enzymes, in Unit Students could draw a spider diagram of the alimentary canal. This can help them visualise from where the enzymes are secreted and where they act on specific substrates. The importance of optimum ph and temperature should be emphasized, as well as the importance of enzymes in the whole process of digestion. May/June 2011 Paper 0610/22 question 9 May/June 2010 Paper 0610/22 question 8 Oct/Nov 2009 Paper 0610/02 question 4 Core students do not need any detail of the villus structure but they need to understand that the dissolved substances, glucose and amino acids, are transported in the blood to the liver before they can be assimilated into the body. It helps the students to understand the importance of diffusion if the villus is compared with the alveoli in the lungs, Unit 4.4 The two structures can be compared as having a single cell membrane, good blood supply, moist surface area and a large surface area for efficient diffusion. The absorption of glucose should be linked with earlier work on active transport, in Unit 1.9. Revision Digestion and absorption: 4/biology/pc/modules/digestion/di gestion_part_2/index.html Video clip Digestion: /digestion-of-carbohydrates-fatsand-proteins/105.html Nelson Thornes 2009 p84 85 Nelson Thornes 2009 p84 v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 7
8 II capillaries and lacteals State the role of the hepatic portal vein in the transport of absorbed food to the liver. Identify the role of the small intestine and colon in the absorption of water (the small intestine absorbs 5-10 dm 3 per day, the colon dm 3 per day) 2.9 Assimilation Describe assimilation as movement of digested food molecules into the cells of the body where they are used, becoming part of the cells Describe the role of the liver in the: metabolism of glucose to glycogen Amino acids into proteins The destruction of excess amino acids. Describe the role of fat as an energy storage substance II (S) 2.9 Define deamination as removal of the nitrogen-containing part of amino acids to form urea followed by the release of energy from the remainder of the amino acid State that the liver is the site of breakdown of alcohol and other toxins May/June 2011 Paper 0610/31 question 1 Oct/Nov 2009 Paper 0610/31 question 2 For Core students, no detail of the hormonal control of glucose levels is required. They should, however, know that the liver stores excess glucose as glycogen (link back to Unit 2.2) and converts this back to glucose again if blood glucose levels fall. The conversion of excess amino acids to urea should be dealt with very simply; this will be covered again in Unit 5.4. Extension the importance of the liver could be highlighted by looking at causes and effects of liver failure. May/June 2008 Paper 0610/02 question 3 The importance of nitrogen in the body could be discussed in relation to DNA, hormones and enzymes. May/June 2009 Paper 0610/31 question 2 Revision Digestion: evise-it/digestion Nelson Thornes, 2009 p85 v1 2Y05 Cambridge IGCSE Biology (0610) 8
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
05 Animal Nutrition. #49 Diet
 05 Animal Nutrition #49 Diet The food an animal eat everyday is called diet. Most animals need 7 types of nutrients in their diet: carbohydrates, proteins, fats + water, fibre, vitamins, minerals. The
05 Animal Nutrition #49 Diet The food an animal eat everyday is called diet. Most animals need 7 types of nutrients in their diet: carbohydrates, proteins, fats + water, fibre, vitamins, minerals. The
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Human Digestion. Junior Science
 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
Questions on Digestion
 Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
Name: Questions on Digestion Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.1 (Digestion). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the next quiz.
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Dawood Public School Course Outline Science Class IX
 Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-17 Science Class IX BOOKS: Ron Pickering.2012 Fundamental Biology (oxford university Press) Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology (3 rd),singapore; Federal Publication
Dawood Public School Course Outline 2016-17 Science Class IX BOOKS: Ron Pickering.2012 Fundamental Biology (oxford university Press) Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology (3 rd),singapore; Federal Publication
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Proteins their functions and uses revision 4 48 minutes 48 marks Page of 4 Q. The diagram shows the digestive system. (a) Complete the following sentences about digestive enzymes. (i) Amylase works in
Cambridge O Level Biology Syllabus code 5090 All candidates enter for three papers Papers 1 and 2 and Paper 6. PAPER 1 Multiple Choice
 1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
1 Dawood Public School Syllabus for 2010 2011 Class IX Subject Biology Books: Kwan.L. 2000, Comprehensive Biology(3 ed),singapore; Federal Publication Mackean.D, GCE O Level Biology, Oxford University
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration?
 BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Station One: Nutrition
 Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Station One: Nutrition Name that thing! 1. Chemical substances, found in foods, which are used in the human body. 2. Nutrient in human diet where foods are the only possible source of the nutrient. 3.
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion
 Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Title: Dec 12 8:42 AM (1 of 37) Chapter 11: Digestion and Excretion Introduction to Digestion Read pages 352 358 Make summary notes on this section Creat a Concept Map on the Essential Nutrients, including:
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2016
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2016 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
BIOLOGY IGCSE Revision Checklists for Form
 Note: BIOLOGY IGCSE Revision Checklists for Form 3 2014-2015 Items in red and italics are extension topics (and yes, you do need to know them!) Numbers in first column refer to the CIE syllabus. Form 3
Note: BIOLOGY IGCSE Revision Checklists for Form 3 2014-2015 Items in red and italics are extension topics (and yes, you do need to know them!) Numbers in first column refer to the CIE syllabus. Form 3
Absorption definition. Active transport. Aerobic respiration definition. Anaerobic respiration definition. Animal Cell features
 Absorption definition Active transport Aerobic respiration definition Anaerobic respiration definition The movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine into the blood or lymph
Absorption definition Active transport Aerobic respiration definition Anaerobic respiration definition The movement of digested food molecules through the wall of the intestine into the blood or lymph
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014
 HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Digestive System. Science 7 HMS 2015
 Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Digestive System Science 7 HMS 2015 ??? What is the role of the digestive system? 1. Breaks down food into molecules the body can use 2. Molecules are absorbed into the blood stream to be carried to the
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Biology 20 Chapter 8 Review Assignment
 Biology 20 Chapter 8 Review Assignment Part A Nutrients 1. Fats (such as lard) are produced by and are at room temperature. This type of fat would be classified as fat because of the of double bonds between
Biology 20 Chapter 8 Review Assignment Part A Nutrients 1. Fats (such as lard) are produced by and are at room temperature. This type of fat would be classified as fat because of the of double bonds between
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
Name Class Date Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy (page 971) 1. Cells convert
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? A
 1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion
 Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
Section 2.1: Enzymes and Digestion Glands produce enzymes that are used to break down large molecules into smaller ones that are ready for abortion. The digestive system provides an interface between the
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM THE FOUR STEPS OF DIGESTION
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM WHAT IS THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? the digestive system is a long, muscular tube The entire system is approximately 9m in length and is usually a one way tract WHY DO WE NEED A DIGESTIVE
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Body Systems. S2 Science. Homework. Holy Cross High School Page 1
 Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
Body Systems S2 Science Homework Holy Cross High School Page 1 Homework 1 (10 marks) 1. The cells listed below are not matched with their correct description. Match each cell to one correct description
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions.
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Chapter 3 Reading Guide Be sure to use the many figures and tables provided by the book to help answer these questions. 1. What is digestion? What is the difference between mechanical and enzymatic digestion?
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
What are you made of????
 What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
What are you made of???? Approximate composition of a bacterial Cell Adapted from Alberts et.al Molecular Biology of the Cell, 3rd edition Molecule class % total weight # diff. types Water 70 1 Inorganic
The Digestive System CP Biology
 The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The Digestive System CP Biology Objectives Explain how food provides energy. Identify the 6 forms of nutrients your body needs and describe their use in the body. Identify the organs of the digestive system;
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Biochemistry Name: Practice Questions
 Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
CHAPTER 2: NUTRITION
 CHAPTER 2: NUTRITION 1. Living things need food to survive. 2. Food can divided into seven classes as follows: i. carbohydrates ii. proteins iii. fats iv. vitamins v. minerals vi. fibre vii. water Carbohydrate
CHAPTER 2: NUTRITION 1. Living things need food to survive. 2. Food can divided into seven classes as follows: i. carbohydrates ii. proteins iii. fats iv. vitamins v. minerals vi. fibre vii. water Carbohydrate
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
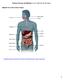 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Digestive System. What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning?
 Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Digestive System What happens to the donut you ate for breakfast this morning? Free Tutoring and Extra Credit!!! Digestive System: Is the basic process of breaking down the food you eat into individual
Higher National Unit Specification. General information for centres. Nutrition for Sports Therapists. Unit code: DP67 34
 Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Nutrition for Sports Therapists Unit code: DP67 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is designed to provide the candidate with a good
Higher National Unit Specification General information for centres Unit title: Nutrition for Sports Therapists Unit code: DP67 34 Unit purpose: The Unit is designed to provide the candidate with a good
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Topic: Human Digestive System Page 1 of 13. The Chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
The function of the digestive system is to break down
 Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
Curriculum Set #3 The function of the digestive system is to break down food into its components for use by the body. This is accomplished both mechanically and chemically. Mechanical digestion changes
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35
 Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Biology Introduction to Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 35 Digestion The breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino acids
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
