Biology. TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption. Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr
|
|
|
- Annabella Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Van Kupffer cells (i) Isolets of langerhans B - cells (ii) Liver sinusoids C Oxyntic cells (iii) Thyroid gland D Paneth cells (iv) Stomach (v) Small intestine (a) A-(iv), B-(v), C-(i), D-(ii) (b) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii) (c) A-(iv), B-(v), C-(iii), D-(i) (d) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(v) (2) What will happen if the secretion of parietal cells of gastric glands is blocked with an inhibitor? (a) In the absence of HCI secretion, inactive pepsinogen is not converted into the active enzyme pepsin (b) Enterokinase will not be released from the duodenal mucosa and so trypsinogen is not converted to trypsin (c) Gastric juice will be deficient in chymosin (d) Gastric juice will be deficient in pepsinogen (3) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below. Column- A Crypts of Lieberkuhn i Loop of duodenum B Pancreas ii Stomach C Adrenal gland iii Intestine D Gastric gland iv Kidney (a) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(ii), D-(iv) (b) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii) (c) A-(i), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(ii) (d) A-(iv), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(i) (4) The diagram given below represents a section of small intestinal mucosa showing villi. Identify A, B, C and D (a) A- Villi, B-Lacteal, C-Capillaries, D-Crypts (b) A-Lacteal, B-Villi, C-Capillaries, D-Crypts (c) A-Villi, B-Lacteal, C-Crypts, D-Capillaries (d) A-Crypts B-Lacteal, C-Capillaries, D-Villi Page 1 of 9
2 (5) Match Colum-I with and select the correct option from the codes given below. (Sphincter) (Location) A Sphincter of ani internus i Opening of hepatopancreatic ampulla into duodenum B Cardiac sphincter ii Between duodenum and posterior stomach C Ileocaecal sphincter iii Guarding the terminal part of alimentary canal D Sphincter of Oddi iv Between oesophagus E Pyloric Sphincter v Between small intestine and large intestine (a) A-(iii), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(i), E-(v) (b) A-(ii), B-(v), C-(iv), D-(iv), E-(iii) (c) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(v), E-(ii) (d) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(ii), E-(v) (6) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below. A Goblet cells i Antibacterial agent B Lysozyme ii Mucus C Saliva iii HCI D Oxyntic cells iv Sublingual gland (a) A-(iii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(ii) (b) A-(i), B-(iii), C-(iv), D-(ii) (c) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(iv) (d) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(iii) (7) The given figure represents the human digestive system. Identify A, B, C, D and E. (a) A-Parotid gland B-Liver C-Panceas D-Caecum E-Vermiform appendix (b) A- Patrotid gland B-Pancreas C-Liver D-Caecum E-Vermiform appendix (c) A-Parotid B-Caecum C-Pancreas D-Liver E-Vermiform appendix (d) A- Parotid gland B-Liver C- Caecum D-Pancreas E- Vermiform appendix Page 2 of 9
3 (8) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Hepatic lobule i Base of villi B Crypts of leiberkuhn ii Glisson s capsule C Sphincter of Oddi iii Gall bladder D Cystic duct iv Hepato-pancreatic duct (a) A-(ii), B-(i), C-(iv), D-(iii) (b) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iv), D-(iii) (c) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv) (d) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i) (9) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Beta cells i Lysozyme B Mast cels ii Mucus C Paneth cells iii Histamines D Acinar cells iv Insulin v Pancreatic enzymes (a) A-(iv), B-(ii), C-(i), D-(v) (b) A-(v), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv) (c) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(v) (d) A-(ii), B-(iii), C-(i), D-(v) (10) Which of the following statements is incorrect? (a) Brunner s glands are submucosal (b) Irregular folds of gastic mucosa are rugae (c) Glisson s capsule is the connective tissue sheath of hepatic lobule (d) Mesothelium or serosa lies in close proximity to the circular layer of muscularis (11) Refer the given flow chart Y Milk casein Paracasein Z In it, letters Y and Z denote (a) rennin and Ca ++ Calcium paracaseinate (Curdling of milk) (b) Ca ++ and rennin (c) rennin, HCi and Ca ++ (d) rennin and Ca ++ (12) Secretin (a) stimulates enzymes secretion by pancreas, inhibits acid secretion in stomach, stimulates gall bladder (b) stimulates bicarbonate secretion by pancreas, inhibits acid secretion in stomach, stimulates bicarbonate secretion in liver (c) stimulates acid secretion in stomach, potentiates action of CCK, inhibits intestinal movement (d) stimulates gall bladder, inhibits acid secretion in stomach, stimulates bicarbonate secretion by pancreas 3 P a g e
4 (13) Fill in the blanks in the following table by selecting the correct option. Hormone Source Target organ Action Gastrin Mucosa of pyloric (i) stomach 1. Stimulates secretion of gastric juice 2. Constricts cardiac sphincter (ii) Duodenal epithelium Stomach 1. Slows gastric contraction to delay its emptying 2. Stops secretion of gastric juice Cholecystokinin (iii) Pancreas, gall bladder 1. release of enzymes in pancreatic juice 2. Release of bile from gall bladder Enterocrinin Intestinal epithelium Intestine (iv) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (a) Small intestine Ducrinin Intestinal Release of mucus from Brunner s gland ephithelium (b) Stomach Villikinin Mucosa of Accelerates movements of villi pyloric stomach (c) Stomach Enterogastrone duodenal release of enzymes from crypts of Liberkuhn Epithelium (d) gall bladder Secretin Duodenal Release of enzymes in pancreatic juice Ehithelium (14) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below. A Salivary amylase i Proteins B Bile salts ii Milk proteins C Rennin iii Starch D Pepsin iv Lipids (a) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(ii), D-(i) (b) A-(iii), B-(iv), C-(i), D-(ii) (c) A-(iv), B-(iii), C-(ii), D-(i) (d) A-(i), B-(ii), C-(iii), D-(iv) Page 4 of 9
5 (15) Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true (T) and which ones are false (F) (i) Amylase hydrolyzes proteins to amino acids (ii) Pancreatic amylase hydrolyses polysaccharides to disaccharides (iii) Enteropeptidase activates pepsinogen to pepsin (iv) Trypsin coagulates the milk protein casein (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (a) T T F F (b) F T F T (c) F T F F (d) F T T F (16) Fill in the blanks with appropriate enzymes that bring the required changes in the following (i) Trypsinogen? Trypsin (ii) Caesin? Paracasein + Whey proteins (iii) RNA? Ribonucleotides (iv) Trigylycerides? Fatty acids + Glycerol (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) a Enterocrinin Pepsin Trypsin Lactase b Rennin Enterokinase Deoxyribonuclease Lipase c Carboxypeptidase Pepsin Chymotrypsin Dextrinase d Enterokinase Rennin Ribonuclease Lipase (17) Consider the following statements each with (1) or (2) blanks. (i) Release of pancreatic juice is caused by two hormones (1) and (2) (ii) Trypsinogen is activated to trypsin by (3) (iii) Fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed into (4) but glucose and amino acids are absorbed into (5) Which one of the following options, give the correct fill ups for the respective blanks from (1) to (5) in the statements? (a) (3)- cholecystokinin, (4)- blood vessels, (5)-lacteals (b) (1)-secretin (2)- cholecystokinin, (4)- lacteals (5)- blood capillaries (c) (1)-duocrinin (2)- enterokinase (3)- secretin (d) (1)-villikinin (2)- secretin (3)- enterokinase (18) Which of the following statements is incorrect (a) Faecal accumulation in the rectum initiates a neural reflex causing an urge for its removal (b) Irregular bowel movements cause constipation (c)in diarrhoea absorption of food is increased (d) All of these (19) If for some reason the parietal cells of the gut ephithelium ecome partially non-functional, what is likely to happen? (a) the pancreatic enzymes and specially the trypsin and lipase will not work efficiently (b) The ph of stomach will fall abruptly (c) Stepsin will be more effective (d) Proteins will not be adequately hydrolysed by pepsin into proteoses and peptones 5 P a g e
6 (20) Which of the following statements is incorrect? (a) Mucosal epithelium has goblet cells which secrete mucus for lubrication (b) Mucosa forms gastric glands in the stomach and crypts in between the bases of villi in intestine (c) cells lining in the villi has brush border or microvilli (d) All the four basic layers in the wall of gut never show modifications in different parts of the alimentary canal. (21) Which of the following statements about pancreas is incorrect? (a) It is a compound gland as it has both exocrine and endocrine (b) Exocrine part secretes like alkaline pancreatic juice having enzymes (c) Endocrine part secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon (d) It is surrounded by Glisson s capsule (22) Crypts of Lieberkuhn are present in (a) pancreas and secrete pancreatic juice (b) small intestine and secrete digestive enzymes (c) Stomach and secret dilute HCI (d) stomach and secrete trypsin (23) During prolonged fasting, in what sequence are the organic compounds used up by the body? (a) First carbohydrates, next fats and last proteins (b) First fats, next carbohydrates and last proteins (c) First carbohydrates, next proteins and last fats (d) First proteins, next lipids and last carbohydrates (24) A child took sugarcane and sucked up all the juice. Regarding this which of the following match is correct? Substrate Enzyme Site of secretion of enzyme Products formed a Proteins Pepsin Duodenum Polypeptides b Starch Amylase Salivary glands Glucose c Lipids Lipase Pancreas Fat globules d sucrose invertase Duodenum Glucose + fructose (25) The food mixes thoroughly with the acidic gastric juice of the stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall. What do we call the food then? (a) Bolus (b) Chyme (c) succus entericus (d) chylomicrons (26) Major utility of breaking up of food into small bits during chewing is (a) to reduce surface area of the food eaten up (b) to increase surface area of the food eaten up (c) to make the food soluble (d) to enjoy taste of food (27) Which category of compound is most concentrated energy source? (a) Lipids (b) Carbohydrates (c) Proteins (d) Vitamins (28) Which of the following statements is false? (a) Intrinsic factor is essential for absorption of vitamin B 12 (b) Gastric gland never secretes even a small amount of lipase (c) Renni, a proteolytic enzyme is found in gastric juice of infants (d) All of these Page 6 of 9
7 (29) Which of the following is not the function of the large intestine? (a) Absorption of water (b) Nutrient absorption (c) Secretion of mucus to lubricate faeces (d) Temporary storage of faeces in rectum (30) Anxiety and eating spicy food together in an otherwise normal human, may lead to (a) Indigestion (b) jaundice (c) diarrhoea (d) vomiting 7 P a g e
8 SOLUTION 1. (d) 2. (a) The parietal cells of gastric glands secrete HCI. Pepsinogen (proenzyme) is converted into pepsin enzyme (active form), in the presence of HCI. This enzyme acts on proteins in the stomach. Therefore, if the secretion of parietal cells is bocked, HCI acid will not be secreted and thus inactive pepsinogen will not be converted into active pepsin. As a result, proteins will not be hydrolysed to proteoses and peptones. 3. (b) 4. (a) 5. (c) 6. (d) 7. (a) 8. (a) : The structural and functional units of liver are hepatic lobules containing hepatic cells. Each lobule is covered by a thin connective tissue sheath called the Glisson s capsule. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are simple tubular glands which occur throughout the small intestine between the villi. Cystic duct is the duct that arises from the gall bladder. Hepatopancreatic duct is formed by the joining of bile duct and the main pancreatic duct, it opens into the duodenum through an opening guarded by sphincter Oddi. 9. (c) 10. (d) : Serosa is the outermost layer of alimentary canal and its made up of a thin mesothelium that lies in close proximity to the longitudinal layer of muscalaris. 11. (a): HCI of the stomach converts proennin (proenzyme) into its active form from rennin.in the stomach, rennin acts on casein (milk protein) and converts it into paracasein. In the presence of calcium ions, paracasein is converted into calcium paracaseinate, ultimately leading to milk coagulation. 12. (d): Secretin is a hormone secreted by the epithelium of duodenum. It stimulates gall bladder to secrete bile, inhibits acid secretion in stomach and stimulates the pancreas to secrete bicarbonate. 13. (c) 14. (a) 15. (c): Amylase hydrolyzes starch to maltose, isomaltose and α-dextrins. Hydrochloric acid activates pepsinogen to pepsin. Rennin coagulates the milk protein casein. 16. (d) 17. (b) 18. (c) In diarrhoea, the absorption of food is reduced. Diarrhoea is abnormal frequency of bowel movement and increased liquidity of the faecal discharge. 19. (d): The parietal cells of gastric glands secrete HCI. Pepsinogen (proenzyme) is converted into pepsin enzyme (active form), in the presence of HCI. This enzyme acts on proteins in the stomach. Therefore, if the secretion of parietal cells is bocked, HCI acid will not be secreted and thus inactive pepsinogen will not be converted into active pepsin. As a result, proteins will not be hydrolysed to proteoses and peptones. 20. (d) All the four basic layers (serosa, muscularis,sub-mucosa and mucosa) in the wall of gut show modifications in different parts of the alimentary canal. EG., mucosal epithelium has goblet cells which secrete mucus. Mucosa also forms glands in the stomach and crypts in between the bases of villi in the intestine. Page 8 of 9
9 21. (d) : Livers lobules are surrounded by Glisson s capsule. 22. (b): The crypts of Lieberkuhn are simple tubular glands that occur throughout the small intestine between the velli. They secrete enzymes and mucus. 23. (a): During prolonged fasting, the organic compounds will be used by the body in the following sequence: Carbohydrates Fats Potein 24. (d) : Sugarcane contains sucrose (disaccharide). In the duodenum, sucrose is acted upon by enzyme invertase which breaks down it into glucose and fructose. 25. (b) : Bolus is the collection of food formed with chewing and mixing with saliva. Chyme is that collection of food which is mixed thoroughly with acidic gastric juice. 26. (b) 27. (a) : Fats act as concentrated fuel, Their caloric value is 9.45 kcal/g and physiological fuel value is 9 kcal/g. They are more suitable as stored food. 28. (b) : The chief cells of gastric glands secrete a small amount of gastric lipase that contributes little to digestion of fat. 29. (b) : The main function of large intestine is absorption of water and elimination of solid wastes. The breakdown of all biomacromolecules like carbohydrates, proteins, fats and nucleic acids takes place in duodenum. A major part of all absorption of digested food takes place in jejunum and ileum. Undigested and unabsorbed substances are passes on to the large intestine for egestion. 30. (a) : Indigestion is a disorder in which the food is not properly digested in the body leading to a feeling of fullness. The causes of this are inadequate enzyme secretion, anxiety, food poisoning, over eating and spicy food. 9 P a g e
NCERT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION 16.1 Digestive System 16.2 Digestion of Food 16.3 Absorption of Digested Products 16.4 Disorders of Digestive System Food is one of the basic requirements of all living
CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION 16.1 Digestive System 16.2 Digestion of Food 16.3 Absorption of Digested Products 16.4 Disorders of Digestive System Food is one of the basic requirements of all living
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The human digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and the associated glands.
 1 CHAPTER 16- DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION The major components of our food are carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Vitamins and minerals are also required in small quantities.
1 CHAPTER 16- DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION The major components of our food are carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Vitamins and minerals are also required in small quantities.
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION POINTS TO REMEMBER Digestion : The process in alimentary canal by which the complex food is converted mechanically and biochemically into simple substances suitable
Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION POINTS TO REMEMBER Digestion : The process in alimentary canal by which the complex food is converted mechanically and biochemically into simple substances suitable
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY. Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
 UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Give the dental formula of adult human being? A. Dental formula represents the arrangement of various types of teeth in each half of both the jaws
DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Give the dental formula of adult human being? A. Dental formula represents the arrangement of various types of teeth in each half of both the jaws
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
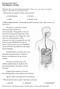
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
Ali Yaghi. Yaseen Fatayer. M.Khatatbeh
 6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Topic No. & Title: Topic 8 Digestion & Absorption of Dietary Components
 [Academic Script] Digestion & Absorption of Dietary Components Subject: Zoology Course: B.Sc. 2 nd Year Paper No. & Title: Z-202B Physiology Topic No. & Title: Topic 8 Digestion & Absorption of Dietary
[Academic Script] Digestion & Absorption of Dietary Components Subject: Zoology Course: B.Sc. 2 nd Year Paper No. & Title: Z-202B Physiology Topic No. & Title: Topic 8 Digestion & Absorption of Dietary
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
Study Aid for D1: Nutrition
 Study Aid for D1: Nutrition Essential nutrient Food only source. Ex. Some Amino acids, minerals, calcium, vitamins, water, some fatty acids Non-essential nutrient Can be made in body. Ex. Glucose, starch.
Study Aid for D1: Nutrition Essential nutrient Food only source. Ex. Some Amino acids, minerals, calcium, vitamins, water, some fatty acids Non-essential nutrient Can be made in body. Ex. Glucose, starch.
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
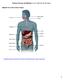 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Mammalian nutrition. In Biology 1, we looked in detail at the human diet CHAPTER 1. An overview of digestion
 ambridge University Press APTER 1 Mammalian nutrition By the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1 explain what is meant by heterotrophic nutrition, and outline the basic principles; 2 explain what
ambridge University Press APTER 1 Mammalian nutrition By the end of this chapter you should be able to: 1 explain what is meant by heterotrophic nutrition, and outline the basic principles; 2 explain what
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
2. A digestive organ that is not part of the alimentary canal is the: a. stomach b. liver c. small intestine d. large intestine e.
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Review Questions Multiple Choice: 1. Which of the following terms are synonyms? a. Gastrointestinal tract b. Digestive system c. Digestive tract d. Alimentary
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Digestive System CHAPTER 14
 Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
