DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
|
|
|
- Tobias George
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
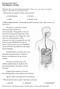
1 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION Very Short Answer Questions 1. Give the dental formula of adult human being? A. Dental formula represents the arrangement of various types of teeth in each half of both the jaws of man in the order Incisors, Canines, Premolars and Molars. In adult man, it is =. Dental formula of milk dentition is 2/2, 1/1, 0/0, 2/2 = 20 I = Incisors teeth P = Premolars teeth C= Canines teeth M = Molars teeth For an adult man with 32 teeth, the formula is written as: I - 2/2 C - 1/1 P - 2/2 M - 3/3 The total number of teeth on one side of the mouth is 16, thus the total number of teeth in the mouth equals 16 x 2 = Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. How? A. Bile juice secreted by liver doesn t contain enzymes, but it has bile salts like sodium/potassium glycocholates and taurocholates, which help in digestion and absorption of fats. Bile salts emulsify fats. Bile activates the lipases of pancreatic and intestinal juice. They act on emulsified fats and convert them into fatty acids and glycerol.
2 3. Describe the role of chymotrypsin. Name two other digestive enzymes of the same category secreted by the same gland? A. Chymotrypsin of pancreatic juice helps in the digestion of proteins, proteoses and peptones and converts them into Tripeptides and dipeptides. Trypsin and carboxy peptidases are the other digestive enzymes produced by the pancreas. 4. What would happen if HCl were not secreted in the stomach? A. HCl is secreted by oxyntic cells of fundic glands present in the wall of stomach. It provides acidic ph which is optimal for the action of pepsin. HCl activates the pro enzyme pepsinogen into pepsin. Pepsin plays an important role in digestion of proteins. If HCl were not secreted in the stomach, then pepsin would not be activated. It would effect on digestion of proteins. 5. Explain the terms thecodont and diphyodont dentitions? A. Thecodont: Arrangement of teeth in the sockets of the jaw bones is called thecodont dentition. Diphyodont: formation of two sets of teeth during the life time, a set of temporary/milk teeth/deciduous teeth replaced by a set of permanent teeth is known as diphyodont dentition. 6. What is autocatalysis? Give two examples? A. Autocatalysis is the catalysis of a reaction in which the catalyst is one of the products of the reaction (or) catalysis caused by a catalytic agent formed during a chemical reaction. E.g.: Trypsinogen Trypsin Trypsin (Autocatalysis)
3 7. What is chyme? A. Semi fluid mass of partly digested acidic food formed in the stomach is called chyme. 8. Name the different types of salivary glands of man and their locations in the human body? A. Three pairs of salivary glands are present in man. They are. 1. Parotid Glands present below the pinna / inner surface of the cheeks 2. Sub maxillary (or) Sub mandibular glands located at the angles of lower jaw 3. Sublingual glands present below the tongue 9. Name different types of papillae present on the tongue of man? A. The upper surface of the tongue has small projections called papillae, representative of taste buds. In humans, the tongue bears 3 (three) types of papillae namely: i) Fungi form papillae present on tip and margins of tongue. ii) Filiform papillae -- present on surface of tongue. iii) Circumvallate papillae present on posterior part / base of tongue.
4 (. 10. What is the hardest substance in the human body? What is its origin? A. Enamel of tooth is the hardest substance in the human body. It covers the crown of tooth. Enamel is secreted by ameloblasts of ectodermal origin. 11. Name the structure of gut which is vestigial in human beings, but well developed in herbivores. And mention the type of tissue with which it is mostly formed? A. Appendix is the vestigial part in human beings. It is a narrow finger like tubular projection, arises from the caecum. In herbivores it is a functional part and useful in the digestion of cellulose. Appendix contains a high concentration of lymphoid tissues. Appendix is known as abdominal tonsil.
5 12. Distinguish between deglutition and mastication? A. Deglutition: Deglutition is the swallowing of food. Mastication: The mastication process includes the biting and tearing of food into pieces. It is involved by using the incisors and canines. The grinding of food is usually performed by the molars and premolars. During this process, food is moistened and mixed with saliva. 13. Distinguish between diarrhea and constipation? A. Diarrhea: The abnormal frequency of bowel movement and increased liquidity of the faecal discharge. It reduces the absorption of food and results in loss of water (dehydration). Constipation: The condition in which the faeces are retained within the rectum as it is hard due to low content of water and the movement of bowel occurs irregularly. 14. Name two hormones secreted by the duodenal mucosa? A. The hormones secreted by epithelium of duodenal mucosa are secretin and cholecystokinin (cck) /cholecystokinin pancreozymin. 15. Distinguish between absorption and assimilation? A. Absorption: Absorption is the process by which the end products of digestion pass through the intestinal mucosa into blood (or) lymph. It is carried out by passive, active (or) facilitated transport mechanisms.
6 Assimilation: The absorbed substances finally reach the tissues, where food materials become integral components of the living protoplasm and used for the production of energy, growth and repair. This process is called assimilation. Short Answer Questions 1. Draw a neat labelled diagram of L.S. of teeth? 2. Describe the process of digestion of proteins in the stomach? A. Digestion of proteins begins in the stomach. The food enters into the stomach is mixed thoroughly with the gastric juice of the stomach by the churning movements of its muscular wall and the product is called chyme. The main components of gastric juice are protein digestive enzymes, hydrochloric acid and mucus. HCl provides the acidic ph (0.9 to 1.8) which is optimal for the action of pepsin. The proenzymes of gastric juice, the pepsinogen and pro-rennin are converted into the active enzymes, pepsin and rennin respectively by the action of Hydrochloric acid. Pepsin converts proteins into proteoses and peptones.
7 Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme found in the gastric juice of infants. It acts on the milk protein, the casein in the presence of calcium ions and converts it into calcium paracaseinate and proteoses. Pepsin acts on calcium paracaseinate and converts it into peptones. The entire process of protein digestion in the stomach takes about 4 hours. Pro rennin (inactive) Pepsinogen (inactive) HCl Rennin (active) HCl Pepsin (active) Casein Rennin Ca +2 Calcium paracaseinate Calcium paracaseinate Pepsin Peptones Proteins Pepsin Proteoses + Peptones 3. Explain the role of pancreatic juice in the digestion of proteins? A. Pancreatic juice is secreted by the pancreas and it plays an important role in protein digestion. Pancreatic juice contains protein hydrolyzing enzymes like trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and pro carboxy peptidase but in inactive form. Enzyme activator, enterokinase of intestinal juice activates Trypsinogen active trypsin, which in turn activates the other enzymes in the pancreatic juice. Enterokinase Trypsinogen Trypsin Trypsinogen Trypsin Trypsin Chymotrypsinogen Trypsin Chymotrypsin
8 Chymotrypsin, trypsin and carboxy peptidase of pancreatic juice act upon proteins, proteoses and peptones in the chyme, results in the formation of tri and dipeptides which in turn hydrolyzed into amino acids by the action of tri and dipeptidases. Proteins Trypsin Chymotrypsin Proteases Tripeptides Dipeptides Carboxy peptidases + Peptones Tripeptides Dipeptides Tripeptidase Dipeptides + Amino acids Dipeptidase Amino acids 4. How are polysaccharides and disaccharides digested? A. Carbohydrates of food principally consist of polysaccharides, Starch and glycogen. It contains disaccharides and small amounts of monosaccharide. Digestion in Mouth: Digestion of carbohydrates starts in the mouth, where they come in contact with saliva. Saliva contains carbohydrase called salivary amylase (ptyalin). It hydrolyses the starch into disaccharides (maltose). Starch amylase Disaccharides (maltose) Digestion in Stomach: Ptyalin action stops in stomach when ph falls to 3.0. No carbohydrate splitting enzymes are available in gastric juice. Digestion in small intestine: Chyme reaches the duodenum where it is mixes with pancreatic juice and intestinal juice. Carbohydrates in the chyme are hydrolysed by the pancreatic amylase into disaccharides. Intestinal disaccharidases act on the disaccharides and convert them into monosaccharide. Carbohydrates Maltose Sucrose Lactose Amylase Maltose, Sucrose, Lactose Maltase Glucose + Glucose Invertase Glucose + Fructose Lactase Glucose + Galactose
9 5. If you take butter in your food how does it get digested and absorbed in the body? Explain? A. Butter contains fat. Fats are partially digested in stomach. Digestion of fat in the small intestine: The major site of fat digestion is the small intestine. It is due to the presence of lipase / (steapsin) in the pancreatic juice and bile juice. Bile juice contains bile salts such as Sodium / Potassium glycocholates and taurocholates which helps in the emulsification of fat i.e., breakdown of fats into very small micelles. Bile also activates lipases of pancreatic juice (steapsin) and intestinal lipases. These lipases act on emulsified fats and convert them into fatty acids and glycerols. Fats Bile salts Emulsified fats Emulsified fats Monoglycerides Lipases Monoglycerides Lipases Fatty acids + Glycerol Absorption: Fatty acid and glycerol being insoluble in water cannot be absorbed into the blood directly. They are first modified into small droplets called micelles, which move into intestinal mucosal cells. They are reformed into very small protein coated fat globules called Chylomicrons which are transported into the lymph capillaries in the villi by exocytosis. They are released into blood stream through left subclavian vein via the thoracic duct. These chylomicrons are broken down to fatty acids and glycerol by the action of an enzyme lipoprotein lipase and they diffuse into the adipocytes of the adipose tissue and liver for storage as neutral fat or tissue fat. 6. What are the functions of liver? A. Liver performs a variety of functions like synthesis, storage and secretion of various substances. 1. Liver secretes the bile juice, which contains bile salts such as glycocholate and taurocholate of sodium and potassium which help in digestion and absorption of lipids. 2. Liver plays the key role in carbohydrate metabolism. a) Glycogenesis: Formation of glycogen from glucose b) Glycogenolysis: Breakdown of glycogen into glucose c) Gluconeogenesis: Synthesis of glucose from certain amino acids or other than carbohydrates.
10 3. Liver plays an important role in synthesis of cholesterol and production of triglycerides. 4. Deamination of proteins occurs in the liver. 5. Liver is the chief organ of detoxification of toxic substances that enter the gut along with food. 6. Liver acts as thermoregulatory organ. 7. Liver acts as a haemopoietic organ in the foetus and erythroclastic organ in the adult. 8. Liver synthesizes the plasma proteins such as albumin, globulins, blood clotting factors such as fibrinogen / prothrombin, etc., and the anticoagulant called heparin. 9. The lactic acid formed during anaerobic muscle contraction is converted into glycogen (gluconeogenesis) in the liver by Cori cycle. 10. Kupffer cells are the largest phagocytic cells which remove unwanted substances and microbes by Phagocytosis. Kupffer cells are known as hepatocytic macrophages. Long Answer Questions 1. Explain the digestive system of man? 1. Digestive Tract/Alimentary Canal: It starts with mouth and ends with anus. It consists, the parts like buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine. a) Mouth and Buccal Cavity: * Mouth leads into buccal or oral cavity. * Palate separates the ventral buccal cavity from dorsal nasal chamber.
11 * Anterior hard palate is bonnie and liney by palatine rugae. Posterior soft palate hangs down into the pharynx as Uvula. * Jaw bones have 4 kinds of teeth and a tongue. *Teeth are ecto-mesoderm in origin. Teeth are thecodont, heterodont, diphyodont * Dental formula of adult man is =. * Dental formula of milk dentition is 2/2, 1/1, 0/0, 2/2 = 20. *Tongue attaches with floor of buccal cavity by frenulum. Upper surface of tongue has papillae with taste buds. They are: a) Fungi form anterior margin and tip. b) Filiform on surface c) Circumvallate on posterior surface. b) Pharynx: * Pharynx is divided into nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx by soft palate. *Epiglottis prevents the entry of food into glottis during swallowing. *pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids, palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils are present as lymphoid tissues. c) Oesophagus: *It is thin long tube extends through neck, thorax and diaphragm and finally leads into stomach. *cardiac sphincter/gastro esophageal sphincter regulates the opening of esophagus into stomach. d) Stomach: * It is a wide J shaped muscular part present in upper left portion of abdominal cavity. It has three major parts like Anterior cardiac stomach middle large fundic stomach and posterior pyloric stomach. * Pyloric stomach opens into duodenum of small intestine through pylorus which is guarded by pyloric sphincter. e)small Intestine: * It is the longest part of alimentary canal. * It has three regions like proximal duodenum, middle long coiled jejunum and distal highly coiled ileum.
12 * Duodenum receives hepatopancreatic duct through the opening which is guarded by sphincter of Oddi. * Ileum opens into large intestine. f) Large Intestine: * It consists of caecum, colon and rectum. * Caecum is a small blind sac which accommodates symbiotic microorganisms. * A narrow finger like vermiform appendix (abdominal tonsil) arises from caecum. * Caecum opens into colon which has 4 regions like ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid parts. * Colon shows external bulged out pouches known as haustra. * Rectum is a small dilated sac that leads into anal canal. * Anal canal opens out through the anus. It is guarded by an internal anal sphincter with smooth muscle and external anal sphincter with voluntary/striped muscles. Digestive Glands: Digestive glands are salivary glands, gastric glands, intestinal glands, liver and pancreas. 3 pairs of salivary glands are present in man..parotid, sub-maxillary and sublingual glands. Gastric glands are present in the wall of stomach in the form of cardiac, fundic and pyloric glands. Liver is the largest gland in the body. It secretes bile juice. Pancreas is the second largest gland. It is mixed gland with both exocrine and endocrine parts. S.No Digestive Juice Secreted by ph & Nature Components 1. Saliva Salivary 6.8, glands slightly acidic 2. Gastric juice Gastric glands 0.9 to 1.8 Acidic Brunner s 7.5 to 8.0, 3. Intestinal juice glands of Alkaline (succus entericus) duodenum and crypts Water, salts, mucin, Ptyalin (α amylase), lysozyme Proenzymes, Pepsinogen, prorennin, Hcl, Castle s intrinsic factor, gastric lipase. Tripeptidases, dipeptidases, aminopeptidases, disaccharidases, Intestinal lipase, enzyme activator, Enterokinase, lysozyme of Lieberkuhn 4. Bile juice Liver Alkaline Bile salts, sodium bicarbonate, bile pigments. 5. Pancreatic juice Pancreas 8.4, alkaline Sodium bicarbonate, trypsinogen, Chymotrypsinogen, carboxypeptidases, lipase (Steapsin), amylase, nucleases like DNAase and RNA ase.
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY. Digestion And Absorption. Finish Line & Beyond send your queries to
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Digestion And Absorption 1. Choose the correct answer among the following : (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin, lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION 16.1 Digestive System 16.2 Digestion of Food 16.3 Absorption of Digested Products 16.4 Disorders of Digestive System Food is one of the basic requirements of all living
CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION 16.1 Digestive System 16.2 Digestion of Food 16.3 Absorption of Digested Products 16.4 Disorders of Digestive System Food is one of the basic requirements of all living
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION
 Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION POINTS TO REMEMBER Digestion : The process in alimentary canal by which the complex food is converted mechanically and biochemically into simple substances suitable
Chapter-16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION POINTS TO REMEMBER Digestion : The process in alimentary canal by which the complex food is converted mechanically and biochemically into simple substances suitable
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The human digestive system consists of the alimentary canal and the associated glands.
 1 CHAPTER 16- DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION The major components of our food are carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Vitamins and minerals are also required in small quantities.
1 CHAPTER 16- DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION The major components of our food are carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Vitamins and minerals are also required in small quantities.
NCERT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
91 CHAPTER 16 DIGESTION AND ABSORPTION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Select what is not true of intestinal villi among followings a. They possess microvilli b. They increase the surface area c. They are
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
c.uma sankar.kanchipuram.
 NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
NAME: GLOBAL COACHING CENTRE XII STANDARD BIO ZOOLOGY DIGESTION ONE MARK PRACTICE PAPER 1. serves to transfer organic molecules, salts and water from the external environment to the body s internal environment.
Digestive System. Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition)
 Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
Digestive System Unit 6.11 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.11 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the digestive system. Explain the locations and functions of three organs in the
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
 UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
Biology. TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption. Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr
 TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Van Kupffer cells (i) Isolets of langerhans B - cells (ii)
TOPIC : Digestion and Absorption Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr (1) Match with and select the correct option from the codes given below A Van Kupffer cells (i) Isolets of langerhans B - cells (ii)
Digestive System Lecture Notes Read Ch 14; review questions start on page 477 S/A # 4, 5, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 21, 22, 26, 35
 The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
The PRINCIPLE structure of the digestive system is the Alimentary Canal (Gastrointestinal Tract) = hollow tube much like a hallway in a home. I. Functions of the Digestive System a. Ingestion: Putting
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
I. The Alimentary Canal (GI track)
 A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
A. About 9 meters long B. Passes through the ventral cavity. C.Movements of the Tube 1. Mixing movements- smooth muscles contract rhythmically. 2. Propelling movements- a wavelike motion called peristalsis.
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Digestive System and Body Metabolism 14PART C Accessory Digestive Organs Teeth Salivary glands
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff
 Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
Digestion Introduction Lecture MMHS Science Chitraroff Digestion is the process that changes food into a form that is usable by your body. The Alimentary Canal The pathway of food from your mouth to your
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion
 NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
NOTES: CH 41 Animal Nutrition & Digestion NUTRITION *Nutrition is the study of nutrients and how the body utilizes them! *ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS: nutrients that human cells cannot synthesize (i.e. certain
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Digestive System. Part 3
 Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
Digestive System CHAPTER 14
 Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
Digestive System CHAPTER 14 Digestive System http://media.pearsoncmg.com/bc/bc_marie b_ehap_8/activities/chapter14/act14a.ht ml Functions of Digestion Ingestion - intake of food Propulsion a. Peristalsis
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY. Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
 UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
UNIT 5 HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Chapter 19 Excretory Products and their Elimination Chapter
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy
 The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART C The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
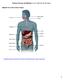 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I Topic: Human Digestive System Page 1 of 13. The Chemical Foundation of Digestion
 Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Page 1 of 13 The Chemical Foundation of Digestion All organisms, regardless of size or complexity, have some method to obtain the essential nutrients they need for survival. Heterotrophs: Organisms that
Biology 12 Unit 5 Pretest
 Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Biology Unit 5 Pretest Name: Date: Block:. Chewing aids digestion by A. stimulating release of bile B. increasing surface area of food C. breaking up polymers into monomers D. stimulating water absorption.
Digestive System Processes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44742 1 Digestive System Processes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function
 Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
Chapter 25 Anatomy and Physiology: The Unity of Form and Function Second Edition Kenneth S. Saladin (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Structures and Location A. Location from mouth through thoracic
MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS
 MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS HOMEOSTASIS BODY DEFENCE AND IMMUNITY DIGESTION CIRCULATION RESPIRATION EXCRETION NERVOUS SYSTEM DIGESTION DIGESTION Structure of digestive system. Process
MAN IN HEALTH AND DISEASES 18 HOURS 27 MARKS HOMEOSTASIS BODY DEFENCE AND IMMUNITY DIGESTION CIRCULATION RESPIRATION EXCRETION NERVOUS SYSTEM DIGESTION DIGESTION Structure of digestive system. Process
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Nutrition and the Digestive System
 C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
C H A P T E R 16 Nutrition and the Digestive System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List and describe the five basic activities of the digestive process. 2. List the four
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition
 Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
Chapter 15 Digestion and Nutrition Digestive System: Digestion refers to the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods so that nutrients can be absorbed by cells. The digestive system consists of the
Chapter 14. The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Textbook and Workbook Assignments Textbook: pg. 463-494 Workbook: 277-281, 283-293, 299 Crash Course Videos: Digestive System part 1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yiotrgfcmqm&t=35s
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Chapter 23: The Digestive System
 Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Chapter 23: The Digestive System I. OVERVIEW Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs. GIT (gastrointestinal tract) and teeth, tongue, gallbladder, salivary glands, liver and pancreas. (A) Digestive
Digestive System. Digestive Processes. The Digestive System. Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells
 The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
The Digestive System Digestive System Digestion Mechanical & chemical breakdown of food into a form that can be used by cells Mechanical breaks large pieces into smaller pieces Chemical breaks food into
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
Digestive System Processes
 Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
Unit 7 Digestive System Processes ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Processes of the Digestive System Ingestion- getting food into the mouth Propulsion- moving foods through the digestive system
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
