Effect of organic wastes on the extractability of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in soil
|
|
|
- Kristin Gregory
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geoderma 122 (2004) Effect of organic wastes on the extractability of cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in soil Ayten Karaca* Ankara University, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Soil Science, Ankara, Turkey Available online 8 February 2004 Abstract A soil incubation experiment lasting 6 months was carried out to ascertain the effects of tobacco dust, mushroom compost, and grape marc, which contain high organic matter, on the extractable cadmium, copper, nickel, and zinc in soil. The rates of organic wastes in its moist state added were 0%, 2%, 4%, and 8% of the air-dried soil on mass basis. Soil ph was decreased significantly in soils treated with the mushroom compost and grape march during the incubation period. The addition of all three organic wastes caused a significant increase in the organic matter content of soils. The application of tobacco dust significantly increased the DTPA-extractable Cd content in soil, whereas the addition of grape marc and mushroom compost caused a significant decrease in the extractable Cd content of soils. The DTPA-extractable Cu decreased significantly with increasing rates of grape marc amendment and increased with increasing rates of tobacco dust amendment, but there was no consistent effect of mushroom compost. The amount of DTPA-extractable Ni was higher in mushroom compost added to soil than in grape marc added to soil due to higher organic matter content of grape march. The DTPA-extractable Zn increased with increasing rates of all three organic wastes amendments. D 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Organic wastes; Heavy metals; ph; Organic matter 1. Introduction Application of organic wastes as a source of organic matter is a common practice to improve soil properties (Baran et al., 2001). However the use of organic wastes can lead to problems pertaining to their heavy metal content and their successive application result in heavy metal accumulation in soil. Land disposal of organic waste materials may directly or * Fax: address: akaraca@agri.ankara.edu.tr (A. Karaca). indirectly alter the heavy metal status of the soil by affecting metal solubility or dissociation kinetics (Del Castilho et al., 1993). The total heavy metal content of the soil is commonly used to indicate the degree of contamination, but the heavy metal concentration in solution mostly determines the actual environmental exposure or risk. Distribution of heavy metals between soil and solute is the key to evaluating the environmental impact of the metals. Despite the complexity of possible reactions, several important soil factors controlling the distribution of heavy metals between soil and solutes have been identified (Sposito, 1989; Temminghoff et al., 1998) /$ - see front matter D 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.geoderma
2 298 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) The sorption behavior of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn in soils varies from soil to soil and is influenced by soil properties, such as ph, organic matter, cation exchange capacity (CEC), and clay contents (McBride, 1989). A strong relationship between soil solution ph and metal adsorption has been demonstrated, with metal adsorption being directly proportional to ph (Elliott et al., 1986). The effects of soil ph on soil solution concentrations and extractabilities of metals have been studied. He and Singh (1993) found that peat addition increased the DTPA extractable Cd in soils due to decrease in soil ph caused by peat application. Yuan and Lavkulich (1997) and Arnesen and Singh (1999) found that the lowering of ph in peat-amended soil decreased the sorption of Cd, Cu, Zn, and Ni in the soil. Soil organic matter has been of particular interest in studies of heavy metal sorption by soils, because of its significant impact on CEC, and more importantly, the tendency of transition metal cations to form stable complexes with organic ligands (Elliott et al., 1986). Organic matter makes strong complexes with heavy metals (Krogstad, 1983). The amount of organic matter in soils affects the binding of heavy metals in soil and speciation in soil solution (Lo et al., 1992). Cadmium is a pollutant and potential toxin that has no known function in any biological organism (Wagner, 1993). Increased adsorption of Cd by soil components with increasing amounts of organic matter has been reported (Christensenn, 1984; Eriksson, 1988). High organic matter content or addition of organic matter decreases solution concentrations of Cd and Ni, but increases the extractability of Zn (McGrath et al., 1988; Arnesen and Singh, 1999). Amendment with organic matter and resulting degradation may change the soil ph and thereby indirectly affect the bioavailability of metals. Many authors have found that all type of organic wastes increased the extractability of Zn in soil (MacLean, 1976; Saviozzi et al., 1997; Arnesen and Singh (1999). The aim of the experiment described here was to study the influence of organic wastes (mushroom compost, grape marc, and tobacco dust) on the DTPA extractable Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn in soil. Release of the metals into solution as a function of ph was also studied. 2. Materials and methods 2.1. Soil and organic wastes description The soil (typic xerofluvent) was a clay loam taken from an experiment field of Ankara University, Faculty of Agriculture, within 0 20 cm of the surface. The soil was air dried and passed through a 2-mm sieve. Composted grape marc (GM), mushroom compost (MC), and tobacco dust (TD) passed through a 6.35-mm sieve. The properties of the organic wastes were determined by Baran et al. (1995). Some physical and chemical properties and total and extractable heavy metal contents of the soil samples and organic wastes are given in Tables 1 and Incubation trial The rates of organic wastes in its moist state added were 0%, 2%, 4%, and 8% of the air-dried soil on mass basis. Triplicate soil samples were homogenized with dry organic wastes and filled in plastic pots (400 cm 3 in each pot). Each pot consisted of 300 g of coarsely sieved soil with various amendments. The water content of the soil was adjusted to 70% of water holding capacity. The pots were placed in an incubator at 28 jc and 70% relative humidity. Throughout the Table 1 Selected properties of the soil and organic wastes used ph EC OM C Texture % CEC N C/N 1:2.5 MS cm 1 % % Sand Silt Clay Cmolkg 1 % Soil GM TD MC GM, grape marc; TD, tobacco dust; MC, mushroom compost; OM, organic matter; CEC, cation exchange capacity.
3 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) Table 2 Total and extractable Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn amounts of soil and organic wastes used (mg kg 1 ) Total Cd Total Cu Total Ni Total Zn Exc. Cd Exc. Cu Exc. Ni Exc. Zn Soil GM TD MC Exc. Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn, DTPA extractable Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn. incubation period, water losses exceeding 10% of the initial values were compensated for by addition of distilled water. Soil samples were taken on the first day and 6 months after incubation and analyzed for ph, organic matter and DTPA extractable Cd, Zn, Cu, and Ni Sample analysis Soil ph and electrical conductivity (EC) was measured in water with a 1:2.5 ratio of soil solution according to Richards (1954). Organic matter content was determined by the method of modified Walkley and Black (Jackson, 1962). Total nitrogen was determined by using Kjeldahl method (Bremner and Mulvaney, 1982). Particle size distribution was determined according to Bouyoucos (1951). CEC was determined according to methods given in Rhoades (1982). Available heavy metals in soils and organic wastes were extracted with a DTPA solution (0.005 M DTPA M CaCl M TEA, ph 7.3), (Lindsay and Norvell, 1978). Total heavy metals in soils and organic wastes were digested in aqua regia (Baker and Amacher, 1982). All solutions with Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn were analysed by atomic absorption spectrophotometer (AAS) with flame or graphite furnace when required. Minitab and Mstat computer programs (Software Company) were used for statistical analyses. 3. Results and discussion Soil ph decreased in soils treated with the TD and GM during the incubation period (Table 3). This decrease was especially noticeable in soils treated with TD. This material has low levels of ph. With addition MC, there was no consistent effect in the first day of incubation period. However, by the sixth month of incubation addition of MC resulted in a significant decrease in soil ph ( P >0.05). The lowest ph was determined in TD added to soil and that was followed by GM and MC added to soil, respectively. Content of organic matter increased significantly with increasing amount of all three organic wastes (Table 4). However, it was lower in the sixth month of incubation than the first day of incubation. A significant loss of organic matter occurred at all rates of added organic wastes. During the 6 months of experiment, the amount of organic matter; and probably also its properties; were altered, resulting in the adsorption of the metals to the organic ligands and to the soil surfaces (Elliott and Denneny, 1982; Japenga et al., 1992; Yuan and Lavkulich, 1997). The amount of extractable Cd was higher in MC added to soil than GM added to soils due to had higher organic matter content. Results showed that the Table 3 Soil ph values at increasing rates of organic wastes applied Time Organic Wastes Rate (%) MC 1st day 7.79Aa 7.70Ca 7.74Ba 7.80Aa 6th month 7.72Ab 7.42Bb 7.38Bb 7.19Cb LSD GM 1st day 7.79Aa 7.70Ba 7.67Ca 7.65Da 6th month 7.72Ab 7.35Bb 7.30Cb 7.03Db LSD TD 1st day 7.79Aa 7.24Ba 7.03Ca 6.85Da 6th month 7.72Ab 7.00Bb 6.87Cb 6.70Db LSD Significant differences between treatments at P < 0.05 level indicated by different letters. Upper letter in row, lower letter in column.
4 300 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) Table 4 Soil organic matter contents at increasing rates of organic wastes applied Time Organic Wastes Rate (%) MC 1st day 1.26 Da 2.85 Ca 4.24 Ba 5.80 Aa 6th month 1.23 Da 2.51 Cb 2.70 Bb 2.99 Ab LSD GM 1st day 1.26 Da 3.60 Ca 4.65 Ba 7.69 Aa 6th month 1.23 Da 2.55 Cb 4.50 Bb 5.50 Ab LSD TD 1st day 1.26 Da 3.85 Ca 6.19 Ba 7.90 Aa 6th month 1.23 Da 2.42 Cb 3.23 Bb 3.42 Ab LSD Significant differences between treatments at P < 0.05 level indicated by different letters. Upper letter in row, lower letter in column. MC and GM treatments caused a marked decrease, whereas TD treatment caused a marked increase in the DTPA-extractable Cd during the incubation period (Table 5, P < 0.05). Extractable Cd was highly but negatively correlated to soil ph in TD added to soils (r = 0.783, P < 0.01), however a positively correlated to soil ph in GM added to soil (r = 0.468, P < 0.05). There was no significant correlation between extractable Cd and ph in MC added to soil. Among factors controlling the adsorption of Cd in soil, ph is probably the most important (Christensenn, 1984). The effect of ph is related to its great influence on the charge and structure of the adsorbing surfaces and on the ionic composition of the soil solution (Garcia-Miragaya and Page, 1978; Abd-Elfattah and Wada, 1981). Ram and Verloo (1985) found that farmyard manure and peat soil enhanced the mobility of Cd at lower ph and decreased it at higher ph. Eriksson (1988) found that soil Cd extracted by 1 M CH 3 COONH 4 was inversely related to the amount of peat added to the soils. He and Singh (1993), who treated different type of soils with different level of peat, found that DTPAextractable Cd in the soils increased with increased addition of peat. Significant negative correlation was found between extractable Cd and organic matter content of Table 5 Concentrations of DTPA-extractable Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn (mg kg 1 ) in the soil at increasing rates of organic matter applied O.M. Cd Cd Cu Cu Ni Ni Zn Zn (%) 1st day 6th month 1st day 6th month 1st day 6th month 1st day 6th month MC Ab 0.057Aa 2.20 Aa 2.10Aa 2.90 Aa 2.50Ab 1.20 Db 1.50Da Ab 0.055ABa 2.10 ABa 2.00ABa 2.10 Ba 1.80Bb 2.10 Cb 2.90Ca Bb 0.055ABa 1.90 Ca 2.00ABa 1.90 Ca 1.74Ca 2.40 Bb 3.10Ba Cb 0.050Ba 2.00 BCa 1.90Ba 1.10 Da 1.00Da 3.70 Ab 4.30Aa LSD GM Ab 0.057Aa 2.20 Aa 2.10Aa 2.90 Aa 2.50Ab 1.20 Db 1.50Ca Bb 0.043Ba 1.80 Ba 1.90Ba 1.10 Ba 1.00Ba 1.90 Cb 2.30Ba Ba 0.041Ba 1.60 Ca 1.70Ca 0.80Ba 0.90Ba 2.10 Bb 2.40Ba Cb 0.031Ca 1.76 Db 2.10Aa 0.65 Ca 0.83Ba 2.70 Ab 2.90Aa LSD TD Cb 0.057Ba 2.20 Ba 2.10Ca 2.90 Da 2.50Db 1.20 Cb 1.50Ca Ba 0.058Ba 2.40 Ba 2.70Ba 3.10 Cb 3.40Ca 1.50 BCb 2.30Ca Aa 0.061ABa 2.50 ABb 2.90ABa 3.30 Bb 3.60Ba 1.70 Bb 2.50Ba Aa 0.063Aa 2.80 Ab 3.20Aa 3.70 Ab 4.10Aa 2.90 Ab 3.70Aa LSD Significant differences between treatments at P < 0.05 level indicated by different letters. Upper letter in row, lower letter in column.
5 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) GM added to soil (r = 0.950, P < 0.01). There were no significant correlations between extractable Cd and organic matter content of MC and TD added to soil. Organic matter is considered to play an important role in reducing plant uptake of Cd from soils due to its high CEC and complexing ability. Nevertheless, the results reported in the literature are not consistent. Many authors have found that high organic matter content or addition of organic matter by organic wastes decreased the Cd concentration in solution. This effect is explained by the high CEC of organic matter and its ability to form chelate complexes with Cd. Haghiri (1974) concluded that the decreased plant Cd concentration with higher levels of organic matter added was predominantly due to the effect of increasing soil CEC. MacLean (1976) and Korcak and Fanning (1985) found a positive relationship between DTPA-extractable Cd and the amount of organic matter in soils. The concentration of Cd in all three organic wastes added to soil was higher at six months of incubation than at first day of incubation. Because of organic matter decomposition, Cd sorption was reduced in organic-wastes amended soil. Reduction in Cd sorption due to organic matter decomposition is also reported by Yuan and Lavkulich (1997) and Arnesen and Singh (1999). DTPA-extractable Cu decreased significantly with increasing rate of GM and increased with increasing rate of TD ( P < 0.05), but there was no consistent effect of MC (Table 5). Significant negative correlation was found between extractable Cu and ph in TD added to soil (r = 0.864, P < 0.01), and a positive correlation in MC added to soils (r = 0.497, P < 0.05). There was no significant correlation between extractable Cu and ph in GM added to soil. However, a significant negative correlation was found between extractable Cu and organic matter content of GM added to soil (r = 0.524, P < 0.05), and there were no significant correlations between extractable Cu and organic matter content of TD and MC added to soil. Cu was affected by ph and organic matter status, suggesting that ph and the organic contents of soils would have a great effect on the extractable Cu (Temminghoff et al., 1998). Many comparative studies have shown that soluble organic matter forms much stronger complexes with Cu than Zn (McBride, 1978). McGrath et al. (1988) found that the total Cu content was more dependent on the organic matter status, as soil and the proportion of Cu present in solution as Cu 2+ increased and as ph decreased. They also implied that extractability of Cu, however, was affected by organic matter status, suggesting that the organic matter content of soils would have a great effect on the fate of Cu whether it was applied in fertilizers, sewage sludges or other organic wastes containing Cu. Arnesen and Singh (1999) found that extractable Cu increased with increasing rate of peat, and they suggested that the lowering of ph in the peat-amended soil probably decreased the sorption of Cu in the soil. The amount of extractable Ni was higher in MC added to soil than GM added to soil due had higher organic matter content of GM. Increasing the rate of wastes addition gradually reduced the DTPA-extractable Ni in MC and GM added to soil (Table 5, P < 0.05). However, the addition of TD increased the extractable Ni. These are supported by the finding of Arnesen and Singh (1999) who found a similar effect of peat on the DTPA-extractable Ni. They suggested that the lowering of ph in the peat-amended to soil decreased the sorption of Ni in the soil and this effect became more significant after degradation of organic matter. The concentration of Ni in all three organic wastes added to soil was higher after 6 months of incubation than in the first day of incubation, but there were no significant differences between first incubation and second incubation in MC added to soil. Significant negative correlations were found between extractable Ni and ph in TD and MC added to soil (r = 0.912, P < 0.01 and r = 0.556, P < 0.05, respectively), and a positive correlation in GM added to soil (r = 0.519, P < 0.05). Significant negative correlations were found between extractable Ni and organic matter content of TD and GM added to soil (r = 0.306, P < 0.1 and r = 0.800, P < 0.01, respectively). But there was no significant correlation between extractable Ni and organic matter content of MC added to soil. DTPA-extractable Zn increased with increasing rates of all three organic wastes added to soil (Table 5, P < 0.05). These results show that the different organic matter sources have about the same effect
6 302 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) on DTPA-extractable Zn in soil. The concentration of Zn in the present study was higher after six months of incubation than in the first day of incubation, probably due to degradation of the organic matter and release of the Zn, which was complexed with organic matter in the first incubation period. Shuman (1975) found that ph, the clay content, organic matter content, and CEC influenced the adsorption of Zn by soils. Mandal and Hazra (1997) found that organic matter application and low ph arrested a decreasing trend in Zn adsorption, and increasing levels of soil organic matter increased extractability of Zn. Significant negative correlations were found between extractable Zn and ph in TD and GM added to soil (r = 0.797, P < 0.01 and r = 0.741, P < 0.01, respectively), and a positive correlation in MC added to soil (r = 0.518, P < 0.05). However, significant positive correlation was found between extractable Zn and organic matter content of GM added to soil (r = 0.811, P < 0.01). There were no significant correlations between extractable Zn and organic matter content of TD and MC added to soil. 4. Conclusion The effect of organic waste application on the extractability of Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn in the CL soil (typic xerofluvent) depended on ph, organic matter content of the organic wastes, the metals studied and the time after its application. The application of TD increased amounts of DTPA-extractable Cd, Cu, Ni, and Zn, probably decreased ph. Increase in extractable Zn was found by the addition of GM and MC, whereas these organic wastes resulted in decreased extractable Cd and Ni. The DTPA-extractable Cu decreased with GM addition, but there was no consistent effect of MC. The concentrations of heavy metals in the present study were higher after 6 months of incubation than in the first day of incubation, probably due to degradation of the organic matter and release of the metals, which were complexed with organic matter at the beginning of incubation. Organic matter content and the ph value of the soil are relatively easy to change. Therefore, the effects of organic matter and ph on the extractability of metals deserve special attention. References Abd-Elfattah, A., Wada, K., Adsorption of Pb, Cu, Zn, Co and Cd by soils that differ in cation-exchange materials. J. Soil Sci 32, Arnesen, A.K.M., Singh, B.R., Plant uptake and DTPA-extractability of Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn in a Norwegian alum shale soil as affected by previous addition of dairy and pig manures and peat. Can. J. Soil Sci., Baker, D.E., Amacher, M.C., Nickel, copper, zinc, cadmium. In: Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. ASA-SSSA, Madison, WI, USA, pp Baran, A., Cayci, G., Inal, A., Some physical and chemical properties of organic wastes. Pamukkale University. J. Eng. Sci. 1 (2-39), Baran, A., Cayci, G., Kutuk, C., Hartmann, R., The effect of grape marc as growing medium on growth of hypostases plant. Bioresour. Technol. 78, Bouyoucos, G.J., A recalibration of hydrometer for making mechanical analysis of soils. Agron. J. 43, Bremner, J.M., Mulvaney, C.S., Nitrogen-total. In: Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. ASA-SSSA, Madison, WI, USA, pp Christensenn, T.H., Adsorption of Cd as influenced various soil properties. Water Air Soil Pollut. 21, Del Castilho, P., Chardon, W.J., Salomons, W., Influence of cattle-manure slurry application on the solubility of Cd, Cu, and Zn in a manured acidic, loamy sand soil. J. Environ. Qual. 22, Elliott, H.A., Denneny, C.M., Soil adsorption of Cd from solutions containing organic ligands. J. Environ. Qual. 22, Elliott, H.A., Liberati, M.R., Huang, C.P., Competitive adsorption of heavy metals by soils. J. Environ. Qual. 15, Eriksson, J.E., The effect of clay, organic matter and time on adsorption and plant uptake of Cd added soils. Water Air Soil Pollut. 40, Garcia-Miragaya, J., Page, A.L., Effect of ph on the extractability of heavy metal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 9, 289. Haghiri, F., Plant uptake of Cd as influenced by CEC, organic matter, Zn and soil temperature. J. Environ. Qual. 3, He, Q.B., Singh, B.R., Effect of organic matter on the distribution, extractability and uptake of Cd in soils. J. Soil Sci. 44, Jackson, M.L., Soil Chemical Analysis Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliff, NJ, USA. Japenga, J., Dalenberg, J.W., Wiersma, D., Scheltens, S.D., Hesterberg, D., Salomons, W., Effect of liquid animal manure applications on the solubilization of heavy metals form soil. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 46, Korcak, R.F., Fanning, D.S., Availability of applied heavy metals as a function of type of soil material and metal source. Soil Sci. 140 (1), Krogstad, T., Effect of liming and decomposition on chemical composition, ion exchange and heavy metal ion selectivity in
7 A. Karaca / Geoderma 122 (2004) sphagnum peat. Scientific Reports of the Agricultural University of Norway AAS, Norway, p. 79. Lindsay, W.L., Norvell, W.A., Development of a DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn, and Cu. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, Lo, K.S.L., Yang, W.F., Lin, Y.C., Effects of organic matter on the specific adsorption of heavy metals by soil. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 34, MacLean, A.J., Cd in different plant species and its availability in soils as influenced by organic matter and additions of lime, Pb, Cd, and Zn. J. Soil Sci 56, Mandal, B., Hazra, G.C., Zn adsorption in soils as influenced by different soil management practices. Soil Sci. 162 (10), McBride, M.B., Transition metal bonding in humic acid: an ESR study. Soil Sci. 126 (4), McBride, M.B., Reactions controlling heavy metal solubility in soils. Adv. Soil Sci. 10, McGrath, S.P., Sanders, J.R., Shabaly, M.H., The effects of soil organic matter levels on soil solution concentrations and extractabilities of manganese, zinc and copper. Geoderma 42, Ram, N., Verloo, M., Effect of various organic materials on the mobility of heavy metals in soil. Environ. Pollut. 10, Rhoades, J.D., Cation exchange capacity. In: Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. ASA- SSSA, Madison, WI, USA, pp Richards, L.A., Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. U.S.D.A. Handb. 60, (USA). Saviozzi, A., Levi-Minzi, R., Riffaldi, R., Vanni, G., Laboratory studies on the application of wheat straw and pig slurry to soil and the resulting environmental implications. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 6, Shuman, L.M., The effect of soil properties on Zn adsorption by soils. Soil Sci. Proc. Am. Proc. 39, Sposito, G., The Chemistry of Soils Oxford Univ. Press, New York, USA. Temminghoff, E.J.M., Van Der Zee, S.E.A.T., Dehaan, F.A.M., Effects of dissolved organic matter on the mobility of copper in a contaminated sandy soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 49, Yuan, G., Lavkulich, L.M., Sorption behavior of Cu, Zn, and Cd in response to simulated changes in soil properties. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 28, Wagner, G.J., Accumulation of Cd in crop plants and its consequences to human health. Adv. Agron. 51,
A. K. M. Arnesen and B. R. Singh
 Plant uptake and DTPA-extractability of Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn in a Norwegian alum shale soil as affected by previous addition of dairy and pig manures and peat A. K. M. Arnesen and B. R. Singh Department of
Plant uptake and DTPA-extractability of Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn in a Norwegian alum shale soil as affected by previous addition of dairy and pig manures and peat A. K. M. Arnesen and B. R. Singh Department of
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
UPTAKE OF MAJOR AND TRACE ELEMENTS BY GRASS BIOMASS AFTER AMELIORATION OF DEGRADED SOIL
 General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
Distribution of Micronutrients in Soil of Garhi Tehsil, Banswara District of Rajasthan, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3765-3772 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.455
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 8 (2017) pp. 3765-3772 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.608.455
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article
 Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Received: 4 th April-2014 Revised: 24 th May-2014 Accepted: 26 th May-2014 Research article BIOCHAR EFFECTS ON COPPER AVAILABILITY AND UPTAKE BY SUNFLOWER IN A COPPER CONTAMINATED CALCAREOUS SOIL Mina
Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils under incubation periods: I. Zinc and copper releases
 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.15, pp 108-114, 2017 Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils
International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.15, pp 108-114, 2017 Influence of sewage sludge and organic composts on different soils
DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster. OLIVEIRA Fernando Carvalho (2) ; MATTIAZZO Maria Emilia (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster Copper, Nickel and Zinc availability to corn plants in acid soils amended with sewage sludge (1) Disponibilité en cuivre, en
Scientific registration number: 2271 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation : poster Copper, Nickel and Zinc availability to corn plants in acid soils amended with sewage sludge (1) Disponibilité en cuivre, en
Welcome. Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories
 Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR. MUTITI SAMUEL DR. UCHIDA YOSHITAKA APPSA CONFERENCE 6 TH NOVEMBER, 2017
 EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
EVALUATION OF THE PHYTOREMEDIATION POTENTIAL OF LEMON GRASS (Cymbopogon citratus) AND VETIVER GRASS (Chrysopogon zizanioides) IN LEAD CONTAMINATED SOILS AUTHORS MWANSA MUKUKA DR. CHISHALA BENSON H. DR.
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient Soil
 387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
Total zinc was determined by digesting the soil ZnSO 4
 ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
ADVANCE RESEARCH JOURNAL OF CROP IMPROVEMENT Volume 2 Issue 2 (December, 2011) Page : 203-207 Received : September, 2011; Revised : October, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Research Paper See end of the
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Recycling of Organic Waste in Agriculture April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran
 PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
PERIODIC MUNICIPAL COMPOST AND SEWAGE SLUDGE APPLICATION ON ACCUMULATION OF HEAVY METALS IN SOIL AND PLANTS Ali R. Marjovvi 1,* and Moslehedin Rezaei 1 1 Soil and Water Department, Isfahan Agricultural
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001
 Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka
 , 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
, 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
Interpreting Soils Report. Beyond N P K
 Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS
 129 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 15 (No 2) 2009, 129-134 Agricultural Academy CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS C. AYDINALP Uludag University,
129 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 15 (No 2) 2009, 129-134 Agricultural Academy CONCENTRATION AND SPECIATION OF Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn IN CULTIVATED AND UNCULTIVATED SOILS C. AYDINALP Uludag University,
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Figure 1. Location of 43 benchmark sites across Alberta.
 1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
1.0 INTRODUCTION This report describes the micronutrient and trace element status of the AESA (Alberta Environmentally Sustainable Agriculture) Soil Quality Benchmark Sites. Previous reports completed
NUTRIENT UPTAKE BY PLANTS FROM DIFFERENT LAND TYPES OF MADHUPUR SOILS
 Bangladesh J. Sci. Res. 28(2): 113-121, 2015 (December) NUTRIENT UPTAKE BY PLANTS FROM DIFFERENT LAND TYPES OF MADHUPUR SOILS Kalpana Begum, Abdul Halim Farhad Sikder, Sayma Khanom, Md. Faruque Hossain
Bangladesh J. Sci. Res. 28(2): 113-121, 2015 (December) NUTRIENT UPTAKE BY PLANTS FROM DIFFERENT LAND TYPES OF MADHUPUR SOILS Kalpana Begum, Abdul Halim Farhad Sikder, Sayma Khanom, Md. Faruque Hossain
TSADILAS Christos, SAMARAS Vasilios, SIMONIS Asterios, SETATOU Helen
 Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
FACT SHEET. Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation
 Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
AVAILABILITY OF Cd, Ni AND Zn TO RYEGRASS IN SEWAGE SLUDGE-TREATED SOILS AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES
 AVAILABILITY OF Cd, Ni AND Zn TO RYEGRASS IN SEWAGE SLUDGE-TREATED SOILS AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES V. ANTONIADIS and B. J. ALLOWAY The University of Reading, Department of Soil Science, P.O. Box 233, Reading,
AVAILABILITY OF Cd, Ni AND Zn TO RYEGRASS IN SEWAGE SLUDGE-TREATED SOILS AT DIFFERENT TEMPERATURES V. ANTONIADIS and B. J. ALLOWAY The University of Reading, Department of Soil Science, P.O. Box 233, Reading,
Discuss the importance of healthy soils Soil properties, physical, chemical and biological that one can manage for soil health How organics play a
 Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass
 asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
asetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 35 : 46-5 (21) Uptake Potential of Some Heavy Metals by Vetiver Grass Nualchavee Roongtanakiat 1 and Prapai Chairoj 2 ABSTRACT The uptake potential of upland vetiver grass (Vetiveria
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster
 Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in
 Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Vol. 28, pp. 39-43, /979 Bioavailability of Cd to Food Crops in Relation to Heavy Metal Content of Sludge-Amended Soil by Frank T. Bingham* Results of greenhouse and laboratory experiments on factors influencing
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
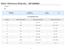 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
AGRONOMIC BIOFORTIFICATION OF GREEN BEAN (PHASELOUS VULGARIS L.) WITH ELEMENTAL SULPHUR AND FARMYARD MANURE
 - 2061 - AGRONOMIC BIOFORTIFICATION OF GREEN BEAN (PHASELOUS VULGARIS L.) WITH ELEMENTAL SULPHUR AND FARMYARD MANURE ORMAN, Ş.* KAPLAN, M. Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
- 2061 - AGRONOMIC BIOFORTIFICATION OF GREEN BEAN (PHASELOUS VULGARIS L.) WITH ELEMENTAL SULPHUR AND FARMYARD MANURE ORMAN, Ş.* KAPLAN, M. Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, Faculty of Agriculture,
Estimating Micronutrient Status and their Relationship with Other Soil Properties of Rewa District in Fiji
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.335
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 01 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.701.335
Distribution of Heavy Metals in Irrigated Vertisol Profiles in Semiarid Region of Turkey
 Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 18, No. 4 (2009), 539-545 Original Research Distribution of Heavy Metals in Irrigated Vertisol Profiles in Semiarid Region of Turkey C. Aydinalp 1, M. S. Cresser 2 1 Uludag
Polish J. of Environ. Stud. Vol. 18, No. 4 (2009), 539-545 Original Research Distribution of Heavy Metals in Irrigated Vertisol Profiles in Semiarid Region of Turkey C. Aydinalp 1, M. S. Cresser 2 1 Uludag
Inorganic Contaminants
 Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Inorganic Contaminants Dr Stephen R Smith Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering Page 1 Scope of Presentation Sources and concentrations Qualifying environmental limits Phytotoxicity Dietary intake Grain
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Pushkarov Institute of Soil Science and Agroecology, Shosse Bankia 7, Sofia 1080, Bulgaria, Fax (359) (2)
 Scientific registration n : 727 Presentation : poster Extraction of Mobile Forms of Nutrients and Heavy Metal Pollutants in Soil Using Ion Exchange Membranes Extraction dans les sols des formes mobiles
Scientific registration n : 727 Presentation : poster Extraction of Mobile Forms of Nutrients and Heavy Metal Pollutants in Soil Using Ion Exchange Membranes Extraction dans les sols des formes mobiles
Time-dependent copper extraction in different soil orders as influenced by soil to extractant Ratio
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 3 (8), 1683-1690, 2012 Available online at http:// www. irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X 2012 Time-dependent copper extraction in different
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences. Vol., 3 (8), 1683-1690, 2012 Available online at http:// www. irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X 2012 Time-dependent copper extraction in different
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Soil Testing and Interpretation
 Introduction Soil testing, interpretation of the test results, and incorporating prescriptive remedies to improve soils should be a fundamental part of any reclamation or revegetation project. Without
Introduction Soil testing, interpretation of the test results, and incorporating prescriptive remedies to improve soils should be a fundamental part of any reclamation or revegetation project. Without
Effect of Application of Increasing Concentrations of Contaminated Water on the Different Fractions of Cu and Co in Sandy Loam and Clay Loam Soils
 agriculture Article Effect of Application of Increasing Concentrations of Contaminated Water on the Different Fractions of Cu and Co in Sandy Loam and Clay Loam Soils John Volk 1 and Olusegun Yerokun 2,
agriculture Article Effect of Application of Increasing Concentrations of Contaminated Water on the Different Fractions of Cu and Co in Sandy Loam and Clay Loam Soils John Volk 1 and Olusegun Yerokun 2,
JORIND 9(2) December, ISSN
 SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
Bioavailability and crop uptake of trace elements in soil columns amended with sewage sludge products
 Plant and Soil 262: 71 84, 2004. 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 71 Bioavailability and crop uptake of trace elements in soil columns amended with sewage sludge products M.B.
Plant and Soil 262: 71 84, 2004. 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 71 Bioavailability and crop uptake of trace elements in soil columns amended with sewage sludge products M.B.
Removal of Cu 2+ and Zn 2+ in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Fly Ash and Fly Ash Mixtures
 Removal of Cu 2+ and Zn 2+ in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Fly Ash and Fly Ash Mixtures V. Héquet 1, P. Ricou 1, I. Lecuyer 2 and P. Le Cloirec 1 1 Ecole des Mines de Nantes, Dept. Systèmes Energétiques
Removal of Cu 2+ and Zn 2+ in Aqueous Solutions by Sorption onto Fly Ash and Fly Ash Mixtures V. Héquet 1, P. Ricou 1, I. Lecuyer 2 and P. Le Cloirec 1 1 Ecole des Mines de Nantes, Dept. Systèmes Energétiques
Assessing Zinc Thresholds for Phytotoxicity and Potential Dietary Toxicity in Selected Vegetable Crops
 COMMUNICATIONS IN SOIL SCIENCE AND PLANT ANALYSIS Vol. 34, Nos. 9 & 10, pp. 1421 1434, 2003 Assessing Zinc Thresholds for Phytotoxicity and Potential Dietary Toxicity in Selected Vegetable Crops X. X.
COMMUNICATIONS IN SOIL SCIENCE AND PLANT ANALYSIS Vol. 34, Nos. 9 & 10, pp. 1421 1434, 2003 Assessing Zinc Thresholds for Phytotoxicity and Potential Dietary Toxicity in Selected Vegetable Crops X. X.
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY
 NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
NUTRIENT AND HEAVY METAL CONTENTS OF HOG MANURE - EFFECT ON SOIL QUALITY AND PRODUCTIVITY G.J. Racz and M.M. Fitzgerald Professor and Research Associate, respectively, Department of Soil Science, University
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations...
 Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Effect of Enhancing Urea-Humic Acid Mixture with Refined Acid Sulphate Soil
 American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (11): 1892-1896, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Effect of Enhancing Urea-Humic Acid Mixture with Refined Acid Sulphate Soil 1 Mohd Taufik Mohd Yusuff,
American Journal of Applied Sciences 6 (11): 1892-1896, 2009 ISSN 1546-9239 2009 Science Publications Effect of Enhancing Urea-Humic Acid Mixture with Refined Acid Sulphate Soil 1 Mohd Taufik Mohd Yusuff,
Changes in C/N ratio and some chemical properties during decomposition of hazelnut husk under field conditions
 PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Changes in C/N ratio and some chemical properties during decomposition of hazelnut husk under field conditions Rıdvan Kızılkaya 1, Tayfun Aşkın 2, Oksana Fotina 3 1 Ondokuz Mayıs
PRELIMINARY COMMUNICATION Changes in C/N ratio and some chemical properties during decomposition of hazelnut husk under field conditions Rıdvan Kızılkaya 1, Tayfun Aşkın 2, Oksana Fotina 3 1 Ondokuz Mayıs
Soil fertility status and nutrient recommendations based on soil analysis of Jaisalmer district of western Rajasthan
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 12 Issue 1 June, 2017 103-107 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/12.1/103-107 Soil fertility status and
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 12 Issue 1 June, 2017 103-107 e ISSN 0976 7231 Visit us : www.researchjournal.co.in Research Article DOI : 10.15740/HAS/AJSS/12.1/103-107 Soil fertility status and
Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid
 5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
5th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2015) Speciation Analysis and Removal of Heavy Metals Zn, Cu, Cd from Sludge by Organic Acid S.W. SONG 1*, L. WANG
Effect of Fly Ash application on Microbial Population in Acid Soil
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 888-894 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.096
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 888-894 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.096
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2017) 6(5):
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 1423-1428 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.155
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 1423-1428 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.155
Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils
 J. Soil Set Soc. Sri Lanka. Vol 11.1999 Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils W.S. Madurapperuma 1 and D. Kumaragamage
J. Soil Set Soc. Sri Lanka. Vol 11.1999 Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils W.S. Madurapperuma 1 and D. Kumaragamage
CHAPTER 5 EFFECT OF POULTRY LITTER-YARD WASTE COMPOST ON CORN GROWTH AND P UPTAKE IN GREENHOUSE STUDIES ABSTRACT
 CHAPTER EFFECT OF POULTRY LITTER-YARD WASTE COMPOST ON CORN GROWTH AND P UPTAKE IN GREENHOUSE STUDIES ABSTRACT Application of animal waste compost to soil can be a valuable source of P for crop production.
CHAPTER EFFECT OF POULTRY LITTER-YARD WASTE COMPOST ON CORN GROWTH AND P UPTAKE IN GREENHOUSE STUDIES ABSTRACT Application of animal waste compost to soil can be a valuable source of P for crop production.
VERTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF DTPA-EXTRACTABLE MICRONUTRIENTS IN SOILS OF CUMBUM VALLEY, TAMIL NADU
 Agric. Sci. Digest., 30 (2) : 79-84, 2010 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com VERTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF DTPA-EXTRACTABLE MICRONUTRIENTS IN SOILS OF CUMBUM
Agric. Sci. Digest., 30 (2) : 79-84, 2010 AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH COMMUNICATION CENTRE www.arccjournals.com / indianjournals.com VERTICAL DISTRIBUTION OF DTPA-EXTRACTABLE MICRONUTRIENTS IN SOILS OF CUMBUM
Effect of enriched sewage sludge on soil urease activity
 Soil & Environ. 27(2): 143-147, 8 www.se.org.pk Abstract Effect of enriched sewage sludge on soil urease activity F.V. Kakhki*, G. Haghnia and A. Lakzian Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture,
Soil & Environ. 27(2): 143-147, 8 www.se.org.pk Abstract Effect of enriched sewage sludge on soil urease activity F.V. Kakhki*, G. Haghnia and A. Lakzian Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture,
DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS
 DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin - Madison Basic concepts of soil fertility How plants
DAFFODILS ARE WHAT THEY EAT: NUTRITIONAL ASPECTS OF SOILS Dick Wolkowski Extension Soil Scientist Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin - Madison Basic concepts of soil fertility How plants
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
EFFECT OF HUMIC ACID ON SOIL MICRONUTRIENTS UNDER DIFFERENT WET AND DRY CYCLES USING TWO SOIL SERIES
 Life Sci. Int. J., Vol: 9, (Issue, 1, 2, 3, & 4) Jan., April, July & Oct. 2015 Page: 3264-3269 EFFECT OF HUMIC ACID ON SOIL MICRONUTRIENTS UNDER DIFFERENT WET AND DRY CYCLES USING TWO SOIL SERIES Muhammad
Life Sci. Int. J., Vol: 9, (Issue, 1, 2, 3, & 4) Jan., April, July & Oct. 2015 Page: 3264-3269 EFFECT OF HUMIC ACID ON SOIL MICRONUTRIENTS UNDER DIFFERENT WET AND DRY CYCLES USING TWO SOIL SERIES Muhammad
International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology
 Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2017 Critical Limits of Zinc
Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.542 International Journal of Advance Research in Engineering, Science & Technology e-issn: 2393-9877, p-issn: 2394-2444 Volume 4, Issue 9, September-2017 Critical Limits of Zinc
Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth
 Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth J Henning, HG Snyman * and TAS Aveling 3 Department of otany, University of Pretoria, Pretoria,
Plant-soil interactions of sludge-borne heavy metals and the effect on maize (Zea mays L.) seedling growth J Henning, HG Snyman * and TAS Aveling 3 Department of otany, University of Pretoria, Pretoria,
Ni and N sources (Urea and ammonium sulphate) affecting growth, yield and quality in maize plant (Zea mays)
 2018; 7(3): 80-84 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 80-84 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 15-01-2018 Accepted: 16-02-2018 Priyanka Pannu HM Patel PV
2018; 7(3): 80-84 ISSN (E): 2277-7695 ISSN (P): 2349-8242 NAAS Rating: 5.03 TPI 2018; 7(3): 80-84 2018 TPI www.thepharmajournal.com Received: 15-01-2018 Accepted: 16-02-2018 Priyanka Pannu HM Patel PV
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations
 Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Recommended Test Procedures for Greenhouse Growth Media
 Chapter 13 Recommended Test Procedures for Greenhouse Growth Media Daryl Warnke NCR-13 Root media used for production of plants in greenhouses and nurseries are composed of light-weight, natural and processed
Chapter 13 Recommended Test Procedures for Greenhouse Growth Media Daryl Warnke NCR-13 Root media used for production of plants in greenhouses and nurseries are composed of light-weight, natural and processed
Immobilizing Arsenic in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates
 Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Effect of Selenium Fertilization on Dry Weight,
 Merit Research Journal of Agricultural Science and Soil Sciences (ISSN: 2350-2274) Vol. 6(1) pp. 001-006, January, 2018 Available online http://meritresearchjournals.org/asss/index.htm Copyright 2018 Merit
Merit Research Journal of Agricultural Science and Soil Sciences (ISSN: 2350-2274) Vol. 6(1) pp. 001-006, January, 2018 Available online http://meritresearchjournals.org/asss/index.htm Copyright 2018 Merit
BIO-CHEMICAL CHANGES OF NUTRIENTS IN RICE PLANT UNDER SODIC SOILS
 International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, www.ijtra.com Volume 1, Issue 1 march-april 2013), PP. 09-18 BIO-CHEMICAL CHANGES OF NUTRIENTS IN RICE PLANT UNDER SODIC
International Journal of Technical Research and Applications e-issn: 2320-8163, www.ijtra.com Volume 1, Issue 1 march-april 2013), PP. 09-18 BIO-CHEMICAL CHANGES OF NUTRIENTS IN RICE PLANT UNDER SODIC
A & L Canada Laboratories Inc Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) Fax: (519)
 Report Number: C13114-10169 Account Number: To: ESSEX-WINDSOR SWA 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 For: ROW "T2-3-12" 519-776-6370 Reported Date:
Report Number: C13114-10169 Account Number: To: ESSEX-WINDSOR SWA 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 For: ROW "T2-3-12" 519-776-6370 Reported Date:
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods
 Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
Bio-accessibility of Trace Metals Using Chemical Fractionation and In Vitro Extraction Methods Naomi Waissman Assadian 1 and Juan Pedro Flores Margez 2 Abstract Rural and urban border communities at Paso
EFFECT OF PHOSPHORUS AND VERMICOMPOST ON ZINC AVAILABILITY IN AN ACIDIC LATERITE SOIL OF WEST BENGAL, INDIA
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1903 1911 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFECT OF PHOSPHORUS AND VERMICOMPOST ON ZINC AVAILABILITY IN AN ACIDIC LATERITE
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 4, 2016, 1903 1911 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EFFECT OF PHOSPHORUS AND VERMICOMPOST ON ZINC AVAILABILITY IN AN ACIDIC LATERITE
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
Limitations to Plant Analysis. John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES
 Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
Evaluation of AB - DTPA Extractant for Multinutrients Extraction in Soils
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
1101 S Winchester Blvd., Ste. G 173 San Jose, CA (408) (408) fax Page 1 of 2
 San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Added Zn, Significant increase, Exchangeable Zn, Aerobic and Anaerobic Condition INTRODUCTION
 J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
J. Sci. Foundation, 9(1&): 9-14, June-December 11 ISSN 178-7855 INCUBATION STUDIES ON EXCHANGEABLE Zn FOR VARYING LEVELS OF ADDED Zn UNDER AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC CONDITIONS IN GREY TERRACE SOILS, NON CALCARIOUS
26 27 April 2012 in Isfahan, Iran. Hamid Reza Rahmani. Scientific Member of Soil and Water Institute of Iran.
 The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
The 1 th International and The 4 th National Congress on Effect of Industrial Recycling and Municipal of Organic Effluent Waste On in Agriculture Soil, Water, and Plants in Isfahan Hamid Reza Rahmani Scientific
Comparison of extractability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn with sequential extraction in contaminated and non-contaminated soils
 Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (2): 169-176, 2007 ISSN: 1735-1472 Spring 2007, IRSEN, CEERS, IAU M.A. Kashem, et al. Comparison of extractability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn with sequential extraction in contaminated
Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (2): 169-176, 2007 ISSN: 1735-1472 Spring 2007, IRSEN, CEERS, IAU M.A. Kashem, et al. Comparison of extractability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn with sequential extraction in contaminated
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue 1 June,
 An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue 1 June, 2012 Research Article Distribution of DTPA-extractable and total micronutrients in association with properties of some reclaimed salt affected soils
An Asian Journal of Soil Science Volume 7 Issue 1 June, 2012 Research Article Distribution of DTPA-extractable and total micronutrients in association with properties of some reclaimed salt affected soils
Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club. Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC
 Project Principal investigators Sponsor Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC Denver Country Club Summary This
Project Principal investigators Sponsor Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC Denver Country Club Summary This
Analytical Services. Services and Retail Prices 2016/May For Agriculture, Horticulture, Amenity and the Environment
 Analytical Services Services and Retail Prices 2016/May 2017 For Agriculture, Horticulture, Amenity and the Environment Soil Analysis BS Broad Spectrum P, K, Mg, ph, L.R, Ca, S, Na, Mn, Cu, Fe, Zn, Mo,
Analytical Services Services and Retail Prices 2016/May 2017 For Agriculture, Horticulture, Amenity and the Environment Soil Analysis BS Broad Spectrum P, K, Mg, ph, L.R, Ca, S, Na, Mn, Cu, Fe, Zn, Mo,
Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application
 COMPO EXPERT EXPERTS FOR GROWTH Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application Highly efficient combination of macro and micro elements Fully chelated trace elements Fast and completely water soluble
COMPO EXPERT EXPERTS FOR GROWTH Water Soluble Fertilizer for Foliar Application Highly efficient combination of macro and micro elements Fully chelated trace elements Fast and completely water soluble
Improvement of Nitrogen Fertilizer Efficiency with Nitrification Inhibitors in Lowland Rice
 Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2 (4): 1184-1187, 1999 Research Article Improvement of Nitrogen Fertilizer Efficiency with Nitrification Inhibitors in Lowland Rice Arafat, S.M., A. Abd El-Gal*
Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2 (4): 1184-1187, 1999 Research Article Improvement of Nitrogen Fertilizer Efficiency with Nitrification Inhibitors in Lowland Rice Arafat, S.M., A. Abd El-Gal*
Compost Analysis. Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System
 Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1703124769 DATE ISSUED : 15/03/2017
Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1703124769 DATE ISSUED : 15/03/2017
Rice is a most important staple food crop in world as
 Research Paper An Asian Journal of Soil Science Vol. 6 No. 2 (December, 2011) : 189-194 Received : September, 2011; Revised : November, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Effect of zinc enriched compost on
Research Paper An Asian Journal of Soil Science Vol. 6 No. 2 (December, 2011) : 189-194 Received : September, 2011; Revised : November, 2011; Accepted : November, 2011 Effect of zinc enriched compost on
Amit K. Gupta, Sarita Sinha *
 Chemosphere 64 (2006) 161 173 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemosphere Chemical fractionation and heavy metal accumulation in the plant of Sesamum indicum (L.) var. T55 grown on soil amended with tannery sludge:
Chemosphere 64 (2006) 161 173 www.elsevier.com/locate/chemosphere Chemical fractionation and heavy metal accumulation in the plant of Sesamum indicum (L.) var. T55 grown on soil amended with tannery sludge:
RemovalofToxicMetalsContaminatedSoilusingDifferentAmendmentsandSunflowerSpeciesHelianthusAnnuus
 Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
Global Journal of Science Frontier Research: H Environment & Earth Science Volume 16 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Year 2016 Type : Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS
 Originators of Your Crop's Dieticians 4915 West Monte Cristo Road Edinburg, Texas 78541 Telephone: 956-383-0739 Facsimile: 956-383-0730 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS TPSL 's Daubeny Carbon
Originators of Your Crop's Dieticians 4915 West Monte Cristo Road Edinburg, Texas 78541 Telephone: 956-383-0739 Facsimile: 956-383-0730 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO SOIL TEST REPORTS TPSL 's Daubeny Carbon
ABREU Cleide Aparecida de (1), BERTON Ronaldo Severiano (1), KOEKKOEK Edwin Peter Josef (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Downloaded from jstnar.iut.ac.ir at 21:58 IRDT on Monday May 14th 2018
 / / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
/ / / *...... (// : // : ).. ( ) ( ) (P ()... ... / / / /..
A & L Canada Laboratories Inc Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) Fax: (519)
 Report Number: C13304-10888 Account Number: 95000 To: ST.LAWRENCE RIVER INSTITUTE 2 ST.LAWRENCE DRIVE Attn: JEN HALEY 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519)
Report Number: C13304-10888 Account Number: 95000 To: ST.LAWRENCE RIVER INSTITUTE 2 ST.LAWRENCE DRIVE Attn: JEN HALEY 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519)
Understanding Your Soil Report. Michael Cook 2018
 Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil
 The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil Zhantai Wang, Minxia Cao, Wenchang Cai, and Heping Zeng Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings
The effect of humic acid and fulvic acid on adsorption-desorption behavior of copper and zinc in the yellow soil Zhantai Wang, Minxia Cao, Wenchang Cai, and Heping Zeng Citation: AIP Conference Proceedings
Chemical Speciation and Phytotoxicity of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge for the Germination of Chinese Cabbage Seeds
 Terrestrial and Aquatic Environmental Toxicology 2007 Global Science Books Chemical Speciation and Phytotoxicity of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge for the Germination of Chinese Cabbage Seeds Po-Hsu Kao
Terrestrial and Aquatic Environmental Toxicology 2007 Global Science Books Chemical Speciation and Phytotoxicity of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge for the Germination of Chinese Cabbage Seeds Po-Hsu Kao
The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit
 Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit Abstract Shirani M. 1 and
Research Journal of Recent Sciences ISSN 2277-2502 Res.J.Recent Sci. The Effect of Composted and Un-Composted Date-Palm Waste as a Media on Some Microelements of Tomato Fruit Abstract Shirani M. 1 and
A Study on Micro-Nutrients of Alkaline Soils by Using Paddy Husk Ash
 American Journal of Environmental Engineering 2014, 4(3): 41-45 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajee.20140403.01 A Study on Micro-Nutrients of Alkaline Soils by Using Paddy Husk Ash Sanjeeva Rayudu E. 1,*, Srimurali M.
American Journal of Environmental Engineering 2014, 4(3): 41-45 DOI: 10.5923/j.ajee.20140403.01 A Study on Micro-Nutrients of Alkaline Soils by Using Paddy Husk Ash Sanjeeva Rayudu E. 1,*, Srimurali M.
Soils and Soil Fertility Management
 Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis
 Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Efficiency of Arsenic Removal from Soil by Vetiveria zizanioides and Vetiveria nemoralis Thares Srisatit 1, Tuearnjai Kosakul 2, and Dusaluk Dhitivara 3 1 Department of Environmental Engineering, Faculty
Trace Elements in Manure
 Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
Trace Elements in Manure Purpose: Whenever soil profiles are examined for nutrient trace elements, it has been demonstrated that the metals tend to accumulate in the topsoil. Soil properties affect plant
