Pushkarov Institute of Soil Science and Agroecology, Shosse Bankia 7, Sofia 1080, Bulgaria, Fax (359) (2)
|
|
|
- Maude Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scientific registration n : 727 Presentation : poster Extraction of Mobile Forms of Nutrients and Heavy Metal Pollutants in Soil Using Ion Exchange Membranes Extraction dans les sols des formes mobiles de nutriments et de métaux lourds polluants, en utilisant les membranes d échange d ions NIKOLOV Nikolay Pushkarov Institute of Soil Science and Agroecology, Shosse Bankia 7, Sofia 1080, Bulgaria, Fax (359) (2) ABSTRACT The use of ion exchange membranes for the extraction of the mobile forms of a number of nutrients and pollutants in soils of different properties has been studied. The amounts of Ca, Mg, K, Mn, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, NO 3 -N and P extracted by ion exchange membranes are in good correlation with the amounts extracted by some commonly used methods. It is suggested that ion exchange membranes may give a satisfactory assessment of the mobile forms of a large number of elements in soils. INTRODUCTION Plants and related living systems can exist and achieve optimal development within certain limits of concentrations of chemical elements and their available forms in the soil. These concentrations must be controlled because as a result of both genetic processes and anthropogenic activities they can vary from extreme deficiency to high toxicity. This requires soil tests able to measure a large number of elements in soils of different properties. Considerable research has been devoted to chemical extractants for simultaneous extraction of a larger number of elements. Mehlich (1953) developed the Double Acid method for P, Ca, Mg, K, Na and NH 4 +. The same author (Mehlich, 1978) suggested a new extractant for P, K, Mg, Ca, Na, Mn and Zn which was later modified into Mehlich 3 (Mehlich et al., 1984) to include also Cu. Soltanpour and Schwab (1977) published the AB-DTPA test for extraction of NO 3 -N, P, K, Zn, Fe, Cu and Mn in alkaline soils. Van Lierop (1986) reported a simultaneous extraction of NO 3 -N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Na and S using the Kelowna extractant. Van Raij et al. (1986 developed a method for extraction of P, K, Ca and Mg based on ion exchange resins. Scogley et al. (1990) published the Phyto Availability Soil Test designed to assay plant available nutrient quantity as a function of diffusive ion movement to a spherical, mixed bed ion exchange resin sink. Somasiri and Edwards 1
2 (1992) developed an ion exchange resin method for nutrient extraction of advisory soil samples which covers Al, Ca, Mg, K, Na, P and S. The objectives of the present research were to study the use of ion exchange membranes (IEM) as an universal and applicable to soils of different properties multielement soil test, able to measure the basic nutrients as well as some pollutants and other ions that the soil can release. Conceptually the method is designed to extract water soluble and exchangeable forms of the elements as well as elements that plants can use from certain compounds of limited solubility in the solid phase of the soil. By measuring these forms of the elements one can asses the fertility and environmental status of the soil and predict the necessary amendments. MATERIALS AND METHODS Extraction sets of ion exchange membranes (ESIEM). A MK-40 cation exchange membrane (CEM) and a MA-40 anion exchange membrane (AEM) produced by Shtchekinskoe Obedinenie Azot (former USSR) were used. Each extraction set consists of 10 meq CEM (6 strips 22 mm by 65 mm wet) and 10 meq AEM (5 strips 22 mm by 65 mm wet). Preparation of new membranes. Before use each ESIEM (saturated initially with 1 N NH 4 CL) was shaken for 30 minutes successively with 50 ml 1 N HCl., 50 ml 1N NaOH, saturated again with 1N NH 4 CL and then washed with distilled water. After that each ESIEM was treated with a "cation" and an"anion" solutions so as to saturate some sites which may cause irreversible sorption and to check the purity of the blanks after such a treatment. For this purpose ESIEM were shaken16 hr. with 50 ml the following concentration in mg/liter: Ca-800 as CaCl 2.2H 2 O, Mg-240 as Mg(NO3) 2.6H 2 O, K-400 as KCL, Na-240 as NaCl, Mn-20 as manganous chloride BDH standard solution for AAS, Fe-100 as FeCl 3.6H 2 O, Cu-20 as Cu(NO 3 ) 2.3H 2 O, Zn-20 as Zn(NO 3 ) 2.4H2O, Cd-10 as CdCl 2.2.5H 2 O, Pb-10 as Pb(NO 3 ) 2. After this treatment the ESIEM were saturated again with 1N NH 4 CL and washed with distilled water. This was followed by shaking the ESIEM for 16 hr. with 50 ml of an "anion" solution of the following concentrations (in mg/liter):no3-n-100 as NH 4 NO 3, P-100 as KH 2 PO 4, Cl as NaCl, S- 320 as Na 2 SO 4. Finally ESIEM were shaken 15 times for 30 min. with 50 ml solution (ph 7) which is 0.35 N ammonium acetate, 0.02 M EDTA and after that 15 times for 30 min. with 50 ml distilled water. The results of the analysis show that the blanks are good and the ESIEM can be used for the extraction of soils. When not in use ESIEM are kept in plastic bottles in distilled water. Extraction of soils. Ten grams (10 g) of air dry soil ground to pass 2 mm sieve was shaken for 16 hours in a 150 ml wide mouth plastic bottle with an ESIEM and 75 ml distilled water on an end-to-end shaker at 23 0 C. The strips were separated from the soil, washed in distilled water and transferred into a plastic bottle. After that 50 ml of a solution (ph 7) 0.9 N ammonium acetate, 0.1N ammonium malate, 0.001M EDTA was added and the bottle was shaken for 30 minutes. This desorption was applied one time for all soils, but for 14 selected soils (4 soils polluted with heavy metals and 10 not polluted) it was repeated 4 times in order to study the recovery of the elements from the ESIEM. The resulting solution was used to measure the extracted elements, and the ESIEM were regenerated. 2
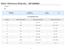
3 Regeneration of used membranes. Each ESIEM is regenerated by shaking it 15 times for 30 minutes with 50 ml solution (ph 7) 0.35N ammonium acetate, 0.02M EDTA, and after that 15 times for 30 min. in 50 ml distilled water. After this ESIEM can be used for extraction of soils. Soils. The method was applied to samples of the surface horizon of 35 representative soils of Bulgaria. Fourteen soils out of them were from polluted areas near Cu, Zn and Pb smelters, and 21 soils were not polluted but two of them had salinity and several contained up to 12 meq/100 g exchangeable Al. The 35 samples were used to measure all elements subject to this study except NO 3 -N. Twenty other samples from field experiments using four rates of application of N on five different soils were used to measure NO 3 -N. Analytical methods. A Perkin Elmer 2100 instrument for atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) was used to measure Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, Mn, Al, Fe, Cd and Pb. K and Na were measured by flame photometry and P by the molybdenum blue method (Murphy and Riley, 1962). For the NO 3 -N determination a 15 ml aliquot was boiled with 5 ml 5 N NaOH until half of the volume was evaporated in order to remove NH 3 and then NO 3 -N was measured by steam distillation. Sulfur was measured using Twin 80 (Garrido, 1964). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Desorption of the elements from the ion exchange membranes. The results of four successive desorptions of the elements from the ESIEM after their reaction with 14 soils show (on the average for all soils and elements) that the largest part (70.9 %) of the total amount of an element extracted by ESIEM was found in the first desorption, a smaller part (18.4 %) in the second desorption, 7.4 % in the third desorption and 3.3 % in the fourth desorption.. The sum of the first and the second desorptions accounts for a high recovery (89.3 %). The percentage of recovery, however. may be a subject to some variation depending on the element and on the soil. Comparison of IEM-extraction with some commonly used methods. The amounts of the elements extracted by some commonly used methods and by IEM (the sum of four desorptions of ESIEM) from 6 soils of contrasting properties are shown in Table 1. The correlation coefficients between the commonly used methods and the IEM (Table 2) are calculated for all 35 soils and separately for the groups of polluted (with the particular element) and not polluted soils using the data of the first desorption of ESIEM as it was found that the correlation coefficients did not vary considerably when the amounts of the elements in the first, the sum of the first two, or the sum of all four desorptions of ESIEM were used to correlate with the "commonly used " methods. Calcium. IEM extracts almost completely (average value 91.2%) exchangeable calcium; in soils containing CaCO 3 it extracts some additional amounts. The correlation between IEM and AA is high for both not polluted and polluted soils. Magnesium. The average value of IEM-extracted exchangeable Mg is 73.9%; in two soils, containing 6.0 and 12.0 meq exchangeable Al/100 g, it extracts respectively 66% and 55% of exchangeable Mg. The correlation with AA is high for the 35 soils and for the not polluted soils, but no correlation was found for the polluted soils. 3
4 Potassium. The average percentage of IEM -extracted exchangeable K is 74.1% but it varies from 58.8% in a vertisol to 88.9% in a light textured soil. High correlation exists between IEM and AA for both polluted and not polluted soils. Sodium. IEM extracted 58.2% of the large amount AA extractable water soluble and exchangeable Na in a saline soil. IEM distinguished the saline soil from soils low in Na. Aluminum. The sorption distribution of Al 3+ between the soil and the IEM is much in favor of the soil. IEM extracted only about 10% of exchangeable Al in the soil. Iron. IEM extracted less Fe than DTPA especially in a very acid and high in humus soil. In the alkaline soil IEM extracted more Fe than DTPA, mainly as a complex anion. IEM was correlated better with AA than with DTPA. Manganese. IEM -extractable Mn is slightly higher than DTPA-extractable and AAextractable Mn. High correlation is found between IEM and DTPA- extractable Mn for both polluted and not polluted soils and also between IEM and AA for polluted soils. Copper. The amount of Cu extracted by IEM is larger than the amount extracted by AA and smaller than that extracted by DTPA and by EDTA. In soils not polluted with Cu IEM is best correlated with EDTA, followed by AA. For the soils polluted with Cu, IEM is highly correlated with EDTA, AA and DTPA. Zinc. IEM extracts more Zn than AA and less than EDTA or DTPA. In soils not polluted with Zn IEM correlates best with EDTA, then comes DTPA, but no correlation was found with AA. In Zn- polluted soils IEM correlates well with (in decreasing order) EDTA, DTPA and AA. Cadmium. Only EDTA extracts enough Cd which can be measured by AAS in soils not polluted with Cd. The amounts of cadmium extracted by IEM and AA from these soils are low and require flameless AAS. In soils polluted with Cd IEM extracted somewhat smaller amounts than AA, DTPA, and EDTA. The correlation of IEM with EDTA, AA and DTPA is high. Lead. IEM extract more Pb than AA but less than EDTA in soils polluted with Pb. There was no correlation between IEM and EDTA for soils not polluted with Pb. A high coefficient of correlation was found between IEM and EDTA for soils polluted with Pb. Phosphorus. There is some positive correlation between IEM and Olsen P but not all soils behave in the same way. IEM extractable P in soils which are polluted with cation pollutants like Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Mn, Na and water soluble salts does not correlate with Olsen's P, while in those soils which are not polluted, the correlation is quite good. The presence of pollutants decreased the extractability of P by IEM. Sulfur. IEM distinguishes the salt affected soil containing large amount of S from the soils which are not salt affected. Nitrate-nitrogen. IEM extract practically the same amounts of NO 3 -N as the KCL extraction does. High correlation exists between the two methods. CONCLUSION IEM can distinguish the soils containing high concentration of mobile forms of some elements from the soils having low concentration. Extraction with ion exchange membranes gave a satisfactory correlation with other commonly used methods of extraction for a large number of elements.on the basis of these preliminary results it is concluded, that ion exchange membranes may give satisfactory assessment of the mobile 4
5 forms of a large number of elements including not only basic nutrients but also some heavy metals and other pollutants. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The author would like to thank Dr. V. I. Savitch for the provision of ion exchange membranes, and The National Research Fund of The Ministry of Education, Science and Technology in Bulgaria for financing part of this study. REFERENCES 1. Bremner, J. M Inorganic forms of nitrogen. In: C.A. Black et al. (ed.). Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Agronomy 9: Am. Soc. of Agron., Inc., Madison, Wis. 2. Garrido, L. M Determination of sulfur in plant material. Analyst 89, van Lierop, W Soil nitrate determination using the Kelowna multiple element extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 17(12), Lindsay, W. L. and W. A. Norvell Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, Mehlich, A Determination of P, Ca, Mg, K, Na and NH 4. North Carolina Soil Testing Division, Mimeo, N. C. Dept. Agr., Raleigh. 6. Mehlich, A New extractant for soil test evaluation of phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, sodium, manganese and zinc. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant. Anal. 9(6), Mehlich, A Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: a modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 15(12), Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food Reference book 427. The analysis of Agricultural materials. HMSO, London. 9. Murphy, J. and J. P. Riley A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta. 27, Olsen, S. R., C.V. Cole, F. S. Watanabe and L. A. Dean Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. US Dep. Of Agr. Circ van Raij, B., J. A. Quaggio, and N. M. da Silva Extraction of phosphorus, potassium, calcium and magnesium from soils by an ion- exchange resin procedure. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 17(5), Skogley, E. O., S. J. Georgitis, J. E. Yang and B. E. Schaff The phyto availability soil test PST. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 21(13-16),
6 13. Soltanpour, P. N. and A. P. Schwab A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macro- and micro- nutrients in alkaline soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 8(3), Somasiri, L. L. W. and A. C. Edwards Anion exchange resin method for nutrient extraction of agricultural advisory soil samples. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 23(7-8), Keywords : ion exchange resins, mobile forms of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, soil pollution, soil nutrients Mots clés : résines d échange d ion, formes mobiles de N, P, K, Ca, Mg, Cu, Zn, Pb, Cd, pollution du sol, éléments nutritifs 6
7 Table 1. Mobile forms of the elements extracted by commonly used methods and by ion exchange membranes (IEM) from soils of contrasting properties Element and method of extraction Calcaric chernozen 2.7 % Humus 1.8 % CaCO 3 ph H2O 8.0 Eutric planosol 1.9 % Humus 62 % Base Satur. ph H2O 5.1 Soil Humic cambisol 20% Humus 12 % Base Satur. ph H2O 4.5 meq/100g Solonetzsolonchak 2 % Humus ph H2O 9.0 Fluvisol 2.2 % Humus ph H2O 4.7 Polluted: 620 mg Cu /kg Ca AA Calcaric Fluvisol 2.0 % Humus ph H2O 7.5 Polluted: 2656 mg Pb 1338 mg Zn 22 mg Cd /kg Ca IEM Mg AA Mg IEM mg/kg K AA K IEM Na AA n.d. n.d. NA IEM Mn DTPA Mn IEM Fe DTPA Fe IEM Cu EDTA Cu IEM Zn EDTA Zn IEM Cd EDTA Cd IEM n.d.* n.d.. n.d n.d. n.d. 7.0 Pb EDTA Pb IEM n.d. n.d. n.d. n.d. n.d P Olsen P IEM S IEM n.d.* not determined 7
8 Table 2. Correlation between the amounts of elements extracted by the commonly used methods and the amounts extracted by ion exchange membranes (IEM) Element and commonly used method of extraction Number of soils Coef. of correlation between the commonly used metho d and IEM Element and commonly used method of extraction Number of soils Coef. of correlation between the commonly used metho d and IEM r r Ca-AA 21 n.p.* Cu-EDTA 7 p Ca-AA 14 p.** Cu-EDTA all Ca-AA all Cu-AA 28 n.p Mg-AA 21 n.p Cu-AA 7 p Mg-AA 14 p Cu-AA all Mg-AA all Zn-DTPA 23 n.p K- AA 21 n.p Zn-DTPA 12 p K- AA 14 p Zn-DTPA all K- AA all Zn-EDTA 23 n.p Mn-DTPA 21 n.p Zn-EDTA 12 p Mn-DTPA 14 p Zn-EDTA all Mn-DTPA all Zn-AA 23 n.p Mn-AA 21 n.p Zn-AA 12 p Mn-AA 14 p Zn-AA all Mn-AA all Cd-DTPA 12 p Fe-DTPA 21 n.p Cd-EDTA 12 p Fe-DTPA 14 p Cd-AA 12 p Fe-DTPA all Pb-EDTA 23 n.p Fe-AA 21 n.p Pb-EDTA 12 p Fe-AA 14 p Pb-EDTA all Fe-AA all Pb-AA 12 p Cu-DTPA 28 n.p NO 3 N (KCl) 20 n.p Cu-DTPA 7 p P-Olsen 18 n.p Cu-DTPA all P-Olsen 17 p Cu-EDTA 28 n.p P-Olsen all n.p.* not polluted p.** polluted 8
Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka
 , 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
, 152-158 Use of A Multi-ionic Extractant to Determine Available P, K, Na, Ca, and Mg in Acid Soils of Sri Lanka W.S. Madurapperuma and D. Kumaragamage 1 Postgraduate Institute of Agriculture University
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster
 Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
Scientific registration n o : 2303 Symposium : 25 Presentation : poster Evaluation of nutrients availability and metals toxicity by different universal extractants in brazilian soils 1 Evaluation de la
A & L GREAT LAKES LABORATORIES, INC.
 Report No. F10035-0027 59018 3505 Conestoga Drive Fort Wayne, Indiana 46808 260-483-4759 Fax 260-483-5274 Account No. Date Reported: 02/08/2010 SOIL TEST REPORT Page: 1 of 2 Cation Lab Organic Phosphorus
Report No. F10035-0027 59018 3505 Conestoga Drive Fort Wayne, Indiana 46808 260-483-4759 Fax 260-483-5274 Account No. Date Reported: 02/08/2010 SOIL TEST REPORT Page: 1 of 2 Cation Lab Organic Phosphorus
Evaluation of AB - DTPA Extractant for Multinutrients Extraction in Soils
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-776 Volume 7 Number 3 (218) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/1.2546/ijcmas.218.73.141
Matrix Reference Materials - SCP SCIENCE
 EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
EnviroMAT SS-1 Catalogue No.: 140-025-001 EnviroMAT Contaminated Soil Lot No.: SC0063618 100 g TOTAL DIGESTION VALUES Elements Reference Value (mg/kg) Confidence Interval (mg/kg) Tolerance Interval (mg/kg)
TSADILAS Christos, SAMARAS Vasilios, SIMONIS Asterios, SETATOU Helen
 Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
Scientific registration n o : 776 Symposium n o : 6 Presentation : poster Changes in DTPA-extractable iron, zinc, manganese and copper after liming Modification de la teneur du sol en fer, zinc, manganèse,
Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management. Hailin Zhang. Department of Plant and Soil Sciences
 Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Hailin Zhang Department of Plant and Soil Sciences C H O P N K 16 ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Ca S Mg B Cl Cu Fe Mn Mo B NON-MINERAL NUTRIENTS Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen
Soil Fertility and Nutrient Management Hailin Zhang Department of Plant and Soil Sciences C H O P N K 16 ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS Ca S Mg B Cl Cu Fe Mn Mo B NON-MINERAL NUTRIENTS Carbon (C) Hydrogen (H) Oxygen
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations...
 Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Understanding your results Acidity... 3 Aluminium.... 3 Base saturation... 3 Boron... 4 Bulk density... 4 Calcium... 4 Cations... 4 CEC - Cation Exchange Capacity... 4 Copper... 5 Conductivity... 6 Deficiencies...
Analysis. Methods of. of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures. Edited by HLS Tandon
 Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures Edited by HLS Tandon Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation 204204A Bhanot Corner, 12 Pamposh Enclave New Delhi
Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures Edited by HLS Tandon Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation 204204A Bhanot Corner, 12 Pamposh Enclave New Delhi
Soil Composition. Air
 Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Soil Composition Air Soil Included Air Approximately 40 to 60% of the volume of a soil is actually empty space between the solid particles (voids). These voids are filled with air and/or water. The air
Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils
 The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
The Supply and Availability of Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Plant Nutrients in Mineral Soils Factors Controlling the Growth of Higher Plants 1. Light 2. Mechanical Support. Heat. Air 5. Water 6. Nutrients
1101 S Winchester Blvd., Ste. G 173 San Jose, CA (408) (408) fax Page 1 of 2
 San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
San Jose Office September 28, 2018 Report 18-262-0106 Zanker Landscape Mateirals 675 Los Esteros Road San Jose, CA 95134 Attn: Beto Ochoa RE: ZB-PPM Reaction at 7.5 is slightly alkaline and with lime absent
Trends in Soil Management for Turf. David C. Smith P.Ag DCS Agronomic Services
 Trends in Soil Management for Turf David C. Smith P.Ag DCS Agronomic Services Points for Today s Discussion Soil Testing Considerations Soil test interpretation How water moves in the soil Recommendations
Trends in Soil Management for Turf David C. Smith P.Ag DCS Agronomic Services Points for Today s Discussion Soil Testing Considerations Soil test interpretation How water moves in the soil Recommendations
Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers
 Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers Bill Argo, Ph.D. Blackmore Company, Tel: 800-874-8660, Intl 734-483-8661, E-mail: bargo@blackmoreco.com Originally printed in 2003 in
Understanding ph management and plant nutrition Part 3: Fertilizers Bill Argo, Ph.D. Blackmore Company, Tel: 800-874-8660, Intl 734-483-8661, E-mail: bargo@blackmoreco.com Originally printed in 2003 in
Assessment of Secondary and Micro Nutrient Status under Long-Term Fertilizer Experiment on Vertisol
 Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
Available online at www.ijpab.com Joga Rao et al Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 6 (4): 328-339 (2018) ISSN: 2320 7051 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.3068 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci.
GREEN 3 Date Date Sample Sample B067921C Received: 15/08/2013 Reported: 20/08/2013 Reference: Green 3 Number: SBA1674 CROP: Cool Season
 Your Simplot Partners Branch Address & Contact Details Your Reps Name & Contact Details ABC GOLF CLUB (SAMPLE ONLY) GREEN Date Date Sample Sample B9C Received: /8/ Reported: /8/ Reference: Green Number:
Your Simplot Partners Branch Address & Contact Details Your Reps Name & Contact Details ABC GOLF CLUB (SAMPLE ONLY) GREEN Date Date Sample Sample B9C Received: /8/ Reported: /8/ Reference: Green Number:
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide. Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University
 Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
Cranberry Nutrition: An A Z Guide Joan R. Davenport Soil Scientist Washington State University Soil Derived Plant Essential Elements Macro Micro Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Sulfur (S) Potassium (K) Calcium
Interpreting Soils Report. Beyond N P K
 Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Interpreting Soils Report Beyond N P K What we will cover We will not discuss Macro Nutrients Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium. We will touch on Secondary Nutrients Magnesium, Calcium and Sulfur. We
Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Supplying Nutrients to Crops What is Plant Nutrition? Plants need nutrients for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on
Understanding a Soil Report
 Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Understanding a Soil Report AGRONOMY SOIL ANALYSIS 1. Soil ph Soil ph is a measure of the acidity in the soil. An acidic soil has a greater amount of hydrogen (H+) ions and a ph below 7.0. Values above
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES
 Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
Determination of available nutrients in soil using the Agilent 4200 MP-AES Application note Agriculture Author Dharmendra Vummiti Agilent Technologies, India Introduction Multielement testing of soil samples
A & L Canada Laboratories Inc Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) Fax: (519)
 Report Number: C13304-10888 Account Number: 95000 To: ST.LAWRENCE RIVER INSTITUTE 2 ST.LAWRENCE DRIVE Attn: JEN HALEY 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519)
Report Number: C13304-10888 Account Number: 95000 To: ST.LAWRENCE RIVER INSTITUTE 2 ST.LAWRENCE DRIVE Attn: JEN HALEY 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519)
Compost Analysis. Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System
 Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1703124769 DATE ISSUED : 15/03/2017
Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1703124769 DATE ISSUED : 15/03/2017
Fertilization Programming
 Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Fertilization Plant Composition Water composes 90% of plant weight (fresh weight) Dry weight is composed of 17 essential elements: Non-fertilizer elements: Carbon (C) -- 41% of dry weight (DW) Hydrogen
Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club. Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC
 Project Principal investigators Sponsor Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC Denver Country Club Summary This
Project Principal investigators Sponsor Rainfall impact on sodium leaching at Denver Country Club Doug Brooks, Denver Country Club, Larry Stowell, Ph.D., PACE Turf LLC Denver Country Club Summary This
Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability
 Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Symposium no. 33 Paper no. 08 Presentation: poster Effect of salinity on Cd and Zn availability KHOSHGOFTARMENSH A.H., JAAFARI B. and SHARIATMADARI H. Department of Soil Science, College of Agriculture,
Nutrient level (EC) in a pot is like a bank
 Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
Dirt, Fert and Squirt (1) Supplying Essential Nutrients What are the most common nutritional problems? Too much fertilizer Not enough fertilizer Paul Fisher pfisher@ufl.edu 1 ph too high ph too low 2 Nutrient
DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DETERMINATION OF SUITABLE CHEMICAL EXTRACTION METHODS FOR AVAILABLE IRON CONTENT OF THE SOILS FROM EDIRNE PROVINCE IN TURKEY ADILOGLU A. ABSTRACT The aim of this research was to determine
Welcome. Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories
 Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Discussion Soil test levels Dropping P,K Organic matter levels dropping Cost of Fertilizer Increasing due to Global Demand Environmental
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs
 Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
Use of Soil and Tissue Testing for Sustainable Crop Nutrient Programs Kelly T. Morgan Soil and Water Science Department Southwest Florida Research and Education Center Immokalee 239 658 3400 conserv@ufl.edu
A & L Canada Laboratories Inc Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) Fax: (519)
 Report Number: C13114-10169 Account Number: To: ESSEX-WINDSOR SWA 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 For: ROW "T2-3-12" 519-776-6370 Reported Date:
Report Number: C13114-10169 Account Number: To: ESSEX-WINDSOR SWA 2136 Jetstream Road, London, Ontario, N5V 3P5 Telephone: (519) 457-2575 Fax: (519) 457-2664 For: ROW "T2-3-12" 519-776-6370 Reported Date:
Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club.
 Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club. The results for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and sodium are reported on a percent
Enclosed are the tissue analysis results for the samples from the greens at Golf Club. The results for nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and sodium are reported on a percent
RELIABILITY OF SOIL AND PLANT ANALYSES FOR MAKING NUTRIENT RECOMMENDATIONS
 RELIABILITY OF SOIL AND PLANT ANALYSES FOR MAKING NUTRIENT RECOMMENDATIONS Robert. O. Miller Soil and Crop Sciences Dept. Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO 80523 Phone: 970-686-5702 Fax: 970-491-0564
RELIABILITY OF SOIL AND PLANT ANALYSES FOR MAKING NUTRIENT RECOMMENDATIONS Robert. O. Miller Soil and Crop Sciences Dept. Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO 80523 Phone: 970-686-5702 Fax: 970-491-0564
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations
 Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Interpretation of Soil Tests for Environmental Considerations Ray Ward Ward Laboratories, Inc Kearney, NE www.wardlab.com Guiding Producers Today to Feed the World Tomorrow www.wardlab.com Saline County
Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils
 J. Soil Set Soc. Sri Lanka. Vol 11.1999 Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils W.S. Madurapperuma 1 and D. Kumaragamage
J. Soil Set Soc. Sri Lanka. Vol 11.1999 Evaluation of AB-DTPA Extractant for the Estimation of Plant Available Macro and Micro Nutrients in Acidic and Neutral Soils W.S. Madurapperuma 1 and D. Kumaragamage
Project: TopCal for sodium management during leaching at Mission Viejo Country Club
 Project: TopCal for sodium management during leaching at Mission Viejo Country Club Principal investigator: Kevin Hutchins, Mission Viejo Country Club Cooperators: Larry Stowell, Ph.D. and Wendy Gelernter,
Project: TopCal for sodium management during leaching at Mission Viejo Country Club Principal investigator: Kevin Hutchins, Mission Viejo Country Club Cooperators: Larry Stowell, Ph.D. and Wendy Gelernter,
STANDARD METHODS FOR CHEMICAL ELEMENTS IN FOOD OF ANIMAL ORIGIN
 EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
EN 13804 Performance criteria, general considerations and sample preparation 2013 EN 13805 Pressure digestion 2014 EN 13806 Determination of mercury by cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry (CVAAS)
AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Global NEST Journal, Vol 9, No 3, pp 195-200, 2007 Copyright 2007 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved AVAILABLE Cd CONTENT OF SALT AFFECTED AND NORMAL SOILS OF HALASTRA KALOHORI AREA TH.
Tim Mundorf Fall 2016
 Page 1 of 12 Tim Mundorf Fall 2016 Introduction In 2014, clients in Iowa and Canada asked Midwest Laboratories to compare Mehlich III extraction of nutrients analyzed by ICP to Midwest Laboratories traditional
Page 1 of 12 Tim Mundorf Fall 2016 Introduction In 2014, clients in Iowa and Canada asked Midwest Laboratories to compare Mehlich III extraction of nutrients analyzed by ICP to Midwest Laboratories traditional
Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 17-23 (2010) Utilization of Slop Ash as a Source of Potassium for Corn Grown on the Pakchong Soil Series Pimolsiri Supasatienchai 1, Jongruk Chanchareoook 1 * and Ed Sarobol
Soil Prescription - Sample 1
 Soil Prescription - Sample 1 Hay Meadow In Eastern Kansas The following soil prescription was prepared for a five acre hay meadow in production for over three decades. The hay is sold to a livestock farmer
Soil Prescription - Sample 1 Hay Meadow In Eastern Kansas The following soil prescription was prepared for a five acre hay meadow in production for over three decades. The hay is sold to a livestock farmer
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis
 Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
Interpreting Plant Tissue and Soil Sample Analysis Dan Fromme Associate Professor-Cotton, Corn, & Grain Sorghum Specialist LSU AgCenter Dean Lee Research & Extension Center Alexandria, Louisiana Fertilization
Recent Developments in Multi-nutrient Extractants Used in Soil Analysis
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 2578-2584 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.290
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 5 (2017) pp. 2578-2584 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.605.290
Soil acidity. Kiyoshi Tsutsuki
 Soil acidity Kiyoshi Tsutsuki http://timetraveler.html.xdomain.jp H = log (H+) oriba Home page ph and crop growth (vegetables and root crops) Low ph tolerance strong (4.0~5.0) A little strong (4.5~6.0)
Soil acidity Kiyoshi Tsutsuki http://timetraveler.html.xdomain.jp H = log (H+) oriba Home page ph and crop growth (vegetables and root crops) Low ph tolerance strong (4.0~5.0) A little strong (4.5~6.0)
FACT SHEET. Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation
 Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
Understanding Cation Exchange Capacity and % Base Saturation FACT SHEET A & L CANADA LABORATORIES, INC. 2136 Jetstream Rd. London, ON N5V 3P5 Phone: 519-457-2575 Fax: 519-457-2664 Aginfo@alcanada.com www.alcanada.com
Animal, Plant & Soil Science. D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients
 Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
Animal, Plant & Soil Science D3-7 Characteristics and Sources of Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Interest Approach Obtain samples of minerals that serve as sources of calcium, magnesium, and sulfur
Soil Testing and Interpretation
 Introduction Soil testing, interpretation of the test results, and incorporating prescriptive remedies to improve soils should be a fundamental part of any reclamation or revegetation project. Without
Introduction Soil testing, interpretation of the test results, and incorporating prescriptive remedies to improve soils should be a fundamental part of any reclamation or revegetation project. Without
ABREU Cleide Aparecida de (1), BERTON Ronaldo Severiano (1), KOEKKOEK Edwin Peter Josef (2)
 Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Scientific registration number: 2207 Symposium number: 25 Presentation : poster Validation of annual and total cumulative loading limits stipulated by USEPA for Zn on oxisol. Validation des apports-limites
Importance of fertigation scheduling
 Importance of fertigation scheduling Mr. C K Patel Sr. Manager Agronomy Ck.patel@netafim.com SBU-WEST-NETAFIM 9687696657 Proper fertigation scheduling can maximize the fertilizers use efficiency & Crop
Importance of fertigation scheduling Mr. C K Patel Sr. Manager Agronomy Ck.patel@netafim.com SBU-WEST-NETAFIM 9687696657 Proper fertigation scheduling can maximize the fertilizers use efficiency & Crop
A Revised Method for Determining Phosphate-Phosphorus Levels in Sugar Beet Leaf Petioles 1
 A Revised Method for Determining Phosphate-Phosphorus Levels in Sugar Beet Leaf Petioles 1 G. E. VARVEL, G. A. PETERSON and F. N. ANDERSON 2 &ceived/orpublicalionj..ne 1,1976 Knowledge of plant nutrient
A Revised Method for Determining Phosphate-Phosphorus Levels in Sugar Beet Leaf Petioles 1 G. E. VARVEL, G. A. PETERSON and F. N. ANDERSON 2 &ceived/orpublicalionj..ne 1,1976 Knowledge of plant nutrient
Plant Food. Nitrogen (N)
 Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
Plant Food Nitrogen (N) Functions: Promote plant growth Increase protein content of crops Improves quality of crop Makes plant more efficient with water Helps for stay green and dry down Plants take up
FACTORS AFFECTING WATER QUALITY
 TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
TECHNICAL PAPER WATER QUALITY PLANT HEALTH FACTORS Water quality is one of the most important factors affecting plant growth, as unwanted components in water can interfere with nutrient availability and
Discuss the importance of healthy soils Soil properties, physical, chemical and biological that one can manage for soil health How organics play a
 Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
Andrew Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against anyone because of race, age, sex, color, sexual orientation, physical or mental disability,
MARGAM SUNITHA, KANWAR L. SAHRAWAT, AND SUHAS P. WANI. Introduction
 Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 46:627 632, 2015 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0010-3624 print / 1532-2416 online DOI: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1005226 Comparative Evaluation
Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 46:627 632, 2015 Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN: 0010-3624 print / 1532-2416 online DOI: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1005226 Comparative Evaluation
We are committed to becoming a watershed to Agriculture and restoring it to its rightful place in the economy. This is substantiated through our
 We are committed to becoming a watershed to Agriculture and restoring it to its rightful place in the economy. This is substantiated through our ability to Envision the Big Picture and pinpoint the inefficiencies
We are committed to becoming a watershed to Agriculture and restoring it to its rightful place in the economy. This is substantiated through our ability to Envision the Big Picture and pinpoint the inefficiencies
Common Salt Ions. Salinity. Soil permeability reflects sodicity problems from sodium concentrations 1/15/2008
 Salinity Water Deficits Ion Toxicities SALT - RELATED PRBLEMS Ion Imbalances Soil Permeability Water deficits reflect salinity problems from salt concentrations Salinity -A measure of the salt concentration
Salinity Water Deficits Ion Toxicities SALT - RELATED PRBLEMS Ion Imbalances Soil Permeability Water deficits reflect salinity problems from salt concentrations Salinity -A measure of the salt concentration
SOILS AND PLANT NUTRITION
 SOILS AND PLANT NUTRITION WHAT IS SOIL? Soil is the medium in which plants grow - the basis for plant growth. I can t get any respect. People treat me like dirt! Four Major Components of Soil Sand Silt
SOILS AND PLANT NUTRITION WHAT IS SOIL? Soil is the medium in which plants grow - the basis for plant growth. I can t get any respect. People treat me like dirt! Four Major Components of Soil Sand Silt
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs. Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison
 Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
Nutrients & Diagnosing Nutrient Needs Carrie Laboski Dept. of Soil Science UW-Madison Sources of nutrients available for plant uptake Nutrients in the soil solution are: In ionic form At low concentration
AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged.
 AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged. Criteria for Essential Elements A. B. C. Essential Elements (17): Nonmineral (3): Mineral (14):
AGRY 515: What do you know? In 10 minutes, fill out what you can. Educated guesses are strongly encouraged. Criteria for Essential Elements A. B. C. Essential Elements (17): Nonmineral (3): Mineral (14):
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops
 3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
3.0 Supplying Nutrients to Crops Plants need for healthy growth and development. Plant nutrition involves the absorption of nutrients for plant growth and is dependent on, often referred to as nutrients.
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA
 DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
DOMOGRAN 45 ACTIVATING YOUR NUTRIENT POTENTIAL THE NITROGEN-SULFUR FERTILIZER FROM LEUNA www.domogran.de DOMOGRAN 45 nitrogen and sulfur fertilizer for positive nutrient dynamics Because of its attraction
Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees. Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 3/1/2013. Johnson - Nutrition 1
 Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees R. Scott Johnson Extension Pomologist UC Kearney Ag Center Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 1. Basic Principles 2. Sampling for Nutrients 3. Environmental Issues 4. BMPs
Mineral Nutrition of Fruit & Nut Trees R. Scott Johnson Extension Pomologist UC Kearney Ag Center Fruit & Nut Tree Nutrition 1. Basic Principles 2. Sampling for Nutrients 3. Environmental Issues 4. BMPs
Greenhouse Horticulture
 Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
Managing Nutrients in Greenhouse Horticulture Original content by Domenic Cavallaro Stoller Australia Pty Ltd Plant HORMONE PRODUCTION follows approx. cycles with changing NUTRIENT requirements Source:
CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph
 BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 2002, 28(3 4), 35 45 35 CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph Antoaneta Arsova * N. Pushkarov
BULG. J. PLANT PHYSIOL., 2002, 28(3 4), 35 45 35 CATION-EXCHANGE CHARACTERISTICS OF WHEAT, BARLEY AND PEA DEPENDING ON THE OSMOTIC PRESSURE IN NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS OF LOW ph Antoaneta Arsova * N. Pushkarov
COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS. Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions
 COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions are diluted water solutions containing one or more inorganic
COMPUTATION & PREPARATION OF NUTRIENT SOLUTIONS Principles, properties & preparation of nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions Nutrient solutions are diluted water solutions containing one or more inorganic
FERTIGATION 24 FERTIGATION WITH DRIPPERS
 24 WITH DRIPPERS A completely different approach is required when fertigation is applied through drippers. This approach also offers numerous other possibilities. The volume of soil treated has a dominant
24 WITH DRIPPERS A completely different approach is required when fertigation is applied through drippers. This approach also offers numerous other possibilities. The volume of soil treated has a dominant
PURE BRAZIL BRAND PRODUCTS
 PURE BRAZIL BRAND PRODUCTS WHAT ARE THE PURE BRAZIL BRAND PRODUCTS? PURE BRAZIL BRAND Essential Micronutrients contains eight micronutrient elements essential to plant growth and health. Five (calcium,
PURE BRAZIL BRAND PRODUCTS WHAT ARE THE PURE BRAZIL BRAND PRODUCTS? PURE BRAZIL BRAND Essential Micronutrients contains eight micronutrient elements essential to plant growth and health. Five (calcium,
The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient Soil
 387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
387 Bulgarian Journal of Agricultural Science, 12 (2006), 387-392 National Centre for Agrarian Sciences The Effect of Boron (B) Application on the Growth and Nutrient Contents of Maize in Zinc (Zn) Deficient
Soils and Soil Fertility Management
 Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Soils and Soil Fertility Management Mark L. McFarland Professor and Soil Fertility Specialist Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Service College Station, Texas Four Principal Components of Soil Air Mineral Solid
Fertilizer Compatibility. Raun Lohry Terry Robinson Doyle Meeker
 Fertilizer Compatibility Raun Lohry Terry Robinson Doyle Meeker NPK s & Micros Concentration Chemistry Constraints Can t put 6 gallons in a 5 gallon bucket! Certain elements need help to stay in solution
Fertilizer Compatibility Raun Lohry Terry Robinson Doyle Meeker NPK s & Micros Concentration Chemistry Constraints Can t put 6 gallons in a 5 gallon bucket! Certain elements need help to stay in solution
Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova
 REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
REPORT ON RESEARCH OF BAE SYNERGY LIQUID PREPARATION INFLUENCE ON MINERAL METABOLISM Edward V. Krizhanovsky, Ph.D., Kamila B. Tursunova Bioenergy Technologies Institute, Sveaborgskaia, 12, Saint- Petersburg,
S1AN: Same as test S1A with carryover Nitrogen as Nitrate With Recommendations: $13.20 Without Recommendations: $11.50
 AGRICULTURE SOIL SOIL TEST PACKAGES S1A (Basic): Organic Matter, Available Phosphorus, (P1 Weak Bray and P2 Strong Bray) Exchangeable Potassium, Magnesium, Calcium and Hydrogen, Soil ph, Buffer Index,
AGRICULTURE SOIL SOIL TEST PACKAGES S1A (Basic): Organic Matter, Available Phosphorus, (P1 Weak Bray and P2 Strong Bray) Exchangeable Potassium, Magnesium, Calcium and Hydrogen, Soil ph, Buffer Index,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION. MACRONUTRIENTS Found in air and water carbon C oxygen hydrogen
 BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
BOTANY AND PLANT GROWTH Lesson 9: PLANT NUTRITION Segment One Nutrient Listing Plants need 17 elements for normal growth. Carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are found in air and water. Nitrogen, phosphorus,
Monitoring & Maintaining the ph and EC of the Root Environment. Bill Fonteno Horticultural Substrates Laboratory NC State University
 Monitoring & Maintaining the ph and EC of the Root Environment Bill Fonteno Horticultural Substrates Laboratory NC State University Substrate ph Maintaining proper substrate ph will PREVENT most nutrient
Monitoring & Maintaining the ph and EC of the Root Environment Bill Fonteno Horticultural Substrates Laboratory NC State University Substrate ph Maintaining proper substrate ph will PREVENT most nutrient
Reading and Analyzing your Fertilizer Bag. Dr. Cari Peters Vice President
 Reading and Analyzing your Fertilizer Bag Dr. Cari Peters Vice President caripeters@jrpeters.com Designer, Formulator, Producer and custom manufacturer of high quality fertilizer products. Hand s on Horticulture
Reading and Analyzing your Fertilizer Bag Dr. Cari Peters Vice President caripeters@jrpeters.com Designer, Formulator, Producer and custom manufacturer of high quality fertilizer products. Hand s on Horticulture
Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests
 Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the aerobic and anaerobic testing. Testing was performed for the potential components of the final media
Appendix D: Aerobic and Anaerobic Leaching Tests This appendix contains the entire data set for the aerobic and anaerobic testing. Testing was performed for the potential components of the final media
Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL)
 Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL) Patty Lucas AAPFCO Laboratory Services Committee Meeting Friday, August 7, 2015 Fertilizer Sample
Challenges with Chelated &/or Complexed Minerals (Chelated and Soluble Methods of Analysis Used in FL) Patty Lucas AAPFCO Laboratory Services Committee Meeting Friday, August 7, 2015 Fertilizer Sample
Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability
 Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability Andrew G. Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against
Importance of Water Quality: ph, buffering, and effects on nutrient availability Andrew G. Ristvey The University of Maryland Extension programs are open to any person and will not discriminate against
Distribution of Available Macro and Micronutrients in Soils of Dewas District of Madhya Pradesh
 Vol.2 No. 2, 108-114 (2013) Received.Feb.2013; Accepted Aug. 2013 Distribution of Available Macro and Micronutrients in Soils of Dewas District of Madhya Pradesh Abstract Ankita Pandey, Laxmi, R. J. Tiwari
Vol.2 No. 2, 108-114 (2013) Received.Feb.2013; Accepted Aug. 2013 Distribution of Available Macro and Micronutrients in Soils of Dewas District of Madhya Pradesh Abstract Ankita Pandey, Laxmi, R. J. Tiwari
Immobilizing Arsenic in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates
 Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
Immobilizing in Contaminated Soil Using Humic Mineral Concentrates Alexander I.Shulgin 1 and D. Joseph Hagerty 2, F. ASCE, PE 1. Research Professor, Chemical Engineering Dept., U. Louisville, Louisville,
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material Fertilizers
 TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
TNPSC Chemistry Study Material A fertilizer is any material of natural or synthetic origin (other than liming materials) that is applied to soils or to plant tissues to supply one or more plant nutrients
Multi-K. Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops
 Multi-K Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops Contents Potassium in the plant Multi-K and its advantages Nutrigation with Multi-K Foliar nutrition with Haifa Bonus Multi-K properties Multi-K products
Multi-K Potassium Nitrate Products For Healthy Crops Contents Potassium in the plant Multi-K and its advantages Nutrigation with Multi-K Foliar nutrition with Haifa Bonus Multi-K properties Multi-K products
Understanding Your Soil Report. Michael Cook 2018
 Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
Understanding Your Soil Report Michael Cook 2018 Soil Sampling Advantage gives nutrient concentrations may shed light on soil issues baseline so look for trends can be done pre-plant timing not as critical
SOIL TESTS & INTERPRETATION
 SOIL TESTS & INTERPRETATION This technical note discusses most of the soil tests used at Hill Laboratories, and gives very general interpretive information for each. Information for this Technical Note
SOIL TESTS & INTERPRETATION This technical note discusses most of the soil tests used at Hill Laboratories, and gives very general interpretive information for each. Information for this Technical Note
Soil Testing Options in High Tunnels. Bruce Hoskins University of Maine anlab.umesci.maine.edu
 Soil Testing Options in High Tunnels Bruce Hoskins University of Maine hoskins@maine.edu anlab.umesci.maine.edu High Tunnel Project Yields (avg. yield ~ 3000 lb/1000 sq. ft. => 65 tons/a) Calculated (lb/a)
Soil Testing Options in High Tunnels Bruce Hoskins University of Maine hoskins@maine.edu anlab.umesci.maine.edu High Tunnel Project Yields (avg. yield ~ 3000 lb/1000 sq. ft. => 65 tons/a) Calculated (lb/a)
CHANGES OF SOIL MICROELEMENTS CONTENT AFTER INTESIVE MINERAL FERTILIZATION
 CHANGES OF SOIL MICROELEMENTS CONTENT AFTER INTESIVE MINERAL FERTILIZATION MODIFICAREA CONTINUTULUI DE MICROELEMENTE DIN SOL IN URMA FERTILIZARII MINERALE INTENSIVE Isidora RADULOV, F. SALA, Adina BERBECEA,
CHANGES OF SOIL MICROELEMENTS CONTENT AFTER INTESIVE MINERAL FERTILIZATION MODIFICAREA CONTINUTULUI DE MICROELEMENTE DIN SOL IN URMA FERTILIZARII MINERALE INTENSIVE Isidora RADULOV, F. SALA, Adina BERBECEA,
JORIND 9(2) December, ISSN
 SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
SEQUENTIAL EXTRACTION OF Cu, Cd, Pb AND Zn FROM SOIL AROUND INDUSTRIAL WASTE DUMP SITES IN KADUNA ENVIRON USING SIMPLE AND SEQUENTIAL PROCEDURES. H.A Zakari, D.D. Adams, M Shimbayev, P. Nyam Department
SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative
 SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative jfasching@midwestlabs.com 507 273-3339 TERMS ppm = parts per million 2 million pounds of soil represented by soil samples taken 6 inches
SOIL TEST INTERPRETATION JIM FASCHING Technical Field Representative jfasching@midwestlabs.com 507 273-3339 TERMS ppm = parts per million 2 million pounds of soil represented by soil samples taken 6 inches
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013.
 Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Terry Richmond s Fertilizer Package mentioned in the panel discussion March 14, 2013. Roles of the 16 essential nutrients in plant development Sixteen plant food nutrients are essential for proper crop
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001
 Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Soil Conditions Favoring Micronutrient Deficiencies and Responses in 2001 K.A. Kelling and P.E. Speth Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison Why micronutrients now: Higher yield, therefore
Compost Analysis. Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System
 Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1504110993 DATE ISSUED : 28/04/2015
Tel: +61 3 9701 6007 Fax: +61 3 9701 5712 ABN: 26 005 031 569 www.swep.com.au Compost Analysis Sustainable Soil Management with the Mikhail Balance System FILE NO : 1504110993 DATE ISSUED : 28/04/2015
Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories
 Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Compost Quality Consumer of the Future Population dynamics - more and more people involved in use of compost Better educated on what is expected
Welcome Greg Patterson C.C.A. President A&L Canada Laboratories Compost Quality Consumer of the Future Population dynamics - more and more people involved in use of compost Better educated on what is expected
USERS GUIDE for the. report
 USERS GUIDE for the report November, 2015 INTRODUCTION: AgVita has been conducting expresssoil analyses since the mid 1990 s, being a pioneer of this method of soil analysis in Australia. This test has
USERS GUIDE for the report November, 2015 INTRODUCTION: AgVita has been conducting expresssoil analyses since the mid 1990 s, being a pioneer of this method of soil analysis in Australia. This test has
Limitations to Plant Analysis. John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison
 Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Limitations to Plant Analysis John Peters & Carrie Laboski Department of Soil Science University of Wisconsin-Madison What is an essential plant nutrient omission of the element will result in abnormal
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients. Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients. Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops
 Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
Potassium and Phosphorus as Plant Nutrients Secondary Nutrients and Micronutrients Potassium is required in large amounts by many crops Yield K 2 O taken up Crop level/ac in total crop, lb Alfalfa 8 tons
By Andrew & Erin Oxford, Bethel
 Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Chemistry in Plant Nutrition & Growth Objectives Review elements of chemistry and apply them to plant nutrition and growth in an agricultural context. Suggested grade levels 9-12 Alaska Content Standards
Manual of Soil, Plant and Water Analysis
 Manual of Soil, Plant and Water Analysis Dr. Tahir Ali Associate Professor, Division of Soil Science, SKUAST-K, Shalimar Mr. Sumati Narayan Assistant Professor, Division of Olericulture, SKUAST-K, Shalimar
Manual of Soil, Plant and Water Analysis Dr. Tahir Ali Associate Professor, Division of Soil Science, SKUAST-K, Shalimar Mr. Sumati Narayan Assistant Professor, Division of Olericulture, SKUAST-K, Shalimar
UPTAKE OF MAJOR AND TRACE ELEMENTS BY GRASS BIOMASS AFTER AMELIORATION OF DEGRADED SOIL
 General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
General and Applied Plant Physiology 2010, Volume 36 (1 2), pp. 12 16 2010 ISSN 1312-8183 Published by the Institute of Plant Physiology Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Available online at http://www.bio21.bas.bg/ipp/
Micronutrient Status in Dairy Farms of Uruguay Etat des micronutriments dans les fermes laitières d'uruguay
 Scientific registration n : 2162 Symposium n : 14 Presentation : Poster Micronutrient Status in Dairy Farms of Uruguay Etat des micronutriments dans les fermes laitières d'uruguay MORON Alejandro (1),
Scientific registration n : 2162 Symposium n : 14 Presentation : Poster Micronutrient Status in Dairy Farms of Uruguay Etat des micronutriments dans les fermes laitières d'uruguay MORON Alejandro (1),
Purity Tests for Modified Starches
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Purity Tests for Modified Starches This monograph was also published in: Compendium
