BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy. GUIDELINES Student's independent work during the preparation to practical lesson
|
|
|
- Arlene Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Student's independent work during the preparation to practical lesson Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 4 The topic of the lesson Muscles of the upper limb Course Medical 1,2,3,4, military,dental Number of hours 3 Kiev -2017
2 1. Specific objectives: After completing the course, the student must know and be able to: 1.1 Classify muscles of the upper limb. 1.2 Demonstrate the muscles of the upper limb, the place where they begin and attach, and determine their functions. 1.3 Determine the participation of individual muscles of the lower limb in the implementation of certain types of movements. 2. Basic level of training: Students must know and be able to: 2.1. Know lectures on general osteology, arthrology and myology Demonstrate areas of the upper limb Demonstrate and describe individual upper limb bones Describe the joints, movements in which provide the muscles of the upper limb Describe possible movements in the joints of the upper limb. 3. Organization of the content of educational material: Study material is studied in a logical sequence from the central to the peripheral parts of the upper limb with the involvement of structural and logical schemes, tables, drawings, which reflect the content of the main issues of the theme, using anatomical drugs and dummies. 4. Content of educational material: Muscles of the upper limb (musculi membri superioris) are divided into muscles of the thoracic belt and muscles of the free upper limb (mm membri superioris liberi). M.deltoideus It has three parts, which are called according to their origin: pars clavicularis, pars acromialis, pars spinalis. Beginning: from the side of the collarbone, the shoulder process and the shoulder blades.attachment: to the humerus. Function: removes the hand from the trunk to the horizontal level; the clavicle folds the shoulder, rotating it in the middle, pushes the raised arm; the abdomen extenses the shoulder, rotating it externally, lifting the raised arm. M. supraspinatus Beginning: from the entire surface of the periosteum fossa. Attachment: to the top of the large humpback of the humerus.
3 Function: diverts the hand to the horizontal.blood supply: umbilical artery of the shoulder blade. M. Infraspinatus Beginning: from the entire surface of the maxillary lobe of the scapula and the glandular fascia. Attachment: to the middle of the posterior surface of the large thighs of the humerus. Function: rotates the outside shoulder and leads it to the body. M. teres minor Beginning: from the lateral edge of the shoulder blade. Attachment: to the lower part of the posterior surface of the large hub of the humerus. Function: rotates the outside of the shoulder and leads it to the body (synergist of the glandular muscle). M. teres major Beginning: from the lower part of the lateral edge and the lower angle of the shoulder blade. Attachment: to the crest of the small tubercle of the pelvic bone, lower than the attachment of the widest muscle to the back. Function: Extends and brings the shoulder to the body, turns it inwards. M. subscapularis Beginning: from the ventricular fossa of the shoulder blade and its medial margin. Attachment: to the crest of the small hump of the humerus. Function: rotates the shoulder inwards and leads it to the body. M. brachii In the shoulder region (regio brachialis), the anterior and posterior shoulder segments are allocated, which have respectively the front and back muscle groups of the shoulder.the front group of muscles of the shoulder, which are folders, include: bee-shoulder muscle, shoulder-headed muscle and shoulder muscle. To the back group of muscles, which are extensors, belong to the head muscles of the shoulder and elbow muscles. Front muscle group of shoulder: M. biceps brachii The muscle has two heads: a long head (caput longum) and a short head (caput breve). Beginning: the long head begins from the hump of the shoulder blade. The tendons of the long head are in the shoulder cavity. The short head begins with a beak-shaped blade prosthesis. Attachment: Long and short heads are connected to the general abdomen. The abdominal two-headed muscle continues in the long tendons.it attaches to the rocks of the radial bone. A thin and wide aponeurosis of the shoulder head muscle (aponeurosis musculi bicipitis brachii) is fascia of Pirogov from the tendon of the two-head muscle of the shoulder. It covers the elbow hole
4 ahead into the fascia of the forearm.function: folds the forearm in the elbow joint and turns it away (sopinaet) if the forearm was previously attracted (penetrated); folds shoulder in the shoulder joint m. coracobrachialis. Beginning: from the top of the beak-shaped blade appendix. Attachment: to the anterior-mediating surface of the pelvic bone, starting from the crest of a small tubercle up to the middle of this bone. Function: flexes the shoulder in the shoulder joint and pulls it to the body, turns out the shoulder if it is turned to the middle. M. brachialis Beginning: from the front surface of the lower two thirds of the body of the humerus below the deltoid mountain. Attachment: to the humpiness of the elbow bone. Function: flexes the forearm in the elbow joint. Back muscle group of the shoulder M. triceps brachii The muscle has three heads: a long capillary capum (caput longum), a caput laterale and a caput medialis.start of muscle heads: the long head starts from the hypothyroid hump of the scapula.the lateral head begins on the posterior side of the shoulder bone laterally and above the spine of the radius nerve. The lateral head goes down and covers the furrow of the radial nerve. Medium head begins on the back of the humerus medially and below the spine of the spinal nerve. Most of the middle head is covered by the side head, with which it partially grows. Between the interstices of the medial and lateral heads and the furrow nerve, a narrow shoulder muscle canal (canalis humeromuscularis), in which the radial nerve and blood vessels pass, appear. Attachment: approximately the middle of the back of the upper shoulder, the three muscle heads are united and form the general abdomen. It passes into a flat broad tendon and attaches to the elbow process of the elbow. Function: Extends the forearm in the elbow joint, and the long head extends the shoulder in the shoulder joint and leads it to the trunk. M. anconeus Beginning: from the back surface of the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. Attachment: to the backbone surface of the elbow appendix, the proximal part of the elbow. Function: Extends forearm in elbow. M. antebrachii Muscles of the forearm are divided into two groups: the anterior and posterior. Front forearm muscle group Most of the forearm muscles of the forearm starts from the medial hypertrophy of the humerus. The first (superficial) layer of forearm muscles of the forearm M. brachioradialis
5 Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus and its crest. Attachment: to the lateral surface of the distal end of the radial bone over its shiploid appendix.function: bends the forearm in the elbow joint, sets it to the middle position between the attraction and the turning away. M. pronator teres Has shoulder and elbow heads (caput humerale et caput ulnare). Beginning: shoulder head - from the medial superficial humerus; elbow head - from the median edge of the hilum of the elbow and from its crown appendix. Attachment: Both heads are immediately connected to one abdomen. It attaches to the middle of the lateral surface of the radial bone. Function: attracts (promotes) the forearm and flexes it in the elbow joint. M. Flexor carpi radialis Beginning: from the medial superficial of the shoulder bone. Attachment: to the palmar surface of the base of the II heel bone. Function: bends and removes the brush in the radial wrist, bends the forearm in the elbow joint. M. palmaris longus Beginning: from the medial hypertrophy of the humerus. Attachment: pass into palmar aponeurosis (aroneurosis palmaris). Function: tines palmar aponeurosis, folds the brush and forearm. M. Flexor carpi ulnaris Has shoulder and elbow heads (caput humerale et caput ulnare). Beginning: shoulder head - from the medial hypertrophy of the shoulder bone; Elliptical head - from the top two thirds of the medial surface of the elbow and elbow appendix. Attachment: to the pectoral bone and hook of the hook bone. Function: bends and brushes the radial wrist joint. The second layer of the muscles of the forearm M.flexor digitorum superficialis It starts with two heads - the shoulder-elbow head (caput humeroulnare) and the head of the bone marrow (caput radiale). Beginning: the shoulder-elbow head starts from the medial hypertrophy of the humerus and from the medial edge of the crown appendix of the elbow bone; the head of the radial bone starts from the upper two thirds of the anterior edge of the radius bone. Both heads are connected to the general abdomen. Distally, this abdomen is divided into 4 long tendons. Attachment: The muscle tendons are divided into 2 legs, which are attached on both sides to the basics of the middle phalanges II-V of the fingers. Due to the split between the legs of each tendon, the corresponding tendon of deep flesh-flexor runs. Function: folds the middle and proximal phalanges II-V of the fingers, the brush, and the forearm.
6 Third layer of muscles of the forearm M. flexor digitorum profundus Beginning: from the proximal two thirds of the front surface of the elbow bone below its hump and from the interstitial peritoneum of the forearm. Attachment: The abdomen of the muscle passes into four tendons. They are attached to the basis of distal phalanx II-V fingers. At the level of proximal phalanges, each tendon of the deep muscle - the folding finger passes through the gap between the legs of the corresponding tendon of the surface muscle - the flexor of the fingers. Function: folds the end, middle and proximal phalanges of the II-V fingers, as well as the brush in the radial wrist joint. M. flexor pollicis longus Beginning: from the upper two thirds of the anterior surface of the radial bone, the interstitial membrane of the forearm and the medial perineum of the humerus. Attachment: to the base of the final phalanx of the thumb. Function: bends the final and proximal phalanges of the thumb, takes part in bending the brush. Fourth (deep) layer of muscles of the forearm M. pronator quadratus Beginning: from the anterior margin and the anterior surface of the lower third of the elbow. Attachment: to the front surface and the anterior edge of the lower third of the radius. Function: rotates inside the radius bone around the elbow - attracts (promotes) the forearm and the brush. Back muscle group of the forearm The muscles of the back of the forearm by function are extensors. Form two layers - superficial and deep. The superficial layer of the muscles of the forearm The muscles of the surface layer of the back group begin from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. M.extensor carpi radialis longus Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. Attachment: to the back surface of the base of the II heel bone. Function: Extends wrist and brush in the radial wrist; Shrinking simultaneously with the radial muscle-bending wrist, remove the brush. Short-limb muscle extension wrist (m extensor carpi radialis brevis) Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. Attachment: to the back surface of the base of the third heel bone. Function: Extends wrist and brush in the radial wrist; Shrinking simultaneously with the radial muscle-bending wrist, remove the brush.
7 M. extensor digitorum Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. Distally, the muscle is divided into 4 tendons. Attachment: Four tendons to the rear surface of the middle and end phalanx of II-V fingers. Function: Extends II-V fingers, as well as a brush. M. extensor digiti minimis Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus. Attachment: to the back surface of the base of the middle and end phalanx V Elbow muscle extensor wrist (m extensor carpi ulnaris) Beginning: from the lateral superficial of the shoulder bone, the posterior surface of the elbow bone. Attachment: to the back surface of the base V of the heel bone. Function: Extends and brushes the radial wrist joint. Deep layer of muscles of the forearm M. supinator Beginning: from the lateral hypertrophy of the humerus and from the crest of the muscle-opener on the elbow bone. Attachment: to the anterolateral surface of the upper third of the radius bone from its rough surface to the point of attachment of the circular muscle - the grafters. Function: Swings off (supine) the forearm, with the radius bone rotating outside around the elbow bone. M. abductor pollicis longus Beginning: from the posterior surface of the elbow and prominous bones, as well as from the interstitial membrane of the forearm. Attachment: to the back surface of the base and the heel bone. Function: draws a thumb and a brush. M.extensor pollicis brevis Beginning: from the posterior surface of the radius and the interstitial membrane of the forearm. Attachment: to the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. Function: Extends the proximal phalanx of the thumb and removes it. M. extensor pollicis longus Beginning: from the posterior surface of the middle third of the elbow and the interstitial membrane of the forearm. Attachment: to the base of the final phalanx of the thumb. Function: Extends thumb and brush. M. extensor indicis Beginning: from the posterior surface of the lower third of the elbow and the interstitial membrane of the forearm. Attachment: to the back of the proximal phalanx of the index finger. Function: expands the index finger, helps to expand the brush. The muscles of the brush
8 The muscles of the brush are divided into 3 groups. M. abductor pollicis brevis Function: draws a big toe of the brush. Opposite muscle of the thumb (m orro nens pollicis) Function: contrasts the thumb with the little finger and the other fingers of the brush. Short fingernail muscle (m.flexor pollicis brevis) Squatted on the medial side of the enlargement of the thumb, partly covered by a short thumb pull of the muscle. It has a superficial and gl-side head (caput superficiale et caput profundum). Function: bends the proximal phalanx of the thumb. M. adductor pollicis It has a braid and a transverse head (caput obliquum et caput transversum). Function: brings the thumb to the index. The muscles increase the little finger M. palmaris brevis It has the appearance of a thin plate. Located transversely in the subcutaneous basis, raising the little finger. Function: wrinkles the skin to increase the thumb. M. abductor digiti minimi Function: removes the little finger. M. opponens digiti minimi Located on the side of the short muscle-flexor of the little finger and under the removable muscle of the little finger. Function: Opposes the little finger to the big finger of the brush. M. flexor digiti minimis brevis Arranged on the side of the muscle of the little finger. Function: bends the little finger. Middle group of muscles of the brush The middle group muscles are located in the interstitial intervals of the heel (palm and posterior interbody muscles) at the level of the deep muscle flexion of the fingers (the scrotum muscles). M. lumbricales are four thin spindle-shaped muscles that lie indisputably under the palmar aponeurosis between the tendons of the flexor muscles. Beginning: from the tendons of the deep muscle flexing the fingers. Attachment: their tendons are woven into the tendons of the muscle-extensor of the fingers. Function: bending proximal phalanges and bending the middle and end phalanges of the II-V fingers. M. Interossei palmares Presented by three muscles. They lie in the second, third and fourth intercutaneous passages, closing them from the palm of the hand. Beginning: from the II, IV and V hemopoiesis.
9 Attachment: Proximal Phalanges I, IV and V Fingers. Function: Brings II, IV and V fingers to III (sore) fingers. M.interossei dorsales They are located in the back of all four interpositions. Beginning: each muscle begins with two heads from the reversed surfaces of the I-V hemopoies. Attachment: to the basis of Proximal Phalanx II-V Fingers. Function: remove the II and IV fingers from the III (middle) finger, hold the third finger or remove and lead it. 5. Methods of organization of educational process in practical lesson 5.1. Preparatory stage Formation of motivation for the purposeful study of anatomy of the muscles of the upper limb for the purpose of professional activity: knowledge of the anatomy of the muscles of the lower limb is the basis for the formation of the clinical thinking of surgeons, orthopedic traumatologists and doctors of sports medicine Conduct standardized control of the initial level of students' training: - by tests of the educational theme "Anatomy of muscles of the upper extremity". - on questions of control of the basic and initial levels of knowledge The main stage The practical work of students with the use of the anatomical preparation of a corpse of a person, drawings, drawings on "muscles of the upper limb" is carried out. Self-study by students of the topic is controlled by a teacher. During this control, the individual techniques of the teacher are implemented to facilitate the study of complex anatomical components, as well as the necessary consultations are carried out The final stage Evaluates the current activity of each student during the class. Standardized final control is carried out. An analysis of student activity is conducted. Announced evaluation of the activities of each student and recorded in the journal of attendance records and student success. An adult group at the same time puts the marks in the record of the record of success and visits of studies by students, the teacher assures them with their signature. The teacher informs the students about the topic of the next lesson and methodical methods for preparing for it. 6. Attachments. Means for control: - practical tasks concerning illustrations in the manual "Anatomy of a person. Control of independent preparation of students for practical classes»
10 - questions for controlling the basic level of knowledge of students - A question for controlling the initial level of knowledge of students - A question for controlling the final level of student knowledge - test tasks of format A (CRIC-1) 1. Practical tasks regarding illustrations in the manual "Anatomy of man. Control of independent preparation of students for practical classes»: - to work out in the manual different colors of the scheme and drawings in accordance with the subject of the lesson. 2. Questions for controlling the basic level of knowledge of students 2.1. Name and show the upper limbs Name and demonstrate the sacrum and caudal, bones of the upper limb Name and demonstrate joints of the upper limb bones Describe the overall structure of the skeletal muscle as an organ Determine what is referring to the auxiliary apparatus of skeletal muscles Classify the muscles in shape, position, fiber direction, joints and functions Identify the following main characteristics of the skeletal muscles, such as the concept of the onset and attachment of muscles and their action on the joints. 3. Questions for controlling the entry level knowledge of students 3.1. Name the muscles of the thumb Name the deep back muscles of the forearm Name the place of attachment of the shoulder muscle Name the place of the beginning of the long head of the trigeminal muscle of the shoulder Name the muscles of the increase of a small finger Name the superficial back muscles of the forearm Name the place of attachment of the two-headed shoulder muscle Name the place of the middle head of the trigeminal muscle of the shoulder What are the forearm muscles of the forearm? What is the function of palmar intercostal muscles? Name the place of attachment of the elbow muscle Name the place of the beginning of the side head of the trigeminal muscle of the shoulder What is the function of the rectal musculoskeletal muscles of the brush Name the place of the beginning of the elbow muscle Name the function of the scrotum muscles. 4. Questions to control the final level of student knowledge 4.1. Classify muscles of the upper limb.
11 4.2. Name and demonstrate the muscles of the thoracic belt. Describe the deltoid, abdominal and glandular muscles. Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Demonstrate small and large round muscles and subcutaneous muscle. Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Classify shoulder muscles. Name the front shoulder muscles. Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Name the back muscles of the shoulder. Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Classify the muscles of the forearm. What are the forearm muscles of the forearm? Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Name the back muscles of the forearm. Demonstrate the places where they are to begin and attach, and identify the moves that can be done with their help Classify the muscles of the brush. Name the muscles of the thumb. Identify the moves that can be done with their help Name the muscles of the increase of a small finger. Identify the moves that can be done with their help What are the muscles that belong to the middle group of muscles of the brush. Identify the moves that can be done with their help? What are the muscles that make flexion and extension in the shoulder joint? What are the muscles that drive and pull off the shoulder joint? What are the muscles that rotate in the shoulder joint outside and to the middle? What are the muscles that flex and flex in the elbow? What are the muscles that make the radius of the radius and the brush out and the middle to the elbow? What are the muscles that perform flexion and extension in the radial wrist joint? What are the muscles that carry and bring to the wrist? What are the muscles that perform flexion and extension in the phyticphalangeal and interphalangeal joints? What are the muscles that carry the reduction and removal in the phyticphalangeal joints? What are the muscles that make flexion and extension, the removal and removal in the wrist of the tooth joint of the thumb, and which muscle contributes this finger to the little finger?
12 Tests 1. After injury, the patient can not bend the upper limb in the elbow joint. Failure of the function of the main muscle can cause this condition? A. M. teres major. B. M. infraspinatus. C. M. levator scapulae. D.M. triceps brachii. E. M. subscapularis. 2. Patient - injury to the shoulder joint. Radiologically, lesions of the hypothalamic mound of the shoulder blade were detected. The tendons of which muscle that begins in this place has been damaged? A. Caput longum m. tricipitis brachii B. Caput breve m. bicipitis brachii. C. Caput mediale m. tricipitis brachii D. Caput laterale m. tricipitis brachii E. Caput longum m. bicipitis brachii. 3. A traumatic point arrived at a man, 38 years old, with a trauma of his right hand. During examination, a cutaneous wound was found in the area of the right thumb enlargement. What muscle is damaged if the end phalanx and finger is not bent? A. M. opponens pollicis. B. M. flexor pollicis brevis. C. M. abductor pollicis brevis. D.M. flexor pollicis longus. E.M. adductor pollicis. 4. A person arrived at the emergency room, 39 years old, with a trauma of the left hand. During examination, the cut wound was detected in the area of the thumb enlargement. What muscle is damaged if the proximal phalanx of the thumb is not bent? A. M. adductor pollicis. B. M. flexor pollicis longus. C. M. abductor pollicis brevis. D. M. opponens pollicis. E.M. flexor pollicis brevis. 5. Having a shoulder injury, the patient complains about the impossibility of removing the shoulder. What muscles are injured? A. M. teres major et m. subscapularis B. M. deltoideus et m. suppressed C. M. supraspinatus et m. teres major D. M. teres minor et m. deltoid
13 E. M. subscapularis et m. coracobrachialis. 6. B as a result of an injury the patient can not raise his hand to the horizontal level. What muscle is affected? A. M. biceps brachii. B.M. deltoideus. C. M. triceps brachii. D.M. trapezius. E.M. latissimus dorsi. 7. Injuries to the anterior shoulder area led to significant limitation of bending in the shoulder and elbow joints. What muscle is damaged? A. M. triceps brachii. B. M. brachialis. C. M. anconeus. D.M. biceps brachii. E. M. brachioradialis. 8. The patient can not remove the upper limb from the trunk, which muscle does not perform its functions? A. M. infraspinatus. B. M. latissimus dorsi. C. M. teres major D.M. deltoideus. E.M. coracobrachialis. 9. A man, 45 years old, was taken to a surgical department with a cut wound on the median edge of the forearm. The examination showed that the patient was cut two muscles of the forearm - elbow flexor muscle and elbow muscle extensor of the wrist. What movement is performed while simultaneously reducing these muscles? A. Bending of the brush. B. Extension and removal of the brush. C. Brushing. D. Disposal of the brush. E. Extension of the brush. 10. At the husband, 26 years old, an industrial injury of the upper third of the shoulder. During examination at the injury point bone damage was not detected. The absence of active extension of the forearm is noted. Which muscle is most likely to be damaged? A. M. triceps brachii. B. M. coracobrachialis. C. M. biceps brachii. D.M. anconeus. E. M. pronator teres. 11. A man, 35 years old, under working conditions received a cutaneous wound in the area of enlargement of the thumb. Restrictions on thumbnail of
14 the brush are detected. What muscle function is damaged? A. M. opponens pollicis. B. M. palmaris brevis. C. M. abductor pollicis brevis. D.M. flexor pollicis brevis. E.M. adductor pollicis. 12. When a 45-year-old female traumatologist was examined, small circular muscle damage was detected. Which shoulder movement will be limited? A. Deduction. B. Rejection, withdrawal. C. Engagement, bringing. D. Bringing, turning away. E. Bending. Answers D A D E B B D D C A C D
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Systematic Anatomy (For international students)
 Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy (For international students) Department of Anatomy,Fudan University Teaching contents Muscles of abdomen & upper limbs Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Locomotor system - Part 6
 Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Systematic Anatomy Locomotor system - Part 6 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Muscles of abdomen Muscles of the upper limb Muscles of abdomen
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Shoulder Girdle New Material Upper Extremities - Bones Anatomy and Physiology II Shoulder Girdle Review Questions From Last Lecture Can you identify the following muscles?
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION
 MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
MUSCLES OF THE ELBOW REGION Dr Bronwen Ackermann COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulation WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Sydney
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology II REVIEW MSAK101-II Session 4 LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this session, the student will be
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Location Terms. Anterior and posterior. Proximal and Distal The term proximal (Latin proximus; nearest) describes where the appendage joins the body.
 HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
HUMAN ANAT OMY Location Terms Anterior and posterior In human anatomical usage, anterior refers to the front of the individual. Similarly, posterior refers to the back of the subject. In standard anatomical
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver
 Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Human Anatomy Lab #7: Muscles of the Cadaver Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 1 Introduction...... 1 Identifying Muscles on Yourself.... 2 Muscles of the Anterior Trunk and Arm.. 2 Muscles
Synergist Muscles. Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Flexion Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis
 Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
Synergist Muscles Dr Gene Desepoli DrGeneLMT@gmail.com Shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid (anterior fibers) Pectoralis major (upper fibers) Biceps Brachii Coracobrachialis Deltoid (posterior fibers)
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
The Elbow and the cubital fossa. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
The Elbow and the cubital fossa Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Elbow and Forearm Anatomy The elbow joint is formed by the humerus, radius, and the ulna Bony anatomy of the elbow Distal Humerus
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Abduction of arm until your hand rich your head. Flexion of forearm at elbow joint. Extension of arm at elbow joint. Flexion of fingers 10.
 Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor. Zygomaticus major Buccinator
 Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
Epicranius (frontal belly) Zygomaticus minor Zygomaticus major Buccinator Masseter Digastric (posterior belly) Stylohyoid Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Scalenus Omohyoid (inferior belly) Orbicularis oris
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016
 LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
LIST OF STRUCTURES TO BE IDENTIFIED IN LAB: UPPER EXTREMITY REVIEW 2016 BONES Ribs, sternum, clavicle Humerus: Head, greater tubercle, lesser tubercle, intertubercular sulcus, surgical neck, anatomical
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
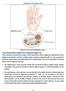 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla.
 1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
1 region of the upper limb between the shoulder and the elbow Superiorly communicates with the axilla. Inferiorly, a number of important structures pass between arm & forearm through cubital fossa. 2 medial
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
Chapter 9. The Muscular System
 1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
1 Chapter 9 The Muscular System 2 Introduction Skeletal muscles: movement in environment Smooth muscles: intestines, ureters, veins and arteries Cardiac muscle: pumps blood through heart and blood vessels
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm
 Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Fascial Compartments of the Upper Arm The upper arm is enclosed in a sheath of deep fascia and has two fascial septa: 1- Medial fascial septum (medial intermuscular septum): attached to the medial supracondylar
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back
 Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Muscles in the Shoulder, Chest, Arm, Stomach, and Back Shoulder Muscles Deltoid Supraspinatus Infraspinatus Teres Major Teres Minor Subscapularis Deltoid (Delts) Function: Raises the upper arm Origin:
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb
 The Upper Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb Table of Contents Upper Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Clavicle...3 2: Scapula...5 3: Shoulder (Glenohumeral) and Proximal Humerus...7 4:
The Upper Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Upper Limb Table of Contents Upper Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Clavicle...3 2: Scapula...5 3: Shoulder (Glenohumeral) and Proximal Humerus...7 4:
PAB Test Manual. Introduction
 PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
PAB Test Manual Introduction PAB stands for Pressure Air Biofeedback and is a very easy to use system for muscular function diagnosis. In connection with chosen inflated TOGU products it can evaluate and
Muscles of the Cat. N Deltoid MUSCLES OF THE CHEST. Pectoralis major. (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) MUSCLES OF THE CHEST
 MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis major (This muscle is superior to Pectoralis minor) 1. MUSCLES OF THE CHEST Pectoralis minor (This muscle is inferior to Pectoralis major) 2. MUSCLES OF THE ARM Deltoid
Thank You for Your Support! Hosford Muscle Tables
 Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed online for your enjoyment and I hope you find it useful. These tables are both a teaching tool, and a study / review tool. I created these
Thank You for Your Support! This PDF document has been placed online for your enjoyment and I hope you find it useful. These tables are both a teaching tool, and a study / review tool. I created these
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR THE FLEXTEND AC Exercise System for The Acromioclavicular (AC) / Shoulder Joint
 INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR THE FLEXTEND AC Exercise System for The Acromioclavicular (AC) / Shoulder Joint FLEXTEND -AC: Congratulations! You have chosen to use the FLEXTEND -AC Upper Extremity Training System,
INSTRUCTION MANUAL FOR THE FLEXTEND AC Exercise System for The Acromioclavicular (AC) / Shoulder Joint FLEXTEND -AC: Congratulations! You have chosen to use the FLEXTEND -AC Upper Extremity Training System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System (Two weeks) 1 This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Gross Anatomy of the Muscular System. Complete the Review
The Role of Muscles in Movement
 The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
In which arm muscle are intramuscular injections most often given? (not in text)
 AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
AP1 Lab 9 - Muscles of the Arms and Legs Locate the following muscles on the models and on yourself. Recall anatomical position. Directional terms such as anterior, posterior, lateral, etc. all assume
5/21/2013. Muscle Anatomy. Thursday January, 24 th, Skeletal Muscle. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle
 Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
Muscle Anatomy Thursday January, 24 th, 2013 Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle 1 Smooth Muscle 1. Found in the walls of the digestive system, bladder, uterus and blood vessels 2. Involuntary
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration-
 This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
This figure (of humerus) is from Dr. Maher's newest slides. -Its added here just for consideration- Slides of Anatomy Please note : These slides are Dr. Maher Hadidi s slides of spring 2016 and were edited
UPPERTONE Exercise Manual
 UPPERTONE Exercise Manual GPK Inc., 535 Floyd Smith Dr., El Cajon, CA 92020, 800-468-8679, 619-593-7381, Fax: 619-593-7514, www.gpk.com Index Introduction...... 3 The Major Muscles... 4 Definitions of
UPPERTONE Exercise Manual GPK Inc., 535 Floyd Smith Dr., El Cajon, CA 92020, 800-468-8679, 619-593-7381, Fax: 619-593-7514, www.gpk.com Index Introduction...... 3 The Major Muscles... 4 Definitions of
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1
 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy. GUIDELINES Student's independent work during the preparation to practical lesson
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Student's independent work during the preparation to practical lesson Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Student's independent work during the preparation to practical lesson Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module
Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body.
 Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
Okay Anatomy Anatomy I: Lesson 11 Myologia Part II Objective: Students will examine the muscles of a canine in order to identify the musculature of the body. Practical Tasks: 6) carpal flexors, pronators
Muscular anatomy of the forelimbs of the lesser grison (Galictis cuja), and a functional and
 Muscular anatomy of the forelimbs of the lesser grison (Galictis cuja), and a functional and phylogenetic overview of Mustelidae and other Caniformia Journal of Mammalian Evolution Marcos D. Ercoli, Alicia
Muscular anatomy of the forelimbs of the lesser grison (Galictis cuja), and a functional and phylogenetic overview of Mustelidae and other Caniformia Journal of Mammalian Evolution Marcos D. Ercoli, Alicia
Contents. Preface xv. SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1. SECTION 2: The Bodynamic Psycho-Motor Anatomy 29
 Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Contents Preface xv SECTION 1: Introduction to the Bodynamic System 1 Definitions in the Bodynamic System 3 Ego Formation through the Coding Elements 9 Examples of Formation of Coding 17 Using This Book
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex. The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow.
 Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
Osteology of the Elbow and Forearm Complex The ability to perform many activities of daily living (ADL) depends upon the elbow. Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Can you think of anything that you do to
Anatomy of the Forearm
 Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
Anatomy of the Forearm Musculoskeletal block- Anatomy-lecture 8 Editing file Objectives List the names of the Flexors Group of Forearm (superficial & deep muscles). Identify the common flexor origin of
A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract.
 Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
Ch 8 Muscles Introduction: A. All movements require muscle which are organs using chemical energy to contract. B. The three types of muscle in the body are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. C. This
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
The Muscular System Lab Power Point
 The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
The Muscular System Lab Power Point Myoneural Junction Sarcoplasm Nucleus Myofibrils Sarcomere (black line to black line) Sarcolemma Myoneural space Nucleus Endomysium Motor Neuron Muscles of Facial Expression
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy
 Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints
 The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing
 Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing Description of Movement While the movement required for a golf swing requires many muscles, joints, & ligaments throughout the body, the
Motion of Left Upper Extremity During A Right- Handed Golf Swing Description of Movement While the movement required for a golf swing requires many muscles, joints, & ligaments throughout the body, the
