MR Imaging of the Knee: Three-Dimensional Fourier Transform G RASS Technique 1
|
|
|
- Shauna Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 심Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996: 34(4) : MR Imaging of the Knee: Three-Dimensional Fourier Transform G RASS Technique 1 Oong Joo Kim, M.O., Young-uk Lee, M.O., Eun Kyung Youn, M.O., In Gye No, M.O., Seoung Bum Chin, M.O., Joon Sik Kim, M.0.2, Jae Yeul Choi, M.0.2 Purpose: To evaluate the usefulness of three-dimensional(30) Fourier transform(ft) gradient refocused acquisition in steady state (GRASS) technique for MR imaging ofthe knee. Materials and Methods: Sixty-three knees in 61 patients were imaged on the 1. 5T MR system. Wecompared 30FTGRASStechniquewith 20spin echo(se) technique in terms of conspicuousness of the lesions of internal knee structures based on the results of arthroscopy or open surgery. As a SE technique, sagittal T1- and T2-weighted, and coronal fat-suppressed T2-weighted sequences were performed. Sixty contiguous axial scans with 0.7 or 1 mm section thickness were performed using 30 GRASS technique, and we also evaluated arbitrarily reformatted images produced from the original axial voxel images. Results: For the depiction of the tear, 30FT GRASS was superior to 20 SE in three cases of medial meniscus, one of lateral meniscus, and two of anterior cruciate ligament. Specificity of 30 GRASS was also higher than that of 20 SE in evaluation of lateral meniscus and anterior cruiciate ligament. There was no significant difference in MR diagnosis fortears ofthe posterior cruciate, medial collateral, and lateral collateralligaments. 30 GRASS wassuperior in evaluating the extent and morphology of the torn menisci. Conclusion: The 30FT GRASS technique was comparable or even superior to the 20 SE technique in the evaluation of the internal structure of the knee, and can be expected to supplement standard MR knee techniques, especially in complicated casesof meniscal or ligamentoustears. Index Words: Knee, MR Knee, i 미 unes Knee, ligaments, menisci, and cantilage Magnetic resonance(mr), p 비 se sequences INTRODUCTION Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has become a preferred method for evaluating the internal derangement of the knee. The imaging technique is diverse. Two -dimensional(20) Fourier transform(ft) spin echo (SE) sequences in sagittal and coronal planes have been most commonly used as a standard technique of 'Department ofradiology, Kangbuk Samsung Hosp ital 2D epartm en t 이 O rth o p e di c Surgery, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital Received November 6,1995 ; Accepted March 19,1996 Address reprint requ ests to: Dong Joo Kim, M.D., Department of Radiology, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital,! 108 Pyeong-dong, Chongro-gu, Seo ul, Korea. Tel Fax MR knee imaging, and a three- dimensional(30) FT gradient- echo sequence has also been proposed for that purpose (1-6). Advantages of the 30 over the 20 technique include an improved signal -to - noise ratio and spatial resolution for a given slice thickness ; truly contiguous and thi n slices ; and the abil ity to obtai n isotropic voxels, enabl ing data reconstruction in any plane (1, 2, 5). Prolonged scanning time, the major disadvantage of the 30 technique can in practice be reduced to an acceptable level by using it in conjunction with the gradient- echo technique. The purpose of this study was to determine whether 30FT gradient- echo imaging is accu rate in evaluating the internal structures of the knee and to compare the results ofthis with those ofthe 20FT SE technique
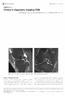
2 Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996 ; 34( 4) MATERIALS and METHODS MR images were obtained of 63 knees in 61 patients referred for suspected internal derangement of the knee. These 61 patients consisted of 45 men and 16 women, aged between 13 and 62 years (mean : 35). The two authors prospectively interpreted these MR images without knowledge of the surgical results. AII the patients had undergone arthroscopic or open surgery and the results used as gold standards in this report were as shown in Table 1. With regard to tears of the medial or lateral collateralligaments which are not accessible to evaluation by arthroscopy and usually need no operative management, we simply compared Table 1. Oiagnoses by Arthroscopy or Open Surgery Tear 01 internal structure Medial meniscus Lateral meniscus A꺼미r 떼뾰띠)Dl P) M h 1 뼈빼때따Others 27 Osteochondral fracture 19 Chondromalacia patella nu R) 5 2 the MR findings on the 20 and 3D images. MR imaging was performed with a 1.5T MR imager (Signa ; GE Medical System, Milwaukee, USA). A dedicated transmit-receive extremity coil was used in all cases. The patients were positioned supine on the magnet with their knees extended naturally. After obtaining axial T1 - weighted SE images (TRITE=500/1 0) for orientation, sagittal T1 - (TR/TE=600/15) and T2 weighted (TR/TE=2500/15, 60) SE sequences and coronal T2 - weighted (TR/TE=2500/20, 60) SE sequences with fat suppression were performed. For the fat suppressed image, we used chemical shifting selective imaging technique. The other scan parameters for these SE images were as follows : 256 X 192 matrix, one excitation, 14-16cm field ofview, and 3mm slice thickness with interslice gap of 1 mm. Gradient refocused aquisition in steady state (GRASS) is the version of the limited - flip - angle, gradient- refocused pulse sequence available on our imager. By using a 30FTtechnique, 60 contiguous axial GRASS images (TRITE/flip angle=50/14/20 0 ) were obtained with a section thickness of 0.7 mm or 1 mm, a matrix size of 256 X 192, a field of view of 14 to 16 cm, and one excitation. The actual scanning time was 7 Table 2. 30FT GRASS * vs 20FT SE **: Medial Meniscus n=63(no. of surgical results) MR sequence 30FTGRASS 20FTSE Negative (36) true( - )lfalse( +) Positive (27) true( + )/false( -) 34 / 2 26 / 1 34 / 2 23 / 4 * 3-dimensional Fourier transform gradient refocused acquisition in steady state **2-dimensional Fourier transform spin-echo Sensitivity Specificity Table 3. 30FT GRASS vs 20FT SE: Lateral Meniscus n=63(no. of surgical results) MR sequence Negative (44) true( - )/false( +) Positive (19) true( + ) / false( -) Sensitivity Specificity 30FTGRASS 20FTSE 43 / 1 18 / 1 42 / 2 17 / Fig. 1. a. A peripheral tear of the medial meniscus is suspected on PO-weighted SE image revealing an uncoverage of the posterior tibial plateau and increased signal intensity between the meniscus and the capsule b. 30 axial image demonstrates the mar ginal irregularity with increased signal in tensity (arrow) along the body-posterior horn junction of medial meniscus, which was also demonstrated on several consecutive upper and lower axial images (not shown ), strongly suggesting peripheral tear which was confirmed arthroscopically a b
3 Dong Joo Kim, et al: MR Imaging 01 the Knee m i ns. 26 secs. with the 0.7 mm - thick section and 10 mins. 12 secs. with the 1mm-thick section. After reviewing the original axial images, reformatted images in arbitrary planes different from case to case were also evaluated at the workstation, and this took between 3 and 10 minutes. MR diagnosis of a meniscal tear was based on the criteria published by Reicher et al (7) and Stoller et al (8). The meniscus was considered torn if a bright line extended to the articular surface or inner or outer edge, or if the meniscus was deformed. The ligament was diagnosed as torn based only on the primary sign of the ligament itself such as a discontinuity with gap, nonvisualization of the normal ligament, or significant sweliing with highly increased signal intensity. 80th SE and 30FT GRASS images were separately reviewed and the results were compared with surgical findings. RESULTS Of the 126 menisci, 46 (27 medial and 19 lateral) had tears and 80 were normal in surgery. Forty (23 medial and 17 lateral) meniscal tears and 76 normal menisci were correctly diagnosed on 20 SE images. Six results were false negative (tour medial and two lateral meniscil, and four were false positive (two medial and two lateral meniscil. Calculated sensitivity and specificity are presented in Tables 2 and 3. 30FT GRASS imaging correctly demonstrated 44 (26 medial and 181ateral menisci) of the 46 tears (Fig. 1, 2) and 77 (34 medial and 431ateral) of 80 normal menisci. Three results (two medial and one lateral meniscil were false negative and two (one medial and one lateral meniscus) were false positive. The sensitivity and specificity ofthe 30FT GRASS technique are presented in Table 2 and 3. Oiagnosis of the small radial tear could be facilitated by the original thin - section axial images of the 30FT GRASS technique. Meticulous reexamination of cases which resulted false negative by both techniques failed to reveal the tears shown by arthroscopy to be small tears extending to the inferior articular surfaces. In some cases, 3D axial images were better than 20 sagittal or coronal images in evaluating the extent of a tear and the relationship between the torn menisci and the fragments (Fig. 1, 2) For the diagnosis of a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), 30FT GRASS technique was superior to 20 SE in three cases (Fig. 3, 4). 20 SE images gave Fig. 2. a, b. The sagittal2d SE images show the medial meniscal tear with inward displacement 01 the torn Iragment into the intercondylar lossa suggesting a buckethandle tear c. The 3D axial image reveals delinitely the handle 01 the bucket (arrows) displaced int the intercondylar lossa. d. On the obl 띠 ue coronal reformatted image, the inward migrated meniscal Iragment (white arrow) looks pushing the PCL (black arrow) upward a b c d
4 Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996; 34(4) : rise to two false positive and two false negative results, and 30 GRASS resulted in one false positive and no false negative results (Table 4). There was no difference in accuracy of diagnosis of tears of the posterior cruciate I igament, and using either technique, diagnostic sensitivity and specificity were 80% and 100%, respectively. Nor were we able to find any difference between the two techniques in the results of evaluation of medial and lateral collateral ligaments (Fig. 5). Axial images of the patellofemoral joint offered by the 30 technique facilitated the detection of chondromalacia patella. The ability to reformat the original voxel images into well - resolved images in any plane disclosed in one case a small osteochondral fracture and displaced fragment which routine 20 SE images failed to depict clearly (Fig. 6) DISCUSSION MR imaging has become a useful tool for imaging the knee joint, and several studies have proved MR to be highly accurate in delineating meniscal and ligamentous tears (9-15). These studies have used the 20 technique mostly with sagittal and coronal SE sequences, but the conventional MR technique has certain limitations. Small tears on the free edge of the meniscus, tears perpendicular to the meniscus, or tears of the nonorthogonal structure such as ACL might not be identified. The very thin, contiguous sections of volume MR imaging offer major advantages over their 20 counterparts (1, 4, 5) ; (1) while 20FT p 비 se sequences may Table 4. 30FT GRASS vs 20FT SE: Anterior Cruciate Ligament n= 63 (No. of surgical results) MR sequence 30FTGRASS 20FTSE Negative (53) true( - )/false( +) Positive (1 이 true( +)/false(-) Sensitivity Specificity 52 / / Fig. 3. The continuity of the posterior fascicle of the ACL which was confirmed surgically and by oblique sagittal reformatted image (a) is not affirmative on routine SE sagittal image (b) a Fig. 4. a. On SE T2WI, the proximal portion of the ACL looks edematous and its distal slope is decreased, suggesting ACL tear somewhere in the proximal portion b. The 3D reformatted image shows midsubstance tear (arrow) of ACL. a b
5 Dong Joo Kim, et al: MR Imaging of the Knee be bothered by cross -talk from adjacent slices, 30FT sequences excite an enti re vol ume of tissue and obtain tr 비 y contiguous slices with resultant minimal volume averaging and no lost pathologic areas in section gaps (2) The signal -to- noise ratio of 30FT GRASS image is greater than that of 20FT GRASS or SE image of comparable thickness, this allows the 30 technique to obtain thinner slices and better in - plane resolution. (3). Because of the small voxel size, image reformation in any orthogonal and nonorthogonal planes is possible without additional scanning time or repositioning ofthe patient. In addition, the excessively prolonged scanning time which is the main disadvantage of the 30 volume technique could be compensated by coupling with gradient-echo sequence. With these, image acquisition times in the order of a second or subsecond are now common, and numerous imaging sequences, including GRASS, based on gradient-echoes have been developed. In GRASS images, short TRs (ie. TR( (12) with appropriately large flip angles produce the signal Fig. 5. The MCL tear from the femoral insertion site is easily diagnosed on both SE coronal (a) and 3D reformated (b) images. The bone bruise rev ealed as reticular hyperintensities in the lateral femoral condyle is obvious only on fat-suppressed SE T2WI(a) contrast related to T2, causing joint effusion to become bright in contrast to hypointense menisci and ligaments (16). The axial 30FT GRASS technique provides images of the menisci just as they are, and these axial plane images are similar to the views seen by the arthroscopic surgeon (2). In this study, axial 30FT GRASS effectively identified meniscal tears and proved its superiority to the 20 SE technique in detecting small radial or peripheral tears. Both the axial imaging plane and the thinner slice thickness with resultant diminution ir) volume - averaging may have been responsible for this. The extent and relationship between torn menisci and fragments were often better delineated on axial than on coronal and sagittal images. In the axial plane, fragments were usually displaced and horizontal tears parallel to the imaging plane or nonperipheral tears involving the superior or inferior aspects of the menisci may be difficult to detect. We found no such case, however, and the reformatted images into sagita b a b c Fig. 6. a. 3D reformatted image shows osteochondral defect (white arrows) and anteriorly displaced fragment (black arrowhead) b, c. Retrograde reevaluation of coronal (b) and sagittal (c) SE images may be suggeting the detached fragments as an ovoid low signal intensity (arrows), however, the osteochondral defect area is skipped. m x
6 Journal of the Korean Radiological Society 1996: 34(4) : tal or coronal planes might compensate for these possible shortcomings. With a sensitivity of 1 00% and a specificity of 98.1 %, the 3D protocol was accurate in the evaluation of the ACL ; this might be because of good resolution of reconstructed images in any arbitrary planes from original thin contiguous axial slices. ACL is a complicated structure of the knee, thinner than other knee ligaments and with a nonorthogonal orientation. On SE imaging, particularly with thicker slices, slight rotational changes in positioning or the presence of an effusion may substantially affect the visibility of the ligament (14). Because it is able to produce high-resolution reformatted images in any 이 ane, the 3D volume technique offers advantages in the evaluation of a nonorthogonal structure such as ACL. With regard to other ligamentous tears and other cartilaginous or osteochondral lesions, detectabilities of both techniques were same, even though 3D reformatted images tended to disclose more clearly subtle changes such as a small osteochondral fracture with anteriorly displaced fragment (Fig. 6). Because of the limited number of cases, we are unable to reach any conclusion concerning the reliability of 30FT GRASS in diagnosing lesions of the articular cartilage. The in-plane resolution of gradient- echo sequence has been known to be insufficientto consistently evaluate low- grade (grade 0 and 1) lesions correctly, even though it can separate cartilage from adjacent tissues and clearly depict high - grade lesions (4, 17, 18). Bone marrow abnormality was not evaluated. Trabecular bone imaged by 3D GRASS was lower in signal intensity and appeared coarser than that imaged by SE technique, probably due to the effect of increased magnetic susceptibility (4); gradient- echo images were less sensitive than fat - suppressed SE images in their depiction of bone bruise (Fig. 5) In summary, a 30FT GRASS sequence revealed itself at least comparable to a conventional SE sequence in the eval uation of internal structu res of the knee joi nt. It offered su perior sensitivity and specificity i n diagnosing tears of menisci and of ACL, and took only about 7.5 or 10 minutes for scanning and an additional several minutes for image reformation; this might not be a problem with regard to patient throughput. We therefore concluded that a 30FT GRASS sequence can be expected to supplement the standard techniques of MR knee i REFERENCES 1. Araki Y, Ootani F, Tsukaguchi 1, et al. MR diagnosis 01 meniscal tears 01 the knee: value 01 axial three-dimensional Fouriertranslorm GRASS images. AJR 1992 : 158: Aubel S, Heyd RL, Thaete FL, Wozney P. MR knee imaging : axial 30FT GRASS pulse sequence versus spin-echo imaging lor detecting meniscal tears. Magn Reson Imaging 1992; 1 이 4) Reeder JO, Matz SO, Becker L, Audelman SM. MR imaging olthe knee in the sagittal pr 이 ection : comparison 01 three-dimensional gradient-echo and spin-echo sequences. AJR 1989; Tyrrell RL, Gluckert K, Pathria M, Modic MT. Fast three-dimensional MR imaging 01 the knee : comparison with arthroscopy Radio/ogy 1988 : 166 : Spritzer CE, Vogler JB, Martinez S, et al. MR imaging olthe knee preliminary results with a 30FT GRASS pulse sequences. AJR 1988 ; 150 : Haggar AM, Froelich JW, Hearshen 00, Sadasvan K. Meniscal abnormalities 01 the knee: 30FT Fast-scan GRASS MR imaging AJR1988 ; 150: Reichen MA, Hartzman S, Ouckwiler GR, Bassett LW, Anderson LJ, Gold RH. Meniscal i 미 uries: detection using MR imaging Radiology 1986; 59: Stoller OW, Martin C, Crues JV 111, Kaplan L, Mink JH. Meniscal tears: pathologic correlation with MR imaging. Radio/ogy 1987; 163 : Manaster BJ. Magnetic resonance imaging 01 the knee. Semin ultrasoundct MR 1990; 11 (4) : Kelly MA, Flock T J, Kimmel JA, et al. MR imaging 01 the knee clarilication 01 its role. Arthroscopy 1991 ; 7(1): Lee JK, Yao L, Phelps CT, Wirth CR, Crajka J, Lozman J. Anterior cruciate ligamenttears: MR imaging compared with arthroscopy and clinical tests. Radiology 1988; 166: Glashow JL, Katz R, Schneider M, Scott WN. Oouble-blinded assessm ent 01 the value 01 magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis 01 anterior cruciate and meniscal lesions. J Bone Joint Surg 1989 ;71 A : Bassett LW, Grover JS, Seeger LL. Magnetic re sonance imaging 1 knee trauma. Skeletal Radio/1990: 19 : Mink JH, Levy T, Crues JVII I. Tears 01 the anterior cruciate ligament and menisci 01 the knee: MR imaging evaluation. Radi logy 1988 : 167: Crues JV, Mink J, Levy TL, Lotysch M, Stoller Ow. Meniscal tears 1 the knee:accuracy 01 MR imaging. Radio/ogy 1987; Price RR. Contrast mechanisms in gradient-echo imaging and an introduction to past imaging. Radiographics 1995 : 15: Recht MP, Kramer J, Marcelis S, et al. Abnormalities 01 articular cartilage in the knee: analysis 01 available MR techniques. Radiology 1993; 187 : Speer KP, Spritzer CE, Goldner JL, Garrett WE. Magnetic resonance imaging 01 traumatic knee articular cartilage i 미 - 548
7 Dong Joo Kim, et al: MR Imaging of the Knee 대한방사선의학회지 1996; 34(4) : 슬관절의자기공명영상 :3 차원퓨리어전환 GRASS 법 1 I 강북삼성병원방사선과 2 강북삼성병원정형외과 김동주 이영욱 윤은경 노인계 진승범 김준식 2 최재열 2 목적 슬관절자기공명영상방법의하나로삼차원퓨리어전환 GRASS 법으 진단적가치를알아보고자하였다. 대상및방법 : 1.5T 자기공명영상장치를이용하여 61 명의환자 63개의슬관절에서통상적인 2차원스핀에코밤법과 3차원 GRASS 방법에의한영상을얻어그결과를슬관절경이나그외수술소견에근거하여비교하였다.2차원스핀에코밤법으로는시상면의 T1 및 T2 강초영상과관상면의지밤신호억제를병행한 T2 강조영상을얻었다.3차원 GRASS 법으로는 0.7 또늠 1 mm 두께의 607H 연속횡단면영상을얻었고, 이때얻은영상과필요에따라여러방향으로재구성한영상을함쩨관찰하였다. 결과 :3차원 GRASS 법은 2차원스핀에코법에서발견하지못한 3예의내측반월판, 1 예의외측반월판, 3예의전방십자인대파열을진단하였고, 외측반월판과전방십자인대에있어서는특이도에서도우월한결과를보였다. 그외인대의파열이나글연글성병변의진단에있어서늠의미있는차이점은발견할수없었다.3차원 GRASS 법은반월판파열의정도나모앙판독에있어서우수하였다. 결론 :3차원 GRASS 법은슬관절내부구조이상의진단에있어적어도 2차원스핀에코법에견줄만하며, 특히반월판이나인대파열유무의진단이통상적 2차원스핀에코법으로어려운경우보조적자기공명영상법으로유용하리라사료된다
8 딩1. 시상부문 : 의학부분 2. 수상후보자의업적및자격 엽적기준 -창조, 탐구, 봉사정신무로국가빛인류발전에탁월한엽적을남긴자연구업적이사회의귀감이되고해당분야및사회적으로평가를받고있는자 -공공의이익에현저히공허한자 수상후보자의자격 -한국인및한국계인사로서추천일현재생존해있는자 3. 후보자추천인자격 호암상위원회위원 본위원회에서추천인으로위촉한분 ( 단체장및전문인사 ) 국제적인권위를지난상의수상자 호암상수상자및심사위원을역임한자 4. 구비서류 추천서 ( 본위원회소정양식, 학회비치 ) 2부 엽적증빙자료 ( 대표논문 3편이내 ) 5. 추천서접수및발표 접수기한 : 199 6년 9월 16일까지 접수처 : 본학회사무국또는호암상위원회접수처 발표및시상 : 1997년 2월일간지에발표후 3월 22일시상예정 기타자세한사항은본학회로문의바랍니다. 쉽터원고모집안내 쉽터의원고는방사선의학또는영상과관계가있는사진또는그럼으로서독자들에게흥미를줄수있는내용이어야합니다. 한쪽단위가되어야하며두쪽이상인경우는독립적으로가치가있어야하며, 게재여부는대한방사선의학회편집위원회에서결정하며게재료는학회에서부담합니다. n U
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries
 Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Original Research Article Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of traumatic knee joint injuries Dudhe Mahesh 1*, Rathi Varsha 2 1 Resident, 2 Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Grant
Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma
 Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original Research Article Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Knee Trauma Bhautik Kapadia 1, Bhumika Suthar 2* 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel
 ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
ROLE OF MRI IN EVALUATION OF TRAUMATIC KNEE INJURIES Saurabh Chaudhuri, Priscilla Joshi, Mohit Goel 1. Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis & imaging, Bharati Vidyapeeth Medical College and
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know.
 Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
Meniscal Tears with Fragments Displaced: What you need to know. Poster No.: C-1339 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. V. Ferrufino, A. Stroe, E. Cordoba, A. Dehesa,
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
a - CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) CASE PRESENTATION
 !Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
!Medical Education Singapore Med J 2012; 53(4) 283 CM EARTICLE Clinics in diagnostic imaging (139) Wei Yang Liml, MBBS, FRCR, Nor Azam Mahmud2, MD, MMed, Wilfred CG Peh3, FRCP, FRCR a - - - Fig. 1 Sagittal
MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee
 Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Original Research Article MRI versus clinical examination for the diagnosis of meniscal and ligamentous injuries of kneee Rakesh Gujjar *, R. P. Bansal, L. K. Gotecha, Raja Kollu Department of Radio-diagnosis
Key words: arthroscopy, orthopaedic examination, magnetic resonance imaging, knee injury.
 Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
Original paper Videosurgery Arthroscopic verification of objectivity of the orthopaedic examination and magnetic resonance imaging in intra-articular knee injury. Retrospective study Julian Dutka, Michał
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci. Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System
 MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
MRI of the Knee: Part 2 - menisci Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health System Learning Objectives At the end of the presentation, each participant should be able to: describe the normal anatomy
Knee: Cruciate Ligaments
 72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
72 Knee: Cruciate Ligaments R. Kent Sanders Sagittal oblique 2.5-mm sequences along the plane of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) typically yield three to four images of the ACL, with the first medial
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title MR-IMAGING OF TIBIAL COLLATERAL LIGAMENT INJURY - COMPARISON WITH CLINICAL EXAMINATION Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2bs9g934 Journal SKELETAL RADIOLOGY,
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MRI Evaluation of Internal derangement of the Knee Joint - A PICTORIAL REVIEW Poster No.: C-1386 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Nadaraja, F. Abubacker Sulaiman; Chennai/IN Keywords:
MENISCAL INJURY. Meniscus. Anterior Roots. Medial Meniscus. Lateral Meniscus. Posterior Roots. MRI and Arthroscopic Findings
 Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Meniscus Anterior Roots MENISCAL INJURY MRI and Arthroscopic Findings Medial Meniscus AH PH PH AH Lateral Meniscus Rawiwan Pattaweerakul Naresuan University Hospital Posterior Roots Meniscus Normal Meniscus
Original Research Article. Atul Bucha 1, Sunita Dashottar 2 *, Surabhi Sharma 2, Preeth Pany 2, Rushabh Bhikhanhai Suthar 2
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20184747 A study to evaluate
Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/442 Evaluation of Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Knee Joint Injuries in Correlation with Arthroscopy T Sundara
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 199-204 199 Stability of Post Traumatic Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee: MR Imaging Findings YU-CHUNG HUNG 1 JON-KWAY HUANG 1,2 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics
 Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Knee: Meniscus Back to Basics Kyung Jin Suh kyungjin.suh@gmail.com Doctor Radiology, Daegu, KOREA Medial Lateral 7.7 10.2 11.6 9.6 10.6 mm Posterior > Anterior horn 10.6 mm Posterior = Anterior horn Medial
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of age?
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:1129 1139 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0384-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:1129 1139 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0384-5 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Are radiographs needed when MR imaging is performed for non-acute knee symptoms in patients younger than 45 years of
2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion
 1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
1 2 1 1 1 2 A B Fig. 1. Lateral tibial condyle fracture with joint effusion in a 35-year-old man. Sagittal T2-weighted MRI shows a large amount of effusion (between arrowheads) in the suprapatellar pouch,
MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 5, September: 1865-1872, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net MRI Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears: What is the Added Value of Oblique Sagittal Technique?
"BONE BRUISES" OF THE KNEE: A REVIEW
 "BONE BRUISES" OF THE KNEE: A REVIEW Chad E. Mathis, M.D. Ken Noonan, M.D. Kosmas Kayes, M.D. ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is often used - to assess the location and degree of ligamentous wm.
"BONE BRUISES" OF THE KNEE: A REVIEW Chad E. Mathis, M.D. Ken Noonan, M.D. Kosmas Kayes, M.D. ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is often used - to assess the location and degree of ligamentous wm.
Table 2. Mean Scores of Articular Cartilage by Qualitative E v a l u a t i o n
 5 7 7 Table 2. Mean Scores of Articular Cartilage by Qualitative E v a l u a t i o n S e q u e n c e s without MTC (scores, 04 ) with MTC (scores, 04 ) E f f e c t s (scores, 03 ) PDWSE 1.2 1.6 0. 8 T2WSE
5 7 7 Table 2. Mean Scores of Articular Cartilage by Qualitative E v a l u a t i o n S e q u e n c e s without MTC (scores, 04 ) with MTC (scores, 04 ) E f f e c t s (scores, 03 ) PDWSE 1.2 1.6 0. 8 T2WSE
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls
 Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Meniscal tears on 3T MR: Patterns, pearls and pitfalls Poster No.: C-2221 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: J. C. Kandathil; Singapore/SG Keywords: Knee injuries,
Imaging the Athlete s Knee. Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado
 Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
Imaging the Athlete s Knee Peter Lowry, MD Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Colorado None Disclosures Knee Imaging: Radiographs Can be performed weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing View options
B one contusion is a finding substantiated by magnetic
 592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
592 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The appearance of kissing contusion in the acutely injured knee in the athletes I P Terzidis, A G Christodoulou, A L Ploumis, S R Metsovitis, M Koimtzis, P Givissis... See end of article
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears
 Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Do Not Fall on Your Knees - Recognizing Common and Uncommon Pitfalls that May Simulate Meniscal Tears Poster No.: C-1146 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Musa Aguiar, J. Goncalves,
Ultrasound assessment of internal derangement of the knee
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 72-76 ORIGINAL STUDY sound assessment of internal derangement of the knee Zaka KHAN, Zia FARUQUI, Olajide OGYUNBIYI, Guy ROSSET, Javaid IQBAL From Armed Forces Hospital, Southern
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ULTRASOUND EVALUATION OF NORMAL AND ABNORMAL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Palle Lalitha, 1 M. Ch. Balaji Reddy, 1 K. Jagannath Reddy, 1 Vijaya Kumari 2 1 Department
Imaging the Knee 17/10/2017. Friction syndrome Common in runners or cyclists Fluid between ITB and Lateral femoral condyle
 17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
17/10/2017 Imaging the Knee Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Iliotibial Band Syndrome Ligamentous Tears (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL) Meniscal Tears Cartilage Degeneration Quadriceps/Patellar tendinosis Osteochondral
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 118 No 1209 ISSN 1175 8716 Reliability of magnetic resonance imaging for traumatic injury of the knee Keith Winters, Russell Tregonning Abstract Background: Magnetic
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE
 MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
MENISCAL ANATOMY ADVANCED IMAGING OF THE KNEE MENISCAL ABNORMALITIES MENISCAL FUNCTION MENISCAL FUNCTION load transmission shock absorption stability The menisci DO NOT function as primary stabilizers
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177)
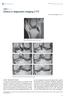 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(5): 241-245 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017038 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (177) Poh Lye Paul See, MBBS, FRCR Fig. 1 Sagittal proton density (PD)-weighted fast spin-echo
Unlocking the locked Knee
 Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Unlocking the locked Knee Poster No.: P-0027 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. P. SINGH, S. Srivastava, S. S. BAIJAL ; Gurgaon, Delhi 1 1 2 1 2 NCR/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR PRADESH/IN
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis?
 Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
Skeletal Radiol (2012) 41:273 280 DOI 10.1007/s00256-011-1169-4 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Stable or unstable tear of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee: an MR diagnosis? Pieter Van Dyck & Jan L. Gielen
The Meniscus. History. Anatomy. Anatomy. Blood Supply. Attachments
 History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
History The Meniscus W. Randall Schultz, MD, MS Austin, TX January 23, 2016 Meniscus originally thought to represent vestigial tissue 1883 first reported meniscal repair (Annandale) Total menisectomy treatment
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION
 LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
LATERAL MENISCUS SLOPE AND ITS CLINICAL RELEVANCE IN PATIENTS WITH A COMBINED ACL TEAR AND POSTERIOR TIBIA COMPRESSION R. ŚMIGIELSKI, B. DOMINIK, U, ZDANOWICZ, Z. GAJEWSKI, K. SKIERBISZEWSKA, K. SIEWRUK,
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and
 MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
MR Imaging of a Posterior Root Tear of the Medial Meniscus: Diagnostic Accuracy of Various Tear Configurations and Associated Knee Abnormalities 1 Hyang Mi Lee, M.D., Jae Chan Shim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim,
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy
 Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
Open Access Original Article Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of Meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy Jamal Yaqoob 1, Muhammad Shahbaz Alam 2, Nadeem Khalid
MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26026:2263 Radiology Section Original Article MR Imaging Based Diagnosis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears in Patients with Internal Derangement of Knee Hemanth Purigali Naganna,
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol
 KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
KNEE ALIGNMENT SYSTEM (KAS) MRI Protocol Sample referral sticker Referral Sticker Insert here Corin 17 Bridge Street Pymble NSW Australia 2073 P: +61 (0)2 9497 7400 F: +61 (0)2 9497 7498 E: KAS.customerservice@coringroup.com
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance
 Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Multi-ligamentous knee injuries - MRI injury patterns at a glance Poster No.: P-0068 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Rastogi, D. Whelan, R. Martin, W. Mak, D. Pearce ; 1 1 1 2
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA
 Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Knee MRI Update Case Review 2009 Russell C. Fritz, M.D. National Orthopedic Imaging Associates San Francisco, CA Meniscal Tears -linear increased signal extending to an articular surface is the hallmark
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study
 Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
Proximal tibial bony and meniscal slopes are higher in ACL injured subjects than controls: a comparative MRI study Ashraf Elmansori, Timothy Lording, Raphaël Dumas, Khalifa Elmajri, Philippe Neyret, Sebastien
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
A comparative study of MRI versus arthroscopic findings in ACL and meniscal injuries of the knee
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kulkarni OP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):198-202 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180123
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE?
 HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
HOW DO WE DIAGNOSE LAMENESS IN YOUR HORSE? To help horse owners better understand the tools we routinely use at VetweRx to evaluate their horse s soundness, the following section of this website reviews
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
The Meniscal Roots: Gross Anatomic Correlation with 3-T MRI Findings
 rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
rody et al. Meniscal Root MRI Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey M. rody 1 Michael J. Hulstyn 2 raden. Fleming 3 Glenn. Tung 1 rody JM, Hulstyn MJ, Fleming, Tung G Keywords: anatomy, knee,
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
A picture is worth a thousand words - MRI in ACL injury
 A picture is worth a thousand words - MRI in ACL injury Poster No.: C-0820 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, V. Elangovan; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal
A picture is worth a thousand words - MRI in ACL injury Poster No.: C-0820 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Abubacker Sulaiman, V. Elangovan; Chennai/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic Acute vs Chronic Mechanism of injury Swelling, catching, instability Previous evaluation and treatment General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate
Physical Examination of the Knee
 History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
History: Pain Traumatic vs. atraumatic? Acute vs Chronic Previous procedures done on the knee? Swelling, catching, instability General Setup Examine standing, sitting and supine Evaluate gait Examine hip
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
BASELINE QUESTIONNAIRE (SURGEON)
 SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
SECTION A: STUDY INFORMATION Subject ID: - - Study Visit: Baseline Site Number: Date: / / Surgeon ID: SECTION B: INITIAL SURGEON HISTORY B1. Previous Knee Surgery: Yes No Not recorded B2. Number of Previous
IMAGING TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 4. Imaging techniques
 IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
Disclosures. Background. Background
 Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Kinematic and Quantitative MR Imaging Evaluation of ACL Reconstructions Using the Mini-Two Incision Method Compared to the Anteromedial Portal Technique Drew A. Lansdown, MD Christina Allen, MD Samuel
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
MRI Appearance of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations William Rodriguez, Jr. 1 Emily N. Vinson 1 Clyde. Helms 1 lison P. Toth 2 Rodriguez W Jr, Vinson EN, Helms C,
MRI of Osteochondral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle: Incidence and Pattern of Injury After Transient Lateral Dislocation of the Patella
 Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Sanders et al. MRI of Osteochond ral Defects of the Lateral Femoral Condyle Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:1332 1337 0361 803X/06/1875
Overview Ligament Injuries. Anatomy. Epidemiology Very commonly injured joint. ACL Injury 20/06/2016. Meniscus Tears. Patellofemoral Problems
 Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
Overview Ligament Injuries Meniscus Tears Pankaj Sharma MBBS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Manchester Royal Infirmary Patellofemoral Problems Knee Examination Anatomy Epidemiology Very
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
