Namma Kalvi NEW CHALLENGE TUITION CENTRE 11 TH BIO-ZOOLOGY UNIT- 4 STUDY MATERIAL 9. LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
|
|
|
- Frederick Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Locomotion: Uses of locomotion Namma Kalvi NEW CHALLENGE TUITION CENTRE 11 TH BIO-ZOOLOGY UNIT- 4 STUDY MATERIAL 9. LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT Movement of the organism from one place to another is called locomotion. Search for food Shelter mating (reproduction) To escape from the predator Locomotion has evolutionary significance and etc. Types of movement: The different types of movements that occur in the cells of our body. 1. Amoeboid movement: The movement by means pseudopodium is called amoeboid movement. Amoeboid movement characteristic feature of an amoeba. Pseudopodium is a temporary projection of cytoplasm formed on the body to protect pathogens. It occurs in macrophages. 2. Ciliary movement: Ciliary movement occurs in the respiratory passages and genital tract. It is made of ciliated epithelial cells. 3. Flagellar movement: Flagellar movement is the swimming brought about by the beating of flagella. The sperm cells show flagellar movement
2 4. Muscular movement: This type of movement occurs in the muscle cells so it is called muscular movements. E.g. the movements of hand, legs, jaws, and tongue etc.. Muscular systems: Types of muscles: Types: ********$************* Muscles are specialized tissues which are derived from the embryonic `mesoderm s` Muscles are made of a group of cells called `myocytes`. Muscle is a soft tissue found in most of the animals. The study of tissue is called `Histology`. The muscle is classified into three types, based on the locomotion. 1. Skeletal muscles (Striated muscles) Skeletal muscle is closely associated with skeletal components. So it is called skeletal muscles. These muscles are exhibit striation so it is also called `striated muscles` They are voluntary in nature.
3 2. Visceral muscle (Striated muscles) 3. Cardiac muscles Visceral muscles are located in the inner walls of hollow visceral organs of the body like an alimentary canal, and reproductive tract etc... They do not exhibit any striation. So they are called smooth muscles or nonstriated muscles. Cardiac muscles are the muscles of the heart. It is striated and voluntary in nature. ***************$*********** Types of skeletal muscle contraction: 1. Isometric contraction: Iso - same The process by which muscles are shortening is termed `muscle contraction` They are two types of muscle contractions namely isometric and isotonic contraction. Metric - Length 2. Isotonic contraction: Iso - same A contracting muscle retains its original length so this type of contraction is called an isometric contraction. E.g pushing against a wall, holding a heavy bag etc Tonic tension The muscle is able to move a load and it shortens during a contraction so it is called `isometric contraction` E.g the body muscle help in the process of walking. **************$*************
4 Types of skeletal muscle fibers: 1. Red / slow: 2. Red / fast: 3. White / fast: The skeletal muscle fibers are classified as different types. Based on Rate of shortening Either fast or slow ATP needed for contraction and Either oxidative or glycolytic. Type I fibers slow twitch fibers Type II a fibers fast oxidative fibers or termed as red muscle fibers. Type II b fibers fast glycolytic fibers or termed as white muscle fibers. a) Oxidative fibers b) Glycolytic fibers (GF) Oxidative fibers primarily use oxidative phosphorylation. The oxidative fibers are termed as `red muscle fibers` Large stores of glycogen are called glycolytic fibers. Gf are termed as white muscle fibers because there is myoglobin are absent ****************$**************** Mechanism of muscle contraction: Mechanism of muscle contraction is processed by which muscle are shortening is termed `muscle contraction` The mechanism of muscle contraction is best explained by `sliding filament theory`. This theory was proposed by Huxley, Andrew F. and Rolf Niedergerke in Mechanisms: An action potential is originating in the central nervous system (CNS) and reach as to the alpha motor neuron. The junction between an alpha motor neuron and sarcolemma of the muscle fibers is called neuromuscular junction (JMN) or motor end plate.
5 The signal reaching this junction releases a chemical called acetylcholine. It leads to the depolarization of the motor end plate. Utilizing the energy from ATP hydrolysis, the head of the myosin bind active sites on actin and form a cross bridge and causes of muscle contraction. The ATP molecule split again and myosin head is reactive for the next cycle to begin. Structure of contractile proteins: *************$************* o Contraction of the muscle depends on the presence of contractile proteins such as actin and myosin in the myofilaments. o Each myosin molecule is made up of a monomer called meromyosin. o Meromyosin: (two regions) a) Short arm-heavy meromyosin (HMM) b) Tail portion- Light meromyosin (LMM) *************$************
6 Skeletal functions its function: Functions: The skeletal system is constituted by a framework of bones and cartilages. It is derived from the embryonic mesoderm. Muscles are attached to the bones by means of tendons and provide the necessary force required for the bones of the skeleton to operate as levers. There are three types of skeletal systems. They are, 1. Hydrostatic skeleton 2. Exoskeleton and 3. Endoskeleton In human beings, the skeletal system is made up of 206 bones and cartilages. It is grouped into two principal divisions the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones and the appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones 1. Supports surrounding tissues (Total body) 2. Protects vital organs and soft tissues. 3. Manufactures blood cells. 4. Stores minerals & salts 5. Locomotion- It acts as a liver along with the muscles attached to it. Parts of skeletal muscles: *************$*********** Each muscle cell is called muscle fibers Each muscle fiber is surrounded by endomysium A group of muscle fibers bundled together by collagen to form fasciculi or fascicle. Each fascicle is surrounded by perimysium. All the fascicle collectively from the muscle belly. Each muscle belly is surrounded by a connective layer called epimysium. The plasma membrane of the muscle fiber is called sarcolemma and the cytoplasm is called sarcoplasm.
7 The sarcoplasm contains numerous protein filaments are called myofibrils. Each myofibril contains thin filament actin and thick filament myosin. Myofibrils are surrounded by a network of tubules and channels called sarcoplasmic reticulum. The calcium stored in this area. Actin Actin is a muscle protein. It is present in the thin filament of muscles. It is a fibrous protein It is an insoluble protein. It exists in two forms, namely G-actin and F-actin. The formation of F-actin from G-actin is called polymerization. Polymerization requires salts and ATP. During muscle contraction, actin combines with myosin to form actomyosin. Actin + myosin Actomyosin Myosin Myosin is a muscle protein. It is present in the thick filaments brings about the contraction. It is a fibrous protein. It is an insoluble protein. It consists of a rod-like tail, a neck, and a head. When myosin is treated with trypsin (enzyme). It is split into two components, namely light meromyosin and heavy meromyosin. Tropomyosin and troponin: Tropomyosin and troponin are the two main proteins that regulate actin and myosin interactions. OR Tropomyosin is a long strand that twisted around F-actin filaments and prevents muscle contraction. Troponin is distributed in regular intervals on the surface of tropomyosin.
8 Structure of Sarcomere: A sarcomere is the basic unit of skeletal muscle tissue. It is made of central dark band and two half - light bands. The light band contains actin and it is called I band or isotropic band. The dark band contains myosin and it s called A band or anisotropic band. The actin is a thin filament and myosin is a thick filament. ***************$**************
9 Human skeletal system: In human beings, the skeletal system is made up of 206 bones and cartilages. It is grouped into two principal divisions. They are, 1. Axial skeletal and (consist of 80 bones) 2. Appendicular skeleton (consist of 126 bones) 1. Axial skeletal and (consist of 80 bones) a) Skull: Axial skeleton forms the main axis of the body. It consists of the skull, hyoid bone, vertical column, and thoracic cage. The skull is composed of two sets of bones a) Cranial bones and b) Facial bones (consistn14 bones) The cranial bones form the hard protective outer covering of the brain is called the brain box. The capacity of the cranium is 1500 cm 3 The upper jaw is formed of the maxilla. The lower jaw is formed of the mandible.
10 b) Hyoid bone: o The hyoid bone is a U-shaped bone present at the base of the buccal cavity. o It is the only one bone without joints. o It is movable bone. o It is connected to the cranium. c) Vertibral column (consist 33 bones) The vertibral column is also called the backbone. The vertebral column has five major regions. They are, Vertebral column 1. Cervical 2. Thoracic 3. Lumbar 4. Sacrum and 5. Coccyx
11 Atlas and axis The first vertebra is called the atlas and the second vertebra is called the axis. The Sternum (chest bone 1) The sternum is a flat bone on the mid-ventral line of the thorax. It provides space for the attachment of the thoracic ribs and abdominal muscle. d) The rib cage (consist of 24 bones) There are 12 bones pairs of ribs. Each rib is a thin flat bone connected dorsally to the vertebral column. It has two articulation surfaces on its dorsal end, hence called bicephalic The first seven pairs of ribs called true ribs or vertebra-sternal rib. Rib cage protects the lungs, heart liver and also plays a role in breathing. 2. The appendicular skeleton. The bones of the upper their girdles constitute the appendicular skeleton. The appendicular skeleton is composed of 126 bones.
12 a) The pectoral girdle or shoulder girdle The pectoral girdle is a set of bones in the appendicular skeleton. The pectoral girdle consists of a clavicle or collarbone and a scapula. The upper limbs are attached to the pectoral girdles. Acromion: The acromion is a bony process. Together with the coracoid process, it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. Glenoid cavity or fossa; Below the acromion is a depression is called the glenoid cavity. The upper limb: The upper limb consists of 30 separate bones and is specialized for mobility. The skeleton of the arm, the region between the shoulder and elbow is the humans. b) The pelvic girdle The pelvic girdle is a heavy structure specialized for weight bearing. It is composed of two hip bones called coxal bones.
13 The lower limb The lower limb consists of 30 bones which carry the entire weight of the erect body and is subjected to exceptional forces when we jump or run. ************$********** Joints: A joint, or articulation, is the place where two bones come together. Fibrous- Immovable: connect bones, no movement. (Skull and pelvis). Cartilaginous- slightly movable, bones are attached by cartilage, a little movement (spine or ribs). Synovial- freely movable, much more movement than cartilaginous joints. Cavities between bones are filled with synovial fluid. This fluid helps lubricate and protect the bones. Types of bone cells 1. Osteocytes 2. Osteoblasts 3. Osteoclasts Mature bone cells Bone-forming cells Bone-destroying cells Break down bone matrix for remodeling and release of calcium Bone remodeling is a process by both osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Disorders of muscular system: o Myasthenia gravis o Tetany o Muscle fatigue o Atrophy o Muscle pull o Muscular dystrophy *************$************
14 Disorders of skeletal system: 1. Arthritis - Inflammation of the joints 2. Osteoporosis 3. Osteomyelitis Osteo arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis Gouts arthritis or gout Joint damage that occurs when articular cartilage softens & breaks down = pain, stiffness, & restricted movement Causes include: aging, irritation, wear & abrasion of joints Most common type of chronic arthritis Frequently affects fingers, spine, knees & hips Infection of the bone Causes include: invading bacteria, pneumonia, typhoid, inflammation of teeth, and injury to bone ************$********** ALL THE BEST Issued By New challenge tuition group Nannilam Thiruvarur-Dt Tamilanadu newchallengetuition.ed@gmail.com Cell:
Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012
 Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012 Definition Learning Objectives Types of movement Muscle Skeletal system Joints Disorders of muscular and skeletal system What is locomotion? Displacement of an animal from one
Vikasana Bridge Cource 2012 Definition Learning Objectives Types of movement Muscle Skeletal system Joints Disorders of muscular and skeletal system What is locomotion? Displacement of an animal from one
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 36
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 36 Impacts, Issues Pumping Up Muscles Increasing muscle size and strength with drugs such as andro has unwanted side effects and can damage other organ systems 36.1
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT
 114 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 20 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Match the following and mark the correct option Column I Column II A. Fast muscle fibres i. Myoglobin B. Slow
114 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 20 LOCOMOTION AND MOVEMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Match the following and mark the correct option Column I Column II A. Fast muscle fibres i. Myoglobin B. Slow
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
 Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Skeletal system. Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments
 Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
Skeletal System 1 Skeletal system Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilage and ligaments Functions: Support (structural support of whole body) Storage of minerals (calcium) Storage of
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Motion the skeleton and muscles The musculoskeletal system
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Motion the skeleton and muscles The musculoskeletal system
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Anatomy & Physiology Muscular System Worksheet 1. What are the three categories of muscle tissue? a) b) c) 2. The smallest functional unit of a muscle fiber is called a. 3. What are the four characteristics
Lecture 5. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2.
 Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 33
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Chapter 50. You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium. Chemoreception taste and smell
 1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
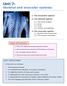 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Chapter 30 How Animals Move
 Chapter 30 How Animals Move PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Chapter 30 How Animals Move PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 09: The Muscular System Question No. 1 of 10 The muscular system of the human body fulfills many different roles. Which of the following statements about the
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Bones are made up of bone cells and tissues Hard, dense and smooth outer materials, which are made of calcium, give bones there shape and strength.
 1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Animal Skeletons. Earthworm peristaltic movement. Hydrostatic Skeletons
 Animal Skeletons The Musculo-Skeletal System Functions: Support Protection Movement all movement results from: muscle working against a skeleton 3 Types of skeletons hydrostatic exoskeleton endoskeleton
Animal Skeletons The Musculo-Skeletal System Functions: Support Protection Movement all movement results from: muscle working against a skeleton 3 Types of skeletons hydrostatic exoskeleton endoskeleton
BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan
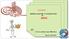 Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
BIO 130 Anatomy and Physiology Spring, 2016 Exam 3 Name: Course ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial tissue? a. It
Station 1. Match the structures of the gross anatomy of the muscle.
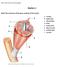 NCSO 2016 Anatomy and Physiology B Station 1 Match the structures of the gross anatomy of the muscle. A. Tendon B. Epimysium C. Muscle fiber D. Bone E. Perimysium F. Blood vessels G. Endomysium H. Fascicle
NCSO 2016 Anatomy and Physiology B Station 1 Match the structures of the gross anatomy of the muscle. A. Tendon B. Epimysium C. Muscle fiber D. Bone E. Perimysium F. Blood vessels G. Endomysium H. Fascicle
Muscle Physiology. Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College
 Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
Muscle Physiology Bio 219 Dr. Adam Ross Napa Valley College Muscle tissue Muscle is an excitable tissue capable of force production Three types Skeletal- striated, voluntary Cardiac- non-striated, involuntary
Types of Muscle. Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart
 Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
Muscular System Types of Muscle Skeletal striated & voluntary Smooth involuntary Cardiac - heart The word striated means striped. Skeletal muscle appears striped under a microscope. Muscles and Muscle
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function
 Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Anatomy & Physiology. Unit Two. Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection
 Anatomy & Physiology 9 Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection http://curry.edschool.virginia.edu/go/frog/home.html Cat Dissection http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/cat_dissect/index.htm List of Muscles http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/
Anatomy & Physiology 9 Muscular System URLs Frog Dissection http://curry.edschool.virginia.edu/go/frog/home.html Cat Dissection http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/ap/cat_dissect/index.htm List of Muscles http://www.meddean.luc.edu/lumen/meded/
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 ( ) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 1 (101-805) For Intensive Nursing PAUL ANDERSON SAMPLE TEST 3 2011 1. If calcium levels in the extracellular fluid are too low, parathyroid hormone secretion would and osteoclast activity
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Muscle and Muscle Tissue
 Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Muscle and Muscle Tissue Make up about half of total body mass Exerts force by converting chemical energy, ATP, to mechanical energy Muscle tissue is classified based on Shape Number and position of nuclei
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
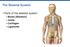 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Bone myths
 Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Skeletal and Muscular Systems Bone myths Myth No. 1: A fracture is a milder form of bone injury than a broken bone. Myth No. 2: Once bones are fully developed, they stop changing. Myth No. 3: Osteoporosis
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Types of Skeletal Systems. Hydrostatic Skeletons. Hydrostatic Skeletons. Hydrostatic Skeletons. The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 47 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure, called the skeletal system -Zoologists recognize three types:
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 47 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure, called the skeletal system -Zoologists recognize three types:
The Skeletal System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
(c) sarcolemma with acethylcholine (protein) receptors
 (slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
(slide 1) Lecture Notes: Muscular System I. (slide 2) Introduction to Muscular System A) Tissues of the Muscular System: 1) Connective Tissues (a) dense fibrous (tendons and ligaments) 2) Nervous Tissue
