Use of a Trochanteric Flip Osteotomy Improves Outcomes in Pipkin IV Fractures
|
|
|
- Kimberly Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2009) 467: DOI /s z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Use of a Trochanteric Flip Osteotomy Improves Outcomes in Pipkin IV Fractures Brian D. Solberg MD, Charles N. Moon MD, Dennis P. Franco MD Received: 24 March 2008 / Accepted: 26 August 2008 / Published online: 18 September 2008 Ó The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons 2008 Abstract The optimal surgical approach for combined femoral head and acetabular fractures (Pipkin IV) is controversial because of their rarity and lack of definitive reports. Surgical dislocation with trochanteric flip osteotomy (TFO) allows simultaneous exposure of the acetabulum and femoral head. We protected the obturator internus and inferior capsule during repair with a heavy suture at the inferior extent of the traumatic capsulotomy. We retrospectively reviewed 12 patients with Pipkin IV fractures treated using this approach during a 6-year period. The minimum followup was 24 months (mean, 47 months; range, months). Clinical outcomes were measured using the Merle d Aubigné-Postel and Thompson-Epstein scoring scales. Radiographically, all patients achieved healing of their acetabular fractures; 11 achieved healing of the femoral head fracture and osteonecrosis developed in one patient. The average Merle d Aubigné-Postel score was 15.6 of 18; using the Thompson-Epstein score, 10 of the 12 patients had good or excellent outcomes, one had a fair outcome, and one had a poor outcome. Trochanteric flip osteotomy allowed for simultaneous exposure and repair of both lesions in Pipkin IV fractures. Using a uniform surgical Each author certifies that he or she has no commercial associations (eg, consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangements, etc) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article. Each author certifies that his or her institution has approved the human protocol for this investigation, that all investigations were conducted in conformity with ethical principles of research, and that informed consent for participation in the study was obtained. B. D. Solberg (&), C. N. Moon, D. P. Franco Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, 444 South San Vicente Boulevard, Suite 603, Los Angeles, CA 90048, USA brian.solberg@cshs.org protocol with TFO rendered clinical results comparable to previously reported outcomes in series of isolated femoral head fractures. Level of Evidence: Level IV, therapeutic study. See the Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence. Introduction Combined femoral head and acetabular fractures (Pipkin IV) are relatively rare injuries with an incidence of one in seven to one in 15 traumatic hip dislocations in adults [2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 14, 18, 21] (Fig. 1). The original description of Pipkin fractures by Thompson and Epstein included a heterogeneous group of hip dislocations and fractures [14, 20]. They concluded a majority could be treated with observation and traction or fragment excision in cases with femoral head comminution. Currently, evidence supports treatment of isolated, displaced femoral head fractures through a modified anterior (Smith-Petersen) approach with approximately 80% good and excellent long-term outcomes using the Merle d Aubigné-Postel scoring system [2, 4, 9, 11, 15, 17]. The optimal surgical approach for combined lesions remains controversial because of the inability to address both fractures through a single surgical approach. No outcomes data are available regarding the use of combined anterior and posterior approaches for Pipkin IV fractures. Some authors believe repair of the posterior wall fracture is essential to restore hip stability and should take priority surgically, but it is unclear whether concomitant repair of the femoral head is warranted [15, 17, 19]. Larger series suggest Pipkin IV fractures have poorer outcomes compared with isolated femoral head fractures [9, 15, 17, 19]. Drawing meaningful conclusions from the
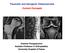
2 930 Solberg et al. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research Fig. 1 The typical radiographic appearance of a Pipkin IV fracture after closed reduction of hip dislocation is shown. The intraoperative photograph was taken of the right hip in the lateral decubitus position with directional orientation indicated. data is difficult because of the rarity of the injury and heterogeneity of the surgical approaches used to treat them in these series [9, 15, 17]. Surgery for Pipkin IV fractures generally has focused on repair of the posterior wall fractures through a standard posterior (Kocher-Langenbeck) approach [2, 17 19]. Problems included considerable risk of femoral head osteonecrosis (ON) using the posterior approach and inability to simultaneously address the anterior femoral head fracture without a second approach. Trochanteric flip osteotomy has been described for management of femoral-acetabular impingement, acetabular fractures, and femoral head fractures [7 9, 16]. This technique allows simultaneous exposure and repair of both elements of Pipkin IV fractures without compromising the femoral head vasculature [12]. We report the radiographic outcomes, including rates of ON and heterotopic ossification, and clinical outcomes using the Merle d Aubigné-Postel and Thompson-Epstein scoring systems in 12 patients with Pipkin IV fractures managed surgically with a TFO approach during a 6-year period. Materials and Methods We retrospectively reviewed the records and radiographs of 15 patients treated with a TFO for Pipkin IV fractures between May 2000 and January During this same time, 67 patients presented to our institution with traumatic posterior hip dislocation. Inclusion criteria were documented posterior hip dislocation in an adult, Pipkin IV fracture with greater than 2 mm displacement of the femoral head or acetabular fragment, and complete radiographic and clinical followups for a minimum of 24 months (mean, 47 months; range, months). Complete radiographic and clinical followup data were available for 12 of the 15 patients and these 12 patients constitute the basis of the report. Ten patients were male and two were female. Associated injuries were present in 10 of the 12 patients with an average Injury Severity Score of 17 (range, 9 42). No patients were recalled specifically for this review. Three patients were lost to followup. Institutional Review Board approval was obtained for retrospective data analysis. We classified fracture patterns using the Pipkin, Brumback, and Orthopaedic Trauma Association classifications [1, 13, 14]. Ten patients had infrafoveal femoral head fractures we classified as Brumback Type 1B, and two patients had a transfoveal fracture classified as Type 2B. Using the Orthopaedic Trauma Association classification, all femoral head fractures were Type 31.C1; 11 acetabular fractures were Type 62.A2 (posterior wall); and one was a Type 62-B2.3a [3] (transverse posterior wall). Patients presenting to our emergency department had closed reduction of the hip dislocation in the emergency department within 1 hour of presentation. All patients underwent CT of the pelvis with 3-mm cuts through the acetabulum and proximal femur. Patients with continued hip instability after closed reduction were treated with distal femoral traction. We performed the surgery with the patients in the lateral position on a standard flat radiolucent table using the previously described technique for TFO. The piriformis was tagged and released, but the short external rotators (gemelli and obturator internus) and inferior capsule were preserved during the approach. We identified the posteroinferior-most extent of the traumatic capsulotomy and protected it with a heavy suture to prevent further inferior extension of the capsulotomy at the time of surgical dislocation (Fig. 2). The femoral head fracture was repaired first with headless variable-pitch screws (Accutrac; Acumed, Hillsboro, OR, or Herbert; Zimmer, Warsaw, IN) countersunk below the articular surface (Fig. 3). The repaired femoral head then was reduced and used as a template for posterior wall repair using standard pelvic plates (Stryker, Mahwah, NJ; Synthes, West Chester, PA). None of the acetabular fractures extended below the level of the obturator internus and were exposed in the cephalad portion of the TFO approach. The superior portion of the posterior column was exposed by subperiosteal elevation of the gluteus minimus allowing access to the anterior aspect of the fracture. The trochanteric osteotomy was repaired using either 3.5-mm cortical screws or 6.5-mm cancellous screws. The overlying
3 Volume 467, Number 4, April 2009 TFO for Pipkin IV Fractures 931 Fig. 2 The inferior margin of the traumatic capsulotomy is identified and protected with a tag suture. The intraoperative photograph was taken of the right hip in the lateral decubitus position with directional orientation indicated. GMED = gluteus medius; G MIN = gluteus minimus; OI = obturator internus; PI = piriformis tendon; Q = quadratus femoris; VLAT = vastus lateralis; Ant = anterior; Inf = inferior; Post = posterior; Sup = superior; FH = femoral head. structures were closed over a small suction drain. At the time of surgical repair, there was no active bleeding from the inferior head fragment in 11 of 12 cases; limited bleeding occurred in one case. Eleven patients underwent femoral head repair and one patient had excision of the femoral head fragments. Labral tears were present in all patients and were located in the superior acetabular rim. Seven of 12 tears were firmly adherent to the posterior wall fragment and were repaired indirectly by osteosynthesis. The other five were detached from the posterior wall fragments and excised. Average surgical time was 121 minutes (range, minutes); average blood loss was 350 ml (range, ml); and the average time to surgery was 3 days postinjury (range, 1 12 days). Postoperatively, pain was managed with patient-controlled analgesia for the first 48 hours. We applied Fig. 3 A displaced femoral head fracture after hip dislocation is shown. The intraoperative photograph was taken of the right hip in the lateral decubitus position with directional orientation indicated. GMED = gluteus medius; G MIN = gluteus minimus; OI = obturator internus; PI = piriformis tendon; Q = quadratus femoris; VLAT = vastus lateralis; Ant = anterior; Inf = inferior; Post = posterior; Sup = superior; AC = anterior capsule; FH = femoral head; La = acetabular labrum; TO = trochanteric osteotomy. sequential compression stockings intraoperatively and patients were administered low-molecular-weight heparin (Fragmin [Pfizer-Eisai, Woodcliff, NJ] or Lovenox [Sanofi Aventis, Bridgewater, NJ]) starting on postoperative Day 1 and continued for 14 days. Radiation therapy (700 cgy) was administered within 48 hours of surgery to prevent heterotopic ossification. Duplex ultrasound was performed routinely before discharge to rule out deep venous thrombosis. One patient had wound dehiscence treated with local wound care and antibiotics. None of the patients had deep venous thrombosis by screening ultrasound. Patients were kept touchdown weightbearing for 6 weeks followed by gradual weightbearing and gait training with full weightbearing by 8 weeks after surgery. Fig. 4A B (A) Iliac and (B) obturator oblique-view radiographs taken at 41 months followup show maintenance of reduction without degenerative changes.
4 932 Solberg et al. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research We followed patients clinically and radiographically at 4 and 8 weeks postoperatively and every 3 months afterward. At each time, patients were examined by the treating surgeon for active range of motion, passive range of motion and power, gait assessment, activity of daily living assessment, visual analog pain scale assessment, and oblique (Judet view) radiographs of the repaired hip. Clinical outcome scores were calculated using the Merle d Aubigné-Postel [4] and Thompson and Epstein [20] scales. The Merle d Aubigné-Postel scale is a numeric scale with a maximum of 18, which accounts for pain and functional outcome, whereas the Thompson-Epstein scale accounts for pain, function, and radiographic appearance and is graded as excellent, good, fair, or poor. Radiographs were independently reviewed by one skeletal radiologist (JD) for evidence of nonunion, heterotopic ossification, and/or ON (Fig. 4). Heterotopic ossification was graded using the Brooker classification based on appearance on the Judet-view radiographs [1]. Results Eleven of the 12 patients had radiographic union of both fractures without loss of fixation, hardware failure, or progressive loss of joint space at latest followup. Trochanteric osteotomies were visible radiographically for an average of 23 weeks (range, weeks); one patient had ON of the femoral head develop and underwent revision surgery to a THA 27 weeks postoperatively. Three patients had Brooker Class II heterotopic ossification and one had Brooker Class III heterotopic ossification develop. None of the patients elected to undergo surgical excision of the ectopic bone. The average Merle d Aubigné-Postel score was 15.6 of a possible 18. Five patients had scores of 18, five patients scored between 15 and 17, one patient scored 13, and one patient scored 11. Using the Thompson-Epstein scoring scale, 10 of the 12 patients had good or excellent results, one patient with Grade III heterotopic ossification had a fair result, and one patient with ON had a poor result. Discussion Pipkin IV fractures have been well described in the literature, but meaningful conclusions have proven difficult because of the heterogeneity of data, even within a given series [2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 11, 14, 18, 21]. Information regarding treatment of the acetabulum or femoral head alone does not allow meaningful conclusions about optimal treatment for combined lesions. We therefore report the radiographic outcomes, including rates of ON and heterotopic ossification, and clinical outcomes using the Merle d Aubigné-Postel and Thompson-Epstein scoring systems in 12 patients with Pipkin IV fractures managed surgically with a TFO approach during a 6-year period. Our study had several limitations. Given the small number of study subjects, contrasts with previous studies are difficult and do not allow for ready comparison. However, we analyzed a single fracture pattern treated with a uniform approach decreasing the heterogeneity of the study group and allowing some conclusions regarding the usefulness of the approach for this fracture type. The Merle d Aubigné-Postel and Thompson-Epstein scoring systems are less objective outcome measures compared with more modern techniques such as the SF-36 and may overestimate the end result by introducing bias on the part of the surgeon and rater. These scoring systems, however, allowed us to compare our data with historical data using these scoring systems. We do not know whether a more sensitive outcome measure would influence our conclusions. We lost three patients to followup, and given the small numbers, it is unclear whether the data from these patients would alter our data, but we presume a capture of 12 of 15 patients provides representative results. Our surgical protocol of repairing the femoral head before acetabular fixation was used for two reasons. Leaving the posterior wall unrepaired allowed us to manipulate and observe the femoral head more easily. This was an important factor in femoral head fixation in which the lag screws are placed from an anteroinferior position. Repair of the femoral head fragment restored the effective femoral head diameter, but stability was difficult to assess in patients with posterior wall fractures and concomitant trochanteric osteotomy. Once repaired, the femoral head was congruent in the acetabulum and aided in reduction of the posterior wall fragment. In our patients, the posterior wall fractures were high and did not require release of the obturator internus or inferior extension of the traumatic posterior capsulotomy. We attempted to minimize iatrogenic damage to the medial circumflex perforators by placing a tag suture at the apex of the capsulotomy and not releasing the obturator internus. Several series have reported poorer outcomes in patients with Pipkin IV fractures than with isolated femoral head fractures [10, 17, 19, 20]. Aside from the presence of ON, the cause of the worse outcomes is unclear. Although nonoperative management of displaced femoral head fragments has been reported to lead to malunion and loss of motion often requiring surgical resection, the majority of isolated infrafoveal femoral head fractures can be treated nonoperatively with good outcomes [22]. Some series of combined fractures have emphasized acetabular repair to stabilize the hip, but it is unclear whether neglect of the femoral head lesion, per se, led to worse outcomes [9]. The
5 Volume 467, Number 4, April 2009 TFO for Pipkin IV Fractures 933 data from our patients suggest repairing the femoral head component of Pipkin IV fractures might lead to better outcomes; however, the necessity of repairing an infrafoveal femoral head component of a combined lesion is unclear. More recent series report the utility of the TFO technique in femoral head fractures [9], but these data did not stratify outcomes based on fracture type. To our knowledge, our report includes the largest series of consecutive Pipkin IV fractures treated using a uniform surgical approach. Our clinical outcomes using a TFO compared favorably with previous data with an overall good to excellent outcome in 80% of patients at an average 4-year followup. The surgical technique of TFO allowed simultaneous exposure and fixation of acetabular and femoral head fractures. The use of a uniform surgical protocol using the TFO technique gave 80% good and excellent midterm results comparable to reported outcomes of isolated femoral head fractures. The use of a stitch at the caudad apex of the posterior capsular tear may be beneficial in preventing further capsular tearing and vascular compromise of the femoral head. Acknowledgments We acknowledge Dr. Jeff Dym for assistance in radiographic assessment, Beth Habelow for assistance with our trauma database, and Dr. Jim Mirocha for assistance in statistical evaluation of the data. References 1. Brooker AF, Browerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement: incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55: Brumback RJ, Kenzora JE, Levitt LE, Burgess AR, Poka A. Fractures of the femoral head. Hip. 1987: Butler JE. Pipkin Type-II fractures of the femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981;63: d Aubigne RM, Postel M. Functional results of hip arthroplasty with acrylic prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1954;36: Epstein HC. Posterior fracture dislocations of the hip: long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974;56: Epstein HC, Wiss DA, Cozen L. Posterior fracture dislocation of the hip with fractures of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;201: Ganz R, Gill TJ, Gautier E, Ganz K, Krugel N, Berlemann U. Surgical dislocation of the adult hip: a technique with full access to the femoral head and acetabulum without the risk of avascular necrosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001;83: Gardner MJ, Suk M, Pearle A, Buly RL, Helfet DL, Lorich DG. Surgical dislocation of the hip for fractures of the femoral head. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19: Henle P, Kloen P, Siebenrock KA. Femoral head injuries: which treatment strategy can be recommended? Injury. 2007;38: Marchetti ME, Steinberg GG, Coumas JM. Intermediate term experience of Pipkin fracture-dislocations of the hip. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10: Mowery C, Gershuni DH. Fracture dislocation of the femoral head treated by open reduction and internal fixation. J Trauma. 1986;26: Notzli HP, Siebenrock KA, Hempfing A, Ramseier LE, Ganz R. Perfusion of the femoral head during surgical dislocation of the hip: monitoring by laser Doppler flowmetry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2002;84: Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. Fracture and dislocation compendium. J Orthop Trauma. 1996;10(suppl 1): Pipkin G. Treatment of Grade IV fracture-dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39: ; passim. 15. Routt ML, Simonian PT, Hansen ST. Young patients with femoral head fractures. In: Sledge CB, ed. Master Techniques in Orthopaedic Surgery. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott-Raven; 1998: Siebenrock K, Gautier E, Ziran BH, Ganz R. Trochanteric flip osteotomy for cranial extension and muscle protection in acetabular fracture fixation using a Kocher-Langenbeck approach. J Orthop Trauma. 1998;12: Stannard JP, Harris HW, Volgas DA, Alonso JE. Functional outcome of patients with femoral head fractures associated with hip dislocations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;377: Swiontkowski MF. Evaluation of outcomes for musculoskeletal injury: intracapsular hip fractures. In: Browner B, Jupiter J (Eds), Skeletal Trauma. 2nd Ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders; 1998: Swiontkowski MF, Thorpe M, Seiler JG, Hansen ST. Operative management of displaced femoral head fractures: case-matched comparison of anterior versus posterior approaches for Pipkin I and Pipkin II fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1992;6: Thompson VP, Epstein HC. Traumatic dislocation of the hip: a survey of two hundred and four cases covering a period of twenty-one years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1951;33: ; passim. 21. Warren PJ. Fixation of a fracture of the femoral head with preservation of remaining soft-tissue attachments: a case report. J Orthop Trauma. 1991;5: Yoon TR, Chung JY, Jung ST, Seo HY. Malunion of femoral head fractures treated by partial osteotomy: three case reports. J Orthop Trauma. 2003;17:
Medial circumflex artery Lateral circumflex artery
 Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Femoral Head Fractures: A Critical But Frequently Missed Injury Susanna C. Spence MD Manickam Kumaravel MBBS University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Background Femoral head fractures: A complication
Birkett was the first to discover
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2018) 476:1114-1119 DOI 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000045 Published online: 22 February 2018 Copyright 2018 by the ssociation of one and Joint Surgeons Classifications in rief: The
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2018) 476:1114-1119 DOI 10.1007/s11999.0000000000000045 Published online: 22 February 2018 Copyright 2018 by the ssociation of one and Joint Surgeons Classifications in rief: The
Fractures of the femoral head associated with
 Hip Arthroscopic Management for Femoral Head Fractures and Posterior Acetabular Wall Fractures (Pipkin Type IV) Myung-Sik Park, M.D., Sun-Jung Yoon, M.D., and Seung-Min Choi, M.D. Abstract: Femoral head
Hip Arthroscopic Management for Femoral Head Fractures and Posterior Acetabular Wall Fractures (Pipkin Type IV) Myung-Sik Park, M.D., Sun-Jung Yoon, M.D., and Seung-Min Choi, M.D. Abstract: Femoral head
대퇴골두골절에서시행한대전자 Flip 절골술의유용성
 205 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Original Article J Korean Orthop Assoc 2013; 48: 205-212 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.3.205 www.jkoa.org 대퇴골두골절에서시행한대전자 Flip 절골술의유용성 이경재 민병우 사공협 임영재 민경근
205 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Original Article J Korean Orthop Assoc 2013; 48: 205-212 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2013.48.3.205 www.jkoa.org 대퇴골두골절에서시행한대전자 Flip 절골술의유용성 이경재 민병우 사공협 임영재 민경근
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY. Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA
 DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
DIRECT SUPERIOR HIP APPROACH IN TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY Anil Thomas, MD Adult Reconstruction Peachtree Orthopedics Atlanta, GA Disclosures None Direct Superior Approach History and development of the approach
Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on the Results of Transtrochanteric Rotational Osteotomy for Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Surgical Technique
 75 Copyright 2011 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on the Results of Transtrochanteric Rotational Osteotomy for Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Surgical
75 Copyright 2011 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated Effects of Age and Body Mass Index on the Results of Transtrochanteric Rotational Osteotomy for Femoral Head Osteonecrosis Surgical
Traumatic posterior hip instability and reconstruction with a femoral head allograft in a young man
 CASE Case REPORT in Images Turhan et al. 1 Peer Reviewed OPEN ACCESS Traumatic posterior hip instability and reconstruction with a femoral head allograft in a young man Yalçin Turhan, Mehmet Arican, Zekeriya
CASE Case REPORT in Images Turhan et al. 1 Peer Reviewed OPEN ACCESS Traumatic posterior hip instability and reconstruction with a femoral head allograft in a young man Yalçin Turhan, Mehmet Arican, Zekeriya
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY
 ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
ANTERIOR TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY And Other Approaches Bill Rhodes PTA 236 Total Hip Arthoplasty (THA) Background THA, also know as Total Hip Replacement Regarded as the most valued development in orthopedics
Swiss Medical Network Musculoskeletal Conference Surgical Technique and 30-Year Results of the Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO)
 Swiss Medical Network Musculoskeletal Conference 2017 Surgical Technique and 30-Year Results of the Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) Simon D. Steppacher Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inselspital, University
Swiss Medical Network Musculoskeletal Conference 2017 Surgical Technique and 30-Year Results of the Periacetabular Osteotomy (PAO) Simon D. Steppacher Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inselspital, University
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy
 Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
The aging epidemic is upon us. The baby boomer
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 62, Numbers 1 & 2 2004 47 Management of Acetabular Fractures in the Elderly Elton Strauss, M.D. The aging epidemic is upon us. The baby boomer generation is
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 62, Numbers 1 & 2 2004 47 Management of Acetabular Fractures in the Elderly Elton Strauss, M.D. The aging epidemic is upon us. The baby boomer generation is
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction
 Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction Percutaneous Rx of Dysplastic & Deformed Hips! For many young people with Hip Joint problems with limb shortening, this is the ideal procedure. Dr MilindChaudhary Chief Orth.
Ilizarov Hip Reconstruction Percutaneous Rx of Dysplastic & Deformed Hips! For many young people with Hip Joint problems with limb shortening, this is the ideal procedure. Dr MilindChaudhary Chief Orth.
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 548-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy Joaquin SANCHEZ-SOTELO, John GIPPLE, Daniel BERRY, Charles ROWLAND, Robert
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 548-554 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary hip arthroplasty through a limited posterior trochanteric osteotomy Joaquin SANCHEZ-SOTELO, John GIPPLE, Daniel BERRY, Charles ROWLAND, Robert
Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of 20 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 10 Number 1 Clinical outcomes of muscle pedicle bone grafting (Meyer's Procedure) in cases of old displaced femur neck fractures: A Study Of
Use of the HemiCAP partial hip resurfacing technique for traumatic femoral head osteochondral defects following obturator hip dislocations
 SICOT-J 2018, 4, 3 The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2017059 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Use of the HemiCAP partial hip resurfacing
SICOT-J 2018, 4, 3 The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2018 https://doi.org/10.1051/sicotj/2017059 Available online at: www.sicot-j.org SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Use of the HemiCAP partial hip resurfacing
EBM. Comparative Systematic Review of the Open Dislocation, Mini-Open, and Arthroscopic Surgeries for Femoroacetabular Impingement
 EBM Comparative Systematic Review of the Open Dislocation, Mini-Open, and Arthroscopic Surgeries for Femoroacetabular Impingement ~ Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery, Vol 27,
EBM Comparative Systematic Review of the Open Dislocation, Mini-Open, and Arthroscopic Surgeries for Femoroacetabular Impingement ~ Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery, Vol 27,
Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Locked Plating of 3- and 4-Part Proximal Humerus Fractures in Older Patients: The Effect of Initial Fracture Pattern on Outcome Brian D. Solberg, MD,* Charles N. Moon, MD, Dennis P. Franco,
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Total hip arthroplasty performed using conventional and navigated tissue-preserving techniques
 Total hip arthroplasty performed using conventional and navigated tissue-preserving techniques 1. Introduction Stephen B. Murphy, Timo M. Ecker and Moritz Tannast Center for Computer Assisted and Reconstructive
Total hip arthroplasty performed using conventional and navigated tissue-preserving techniques 1. Introduction Stephen B. Murphy, Timo M. Ecker and Moritz Tannast Center for Computer Assisted and Reconstructive
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
A study of comparitive analysis of the outcome of Hardinge s and Moore s approach of hemi arthroplasty of hip
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Divya V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):72-78 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175653
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Divya V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Jan;4(1):72-78 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20175653
Safe surgical technique: iliac osteotomy via the anterior approach for revision hip arthroplasty
 Safe surgical technique: iliac osteotomy via the anterior approach for revision hip arthroplasty Ziran et al. Ziran et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014, 8:32 Ziran et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014,
Safe surgical technique: iliac osteotomy via the anterior approach for revision hip arthroplasty Ziran et al. Ziran et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014, 8:32 Ziran et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014,
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Anterior Approach to the Hip Orthopaedic surgeon What s the fuss all about this NEW surgery? Not a new approach or surgery
www.orthosports.com.au 47 49 Burwood Road, Concord 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Anterior Approach to the Hip Orthopaedic surgeon What s the fuss all about this NEW surgery? Not a new approach or surgery
Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, 93-97 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates Valentinas Uvarovas, Igoris Šatkauskas, Giedrius Petryla,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2017, 83, 93-97 ORIGINAL STUDY Primary total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture using intra-acetabular bended plates Valentinas Uvarovas, Igoris Šatkauskas, Giedrius Petryla,
Snapping Hip and Impingement
 Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
Snapping Hip and Impingement Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board: GE,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP. Dr Károly Fekete
 DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
DISLOCATION AND FRACTURES OF THE HIP Dr Károly Fekete 1 OUTLINE Epidemiology Incidence Anatomy Patient s examination, clinical symptons Diagnosis Classification Management Special complications 2 EPIDEMIOLOGY,
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts. Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras
 Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras Definition AVN = massive necrosis of bone and bone marrow occurring
Traumatic and Iatrogenic Osteonecrosis Current Concepts Andreas Panagopoulos Assistan Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras Definition AVN = massive necrosis of bone and bone marrow occurring
Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases G Khanna, R Sharma, D Singh, T A Chandy Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 21 Number 2 Management Of Acetabular Deficiency In Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Series Of 15 Cases G Khanna, R Sharma, D Singh, T A Chandy Citation
Current Management of Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum
 12 Current Management of Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum Berton R. Moed, MD Philip J. Kregor, MD Mark C. Reilly, MD Michael D. Stover, MD Mark S. Vrahas, MD Abstract The general goals for treating
12 Current Management of Posterior Wall Fractures of the Acetabulum Berton R. Moed, MD Philip J. Kregor, MD Mark C. Reilly, MD Michael D. Stover, MD Mark S. Vrahas, MD Abstract The general goals for treating
Small Incision Total Hip Replacement by the Lateral Approach Using Standard Instruments
 4ilizaliturri.qxd 4/6/04 4:07 PM Page 377 Small Incision Total Hip Replacement by the Lateral Approach Using Standard Instruments Victor M. Ilizaliturri, Jr, MD; Pedro A. Chaidez, MD; Fernando S. Valero,
4ilizaliturri.qxd 4/6/04 4:07 PM Page 377 Small Incision Total Hip Replacement by the Lateral Approach Using Standard Instruments Victor M. Ilizaliturri, Jr, MD; Pedro A. Chaidez, MD; Fernando S. Valero,
MIAA. Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique
 MIAA Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique Contents Introduction 3 With-Table MIAA technique 4 A1. Patient positioning/draping 4 A2. Skin incision 4 A3. Muscular dissection 4 A4. Muscle
MIAA Minimally Invasive Anterior Approach Surgical technique Contents Introduction 3 With-Table MIAA technique 4 A1. Patient positioning/draping 4 A2. Skin incision 4 A3. Muscular dissection 4 A4. Muscle
CLINICAL RESEARCH. Background:
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.901966 Received: 2016.10.14 Accepted: 2016.12.02 Published: 2017.06.07 Treatment of Transverse with or without Posterior Wall Fractures of Acetabulum Using a Modified
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.901966 Received: 2016.10.14 Accepted: 2016.12.02 Published: 2017.06.07 Treatment of Transverse with or without Posterior Wall Fractures of Acetabulum Using a Modified
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Zimmer MIS Mini-Incision THA Anterolateral Approach
 Zimmer MIS Mini-Incision THA Anterolateral Approach Retractor Placement Guide Optimizing exposure and preserving soft tissue during MIS THA Minimally invasive surgery allows you to follow the basic principles
Zimmer MIS Mini-Incision THA Anterolateral Approach Retractor Placement Guide Optimizing exposure and preserving soft tissue during MIS THA Minimally invasive surgery allows you to follow the basic principles
The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification D Iyer Citation D Iyer. The Orthopaedic Enigma: A Simplified Classification. The
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip
 Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Traumatic injuries of knee and hip Martin W. Korn, MD The United States secretary of transportation recently announced that highway deaths had risen from the previously announced 56,000 for 1969 to a new
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Index. orthopedic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures thromboembolic disease after, 341 Achilles tendon rupture ACL. See Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) Adolescent idiopathic
Shuichi Miyamoto, 1 Junichi Nakamura, 1 Satoshi Iida, 2 Chiho Suzuki, 2 Seiji Ohtori, 1 Sumihisa Orita, 1 and Kazuhisa Takahashi 1. 1.
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1450842, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1450842 Case Report Femoral Varus Osteotomy for Hip Instability after Traumatic Fracture Dislocations
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1450842, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1450842 Case Report Femoral Varus Osteotomy for Hip Instability after Traumatic Fracture Dislocations
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
SURGICAL EXPOSURES SURGERY OF THE HIP
 1 of 24 11/19/03 1:11 PM SURGICAL EXPOSURES SURGERY OF THE HIP by R. CALANDRUCCIO In: Atlas of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume 3 Lower Extremity; Editors: Laurin, CA, Riley Jr. LH, Roy-Camille R Reprinted with
1 of 24 11/19/03 1:11 PM SURGICAL EXPOSURES SURGERY OF THE HIP by R. CALANDRUCCIO In: Atlas of Orthopaedic Surgery Volume 3 Lower Extremity; Editors: Laurin, CA, Riley Jr. LH, Roy-Camille R Reprinted with
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Current concepts in management of femoroacetabular impingement
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjo@wjgnet.com doi:10.5312/wjo.v3.i12.204 World J Orthop 2012 December 18; 3(12): 204-211 ISSN 2218-5836 (online) 2012 Baishideng. All rights reserved. Quanjun
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjo@wjgnet.com doi:10.5312/wjo.v3.i12.204 World J Orthop 2012 December 18; 3(12): 204-211 ISSN 2218-5836 (online) 2012 Baishideng. All rights reserved. Quanjun
Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures
 Techniques in Orthopaedics 23(4):0 0 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures Why I Use the Anterior Approach Philip J. Kregor, MD,* Jeffery W. Mast, MD, and Kurtis
Techniques in Orthopaedics 23(4):0 0 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Arthroplasty for Femoral Neck Fractures Why I Use the Anterior Approach Philip J. Kregor, MD,* Jeffery W. Mast, MD, and Kurtis
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay
 Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Pelvis injuries Fractures of the femur (proximal,shaft) Dr Tamás Bodzay Pelvis anatomy Pelvis function - axial load bearing - protection: abdominal, pelvic structures Pelvic injury mechanism Falling from
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 425, pp. 82 86 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins The Lateral Trochanteric Wall A Key Element in the Reconstruction of Unstable Pertrochanteric Hip Fractures
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Influence of age on results following surgery for displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly
 Zha et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (217) 18:489 DOI 1.1186/s12891-17-1817-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of age on results following surgery for displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly
Zha et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (217) 18:489 DOI 1.1186/s12891-17-1817-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Influence of age on results following surgery for displaced acetabular fractures in the elderly
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Faculty Papers Department of Orthopaedic Surgery 6-2011 Femoroacetabular Impingement: Saving the Joint Ronald Huang
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort
 Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Hip Preservation Timothy J Sauber MD Orthopaedic Update March 22, 2015 Nemacolin Woodlands Resort Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this topic Objectives Evaluate and recognize common hip pathology
Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric fractures
 Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
Injury, Int. J. Care Injured (2005) xxx, xxx xxx 1 www.elsevier.com/locate/injury 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Salvage of failed dynamic hip screw fixation of intertrochanteric s G.Z. Said, O. Farouk
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
RADIOLOGY OF THE NORMAL ACETABULUM. X-ray X-ray X-ray. Figure. Figure ILIAC OBLIQUE VIEW OBTURATOR OBLIQUE VIEW AP VIEW
 RADIOLOGY OF THE NORMAL ACETABULUM Six radiological landmarks should be recognized on the Anterior Posterior radiograph: 1. Posterior wall of the acetabulum 2. Anterior wall of the acetabulum 3. Roof /
RADIOLOGY OF THE NORMAL ACETABULUM Six radiological landmarks should be recognized on the Anterior Posterior radiograph: 1. Posterior wall of the acetabulum 2. Anterior wall of the acetabulum 3. Roof /
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
High Association of Posterior Malleolus Fractures with Spiral Distal Tibial Fractures
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:1692 1698 DOI 10.1007/s11999-008-0224-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Association of Posterior Malleolus Fractures with Spiral Distal Tibial Fractures Sreevathsa Boraiah MD, Michael
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:1692 1698 DOI 10.1007/s11999-008-0224-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Association of Posterior Malleolus Fractures with Spiral Distal Tibial Fractures Sreevathsa Boraiah MD, Michael
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of open reduction of slipped capital femoral epiphysis The capital femoral epiphysis
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of open reduction of slipped capital femoral epiphysis The capital femoral epiphysis
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Direct anterior approach for revision total hip arthroplasty
 Visualized Surgery Page 1 of 5 Direct anterior approach for revision total hip arthroplasty Jorge Manrique, Antonia F. Chen, Snir Heller, William J. Hozack Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University,
Visualized Surgery Page 1 of 5 Direct anterior approach for revision total hip arthroplasty Jorge Manrique, Antonia F. Chen, Snir Heller, William J. Hozack Rothman Institute at Thomas Jefferson University,
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
4/1/2016. Total Hip Arthroplasty. DAHR Procedure. Direct Anterior Hip Replacement. DAHR Procedure. DAHR Procedure
 Mercy Orthopedist Types of Approaches Total Hip Arthroplasty Mercy Has a total of 16 Orthopedist that perform all three different approaches Posterior Anterior Lateral Direct Anterior Direct Anterior Hip
Mercy Orthopedist Types of Approaches Total Hip Arthroplasty Mercy Has a total of 16 Orthopedist that perform all three different approaches Posterior Anterior Lateral Direct Anterior Direct Anterior Hip
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION
 EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
EXTENDED TROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FPO EXTENSIVELY COATED FIXATION SINCE 1983 PREOPERATIVE PLANNING EXPLANTATION OPTIONS the cement from inside the cement canal until the bone/ cement bond
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES
 C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
C H A P T E R 1 2 PRONATION-ABDUCTION FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM (The opinions of the author should not be considered as reflecting official policy of the US Army Medical Department.) Pronation-abduction
PERIPROSTHETIC FRACTURES FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY
 PERIPROSTHETIC FRACTURES FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY Jon Minter, DO Arthritis and Total Joint Specialists Atlanta, Georgia ArthritisAndTotalJoint.Com Intra Op Incidence of Periprosthetic Hip Fractures
PERIPROSTHETIC FRACTURES FOLLOWING TOTAL HIP ARTHOPLASTY Jon Minter, DO Arthritis and Total Joint Specialists Atlanta, Georgia ArthritisAndTotalJoint.Com Intra Op Incidence of Periprosthetic Hip Fractures
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol.16, No.1, January, 2003
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol16, No1, January, 2003 : 351 ( )463-712 TEL: (031) 780-5270/5271 FAX : (031) 708-3578 E-mail: bskima@netsgocom 16,, ( > 20mm ) 5, ) 20 % 1 ), 6,, 3 8 8
Case Presentation: Comminuted Radial Head Fracture
 11/28/2017 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Radial Head Fracture Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
11/28/2017 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Radial Head Fracture Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Kyle F. Dickson, M.D. M.B.A. I Need a Special Table to Treat Some Acetabular Fractures. I Prefer a Special Table to Treat Most Acetabular Fractures
 Kyle F. Dickson, M.D. M.B.A. Professor Baylor College of Medicine Southwest Orthopaedic Group, Houston, Texas kyledickson99@gmail.com cell 713-208-4168 I Need a Special Table to Treat Some Acetabular Fractures
Kyle F. Dickson, M.D. M.B.A. Professor Baylor College of Medicine Southwest Orthopaedic Group, Houston, Texas kyledickson99@gmail.com cell 713-208-4168 I Need a Special Table to Treat Some Acetabular Fractures
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications. Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout
 Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 04 Page April 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.176 Functional Outcome of Fracture Neck of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i4.176 Functional Outcome of Fracture Neck of
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
Young Adult Hip problems. Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth)
 Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Young Adult Hip problems Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) RNOH founded 1837 by William Little 14 year old presenting with limp Knee pain on and off 4 months Limps Aresh Hashemi-Nejad FRCS(Orth) The Royal
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation
 Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
