Two-year follow-up of closed reduction and external fixation treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal.
|
|
|
- Barbra Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (3): ISSN X Two-year follow-up of closed reduction and external fixation treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal. Zhang Y *, Xu N, Gu W, Jiang S Department of Orthopaedics, Changzhou No.2 People's Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, PR China Abstract This retrospective analysis investigated the clinical effect of closed reduction and external fixation on unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal. A total of 23 patients with unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal were treated, including six with Bennett fractures, three with Rolando fractures, six with extra-articular transverse fractures, and eight with extra-articular oblique fractures. If closed reduction by all fracture manual reset techniques was satisfactory, external fixation was used. Postoperative fracture healing was assessed by X-ray imaging. In the 24-month follow-up period, functional recovery was assessed by, Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH), total active motion test of the thumb, Jamar dynamometer thumb muscle testing. The fracture healing time was 8-12 weeks. Nineteen cases were followed up for up to 24 months (82.6%). The average DASH score was 3.4 ± 0.8. The total active motion loss of the thumb was 7.5 ± 1.3. The thumb grip strength of the affected side on Jamar dynamometer testing was % of the uninjured side, while the pinch strength of the affected side was % of the uninjured side. Patients with unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal treated with closed reduction and external fixation underwent 2 years of follow-up, which revealed good functional thumb recovery. Keywords: Unstable fracture, Closed reduction, External fixation. Accepted on September 12, 2016 Introduction The base of the first metacarpal and trapezium constitutes the thumb carpometacarpal joint, an important anatomical structure that enables complete complex thumb activities. When the thumb endures axial force, damage can be transmitted to the epiphysis along the first metacarpal, resulting in fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone. Malreduction at the base of the first metacarpal fracture leads to malunion and traumatic arthritis, particularly affecting thumb opposition [1]. Since conservative treatment makes it difficult to achieve accurate setting of the articular surface and maintain the metacarpal length, it is widely accepted that surgery should be chosen as treatment of an unstable fracture at the base of the first metacarpal, but the choice of surgical approach has not gained consensus [2,3]. Closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation have been widely used and shown to have high efficacy in long-term follow-up [4]. The fixation effect of open reduction using pins or screws is more reliable [5]. However, in most of these methods, the fixture penetrates the articular cartilage surface to increase cartilage damage, which creates the potential risk of traumatic arthritis. Open reduction by plates and screws has the same satisfactory results [6] but also involves disadvantages such as higher cost and the need for a second surgery to remove the internal fixation. After closed reduction, fixation of the first and the second metacarpal bones indirectly fixes the fractures, which can effectively maintain the metacarpal length, but limits the activities of the second metacarpal and reduces the first web space [7,8]. Therefore, closed reduction and external fixation is a minimally invasive and effective treatment for fractures at the base of the first metacarpal that can achieve a better stabilizing effect than that of Kirschner wire internal fixation [9], which has been widely reported in clinical studies [10-13], but long-term follow-up studies are lacking. From 2008 to 2013, 23 cases of unstable fracture at the base of the first metacarpal were subjected to external fixation after closed reduction, radiological evaluation, and clinical observation for 2 years after surgery. Material and Methods Clinical data Patients with unstable fracture at the base of the first metacarpal treated at our hospital with closed reduction and external fixation between January 2008 and January 2013 were retrospectively analyzed. A total of 23 patients (16 men and seven women) with a mean age of 43.8 years (range, years) were enrolled. This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Medical University. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue
2 Zhang/Xu/Gu/Jiang The causes of injury included 10 cases of motorcycle traffic accident, 10 cases of falls, and three cases of hits. The treatment time after injury was hours. Clinical manifestations included thumb pain and swelling. Physical examination showed deformity, tenderness, and bone friction sensitivity at the base of the first metacarpal, and restricted thumb flexion and extension activities. All cases had closed fractures, but two also had partial abrasion bleeding. X- ray examinations showed fractures at the base of the first metacarpal. In accordance with the classification criteria of Green and O Brien in 1972, there were six cases of type I fracture (Bennett fracture), three cases of type II fracture (Rolando fracture), six cases of type IIIA fracture (extraarticular transverse fracture), and eight cases of type IIIB fracture (extra-articular oblique fracture). All patients were subjected to manual reduction in outpatient service, but the reset could not be maintained due to significant fracture displacement. Of all patients, one had a double fracture of the right radius and ulna, one had a combined pelvic fracture, and two had combined distal radial fractures. The surgery was performed 2-7 days after the injury and finished by the same group of physicians (Table 1). Table 1. Patients basic information Number Gender Age Injury causes Fracture type 1 Male 68 Falling I Combined injury 2 Male 63 Falling II Y Distal radius fractures 3 Male 26 Hit III A 4 Female 24 Traffic I 5 Male 28 Falling III A 6 Male 19 Traffic III B Fracture of ulna and radius 7 Male 58 Traffic I 8 Female 33 Falling III B 9 Female 61 Traffic II T 10 Male 26 Falling III B 11 Male 27 Traffic I 12 Female 38 Falling III B 13 Male 35 Traffic I 14 Male 57 Falling III A Pelvic fracture 15 Male 43 Falling III B 16 Female 49 Traffic III B 17 Female 63 Falling I 18 Male 39 Traffic III B 19 Male 71 Hit III A 20 Male 38 Falling III A 21 Male 45 Hit III B 22 Male 37 Traffic II T 23 Female 59 Traffic III A Distal radius fractures Treatment methods Patients were positioned supine and anesthetized by a brachial plexus block. The upper limb was outreached and placed on a hand surgery operating table. A bar tourniquet was tied on the proximal upper arm and inflated to a pressure of 40 Kpa. Conventional povidone-iodine disinfection was used for the operative field, and a sterile towel and C-arm were placed. Closed reduction techniques Under X-ray perspective of the C-arm, the manual reset technique was used first. (1) In Rolando fracture reduction, the first metacarpal bone can be subjected to internal rotation, axial traction, and outreaching dorsiflexion to the first metacarpophalangeal joints to shorten the angular deformity and restore the force lines of the first metacarpal bone (2). For transverse and oblique fractures outside the joints, the surgeons turned the top over in traction by the thumb to correct the angular deformity (3). The Bennett fracture used screw home reset, that is, tensing of the dorsal ligaments of the first carpometacarpal joint to achieve indirect reduction. During surgery, the surgeons placed the patient s thumb in the passive opposition position and tried to internally rotate the first metacarpal to position the thumb mound opposite to the index and middle finger mounds. The dorsal ligament was placed under tension to help reset the ulnar displacement bone of the Bennett fracture. The reduction quality was confirmed by X- ray. Surgeons must ensure that the articular surface is smooth and avoid articular surface displacement >2 mm. External fixation bracket type selection Combined unilateral external fixators provided by the Beijing External Fixation Institute consisted of threaded half needles, clamps, connecting pieces, and other components. All items were made of medical-grade stainless steel. After successful resetting confirmed by X-ray, traction was continued to maintain the reset state. After pre-drilling by a 2.5 mm diameter Kirschner wire, the screws were screwed into a threaded 2.5 mm diameter half needle perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the first metacarpal. Surgeons should avoid making the two threaded half needles parallel; rather, the proximal threaded half needle should be as close to the fracture line as possible and the two threaded half needles should be kept as far apart as possible. In the same way, after pre-drilling with the 2.5 mm diameter Kirschner wire is performed, two threaded 2.5 mm diameter half needles were screwed crosswise into the centre of the trapezium at an angle of approximately 60 C. For extra-articular transverse fractures, if the proximal end of the first metacarpal bone was of sufficient length, the 1397 Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue 3
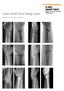
3 Two-year follow-up of closed reduction and external fixation treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal two threaded half needles could be placed at the base of the first metacarpal bone. When the threaded half needles are placed, the surgeon should carefully avoid the extensor pollicis longus muscle tendon. Perspective was carried out to determine the satisfaction of needle position, both the length penetrated the cortex to connecting pieces in order to fix and lock the threaded half needles, connect the components. We moved the thumb, assessed the stability of fracture fixation again in perspective. Postoperative treatment None of the patients required plaster casting after surgery, and the needle tract was disinfected daily by 75% alcohol. The external fixation was removed when the X-ray showed continuous callus through the fracture line. After bracket removal, patients were gradually allowed to hold heavy objects and exercise. Statistical analysis The SPSS version 14.0 statistical package was used for the statistical analysis. Quantitative normally distributed data are expressed as ± s. Non-normally distributed data were analyzed by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney test method to compare the function of the uninjured and the affected sides. Significance was indicated at α=0.05. Imaging evaluation One month after surgery, radiographs of the hand were taken in the anteroposterior and oblique view every 2 weeks to assess fracture healing. Once the external fixation on X-ray images showed continuous callus through the fracture line, we took X- ray images every month until the fracture line disappeared and the fracture completely healed. After 24 months, images were taken to assess the extent of traumatic arthritis. Arthritis was classified according to the Eaton-Littler classification criteria modified by van Niekerk and Owens as follows: class 1, no clear changes in arthritis; class 2, osteophytes <2 mm; class 3, osteophytes >2 mm or showed joint space narrowing; and class 4:partial or total disappearance of the joint space. Clinical evaluation In the 24-month follow-up period, questionnaires were used to assess each patient s thumb function. The main included contents were as follows. (1) Joint function was assessed according to the Disability of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) scale of points in which a higher score indicated a greater loss of functionality. (2) The Total Active Motion (TAM) between the uninjured and affected side of the thumb was compared. For the thumb, the total active activity was equal to the flexion sum of the thumb carpometacarpal joint, metacarpophalangeal joints, and interphalangeal joint subtracted from the extension sum of the carpometacarpal joint, metacarpophalangeal joints, and interphalangeal joint. Compared with the uninjured side, the TAM of the affected side did not become better: 76-99% maintenance was taken as good, 50-75% as moderate, and <50% as poor. (3) The Jamar grip dynamometer was used to evaluate the thumb muscle force of the uninjured and affected sides of the thumb, including grip and pinch strength [14]. The calculated percentage of the muscle strength of the affected side was compared to that of the uninjured side. Figure 1. Male patients, aged 49 years old, falling injury, the transverse fracture at the base of the first right metacarpal bone, Green and O`Brien type IIIA type, with pelvic fractures. Results Patients attended follow-up appointments once every 2 weeks starting at 1 month after surgery until the fracture healed completely. Four patients were lost when the follow-up lasted for 6 months after surgery, whereas the other 19 patients (82.6%) completed the entire 24-month follow-up period. The mean intraoperative time was minutes (range, minutes). The operative times of three cases of multiple fractures that were simultaneously subjected to multi-site surgery were not included in the statistics. Analysis of variance showed that surgery duration and fracture type did not differ among patients (P>0.05). Three patients had swelling and exudate in the needle tract within about a week, including one case with primary skin abrasions. The exudate decreased after local cleaning and dressing and the administration of oral antibiotics. The needle tracts of all patients healed after external fixator removal. Imaging evaluation Approximately 1 month after surgery, X-ray of the 23 patients showed no fracture displacement and no loose or pulled-out threaded half needles. There were 18 cases of well-growing Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue
4 Zhang/Xu/Gu/Jiang callus and a blurred fracture line, and the external fixator was removed. that of an elderly patient was extended to 2 months when the images showed callus growth after surgery. Mean external fixation removal was days (range, days). The 3- month review radiography revealed fracture healing in all patients. Mean fracture healing time was 10 weeks (range, 8-12 weeks) (Figures 1-3). X-rays of the 24-month follow-up showed that carpometacarpal joints of one case with Bennett fracture and two cases with Rolando fracture had osteophytes <2 mm with Eaton-Littler class 2. The remaining patients had no significant osteoarthritis change with Eaton-Littler class 1 (Figure 4). Figure 2. Appearance of photos of patients with transverse fracture at the base of the first right metacarpal bone 3 days after closed reduction and external fixation. Figure 4. X-ray review of patients hand in 24 months after surgery, the fracture healed completely and no significant osteoarthritis change was showed. Figure 3. X-ray review of patients hand in 28 days after surgery, the transverse fractures showed good reduction at the base of the first right metacarpal bone, there was continuous callus through the fracture line, removed the external fixator. Callus growth of five cases was unsatisfactory; of them, the bracket removal in four was extended to about 6 weeks, while Clinical evaluation The 24-month investigation questionnaire after surgery showed that the average DASH score was 3.4 ± 0.8, indicating that the patients in the follow-up could recover their pre-injury thumb activity level without negative effects on their daily life and work and physical exercise activities. The mean thumb TAM loss was 7.5 ± 1.3 ; there were four cases of TAM>10, including two elderly patients with TAM>30. Compared with those in the uninjured side, seven cases were excellent, 11 were good, one was moderate, and none was bad. On Jamar thumb muscle testing in 24-month follow-up, grip force of the affected side was % of the uninjured side. The grip force of the affected side for one case with type IIIB fractures showed a 34.5% loss compared with that of the uninjured side without any loss of function, DASH score was 2 points, and TAM was good. The pinch strength of the affected side was % of the uninjured side. The pinch strength of the affected side for one case with type I fractures was a 26.7% loss compared with that of the uninjured side without functional limitations, DASH score was 3 points, and TAM 1399 Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue 3
5 Two-year follow-up of closed reduction and external fixation treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal was excellent. Among the patients with type II fracture, one had a 33.4% loss of pinching force, DASH score was 2 points, and TAM was good. In statistical analysis, the grip strength of the affected side did not differ significantly from the grip or pinch strength of the uninjured side (P<0.05). Discussion Common unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal include both intra-articular fractures such as Bennett fractures and Rolando fractures and extra-articular oblique fracture and transverse fractures. Treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal is challenging. Before the 1970s, closed reduction and cast immobilization were the conventional treatments and considered to have good results as non-surgical treatments in some historical reports. However, currently, surgical intervention is generally recommended as first-line treatment for unstable fracture at the base of the first metacarpal. The common available internal fixations consist of screws or Kirschner wire. However, this direct fixation method requires open reduction to ensure stability between ends during screw placement to prevent bone piece separation and displacement. This increases the degree of local trauma, which can damage the articular cartilage and cause traumatic arthritis. Another method was percutaneous fixation of the first and second metacarpal bones and the use of Kirschner wire to achieve indirect fixation [7]. However, this technique may damage the tenor muscles and limit the thumb s flexion and extension activities. Therefore, the use of closed reduction and external fixation in the treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal is a better choice. Closed reduction can be the treatment for the vast majority of Bennett fractures [15]. Closed reduction was indirect, and the chosen technique is very important. In conventional techniques, it was particularly stressed that the thumb be placed in an outreaching dorsal extension position and the abductor pollicis longus tensed through axial traction or pressure be applied simultaneously to the base of the thumb metacarpal to reduce the fracture. However, practice showed that this reduction technique often failed to achieve a satisfactory reduction effect. This incorrect reduction technique was derived from the understanding that abductor pollicis longus is the main cause of Bennett fracture dislocation. This misunderstanding was widely present in the literature as well as textbooks. Many surgeons have found that the thumb was in extreme opposition since the abductor pollicis longus was relaxed when three fingers grasped things but was tensed when the thumb was in abduction and dorsal extension. As such, the traction force of the abductor pollicis longus was not the main cause of Bennett fracture displacement, so there was no need to put the thumb in the abduction and dorsal extension state to neutralize the traction force of the abductor pollicis longus in fracture reduction [16]. However, in the abduction and dorsal extension position, the base of the first metacarpal and the volar bone was separated to increase the fracture-separating gap and impede the fracture s anatomical reduction. A large number of anatomical studies confirmed that when the carpometacarpal joint was in a rest position, the palmaris of the first metacarpal bone was separated from the trapezium, carpometacarpal joint space was large, and palm oblique ligament and dorsal ligamentous complex were in a relaxed state. When the thumb was in a clenched clinched state, that is, when the thumb was in an active opposition or passive palm rotation position, the dorsal ligament was tensed and the palm oblique ligament was more relaxed than the rest, while the metacarpal palmaris was closer to the trapezium, carpometacarpal joint space was narrowing, and extension forces provided by the abductor pollicis longus and dorsal tension formed a dynamic couple with the strained oblique ligaments, which steered the instability of the carpometacarpal joint toward stability. This was the reset principle of the screw home technique. In the use of closed reduction, physicians still need to pay attention to reduction quality; it must be repeatedly confirmed on the X-ray prior to fixation. Some authors studied the correlation between the quality and surgical reduction effect. The early literature reported that fracture reduction quality was not correlated with postoperative pain, activity, or incidence of osteoarthritis. Demir retrospectively studied 24 cases of Bennett fractures and six of comminute intra-articular fractures and reported that metacarpal base articular surface reduction quality and radiographic results had no correlation with subjective perception [17]. Cullen conducted a series of biomechanical studies and suggested that a partial shift of 2 mm on the articular surface can significantly increase the contact area of the carpometacarpal joint surfaces. Therefore, an intra-articular shift 2 mm was considered acceptable [18]. In recent years, a variety of clinical studies have reported on the importance of anatomical reduction and decreasing the articular surface step. Many scholars believed that reduction quality was associated with the incidence of osteoarthritis. The reduction standard should be more stringent, especially when the first carpometacarpal joint cartilage contact area was small. Kjaer-Petersen reported the treatment of 41 cases with Bennett fractures, including closed reduction and cast immobilization, closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation, and open reduction and internal fixation and analyzed the correlation between reduction treatment and clinical efficacy and found that anatomical reduction was achieved with a step <1 mm in 86% of patients, none of whom had any local symptoms; in contrast, only 46% of the patients with poor reduction and a step >1 mm did not have local complications [19]. Lutz reported the 7-year follow-up data of 32 cases of Bennett fracture treated with open reduction and internal fixation or closed reduction and percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation across the joints. Treatment methods and final clinical results were not correlated with the incidence of osteoarthritis. However, during surgery, the approach should be shifted to open reduction if the intra-articular displacement is >1 mm after closed reduction. This finding suggested that our longterm efficacy depended on reset quality rather than surgical method [5]. In our study, the reduction standard was also Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue
6 Zhang/Xu/Gu/Jiang defined as articular surface displacement 1 mm, and the clinical results were satisfactory. Many studies to date have examined the treatment of the base of the first metacarpal fractures using external fixators but lacked longer-term follow-up observations, particularly a description of specific functional recovery. In our study, a 24- month follow-up study was performed of the external fixation of fractures at the base of the first metacarpal in addition to radiographic comparisons, while other studies focused on subjective and objective evaluations of thumb function to fully evaluate the effect of surgery. The follow-up revealed that the treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal using closed reduction and external fixation had good therapeutic effect according to both, subjective indicators reflecting pain and function and objective indicators reflecting range of motion and muscle strength. However, age was an important prognostic factor, and elderly patients were more likely to have postoperative partial pain and decreased muscle strength and were more prone to joint degeneration in the advanced disease stage. It was generally believed that the subcutaneously implanted threaded half needles reduced soft-tissue irritation to the maximum degree, reducing the possibility of infection and tendon injury [20]. However, there were three cases of needle tract infection treated with oral antibiotics. Needle tract infection can occur both inside and outside articular fractures. One patient had preoperative skin abrasions. As such, even in treatment using external fixators, surgeons should closely examine the soft tissue during the preoperative assessment and strengthen postoperative needle tract management to prevent infection. In summary, closed reduction and external fixation can be effective and safe treatments for unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal. Such external fixation structures are simple and versatile and able to simultaneously achieve effects such as meeting the retractor, adjusting the angulation, and shortening the displacement, especially for local wounds. However, exposed external fixation is inconvenient in daily life and there was a certain needle tract infection rate. The limitations of the present study were that nearly 20% of patients did not complete the 24-months follow-up period. This was a case study that lacked a control group. In addition, objective assessment criteria were lacking. Finally, during the Jamar dynamometer strength test, the dominant hand was not considered and some errors occurred. Conflicts of Interest All of the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this paper. References 1. Mahmoud M, El Shafie S, Menorca RM, Elfar JC. Management of neglected Bennett fracture in manual laborers by tension fixation. J Hand Surg Am 2014; 39: Giddins GE. The non-operative management of hand fractures. J Hand Surg Eur 2015; 40: Liverneaux PA, Ichihara S, Hendriks S, Facca S, Bodin F. Fractures and dislocation of the base of the thumb metacarpal. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2015; 40: Middleton SD, McNiven N, Griffin EJ, Anakwe RE, Oliver CW. Long-term patient-reported outcomes following Bennett's fractures. Bone Joint J 2015; 97-B: Lutz M, Sailer R, Zimmermann R, Gabl M, Ulmer H, Pechlaner S. Closed reduction transarticular kirschner wire fixation versus open reduction internal fixation in the treatment of Bennett fracture dislocation. J Hand Surg Br 2003; 28: Diaconu M, Facca S, Gouzou S, Liverneaux P. Locking plates for fixation of extra-articular fractures of the first metacarpal base. Chir Main 2011; 30: Greeven AP, Alta TD, Scholtens RE, de Heer P, van der Linden FM. Closedreduction intermetacarpal Kirschner wire fixation in the treatment of unstablefractures of the base of the first metacarpal. Injury 2012; 43: Abid H, Shimi M, El Ibrahimi A, El Mrini A. Articular fracture of the base of the thumb metacarpal: comparative study between direct open fixation and extrafocal pinning. Chir Main 2015; 34: Meng L, Zhang Y, Lu Y. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mini-external fixation and Kirschner wire internal fixation in Bennett fracture treatment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 2013; 99: Marsland D, Sanghrajka AP, Goldie B. Static monolateral external fixation for the Rolando fracture: a simple solution for a complex fracture. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2012; 94: Zhang X, Shao X, Zhang Z, Wen S, Sun J, Wang B. Treatment of a Bennett fracture using tension band wiring. J Hand Surg Am 2012; 37: El-Sharkawy AA, El-Mofty AO, Moharram AN, Abou Elatta MM, Asal F. Management of Rolando fracture by modified dynamic external fixation: a new technique. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg 2009; 13: Niempoog S, Waitayawinyu T. Comminuted Rolando s fracturess: treatment with modified wrist external fixator and transmetacarpal pinning. J Med Assoc Thai 2007; 90: Maru M, Jettoo P, Tourret L, Jones M, Irwin L. Thumb carpometacarpal osteoarthritis: trapeziectomy versus pyrocarbon interposition implant (Pi2) arthroplasty. J Hand Surg Eur Vol 2012; 37: Roth JJ, Auerback DM. Fixation of hand fractures with bicortical screws. J Hand Surg Am 2005; 30: Weinstein LP, Hanel DP. Metacarpal fractures. J Am Soc Surg Hand 2002; 2: Demir E, Unglaub F, Wittemann M, Germann G, Sauerbier M. Surgically treated intraarticular fractures of the trapeziometacarpal joint-a clinical and radiological outcome study. Unfallchirurg 2006; 109: Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue 3
7 Two-year follow-up of closed reduction and external fixation treatment of unstable fractures at the base of the first metacarpal 18. Cullen JP, Parentis MA, Chinchilli VM, Pellegrini VD Jr. Simulated Bennett fracture treated with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning. A biomechanical analysis of residual incongruity of the joint. J Bone Joint Surg 1997; 79: Kjaer-Petersen K, Langhoff O, Andersen K. Bennett s fracture. J Hand Surg Br 1990; 15: Kozin SH, Thoder JJ, Lieberman G. Operative treatment of metacarpal and phalangeal shaft fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2000; 8: * Correspondence to Zhang Y Department of Orthopaedics Changzhou No.2 People's Hospital affiliated to Nanjing Medical University PR China Biomed Res- India 2017 Volume 28 Issue
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. Hand Clin 21 (2005)
 Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand Clin 21 (2005) 501 505 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Antibiotics, following distal radius fracture treatment, 295, 296 Arthritis, following malunion of distal
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 02 Page February 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Isolated Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report Authors Dr. Rajendraprasad. R. Butala 1, Dr. Mishil S. Parikh 2, Prof. Sunil H. Shetty
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Isolated Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report Authors Dr. Rajendraprasad. R. Butala 1, Dr. Mishil S. Parikh 2, Prof. Sunil H. Shetty
Technique Guide. 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Chapter 24. Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty. Introduction. Operative Technique. Patient Preparation and Positioning
 Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
 Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures.
 Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Distraction Arthroplasty of the Trapeziometacarpal Joint Without Trapeziectomy
 Original Article Distraction Arthroplasty of the Trapeziometacarpal Joint Without Trapeziectomy Kin Weng Wong, Chi-Rung Chung, Shun-Chien Cheng and Chung-Da Wu, Department of Orthopaedics, Chi-Mei Medical
Original Article Distraction Arthroplasty of the Trapeziometacarpal Joint Without Trapeziectomy Kin Weng Wong, Chi-Rung Chung, Shun-Chien Cheng and Chung-Da Wu, Department of Orthopaedics, Chi-Mei Medical
Jacqueline C. Vanderzanden, Brian D. Adams & Justin J. Guan
 MCP arthrodesis using an intramedullary interlocking device Jacqueline C. Vanderzanden, Brian D. Adams & Justin J. Guan HAND ISSN 1558-9447 HAND DOI 10.1007/s11552-013-9579-5 1 23 Your article is published
MCP arthrodesis using an intramedullary interlocking device Jacqueline C. Vanderzanden, Brian D. Adams & Justin J. Guan HAND ISSN 1558-9447 HAND DOI 10.1007/s11552-013-9579-5 1 23 Your article is published
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize. Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique
 Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
Visualize, stabilize, mobilize Wristore * Distal Radius Fracture Fixator Abbreviated Surgical Technique Wristore Distal Radius Fracture Fixator 1 Pin Placement Identify anatomy and make a direct (open)
Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/577 Closed Proximal Phalangeal Fracture Management in Hand: An Outcome Analysis R Senthilkumar 1, E Kovarthini 2, Heber
Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures.
 Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame When to use
Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame When to use
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y.
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 MINIMALLY INVASIVE PLATE OSTEOSYNTHESIS FOR DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES: SURGICAL TECHNIQUE M. TOBE 1, K. MIZUTANI 1, Y. TSUBUKU 1, Y. YANAGIHARA 2 1 Department of 2nd Orthopaedic
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are
 The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
The NBX Non-Bridging External Fixator A Non-Bridging External Fixator/Locking Plate capturing a series of.062mm K-wires and 3mm half-pins that are inserted in a multiplanar and multi-directional fashion
Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results in 24 Cases Treated by In Situ Osteotomy
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org 468 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 468-472 Open Access Post-Traumatic Malunion of the Proximal Phalanx of the Finger. Medium- Term Results
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 22, No. 4, February, 2009. pp. 159-163 Acomparison of percutaneous and pin-and-plaster techniques in distal radius fracture Farshid
Technique Guide. Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges.
 Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Technique Guide Rotation Correction Plates 1.5 and 2.0. Reposition plates for fractures and osteotomies at the metacarpals and phalanges. Table of Contents Introduction Rotation Correction Plates 1.5
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
Comparison between Intramedullary Nailing and Percutaneous K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone
 Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
Comparison between Nailing and K-Wire Fixation for Fractures in the Distal Third of the Metacarpal Bone Original Article Sung Jun Moon 1, Jae-Won Yang 2, Si Young Roh 1, Dong Chul Lee 1, Jin Soo Kim 1
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 2 Introduction When the joint surfaces of an elbow are forced apart, the elbow is dislocated. The elbow is the second most commonly dislocated joint in adults (after
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Complications of Distal Radius Fractures. How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx 11/13/2017. Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago
 Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx Need to restore motion, begin with uninvolved parts Need to reduce an unreduced
Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx Need to restore motion, begin with uninvolved parts Need to reduce an unreduced
journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 texas orthopaedic journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment of Volar Tilt Measurements with Variations in X-Ray Beam Centralization Along the Longitudinal Axis of the Radius Russell A. Wagner, MD; Will Junius,
texas orthopaedic journal ORIGINAL RESEARCH Assessment of Volar Tilt Measurements with Variations in X-Ray Beam Centralization Along the Longitudinal Axis of the Radius Russell A. Wagner, MD; Will Junius,
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set. Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1)
 Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
Distal Radius Plate Instrument and Implant Set Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2017 DSUS/TRM/0916/1063(1) The Distal Radius Plates Indications For fixation of fractures and osteotomies, including
Technique Guide. Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems.
 Technique Guide Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems. Table of Contents Introduction Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator 2 Indications 3 Surgical Technique Configure
Technique Guide Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator. Part of the Synthes External Fixation Systems. Table of Contents Introduction Adjustable Distal Radius Fixator 2 Indications 3 Surgical Technique Configure
Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article Tarek Aly* Management of Unstable Metacarpal Fractures with Traversing Kirschner Wiring Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Tanta University School of
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
INTERNAL FIXATION OF THE METACARPALS AND PHALANGES P. BURGE
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures. Mariusz Bonczar
 The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar The Kienböck disease and scaphoid fractures Mariusz Bonczar Kienböck disease personal experience My special interest for almost 25 years Thesis
Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ORTHOPAEDICS Research Article How Early Can We Mobilise 4 th And 5 th Metacarpal Shaft Fractures? A Retrospective Study Mohammed KM Ali 1, Abid Hussain 1, CA Mbah 1, Alaa Mustafa 1,
Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture
 Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture Jansri Janpanya Product specialist The Bangkok Unitrade Co,.ltd. Objectives Type of LCP for distal radius Fx. The new LCP design for distal radius Fx. Have knowledge
Instrument and Implant for wrist fracture Jansri Janpanya Product specialist The Bangkok Unitrade Co,.ltd. Objectives Type of LCP for distal radius Fx. The new LCP design for distal radius Fx. Have knowledge
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. The Pennig Dynamic Wrist Fixator. Part A: Trans-articular application
 10 The Pennig Dynamic Wrist Fixator Part A: Trans-articular application B1 B2 B3 III IV TRANS-ARTICULAR APPLICATION The fractures that can be treated with this technique include AO type B and C fractures,
10 The Pennig Dynamic Wrist Fixator Part A: Trans-articular application B1 B2 B3 III IV TRANS-ARTICULAR APPLICATION The fractures that can be treated with this technique include AO type B and C fractures,
Carpal rows injuries!
 Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
Carpal rows injuries! Michael Papaloïzos! Center for Hand Surgery and Therapy Geneva, Switzerland no conflict of interest to declare Fractures of carpal bones! The fractured scaphoid! Fracture-dislocations
D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System. A series of case studies
 D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System A series of case studies AO fracture classification: C3 Eben A. Carroll, MD Associate Professor Director Orthopaedic Trauma Service Director Orthopedic Trauma Fellowship
D-RAD SMART PACK Plating System A series of case studies AO fracture classification: C3 Eben A. Carroll, MD Associate Professor Director Orthopaedic Trauma Service Director Orthopedic Trauma Fellowship
Surgical Management of Distal end Radius Fractures by Various Methods: A Prospective Study
 Original Article 1, 3 Assoc. Professor 2 Professor & HOD 4, 5 PG Students Department of Orthopedics MGM Hospital Kakatiya Medical College Warangal. Telangana State India. CORRESPONDENCE : Dr.Jhatosh.Venkateshwarlu,
Original Article 1, 3 Assoc. Professor 2 Professor & HOD 4, 5 PG Students Department of Orthopedics MGM Hospital Kakatiya Medical College Warangal. Telangana State India. CORRESPONDENCE : Dr.Jhatosh.Venkateshwarlu,
WINSTA-R. Distal Radius System
 Distal Radius System Table of Contents Introduction WINSTA-R System 2 Indication 2 Surgical Technique Palmar Access for Radius Plate 3 Dorsal Access for Radius Plate 3 Positioning of the Radius Plate
Distal Radius System Table of Contents Introduction WINSTA-R System 2 Indication 2 Surgical Technique Palmar Access for Radius Plate 3 Dorsal Access for Radius Plate 3 Positioning of the Radius Plate
Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing
 Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Original article 21 Primary internal fixation of fractures of both bones forearm by intramedullary nailing Nepal Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal Correspondenc to: Dr R P Singh,
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique
 Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique Sharat Agarwal 1, Mohammad Nasim Akhtar 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics & Trauma,
Management of Mallet Fracture by Closed Extension-Block Pinning A case based review of a novel technique Sharat Agarwal 1, Mohammad Nasim Akhtar 2 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics & Trauma,
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis.
 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table
Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First Carpometacarpal Arthritis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar
 Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Distal Radius Plate
Distal Radius Plate 2.4/2.7 dorsal and volar Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Distal Radius Plate
Technique Guide. VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis.
 Technique Guide VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Table of Contents Introduction VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System 2 Indications
Technique Guide VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Table of Contents Introduction VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System 2 Indications
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature M Suthersan, S Chan Citation M Suthersan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Isolated Comminuted Fracture of the Trapezium: A Case Report and Review of the Literature M Suthersan, S Chan Citation M Suthersan,
Finger Mobility Deficits Fracture of metacarpal Fracture of phalanx of phalanges
 1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
1 Finger Mobility Deficits ICD-9-CM codes: 715.4 Osteoarthrosis of the hand 815.0 Fracture of metacarpal 816.0 Fracture of phalanx of phalanges ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4301 Carrying
Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):211-5 Dynamic treatment for proximal phalangeal fracture of the hand G Rajesh, WY Ip, SP Chow, BKK Fung Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, University
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation
 A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Elbow Dislocation 20295 NE 29th Place, Ste 300 Aventura, FL 33180 Phone: (786) 629-0910 Fax: (786) 629-0920 admin@instituteofsports.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
University of Groningen. Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob
 University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Fracture of the distal radius Oskam, Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
Union Surgical. T-Pin. Fixation System for Distal Radius & Distal Ulna Fractures. Surgical Technique
 Union Surgical T-Pin Fixation System for Distal Radius & Distal Ulna Fractures Surgical Technique 1 Table of Contents 02 The T-Pin 03 Historical Perspective 04 Indications & Contraindications 05 Surgical
Union Surgical T-Pin Fixation System for Distal Radius & Distal Ulna Fractures Surgical Technique 1 Table of Contents 02 The T-Pin 03 Historical Perspective 04 Indications & Contraindications 05 Surgical
Management of intra-articular fractures of distal end radius in adults
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Gawali SR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):220-228 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20163148
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Gawali SR et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):220-228 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20163148
Management of metacarpal and phalangeal fractures with JESS fixator: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 383-387 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 383-387 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-11-2017 Accepted: 06-12-2017 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konaseema Institute
2018; 4(1): 383-387 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 383-387 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 05-11-2017 Accepted: 06-12-2017 Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konaseema Institute
Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures
 The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
The THAI Journal of SURGERY 2009; 30:5-10. Official Publication of the Royal College of Surgeons of Thailand Comparison of Miniplate and K-wire in Treatment of Metacarpal and Phalangeal Fractures Somboon
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system
 External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013
 Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
IS CASTING AN ACCEPTABLE TREATMENT APPROACH FOR A DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURE THAT HAS UNDERGONE A SATISFACTORY CLOSED REDUCTION?
 Original Article FOR A DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURE THAT HAS UNDERGONE A SATISFACTORY CLOSED REDUCTION? Khalid Masood *, Muhammad Jamil **, Farooq Ibrahim Pasha*, Khalid Zulfiqar Quresshi **, Naveed Ishaq Malik
Original Article FOR A DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURE THAT HAS UNDERGONE A SATISFACTORY CLOSED REDUCTION? Khalid Masood *, Muhammad Jamil **, Farooq Ibrahim Pasha*, Khalid Zulfiqar Quresshi **, Naveed Ishaq Malik
THE THUMB PROVIDES up to 40% of hand function.
 CURRENT CONCEPTS Thumb Trauma: Bennett Fractures, Rolando Fractures, and Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries Brian T. Carlsen, MD, Steven L. Moran, MD Injuries to the thumb are predominated by fractures
CURRENT CONCEPTS Thumb Trauma: Bennett Fractures, Rolando Fractures, and Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries Brian T. Carlsen, MD, Steven L. Moran, MD Injuries to the thumb are predominated by fractures
Comparison between Distractor Application on Both Radial & Ulnar Side and Radial Side Only for Fracture Distal Radius with Ulnar Styloid Fracture
 Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 227-233 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.35043 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) 227 Comparison between Distractor Application on
Open Journal of Orthopedics, 2013, 3, 227-233 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojo.2013.35043 Published Online September 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojo) 227 Comparison between Distractor Application on
PROXIMAL TIBIAL PLATE
 SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
SURGICAL NÁSTROJE TECHNIQUE PRO ARTROSKOPII PROXIMAL INSTRUMENTS TIBIAL FOR PLATE ARTHROSCOPY Proximal Tibial Plate Description of medical device The Proximal Tibial Plate is used in epyphyseal and metaphyseal
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Epidemiology in USA: Metacarpal fractures: Page 1
 Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
Hand Fractures: When is closed treatment OK? Robert J Strauch MD Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Columbia University New York City Epidemiology in USA: 2009 Distal radius fx s: 16/10,000 Phalangeal fx
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Case Report Bone Resection for Isolated Ulnar Head Fracture
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 3519146, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3519146 Case Report Bone Resection for Isolated Ulnar Head Fracture Hiromasa Akino, Shunpei Hama,
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 3519146, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3519146 Case Report Bone Resection for Isolated Ulnar Head Fracture Hiromasa Akino, Shunpei Hama,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. possible. Accurate assessment of standard radiographs is essential for appropriate 3. management. And includes true posterior- 4
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment of Colle's Fracture with Wrist Immobilization in Palmar flexed & Dorsiflexed Position Sohail Iqbal Shaikh, Abdul Basit, Javed Iqbal, Saba Sohail Shaikh, Imran Sohail Shaikh 26
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment of Colle's Fracture with Wrist Immobilization in Palmar flexed & Dorsiflexed Position Sohail Iqbal Shaikh, Abdul Basit, Javed Iqbal, Saba Sohail Shaikh, Imran Sohail Shaikh 26
Distal Radius and Distal Ulna Plates System Self-Tapping Spherical Locking Screw Self-Tapping Conical Locking Screw Cortex Screw
 DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA LOCKING PLATE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Distal Radius and Distal Ulna Plates System Self-Tapping Spherical Locking Screw Self-Tapping Conical Locking Screw Cortex Screw Approved
DISTAL RADIUS AND ULNA LOCKING PLATE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Distal Radius and Distal Ulna Plates System Self-Tapping Spherical Locking Screw Self-Tapping Conical Locking Screw Cortex Screw Approved
Functional outcome of ligament reconstruction tendon interposition for basal joint arthritis of thumb
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Jagdev SS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 217 May;3(3):492-496 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/issn.2455-451.intjresorthop217189
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Jagdev SS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 217 May;3(3):492-496 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/issn.2455-451.intjresorthop217189
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Hand Surgery, Nagoya University School of Medicine ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 74. 167 ~ 171 2012 ORIGINAL PAPER TILT OF THE RADIUS FROM FOREARM ROTATIONAL AXIS RELIABLY PREDICTS ROTATIONAL IMPROVEMENT AFTER CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY FOR MALUNITED FOREARM FRACTURES
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 74. 167 ~ 171 2012 ORIGINAL PAPER TILT OF THE RADIUS FROM FOREARM ROTATIONAL AXIS RELIABLY PREDICTS ROTATIONAL IMPROVEMENT AFTER CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY FOR MALUNITED FOREARM FRACTURES
Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid Perilunate Fracture Dislocation
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(3):127-132. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.3.127 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Bilateral Trans-Scaphoid
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
UZZAMAN KS 1, AWAL KA 2, ALAM MK 3
 CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION COMBINED WITH PLASTER CAST VERSUS CONVENTIONAL PLASTER CAST IMMOBILIZATION IN THE TREATMENT OF COLLES FRACTURE A PROSPECTIVE RANDOMIZED COMPARATIVE
CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS KIRSCHNER WIRE FIXATION COMBINED WITH PLASTER CAST VERSUS CONVENTIONAL PLASTER CAST IMMOBILIZATION IN THE TREATMENT OF COLLES FRACTURE A PROSPECTIVE RANDOMIZED COMPARATIVE
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments
 Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Ligaments of Elbow hinge: sagittal plane so need lateral and medial ligaments Ulnar Collateral ligament on medial side; arising from medial epicondyle and stops excess valgus movement (lateral movement)
Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results
 Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results Eirini Liodaki, MD, Tobias Kisch, MD, Eike Wenzel, MD, Peter Mailänder,
Percutaneous Cannulated Compression Screw Osteosynthesis in Phalanx Fractures: The Surgical Technique, the Indications, and the Results Eirini Liodaki, MD, Tobias Kisch, MD, Eike Wenzel, MD, Peter Mailänder,
A STUDY OF THE FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF LOW PROFILE DORSAL PLATING IN DISTAL END RADIUS FRACTURES
 Original Article Orthopaedics A STUDY OF THE FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF LOW PROFILE DORSAL PLATING IN DISTAL END RADIUS FRACTURES Sunil H. Shetty 1, Amit B. Dhond 2, Manavdeep Singh 3, Atul Kharat 4, Abhimanyu
Original Article Orthopaedics A STUDY OF THE FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF LOW PROFILE DORSAL PLATING IN DISTAL END RADIUS FRACTURES Sunil H. Shetty 1, Amit B. Dhond 2, Manavdeep Singh 3, Atul Kharat 4, Abhimanyu
Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
Scaphoid Fractures. Mohammed Alasmari. Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University
 Scaphoid Fractures Mohammed Alasmari Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University 1 2 Scaphoid Fractures Introduction Anatomy History Clinical examination Radiographic evaluation Classification
Scaphoid Fractures Mohammed Alasmari Orthopaedic Surgery Demonstrator Majmaah University 1 2 Scaphoid Fractures Introduction Anatomy History Clinical examination Radiographic evaluation Classification
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2010) 28, 1002 1008 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Original Contribution Ultrasound-guided reduction of distal radius fractures Shiang-Hu Ang, Shu-Woan Lee, Kai-Yet
