Brachial Neuritis: An Uncommon Cause of Shoulder Pain
|
|
|
- Lynne Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
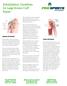
1 Brachial Neuritis: An Uncommon Cause of Shoulder Pain ROBERT G. HOSEY, MD; RICHARD E. RODENBERG, MD Brachial neuritis, an uncommon idiopathic syndrome, should be considered in the differential diagnosis of acute nontraumatic shoulder pain with weakness. Shoulder pain is one of the leading complaints of athletes seeking care from sports medicine physicians. Differential diagnosis includes a spectrum of orthopedic and nonorthopedic problems. In individuals who report acute atraumatic onset of shoulder pain followed by weakness, brachial neuritis should be considered. Brachial neuritis is an uncommon, idiopathic syndrome that typically affects the lower motor neurons of the brachial plexus. Involvement of a single nerve or nerve branches can also occur. Although symptomatology and physical From the Division of Sports Medicine, University of Kentucky, Lexington, Ky. Reprint requests: Robert G. Hosey, MD, K308 Kentucky Clinic, 740 S Limestone, Lexington, KY examination findings may vary, the clinical course is generally characterized by acute onset of severe pain followed by weakness and gradual recovery. CASE REPORT A 31-year-old recreational swimmer and weightlifter presented with severe right shoulder pain and weakness of 3 weeks duration. No inciting injury or trauma was reported. Initially, pain involved the deltoid and periscapular region followed by radiation to the proximal arm. Parasthesias and weakness subsequently developed in the same locations. The patient was initially treated by his primary physician with anti-inflammatories and muscle relaxers without symptom improvement. Medical history revealed a viral illness 3 weeks prior to symptom onset. Physical examination revealed Figure: Winging of the right scapula in a patient with brachial neuritis. significant atrophy of the trapezius, supraspinatus, and infraspinatus muscles on the affected side. Full active range of motion of the right shoulder resulted in moderate right shoulder (Figure). Muscular weakness 4/5 was noted with resisted shoulder internal/external rotation. Cervical spine examination was unremarkable. The to severe discomfort. remainder of the musculoskele- Significant scapular winging was present on forward flexion of the tal/neurologic examination was normal. AUGUST 2004 Volume 27 Number 8 833
2 Plain radiographs of the cervical spine and right shoulder revealed no significant bony abnormality. Electromyography (EMG) revealed decreased motor action potential of the serratus anterior and abnormal fasciculation of the extensor carpi radials and pronator teres muscles on the affected side. These findings corresponded to involvement of C5, C6, and C7 nerve roots. Rehabilitation, consisting of rotator cuff strengthening and scapular stabilization exercises, was prescribed. At 1-month follow-up, the patient had significant improvement in pain and weakness symptoms. Resisted shoulder internal/external rotation had improved to 5/5. The patient was subsequently lost to follow-up, presumably secondary to symptom resolution. DISCUSSION Brachial neuritis is bestknown secondary to neuralgic amyotrophy, a condition in 136 servicemen during World War II by Parsonage and Turner. 1 Although the disorder is known by many names (including acute brachial neuropathy, acute brachial radiculitis, acute shoulder neuritis, brachial neuropathy, brachial plexus neuropathy, idiopathic brachial neuropathy, multiple or localized neuritis of the shoulder gir- Brachial neuritis is an uncommon, idiopathic syndrome that typically affects the lower motor neurons of the brachial plexus. dle, and paralytic brachial neuritis), the most notable has been Parsonage-Turner syndrome. 2-4 The difficulty naming this disorder reflects the lack of understanding regarding the etiology and pathophysiology of brachial neuritis. The ability of this disorder to affect the brachial plexus with involvement of one or more nerves allows its presentation to mimic multiple other diagnoses. This confusion at presentation makes diagnosis difficult, leading to inappropriate treatment, including unnecessary surgery. 2,3,5,6 Epidemiology Brachial neuritis has been described to occur from age 3 months to 75 years. 2 According to Tsairis et al, 7 the highest incidence occurs in patients in their 30s and 70s. Predilection to affect males more than females has been reported to occur at a 2:1 ratio. 7,8 Magee and DeJong 9 reported an 11.5:1 male to female ratio in their patient population. The condition does not seem to affect one extremity more than another, or correlate to hand dominance. 2,9 The condition can affect both upper extremities but usually reveals an asymmetric onset and presentation. 2,7,10 Etiology According to McCarty et al, 2 as of yet, there has been no substantial evidence supporting an etiologic mechanism for the pathogenesis of brachial neuritis. A viral etiology is the most emphasized etiology, with various infections preceding symptom onset in up to 25% of cases in various study populations. 2,7,9,10 Brachial neuritis has been reported in up to 15% of cases following vaccination. 7,9 Others have proposed autoimmune mechanisms, surgery, heavy exertion, and trauma as etiologies for brachial neuritis. 2,7,8-10 A hereditary form has also been reported. 2 Trauma is not believed to play a role as an etiology for this condition. 10 Clinical Presentation Despite the lack of evidence supporting an etiology for brachial neuritis, the clinical presentation appears to be consistent based on two symptoms. The first symptom is severe, acute, burning pain in the shoulder and upper arm. The pain normally subsides within a few hours to 2-3 weeks. As the pain diminishes, the second symptom to present is muscle weakness. 2,3 Physical examination reveals abnormalities in the distribution of the brachial plexus (usually the upper trunk) with involvement of one or more nerves. 2,3,5,6 Weakness usually involves muscles innervated by the suprascapular, axillary, long thoracic, and musculocutaneous nerves. Involvement of the radial, anterior interosseous, and median nerves has been described. 2 Weakness, therefore, commonly occurs in the deltoid, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, serratus anterior, biceps, triceps muscles, and wrist and finger extensors. 2 The phrenic nerve has been involved in rare cases, either unilaterally or bilaterally, with the most common presenting symptom being dyspnea. 11 Sensory changes have been noted but usually are minimal in degree compared to the motor deficits. Sensory loss usually follows the distribution of the affected motor nerves. 2,12 When bilateral shoulders are affected, the presentation usually is asymmetric. The contralateral shoulder is subclinical in presentation for weakness and sensory changes. Abnormal findings are detected by EMG. 2,12 Differential Diagnosis The differential diagnosis of brachial neuritis can be vast, allowing for misdiagnosis. The physical findings consistent with brachial neuritis can be misconstrued for other conditions that cause acute pain and weakness around the shoulder, including rotator cuff tears, impingement syndromes, adhesive capsulitis, and calcific tendinitis. Less common conditions that mimic brachial neuritis include diskogenic cervical spine disorders, poliomyelitis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, herpes zoster, spinal or brachial plexus tumors, and traumatic compressive nerve injuries. 2 Two conditions that closely mimic brachial neuritis are acute upper cervical disease and compressive lesions of peripheral nerves. By paying 834 ORTHOPEDICS
3 close attention to the history, many conditions can be eliminated. Acute upper cervical disk disease (C4, C5, and C6) can present with acute pain with or without a history of trauma. However, the pain usually is related to the simultaneous presentation of weakness and sensory changes in a dermatomal distribution restricted to one nerve root. The sensory deficit seen with cervical disk disease generally is greater than that seen in brachial neuritis. 2,3 Compressive peripheral nerve lesions can be difficult to distinguish from brachial neuritis. Patients with this disorder usually present with a more insidious onset of pain. Pain duration is longer compared to brachial neuritis. 2,12 Diagnostic Studies Most diagnostic tests, including laboratory tests and plain film radiographs, are negative in patients with brachial neuritis. Even cerebral spinal fluid has been found to be normal, with only a few reports revealing slight increases in total protein. 2,7,9,10 Immunologic studies are typically normal. 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of the affected shoulder girdle may show high-signal intensity of the affected muscles on T2 images that can occur within days of symptom onset, revealing edema. Helms et al 4 demonstrated these findings in the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and deltoid muscles. Muscle atrophy without fatty infiltrate was found after prolonged periods of muscle weakness. 4 These findings were confirmed in a study by Bredella et al 13 correlating to EMG findings consistent with three patients diagnosed with brachial neuritis. Magnetic resonance imaging is also valuable in eliminating other disorders such as rotator cuff tears, impingement syndromes, and ganglion cysts, which can compress peripheral nerves causing compressive neuropathies. Ganglion cysts most commonly occur around labral tears with compression along the suprascapular nerve. 4 Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine is useful in determining cervical disk disease with root compression. 3 Electromyography is the cornerstone for diagnosis of brachial neuritis, as it differentiates brachial neuritis from traumatic upper trunk or plexus lesions. Lesions are usually localized to the upper plexus. Findings can vary depending on the severity of neural damage and the timing of the examination. Nerve conduction velocities usually are normal. Electromyography reveals acute denervation indicating axonal neuropathy. The most common findings on EMG include fibrillation potentials and positive waves suggestive of muscle denervation. Delayed distal latencies and decreased amplitude of active potentials are also present. Three weeks following symptom onset is sufficient time to determine findings on EMG. 2,3,5 Treatment Treatment of brachial neuritis is supportive secondary to the self-limiting disease process. A combination of narcotic and nonsteroidal analgesics are used to control acute pain. During the pain phase, the extremity is rested secondary to increased activity exacerbating pain. A sling may provide a more comfortable position during this acute time. 2,3,5 As pain subsides, the entire upper extremity and upper body (secondary to subclinical involvement) must be rehabilitated to regain strength. Therapy is recommended although it has not been proven to correlate with faster recovery. 2,3,5,7 Range of motion begins passively and is switched to active rehabilitation once the patient begins to recover in strength. 2 Corticosteroid use has not been proven to decrease recovery time. 2,3,5 Prognosis Recovery is generally good. Improvement in strength begins from 1 month after symptom onset to 3 years. The majority of patients have substantial improvement within 3 years. 1,2 Misamore and Lehman 12 found that patients could be subjected to persistent mild weakness for 3 years. Magee and DeJong 9 reported that full recovery of strength may take as long as 8 years. McCarty et al 2 and Tsairis et al 7 estimated the rate of complete recovery to be 89% by the end of 3 years. According to McCarty et al, 2 the greater the severity and duration of pain and/or weakness usually leads to prolonged recovery. Bilateral involvement may have a longer recovery, and patients with upper trunk lesions tend to do best. 2,7 Return to sport is determined on a case-by-case basis. A plateau in strength recovery must be attained before allowing return to sport. Some athletes fully recover with no limitations, whereas other athletes As pain subsides, the entire upper extremity and upper body (secondary to subclinical involvement) must be rehabilitated to regain strength. may require counseling concerning limitations. Decisions are made on an individual basis taking into account the individual s abilities. 2,5,6 CONCLUSION The recognition of a few key historical and physical examination findings includes acute brachial neuritis in the differential diagnosis of acute nontraumatic shoulder pain with weakness. The awareness of this disorder, although uncommon, helps prevent unwarranted treatment and possibly inappropriate surgical procedures, which could change a relatively AUGUST 2004 Volume 27 Number 8 835
4 benign prognosis into a worse outcome. REFERENCES 1. Parsonage MJ, Turner JW. The shoulder-girdle syndrome. Lancet. 1948; 1: McCarty EC, Tsairis P, Warren RF. Brachial neuritis. Clin Orthop. 1999; 368: Miller JD, Pruitt S, McDonald TJ. Acute brachial plexus neuritis: an uncommon cause of shoulder pain. Am Fam Physician. 2000; 62: Helms CA, Martinez S, Speer KP. Acute brachial neuritis (Parsonage-Turner syndrome): MR imaging appearance report of three cases. Radiology. 1998; 207: Hershman EB. Brachial plexus injuries. Clin Sports Med. 1990; 9: Hershman EB, Wilbourn AJ, Bergfeld JA. Acute brachial neuropathy in athletes. Am J Sports Med. 1989; 17: Tsairis P, Dyck PJ, Mulder DW. Natural history of brachial plexus neuropathy. Report on 99 patients. Arch Neurol. 1972; 27: Turner JW, Parsonage MJ. Neuralgic amyotrophy (paralytic brachial neuritis); with special reference to prognosis. Lancet. 1957; 2: Magee KR, DeJong RN. Paralytic brachial neuritis. Discussion of clinical features with review of 23 cases. JAMA. 1960; 174: Dillin L, Hoaglund FT, Scheck M. Brachial neuritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985; 67: Lahrmann H, Grisold W, Authier FJ, Zifko UA. Neuralgic amyotrophy with phrenic nerve involvement. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22: Misamore GW, Lehman DE. Parsonage-Turner syndrome (acute brachial neuritis). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996; 78: Bredella MA, Tirman PF, Fritz RC, Wischer TK, Stork A, Genant HK. Denervation syndromes of the shoulder girdle: MR imaging with electrophysiologic correlation. Skeletal Radiol. 1999; 28: Section Editor: Darren L. Johnson, MD 836 ORTHOPEDICS
5 trauma update AUGUST 2004 Volume 27 Number 8 837
Case 3. Your Diagnosis?
 Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Case 3 45 year-old presenting with a history of injury to the right shoulder whilst working in the freezing work. He was loading a sheep over an incline with his arm around the sheep. He felt pain in the
Patients with cervical radiculopathy (CR) are frequently encountered
 Cervical Radiculopathy or Parsonage-Turner Syndrome: Differential Diagnosis of a Patient With Neck and Upper Extremity Symptoms Christopher J. Mamula, MPT, ATC 1 Richard E. Erhard, PT, DC 2 Sara R. Piva,
Cervical Radiculopathy or Parsonage-Turner Syndrome: Differential Diagnosis of a Patient With Neck and Upper Extremity Symptoms Christopher J. Mamula, MPT, ATC 1 Richard E. Erhard, PT, DC 2 Sara R. Piva,
Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner syndrome: two case reports
 Kumar et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:255 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner
Kumar et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:255 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Utility of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of unsuspected cases of Parsonage-Turner
Advances in Knowledge Of 30 shoulders examined with MR imaging in patients with Parsonage-Turner syndrome, 29 (97%) had involvement of the suprascapul
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Cree M. Gaskin, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Cree M. Gaskin, MD
MRI Findings of 26 Patients with
 MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
MRI of Patients with Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Richard E. Scalf 1 Doris E. Wenger 1 Matthew. Frick 1 Jayawant N. Mandrekar 2 Mark C. dkins 1 Scalf RE, Wenger
IDIOPATHIC BRACHIAL NEURITIS
 IDIOPATHIC BRACHIAL NEURITIS Pedro Gonzalez-Alegre, MD; Ana Recober, MD and Praful Kelkar, MD ABSTRACT Idiopathic brachial neuritis is a well defined clinical condition that most commonly affects young
IDIOPATHIC BRACHIAL NEURITIS Pedro Gonzalez-Alegre, MD; Ana Recober, MD and Praful Kelkar, MD ABSTRACT Idiopathic brachial neuritis is a well defined clinical condition that most commonly affects young
Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player Brachial Plexus Injuries in Sport Typically a transient neurapraxia - 70% of injured players said they did not always report
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Brachial Plexopathy in a Division I Football Player Brachial Plexus Injuries in Sport Typically a transient neurapraxia - 70% of injured players said they did not always report
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University
 Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Assessment of the Brachial Plexus EMG Course CNSF Halifax 2018 Fraser Moore, Canadian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology McGill University Angela Scott, Association of Electromyography Technologists of
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG
 Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Nerve Conduction Studies and EMG Limitations of other methods of investigations of the neuromuscular system - Dr Rob Henderson, Neurologist Assessment of Weakness Thanks Peter Silburn PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression. Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre
 Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
Differential Diagnosis of Neuropathies and Compression Dr Ashwin Pinto Consultant Neurologist Wessex Neurological Centre Outline of talk Mononeuropathies median and anterior interosseous nerve ulnar nerve
The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy
 Neurology Asia 2017; 22(1) : 9 13 The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy 1 Jung Soo Lee MD PhD, 2 Yoon Tae Kim MD PhD, 3 Joon Sung Kim MD PhD, 3 Bo Young Hong MD PhD, 3 Lee Chan
Neurology Asia 2017; 22(1) : 9 13 The clinical manifestations and outcomes of neuralgic amyotrophy 1 Jung Soo Lee MD PhD, 2 Yoon Tae Kim MD PhD, 3 Joon Sung Kim MD PhD, 3 Bo Young Hong MD PhD, 3 Lee Chan
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group
 Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies
 18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
18 Electrophysiology of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexopathies Juan A. Acosta and Elizabeth M. Raynor Summary Brachial and lumbosacral plexopathies represent a heterogeneous group of disorders including
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Speaker Disclosure
 Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
Suprascapular Nerve: How to identify when it is a problem and what to do? Eric C. McCarty, MD Associate Professor Chief of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery University of Colorado School of Medicine
Neurology Topics. Ian Rosemergy
 Neurology Topics Ian Rosemergy Plan An unusual presentation of a not so unusual problem Some seizure cases 49 year old female Patient 1 Hit on back and neck by swinging car door o Severe neck and shoulder
Neurology Topics Ian Rosemergy Plan An unusual presentation of a not so unusual problem Some seizure cases 49 year old female Patient 1 Hit on back and neck by swinging car door o Severe neck and shoulder
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy
 MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy
 MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
MRI Patterns Of Shoulder Denervation: A Way To Make It Easy Poster No.: C-2059 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Rossetto, P. Schvartzman, V. N. Alarcon, M. E. Scherer, D. 1 2 3
June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month
 June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month This case is no longer available for CME credit. Cases prepared by: Ian MacLean, MD; Daniel Dumitru, MD; Lawrence R. Robinson, MD HISTORY Six weeks ago a 28-year-old woman
June 1996 EMG Case-of-the-Month This case is no longer available for CME credit. Cases prepared by: Ian MacLean, MD; Daniel Dumitru, MD; Lawrence R. Robinson, MD HISTORY Six weeks ago a 28-year-old woman
Anatomical Considerations/ Pathophysiology The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body. : Three bones:
 Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s -
 3 2 Vol. 3, No 2, November 1998. - 3 -, * * =A bs trac t = A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s - Min Jong P ark, M.D., Jong Yoon Lee, M.D.,
3 2 Vol. 3, No 2, November 1998. - 3 -, * * =A bs trac t = A nt erior Int ero s s eou s N erv e Sy n drom e - Obs erv ation s f or T hree Surg ical Ca s e s - Min Jong P ark, M.D., Jong Yoon Lee, M.D.,
Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit?
 Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit? Scott D Boden, MD The Emory Spine Center Atlanta, Georgia History of Trauma? 2 History of Trauma? 3 Sometimes
Cervical Radiculopathy: My 32 Year-Old Cyclist is Nervous What do I do on the initial visit? Scott D Boden, MD The Emory Spine Center Atlanta, Georgia History of Trauma? 2 History of Trauma? 3 Sometimes
Joint G*H. Joint S*C. Joint A*C. Labrum. Humerus. Sternum. Scapula. Clavicle. Thorax. Articulation. Scapulo- Thoracic
 A*C Joint Scapulo- Thoracic Articulation Thorax Sternum Clavicle Scapula Humerus S*C Joint G*H Joint Labrum AC Ligaments SC Ligaments SC JOINT AC Coracoacromial GH GH Ligament Complex Coracoclavicular
A*C Joint Scapulo- Thoracic Articulation Thorax Sternum Clavicle Scapula Humerus S*C Joint G*H Joint Labrum AC Ligaments SC Ligaments SC JOINT AC Coracoacromial GH GH Ligament Complex Coracoclavicular
Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII
 Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch, Anne Kerbrat, Paul Sauleau To cite this version: Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch,
Unusual presentation of neuralgic amyotrophy with impairment of cranial nerve XII Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch, Anne Kerbrat, Paul Sauleau To cite this version: Margaux Genevray, Mathieu Kuchenbuch,
G24: Shoulder and Axilla
 G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF CERVICAL VS. SHOULDER PAIN: A PHYSIATRIST S PERSPECTIVE
 Russ Cantrell, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Orthopedic Sports Medicine and Spine Care Institute DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF CERVICAL VS. SHOULDER PAIN: A PHYSIATRIST S PERSPECTIVE PHYSIATRIST
Russ Cantrell, M.D. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Orthopedic Sports Medicine and Spine Care Institute DIAGNOSTIC EVALUATION OF CERVICAL VS. SHOULDER PAIN: A PHYSIATRIST S PERSPECTIVE PHYSIATRIST
Obstetric Brachial Plexus Injuries. Surgery department grand rounds Bassam MJ Addas, FRCSC Neurological Surgery, KAUH
 Obstetric Brachial Plexus Injuries. Surgery department grand rounds Bassam MJ Addas, FRCSC Neurological Surgery, KAUH Definition Obstetric versus birth palsy Obstetric versus congenital palsy Not all birth
Obstetric Brachial Plexus Injuries. Surgery department grand rounds Bassam MJ Addas, FRCSC Neurological Surgery, KAUH Definition Obstetric versus birth palsy Obstetric versus congenital palsy Not all birth
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurophysiological Diagnosis of Birth Brachial Plexus Palsy. Dr Grace Ng Department of Paed PMH
 Neurophysiological Diagnosis of Birth Brachial Plexus Palsy Dr Grace Ng Department of Paed PMH Brachial Plexus Anatomy Brachial Plexus Cords Medial cord: motor and sensory conduction for median and ulnar
Neurophysiological Diagnosis of Birth Brachial Plexus Palsy Dr Grace Ng Department of Paed PMH Brachial Plexus Anatomy Brachial Plexus Cords Medial cord: motor and sensory conduction for median and ulnar
Personal use only. MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality
 MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality Christian W. A. Pfirrmann Orthopedic University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland Atrophy of Infraspinatus Infraspinatus Atrophy: Diagnosis?
MR Imaging Assessment of Rotator Cuff Muscle Quality Christian W. A. Pfirrmann Orthopedic University Hospital Balgrist University of Zurich Switzerland Atrophy of Infraspinatus Infraspinatus Atrophy: Diagnosis?
C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment
 Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Arm Pain, Numbness, and Tingling: Etiologies and Treatment Steve Fowler MD Confluence Health Department of Physiatry Education Medical School: University of Utah Residency: Mayo Clinic Work Confluence
Physical Examination of the Shoulder
 General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Shoulder examination. P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College
 Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
MUSCLES OF SHOULDER REGION
 Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
Dr Jamila EL Medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the name of muscles of the shoulder region. Describe the anatomy of muscles of shoulder region regarding: attachments of
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Lab Workbook. ANATOMY Manual Muscle Testing Lower Trapezius Patient: prone
 ANATOMY Manual Muscle Testing Lower Trapezius Patient: prone Lab Workbook Fixation: place on hand below the scapula on the opposite side Test: adduction and depression of the scapula with lateral rotation
ANATOMY Manual Muscle Testing Lower Trapezius Patient: prone Lab Workbook Fixation: place on hand below the scapula on the opposite side Test: adduction and depression of the scapula with lateral rotation
CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF THE SHOULDER JOINT 대한신경근골격연구회 분당제생병원재활의학과 박준성
 CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF THE SHOULDER JOINT 대한신경근골격연구회 분당제생병원재활의학과 박준성 Clinical Examination of the Shoulder Good history, full clinical examination Detailed knowledge of the anatomy solve the majority of
CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF THE SHOULDER JOINT 대한신경근골격연구회 분당제생병원재활의학과 박준성 Clinical Examination of the Shoulder Good history, full clinical examination Detailed knowledge of the anatomy solve the majority of
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck.
 Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
Region of upper limb attachment to the trunk Proximal segment of limb overlaps parts of the trunk (thorax and back) and lower lateral neck. includes Pectoral Scapular Deltoid regions of the upper limb
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
CNS & PNS Entrapment. Disclosure - Nothing
 Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Peripheral Nerve Entrapments That Mimic Spinal Pathology: Evaluation And Treatment Both Medical And Surgical Michel Kliot MD Clinical Professor UCSF Department of NeuroSurgery Director Center For Evaluation
Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 763201, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/763201 Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Marcus Vinicius Pinto,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2013, Article ID 763201, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/763201 Case Report Recurrent Vocal Fold Paralysis and Parsonage-Turner Syndrome Marcus Vinicius Pinto,
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
2015 OPSC Annual Convention. syllabus. February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California
 2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
2015 OPSC Annual Convention syllabus February 4-8, 2015 Hyatt Regency Mission Bay San Diego, California THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 5, 2015: 3:30pm - 4:30pm The Shoulder: 2 View or Not 2 View * Presented by Alexandra
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT
 FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY OF SHOULDER JOINT ARTICULATION Articulation is between: The rounded head of the Glenoid cavity humerus and The shallow, pear-shaped glenoid cavity of the scapula. 2 The articular surfaces
BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY INVESTIGATION, LOCALIZATION AND TREATMENT. Presented By : Dr.Pankaj Jain
 BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY INVESTIGATION, LOCALIZATION AND TREATMENT Presented By : Dr.Pankaj Jain EMBRYOLOGY l Brachial plexus (BP) is developed at 5 weeks of gestation l Afferent fibers develop from neuroblast
BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURY INVESTIGATION, LOCALIZATION AND TREATMENT Presented By : Dr.Pankaj Jain EMBRYOLOGY l Brachial plexus (BP) is developed at 5 weeks of gestation l Afferent fibers develop from neuroblast
Vascular Injuries in the Throwing Shoulder MLB Winter Meeting 2015
 Neurovascular Problems in the Throwing Athlete s Shoulder Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor,
Neurovascular Problems in the Throwing Athlete s Shoulder Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor,
Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain
 Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain David B. Bumpass, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery UAMS Depts. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Neurosurgery May 12, 2018 Disclosures Medtronic Spine speaking fees
Diagnosis of Neck & Upper Extremity Pain David B. Bumpass, MD Assistant Professor, Spine Surgery UAMS Depts. of Orthopaedic Surgery & Neurosurgery May 12, 2018 Disclosures Medtronic Spine speaking fees
REMINDER. Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns
 Understanding Shoulder Dysfunction REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns What is a healthy shoulder?
Understanding Shoulder Dysfunction REMINDER Obtain medical clearance and physician s release prior to beginning an exercise program for clients with medical or orthopedic concerns What is a healthy shoulder?
Chronic Shoulder Disorders
 Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
Chronic Shoulder Disorders Dr. Mustafa Elsingergy Consultant orthopedic surgeon Dallah Hospita Prof. Mamoun Kremli Almaarefa Medical College Contents INTRINSIC Shoulder Pain Due to causes in the shoulder
D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y
 Thoracic Outlet (TOS), Winged Scapula, Brachial Plexus Compression 12 D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y 1122 KENILWORTH DRIVE, SUITE 18, TOWSON, MARYLAND
Thoracic Outlet (TOS), Winged Scapula, Brachial Plexus Compression 12 D E L L O N I N S T I T U T E S F O R P E R I P H E R A L N E R V E S U R G E R Y 1122 KENILWORTH DRIVE, SUITE 18, TOWSON, MARYLAND
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities
 Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
Evaluation of Tingling and Numbness in the Upper Extremities DR. W. ANTHONY FRISELLA M.D. ADVANCED BONE & JOINT, ST CHARLES MO MONA 2018 Overview Polyneuropathy Compressive nerve lesions Carpal tunnel
A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Quadrilateral Space Syndrome Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Pain Assessment Patient Interview (location/nature of symptoms), Body Diagram. Observation and Examination: Tests and Measures
 Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Shoulder Joint Examination. Shoulder Joint Examination. Inspection. Inspection Palpation Movement. Look Feel Move
 Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
Ultrasound of the Shoulder
 Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
Ultrasound of the Shoulder Patrick Battaglia, DC, DACBR Logan University, Department of Radiology Outline Review ultrasound appearance of NMSK tissues Present indications for ultrasound of the shoulder.
HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT:
 submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
submitted by Keith M. Bartley, D.C. Jasper, IN 07/21/11 presented at Cox Seminar in Nashville, TN, on October 8 9, 2011 HISTORY AND CHIEF COMPLAINT: 01/21/11 55 year old male press operator for Jasper
Shoulder Exam Break-out with Case Highlights. Teri Metcalf McCambridge, MD, FAAP, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Orthopedics University
 Shoulder Exam Break-out with Case Highlights. Teri Metcalf McCambridge, MD, FAAP, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Orthopedics University of Maryland School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Information
Shoulder Exam Break-out with Case Highlights. Teri Metcalf McCambridge, MD, FAAP, CAQSM Assistant Professor of Pediatrics and Orthopedics University of Maryland School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Information
The Upper Limb III. The Brachial Plexus. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
 Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder
 Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Scapular and Deltoid Regions
 M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy Scapular and Deltoid Regions Dr. Peters 1 Outline I. Skeleton of the Shoulder and Attachment of the Upper Extremity to Trunk II. Positions and Movements of the Scapula
M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy Scapular and Deltoid Regions Dr. Peters 1 Outline I. Skeleton of the Shoulder and Attachment of the Upper Extremity to Trunk II. Positions and Movements of the Scapula
If head is rapidly forced away from shoulder the injury is generally at C5,C6. If arm is rapidly abducted the lesion is generally at C8-T1.
 BRACHIAL PLEXUS Etiology Generally caused by MVA in adults. Generally males aged 15 to 25 years old. Naracas: Rule of seven seventies. 70% occur secondary to MVA; 70% involve motorcycles or bicycles. 70%
BRACHIAL PLEXUS Etiology Generally caused by MVA in adults. Generally males aged 15 to 25 years old. Naracas: Rule of seven seventies. 70% occur secondary to MVA; 70% involve motorcycles or bicycles. 70%
Muscles of the Upper Limb
 Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Muscles of the Upper Limb anterior surface of ribs 3 5 coracoid process Pectoralis minor pectoral nerves protracts / depresses scapula Serratus anterior Subclavius ribs 1-8 long thoracic nerve rib 1 ----------------
Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders
 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 13: 29 34, 2000 2000 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders SAMI L. KHELLA, M.D. Introduction This
The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal 13: 29 34, 2000 2000 The University of Pennsylvania Orthopaedic Journal Electromyography in Shoulder Disorders SAMI L. KHELLA, M.D. Introduction This
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Labral/Bankert Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity. Dr Ayesha Basharat BSPT, PP.DPT. M.PHIL
 The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity Dr Ayesha Basharat BSPT, PP.DPT. M.PHIL Sternoclavicular Joint Provides major axis of rotation for movement of clavicle and scapula Freely permitted frontal
The Biomechanics of the Human Upper Extremity Dr Ayesha Basharat BSPT, PP.DPT. M.PHIL Sternoclavicular Joint Provides major axis of rotation for movement of clavicle and scapula Freely permitted frontal
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned
 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
The Shoulder. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Shoulder Jennifer R Marks, MD Shoulder Anatomy Skeletal & ligamentous components: The joint is comprised of a confluence of Scapula Clavicle Humerus https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/ http/ www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/117777
The Shoulder Jennifer R Marks, MD Shoulder Anatomy Skeletal & ligamentous components: The joint is comprised of a confluence of Scapula Clavicle Humerus https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/ http/ www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/117777
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods )
 Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017
 Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle. Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop)
 Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Anatomy of the Shoulder Girdle Prof Oluwadiya Kehinde FMCS (Orthop) www.oluwadiya.com Bony Anatomy Shoulder Complex: Sternum(manubrium) Clavicle Scapula Proximal humerus Manubrium Sterni Upper part of
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Large Rotator Cuff Repair The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy
 Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Evaluating concomitant lateral epicondylitis and cervical radiculopathy March 06, 2010 This article describes a study of the prevalence of lateral epicondylitis or tennis elbow among patients with neck
Official Definition. Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
 Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW
 PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
