A New Septum in the Female Breast
|
|
|
- Sharon Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A New Septum in the Female Breast Mostafa Abdel Rahman Awad 1, Mahmoud Magdi Sherif 1, Eaman Yahya Sadek 1, Hesham Aly Helal 1, Wafaa Raafat Abdel Hamid 2 Departments of 1 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and 2 Radiodiagnosis, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt Original Article Background Understanding the female breast fascial system is of paramount importance in breast surgery. Little was written about breast ligaments. Most articles refer to Cooper s work without further anatomical studies. Lately, a horizontal septum has been described conveying nerves and vessels to the nipple areola complex. Methods During the surgical dissection of the lower part of the breast, in supero-medial technique for breast reduction operations, a fascial septum between the lower two quadrants was detected. This fibrous septum was studied through anatomic dissection of breast tissues during routine breast reshaping procedures that was done on 30 female patients. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed preoperatively in all cases and correlated with the intraoperative findings. In the other five cases, outside the clinical study, the imaging was done during routine investigation for breast swellings. Results A vertical septum was identified in the lower part of the breast, lying at the breast meridian between the two lower quadrants. It is a tough bi-laminated structure that extends from the middle of the infra-mammary crease caudally to nipple-areola complex cranially and from the pectoral fascia posteriorly to the overlying skin anteriorly. This was proved by MRI findings. Conclusions This study describes a new inferior vertical septum which separates the lower half of the breast into two definite anatomical compartments: medial and lateral. Keywords Breast / Mammaplasty / Fascia / Ligaments Correspondence: Hesham Aly Helal Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Ain Shams University, 80A Thawra Street, Heliopolis, Cairo, Egypt Tel: Fax: drheshamhelal75@yahoo.com Special thanks to Mr. Mohammad El- Hamahmy (Lecturer, Faculty of Arts) for drawing the illustrations which are the authors own creation. This study was presented in the 44th Annual Congress of the Egyptian Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons on February 2014, in El Gouna, Egypt. No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. Received: 12 Dec 2015 Revised: 10 Nov 2016 Accepted: 10 Dec 2016 pissn: eissn: Arch Plast Surg 2017;44: INTRODUCTION Despite the importance of fascial ligaments and supporting septa in the female breast, little was written about them. Cooper [1] in 1840, described fibrous septa extending from the skin to the pectoral fascia dividing the breast into lobes and lobules. He considered these septa as the supporting system of the breast parenchyma. Bayati and Seckel [2] identified a ligament originating from the fifth rib medially and the fascia between the fifth and sixth ribs laterally to insert into the deep dermis of the infra-mammary crease (IMF). Presence of such ligament has its proponents [3,4] as well as opponents [5-7]. Nava et al. [4] identified a pseudo-ligamentous lamina detaching off the superficial fascia along the entire infra-mammary fold and runs in subcutaneous tissue to reach the areola, essential in the formation of its contour. The adherence between superficial and deep fascia is made up of multiple short fibrous connections that don t cross the muscular wall [5]. Wuringer and Collegues [8,9] described a horizontal septum delivering nerve and vessels to the nipple. At its borders the septum curves upward into vertical medial and lateral extensions Copyright 2017 The Korean Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited
2 Awad MA et al. New septum in female breast attaching the breast to the sternum and lateral edge of pectoralis minor respectively. It acts with its extensions as a brassiere-like suspensory system. Since many years, we have been using the medially-based pedicle; Findlay s technique [10], in breast reduction and during this procedure, a vertical tough midline fibrous structure was usually noticed in the lower central part of the breast. The aim of our recent study is to confirm its existence and investigate all the characteristics of this newly described septum. To this purpose, an anatomical study was performed on 30 female patients to demonstrate the location, structure, shape, length and thickness of this vertical septum. Additionally a radiological study using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was done to confirm and correlate with the anatomical findings. Fig. 1. Anatomical location of septum The septum (thick white arrow) at mid IMF (black arrow) dividing the lower part of breast into medial and lateral compartments. IMF, infra-mammary crease. METHODS The study included: Anatomical study The fibrous septum was studied through anatomic dissection of breast tissues of 30 female patients (60 breasts) during breast reduction. All the data gathered for the study was from the right breast only while dissection of the left breast was only for verification of presence. Age ranged between 25 and 40 years old. Transposition of nipple and areola complex (NAC) was done using supero-medial pedicle in 10 cases, inferior pedicle in 5 cases and superior pedicle in 15 cases. Excised tissue ranged from 480 g to 2.2 kg, from each breast. Patients with previous breast surgery or breast diseases were excluded. The septum was accessed clinically by dissecting the lower pole of the breast starting by incising the skin at medial and lateral margins of skin resection down to the pectoral fascia then meticulous blunt dissection proceeds towards the already marked breast meridian where a tough fibrous barrier stretching from mid-inframammary point up to the NAC is present and hinder crossing the meridian (Fig. 1). Specific fragment measuring 3 3 cm of both the horizontal and the newly described septum was taken as surgical specimens and submitted to histological examination and collagen content quantification. MRI study Comprehensive MRI study of breast was performed including T1 weighted (T1W), T2W, fat suppressed (vessel sensitive sequence), diffusion weighted images (DWI) and axial images with or without post contrast enhancement as recommended [11,12]. All of the 30 cases that had reduction mammaplasty had preoperative MRI and imaging findings were correlated with intraoperative findings. Five more patients with suspected breast tumors had MRI as routine imaging to provide evidence of existence and give a more concrete concept of its structure. RESULTS The anatomical study A well-formed, tough, bi-laminar vertical septum was found in the midline of the lower part of the breast in all of the cases. It divides the lower part of breast into medial and lateral compartments. It extends from pectoral fascia posteriorly to overlying skin anteriorly with a length ranging from 6 to 12 cm (measured midway between the NAC and IMF using a ruler). It also extends from mid IMF caudally to NAC cranially with a length ranging from 10 to 17 cm (Fig. 2). It is a thick bi-laminar structure with its thickness ranged from 0.5 to 1.3 cm (measured by a sliding caliber) and could be split into two definite layers (Fig. 3). An intercostal perforator could be detected piercing the pectoralis major muscle and apparently heading towards the NAC guided by the fibrous septum (Fig. 4). The amount of fat found within the septum was proportional to the general fat content of the breast. In very large breasts, surrounding fat globules penetrate the septum causing its thinning (Fig. 5). The result of the histological examination showed that both septa were composed of collagenous tissue, predominantly of type I collagen with quantitative assessment showing more content of collagen type I in our vertical septum than the horizontal one in 25 breasts (83.3%). All patients data and results of the anatomical study are sum- 102
3 Vol. 44 / No. 2 / March 2017 Fig. 2. Extension of septum Fig. 4. Intercostal perforator within septum The septum extending from mid IMF (black arrow) caudally to the level of the NAC cranially. IMF, infra-mammary crease; NAC, nipple areola complex. Intercostal perforator piercing pectoralis major muscle. Fig. 5. Septum in fatty breast Fig. 3. Split of septum Fat globules penetrating the septum (black arrow). Split of vertical septum. marized in Table 1. The MRI study The breast is made up of glandular content normally acquiring dark signals on T1W images and T2W images and being of mixed signal intensity on fat suppressed images. The fatty background is diffusely bright on T1W and T2W images and turns dark on fat suppressed images. Cooper s ligaments and connective tissue contents appear dark on all sequences. The vertical septum was better demonstrated in axial images. It appeared as a linear dark structure extending from pectoral fascia posteriorly into breast parenchyma anteriorly. It was usually central in location, beginning inferiorly from the mid-inframammary point upwards toward NAC. It represented an invagination of the pectoral fascia into breast parenchyma, dividing the inferior aspect of breast into medial and lateral quadrants. In 3 breasts of them, there was minimal lateral paramedian deviation by: 5.3, 6.8, and 10.4 mms. The length of the septum ranged from 6.2 to 10.4 cm. Its thickness was between 4.3 and 12.8 mm. Moderately sized breasts showed a septum with uniform thickness all through its length, others have a septum which is thickened posteriorly, thinned out anteriorly with a difference in thickness and in fat content (Fig. 6). Large fatty breasts had equally fatty and fibroglandular tissues (ACR 2) except for three cases that were predominantly fatty on expense of fibro-glandular components (ACR 1). The septum was either: attenuated, appearing as an interrupted linear structure or completely non-visualized. It showed an uneven thickness with signal interruption ranging between zones of non-visualization and the 3.8 mm thick-wall 103
4 Awad MA et al. New septum in female breast Table 1. Patients data and septum characteristics No. Age (yr) Marital status Lactation Breast volume Dimensions of the septum (W-L-T) Type I collagen in vertical septum Type I collagen in transverse septum 1 28 Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes 1, Married Yes Single No Married Yes Married Yes 1, Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Single No Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes 1, Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Single Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Single No Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes Married Yes W, for width measured from mid infra-mamma ry crease caudally to nipple areola complex cranially; L, for length measured from pectoral fascia posteriorly to overlying skin anteriorly; T, for thickness. Fig. 6. Radiological view of septum Right side: the two laminae (red arrows) split anteriorly, accommodating fat within its potential space. Left side: septum (green arrow) is thicker posteriorly, thinned out anteriorly with no definite contents. T2W, T2 weighted. Fig. 7. Radiological view of perforator Right inferior septal predominance accommodating a vessel of caliber 3.1 mm (red arrows) in comparison to the left. 104
5 Vol. 44 / No. 2 / March 2017 Fig. 8. Radiological view of septum in fatty breast Very thin right breast septum accommodating a vessel only visualized within its posterior half (red arrow). The anterior half of septum appears remarkably attenuated with interrupted signal likely attributed to invaginations by fat lobules. The left breast septum could not be visualized on any of the magnetic resonance sequences. T2W, T2 weighted. Fig. 10. Septum in breast cancer A case of right breast malignancy involving the lower outer quadrant (yellow arrow) for which the patient was subjected to core biopsy (biopsy track=green arrow) for histopathology. Right breast shows an inferior septal vessel of caliber 5.4 mm (red arrow) with no definite intra-septal. T2W, T2 weighted. Fig. 11. Septum in fibroglandular predominance Fig. 9. Septum in mastectomy case A case had a left side mastectomy, with the septum on the right side is seen as a uniform structure containing a vessel within its confines (red arrows). A 19-year-old female with huge breasts; fibroglandular predominance with multiple well defined soft tissue mass lesions (fibroadenomata). On the right side the inferior septum (red arrows) is remarkably thickened with a posterior width of 23 mm accommodating fat, thinning out anteriorly reaching a thickness of 8 mm, deviated medially by one of the fibroadenomata. In left breast, septum is extremely difficult to verify attributed to the accentuated fibroglandular tissue and multiple deep lesions resting on the pectoral fascia. T2W, T2 weighted. of the septum. A vessel was detected in the potential space of the septum in 28 cases; the caliber varied between 3.1 and 3.8 mm (Figs. 7, 8). For the other five patients who had a routine imaging for suspected breast tumor; two cases were operated upon by conservative surgery for right breast malignancy in the upper halves, one case had modified mastectomy on the left side, one case with right breast malignancy in the lower outer quadrant and one case with fibroadenomas, the results are shown in (Figs. 9 11). DISCUSSION Cooper [1] in 1840, described fascial extensions between skin and pectoral fascia, dividing the parenchyma into lobes and lob- 105
6 Awad MA et al. New septum in female breast ules. Since then, all authors referred to his work when writing about ligaments or septa of the breast without further anatomical studies. It was only at the end of the 20th century when anatomical studies began to appear regarding the infra-mammary ligament, supporting or denying its presence [2-5]. According to Taylor and Palmer [13], 1987; the connective tissue in a parenchymatous organ, is what is left over after the glandular tissue has been formed (breast included). This is also the normal route and path for entry of nutrition and sensation for the organ by guiding arteries and nerves in and lymphatics and veins out. Connective tissue in the breast produces some sort of curtains separating the mammary gland into lobes and lobules guiding the major supply within the glandular tissue before spread within and around the secretory units. So it is not surprising to find a vessel or a nerve running within or guided by these connective tissue condensations, the surprising is rather not to find one. To date, the ligamentous system of the breast comprises deep and superficial components. The deep one includes horizontal, medial vertical, lateral vertical, cranial and posterior ligaments connecting the breast to the chest wall, while the superficial component includes horizontal, vertical medial and vertical lateral ligaments attached to the dermis and defining the breast [14]. In the present study, a median vertical septum is described extending from the mid IMF inferiorly to the lower border of the NAC superiorly and from pectoralis muscle posteriorly to overlying skin anteriorly, dividing the caudal part of breast into medial and lateral compartments. It is formed of two leaflets with a potential space in-between. It is of variable length and thickness and to our knowledge this vertical, centrally located septum was not described before. Several anatomical studies have given special interest to the ligamentous anatomy in the inferior breast pole and the inframammary region. Riggio et al. [15], 2,000 studied the inframammary region in 6 cadavers and 21 patients during breast surgery. They found neither ligament nor fibrous band taking origin from the superficial fascia at IMF. The only recognized a prepectoralis adherence, its orientation follows the breast shape instead of the inferior pectoral border, providing major resistance to blunt dissection of the superficial fascia from the deep fascia in the central part of the presumed IMF at 5 cm from the areola at the sixth rib. Matousek et al. [16], stated that in the inferior pole of the breast, ligaments run obliquely and inferiorly to insert directly into the dermis. They fan out at the level of the fifth rib in a triangular fashion from the periosteum of the superior aspect of Fig. 12. Relation between vertical septum and horizontal septum Vertical septum meets the horizontal septum at NAC. NAC, nipple areola complex. fifth rib inserting into the dermis of the IMF. The remaining superior fibers insert into the inferior pole of the breast. In addition, the condensation has radial fibers running perpendicular to these along the length of the fold. In 1998, Wuringer et al. [8], described an intra-glandular horizontal septum that originates from the pectoral fascia at the level of fifth rib. At the medial and lateral ends, it is curved upwards to the sternum from the second to the fifth rib stretching into the skin overlying the sternum and along the lateral border of the pectoralis minor respectively to form the medial and lateral vertical ligaments. Also she stated that the origin of the transverse septum from the thoracic wall at the level of fifth rib connected with a ligament originating from the pectoral fascia at the same level, which extends to the IMF which corresponds to Bayati s description which is known to be crescent-shape sagittally oriented. On the contrary our newly described septum was constantly seen running vertically along the breast meridian in the inferior pole of the breast from mid IMF upwards till it meets the horizontal septum at the level of NAC (Figs. 12, 13).With this anatomical variation, in addition to the histological differ- 106
7 Vol. 44 / No. 2 / March 2017 Fig. 13. Schematic illustration of the vertical and transverse septa The horizontal septum is represented in blue and the vertical septum is represented in green in both sagittal (A) and anterior (B) views. A B ence proved, both the transverse and vertical septa cannot be mistaken as one entity. Being a part of breast fascial system, it can change in relation to age, breast size, weight, adiposity and glandular activity [4]. In large fatty breasts, the septal walls are thinned out, attenuated and largely penetrated by fat globules clinically (Fig. 5) and seen as interrupted linear structure on MR imaging (Fig. 8). This correlates with Hammond [17] who stated that although Wuringer septum is uniformly present in breasts with any degree of hypertrophy; it tends to be more distinct in thinner patients, while in breasts with a greater fat content the septum becomes less readily identifiable. It is logic to assume that the vessel running within this septum, is supplying the NAC in the inferior pedicle type of breast reduction. However, this vessel was not constantly found in either the clinical series or in MRI study. Clinically, this may be related to the limited dissection in this area for fear of affecting the viability of the NAC. The sensitivity of MRI to visualize vessels with a caliber equal to/or less than 2 mm may not exceed 38%. This fact may explain the lack of appearance of intra-septal vessels in some MR images [18]. Wuringer [19] tightens the vertical extensions of the horizontal ligament, minimizing the descent of NAC in breast reduction operation. In our cases, the two lamina of the vertical septum, based on the NAC (Fig. 3), can be rotated separately to support either a superiorly, medially or a laterally-based pedicle in reduction mammaplasty operations to prevent postoperative bottoming out. This may not be applied in very fatty breasts as the septum may be thinned out discarding its use in large breast. Thus, only small or average sized breasts amenable for augmentation, are the suitable candidates for its use in supporting breast implants in augmentation procedures. As proved by MRI, the case having breast malignancy in the lower lateral quadrant of the right breast showed thickening of the right septum in comparison to the left. Also in the case with benign growth, the septum is pushed towards the opposite side of the growth and not penetrated. Being a tough fibrous tissue separating infero-medial from infero-lateral compartments, it certainly has a role in delaying the spread of malignancy from one quadrant to another. This oncological importance is yet to be investigated thoroughly by further studies. The research results describe a new inferior vertical septum which separates the lower half of the breast into two definite anatomical compartments: medial and lateral. This is a true and constant ligament to be added to the ligamentous apparatus of the breast. It is not an anatomical variation or a part of other previously described ligaments and the research will continue in order to postulate possible clinical applications of this vertical septum. REFERENCES 1. Cooper AP. Of the internal parts of the breast or mammary gland. In: Cooper A, editor. On the anatomy of the breast. London: Longman, Orme, Green, Brown, and Longmans; p Bayati S, Seckel BR. Inframammary crease ligament. Plast Reconstr Surg 1995;95: van Straalen WR, Hage JJ, Bloemena E. The inframammary ligament: myth or reality? Ann Plast Surg 1995;35: Nava M, Quattrone P, Riggio E. Focus on the breast fascial system: a new approach for inframammary fold reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;102: Garnier D, Angonin R, Foulon P, et al. The inframammary 107
8 Awad MA et al. New septum in female breast fold: myth or reality? Ann Chir Plast Esthet 1991;36: Muntan CD, Sundine MJ, Rink RD, et al. Inframammary fold: a histologic reappraisal. Plast Reconstr Surg 2000;105: Boutros S, Kattash M, Wienfeld A, et al. The intradermal anatomy of the inframammary fold. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;102: Wuringer E, Mader N, Posch E, et al. Nerve and vessel supplying ligamentous suspension of the mammary gland. Plast Reconstr Surg 1998;101: Wuringer E. Secondary reduction mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 2002;109: Hall-Findlay EJ. A simplified vertical reduction mammaplasty: shortening the learning curve. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;104: Pike MC, Pearce CL. Mammographic density, MRI background parenchymal enhancement and breast cancer risk. Ann Oncol 2013;24 Suppl 8:viii Schnall MD, Blume J, Bluemke DA, et al. Diagnostic architectural and dynamic features at breast MR imaging: multicenter study. Radiology 2006;238: Taylor GI, Palmer JH. The vascular territories (angiosomes) of the body: experimental study and clinical applications. Br J Plast Surg 1987;40: Santos DC, Cardoso A, Martins JM, et al. suspensory ligament of the mammary gland: a case report. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2016;40: Riggio E, Quattrone P, Nava M. Anatomical study of the breast superficial fascial system: the inframammary fold unit. Eur J Plast Surg 2000;23: Matousek SA, Corlett RJ, Ashton MW. Understanding the fascial supporting network of the breast: key ligamentous structures in breast augmentation and a proposed system of nomenclature. Plast Reconstr Surg 2014;133: Hammond DC. Atlas of aesthetic breast surgery. New York: Saunders/Elsevier; Yucel EK, Anderson CM, Edelman RR, et al. AHA scientific statement. Magnetic resonance angiography: update on applications for extracranial arteries. Circulation 1999;100: Wuringer E. Refinement of the central pedicle breast reduction by application of the ligamentous suspension. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999;103:
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017
 Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017 Reduction Mammaplasty SAFE Good Size Reduction Minimal Scar Aesthetic & Long Lasting Breast Shape Reduction Mammaplasty
Breast Reduction By Dr. Tarek Ahmed Said Professor of Plastic Surgery Cairo University 2017 Reduction Mammaplasty SAFE Good Size Reduction Minimal Scar Aesthetic & Long Lasting Breast Shape Reduction Mammaplasty
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
Vertical mammaplasty has been developed
 BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
BREAST Y-Scar Vertical Mammaplasty David A. Hidalgo, M.D. New York, N.Y. Background: Vertical mammaplasty is an effective alternative to inverted-t methods. Among other benefits, it results in a significantly
Intra-Capsular Versus Extra-Capsular Breast Mastopexy of Previously Augmented Breast
 Original Hela Article et al. 301 Intra-Capsular Versus Extra-Capsular Breast Mastopexy of Previously Augmented Breast Hesham A. Helal*, Asser El-Hilaly, Nahed Samir Boughdadi Department of Plastic and
Original Hela Article et al. 301 Intra-Capsular Versus Extra-Capsular Breast Mastopexy of Previously Augmented Breast Hesham A. Helal*, Asser El-Hilaly, Nahed Samir Boughdadi Department of Plastic and
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Breast. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST
 Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST Mahmoud El-Tamer and Sunny Mitchell Breast Service, Department of Surgery, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065, USA Women s Breast Center,
Chapter 1 SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE BREAST Mahmoud El-Tamer and Sunny Mitchell Breast Service, Department of Surgery, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York, NY 10065, USA Women s Breast Center,
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Inframammary Fold: A Histologic Reappraisal
 Inframammary Fold: A Histologic Reappraisal Charles D. Muntan, B.S., Michael J. Sundine, M.D., Richard D. Rink, Ph.D., and Robert D. Acland, M.D. Louisville, Ky. The inframammary fold is a defining element
Inframammary Fold: A Histologic Reappraisal Charles D. Muntan, B.S., Michael J. Sundine, M.D., Richard D. Rink, Ph.D., and Robert D. Acland, M.D. Louisville, Ky. The inframammary fold is a defining element
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
Anatomical Landmarks for Safe Elevation of the Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap: A Cadaveric Study Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ron Hazani, MD, Philip Collis, BS, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD University of
complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative
 Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Il trattamento delle complicanze in chirurgia senologica ricostruttiva Tecniche per la prevenzione delle complicanze nelle mastectomie conservative Dr. Christian Rizzetto UOC Chirurgia Senologica - Breast
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Prevention of Implant Malposition in Inframammary Augmentation Mammaplasty
 Prevention of Implant Malposition in Inframammary Augmentation Mammaplasty Yoon Ji Kim, Yang Woo Kim, Young Woo Cheon Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center,
Prevention of Implant Malposition in Inframammary Augmentation Mammaplasty Yoon Ji Kim, Yang Woo Kim, Young Woo Cheon Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gachon University Gil Medical Center,
Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling
 Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
Clinical case study Strattice Tissue Matrix Strattice Reconstructive Tissue Matrix used in the repair of rippling Steven Teitelbaum, MD* Santa Monica, CA Case summary A 48-year-old woman with a history
POSITIONING ACR REQUIREMENTS IMAGE REVIEW CATEGORIES DEFICIENCIES IN POSITIONING ACR REQUIREMENTS 3/28/2016 NUMBER 1 REASON FOR ACR FAILURE
 CERTIFYING AGENCIES MAMMOGRAPHY CLINICAL IMAGE EVALUATION Pam Fulmer, BA RT (R)(M)(QM) FDA approved certifying states States can only certify facilities within their state borders Illinois Iowa South Carolina
CERTIFYING AGENCIES MAMMOGRAPHY CLINICAL IMAGE EVALUATION Pam Fulmer, BA RT (R)(M)(QM) FDA approved certifying states States can only certify facilities within their state borders Illinois Iowa South Carolina
Circumareolar Mastopexy
 Circumareolar Mastopexy and Moderate Reduction drien iache n mastopexy the problems created by the doughnut-type excision and scarring are relatively minimal, because the breast tissue is not excised and
Circumareolar Mastopexy and Moderate Reduction drien iache n mastopexy the problems created by the doughnut-type excision and scarring are relatively minimal, because the breast tissue is not excised and
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy. Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD
 How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
How To Make a Good Mastectomy for Reconstruction Based on the Anatomy Zhang Jin, Ph.D MD Deputy Director and Professor Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital People s Republic of China
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
In the Name of God, the Most Merciful, the Most Compassionate. Breast
 In the Name of God, the Most Merciful, the Most Compassionate What is the Breast? Breast Definition: a modified sweat gland (sometimes called skin gland) present in both genders, well developed in females
In the Name of God, the Most Merciful, the Most Compassionate What is the Breast? Breast Definition: a modified sweat gland (sometimes called skin gland) present in both genders, well developed in females
Despite breast reduction being one of the BREAST. Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction?
 BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
BREAST Does Knowledge of the Initial Technique Affect Outcomes after Repeated Breast Reduction? Jamil Ahmad, M.D. Sarah M. McIsaac, M.D. Frank Lista, M.D. Mississauga and Ottawa, Ontario, Canada Background:
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction
 A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
A Clinical Anatomic Study of Internal Mammary Perforators as Recipient Vessels for Breast Reconstruction In-Soo Baek 1, Jae-Pil You 1, Sung-Mi Rhee 1, Gil-Su Son 2, Deok-Woo Kim 1, Eun-Sang Dhong 1, Seung-Ha
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander.
 Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Postmastectomy. Using DermaMatrix Acellular Dermis in breast reconstruction with tissue expander. Strong and flexible Bacterially inactivated Provides implant support Breast Reconstruction
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:333 340 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9612-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Breast Augmentation and Mastopexy Using a Pectoral Muscle Loop André Auersvald Luiz Augusto Auersvald Received: 28 April
Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique
 Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique 4 Foad Nahai A man honours himself by not displaying all the knowledge he has acquired. Folk Tradition Introduction I first tried the vertical
Superior Pedicle Vertical Scar Mammaplasty: Surgical Technique 4 Foad Nahai A man honours himself by not displaying all the knowledge he has acquired. Folk Tradition Introduction I first tried the vertical
Modified ''Lejour Technique'': A Safe Option for Large Breasts Reductions
 Egypt, J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg., Vol. 34, No. 1, January: 1-7, 2010 Modified ''Lejour Technique'': A Safe Option for Large Breasts Reductions KARIM KHALIL EL-LAMIE, M.D. The Department of Plastic Surgery,
Egypt, J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg., Vol. 34, No. 1, January: 1-7, 2010 Modified ''Lejour Technique'': A Safe Option for Large Breasts Reductions KARIM KHALIL EL-LAMIE, M.D. The Department of Plastic Surgery,
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament
 접수번호 : 2008-087 Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;23:183-187 ISSN : 1011-8942 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.183 A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament Han Woong
접수번호 : 2008-087 Korean Journal of Ophthalmology 2009;23:183-187 ISSN : 1011-8942 DOI : 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.183 A Cadaveric Anatomical Study of the Levator Aponeurosis and Whitnall s Ligament Han Woong
Evolution of the Vertical Reduction Mammaplasty
 CME Evolution of the Vertical Reduction Mammaplasty Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Michael A. Howard, M.D. Washington, D.C. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able to:
CME Evolution of the Vertical Reduction Mammaplasty Scott L. Spear, M.D., and Michael A. Howard, M.D. Washington, D.C. Learning Objectives: After studying this article, the participant should be able to:
An anatomical structure which results in puffiness of the upper eyelid and a narrow palpehral fissure in the Mongoloid eye
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2000), 53, 466-472 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons DOI: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3387 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical structure which
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2000), 53, 466-472 9 2000 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons DOI: 10.1054/bjps.2000.3387 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ~ PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical structure which
THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling
 Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling Idea and Innovation Bok Ki Jung 1, Ji Hae Nahm 2, Dae Hyun Lew 1, Dong Won
Treatment of Pseudoangiomatous Stromal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Implant-Based Reconstruction with a Vascularized Dermal Sling Idea and Innovation Bok Ki Jung 1, Ji Hae Nahm 2, Dae Hyun Lew 1, Dong Won
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Plastic Surgery of the Breast: Keeping the Nipple Sensitive
 Plastic Surgery of the Breast: Keeping the Nipple Sensitive Charles A. Riccio, MS, Matthew R. Zeiderman, BA, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ronald M. Brooks, MD, Shahrooz S. Kelishadi, MD, John Paul Tutela, MD, Joshua
Plastic Surgery of the Breast: Keeping the Nipple Sensitive Charles A. Riccio, MS, Matthew R. Zeiderman, BA, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, Ronald M. Brooks, MD, Shahrooz S. Kelishadi, MD, John Paul Tutela, MD, Joshua
LECTURE -I. Intercostal Spaces & Its Content. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Date:
 LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES
 BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES Breast Augmentation Top Surgical Procedure in 2015 (Worldwide) Surgical Procedure : Breast Augmentation Rank : 1 Total : 1,488,992 Percent of Total Surgical Procedures :
BREAST AUGMENTATION TECHNIQUES Breast Augmentation Top Surgical Procedure in 2015 (Worldwide) Surgical Procedure : Breast Augmentation Rank : 1 Total : 1,488,992 Percent of Total Surgical Procedures :
Chapter 28. Breasts and Mammary Glands
 Chapter 28 Breasts and Mammary Glands Breasts and Mammary Glands breast mound of tissue overlying the pectoralis major enlarges at puberty and remains so for life most of the time it contains very little
Chapter 28 Breasts and Mammary Glands Breasts and Mammary Glands breast mound of tissue overlying the pectoralis major enlarges at puberty and remains so for life most of the time it contains very little
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY. Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services. Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow
 Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Hessa St ONCOPLASTIC SURGERY Dr. Sadir Alrawi Director of Surgical Oncology Services Dr. Humaa Darr Surgical Oncology Fellow Al Sufouh Rd AL SUFOUH AL SUFOUH Sharaf DG Mall of the Emirates Mall Of the
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Autoaugmentation Mastopexy with an Inferior-Based Pedicle
 Aesth Plast Surg (2009) 33:302 307 DOI 10.1007/s00266-009-9310-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Autoaugmentation Mastopexy with an Inferior-Based Pedicle Johannes Franz Hönig Æ Hans Peter Frey Æ Frank Michael Hasse
Aesth Plast Surg (2009) 33:302 307 DOI 10.1007/s00266-009-9310-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Autoaugmentation Mastopexy with an Inferior-Based Pedicle Johannes Franz Hönig Æ Hans Peter Frey Æ Frank Michael Hasse
Superomedial Pedicle Reduction with Short Scar
 Superomedial Pedicle Reduction with Short Scar Scott L. Spear, M.D., F.A.C.S., 1 Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S., F.A.C.S., 1 and Ivan Ducic, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Reduction mammaplasty combining a superomedial
Superomedial Pedicle Reduction with Short Scar Scott L. Spear, M.D., F.A.C.S., 1 Steven P. Davison, M.D., D.D.S., F.A.C.S., 1 and Ivan Ducic, M.D., Ph.D. 1 ABSTRACT Reduction mammaplasty combining a superomedial
Breast Reduction
 Breast Reduction Breasts that are excessively large in proportion to body size are a frequent cause of back and neck pain as well as shoulder irritation from bra straps. Additionally, sleep and participation
Breast Reduction Breasts that are excessively large in proportion to body size are a frequent cause of back and neck pain as well as shoulder irritation from bra straps. Additionally, sleep and participation
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer
 Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
Advances in Localized Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD, MPH and Fariba Asrari, MD June 18, 2018 Moderated by Elissa Bantug 1 Advances in Surgery for Breast Cancer Melissa Camp, MD June 18, 2018 2 Historical
INTRODUCTION. Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee. Original Article
 Comparison of the Multidetector-row Computed Tomographic ngiography xial and Coronal Planes Usefulness for Detecting Thoracodorsal rtery Perforators Original rticle Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee Department
Comparison of the Multidetector-row Computed Tomographic ngiography xial and Coronal Planes Usefulness for Detecting Thoracodorsal rtery Perforators Original rticle Jong Gyu Kim, Soo Hyang Lee Department
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts. Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D.
 Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D. Disclosures None Objectives Ultrasound characteristics of parathyroid adenomas vs. lymph nodes 4D-CT evaluation of hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid Imaging: Current Concepts Maria Gule-Monroe, M.D. Nancy Perrier, M.D. Disclosures None Objectives Ultrasound characteristics of parathyroid adenomas vs. lymph nodes 4D-CT evaluation of hyperparathyroidism
Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 556 560 CASE REPORT Aesthetic surgery techniques after excision of dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: a case report G. Dagregorio a, *, V. Darsonval b a Department
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
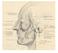 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2013 June; 16(2): 236-243 bdominal dvancement Flap as Oncoplastic reast Conservation: Report of Seven Cases and Their Cosmetic Results Tomoko Ogawa, Noriko
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2013 June; 16(2): 236-243 bdominal dvancement Flap as Oncoplastic reast Conservation: Report of Seven Cases and Their Cosmetic Results Tomoko Ogawa, Noriko
Mitchell Buller, MEng, a Adee Heiman, BA, a Jared Davis, MD, b ThomasJ.Lee,MD, b Nicolás Ajkay, MD, FACS, c and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD, FACS b
 Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
Immediate Breast Reconstruction of a Nipple Areolar Lumpectomy Defect With the L-Flap Skin Paddle Breast Reduction Design and Contralateral Reduction Mammoplasty Symmetry Procedure: Optimizing the Oncoplastic
University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova DOCTORAL SCHOOL. PhD Thesis
 University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova DOCTORAL SCHOOL PhD Thesis BREAST RECONSTRUCTION AFTER SURGERY FOR BREAST HIPERTROPHY AND BENIGN TUMORS Summary Ph.D. SUPERVISOR: Prof. univ. dr. Mihai Brăila
University of Medicine and Pharmacy of Craiova DOCTORAL SCHOOL PhD Thesis BREAST RECONSTRUCTION AFTER SURGERY FOR BREAST HIPERTROPHY AND BENIGN TUMORS Summary Ph.D. SUPERVISOR: Prof. univ. dr. Mihai Brăila
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Technical refinements of the modified central mound breast reduction
 Nicholson et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:34 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.30 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Original Article Open Access Technical refinements of the modified central mound breast reduction
Nicholson et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2018;5:34 DOI: 10.20517/2347-9264.2018.30 Plastic and Aesthetic Research Original Article Open Access Technical refinements of the modified central mound breast reduction
Upside-Down Augmentation Mastopexy
 Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:593 600 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9623-6 INNOVATIVE TECHNIQUE Upside-Down Augmentation Mastopexy Franco Migliori Received: 27 July 2010 / Accepted: 14 October 2010 / Published online:
Aesth Plast Surg (2011) 35:593 600 DOI 10.1007/s00266-010-9623-6 INNOVATIVE TECHNIQUE Upside-Down Augmentation Mastopexy Franco Migliori Received: 27 July 2010 / Accepted: 14 October 2010 / Published online:
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
INTRODUCTION. Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2, Kazunori Yasumura 1, Taro Mikami 2, Shinji Kobayashi 3, Jiro Maegawa 2. Idea and Innovation
 Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Mini-Flow-Through Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction with Preservation of Both Internal Mammary and Deep Inferior Epigastric Vessels Toshihiko Satake 1, Jun Sugawara 2,
Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 552 556 Anatomical relationship between arteries and veins in the paraumbilical region q N. Imanishi a, *, H. Nakajima b, T. Minabe c, H. Chang d,
Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936
 Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 05.March.2014 the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray 1.1. REGIONS/T ERMS Thoracic cavity cavity between neck
Salvador Dali - Anthropomorphic Chest of Drawers, 1936 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 05.March.2014 the part between the neck and the abdomen Chest X-ray 1.1. REGIONS/T ERMS Thoracic cavity cavity between neck
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features
 Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Facial Features Vardan Papoian, Vartan Mardirossian 2, Donald Thomas Hess 2, Jeffrey H Spiegel 2 MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC; 2 Department of Surgery,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study
 Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Anatomical Background of the Perforator Flap Based on the Deep Branch of the Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery (SCIP Flap): A Cadaveric Study Raphael Sinna, MD, a Hassene Hajji, MD, b Quentin Qassemyar,
Model of female breast
 L56 Latin A Milk-giving right breast and chest wall, front view, medially divided, representation of the externally visible changes for breast gland inflammation (mastitis) on the inner half B Milk-giving
L56 Latin A Milk-giving right breast and chest wall, front view, medially divided, representation of the externally visible changes for breast gland inflammation (mastitis) on the inner half B Milk-giving
An estimated 40,000 breast reduction procedures were performed in the United. The Common Principles of Effective Breast Reduction Techniques
 Special Topic Alexandre de Souza, MD; and Renato Saltz, MD Background: The evolution of breast reduction surgery is discussed to shed light on the various principles and techniques used in this 4-step
Special Topic Alexandre de Souza, MD; and Renato Saltz, MD Background: The evolution of breast reduction surgery is discussed to shed light on the various principles and techniques used in this 4-step
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
From ancient times to the present day, the aesthetic female breast has been portrayed. A Classification and Algorithm for Treatment of Breast Ptosis
 lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
lassification and lgorithm for Treatment of reast Ptosis Laurence Kirwan, M ackground: The Regnault classification of breast ptosis is insufficient for determining surgical strategies for different stages
Tips for using shaped implants in breast augmentation
 Tips for using shaped implants in breast augmentation Sientra would like to thank Dr. Patricia McGuire of St. Louis, MO for her significant contributions to Sientra s educational efforts. Dr. McGuire has
Tips for using shaped implants in breast augmentation Sientra would like to thank Dr. Patricia McGuire of St. Louis, MO for her significant contributions to Sientra s educational efforts. Dr. McGuire has
Intercostal Muscles LO4
 Intercostal Muscles LO4 4 List the structures, from superficial to deep, in an intercostal space. Describe their relationships to each other, to the associated neurovascular bundle and to the pleural cavity.
Intercostal Muscles LO4 4 List the structures, from superficial to deep, in an intercostal space. Describe their relationships to each other, to the associated neurovascular bundle and to the pleural cavity.
Periareolar Extra-Glandular Breast Augmentation
 Original Article 93 Periareolar Extra-Glandular Breast Augmentation Muhammad Humayun Mohmand 1 *, Muhammad Ahmad 2 1. Cosmetic Plastic Surgeon, La Chirurgie, Islamabad Cosmetic Surgery Centre, Islamabad,
Original Article 93 Periareolar Extra-Glandular Breast Augmentation Muhammad Humayun Mohmand 1 *, Muhammad Ahmad 2 1. Cosmetic Plastic Surgeon, La Chirurgie, Islamabad Cosmetic Surgery Centre, Islamabad,
Breast Lift
 Breast Lift Changes to the breasts can be dissatisfying and make a woman feel as if she is losing her femininity and youthfulness. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy and breast feeding,
Breast Lift Changes to the breasts can be dissatisfying and make a woman feel as if she is losing her femininity and youthfulness. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy and breast feeding,
21/05/2012. GROSS ANATOMY: fasciae of the upper limb. MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS: the deep fasciae of the limbs
 GROSS ANATOMY: fasciae of the upper limb Subcutaneous tissue of the forearm Deep fascia of the posterior region of the forearm Deep and epimysial fascia of the biceps brachii muscle MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS:
GROSS ANATOMY: fasciae of the upper limb Subcutaneous tissue of the forearm Deep fascia of the posterior region of the forearm Deep and epimysial fascia of the biceps brachii muscle MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS:
Pseudoptosis Correction With the 270 Pedicle Reduction Mammoplasty: An Anatomic and Clinical Study
 Pseudoptosis Correction With the 270 Pedicle Reduction Mammoplasty: An Anatomic and Clinical Study Matthew R. Zeiderman, BA, a Steven Schulz, MD, b Charles A. Riccio, MS, a Jonathan Nguyen, BS, a Saeed
Pseudoptosis Correction With the 270 Pedicle Reduction Mammoplasty: An Anatomic and Clinical Study Matthew R. Zeiderman, BA, a Steven Schulz, MD, b Charles A. Riccio, MS, a Jonathan Nguyen, BS, a Saeed
Safe Plastic Surgery of the Breast II: Saving Nipple Sensation
 Safe Plastic Surgery of the Breast II: Saving Nipple Sensation Steven Schulz, MD, a,b Matthew R. Zeiderman, MD, c J. Stephen Gunn, MD, a Charles A. Riccio, MD, d Saeed Chowdhry, MD, a,e Ronald Brooks,
Safe Plastic Surgery of the Breast II: Saving Nipple Sensation Steven Schulz, MD, a,b Matthew R. Zeiderman, MD, c J. Stephen Gunn, MD, a Charles A. Riccio, MD, d Saeed Chowdhry, MD, a,e Ronald Brooks,
The vertical reduction mammaplasty was first
 Special Topic Technical Refinements of the Vertical Mammaplasty: A Modified Lejour Approach Steven G. Wallach, MD Dr. Wallach is Assistant Clinical Professor of Plastic Surgery, Albert Einstein College
Special Topic Technical Refinements of the Vertical Mammaplasty: A Modified Lejour Approach Steven G. Wallach, MD Dr. Wallach is Assistant Clinical Professor of Plastic Surgery, Albert Einstein College
Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions
 Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions 1 Collaborators Julia White 1, An Tai 1, Douglas Arthur 2, Thomas Buchholz 3, Shannon MacDonald 4, Lawrence Marks 5, Lori Pierce
Breast Cancer Atlas for Radiation Therapy Planning: Consensus Definitions 1 Collaborators Julia White 1, An Tai 1, Douglas Arthur 2, Thomas Buchholz 3, Shannon MacDonald 4, Lawrence Marks 5, Lori Pierce
Acta Medica Okayama OCTOBER Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals. Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 5 2009 Article 4 OCTOBER 2009 Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 5 2009 Article 4 OCTOBER 2009 Mastectomy in Female-to-male Transsexuals Yuzaburo Namba Toshiyuki Watanabe Yoshihiro Kimata Department of Plastic and Reconstructive
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery.
 This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery. 1 The border of the anterior abdominal wall is defined superiorly by the
This presentation will discuss the anatomy of the anterior abdominal wall as it pertains to gynaecological and obstetric surgery. 1 The border of the anterior abdominal wall is defined superiorly by the
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery
 Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Medial Pedicle Reduction Mammaplasty for Severe Mammary Hypertrophy
 Medial Pedicle Reduction Mammaplasty for Severe Mammary Hypertrophy Maurice Y. Nahabedian, M.D., Bernard M. McGibbon, M.D., and Paul N. Manson, M.D. Baltimore, Md. Current options in reduction mammaplasty
Medial Pedicle Reduction Mammaplasty for Severe Mammary Hypertrophy Maurice Y. Nahabedian, M.D., Bernard M. McGibbon, M.D., and Paul N. Manson, M.D. Baltimore, Md. Current options in reduction mammaplasty
Breast Augmentation - Saline Implants
 Breast Augmentation - Saline Implants Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy,
Breast Augmentation - Saline Implants Breast augmentation, or augmentation mammoplasty, is one of the most common plastic surgery procedures performed today. Over time, factors such as age, genetics, pregnancy,
Borders of the Abdomen
 Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
INTRODUCTION. There are three main approaches to studying anatomy: 1. Systemic anatomy 2. Regional anatomy (topographic) 3.
 INTRODUCTION Anatomy is the science of the structure and function of the body. It is the study of internal and external structures, and the physical relationships between the various body parts. INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION Anatomy is the science of the structure and function of the body. It is the study of internal and external structures, and the physical relationships between the various body parts. INTRODUCTION
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Reduction Mammoplasty Operative Techniques for Improved Outcomes in the Treatment of Gigantomastia
 Reduction Mammoplasty Operative Techniques for Improved Outcomes in the Treatment of Gigantomastia Brent R. DeGeorge, Jr., MD, PhD, David L. Colen, MD, Alexander F. Mericli, MD, and David B. Drake, MD
Reduction Mammoplasty Operative Techniques for Improved Outcomes in the Treatment of Gigantomastia Brent R. DeGeorge, Jr., MD, PhD, David L. Colen, MD, Alexander F. Mericli, MD, and David B. Drake, MD
