Life Science Journal 2014;11(12) Normal Mode Analysis of a Human Fibula.
|
|
|
- Bruno Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Normal Mode Analysis of a Human Fibula J.-G. Tseng 1 *, B.W. Huang 2, S.-H. Liang 2, K.T. Yen 1, Y.C. Tsai 2 1 Department of Leisure and Sports Management, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C. 2 Graduate Institute of Mechatronics Engineering, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C. james.tseng@csu.edu.tw Abstract: The human fibula is not a structural bone. It is positioned on the outer edge of the lower leg, formed part of the ankle joint and provided for stability of the lower extremity in movement. Inverse engineering technique is used to obtain a 3D complex geometry of the real human fibula by white light scanning a synthesis human fibula. Modal tests are performed to get the natural frequencies of the synthesis human fibula. The experimental data are then verified with that obtained from finite element method (FEM). After confirming the correctness of the finite element 3D synthesis human fibula model, the real human bone properties are brought into models for numerical modal analysis. Several fundamental normal modes are found. A higher frequency torsion and dilation coupled mode is also obtained to prove that the combination of bending, torsion, dilation, etc. modes can be coupled to form a normal modes. [J.-G. Tseng, B.W. Huang, S.-H. Liang, K.T. Yen, Y.C. Tsai.. Normal Mode Analysis of a Human Fibula. Life Sci J 2014;11(12): ]. (ISSN: ) Keywords Human fibula, normal mode, experiments, FEM. 1. Introduction The fibula does not reach up as far as the knee joint; rather, its lower portion, including the specialized groove and tendon mechanism, forms part of the ankle joint, allowing for stability in movement. This is due to the fibula's major role as an anchor point for the various muscles and ligaments of the leg and ankle. The fibula is not a structural bone and it is positioned on the outer edge of the lower leg. Because of this, it is sometimes used as donor stock for bone grafts. But knee or ankle injuries are the most encountered cases in sporting and physical activities. These injuries have affected the knee or ankle joints and ligaments severely even transform into the chronic disease. Cornelissen, et al. [1] examined the influence of soft tissues and joints on the vibration of the human tibia by modal analysis on amputated lower limbs, where the soft tissues and the fibula were dissected gradually. The fibula was found to have a stiffening effect on the tibia. Scaglioni et al. [2] discussed The role of the fibula head flap for joint reconstruction after oasteoarticular resection. Rutten et al. [3] investigated how LIPUS affects bone healing at the tissue level in patients with a delayed union of the osteotomized fibula, by using histology and histomorphometric analysis to determine bone formation and bone resorption parameters. suggest that LIPUS accelerates clinical fracture healing of delayed unions of the fibula by increasing osteoid thickness, mineral apposition rate, and bone volume, indicating increased osteoblast activity, at the front of new bony callus formation. Bediz et al. [4] observed the structural dynamic property changes of the tibia extracted from the vibration analysis data. bone mineral density and vibration measurements were made both in in vivo and in vitro conditions. The relationship between structural dynamic properties, obtained and bone mineral densities measured were investigated. Also, the effect of soft tissues on measured structural dynamic properties was analyzed. Seikaly et al. [5] mentioned that the major advantage of osseous free flaps in head and neck reconstruction is the potential of implants which would aid oral or craniofacial rehabilitation. The fibula is the most commonly used bone in these reconstructions. Bone impacted fibulas (BIF) were found to have a higher marrow bone density when it is compared to the unmodified fibular free flaps. Lower degree of dental implant vibration was observed in the BIF and compared to original fibulas. All modified fibular free flaps survived in the study. Brooke and McIlroy [6] investigated the afferent source of a human lower limb reflex that spans two joints and may link limb muscular activity during movement. Low threshold (motor nerve threshold (MT) to 1.6 MT) single, 1 msec, pulses were delivered to the common personal nerve at caput fibula. Hetsroni and Mann [7] reviewed the literature and proposed that the fibula stress fractures should be managed with rest from any precipitating activity, physical therapy, and treatment of any contributing factor, whether metabolic, nutritional, postural, or other. Pacifico et al. [8] discussed that the pattern of load-bearing in the tibia increases following the removal of the fibula. A further contribution to the 711
2 problem may be a degree of relative ischaemia as a result of the harvest of the personal artery. Sherbondy and Sebastianelli [9] discussed that the stress fractures of the medial malleolus and distal fibula typically affect the athletic and running population and manifest the usual signs and symptoms of stress fractures. Axial and torsional forces, muscular contractions, and alignment are believed to play a role in their development. Stress fractures are often confused with malignancy or osteomyelitis. Distal fibula stress fractures are usually seen in distance runners or dancers. Anand and Asumu [10] reported a case of bilateral distal fibula stress fractures in a 9-year-old girl caused by roller blade boots. Pekedis et al. [11] developed an ankle model (tibia, fibula, calcaneus, and talus) with computer tomography and the finite element method was applied to analyze the stresses and strains occurred in ligaments and bones for four different positions (10 o dorsiflexion, 0 o neutral position, 10 o plantar flexion, 20 o plantar flexion). Faustini et al. [12] acquired the geometry of the residual limb, liner and socket from computed tomography (CT) data of a transtibial amputee. Three different compliant designs were analyzed using finite element method (FEM) to assess the structural integrity of the sockets and their ability to relieve local pressure at the fibula head during normal walking. Cheung and Zhang [13] developed a 3D finite element model of the human ankle-foot complex and a custom-molded insole from 3D reconstruction of magnetic resonance images (MRI) and surface digitization. The distal tibia and fibula, together with 26 foot bones and 72 major ligaments and the plantar fascia, were embedded in a volume of soft tissues. Badawi et al. [14] used MRI image enhancements using different contrast agents. And considered the magnetized-saline (MS) as a new MRI brain contrast agent (CA). Leading to the result; magnetized saline injection affect signal intensity and enhance contrast in MRI brain images. Guo et al. [15] measured the quadriceps forces along with varied squat angles and built a simplified three-dimensional finite element model, including tibia, fibula, patella, ligaments and quadriceps tendon. Then, the contact pressure of knee joint was analyzed for the squat with the established model of knee joint involving the obtained quadriceps forces from finite element analysis. Huang et al. [16] examined the fundamental dynamic characteristic of both the solid and hollow femur, experimentally and numerically. Then, they are imported to the finite element package, ANSYS, to perform the analysis. Huang et al. [17] investigated the dynamic property of cranium by experimental and theoretical analysis through skull model made in polystyrene. Reverse engineering analysis is adopted to build up geometric 3D skull CAD model by transferring this 3D skull CAD model into ANSYS (FEA package) acceptable model. This research studies the fibula of the human lower extremity structure via experimental modal test and vibration modal analysis by FEM. The FEM is a powerful tool in the simulation of living structures. Using of noninvasive methods such as finite element method can help to determine the dynamic behavior of fibula, knee, ligament, etc., before the treatment (such as anterior drawer test and posterior drawer test) applied to the patients. To understand the dynamic characteristics of the human fibula structure will help to operative need and even avoid injuries. Figure 1. A teaching synthesis human fibula (made by polypropylene) Experiment Use Impact hammer, spectrum analyzer, to get natural frequency of a synthesis fibula No Begin Are the experimental and FEA natural frequencies matched? Reverse Engineering Scan synthesis fibula to obtain its geometry Finite Element Analysis (FEA) The scanned geometry input into ANSYS program Employ the mechanical properties of real human fibula for finite element analysis End Yes No Figure 2. Flow chart of the human fibula analysis 712
3 2. Methodology It is hard to obtain the geometry of real human fibula. A typical teaching synthesis human fibula made by plastic material, polypropylene, bought from 3B Incorporation, is shown in Figure 1. The procedure of this research includes three major parts, reverse engineering, experiment and finite element analysis, etc. as shown in the flow chart in Figure 2 and will be described in the following subsections. 2.1 Reverse Engineering As computer-aided design (CAD) has become more popular, reverse engineering (RE) has become a viable method to create a 3D virtual geometry of an existing physical component for use in three dimensional CAD, CAM, CAE or other software [18]. The reverse engineering process involves measuring an object, reconstructing it as a 3D model, manufacturing the mold and product. The physical object can be measured using 3D scanning technologies like laser scanners, structured light digitizers, CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machine), or computed tomography. The measured data alone, usually represented as a set of points, lacks topological information and is therefore often processed and modeled into a more usable format such as a set of NURBS surfaces, a triangular-faced mesh or a CAD model. Reverse engineering is also used by businesses to bring existing physical geometry into digital product development environments, to make a digital 3D record of their own products or to assess competitors' products. It is used to analyze, for instance, how a product works, what it does, and what components it consists of, estimate costs, and identify potential patent infringement, etc. The reverse engineering is employed by using scanner to obtain the outer profile of a teaching synthesis human fibula. In this study, 3D white light four-axis laser scanner is used to build the geometry of the plastic fibula in reverse engineering sense. The plastic fibula is placed on the four-axis laser scanner platform for 3D digital scanner to scan and measure. The scanning process requires overlaps of scanned dots in different directions, coordinate and matrix transformation in order to complete the modeling. Because the surface of just created model from 3D digital scanner is very rough and have a bunch of little holes. This built model will be imported into automated reverse engineering software, Geomagic Studio, to precede multiple repairing, patching and smoothing of the surface for the 3D model. When the model meets the 3D geometric smooth requirements without any hole, it will be transmitted to finite element software ANSYS for modal analysis [19]. 2.2 Finite Element Analysis Begin Import the synthesis fibula 3D model into ANSYS program Preprocess Select elements, materials, mesh, setup material parameters Setup boundary conditions Solve for solutions Pass element convergence test? Yes Post process Save files, Plot analysis diagrams End No Figure 3. Flow chart of the finite element analysis Figure 4. Geometry of ANSYS Solid187 element In this study, the finite element (FE) software ANSYS is employed to analyze the dynamic characteristics of a human fibula [9]. Various ANSYS software analyzers are used to identify the natural vibration frequency, amplitude intensity. Because real human fibula is not easy to get, a synthesis polypropylene fibula manufactured by 3B products company is used to establish geometric model for the FE analysis and experimental verification with the correctness of the model. Once the FE model of the synthesis fibula is confirmed to be accurate, the parameters of real human bone are used to carry on the normal mode analysis. Figure 3 is a flow chart of finite element analysis. After import 3D fibula model into ANSYS software, select element and material, mesh, setup boundary condition, it can be solved for the solution. It should be noted that the size, shape, and its sparse density of the element will affect the accuracy of the analysis. The wisdom of using ANSYS grid established technology will strengthen the ability of grid elements, analytical precision and accuracy. 713
4 Element type Solid187 is selected for this study as shown in Figure 4. This element is a 3D solid element and an entity does not need to set the structure constant (Real constant). Solid187 is a three-dimensional 10-node entities. Each node has displacement in x, y, z direction, i.e. 3 degrees of freedom. This element has a secondary displacement and is suitable for irregular grid. It also possesses plasticity, hyper-elasticity, strengthen stress, large deformation, large strain characteristics, etc. And it can reduce the poor precision problem caused by auto mesh. The mesh diagram of a synthesis human fibula is shown in Figure 5. It can be easily seen that the boundary condition of the synthesis human fibula is free at both end which is conformed to that in experimental setup. Table 2. Number of elements and nodes selected in ANSYS for 3B polypropylene synthesis human fibula Number of Number of Element Model elements nodes type Fibula 7,236 13,370 Solid 187 Natural frequency, Hz No. of Elements Figure 6. Convergence test of a human fibula Figure 5. Mesh diagram of a synthesis human fibula. Table 1. Material properties of 3B polypropylene synthesis human fibula Mechanical properties values Young s modulus 1.3 GPa Poisson s Ratio 0.42 Density 950 Kg/m 3 The mechanical properties, Young s modulus, Poisson s ratio and density, of the 3B polypropylene synthesis human fibula are shown in Table Convergence Analysis Dynamic convergence analysis is performed for the synthesis human fibula by examine the convergence of fundamental natural frequency to find the best elements of size for the dynamic analysis. If the convergence analysis diagram presents a divergence phenomenon, one must return to pre-treatment section, adjust the settings of material parameters, contact conditions, or boundary conditions, and begin to re-analyze again. The fundamental natural frequency is converged to 26.49Hz when the number of elements near 7,200, as shown in Figure 6. Therefore, 7,236 elements are used for the following FE analysis, as shown in Table 2. Figure 7. The human fibula is set at free-free position with 3 axes accelerometer and an impact hammer by using PW700 spectrum analyzer experimentally. 2.3 Experimental Analysis Impact vibration experiments are conducted for synthesis human fibula in order to obtain its vibration characteristics including natural frequencies and mode shapes. The equipment used in the experiment includes PW 700 spectrum analyzer, PC computer, impact hammer, 3-axis accelerometer, etc., as shown in Figure 7. The surface geometry of fibula is very complicated and its dimension is much smaller than femur or tibia. 714
5 The synthesis fibula is hung in the air as free-free boundary condition. Twelve experimental hit positions are marked on both front and side surfaces of the fibula. Each surface has six impact positions which are separated by 5 cm. The tri-axial accelerometer is fixed in the middle of the fibula for contentment of measuring data. Three hit points are marked for the impact hammer on each side of the accelerometer. The experiment setup schematic diagram of the front side of the fibula is shown in Figure 8. Since the synthesis fibula is thin, flat, soft and no uniform in shape, the hit positions (red dots in Figure 7) are not in the same plane. Therefore, it is very hard to perform the impact modal tests. Human fibula 6 PC Rope 5 PW 700 Spectrum Analyzer Impact hammer 4 6 hit positions Accelerometer 3 Rope Figure 8. Experimental setup for modal test of a synthesis human fibula (front side) with six hit positions for impact hammer and one fixed position for accelerometer. 20Hz 180Hz 48Hz 80Hz 352Hz Figure 9. The experimental frequency spectrum of a synthesis human fibula. Table 3. Comparison between measured and FEM natural frequencies Measured natural Natural frequency from Error frequency (Hz) FEM (Hz) (%) To reduce the error of measuring data, the spectrum analyzer is set to get average response from couple of hits. After A large number of tests, several fundamental natural frequencies are found in the spectrum within 800Hz as shown in Figure Comparison between finite element and experimental analysis The modal analysis simulation results are verified with the experimental data to make sure the accuracy of the FEM model. Four fundamental natural frequencies are compared between measured and FEM natural frequencies as shown in Table 3. The first mode is measured 20 Hz against to FEM 26.5 Hz with 24.5% error. The second mode is measured 48 Hz against to FEM 38.1 Hz with 20.0% error. This might due to the flat, soft, and irregular shape of the synthesis human fibula and cause bigger error in the experiment for measuring lower modes. Except the higher error percentage of the first two modes, the rest of the modes are within 5% error percentage. Therefore the 3D finite element model is acceptable and ready for replacing real human bone properties, Young's modulus, Poisson s ratio, and density, into the material parameters in ANSYS package. 3. Results and Discussions After confirming the correctness of the 3D human fibula finite element model, the mechanical properties of the real human fibula, Young s modulus, Poisson s ratio, density, etc., shown in Table 4, is used in the following modal analysis. For the free-free boundary conditions at both end of the human fibula, there are six zero Hz rigid body modes, three translation modes and three rotation modes. Table 4. Material properties of real human fibula Mechanical properties values Young s modulus 17 GPa Poisson s Ratio 0.3 Density Kg/m 3 Those are not interested in the study. The first four fundamental flexible body modes with different natural frequencies and the 12th mode, Hz, Hz, Hz, Hz and 3,448Hz are obtained and shown in Table 5, respectively. For easy viewing the diagram, each mode shape is shown in pairs, one unreformed and one deformed mode shape. Table 5. Finite element simulated natural vibration frequency with mechanical properties of real human fibula. Mode Natural frequencies (Hz) ,
6 The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the first mode shape is shown in Figure 10. The first flexible mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (bending mode in x-y plane) is shown in Figure 11. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the second mode shape is shown in Figure 12. The second flexible mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (bending mode in x-z plane) is shown in Figure 13. Figure 13. Second mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (bending in x-z plane) Figure 10. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the first mode shape. Figure 14. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the third mode shape. Figure 11. The first mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (bending mode in x-y plane). Figure 15. The third mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (second bending mode in x-y plane). Figure 12. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the second mode shape. Figure 16. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the fourth mode shape. 716
7 Although the higher mode is not significant in modal analysis, the twelfth mode is still discussed here for its being a combine mode. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the twelfth mode shape is shown in Figure 18. The twelfth flexible mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (Torsion and dilation combined mode in y axis) is shown in Figure 19. Figure 17. The fourth mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (S shape second bending mode in y-z plane). Figure 18. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the twelfth mode shape. Figure 19. The twelfth mode shape of real human fibula at 3,448 Hz (Torsion and dilation combined mode in y axis). The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the third mode shape is shown in Figure 14. The third flexible mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (second bending mode in x-y plane) is shown in Figure 15. The original unreformed human fibula corresponded to the fourth mode shape is shown in Figure 16. The fourth flexible mode shape of real human fibula at Hz (S shape second bending mode in y-z plane) is shown in Figure Summary The synthesis and real human fibula, with real bone material parameters, is studied via vibration modal analysis experimentally and numerically. Results obtained from this study are summarized as follows: 1. Reverse engineering technique is employed to obtain a 3D complex geometry of the real human fibula for finite element analysis. 2. The modal analysis simulation results are verified with the experimental data from the synthesis human fibula to make sure the accuracy of the FEM 3D model. 3. The torsion and dilation coupled mode is found. The phenomenon indicates that there exist some combinations of the pure bending, torsion, expanding/contraction modes in three dimensional FEM model. 4. The results from this modal analysis can be a helpful reference for future impact analysis, biomechanical study and medical industry applications. References 1. Cornelissen, P., Cornelissen, M., Van der Perre, G., Christensen, A.B., Ammitzbøll, F., Dyrbye, C., Assessment of tibial stiffness by vibration testing in situ II. Influence of soft tissues, joints and fibula. Journal of Biomechanics, 19 (7), Scaglioni, M.F., Chang, E.I., Gur, E., Barnea, Y., Meller, I., Kollander, Y., Bickels, J., Dadia, S., Zaretski, A., The role of the fibula head flap for joint reconstruction after oasteoarticular resection. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery 67, Rutten, S., Nolte, P.A., Korstjens, C.M., van Duin, M.A., Klein-Nulend, J., Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound increases bone volume, osteoid thickness and mineral apposition rate in the area of fracture healing in patients with a delayed union of the osteotomized fibula. Bone 43, Bediz, B., Özgüven, H.N., Korkusuz, F., Vibration measurements predict the mechanical properties of human tibia, Clinical Biomechanics 25,
8 5. Seikaly, H., Mlynarek, A.M., Rieger, J., Harris, J.R., Bone impacted fibula (bif), a new technique of increasing bone density for placing dental implants. Oral Oncology Supplement 3, Brooke, J.D., McIlroy, W.E., Vibration insensitivity of a short latency reflex linking the lower leg and the active knee extensor muscles in humans. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 75 (5), Hetsroni, I., Mann, G., Fibula Stress Fractures: A Treatment Review. Operative Technique on Sports Medicine 17, Pacifico, M.D. Floyd, D., Wood, S.H., Further reporting of tibia stress fractures complicating free fibula grafts, Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive & Aesthetic Surgery, 61 (3), Sherbondy, P.S., Sebastianelli, W.J., Stress Fractures of the Medial Malleolus and Distal Fibula, Clinics in Sports Medicine, 25 (1), Anand, S., Asumu, T., Bilateral distal fibula stress fractures in a young child, Injury Extra, 36 (7), Pekedis, M., Ozan. F., Yildiz, H., Developing of a three-dimensional foot ankle model based on CT images and non-linear analysis of anterior drawer test by using the finite element method, Journal of Biomechanics, 44, ee Faustini, M.C., Neptune, R.R., Crawford, R.H., The quasi-static response of compliant prosthetic sockets for transtibial amputees using finite element methods, Medical Engineering & Physics, 28, Cheung, J.T., Zhang, M., A 3-dimensional finite element model of the human foot and ankle for insole design, Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 86 (2), Badawi, S.M., Ahmed, W.A. EL-wafa, Kadah, Y.M., "Magnetized water and saline as a Contrast agent to Enhance MRI Images", Life Science Journal, Volume 8, Issue 1, Guo, Y., Zhang, X., An, M., Chen, W., Determination of quadriceps forces in squat and its application in contact pressure analysis of knee joint, Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 25 (1), Huang, B.W., Huang, M.Y., Tseng, J.-G., Chang, C.H. Wang, F.-S., Lin, A.D., Tsai. Y.C., "Dynamic Characteristics of a Hollow Femur," Life Science Journal, 2012;9(1). 17. Huang, B.W., Kung, H.K., Chang, K.Y., Hsu, P.K., Tseng, J.-G. Human Cranium Dynamic Analysis. Life Science Journal. 2009; 6(4): (ISSN: ). 18. Chang, C.-C., Reverse engineering and the integration application, 1999, Gau Lih Book Co. Ltd., ISBN Kung, H.K., Huang, B.W., Chen, H.S., ANSYS and Computer Aided Engineering Analysis, 2004, Cheng Shiu University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, R.O.C. 7/10/
Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion
 ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
ISSN 1746-7659, England, UK Journal of Information and Computing Science Vol. 13, No. 1, 2018, pp.044-048 Modeling of human knee joint and finite element analysis of landing impact motion Bao Chunyu 1,3,Meng
An effort is made to analyse the stresses experienced by the human femur. In order
 Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic
 MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic Reza Fakhrai, Bahram Saadatfar,
MACROJOURNALS The Journal of MacroTrends in Health and Medicine Numerical predicting of contact and pressure sore of lower extremity parts caused by prosthetic and orthotic Reza Fakhrai, Bahram Saadatfar,
Modal Analysis of Hip Joint Implant Used In the Human Body
 Modal Analysis of Hip Joint Implant Used In the Human Body Patil Sagar Rajendra 1, Prof. R.N. Yerrawar 2, Prof. S.L. Gavali 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MESCOE, Pune, Maharashtra,
Modal Analysis of Hip Joint Implant Used In the Human Body Patil Sagar Rajendra 1, Prof. R.N. Yerrawar 2, Prof. S.L. Gavali 3 P.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, MESCOE, Pune, Maharashtra,
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint
 Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint V Jeevan Kumar 1, P Satish Reddy 2,N Guru Murthy 3 PG Student, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor Prasiddha College of Engg & Tech, Amalapuram jvankaya@yahoo.in,
Modeling And Biomechanical Analysis Of Human Knee Joint V Jeevan Kumar 1, P Satish Reddy 2,N Guru Murthy 3 PG Student, Assoc. Professor, Asst Professor Prasiddha College of Engg & Tech, Amalapuram jvankaya@yahoo.in,
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And
 Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor
![[ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor [ICESTM-2018] ISSN Impact Factor](/thumbs/88/117546298.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES MODELING AND FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE JOINT PROSTHESIS U.D.S.Prathap varma *1,S.Rajesh 2, B.Suresh Kumar 3 & P.Rama Murthy Raju 4 *1 M.TechScholar,
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Presenter: Mark Yeoman PhD Date: 19 October Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment. Continuum Blue Ltd
 Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
Research & Development, FEA, CFD, Material Selection, Testing & Assessment Investigating the loading behaviour of intact & meniscectomy knee joints & the impact on surgical decisions M S Yeoman PhD 1 1.
.org. Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Anatomy
 Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Ankle Fractures (Broken Ankle) Page ( 1 ) A broken ankle is also known as an ankle fracture. This means that one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint are broken. A fractured ankle can range
Project of a medical device to support the diagnosis of the ankle pathologies
 Project of a medical device to support the diagnosis of the ankle pathologies Rita Ferreira, February 6, 2015 Filipe Samuel Silva Paulo Flores MicroElectroMechanical Systems Centre University of Minho
Project of a medical device to support the diagnosis of the ankle pathologies Rita Ferreira, February 6, 2015 Filipe Samuel Silva Paulo Flores MicroElectroMechanical Systems Centre University of Minho
Life Science Journal 2014;11(12) Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint
 Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint Chin YU Wang 1*, Chien Fen Huang 2, Yi-Lin Liou 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cheng Shiu University 2 Department of Physical
Surface Modification and Software Design of Customized Knee Joint Chin YU Wang 1*, Chien Fen Huang 2, Yi-Lin Liou 1 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Cheng Shiu University 2 Department of Physical
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions
 Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
Investigating the loading behaviour of intact and meniscectomy knee joints and the impact on surgical decisions M. S. Yeoman 1 1. Continuum Blue Limited, One Caspian Point, Caspian Way, CF10 4DQ, United
FULL PAPER PROCEEDING Multidisciplinary Studies Available online at
 FULL PAPER PROCEEDING Multidisciplinary Studies Available online at www.academicfora.com Full Paper Proceeding ECBA-2016, Vol. 127- Issue.5, 10-21 ISBN 978-969-670-378-5 ECBA -16 Dynamics Analyses of Human
FULL PAPER PROCEEDING Multidisciplinary Studies Available online at www.academicfora.com Full Paper Proceeding ECBA-2016, Vol. 127- Issue.5, 10-21 ISBN 978-969-670-378-5 ECBA -16 Dynamics Analyses of Human
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF KNEE IMPLANT AND PROTOTYPE FABRICATION USING RPT PROCESS
 International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 12, December 2017, pp. 197 205, Article ID: IJMET_08_12_020 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=12
International Journal of Mechanical Engineering and Technology (IJMET) Volume 8, Issue 12, December 2017, pp. 197 205, Article ID: IJMET_08_12_020 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijmet/issues.asp?jtype=ijmet&vtype=8&itype=12
Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability
 Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability Takumi Kobayashi 1,2, Eiichi Suzuki 3, Naohito Yamazaki 3, Makoto Suzukawa 4, Atsushi Akaike 4, Kuniaki Shimizu 4, Kazuyoshi Gamada 1. 1
Fibular Malalignment in Subjects with Chronic Ankle Instability Takumi Kobayashi 1,2, Eiichi Suzuki 3, Naohito Yamazaki 3, Makoto Suzukawa 4, Atsushi Akaike 4, Kuniaki Shimizu 4, Kazuyoshi Gamada 1. 1
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR
 CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
CONTROL OF THE BOUNDARY CONDITIONS OF A DYNAMIC KNEE SIMULATOR J. Tiré 1, J. Victor 2, P. De Baets 3 and M.A. Verstraete 2 1 Ghent University, Belgium 2 Ghent University, Department of Physical Medicine
Lever system. Rigid bar. Fulcrum. Force (effort) Resistance (load)
 Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation. William R. Ledoux
 In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation William R. Ledoux RR&D Center of Excellence for Limb Loss Prevention and Prosthetic Engineering, VA Puget Sound Departments of
In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation William R. Ledoux RR&D Center of Excellence for Limb Loss Prevention and Prosthetic Engineering, VA Puget Sound Departments of
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS
 COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS Kaitaro,Nambu Hisaki, Sugaya Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
COMPARISON OF ANKLE INJURY MECHANISM IN FULL FRONTAL AND OBLIQUE FRONTAL CRASH MODES WITH THOR DUMMY AND HUMAN FE MODELS Kaitaro,Nambu Hisaki, Sugaya Hiroyuki, Mae Honda R&D Co., Ltd. Automobile R&D Center
875. Modeling the dynamic characteristics of human ossicles
 875. Modeling the dynamic characteristics of human ossicles Jen-Fang u 1, 2, Ching-I Chen 3 1 Graduate Institute of Medical Mechatronics, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, R. O. C. 2 Taiouan Interdisciplinary
875. Modeling the dynamic characteristics of human ossicles Jen-Fang u 1, 2, Ching-I Chen 3 1 Graduate Institute of Medical Mechatronics, Chang Gung University, Taoyuan, Taiwan, R. O. C. 2 Taiouan Interdisciplinary
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 97 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 97 (2014 ) 2298 2305 12th GLOBAL CONGRESS ON MANUFACTURING AND MANAGEMENT, GCMM 2014 Application of Rapid Prototyping in the
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 97 (2014 ) 2298 2305 12th GLOBAL CONGRESS ON MANUFACTURING AND MANAGEMENT, GCMM 2014 Application of Rapid Prototyping in the
Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding
 Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 257 Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding S. Shuib 1, M. I. Z. Ridzwan 1, A. Y. Hassan 1 & M. N. M. Ibrahim 2 1 School of Mechanical
Computer Aided Optimum Design in Engineering IX 257 Topology optimisation of hip prosthesis to reduce stress shielding S. Shuib 1, M. I. Z. Ridzwan 1, A. Y. Hassan 1 & M. N. M. Ibrahim 2 1 School of Mechanical
Intact and ACL-Deficient Knee MODEL Evaluation
 Abstract The human knee joint has a three dimensional geometry with multiple body articulations that produce complex mechanical responses under loads that occur in everyday life and sports activities.
Abstract The human knee joint has a three dimensional geometry with multiple body articulations that produce complex mechanical responses under loads that occur in everyday life and sports activities.
ASSESSMENT ON MECHANICAL STRESS AND STRAIN OF PLANTAR FASCIA: A REVIEW
 ASSESSMENT ON MECHANICAL STRESS AND STRAIN OF PLANTAR FASCIA: A REVIEW A. H. Abdul Razak 1, K. S. Basaruddin 2, A. F. Salleh 3 and W. M. R. Rusli 4 1,2,3,4 School of Mechatronic Engineering, Universiti
ASSESSMENT ON MECHANICAL STRESS AND STRAIN OF PLANTAR FASCIA: A REVIEW A. H. Abdul Razak 1, K. S. Basaruddin 2, A. F. Salleh 3 and W. M. R. Rusli 4 1,2,3,4 School of Mechatronic Engineering, Universiti
The Development and Analysis of an FEA Simulation on an Artificial Knee
 ME 461: Finite Element Analysis Fall 2015 The Development and Analysis of an FEA Simulation on an Artificial Knee Daniel Offley, Joseph Martin, Harrison Wostein Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
ME 461: Finite Element Analysis Fall 2015 The Development and Analysis of an FEA Simulation on an Artificial Knee Daniel Offley, Joseph Martin, Harrison Wostein Department of Mechanical and Nuclear Engineering,
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method
 Research Article Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method Mitsugu Todo * Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University, Kasuga, Japan
Research Article Biomechanical Analysis of Hip Joint Arthroplasties using CT-Image Based Finite Element Method Mitsugu Todo * Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University, Kasuga, Japan
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia
 Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia Leonid Maslov 1, Jean-Baptiste Etheve 2, Nikolay Sabaneev 3 Ivanovo State Power Engineering University, Ivanovo, Russia 1 Corresponding
Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia Leonid Maslov 1, Jean-Baptiste Etheve 2, Nikolay Sabaneev 3 Ivanovo State Power Engineering University, Ivanovo, Russia 1 Corresponding
Sprains. Initially the ankle is swollen, painful, and may turn eccyhmotic (bruised). The bruising, and the initial swelling, is due to ruptured
 Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Correlation of Femoral Component Micromotion to a Physical Test Using an FEA Model.
 Correlation of Femoral Component Micromotion to a Physical Test Using an FEA Model. Robert Davignon, Ananthkrishnan Gopalakrishnan. Stryker Corporation, Parsippany, NJ, USA. Disclosures: R. Davignon: 3A;
Correlation of Femoral Component Micromotion to a Physical Test Using an FEA Model. Robert Davignon, Ananthkrishnan Gopalakrishnan. Stryker Corporation, Parsippany, NJ, USA. Disclosures: R. Davignon: 3A;
Mechanical Aspects of an Interference Screw Placement in ACL Reconstruction
 Mechanical Aspects of an Interference Screw Placement in ACL Reconstruction Mahmoud Chizari 1, Mohammad Alrashidi 2, Khaled Alrashdan 2, Ibrahim Yildiz 3, Jamaluddin Mahmud 4 1 School of Engineering and
Mechanical Aspects of an Interference Screw Placement in ACL Reconstruction Mahmoud Chizari 1, Mohammad Alrashidi 2, Khaled Alrashdan 2, Ibrahim Yildiz 3, Jamaluddin Mahmud 4 1 School of Engineering and
Analysis of Plate Bone Construct Failure Following Tibial Tuberosity Advancment
 Analysis of Plate Bone Construct Failure Following Tibial Tuberosity Advancment W. T. McCartney 1,2 E. Galvin 2 B Mac Donald D Comiskey 3 1 Marie Louise Veterinary Hospital, Baldoyle, Dublin 13, Ireland
Analysis of Plate Bone Construct Failure Following Tibial Tuberosity Advancment W. T. McCartney 1,2 E. Galvin 2 B Mac Donald D Comiskey 3 1 Marie Louise Veterinary Hospital, Baldoyle, Dublin 13, Ireland
Figure 1 The Human Heart
 ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE MODEL INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular pump with four chambers and four heart valves. The upper chambers, the right atrium and left, are thin walled filling chambers. Blood flows
ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE MODEL INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular pump with four chambers and four heart valves. The upper chambers, the right atrium and left, are thin walled filling chambers. Blood flows
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee
 Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Medical Diagnosis for Michael s Knee Introduction The following report mainly concerns the diagnosis and treatment of the patient, Michael. Given that Michael s clinical problem surrounds an injury about
Vibration Analysis of Finger Using Non linear FEM to Understand HAV Syndrome
 Vibration Analysis of Finger Using Non linear FEM to Understand HAV Syndrome Shrikant Pattnaik, Jay Kim Dept. of Mechanical Engineering University of Cincinnati What is HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome
Vibration Analysis of Finger Using Non linear FEM to Understand HAV Syndrome Shrikant Pattnaik, Jay Kim Dept. of Mechanical Engineering University of Cincinnati What is HAVS Hand Arm Vibration Syndrome
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions
 Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from
Integrated Manual Therapy & Orthopedic Massage For Complicated Lower Extremity Conditions Assessment Protocols Treatment Protocols Treatment Protocols Corrective Exercises Artwork and slides taken from
New methods for the simulation with finite element of the human elbow
 New methods for the simulation with finite element of the human elbow R. Lungu, E. Borgazi, M. Lungu, D. Popa, D. Tutunea, M. X. Calbureanu Abstract In this paper one presents on virtual models of bones
New methods for the simulation with finite element of the human elbow R. Lungu, E. Borgazi, M. Lungu, D. Popa, D. Tutunea, M. X. Calbureanu Abstract In this paper one presents on virtual models of bones
(c) B. Ravi, IIT Bombay 1
 Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
Collaborative Engineering Evaluation, Testing TKP Safety, TKP System Mechanism FEA Physical testing Fatigue Wear What How Evaluate Testing Judgement Criteria's Testing Conditions Parameters Measured OrthoCAD
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Simulating the Motion of Heart Valves Under Fluid Flows Induced by Cardiac Contraction
 Simulating the Motion of Heart Valves Under Fluid Flows Induced by Cardiac Contraction Eann A. Patterson Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield Mappin Street, Sheffield, S1 3JD
Simulating the Motion of Heart Valves Under Fluid Flows Induced by Cardiac Contraction Eann A. Patterson Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Sheffield Mappin Street, Sheffield, S1 3JD
Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo 3D study
 Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo D study Hara Y, Ikoma K, Kido M, Imai K, Maki M, Takatori R, Tokunaga D, Inoue N,, Kubo T Department of Orthopaedics,
Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo D study Hara Y, Ikoma K, Kido M, Imai K, Maki M, Takatori R, Tokunaga D, Inoue N,, Kubo T Department of Orthopaedics,
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가?
 BK amputation 재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가? Soo-Kyung, Bok. M.D., Ph.D Chungnam National University Hospital Contents Level selection of BKA Rehabilitation Preoperative management Immediate postoperative management
BK amputation 재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가? Soo-Kyung, Bok. M.D., Ph.D Chungnam National University Hospital Contents Level selection of BKA Rehabilitation Preoperative management Immediate postoperative management
The value of weight-bearing functional CT scans
 The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
The nomenclature describing the orthosis is basically the same as that suggested for the molded ankle-foot orthosis (2), but the anterior shank enclos
 VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws
 Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws Jorgen Bergstrom, Ph.D., David Quinn, Ph.D., Eric Schmitt jbergstrom@veryst.com, LLC September 14, 2011 Introduction Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction
Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws Jorgen Bergstrom, Ph.D., David Quinn, Ph.D., Eric Schmitt jbergstrom@veryst.com, LLC September 14, 2011 Introduction Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG
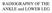 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ANKLE and LOWER LEG Patient Position: ANKLE AP Projection Part Position: True Slight to place foot s long axis Center to Central Ray: to IR Midway Note: Ankle joint is to tips of malleoli
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques
 TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
Freedom and safety in treatment
 medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
medi GmbH & Co. KG Medicusstraße 1 95448 Bayreuth Germany T +49 921 912-0 F +49 921 912 780 ortho@medi.de www.medi.de 97E37/09.2012 Freedom and safety in treatment An informative brochure with an individual
ACCURATE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEAR STRENGTH BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 31 st December 212. Vol. 46 No.2 25-212 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ACCURATE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEAR STRENGTH BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT METHOD XUEYI LI, CHAOCHAO LI, DAQIAN GENG, SHOUBO JIANG, BINBING
31 st December 212. Vol. 46 No.2 25-212 JATIT & LLS. All rights reserved. ACCURATE NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF GEAR STRENGTH BASED ON FINITE ELEMENT METHOD XUEYI LI, CHAOCHAO LI, DAQIAN GENG, SHOUBO JIANG, BINBING
Fracture fixation. Types. Mechanical considerations. Biomechanics of fracture fixation. External fixation. Internal fixation
 Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Posture. Posture Evaluation. Good Posture. Correct Posture. Postural Analysis. Endomorphs
 Posture Posture Evaluation Martha Macht Sliwinski PT PhD The alignment and positioning of the body in relation to gravity, center of mass and base of support The physical therapist uses posture tests and
Posture Posture Evaluation Martha Macht Sliwinski PT PhD The alignment and positioning of the body in relation to gravity, center of mass and base of support The physical therapist uses posture tests and
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery
 Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy Pond View Professional Park 301 Professional View Drive Freehold, NJ 07728 Phone: 732-720-2555 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy Pond View Professional Park 301 Professional View Drive Freehold, NJ 07728 Phone: 732-720-2555 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Index. Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Introduction An ankle injury common to athletes is the ankle syndesmosis injury. This type of injury is sometimes called a high ankle sprain because it involves
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Syndesmosis Injuries Introduction An ankle injury common to athletes is the ankle syndesmosis injury. This type of injury is sometimes called a high ankle sprain because it involves
Anterior knee pain.
 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Lateral knee injuries
 Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
Created as a free resource by Clinical Edge Based on Physio Edge podcast episode 051 with Matt Konopinski Get your free trial of online Physio education at Orthopaedic timeframes Traditionally Orthopaedic
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy 245 North College Lafayette, LA 70506 Phone: 337.232.5301 Fax: 337.237.6504 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy 245 North College Lafayette, LA 70506 Phone: 337.232.5301 Fax: 337.237.6504 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources. It may
Improved Processing Research on Arc Tooth Cylindrical Gear
 International Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Analysis 2017; 5(3): 91-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijema doi: 10.11648/j.ijema.20170503.14 ISSN: 2328-7659 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7667
International Journal of Environmental Monitoring and Analysis 2017; 5(3): 91-95 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijema doi: 10.11648/j.ijema.20170503.14 ISSN: 2328-7659 (Print); ISSN: 2328-7667
Financial Disclosure. Turf Toe
 Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
Seth O Brien, CP, LP Financial Disclosure Mr. Seth O'Brien has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. Turf Toe Common in athletes playing on firm, artificial turf Forceful
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
 Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
3D MODELLING AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF LASTS USED TO OBTAIN SPECIAL FOOTWEAR FOR PATIENTS WITH ARTHRITIS
 3D MODELLING AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF LASTS USED TO OBTAIN SPECIAL FOOTWEAR FOR PATIENTS WITH ARTHRITIS MARIANA PĂŞTINĂ 1, AURA MIHAI 1 1 Gh.Asachi Technical University of Iaşi, Romania, mpastina@tex.tuiasi.ro,
3D MODELLING AND RAPID PROTOTYPING OF LASTS USED TO OBTAIN SPECIAL FOOTWEAR FOR PATIENTS WITH ARTHRITIS MARIANA PĂŞTINĂ 1, AURA MIHAI 1 1 Gh.Asachi Technical University of Iaşi, Romania, mpastina@tex.tuiasi.ro,
The Problem of Patellofemoral Pain. The Low Back Pain of the Lower Extremity. Objectives. Christopher M. Powers, PhD, PT, FACSM, FAPTA
 Mechanisms Underlying Patellofemoral Joint Pain: What have we learned over the last 20 years? Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory Objectives 1. Highlight recent research
Mechanisms Underlying Patellofemoral Joint Pain: What have we learned over the last 20 years? Professor Co Director, Musculoskeletal Biomechanics Research Laboratory Objectives 1. Highlight recent research
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Sprain and Instability. Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, P.C.
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Sprain and Instability Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Sprain and Instability Welcome to Foot and Ankle Center of Massachusetts, where we believe in accelerating your learning curve with educational materials that are clearly written
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
ANATOMIC. Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0
 ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis
 Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
Acta of Bioengineering and Biomechanics Vol. 8, No. 1, 2006 Modelling of temporomandibular joint and FEM analysis MARTINA FRIOVÁ, ZDENK HORÁK, SVATAVA KONVIKOVÁ Laboratory of Biomechanics, Department of
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Biokinesiology of the Ankle Complex
 Rehabilitation Considerations Following Ankle Fracture: Impact on Gait & Closed Kinetic Chain Function Disclosures David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS, CSCS I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
Rehabilitation Considerations Following Ankle Fracture: Impact on Gait & Closed Kinetic Chain Function Disclosures David Nolan, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, SCS, CSCS I have no actual or potential conflict of interest
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Ankle Anatomy 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
