Prosthetics Trans-Tibial Interface Theory Unit Educational Module Module 1 of 2 in this unit**
|
|
|
- Frederica Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prosthetics Trans-Tibial Interface Theory Unit Educational Module Module 1 of 2 in this unit** M. Jason Highsmith, PT, DPT, CP, FAAOP University of South Florida College of Medicine School of Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation Sciences Jason T. Kahle, CPO Westcoast Brace & Limb Objectives At the conclusion of this module, you will Recall history associated with the PTB interface Recall the 3 contemporary trans-tibial interface theories Identify load tolerant areas of the trans-tibial residuum Identify pressure sensitive areas of the trans-tibial residuum Recall fundamental sagittal and frontal plane alignment considerations of the PTB interface Identify unique characteristics of the 4 walls of the PTB interface Trans-Tibial Interfaces Three Design Theories This module on Trans-Tibial Interface Theories is the first of two modules in this unit. This module will cover the Patella Tendon Bearing Socket theory. Module 2 will cover Total Surface Bearing and Hydrostatic Design Theories. A test will accompany the unit. 1
2 Trans-Tibial Interfaces Three Design Theories 1. Patella Tendon Bearing (PTB) 2. Total Surface Bearing (TSB) 3. Hydrostatic Design (HSD) Patella Tendon Bearing Design or PTB History Invented in 1950 s James Foort & Charles Radcliffe State of the art was the plug fit socket Plug Fit Typically wood socket lined with leather Essentially a cylinder No provision for volume change Depth of limb engaged in socket was volume dependent Depth could change By the day By the hour 2
3 Plug Fit Schurr and Michael: state that the plug fit is comparable to a cork in a bottle Volume fluctuation would impact fit No distal (total) contact Lack of distal (total) contact in blue Red and blue areas subject to volume fluctuation PTB New Concepts Total Contact Loading Pressure Tolerant Areas Relieving Pressure Sensitive Areas PTB: Total Contact Total Contact started as a means of decreasing distal edema Leaving voids in the interface (as in the plug fit), gave places for fluid to collect Distal aspect of transected bones can tolerate gentle quantities of pressure Lack of distal contact could lead to verrucose hyperplasia** Distal end of a transtibial residual limb. Note the redness and wart-like appearance due to proximal constriction of the socket. **See the Dermatology Modules from this project for more on verrucose hyperplasia 3
4 PTB-Loading Pressure Tolerant Areas It was theorized that certain places on the residual limb would be better at pressure dissipation and thus Could tolerate load better than other areas These were areas that contained Soft tissue Neurovascular areas Muscular areas PTB-Loading Pressure Tolerant Areas Patella Tendon Anterior Muscular Compartment Medial Tibial Flare Lateral Stabilizing bar/ Shaft of Fibula Gastrocnemius muscle bellies Popliteal Fossa Distal end to some extent PTB-Relieving Pressure Sensitive Areas If soft tissue and vascular areas can tolerate load, then remaining areas must be less tolerant of load. This includes areas of Less vasculature Less soft tissue 4
5 PTB-Relieving Pressure Sensitive Areas Patella Lateral Tibial (Gerdy s)tubercle/iliotibial Band Fibula Head/Common Peroneal Nerve Tibial Tubercle Tibial Crest Distal cut end of Fibula/Tibia Hamstring Tendons PTB- Casting Casting or taking an impression can be done in 1 or more stages Many current designs are cast in 1 stage with a circumferential wrapping technique The PTB design may be cast in 1 to 3 stages depending on the height of the trimlines or how tall the walls are. Each stage serves a different function PTB- Casting/ Anterior Panel Stage 1- Anterior Panel 6-9 layers of plaster are trimmed to fit: From sagittal midline medially to laterally Approximately the joint line (superiorly) to the middle of the distal end of the residuum Photo courtesy of Otto Bock Healthcare Red line outlines a typical anterior panel shape 5
6 PTB- Casting/ Anterior Panel The anterior panel has several purposes: Pre-relieve the condyles Demarcate The patella tendon Anterior compartment Anterior aspect of the medial tibial flare Tibial crest and tubercle PTB- Casting Depicted here are the circumferential wrap removed from the positive model (cut posteriorly) The anterior panel has been removed as well Note the patellar tendon demarcations and the patellar outline Circumferential wrap (2 nd Stage) removed via posterior cut Front view of Anterior Panel. Anterior Panel is applied first (stage 1) followed by circumferential wrap (stage 2) PTB-Features and Cast Markings of the Anterior Panel and Residuum Gerdy s Tubercle Fibula Head Patellar notch and outline in Ant Panel Med Tibial Flare Peri-patellar tendon Mid Patella Tendon Tibial Plateau Trim Line of Ant Panel Tibial Tuberosity bisects leg distally and Med Tib Shaft laterally Cut/distal Tibia Lat Tibial shaft to lateral flare 6
7 PTB- Shape (Transverse View) Viewed transversely, the PTB interface has a somewhat triangular shape when compared to other, more rounded socket designs. legs of the triangle are comprised of lines in plane with the following: Popliteal modification (1) Medial tibial flare (2) Anterior muscular compartment (3) PTB PTB- Construction/Design Generally the PTB socket is designed as either a Thermoplastic or Thermosetting laminated frame Generally there are the following four sides or walls Anterior Posterior Medial Lateral PTB- Anterior Wall Features of the Anterior Wall: Patella Notch/Relief Patella Tendon Bar Relief for tibial tubercle Relief for anterior distal Tibia Relief for tibial crest Anterior Muscular Compartment Medial Tibial Flare (anterior aspect) 7
8 PTB- Anterior Wall The anterior wall is considered the primary weight bearing surface of the socket As more of the anterior wall is exposed with an increased flexion attitude 5-10 of socket flexion exposes more of the anterior wall for weight bearing 0 of socket flexion only permits loading of the distal end of the residuum PTB- Posterior Wall Features of the posterior wall Popliteal modification Deepest point is 12-15mm inferior to MPT level Provides anterior directed counterforce to keep Patella Tendon on Patella Bar which Keeps limb from excessive end bearing Gastrocnemius modification Hamstring relief Virtually the entire posterior wall can accommodate reasonable quantities of loading 10-15mm PTB- Posterior Wall Hamstring relief can take may shapes. Dependent upon: Limb Length Quantity of soft tissue Patient Preference Typical shapes are: Straight line sloping distally-medially W shape Semi-circular or arc -ed for long limbs and Symes 8
9 PTB- Posterior Wall Counterforce of the popliteal modification against the patella bar keeps the limb from excess end bearing. The anterior to posterior distance (AP) must be appropriate to support body weight during stance If AP directed force is insufficient, forces at the distal end will be in excess. When AP forces are sufficient to support body weight, end bearing is tolerable. PTB- Trimline Height Medial & Lateral Walls The trimlines are the upper most (proximal) aspect of where the socket ends or has been cut Several options available MPT Proximal aspect of patella Also with regard to the trimlines, the patella may be entirely relieved, partially relieved or entirely enclosed. NOTE: 65mm between MPT and trimline is considered starting point for standard PTB 25mm between proximal aspect of the proximal patella and the trimline is considered starting point for a PTB SC- SP PTB: patella tendon bearing PTB SC: patella tendon bearing, supracondylar PTB SC SP: patella tendon bearing, supracondylar, suprapatellar PTB- Trimline Height for Medial & Lateral Walls Start with high, supracondylar trimlines can be trimmed down to suit the situation cannot be lengthened Individually specific based on anatomy Specific based on suspension mechanism 2. Two cases requiring lower trimlines: 1. PTB with supracondylar cuff strap. Lower, swooped trimlines are needed to prevent the strap from bridging the patella; where suspension is primarily borne. Probably used with a longer limb with good ligamentous stability PTB with joints and corset. Lower trimlines are needed to permit inherent pistoning that will occur with this design. This design represents maximal stability offered in a trans-tibial prosthesis without locking the knee joint. 9
10 PTB- Medial Wall Weight Bearing Characteristics: Broad area for vertical loading (weight bearing) by virtue of Anatomic shape Soft tissue structures in the region Note the contour of the medial wall. It is well suited for loading. PTB- Medial Wall Features of the Medial Wall: Broad area for weight distribution Broad flat bony surface Vast soft tissue including Pes Anserinus group Popliteus Muscle Insertion Medial Head of Gastrocnemius Medial Origin of Soleus Medial Colateral Ligament Prominent Medial condyle for Suspension Frontal plane stability PTB- Medial Wall Alignment and the medial wall Normal alignment calls for a slight inset of the prosthetic foot To induce a varus moment at midstance Valgus Moment Varus Moment: 1. Narrows the Base of support for improved gait efficiency 2. More closely mimics a normal anatomic gait pattern 3. Loads pressure tolerant structures or, said differently, aids in relieving pressure intolerant structures 4. Appropriately distributes stress to stronger ligaments: i.e. loading the lateral colateral knee ligament versus the medial colateral ligament. 10
11 PTB- Lateral Wall Weight Bearing Characteristics: Many Sensitive Structures. Relief for the following: Iliotibial band Fibula head/peroneal Nerve Distal, cut end of Fibula Design Consideration: A Varus Moment Loads many pressure tolerant structures but has the tendency to load the distal cut end of the femur. Therefore, relief here is very important. Best location for loading is along the fibula shaft or lateral stabilizing bar PTB- Lateral Wall Alignment and the Lateral wall REMEMBER: Normal alignment calls for a slight inset of the prosthetic foot to induce a varus moment at midstance. If a Valgus moment is introduced Valgus Moment 1. A valgus moment will stress the medial colateral ligament of the knee 2. The base of support will be abnormally widened 3. Pressure will be induced at the proximal, lateral aspect of the socket, in the vicinity of the Fibula head. This region tends to be irritable. PTB- More Design Choices As previously mentioned, the PTB socket may be fabricated as either A thermoplastic or A thermosetting lamination The socket too may be fabricated as either a Hard socket or With a soft interface such as Pelite, Bock-Lite, or other soft foams These topics are reviewed in greater depth in other modules. Hard socket and soft interface choices will briefly be described here Thermoplastic (polypropylene) Laminated (thermosetting) Cross section of numerous types socket frames. Left socket has sockets with soft inserts. Left of gel liners (i.e. silicone, urethane, a soft, Pelite liner. Right socket socket has a bioelastic insert polymer, etc). Use of a gel liner has a soft, Bioelastic and right socket has a Pelite creates a soft interface for the (thermoplastic) liner. insert. residual limb. 11
12 PTB- Hard Socket A Hard socket or a socket that lacks a soft insert, will typically utilize prosthetic socks as the interface between the skin and socket. Generally, hard sockets are Fit with a 3-6 ply sock fit initially Used with those that have Hygiene issues Sensation intact Not very accommodating to heavy volume fluctuation Hard socket with PTB (specific weight bearing) modifications and removable medial brim suspension. Hard socket should be fit with at least 3 plies of socks against the skin. PTB- Soft Interface or Insert The Soft Insert is more widely used in prosthetics. The soft insert May be made of numerous choices of materials Is more accommodating of volume fluctuation Is fit between 0 and 3 ply of prosthetic socks initially May present skin problems if hygiene is an issue Is a better choice is sensory modalities are impaired Gel liners used as soft inserts. Soft Inserts shown here. Left is a foam Pelite Transtibial prosthesis Gel liners can be used without insert and the remaining 3 at right are Bioelastic incorporating a soft, socks. thermoplastic. thermoplastic insert in addition to a gel liner for maximal skin protection and adjustability. PTB- Benefits & Drawbacks Benefits Still widely used and accepted today Time tested and proven First design the student prosthetist learns in professional curricula Heavily tested on professional licensure & board examinations for several types of professionals May be offered as a first option or fall back option 12
13 PTB- Benefits & Drawbacks Drawbacks Pressing more forcefully into muscular and vascular areas has been argued to Limit the ability of muscles to contract Promote atrophy which Leads to characteristic shaping That may result in a residuum that is more difficult to fit later It has also been argued that focal loading can overload certain areas making the PTB user more susceptible to skin breakdown REFERENCES 1. Kahle JT. Conventional and Hydrostatic Transtibial Interface Comparison. J Prosthet Orthot (4); Fergason J, Smith DG. Socket considerations for the patient with a trans-tibial amputation. Clin Othop Rel Res 361; Polliack AA, Craig DD, Seigh RC, Landsherger S, Mcneal DR. Prosthet Orthot Int Apr;26(1):23-34.Laboratory and clinical tests of a prototype pressure sensor for clincial assessment of prosthetic socket fit. 4. Yigiter K, Sener G, Bavar K. Prosthet Orthot Int Dec;26(3): Comparison of the effects of patellar tendon bearing and total surface bearing sockets on prosthetic fitting and rehabilitation. 5. Kim WD, Lim D, Hong KS. An evaluation of the effectiveness of the patellar tendon bar in the trans-tibial patellar-tendon-bearing prosthesis socket. Prosthet Orthot Int Apr;27(1): Datta D, Harris I, Heller B, Howitt J, Martin R. Gait, cost and time implications for changing from PTB to ICEX sockets. Prosthet Orthot Int Aug;28(2): American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. Atlas of Amputations and Limb Deficiencies: Surgical, Prosthetic, and Rehabilitation Principles. 3rd ed. Smith. 8. Seymour R. Prosthetics and Orthotics. Lower Limb and Spinal. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins ISBN Shurr DG, Michael JW. Prosthetics and Orthotics. 2nd ed. Pearson Education, Inc ISBN Lusardi M & Nielsen C. Orthotics and Prosthetics in Rehabilitation. Butterworth- Heinemann ISBN: Prosthetics-Orthotics Center, Northwestern University Medical School. Course Manual for Prosthetics 621: Transtibial Prosthetics for Prosthetists. Chicago, IL. 09/2003. For further about the content of the module, contact University of South Florida dpt@health.usf.edu (813) Fax: (813) Westcoast Brace & Limb (813) Fax: (813)
14 Funded by the Department of Education, Rehabilitation Services Administration Award# H235J Demonstration Project on Prosthetics and Orthotics University of South Florida College of Medicine: School of Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation Sciences College of Engineering: Mechanical Engineering Department M. Jason Highsmith, PT, DPT, CP, FAAOP William S. Quillen, PT, PhD, SCS, FACSM Rajiv Dubey, PhD 14
Fig. 1. Antero-medial view of the knee cylinder. Fig. 2. Lateral view of the knee cylinder. thought of as for asuprapatellar/supracondylar PTB prosthe
 Knee Cylinder CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN STILLS2 For a variety of reasons it is not uncommon to wish to hold the knee it difficult to lock the joints of the orthosis about all edges of the orthosis, but
Knee Cylinder CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN STILLS2 For a variety of reasons it is not uncommon to wish to hold the knee it difficult to lock the joints of the orthosis about all edges of the orthosis, but
Technical Manual. Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2
 Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2 Introduction The successful fitting of Transtibial prosthesis is dependent on the fit of the hard socket. Appropriate socket design is fundamental
Transtibial Hand Casting & Modification Version no. 2 Introduction The successful fitting of Transtibial prosthesis is dependent on the fit of the hard socket. Appropriate socket design is fundamental
Flexible Below Knee Socket With Supracondylar Suspension
 Flexible Below Knee Socket With Supracondylar Suspension by James Breakey*, B.P.T. with an Introduction by James Foort**, M.A.Sc. Semi-flexible plastic laminate sockets have been used in the prostheses
Flexible Below Knee Socket With Supracondylar Suspension by James Breakey*, B.P.T. with an Introduction by James Foort**, M.A.Sc. Semi-flexible plastic laminate sockets have been used in the prostheses
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures
 Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
Application of Cast Brace for Post Acute Care of Lower Extremity Fractures Roy Snelson, C.P.O.*, George Irons, C.P.O.**, and Vert Mooney, M.D.*** The fracture cast brace is designed to allow early ambulation
taken for a patellar-tendon-bearing socket. After these have partly dried, the balance of the shin is wrapped with a roll of plaster bandage. When the
 A PATELLAR-TENDON-BEARING ORTHOSIS Bert R. Titus, C.P.O. 1 1Associate Professor of Prosthetics and Orthotics, Director of Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics, Duke University Medical Center, P. O.
A PATELLAR-TENDON-BEARING ORTHOSIS Bert R. Titus, C.P.O. 1 1Associate Professor of Prosthetics and Orthotics, Director of Department of Prosthetics and Orthotics, Duke University Medical Center, P. O.
The Transtibial Amputation
 The Transtibial Amputation Site of Previous Surgeries: Amputation indication: four unsuccessful previous surgeries. Patient experiences chronic pain and disfunction along with a limited range of motion.
The Transtibial Amputation Site of Previous Surgeries: Amputation indication: four unsuccessful previous surgeries. Patient experiences chronic pain and disfunction along with a limited range of motion.
Assessment and problem solving: starting with a temporary prosthesis
 Assessment and problem solving: starting with a temporary prosthesis Stump assessment Skin Colour, temperature, appearance sensitivity and allergies to materials Integrity eg frail, thin, dry Abrasions,
Assessment and problem solving: starting with a temporary prosthesis Stump assessment Skin Colour, temperature, appearance sensitivity and allergies to materials Integrity eg frail, thin, dry Abrasions,
Two-Stage Cast-taking Procedure for PTS Prosthesis
 Two-Stage Cast-taking Procedure for PTS Prosthesis by Kurt Marschall, CP Proper cast-taking and accurate measurements of a patient's remaining extremity, combined with careful evaluation and modification
Two-Stage Cast-taking Procedure for PTS Prosthesis by Kurt Marschall, CP Proper cast-taking and accurate measurements of a patient's remaining extremity, combined with careful evaluation and modification
TRANS -TIBIAL CASTING
 TRANS -TIBIAL CASTING ORTHOMANUAL The BUFA - System adapted to the Developing World and War Zones Written by: Markus Thonius OMM / CPO Proof-read: Margaret Ahern reg. Nurse, Australia ICRC - Loki Orthopaedic
TRANS -TIBIAL CASTING ORTHOMANUAL The BUFA - System adapted to the Developing World and War Zones Written by: Markus Thonius OMM / CPO Proof-read: Margaret Ahern reg. Nurse, Australia ICRC - Loki Orthopaedic
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis
 A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
A Single-Bar Above-Knee Orthosis Robert O. Nitschke,* C.P.O. I would like to present a different approach to the design of aboveknee, or "long leg", orthoses. When weight-bearing is not necessary, I have
PLAY PLAY. Hard. Smart. Knee Product Guide
 PLAY Hard. PLAY Smart. Knee Product Guide Osteoarthritis/Ligament Bracing M.4 OA Knee Brace Provides exact and effective valgus and varus pressure adjustment exerted close to the knee joint Physioglide
PLAY Hard. PLAY Smart. Knee Product Guide Osteoarthritis/Ligament Bracing M.4 OA Knee Brace Provides exact and effective valgus and varus pressure adjustment exerted close to the knee joint Physioglide
reason to believe that it could lend, in the form of an orthosis, excellent stability to the knee. On a knee orthosis, the cuffs must be strong enough
 AN EXTERNAL-CRUCIATE-LIGAMENT ORTHOSIS Thomas A. Martin, C.O. 2 Orthopaedic surgeons assigned to our regional health care center observed that many patients with internally deranged knees were unable to
AN EXTERNAL-CRUCIATE-LIGAMENT ORTHOSIS Thomas A. Martin, C.O. 2 Orthopaedic surgeons assigned to our regional health care center observed that many patients with internally deranged knees were unable to
P. CONVERY and A. W. P. BUIS
 Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1999, 23, 107-1 12 Socketlstump interface dynamic pressure distributions recorded during the prosthetic stance phase of gait of a trans-tibia1 amputee wearing a
Prosthetics and Orthotics International, 1999, 23, 107-1 12 Socketlstump interface dynamic pressure distributions recorded during the prosthetic stance phase of gait of a trans-tibia1 amputee wearing a
A Patellar-Tendon-Bearing Socket With A Detachable Medial Brim
 A Patellar-Tendon-Bearing Socket With A Detachable Medial Brim Carlton Fillauer,* C.P.O. * Fillauer Surgical Supplies, Inc., Chattanooga, Tennessee. Following our initial exposure to the German idea of
A Patellar-Tendon-Bearing Socket With A Detachable Medial Brim Carlton Fillauer,* C.P.O. * Fillauer Surgical Supplies, Inc., Chattanooga, Tennessee. Following our initial exposure to the German idea of
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Imler Partial Foot Prosthesis I.P.F.P. "Chicago Boot"
 Imler Partial Foot Prosthesis I.P.F.P. "Chicago Boot" by Clarence D. Imler, CP. Introduction Surgeons are now performing a greater number of distal amputations, including those of the distal forefoot.
Imler Partial Foot Prosthesis I.P.F.P. "Chicago Boot" by Clarence D. Imler, CP. Introduction Surgeons are now performing a greater number of distal amputations, including those of the distal forefoot.
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
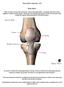
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Fig. 1. Lateral view of the patient showing stockinet in place and indelible pencil marks indicating areas where modification of the positive model wi
 Femoral Immobilizer CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN L. STILLS 2 During the past ten years orthotics has come to play a role in the treatment of selected patients with fractures of the femur. Fundamentally,
Femoral Immobilizer CHARLES H. PRITHAM 1 MELVIN L. STILLS 2 During the past ten years orthotics has come to play a role in the treatment of selected patients with fractures of the femur. Fundamentally,
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
2/24/2014. Outline. Anterior Orthotic Management for the Chronic Post Stroke Patient. Terminology. Terminology ROM. Physical Evaluation
 Outline Anterior Orthotic Management for the Chronic Post Stroke Patient Physical Evaluation Design Considerations Orthotic Design Jason M. Jennings CPO, LPO, FAAOP jajennings@hanger.com Primary patterning
Outline Anterior Orthotic Management for the Chronic Post Stroke Patient Physical Evaluation Design Considerations Orthotic Design Jason M. Jennings CPO, LPO, FAAOP jajennings@hanger.com Primary patterning
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Fig. 2 The Muenster technique determined the posterior trim line and olecranon relief by proper hand cupping and finger pressure proximal to the olecr
 The String Casting Technique for Below Elbow Amputations Timothy B. Staats, M.A., C.P. INTRODUCTION The String Casting Technique + is a method of casting the below elbow amputee for a socket that provides
The String Casting Technique for Below Elbow Amputations Timothy B. Staats, M.A., C.P. INTRODUCTION The String Casting Technique + is a method of casting the below elbow amputee for a socket that provides
Transtibial Amputation with Extended Flap and Bone Bridging
 Transtibial Amputation with Extended Flap and Bone Bridging Pre-Op Plan: Amputation indication: four years status post a crush injury to his left foot. Patient experiences chronic pain and dysfunction
Transtibial Amputation with Extended Flap and Bone Bridging Pre-Op Plan: Amputation indication: four years status post a crush injury to his left foot. Patient experiences chronic pain and dysfunction
INTERFACE DESIGN CRITERIA
 ADVANCEMENT OF UPPER EXTREMITY PROSTHETIC INTERFACE AND FRAME DESIGN Randall D. Alley, B.Sc., C.P. Hanger Prosthetics and Orthotics, Inc. ABSTRACT Although traditional upper extremity prosthetic interface
ADVANCEMENT OF UPPER EXTREMITY PROSTHETIC INTERFACE AND FRAME DESIGN Randall D. Alley, B.Sc., C.P. Hanger Prosthetics and Orthotics, Inc. ABSTRACT Although traditional upper extremity prosthetic interface
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
CLINICIAN INSTRUCTIONS
 CLINICIAN INSTRUCTIONS Contents About the Infinite Socket TT-S Legend Donning the Socket Closure System Engagement Doffing the Socket Torque Specifications Troubleshooting Warranty Information Technical
CLINICIAN INSTRUCTIONS Contents About the Infinite Socket TT-S Legend Donning the Socket Closure System Engagement Doffing the Socket Torque Specifications Troubleshooting Warranty Information Technical
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가?
 BK amputation 재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가? Soo-Kyung, Bok. M.D., Ph.D Chungnam National University Hospital Contents Level selection of BKA Rehabilitation Preoperative management Immediate postoperative management
BK amputation 재활의방법과시기 / 길이는얼마가적당한가? Soo-Kyung, Bok. M.D., Ph.D Chungnam National University Hospital Contents Level selection of BKA Rehabilitation Preoperative management Immediate postoperative management
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
1-Muscles: 2-Blood supply: Branches of the profunda femoris artery. 3-Nerve supply: Sciatic nerve
 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t r i n g p a r t o r i s c h i a l p a r t ) 2-Blood supply:
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN
 V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
V-VAS ORTHOSIS: A NEW CONCEPT IN UNLOADER KNEE ORTHOSIS DESIGN Joseph W. Whiteside CO/LO 1399 E. Western Reserve Road, Poland, OH 44514-3250 (800) 837-3888 www.anatomicalconceptsinc.com Page 1 of 5 The
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES
 A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
BELOW KNEE TEMPORARY PROSTHESIS!
 BELOW KNEl!: TEMPORARY PROSTHESIS 195 BELOW KNEE TEMPORARY PROSTHESIS! PATRICIA BAKER, 1\1.A.P.A. Caulfield Hospital, Vi'ctoria There are definite advantages in using temporary prostheses. Their use reduces
BELOW KNEl!: TEMPORARY PROSTHESIS 195 BELOW KNEE TEMPORARY PROSTHESIS! PATRICIA BAKER, 1\1.A.P.A. Caulfield Hospital, Vi'ctoria There are definite advantages in using temporary prostheses. Their use reduces
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on
 ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
Principles Starting Point Trajectory L/A/R Stable Construct. DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS 5/16/2017
 DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
DISCLOSURES Hassan R. Mir, MD, MBA, FACS Medical/Orthopaedic Publications Editorial/Governing Board OTA Newsletter Editor OsteoSynthesis, The JOT Online Discussion Forum Editor JOT Associate Editor JAAOS
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And
 Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Evaluation Of Contact Pressure On Total Surface Bearing And Patellar Tendon Bearing Sockets During Stair Ascent And Descent Koji Totoribe, Etsuo Chosa, MD, PhD, Xin Zhao, MD, PhD, Go Yamako, PhD, Shinji
Orlando Lite HKAFO/KAFO (Custom-to-Measurement only)
 Orlando HKAFO Hip-Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthosis includes Virtual Hip Joint and Shoe Insert This custom-to-measurements lightweight, durable long-leg orthosis is assembled from modular Orthomerica components
Orlando HKAFO Hip-Knee-Ankle-Foot Orthosis includes Virtual Hip Joint and Shoe Insert This custom-to-measurements lightweight, durable long-leg orthosis is assembled from modular Orthomerica components
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The nomenclature describing the orthosis is basically the same as that suggested for the molded ankle-foot orthosis (2), but the anterior shank enclos
 VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
VACUUM-FORMED ORTHOSES FOR FRACTURE OF THE TIBIA 1 Melvin Stills, C.O. 2 The routine management of fractures of the long bones of the lower limb infers immobilization by use of plaster casts extending
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB.
 ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT OF THE KNEE AND LOWER LIMB www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Overview History Examination X-rays Fractures and Dislocations. Soft Tissue Injuries Other Knee/Lower limb Problems Anatomy
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques
 TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
TRANSTIBIAL AMPUTATION General Principles & Update on Surgical Techniques Douglas G. Smith, MD Harborview Medical Center and University of Washington - Emeritus Prosthetic Research Study Amputee Coalition
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
~, /' ~::'~ EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS. Leg-anterolateral :.:~ / ~\,
 TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Posterior compartment of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
Posterior compartment of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Posterior compartment of the thigh 1-Muscles: Biceps femoris Semitendinosus Semimembranosus Adductor magnus
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO
 Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Checklist for Physical Examination of the Knee Muscuoskeletal Block -- Chris McGrew MD, Andrew Ashbaugh DO This handout is for use as a rough guide and study aid. Your instructor may perform certain maneuvers
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
Christopher Gorrell PT, DPT May 5, 2016
 25th Annual Prosthetics Course Pre and Post-Prosthetic Rehab from a Therapist's Perspective Christopher Gorrell PT, DPT May 5, 2016 1 Objectives To review the primary goals related to treatment of a patient
25th Annual Prosthetics Course Pre and Post-Prosthetic Rehab from a Therapist's Perspective Christopher Gorrell PT, DPT May 5, 2016 1 Objectives To review the primary goals related to treatment of a patient
Care of the Diabetic Patient
 Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
Care of the Diabetic Patient Aarti Deshpande, CPO Clinic Manager Zuckerberg San Francisco General Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, San Francisco March 16, 2017 Diabetes Diabetes
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Pediatric Formula. Product Manual
 Pediatric Formula Product Manual Instructions The Pediatric Formula foot system has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload
Pediatric Formula Product Manual Instructions The Pediatric Formula foot system has been designed and manufactured for specific patient weights. Failure to follow the weight guidelines and/or overload
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module
 Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module Michelle J. Hall, CPO, BSE 1 Ignacio V. Ponseti, MD 2 1. Certified Prosthetist Orthotist at American Prosthetics & Orthotics,
Ponseti Treatment Method for Idiopathic Clubfoot Continuing Education Module Michelle J. Hall, CPO, BSE 1 Ignacio V. Ponseti, MD 2 1. Certified Prosthetist Orthotist at American Prosthetics & Orthotics,
KNEE EXAMINATION. Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective. EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine
 KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
KNEE EXAMINATION Tips & Tricks from an Emergency Physician Perspective Dr P O CONNOR Emergency Medicine Physician EUSEM 10/09/2018 EM Physicians Less Exposed to MSK Medicine Musculoskeletal Medicine becoming
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION
 ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy
 Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
Management of knee flexion contractures in patients with Cerebral Palsy Emmanouil Morakis Orthopaedic Consultant Royal Manchester Children s Hospital 1. Introduction 2. Natural history 3. Pathophysiology
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome
 2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
2. Iliotibial Band syndrome Iliotibial band (ITB) syndrome (so called runners knee although often seen in other sports e.g. cyclists and hill walkers). It is usually an overuse injury with pain felt on
Use of platinum cured silicone for increased comfort, control and moisture management in prosthetics Ana Gallego ProfGradIMMM.
 Use of platinum cured silicone for increased comfort, control and moisture management in prosthetics Ana Gallego ProfGradIMMM. Senior Materials Engineer. New Product Development Section Summary About Blatchford
Use of platinum cured silicone for increased comfort, control and moisture management in prosthetics Ana Gallego ProfGradIMMM. Senior Materials Engineer. New Product Development Section Summary About Blatchford
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
A One-Piece Laminated Knee Locking Short Leg Brace* by
 A One-Piece Laminated Knee Locking Short Leg Brace* by Jimmy Saltiel + In paralysis of the lower extremities, one of the major problems in ambulation is loss of joint stability. This is commonly treated
A One-Piece Laminated Knee Locking Short Leg Brace* by Jimmy Saltiel + In paralysis of the lower extremities, one of the major problems in ambulation is loss of joint stability. This is commonly treated
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
Knee Disarticulation Amputation
 Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
Knee Disarticulation Amputation Pre-Op 64 year old man, previous spinal cord injury, diabetes, renal failure, and a history of spasticity with dynamic knee flexion contracture. He had an open left ankle
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO)
 PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate (PLEO) Left PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates Right PLEO Plates Sizes: 6, 8 and 10 hole plates PediLoc Extension Osteotomy Plate The technique description herein
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
Tibial Plateau Fractures. John Grice, Queen Alexandra Hospital, Dec 2008
 Tibial Plateau Fractures John Grice, Queen Alexandra Hospital, Dec 2008 Introduction Incidence, Epidemiology & aetiology Anatomy Classification Managment Cases Summary 1% of all fractures (8% in old age)
Tibial Plateau Fractures John Grice, Queen Alexandra Hospital, Dec 2008 Introduction Incidence, Epidemiology & aetiology Anatomy Classification Managment Cases Summary 1% of all fractures (8% in old age)
Technique Manual Technique Manual Rev. A 01/11/2011
 Technique Manual Technique Manual Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 5 Instrumentation 6 Frame Assembly 7 Position Guide 8-9 Tips and Tricks 10-13 Cleaning 14 Sterilization 14 Storage Instructions
Technique Manual Technique Manual Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 5 Instrumentation 6 Frame Assembly 7 Position Guide 8-9 Tips and Tricks 10-13 Cleaning 14 Sterilization 14 Storage Instructions
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field
 Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
Lower Extremity Dislocations: Management and Triage on the Field Scott J Tarantino, MD Towson Orthopaedic Associates, Towson, MD None Disclsures Purpose To provide you with knowledge which may guide you
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP Rev D 03/07
 Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP020193 Rev D 03/07 Council Directive 93/2/EEC of 1 June 1993 concerning Medical devices Fast adjustment- Fast Hinge- Fast Straps- Fast Application This
Bledsoe Extender Brace Application Instructions CP020193 Rev D 03/07 Council Directive 93/2/EEC of 1 June 1993 concerning Medical devices Fast adjustment- Fast Hinge- Fast Straps- Fast Application This
Some Experience in Hemipelvectomy Prosthetics
 Some Experience in Hemipelvectomy Prosthetics by Herbert W. Marx, Prosthetist, Prosthetic and Orthotic Laboratories, Institute for the Crippled and Disabled, New York Early attempts in hemipelvectomy prosthetics
Some Experience in Hemipelvectomy Prosthetics by Herbert W. Marx, Prosthetist, Prosthetic and Orthotic Laboratories, Institute for the Crippled and Disabled, New York Early attempts in hemipelvectomy prosthetics
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
FOOT PARTIAL. Support for Better Life AN ILLUSTRATIVE GUIDE. Design & Fabrication for a Partial Foot Prosthesis that will...
 PARTIAL FOOT AN ILLUSTRATIVE GUIDE Design & Fabrication for a Partial Foot Prosthesis that will... Reduce Friction Reduce Shearing Reduce Pressure Restore Propulsion Restore Limb Length Preserve Residual
PARTIAL FOOT AN ILLUSTRATIVE GUIDE Design & Fabrication for a Partial Foot Prosthesis that will... Reduce Friction Reduce Shearing Reduce Pressure Restore Propulsion Restore Limb Length Preserve Residual
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM. TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments
 RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service
 North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
North of England Bone and Soft Tissue Tumour Service Guidelines for rehabilitation after proximal tibial replacement Proximal tibial replacement surgery is usually carried out as part of treatment for
Trans-tibial Prosthetics
 Trans-tibial Prosthetics Tome 2 ( Alignment & Fitting ) Course Work Manual ICRC ( INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE OF THE RED CROSS ) Aknowledgements Substantial parts of the information and reference material
Trans-tibial Prosthetics Tome 2 ( Alignment & Fitting ) Course Work Manual ICRC ( INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE OF THE RED CROSS ) Aknowledgements Substantial parts of the information and reference material
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
