Low Risk Neonatal Nursing
|
|
|
- Cori Perry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NCC believes the individual certified nurse is the best person to determine the specialty code for their CE, as they have the specific content of the CE program. Low Risk Neonatal Nursing NCC Maintenance Requirements The standard process for the NCC Professional Development Certification Maintenance Program makes use of a specialty assessment tool and resulting personal education plan: Complete the specialty assessment tool that reflects the current knowledge competencies aligned with your certification specialty at the beginning of each new certification maintenance cycle. Earn CE as specified by the education plan developed from your specialty assessment. Your education plan outlines the CE needed to maintain your NCC certification. Only CE earned after you have taken your specialty assessment can be used to maintain your certification. It must meet the CE needed in your educational plan National Certificaiton Corporation (NCC) All Rights Reserved.
2 CONTINUING COMPETENCY SPECIALTY ASSESSMENT The CE requirements for your NCC maintenance will be outlined in your education plan! Your educational plan is derived from your specialty assessment and outlines for you the CE needed in each of your core competency areas. Each core area has a code and that code is provided for you as well. Take the specialty assessment as soon as you can in the beginning of your maintenance cycle. The assessment may be taken early, up to 3 months prior to the start of your new maintenance cycle date. The start day for earning CE remains at the first day of the new maintenance cycle. YOU CAN ONLY USE CE EARNED AFTER YOU HAVE TAKEN YOUR ASSESSMENT FOR MAINTENANCE. ANY CE EARNED BEFORE YOU TOOK THE ASSESSMENT CANNOT BE USED (EVEN IF IT MEETS YOUR EDUCATION PLAN). YOUR CE AND NCC MAINTENANCE REQUIREMENTS All CE must be earned during your current maintenance cycle and after you have taken the specialty assessment. All CE used for NCC maintenance is defined by the individuals Education Plan. All CE must be submitted online at NCCwebsite.org. All CE must be coded to the applicable core content area. See listing in this brochure. CE can be entered into the maintenance application any time after the assessment has been taken and on an ongoing basis. All activities will be saved until the application is submitted. All CE must be accredited by an agency recognized by NCC. ACCREDITING AGENCIES Academic credit is accepted as is CME credit. For continuing education credit to be accepted for the purpose of maintenance, the continuing education activity must be accredited by one of the agencies below. NCC State boards of nursing State nursing associations Nursing, medical or health care organizations (this would include, for example, such organizations as: AWHONN, NPWH, NANN, ACOG, AMA etc.) Colleges or universities For profit or not-for-profit continuing education organizations such as Contemporary Forums, Western Schools, Professional Education Consultants, Perifacts etc. provided that programs sponsored by such organizations have been accredited for continuing education. Most of the for-profit organizations have achieved accreditation for their offering through a state board of nursing or health care organization. Review accreditation details in the registration brochure you received when registering for the particular continuing education activity. 2
3 COMMON CODING QUESTIONS I went to a conference with topics that reflect many different codes, how do I code them? I could not list all my CE. I have many more hours but the maintenance application would not let me list them. I was a preceptor for new students, can I use this for maintenance and how do I list it on the application. How do I code it? I have multiple certifications. Can I use the same CE for both. How can I code it for two different certifications. Do I have to submit a Maintenance Pre-approval? You have two options: You can code to the content area that represents the majority of the content presented. OR You can breakout content per code (You may combine different sessions of the same content code.) and record total hours for each code, listing the same conference for every content code entry. Once you meet or the CE requirements designated by your education plan the application will automatically take you to the payment page. There is no need to enter more CE than is required. 10 hours of CE can be used for precepting students, in your same certification specialty area and role. (e.g. In order for a WHNP to use the credit they cannot preceptor nurse midwives or residents only WHNP students.) Orienting new staff is NOT considered as preceptor hours. On the application select the more information link for the preceptorship code 24 and it will give you information on how to list the information. This is also applicable to any of the other codes. You can only use these hours for baseline hours and not hours designated in the education plan assigned to a specific competency area. Baseline hours are listed as hours that are assigned to any competency area and appear at the bottom of your plan. If the CE is applicable to both areas and was earned in the appropriate time frame for each certification, yes. But you still need to file a separate maintenance application and fee for each certification. Each CE activity will be coded to each application. Maintenance Pre-Approval is optional and not required. If you are unsure your continuing education activities will meet your NCC maintenance requirements, you can ask NCC to pre-approve your CE activities. There is a nonrefundable fee for this service. Complete details are in the maintenance section of NCCwebsite.org. 3
4 HOW TO READ THE EDUCATION PLAN Competency areas where 7.5 specialty index is achieved, no CE is needed. Competency areas where 7.5 specialty index is not achieved, the hours of CE needed will be listed. Every plan has a minimum of 15 CE hours - these are called baseline hours. Even if a specialty index above 7.5 is achieved in every competency, there is still a CE commitment of 15 hours. Education plans that need 45 hours, do not have any baseline hours because those hours are assigned to the specific core competencies. Every plan is composed of a maximum of 50 and a minimum of 15 CE hours. Missed keywords are intended to show what specific topics had knowledge gaps within that competency area. They are broad in scope and you are not required to cover all keywords or topics for your NCC certification maintenance Links to NCC CE modules are offered as a convenience. Use of NCC CE modules is optional not required. NCC CE is provided as a way to provide affordable, easily accessible CE for those who may have limited CE options in their area or practice. Also CE earned for successful completion of any NCC CE modules will automatically be entered and coded into your online maintenance application 5 hours of credit is given for taking the assessment and may be applied to any CE need. The total number of hours needed will be listed in each specific core competency. 4
5 LRN Core Competency Area Mother/Fetus (Code 1) *5 hours Mother/Fetus Assess intrauterine environment Antepartal fetal testing Fetal and placental development EDUCATION PLAN Maternal Complications Affecting the Newborn Preexisting maternal conditions Pregnancy related conditions Environmental and lifestyle factors Physical Assessment, Thermoregulation and Normal Management (Code 2) *15 hours Physical Assessment Gestational age assessment Diagnostic laboratory studies Physical and behavioral assessment Basic physiology and anatomy Thermoregulation Physiology Mechanisms of heat loss Temperature management Oxygen and Acid-Base Non-invasive ventilation Blood gas Neonatal Enteral Nutrition Breastfeeding Neonatal nutrition and feeding Normal Management Neonatal transition General care Parent education Developmental Care Motor organization Neurobehavioral development habituation Sensory/interaction capabilities CORE COMPETENCY AREA Your education plan CORE COMPETENCY AREA YOUR SPECIALTY INDEX CE HOURS REQUIRED Mother/Fetus (Code 1) 7.89 Standard met Physical Assessment, Thermoregulation and Normal Management (Code 2) hours Neonatal Complications (Code 3) 8.23 Standard met Pharmacology (Code 4) 6 5 hours Professional Practice (Code 6) hours Physical Assessment, Thermoregulation and Normal Management (Code 2) Missed keywords: Behavioral assessment, Breastfeeding, Gestational age assessment, Laboratory test evaluation, Neonatal nutrition, Thermoregulation Physical Assessment, Thermoregulation and Normal Management (Code 2) Self Assessment modules» Pharmacology (Code 4) Missed keywords: Breastfeeding and Medication, Drug Therapies, Hyperbilirubinemia, Perinatal Substance Abuse, Pharmacokinetics Pharmacology (Code 4) Self Assessment modules» Professional Practice (Code 5) Missed keywords: Legal Issues, Legal/Ethical Issues, Patient Safety, Research Professional Practice (Code 5) Self Assessment modules» CE HOURS 15 hours 5 hours 5 hours 15 Continuing Education hours in any of your content specific specialty areas 15 hours Credit for taking this assessment -5 hours (may be applied to your total required hours) Total hours required 35 hours Family Integration Role adaption Discharge planning Screening Parent education Neonatal Complications (Code 3) *20 hours Management of Complications Cardiac Respiratory Gastrointestinal Renal Genitourinary Hematopoietic Neurological Immunology Endocrine Musculoskeletal Skin Genetics Head, ears, eyes, nose and throat Perinatal substance abuse Hyperbilirubinemia Pharmacology (Code 4) *5 hours Pharmacokinetics General principles Routes of administration Pharmacokinetics, drug therapies Drug Therapies Vitamin K Eye prophylaxis Antibiotics Hepatitis vaccine Other vaccines Pain Management Pharmacologic Nonpharmacologic Professional Practice (Code 5) *5 hours Patient Safety Interprofessional communication Continuing competency Medication error prevention Ethical Principles and Theories Patient advocacy Legal Issues Affecting Newborn Nursing Impaired nurse Scope of practice Expert witness Informed Consent Professional Practice Standards Research Common terms Application of research to practice Evidence based practice *Number of CE hours required if you do not achieve a specialty index of 7.5 or more in the content area. 5
6 DETERMINING WHAT CONTENT MEETS EACH SPECIALTY CODE Core Competency Area Content Topic Keywords Mother/Fetus (Code 1) 1 Mother/Fetus Assess intrauterine environment Antepartal fetal testing Fetal and placental development Maternal Complications Affecting the Newborn Preexisting maternal conditions Pregnancy related conditions Environmental and lifestyle factors Abnormal placentation Age related concerns AIDS and HIV infections Amniotic bands Amniotic fluid disorders Amniocentesis and other genetic testing Antenatal testing Antepartum fetal surveillance Assess intrauterine environment Biophysical profile Cord gas Environmental factors affecting the fetus Fetal and placental development Fetal antepartum testing Fetal heart rate patterns Fetal lung maturation Gestational diabetes Gestational hypertension Health history Hypertensive disorders Instrument assisted birth Intrapartum factors affecting the neonate Intrauterine growth restriction Malpresentation Maternal factors/ diseases affecting the newborn Maternal infection Maternal medication abuse/misuse Maternal medication fetal effects Maternal nutrition Meconium Multiple gestation Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPTs) Nonstress testing Oligohydramnios Placenta previa Placental abruption Polyhydramnios Preterm and Postterm Preeclampsia Rh screening Trauma Physical Assessment, Thermoregulation and NormalManagement (Code 2) 2 Mother/Fetus Gestational age assessment Diagnostic laboratory studies Physical and behavioral assessment Basic physiology and anatomy Thermoregulation Physiology Mechanisms of heat loss Temperature management Oxygen and Acid-Base Non-invasive ventilation Blood gas Neonatal Enteral Nutrition Breastfeeding Nutritional requirements Normal Management Neonatal transition General care Parent education Developmental Care Motor organization Neurobehavioral development habituation Sensory/interaction capabilities Family Integration Role adaption Discharge planning Screening Parent education Bathing the neonate Behavior Behavioral assessment Bilirubin metabolism Blood cultures Blood gas Blood tests Breast milk properties Breastfeeding Calcium Caloric supplements Calorie/energy needs Central lines Car seat challenge CBC CCHD screening Circumcision Cord care CPAP CRP Cultural care Developmental positioning Diagnostic Labs Discharge planning Donor milk Early term Fluid & electrolyte requirements Formula composition Genetic screening Gestational age assessment Glucose metabolism Grieving process Growth velocity Harlequin color change Head circumference Hearing loss Hearing screening Heart sounds Hematocrit and hemoglobin High flow NC Hyperthermia Hypothermia Incubator management Intimate partner violence Kangaroo care/ skin-to-skin Laboratory test evaluation Lactation physiology LGA Late preterm Mechanisms of heat loss Metabolic panel Motor organization Muscle tone assessment Nasal cannula Neonatal transition Neurobehavioral development habituation Non-invasive ventilation Nutrition needs Oxygen hood Oxygen saturation Parent education Parental counseling Pharmacology/ Pharmacokinetics Physical assessment Physical exam and newborn physiology PICC lines PIV management Plagiocephaly Reflexes Renal metabolism Safe sleep Safety Sensory assessment SGA Shaken baby Sleep cycles State cycles Thermoregulation Thermoregulation management Umbilical cord care Umbilical cord physiology Umbilical lines Urinalysis Urine output 6
7 DETERMINING WHAT CONTENT MEETS EACH SPECIALTY CODE Core Competency Area Content Topic Keywords Neonatal Complications (Code 3) 3 Management of Complications Cardiac Respiratory Gastrointestinal Renal Genitourinary Hematopoietic Neurological Immunology Endocrine Musculoskeletal Skin Genetics Head, ears, eyes, nose and throat Perinatal substance abuse Hyperbilirubinemia Acyanotic heart defect AIDS and HIV infections Air leaks Ambiguous genitalia Anemia Arrhythmias Asphyxia Bacterial infection Bilious vomiting Birth defects Birth injuries Birth marks Birthweight effects Bleeding and hemorrhage Blood disorders Blood glucose Blood incompatibilities Blood products Blood transfusion Bowel obstruction Brachial plexus injury Cafe au lait spots Caput succedaneum Cardiac Cardiorespiratory diseases Cardiorespiratory distress Cephalohematoma Chest thoracentesis Choanal atresia Chromosomal abnormalities Chronic lung disease Circumcision Cleft lip and palate Coagulation disorders Coarctation of the aorta Cold stress Common skin disorders Complex Congenital Heart Disease (CCHD) Congenital heart disease Congenital hip dysplasia Congenital malformations Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Conjunctivitis Constipation Craniosynotosis Cryptorchidism Cyanosis Cyanotic heart defect Cystic fibrosis Cystic hygroma Cysts Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Dermoid sinus Developmental dysplasia of the hip Diaper dermatitis Diaphragmatic hernia Diarrhea DIC DiGeorge Dudodenal atresia Dysrhythmias Electrolyte imbalance Endocrine Endocrine disorders ENT and Head Epstein s pearls Erb s palsy Esophageal atresia Exchange transfusion Foot malformations Fractures Fungal infection G6PD Gastroesophageal reflux Gastrointestinal GE reflux Genetic defects Genitourinary Group B streptococcus infection Heart block Hemangioma Hematoma Hematopoietic Hemolytic anemia Hemorrhagic disease of the newborn Hepatitis Herpes HIE Hirschsprung s disease Hydrocephalus Hydronephrosis Hyperbilirubinemia Hyperglycemia Hyperkalemia Hypertension Hypocalcemia Hypoglycemia Hypokalemia Hypospadias Hypotension Hypothermia Hypoxia Hypoxemia Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy Immunology Imperforate anus Inborn errors of metabolism Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) In utero exposure to alcohol In utero exposure to cocaine In utero exposure to narcotics In utero exposure to nicotine Infant of a diabetic mother Infections Inguinal hernia Integumentary Intracranial hemorrhage Jaundice Kernicterus Malrotation Maternal drug effects Meconium aspiration syndrome Meconium ileus Meconium plug syndrome Metabolic Metabolic acidosis Metaboloc alkalosis Metabolic disorders Micrognatnia Multiple gestation Musculoskeletal Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS) withdrawal Neonatal heart diseases Neonatal pain Neural tube defects Neurologic disorders 7
8 DETERMINING WHAT CONTENT MEETS EACH SPECIALTY CODE Core Competency Area Content Topic Keywords Neonatal Complications (Code 3) 3 Management of Complications Cardiac Respiratory Gastrointestinal Renal Genitourinary Hematopoietic Neurological Immunology Endocrine Musculoskeletal Skin Genetics Head, ears, eyes, nose and throat Perinatal substance abuse Hyperbilirubinemia Neurological Neuromuscular maturity scoring systems NRP Omphalitis Osteopenia Otitis media Palsy Patent ductus arteriosus Patent urachus Patterns of inheritance Perinatal loss Perinatal substance abuse Periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn Phototherapy Physiologic anemia of infancy Pierre Robin Platelet disorders Pneumomediastinum Pneumothorax Polycythemia Prematurity PVL periventricular Renal abnormalities Respiratory Respiratory acidosis Respiratory alkalosis Respiratory distress Resuscitation and stabilization Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) RH incompatibility RSV Seizures Sepsis Septal defects Shock Short gut syndrome Sickle cell Skeletal dysplasia S.T.A.B.L.E. Subgaleal Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Testicular abnormalities Tetralogy of Fallot Therapeutic hypothermia/cooling Thoracentesis Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytosis Thyroid disorders TORCH Tracheosophageal fistula Transposition of the great vessels Transient tachypnea of the newborn Trisomy Turner syndromehydroacy Umbilical hernia Urine toxicology Ventricalomegaly Viral infection Volvulus Pharmacology (Code 4) 4 Pharmacokinetics General principles Routes of administration Pharmacokinetics, drug therapies Drug Therapies Vitamin K Eye prophylaxis Antimicrobials/Antibiotics Antiretrovirals Immunizations Resuscitation medications Pain Management Pharmacologic Nonpharmacologic 5 rights of medication administration Antibiotics Anticonvulsants Antimicrobials Antiretroviral AZT Breastfeeding and medications Bronchodilators Cardiac medications CNS stimulants Dietary supplements Diuretics Drug levels Drug therapies Drugs for NAS Epinephrine Erythropoietin Eye prophylactic treatment HIV drugs Immunologic agents Indomethacin Inhalation medication IV fluid IVIG Lipids Medication effects Oxygen as a drug Pain management Parenteral nutrition Perinatal substance abuse Pharmacokinetics PPLs Reflux medications ROP medication/avastin Route of drug administration Steroids Surfactant TPN Vaccines/Immunizations Vitamin K administration 8
9 DETERMINING WHAT CONTENT MEETS EACH SPECIALTY CODE Core Competency Area Content Topic Keywords Professional Practice (Code 5) 5 Patient Safety Interprofessional communication Continuing competency Medication error prevention Ethical Principles and Theories Patient advocacy Legal Issues affecting newborn nursing Impaired nurse Scope of practice Expert witness Informed Consent Professional Practice Standards Research Common terms Application of research to practice Evidence based practice CE poster sessions (6 posters equal 1 hour) Continuing competency Ethical principles and theories Evidence based practice Interprofessional communication Legal Issues affecting newborn nursing Legal/Ethical Issues Medication error prevention Patient advocacy Patient safety Professional practice standards Research 9
10 DETERMINING WHAT CONTENT MEETS EACH SPECIALTY CODE NCC OTHER CODES You can only use these hours for baseline hours and not hours designated in the education plan assigned to a specific competency area. Baseline hours are listed as hours that are assigned to any competency area and appear at the bottom of your plan. NCC Pretest Participant NCC Item Writer NCC CE Reviewer or Author Presenter of a CE Course or Preceptor Author of a Book Chapter or Journal Article If you participated in the NCC sponsored pretest program If you are credentialed by NCC and have participated in the item writing program If you reviewed or authored an NCC continuing education module Presenter of educational program can use the same amount of CE earned by the participants. Such CE presentation CANNOT be part of the individual s job responsibilities. If the activities was presented more than once you can only use the CE hours once. The maximum number of hours that can be earned for preceptorship activity is 10 hours per maintenance cycle. This is limited to preceptoring students in your same certification specialty area. Staff orientation is NOT considered a preceptor activity and cannot be used. Rules for Using Publications for Maintenance The publication date of the article/book/module will determine its applicability for your current certification maintenance. You are limited to using one article, book authorship or service as an NCC continuing education reviewer or monograph author per certification maintenance cycle. Articles/books must be related to the certification specialty area. 5 contact hours will be awarded to those who have written a journal article or a chapter of a book. 15 contact hours will be awarded to those who are a primary or secondary author of a book. 10
The high risk neonate
 The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
The high risk neonate Infant classification by gestational (postmenstrual) age Preterm. Less than 37 completed weeks (259 days). Term. Thirty-seven to 416/7 weeks (260-294 days). Post-term. Forty-two weeks
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals
 Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline.
 Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Lectures 4 Early fetal assessment, screening, ultrasound and treatment modalities during pregnancy. II. Asphyxia and Resuscitation (3 lectures)...
 Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
BASIC TRAINING Knowledge Guide Neonatal and Perinatal Medicine
 COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
COMMON PRESENTATIONS AND CONDITIONS Basic Trainees will require a sufficient depth of knowledge of these presentations and conditions. Antenatal conditions such as cerebral ventricular dilatation, choroid
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
NEONATAL-PERINATAL MEDICINE ROTATION Competency Based Goals and Objectives Competency 1. Patient Care: Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and
Legal aspects in accidents and neglect.
 Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Al-Al Bayt University Princess Salma Faculty of Nursing Adult Health nursing Course Title :Child Health Nursing Course Number :1001341 Credit Hours :3 Pre requisite :1001222 Placement : Instructor:,, Course
Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period.
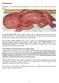 Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Prematurity Premature: is live born infants delivered before 37 wk from the 1 st day of the last menstrual period. Low birth weight (LBW): (birth weight
Emergency Department Suite
 Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
Emergency Department Suite This suite of Pediatric Learning Solutions (PLS) online courseware and curriculums provides 24/7 access to the foundational knowledge and just-in-time job aids clinicians working
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General
![OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General](/thumbs/85/91909911.jpg) OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
Medical Follow-up of the High-Risk NICU Graduate
 Medical Follow-up of the High-Risk NICU Graduate Silvia Fajardo-Hiriart, M.D. Medical Director High-Risk Infant Follow-Up/Early Intervention Program University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Department
Medical Follow-up of the High-Risk NICU Graduate Silvia Fajardo-Hiriart, M.D. Medical Director High-Risk Infant Follow-Up/Early Intervention Program University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Department
ADMISSION/DISCHARGE FORM FOR INFANTS BORN IN 2019 DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
1 Any eligible inborn infant who dies in the delivery room or at any other location in your hospital within 12 hours after birth and prior to admission to the NICU is defined as a "Delivery Room Death."
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. (Note: PLS Courses are in italics under topic area)
 The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. These courses equip candidates with the foundational knowledge necessary to approach
The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Pediatric CRRN Exam Content Outline. These courses equip candidates with the foundational knowledge necessary to approach
Product Catalog. Pediatric Learning Solutions. Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association.
 Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
PEDIATRICS. Module Topic/Content Student Learning Outcomes Resources Clinical Assessment Activities Course/Clinical Outcomes
 PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
PEDIATRICS N332 Outline 1 Welcome back: Instructor Role and Student Role Discuss course requirements. Explain personal learning style and study patterns. Explain critical thinking and clinical judgment
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine
 The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
The Fetal Care Center at NewYork-Presbyterian/ Weill Cornell Medicine Prompt and Personalized Care for Women with Complex Pregnancies A Team of Experts additional training in maternal and fetal complications
PCEP. Perinatal Continuing Education Program. Pretest Answer Key Book IV: Specialized Newborn Care. Unit 1: Direct Blood Pressure Measurement
 1. C. Severe anemia 2. True 3. True 4. False Perinatal Continuing Education Program Pretest Answer Key Book IV: Specialized Newborn Care Unit 1: Direct Blood Pressure Measurement 5. True 6. A. Baby s heart
1. C. Severe anemia 2. True 3. True 4. False Perinatal Continuing Education Program Pretest Answer Key Book IV: Specialized Newborn Care Unit 1: Direct Blood Pressure Measurement 5. True 6. A. Baby s heart
Experience. Initials Medical Staffing Network Rev. 06/15 F01201 NNICU 2 of 5
 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Babies First and CaCoon Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes)
 Babies First and Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes) (Birth through 4 years of age) Medical Risk Factors A1. Drug exposed infant (See A29) A2. Infant HIV positive A3. Maternal PKU or HIV positive A4. Intracranial
Babies First and Risk Factors (A Codes and B Codes) (Birth through 4 years of age) Medical Risk Factors A1. Drug exposed infant (See A29) A2. Infant HIV positive A3. Maternal PKU or HIV positive A4. Intracranial
Neonatology ICD-10 documentation
 Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
Neonatology documentation Seven key impacts to documentation 1. Disease or disorder site 2. Acuity and/or encounter status of treatment 3. Etiology, causative agent, or disease type and injury/ poisoning
How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: How to Recognize a Suspected Cardiac Defect in the Neonate https://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/
NICU Encounter. Patient Label Here. Admission/Demographics; Health Status; Interventions; Screening; Discharge/Outcome Tabs. SCN/Level 2 NICU/Level 3
 Patient Label Here NICU Encounter Admission/Demographics; Health Status; Interventions; Screening; Discharge/Outcome Tabs Birth Location: Hospital Home Birth Centre Nursing Station Other Ontario Hospital
Patient Label Here NICU Encounter Admission/Demographics; Health Status; Interventions; Screening; Discharge/Outcome Tabs Birth Location: Hospital Home Birth Centre Nursing Station Other Ontario Hospital
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE SKILLS CHECKLIST
 NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE SKILLS CHECKLIST NAME: DATE: Please check the appropriate letter of proficiency for the following types of clinical situations and equipment. GENERAL Gestational assessment Physical
NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE SKILLS CHECKLIST NAME: DATE: Please check the appropriate letter of proficiency for the following types of clinical situations and equipment. GENERAL Gestational assessment Physical
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans. Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD
 Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
Standard of Newborn Care in the Age of Birth Plans Stephanie Deal, MD Tiffany McKee-Garrett, MD Disclosure We have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers(s) of any commercial products(s)
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident. Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents
 Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents Prerequisites: Successful completion of NRP course with certification
Standard Rotation: Neonatal Intensive Care at UHB or KCHC Junior Resident Residents: PL-1 pediatrics, EM-1 or EM-2 emergency medicine residents Prerequisites: Successful completion of NRP course with certification
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
Clinical evaluation Jaundice skin and mucous membranes
 JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
JAUNDICE Framework The definition of Neonatal Jaundice Billirubin Metabolism Special characteristic in neonates Dangerous of the Hyperbillirubinemia The diseases in relation with Neonatal Jaundice Objectives:
Neonatal ICU Skills Checklist. Applicant Full Legal Name (please print):
 Applicant Full Legal Name (please print): The following checklist is a profile used to assess your clinical efficiency and assist in matching your skills with available assignments. Your employment is
Applicant Full Legal Name (please print): The following checklist is a profile used to assess your clinical efficiency and assist in matching your skills with available assignments. Your employment is
Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010
 Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Neonatal Hypoglycemia Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 25\7\2010 Definition The S.T.A.B.L.E. Program defines hypoglycemia as: Glucose delivery or availability is inadequate to meet glucose demand (Karlsen,
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Ashley Robson Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070
 1 Ashley Robson 2212 Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070 September 2 nd 2014 Debra Brandon PhD, RN, CCNS, FAAN Duke University School of Nursing Durham, NC Dear Mrs. Brandon- I would like the opportunity
1 Ashley Robson 2212 Canyon Creek Dr. Mckinney, TX 75070 September 2 nd 2014 Debra Brandon PhD, RN, CCNS, FAAN Duke University School of Nursing Durham, NC Dear Mrs. Brandon- I would like the opportunity
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport. Relevant Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara
 Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
EXAMINATION CONTENT CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE
 CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing exam Percentage of Questions in Content Categories 50 40 30 20 10 0 48% General Assessment and Management 44% Assess & Manage Pathophysiologic States
CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing exam Percentage of Questions in Content Categories 50 40 30 20 10 0 48% General Assessment and Management 44% Assess & Manage Pathophysiologic States
Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
EXAMINATION CONTENT CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE
 CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Genl Asst & Mgmt Pathophysiology Psychosocial Professional Issues The above chart shows the percentage distribution of questions on the Neonatal Intensive
CONDENSED EXAM OUTLINE 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Genl Asst & Mgmt Pathophysiology Psychosocial Professional Issues The above chart shows the percentage distribution of questions on the Neonatal Intensive
PEDIATRIC MEDICAL HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
 Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
Division of Otolaryngology Main Phone: 847 504-3300 Main Fax: 847 504-3305 Mihir Bhayani, MD Judy L. Chen, MD Mark E. Gerber, MD, FACS, FAAP Joseph Raviv, MD Ilana Seligman, MD, FACS, FAAP Michael J. Shinners,
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives
 Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Cardiology Competency Based Goals and Objectives COMPETENCY 1. Patient Care. Provide family centered patient care that is developmentally and age appropriate, compassionate, and effective for the treatment
Diuretics: Increased risk of renal dysfunction. (7) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 10/2017 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEOPROFEN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEOPROFEN. NEOPROFEN (ibuprofen
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEOPROFEN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEOPROFEN. NEOPROFEN (ibuprofen
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS AND
 TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
Objectives. Apnea Definition and Pitfalls. Pathophysiology of Apnea. Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes 5/18/2015
 Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
COMPLICATIONS OF PREMATURITY
 ا د. نعمان نافع الحمداني Professor Numan Nafie Hameed COMPLICATIONS OF PREMATURITY Early: RDS, Jaundice, PDA, IVH, Early anemia of prematurity. These occur while the patient in hospital. Late: ROP, BPD
ا د. نعمان نافع الحمداني Professor Numan Nafie Hameed COMPLICATIONS OF PREMATURITY Early: RDS, Jaundice, PDA, IVH, Early anemia of prematurity. These occur while the patient in hospital. Late: ROP, BPD
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN. Other. Other Diseases
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Other Diseases Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Neonate (PPHN) PPHN 3 Also known as Persistent Fetal Circulation (PFC) Seen most frequently in term, post-term
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acid base balance pregnancy-related changes to, 640 Acquired heart disease, 731 Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), 618 Acute kidney
Hematology. Overview. Blood Cell Development. Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC
 Hematology Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Overview l Blood cell development l Normal values l Diagnostic tests l Common hematologic problems and therapies Blood Cell Development l Stem cells from which all blood
Hematology Judy Philbrook, NNP-BC Overview l Blood cell development l Normal values l Diagnostic tests l Common hematologic problems and therapies Blood Cell Development l Stem cells from which all blood
Notes by Harriet Wood. Preterm Infants
 Preterm Infants Prognosis Depends on gestational age at birth. Rate and severity of problems associated with prematurity decrease markedly with increasing gestation. Appearance of very preterm infants
Preterm Infants Prognosis Depends on gestational age at birth. Rate and severity of problems associated with prematurity decrease markedly with increasing gestation. Appearance of very preterm infants
M3 Pediatric Clerkship
 M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
M3 Pediatric Clerkship The overall goals for the third year Pediatric Clerkship are to educate future physicians to provide competent, effective and compassionate care of patients by developing clinical
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials
 Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Intensive Care RN Needs Assessment 2010
 Neonatal Intensive Care RN Needs Assessment 2010 OO9b, 2010 NICU Needs Assessment Survey Results.mht.pdf 1. Identify your highest educational level: Percent Diploma 2.0% 1 Associate Degree 46.9% 23 BSN
Neonatal Intensive Care RN Needs Assessment 2010 OO9b, 2010 NICU Needs Assessment Survey Results.mht.pdf 1. Identify your highest educational level: Percent Diploma 2.0% 1 Associate Degree 46.9% 23 BSN
Neonatal Seizure. Dr.Nawar Yahya. Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan. Supervised by:
 Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Neonatal Seizure Supervised by: Dr.Nawar Yahya Presented by: Sarah Khalil Zeina Shamil Zainab Waleed Zainab Qahtan Objectives: What is neonatal seizure Etiology Clinical presentation Differential diagnosis
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate. Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics
 Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Hypoglycaemia of the neonate Dr. L.G. Lloyd Dept. Paediatrics Why is glucose important? It provides 60-70% of energy needs Utilization obligatory by red blood cells, brain and kidney as major source of
Apnea in the Newborn
 Apnea in the Newborn Developed by - Lisa Fikac, RNC-NIC, MSN Original Author - Stacey Cashwell, MSN, RN Expiration Date - 1/27/17 This continuing education activity is provided by Cape Fear Valley Health
Apnea in the Newborn Developed by - Lisa Fikac, RNC-NIC, MSN Original Author - Stacey Cashwell, MSN, RN Expiration Date - 1/27/17 This continuing education activity is provided by Cape Fear Valley Health
: Provide cardiovascular preventive counseling to parents and patients with specific cardiac diseases about:
 Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Cardiology Primary Goals for this Rotation 5.13 GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening (Cardiovascular). Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing
List of Chapters. 5. Care of the sick child Evidence-based pediatrics (page 77 to 80)
 Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
Illustrated Textbook of Paediatrics, 4th Edition Tom Lissauer, and Graham Clayden, 2012 List of Chapters 1. The child in society 2. History and examination 3. Normal child development, hearing and vision
CONTENT OUTLINE. Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PEDIATRICS CONTENT OUTLINE Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Subspecialty In-Training, Certification, and Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examinations INTRODUCTION This document was
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PEDIATRICS CONTENT OUTLINE Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Subspecialty In-Training, Certification, and Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examinations INTRODUCTION This document was
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone
 34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone 215-590-3630 www.chop.edu/gastroenterology Please complete this form prior to your child s visit. Please fax to (215) 590-7224 or e-mail it
34th St. and Civic Center Blvd, Philadelphia, PA 19104, phone 215-590-3630 www.chop.edu/gastroenterology Please complete this form prior to your child s visit. Please fax to (215) 590-7224 or e-mail it
Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants
 Brand Name: Surfaxin Generic Name: lucinactant Manufacturer 1 : Discovery Laboratories, Inc. Drug Class 2,3 : Synthetic lung surfactant Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome
Brand Name: Surfaxin Generic Name: lucinactant Manufacturer 1 : Discovery Laboratories, Inc. Drug Class 2,3 : Synthetic lung surfactant Uses 1,2,3 : Labeled: Prevention of respiratory distress syndrome
Hypoglycemia. Objectives. Glucose Metabolism
 Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
Hypoglycemia Instructor: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Outline: Janet Mendis, MSN, RNC-NIC, CNS Summer Morgan, MSN, RNC-NIC, CPNP UC San Diego Health System Objectives State the blood glucose level at
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Hypoxic-İschemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy due to hypoxic-ischemic injury [Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS OF HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY HYPOXIC-ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Hypoxic-İschemic Encephalopathy Encephalopathy due to hypoxic-ischemic injury [Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
Preface. The ACoRN Neonatal Society. ACoRN xiii
 Preface For most health professionals, few events are more challenging or stressful than caring for a sick or preterm baby. It is therefore not surprising that the management and stabilization of these
Preface For most health professionals, few events are more challenging or stressful than caring for a sick or preterm baby. It is therefore not surprising that the management and stabilization of these
Congenital Heart Disease. CCCHD In WI. Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Why Screen? 4/20/2018. Early Detection = Better Outcomes
 Congenital Heart Disease A Positive Screen? What Does it Mean? A Review of Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Elizabeth Goetz MD MPH 8-10/1000 livebirths 3% of all infant mortality
Congenital Heart Disease A Positive Screen? What Does it Mean? A Review of Pulse Oximetry Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Elizabeth Goetz MD MPH 8-10/1000 livebirths 3% of all infant mortality
Course Title: General Pediatrics & Neonatology Pharmacotherapy
 Course Title: General Pediatrics & Neonatology Pharmacotherapy Course Number: PHPR 477 Term(s): Fall, 2016 Prerequistes: None Academic Credit (hours): 3 Category: Elective Instructor: Charles M Karnack,
Course Title: General Pediatrics & Neonatology Pharmacotherapy Course Number: PHPR 477 Term(s): Fall, 2016 Prerequistes: None Academic Credit (hours): 3 Category: Elective Instructor: Charles M Karnack,
8/20/12. Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate.
 Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
Sharon Rush MSN NNP-BC Discuss the importance of thermoregulation in the neonate. To maintain correct body temperature range in order to: Reduce oxygen consumption Reduce calorie expenditure Maximize metabolic
NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST
 NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST 1111 North 3rd Street Instructions: Please complete this checklist to enable us to match your skills and interests with available assignments. Place an "X" in the appropriate column
NICU SKILLS CHECKLIST 1111 North 3rd Street Instructions: Please complete this checklist to enable us to match your skills and interests with available assignments. Place an "X" in the appropriate column
Nutrition in the premie World
 SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
SURVIVAL AND GROWTH NUTRITION ESSENTIALS Nutrition in the premie World DR VISH SUBRAMANIAN MD MRCP (UK) FAAP NEONATAL CRITICAL CARE MERCY CHILDRENS HOSPITAL., SPRINGFIELD MO Prematurity Nutritional Requirements
WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT
 WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT Dr. Patrick Sauer Billings Clinic Pediatrics Objective Increase understanding of prenatal tests Increase understanding of routine newborn procedures Increase knowledge to
WHAT IT MEANS or WHY YOU DO IT Dr. Patrick Sauer Billings Clinic Pediatrics Objective Increase understanding of prenatal tests Increase understanding of routine newborn procedures Increase knowledge to
BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June 30, 2009
 MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
MICHIGAN DEPARTMENT OF COMMUNITY HEALTH Division for Vital Records and Health Statistics MICHIGAN BIRTH DEFECTS SURVEILLANCE REGISTRY BIRTH DEFECTS IN MICHIGAN All Cases Reported and Processed by June
Cedars Sinai Medical Center Pediatric Electives
 PE 235.03 MEDICAL GENETICS COURSE CHAIR: John M. Graham, M.D., ScD.. By arrangement - Please contact the Student Coordinator 1. Counseling techniques and the approach to the patient and family with hereditary
PE 235.03 MEDICAL GENETICS COURSE CHAIR: John M. Graham, M.D., ScD.. By arrangement - Please contact the Student Coordinator 1. Counseling techniques and the approach to the patient and family with hereditary
Neonatal sepsis INCIDENCE RISK FACTORS RISK FACTORS 5/18/2015
 Angelica Floren MD.FAAP. Caring for Little Miracles 6 Th Annual Care Of the Sick Newborn Conference Neonatal sepsis Neonatal sepsis is a disease that may start with minimal or nonspecific symptoms and
Angelica Floren MD.FAAP. Caring for Little Miracles 6 Th Annual Care Of the Sick Newborn Conference Neonatal sepsis Neonatal sepsis is a disease that may start with minimal or nonspecific symptoms and
Disclosures. Objectives. Clinical Case. Risk Factors. Not So Sweet: Evaluation and Management of Infants of Diabetic Mothers
 Not So Sweet: Evaluation and Management of Infants of Diabetic Mothers Disclosures None But. I am a neonatologist NOT an endocrinologist Clinical Advances in Pediatrics September 27, 2017 Jessica Brunkhorst,
Not So Sweet: Evaluation and Management of Infants of Diabetic Mothers Disclosures None But. I am a neonatologist NOT an endocrinologist Clinical Advances in Pediatrics September 27, 2017 Jessica Brunkhorst,
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
A Study of Prevalence and Risk Factors of Polycythemia in Neonatal Nursery in Duhok
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Study of Prevalence and Risk Factors of Polycythemia in Neonatal Nursery in Duhok Akrem Mohammad Mostefa 1 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To find the prevalence of neonatal polycythemia among neonates
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Study of Prevalence and Risk Factors of Polycythemia in Neonatal Nursery in Duhok Akrem Mohammad Mostefa 1 ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To find the prevalence of neonatal polycythemia among neonates
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Allied Health Course Number HCE 240 Title Human Pathophysiology Credits 4 Developed by Dr. Robert Richman
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Human Pathophysiology Course Design 2016-2017 Course Information Division Allied Health Course Number HCE 240 Title Human Pathophysiology Credits 4 Developed by Dr. Robert Richman
SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS
 SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS 1 SUBSTANCE-EXPOSED INFANTS Refers to infants exposed to alcohol and or other substances ingested
SUBSTANCE EXPOSED INFANTS PRESENTED BY ECOLE J. BARROW-BROOKS M.ED & DARLENE D. OWENS MBA, LBSW, CADC, ADS 1 SUBSTANCE-EXPOSED INFANTS Refers to infants exposed to alcohol and or other substances ingested
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
TERMS: Neonatal Period: Birth --> 28 days of life. Term Infant: weeks of gestation
 Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Normal newborn objectives Quickly identify any danger signs Assess the normal adaptations of a newborn after birth Identify conditions requiring special care or follow-up observation. Identify any birth
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate. Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA
 Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Neonatal abstinence syndrome
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on the Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency
 trekk.ca 1 1 Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency Emma Burns, MD, FRCPC IWK Health Centre 2 1 Objectives Critically ill neonate approach and tips Stay on time! Thanks to: Shannon MacPhee, Mike Young, Jon Cherry,
trekk.ca 1 1 Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency Emma Burns, MD, FRCPC IWK Health Centre 2 1 Objectives Critically ill neonate approach and tips Stay on time! Thanks to: Shannon MacPhee, Mike Young, Jon Cherry,
Pediatric Surgery MUHC MCH Siste. Objectives of Training
 Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
Preamble A rotation in Pediatric Surgery must give residents the opportunity to become familiar with the unique needs of infants and children as surgical patients. Some of the surgical diseases encountered
High-Acuity Nursing. Global edition. Global edition. Kathleen Dorman Wagner Melanie G. Hardin-Pierce
 High-Acuity Nursing For these Global Editions, the editorial team at Pearson has collaborated with educators across the world to address a wide range of subjects and requirements, equipping students with
High-Acuity Nursing For these Global Editions, the editorial team at Pearson has collaborated with educators across the world to address a wide range of subjects and requirements, equipping students with
Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Evidence-Based Update: Using Glucose Gel to Treat Neonatal Hypoglycemia http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/
Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes
 Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Francis S. Nuthalapaty, MD Greenville Health System University of South Carolina School of Medicine - Greenville Case History 30 year old black female presents to
Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Francis S. Nuthalapaty, MD Greenville Health System University of South Carolina School of Medicine - Greenville Case History 30 year old black female presents to
Hypotension in the Neonate
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Hypotension in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/ Neonatal
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Hypotension in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcare-professionals/education/continuing-medicalnursing-education/neonatal-nursing-education-briefs/ Neonatal
 NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 413 Active treatment, survival rate and, 294 296 Air displacement plethysmography, 397 Airway obstruction, 309 310 Aluminum
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 413 Active treatment, survival rate and, 294 296 Air displacement plethysmography, 397 Airway obstruction, 309 310 Aluminum
Clerkship Learning Activity Objectives
 Clerkship Learning Activity Objectives Inpatient Rotation 1. Conduct a pediatric history and physical examination appropriate to the nature of the visit (initial vs follow up) or complaint (complete vs
Clerkship Learning Activity Objectives Inpatient Rotation 1. Conduct a pediatric history and physical examination appropriate to the nature of the visit (initial vs follow up) or complaint (complete vs
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
Home Pulse Oximetry for Infants and Children
 Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.12aC2v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.12aC2v2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
General Principles: 5% 7%
 General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
General Principles: 5% 7% International Foundations of Medicine Clinical Science Exam Blueprint Infancy and Childhood (normal growth and development) Adolescence (sexuality, separation from parents/autonomy,
