Preface. The ACoRN Neonatal Society. ACoRN xiii
|
|
|
- Ira Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preface For most health professionals, few events are more challenging or stressful than caring for a sick or preterm baby. It is therefore not surprising that the management and stabilization of these babies is repeatedly identified as a priority for new educational programs. The Acute Care of at-risk Newborns () program was developed in response to this need. It is designed for any practitioner who may be called upon to care for at-risk babies and their families, regardless of experience or training in neonatal emergencies. provides a systematic approach to the identification and management of babies requiring stabilization. It serves as the foundation for an educational program that aims to teach the concepts and basic skills of neonatal stabilization and where necessary, preparation for transport to a referral facility. The process applies to babies who need assistance in the transition from fetal life, and babies who become unwell or are at risk of becoming unwell in the first few hours or days after birth. Through the creative efforts of individuals with diverse educational backgrounds and clinical practices, an innovative textbook has evolved that is designed to help the practitioner gather and organize information, establish priorities, and initiate interventions aimed at delivering a level of care that results in the best possible outcome. combines evidence- and consensus-based guidelines and acknowledges the clinical wisdom of those who have taught this material to health care professionals for many years. As new practices evolve, there will undoubtedly be changes and improvements in newborn care. We invite your comments and encourage constructive feedback for incorporation into future editions. The Neonatal Society xiii
2 Overview What is? The Acute Care of at-risk Newborns () is a priority-based, clinically oriented framework that sequentially integrates assessment, monitoring, diagnostic evaluation, intervention, and on-going management for at-risk and unwell newborns. is also appropriate for further stabilization of babies who have been resuscitated at birth. As the baby s condition changes and more information is collected during the process of stabilization, all components of the framework are systematically revisited. What are the objectives of the program? The objectives of the program are to: 1. Identify the at-risk or unwell baby who will benefit from the process. 2. Determine whether the baby needs to be resuscitated immediately. 3. Conduct a systematic evaluation of the baby. 4. Develop working diagnoses and institute specific treatments for acute neonatal conditions. 5. Describe the types of support that may be required by the baby, the family, and the health care team. 6. Identify resources available for newborn care in local and referral facilities. 7. Identify and prepare babies who require transport to a referral facility. What is the textbook? The textbook illustrates the process and adds knowledge sequentially, chapter by chapter, and case by case. In order to derive the greatest benefit, the textbook should be read from start to finish, within the context of the professional roles, responsibilities and level of training of the learner. How are the chapters designed? Each chapter is designed to illustrate the process around one area of interest. All chapters contain: Learning Objectives, Key Concepts and a list of Skills required for the chapter Introduction The Sequence specific to the area of interest being covered Core content specific to the Sequence Illustrative case studies to advance the reader, step by step, through the Process and to provide additional content Questions to reinforce previously presented content, or to introduce new knowledge Bibliography xv
3 Overview This symbol appears at various places throughout the text to introduce a particular skill that may require review. The symbol directs you to the Skills section in the Appendix where practical and technical information about that skill is provided. AAP/AHA In this textbook, the NRP logo indicates resuscitation skills 1 that are taught by the AAP/AHA Neonatal Resuscitation Program. These skills are included with an perspective for the purpose of providing a review for professionals with current training in NRP. Review or completion of this Appendix does not constitute an NRP activity. What is in the Appendices? The Appendices of the textbook contains the following additional information: Neonatal Assessment Tool: A sample assessment tool is provided for easy reference and documentation of clinical findings. Neonatal Resuscitation Skills Procedures Interpretation of Investigations Medications. What is the workshop? The workshop is an interactive session that utilizes case-based learning and practice stations to apply the concepts and skills presented in the textbook. Learners are encouraged to participate in an workshop in addition to reading this textbook. The workshops should be designed to best meet the specific needs of the learners by the prior identification of the content and specific skills that will need to be emphasized and reviewed. Administration of a prior-learning assessment tool and identification of institutional objectives assist the Education Team to tailor the design of each workshop. Like neonatal resuscitation, stabilization is most effective when performed by a coordinated team. Teamwork and an interdisciplinary approach are emphasized along with sharing of clinical scenarios. Are there pre-requisites to participate in an workshop? assumes familiarity with the American Academy of Pediatrics/American Heart Association s Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) at the provider level. 1 All NRP diagrams reproduced in have been kindly provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) / American Heart Association (AHA). xvi
4 A brief review of core knowledge and skills in neonatal resuscitation is integrated into the textbook and workshop. In preparation for an workshop, participants are asked to read the complete textbook, or the sections pertaining to the workshop being offered. This preparation should always include a thorough understanding of Chapter 1, and a review of the eight Sequences as they apply to the professional roles, responsibilities and level of training of the learners. The objective of the education program is not to memorize the textbook but to understand the process, its application in the clinical setting, and to learn how to use the textbook as a resource. The Skills section of the Appendices contain information on equipment, procedures and medications. These should be reviewed as applicable to the workshop being offered and the roles and responsibilities of the learners. Overview Does workshop completion imply clinical competence? Participation in an workshop does not imply the participant has achieved clinical competence. The responsibility to determine the readiness of an individual for their clinical responsibilities belongs to the institution and professional organization with which the learner is associated. An workshop is a learning experience. At the conclusion of a workshop, participants are asked to complete a case-based evaluation of key concepts (for example, how to apply the Primary Survey). The evaluation may also include demonstration of knowledge and skills using simulations or models. Do I get CME credit for completing an program? workshops can be designed to comply with the requirements set by professional organizations to provide their members with educational credits. Regional networks and/or professional organizations are encouraged to apply for continuing professional education credits for participants in an workshop. xvii
5 Standard Precautions Health care providers are advised to use standard precautions against disease transmission. These precautions are used for contact with blood; all body fluids, secretions, and excretions except sweat (regardless of whether these fluids, secretions, or excretions contain visible blood); non-intact skin; and mucous membranes. Barrier techniques are designed to decrease exposure of health care personnel to body fluids containing human immunodeficiency virus or other blood-borne pathogens. Precautions are used at all times because medical history and examination cannot reliably identify all patients infected with these agents. Standard precautions decrease transmission of microorganisms from patients who are not recognized as harbouring potential pathogens, such as antimicrobialresistant bacteria. Standard precautions include the following techniques: hand hygiene gloves masks, eye protection, and face shields non-sterile gowns proper handling of patient care equipment, used linen, mouthpieces, resuscitation bags, and other ventilation devices proper cleaning and disposition of needles, scalpels, and other sharp instruments and devices. i i From: American Academy of Pediatrics. Infection control for hospitalized children. In: American Academy of Pediatrics et al, eds. Red Book: 2009 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases. 28 th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics; xviii
6 Preface Overview What is? What are the objectives of the Program? What is the Textbook? What is the Workshop? xiii xv xv xv xvi Chapter 1 The Process Objectives 1-1 Key Concepts 1-2 The Framework 1-3 The Process 1-5 Illustrative Case Study 1-12 Summary 1-14 Sequences Resuscitation 1-15 Respiratory 1-16 Cardiovascular 1-17 Neurology 1-18 Surgical Conditions 1-19 Fluid & Glucose Management 1-20 Thermoregulation 1-21 Infection 1-22 Chapter 2 Resuscitation Objectives 2-1 Key Concepts and Skills 2-2 Introduction 2-3 Resuscitation Signs Ineffective breathing 2-3 Heart rate < 100 bpm 2-3 Central cyanosis 2-4 The Resuscitation Sequence 2-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, and Next Steps 2-4 Case 1 Apnea during feeding 2-10 Case 2 Apneic episodes in a preterm baby 2-13 Answers to Questions 2-16 Bibliography 2-16 Chapter 3 Respiratory Objectives 3-1 Key Concepts and Skills 3-2 Introduction 3-3 vii
7 Labored respiration 3-6 Respiratory rate > 60/min 3-6 Receiving respiratory support 3-6 The Respiratory Sequence 3-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 3-6 The Respiratory Score 3-7 Transient tachypnea of the newborn 3-11 Respiratory distress syndrome 3-13 Meconium aspiration syndrome 3-16 Pneumothorax 3-17 Pneumonia 3-21 Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn 3-22 Lung hypoplasia 3-23 Case 1 Mild respiratory distress in a term newborn 3-25 Case 2 Respiratory distress in a preterm newborn, initiating CPAP 3-35 Case 3 Respiratory distress in a preterm newborn, initiating mechanical ventilation 3-44 Case 4 Sudden deterioration in a ventilated baby 3-53 Case 5 Meconium aspiration 3-62 Answers to Questions 3-71 Bibliography 3-73 Chapter 4 Cardiovascular Objectives 4-1 Key Concepts and Skills 4-2 Introduction 4-3 Pale, mottled or grey 4-3 Weak pulses or low blood pressure 4-3 Cyanosis unresponsive to oxygen therapy 4-4 Heart rate > 220 bpm 4-4 The Cardiovascular Sequence 4-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 4-6 Case 1 The baby presenting with shock 4-16 Case 2 Baby with persistent cyanosis 4-26 Case 3 Baby with supraventricular tachycardia 4-37 Answers to Questions 4-48 Bibliography 4-49 Chapter 5 Neurology Objectives 5-1 Key Concepts and Skills 5-2 Introduction 5-3 Abnormal tone 5-3 Jitteriness 5-3 Seizures 5-4 The Neurology Sequence 5-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 5-4 Case 1 The floppy baby 5-11 Case 2 A 6-hour old baby with seizures 5-21 Case 3 Baby born to a substance-using mother 5-32 Answers to Questions 5-39 viii
8 Bibliography 5-41 Chapter 6 Surgical Conditions Objectives 6-1 Key Concepts and Skills 6-2 Introduction 6-3 Anterior abdominal wall defect 6-3 Vomiting or inability to swallow 6-3 Abdominal distension 6-4 Delayed passage of meconium or imperforate anus 6-4 The Surgical Conditions Sequence 6-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 6-6 Case 1 Abdominal wall defect 6-12 Case 2 Inability to pass a nasogastric tube 6-18 Bibliography 6-23 Chapter 7 Fluid & Glucose Management Objectives 7-1 Key Concepts and Skills 7-2 Introduction 7-3 Blood glucose < 2.6 mmol/l 7-6 At risk for hypoglycemia 7-6 Not feeding or should not be fed 7-8 The Fluid & Glucose Management Sequence 7-7 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 7-8 Case 1 Infant of a diabetic mother 7-16 Case 2 Symptomatic hypoglycemia 7-24 Answers to Questions 7-30 Bibliography 7-31 Chapter 8 Thermoregulation Objectives 8-1 Key Concepts 8-2 Introduction 8-3 Axillary temperature < 36.3ºC or > 37.2ºC 8-3 Increased risk for temperature instability 8-3 The Thermoregulation Sequence 8-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 8-6 Case 1 The cold, outborn baby 8-11 Case 2 A baby with hyperthermia 8-19 Answers to Questions 8-24 Bibliography 8-24 Chapter 9 Infection Objectives 9-1 Key Concepts and Skills 9-2 Introduction 9-3 Risk factors for infection 9-3 ix
9 alerting signs with an asterisk (*) 9-3 Clinical deterioration 9-4 The Infection Sequence 9-5 Core Steps, Organization of Care, Response, Next Steps, and Specific Management 9-4 Case 1 Baby with respiratory distress and prolonged rupture of membranes 9-10 Answers to Questions 9-19 Bibliography 9-20 Chapter 10 Transport Objectives 10-1 Key Concepts 10-2 Introduction 10-3 The Transport Process 10-4 Sample Neonatal Pre-transport Information Sheet 10-5 Responsibilities of: The sending facility 10-6 The transport clinical coordinator 10-7 The receiving physician 10-8 The transport team 10-8 Shared responsibilities 10-9 Communicating with the family 10-9 Bibliography Chapter 11 Support Objectives 11-1 Key Concepts 11-2 Introduction 11-3 Supporting the Baby 11-4 Stability and stress responses 11-4 Developmentally supportive care 11-6 Illustrative Case Study 11-7 Assessment and management of pain 11-8 Supporting the Family Supporting the Health Care Team Palliative Care Answers to Questions Bibliography Appendix A Neonatal assessment Sample neonatal assessment tool A-3 Appendix B Review of Neonatal Resuscitation Skills Free-flow oxygen administration during resuscitation B-3 Manual ventilation B-4 Endotracheal intubation B-6 Exhaled CO 2 detectors for endotracheal tube placement B-9 Laryngeal mask airway B-11 Chest compressions B-13 Emergency vascular access: Umbilical vein catheterization B-14 Emergency vascular access: Intraosseous vascular access B-16 Epinephrine B-19 x
10 Volume expander B-20 Sodium bicarbonate B-21 Appendix C Procedures Blood pressure measurement C-3 Blood sampling, capillary C-5 Bowel bag application C-7 Cardiorespiratory monitoring C-9 Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) C-11 Mechanical ventilation C-13 Pneumothorax, chest transillumination C-17 Pneumothorax, chest tube insertion C-18 Pneumothorax, needle aspiration C-22 Pulse oximetry C-24 Appendix D Investigations (interpretation) Blood gases D-3 Complete blood count (CBC) and differential count D-5 Chest radiographs D-7 Appendix E Medications Ampicillin E-3 Cefotaxime E-4 Cloxacillin E-5 Dopamine E-7 Fentanyl E-9 Gentamicin E-10 Morphine E-12 Penicillin G E-14 Phenobarbital E-15 Phenytoin E-16 Premedication for intubation E-18 Prostaglandin E 1 (PGE 1 ) E-19 Surfactant E-21 Vancomycin E-24 Appendix F Initiating Therapeutic Hypothermia for Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy Initiating Therapeutic Hypothermia or Therapeutic Normothermia F-3 Using Cool Gel Pack for the Initiation of Therapeutic Hypothermia F-7 Index I-1 Sequences The Framework 1-4 The Process 1-5 The Primary Survey 1-7 The Problem List 1-9 The Sequence design 1-10 The Resuscitation Sequence 1-15 The Respiratory Sequence 1-16 The Cardiovascular Sequence 1-17 xi
11 The Neurology Sequence 1-18 The Surgical Conditions Sequence 1-19 The Fluid & Glucose Management Sequence 1-20 The Thermoregulation Sequence 1-21 The Infection Sequence 1-22 Tables Target preductal pulse oximetry values after birth 2-7 The Respiratory Score 3-7 Clinical assessment of circulation 4-8 Tolerance to different levels of SpO Key features of sinus tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia and atrial flutter 4-45 Jitteriness vs seizures 5-4 Clinical assessment of neurological dysfunction 5-9 Baseline fluid intake (oral and intravenous) for the first few days of life 7-4 Suggested steps for increasing glucose intake for the treatment of hypoglycemia 7-15 The amount of glucose provided by milk and intravenous dextrose 7-22 Initial incubator temperature settings in the first 12 hours of life 8-9 Strategies for preventing heat loss 8-14 Common organisms causing neonatal sepsis (early and late onset) 9-16 Choosing initial antibiotics 9-17 Stability cues and stress cues 11-5 Morphine and fentanyl 11-9 Endotracheal tube size B-7 Sample Forms Contact Form for Newborn Resuscitation and Stabilization 2-11 Seizure log 5-31 Neonatal abstinence score 5-36 Neonatal Pre-Transport Information Sheet 10-5 Template for case review Neonatal Assessment Tool A-3 Radiographs Transient tachypnea of the newborn 3-12 Respiratory distress syndrome 3-13 Meconium aspiration syndrome 3-16 Pneumothorax 3-17 Pneumomediastinum 3-20 Pneumonia 3-21 Congenital diaphragmatic hernia 3-23 Normal chest radiograph 4-13 Transposition of the great arteries 4-13 Patent ductus arteriosus 4-14 Duodenal atresia 6-9 Ileal atresia 6-10 Esophageal atresia/tracheo-esophageal fistula 6-21 Correct/incorrect endotracheal tube placement B-9 Umbilical venous catheter in portal system (incorrect placement) B-16 Chest radiograph interpretation D-9 xii
Infection. Risk factor for infection ACoRN alerting sign with * Clinical deterioration. Problem List. Respiratory. Cardiovascular
 The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
The ACoRN Process Baby at risk Unwell Risk factors Post-resuscitation requiring stabilization Resuscitation Ineffective breathing Heart rate < 100 bpm Central cyanosis Support Infection Risk factor for
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context
 Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials
 Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery
 Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
 NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NLSP) CERTIFICATION EXAMINATION 1. To determine if an infant requires resuscitation, you must rapidly assess gestation period, presence of meconium in amniotic fluid, breaths
NRP Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors
 NRP 2011 Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors What is the same? 1. Minimum course requirement is Lessons 1 through 4 and Lesson 9. The NRP Provider Card requires renewal every 2 years. Your facility
NRP 2011 Raising the Bar for Providers and Instructors What is the same? 1. Minimum course requirement is Lessons 1 through 4 and Lesson 9. The NRP Provider Card requires renewal every 2 years. Your facility
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia Main cause of perinatal and neonatal
PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني
 Lecture 6 PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) 2010 MCQ? In neonatal resuscitation program, the preterm neonates need special preparations
Lecture 6 PROFESSOR DR. NUMAN NAFIE HAMEED الاستاذ الدكتور نعمان نافع الحمداني Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) 2010 MCQ? In neonatal resuscitation program, the preterm neonates need special preparations
MODULE VII. Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care
 MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
MODULE VII Delivery and Immediate Neonatal Care NEONATAL ASPHYXIA About one million deaths per year In Latin America 12% of newborns suffer some degree of asphyxia A major cause of perinatal and neonatal
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport. Relevant Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
Stabilization of the Newborn for Transport Arlen Foulks, DO FAAP FACOP Medical Director, CCMH Level II NICU Medical Director, NeoFlight Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Neonatal Perinatal Medicine Section,
ACoRN First Edition Update. What s new in this third printing? ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN.
 ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia www.acornprogram.net ACoRN First Edition 2010 Update What s new in this third printing? What What
ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia www.acornprogram.net ACoRN First Edition 2010 Update What s new in this third printing? What What
ACoRN Workbook 2012 Update
 ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN www.acornprogram.net A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia ACoRN Workbook 2012 Update Name: The ACoRN Process The Resuscitation Sequence
ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN www.acornprogram.net A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia ACoRN Workbook 2012 Update Name: The ACoRN Process The Resuscitation Sequence
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update What s New for 2010? 3 CPR. 4 4 Steps of BLS Survey 5 CPR 6 CPR.
 1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
1 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Science Update 2010 2 What s New for 2010? 3 CPR Take no longer than seconds for pulse check Rate at least on per minute (instead of around 100 per minute ) Depth change:
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal resuscitation guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005
 Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO 2 table Warm
 NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
NRP Skills Stations Performance Skills Station OR Integrated Skills Station STATION: Assisting with and insertion of endotracheal tube (ETT) Equipment: NRP algorithm, MRSOPA table, medication chart, SpO
HeartCode PALS. PALS Actions Overview > Legend. Contents
 HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
HeartCode PALS PALS Actions Overview > Legend Action buttons (round buttons) Clicking a round button initiates an action. Clicking this button, for example, checks the child s carotid pulse. Menu buttons
The Blue Baby. Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin
 The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
The Blue Baby Network Stabilisation of the Term Infant Study Day 15 th March 2017 Joanna Behrsin Session Structure Definitions and assessment of cyanosis Causes of blue baby Structured approach to assessing
Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease This guideline has been agreed by both NTS & CATS Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease This guideline has been agreed by both NTS & CATS Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position
Surfactant Administration
 Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
MASTER SYLLABUS
 A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
A. Academic Division: Health Sciences B. Discipline: Respiratory Care MASTER SYLLABUS 2018-2019 C. Course Number and Title: RESP 2330 Advanced Life Support Procedures D. Course Coordinator: Tricia Winters,
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara
 Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Guslihan Dasa Tjipta Division of Perinatology Department of Child Health Medical School University of Sumatera Utara 1 Definition Perinatal asphyxia is a fetus/newborn, due to: is an insult to the Lack
Experience. Initials Medical Staffing Network Rev. 06/15 F01201 NNICU 2 of 5
 Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Self Assessment Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline.
 Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
Pediatric Learning Solutions course alignment with the Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline. The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the
TRAINING NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS
 TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
TRAINING ON NEONATOLOGY SILVANA PARIS RESUSCITATION IN DELIVERY ROOM INTRODUCTION THE GLOBAL RESUSCITATION BURDEN IN NEWBORN 136 MILL NEWBORN BABIES EACH YEAR (WHO WORLD REPORT) 5-8 MILL NEWBORN INFANTS
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care
 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Resuscitation 2 When To Resuscitate Need usually related Combination of Can occur in 3 Causes of Fetal Asphyxia 1 4 Apnea Hypoxia Stimulates chemoreceptors & baroreceptors
Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Resuscitation 2 When To Resuscitate Need usually related Combination of Can occur in 3 Causes of Fetal Asphyxia 1 4 Apnea Hypoxia Stimulates chemoreceptors & baroreceptors
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals
 Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Pediatric Learning Solutions A clinical education program exclusively for pediatric professionals The following Pediatric Learning Solutions courses align to focus areas of the Neonatal CCRN Exam Content
Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position CC Transport Services Document Owner E. Polke
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Duct Dependant Congenital Heart Disease Document Control Information Author CATS/NTS Author Position CC Transport Services Document Owner E. Polke
2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol Medical Newborn/Neonatal. Protocol 8-3 Resuscitation 4. Medical Supraventricular
 PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
PEDIATRIC CARDIAC SECTION: Pediatric Cardiovascular Emergencies REVISED: 06/2017 Section 8 1. Cardiac Arrest Unknown Rhythm (i.e. Protocol 8-1 BLS) 2. General Cardiac Arrest Protocol 8-2 3. Medical Newborn/Neonatal
Resuscitation efforts for Mom & Baby
 Resuscitation efforts for Mom & Baby Beth Ann Clayton, CRNA, MS AmSol Obstetric Anesthesia CRNA Educator Obstetric Anesthesia Clinical Coordinator Mercy Health-Fairfield Hospital Assistant Professor, University
Resuscitation efforts for Mom & Baby Beth Ann Clayton, CRNA, MS AmSol Obstetric Anesthesia CRNA Educator Obstetric Anesthesia Clinical Coordinator Mercy Health-Fairfield Hospital Assistant Professor, University
ENDOTRACHEAL INTUBATION POLICY
 POLICY Indications: Ineffective ventilation with mask and t-piece, or mask and bag technique Inability to maintain a patent airway Need or anticipation of need for prolonged ventilation Need for endotracheal
POLICY Indications: Ineffective ventilation with mask and t-piece, or mask and bag technique Inability to maintain a patent airway Need or anticipation of need for prolonged ventilation Need for endotracheal
Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in Please DO NOT mail or fax this form to the CPQCC Data Center. This form is for internal use ONLY.
 Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Selection Criteria Admission/Discharge Form for Infants Born in 2016 To be eligible, you MUST answer YES to at least one of the possible criteria (A-C) A. 401 1500 grams o Yes B. GA range 22 0/7 31 6/7
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case. VF/Asystole
 Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Prehospital Resuscitation for the 21 st Century Simulation Case VF/Asystole Case History 1 (hypovolemic cardiac arrest secondary to massive upper GI bleed) 56 year-old male patient who fainted in the presence
Credential Maintenance Program
 First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 3 7 0 A. Assess Patient Information 0 2 2. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing
First Quarter of the Calendar 5 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 3 7 0 A. Assess Patient Information 0 2 2. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing
Objectives. Birth Depression Management. Birth Depression Terms
 Objectives Birth Depression Management Regional Perinatal Outreach Program 2016 Understand the terms and the clinical characteristics of birth depression. Be familiar with the evidence behind therapeutic
Objectives Birth Depression Management Regional Perinatal Outreach Program 2016 Understand the terms and the clinical characteristics of birth depression. Be familiar with the evidence behind therapeutic
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat
 Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
Product Catalog. Pediatric Learning Solutions. Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association.
 Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Product Catalog Pediatric Learning Solutions Listing of all current products (as of May, 2013) offered by Children's Hospital Association. Acquired Heart Disease in Children WBT Acute Respiratory Distress
Pediatric Assessment Triangle
 Pediatric Assessment Triangle Katherine Remick, MD, FAAP Associate Medical Director Austin Travis County EMS Pediatric Emergency Medicine Dell Children s Medical Center Objectives 1. Discuss why the Pediatric
Pediatric Assessment Triangle Katherine Remick, MD, FAAP Associate Medical Director Austin Travis County EMS Pediatric Emergency Medicine Dell Children s Medical Center Objectives 1. Discuss why the Pediatric
5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide. 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia. Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year
 1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes
 NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
NEONATOLOGY Healthy newborn. Neonatal sequelaes Ágnes Harmath M.D. Ph.D. senior lecturer 11. November 2016. Tasks of the neonatologist Prenatal diagnosed condition Inform parents, preparation of necessary
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR
 CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR THE BUNNELL LIFE PULSE HIGH-FREQUENCY JET VENTILATOR 801-467-0800 Phone 800-800-HFJV (4358) Hotline TABLE OF CONTENTS Respiratory Care Considerations..3 Physician Considerations
Summary of Changes: References/content updated to reflect most current standards of practice.
 Alaska Native Medical Center: Mother Baby Unit Guideline: Neonatal Hypoglycemia Subject: Neonatal Hypoglycemia REVISION DATE: Jan 2015,12/2011, 02/2009, 11, 2007, 07/2007,04/2001, 04/1999 REPLACES: NSY:
Alaska Native Medical Center: Mother Baby Unit Guideline: Neonatal Hypoglycemia Subject: Neonatal Hypoglycemia REVISION DATE: Jan 2015,12/2011, 02/2009, 11, 2007, 07/2007,04/2001, 04/1999 REPLACES: NSY:
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress
 Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
Neonatal/Pediatric Specialty Examination Detailed Content Outline
 I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 10 32 17 59 A. Assess Patient Information 1 5 7 13 1. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing conditions 2. Physical
I. COMPETENCIES SHARED BETWEEN CRITICAL AND GENERAL CARE 10 32 17 59 A. Assess Patient Information 1 5 7 13 1. Patient history, for example, immunizations environmental pre-existing conditions 2. Physical
Pediatric Shock. Hypovolemia. Sepsis. Most common cause of pediatric shock Small blood volumes (80cc/kg)
 Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
Critical Concepts: Shock Inadequate peripheral perfusion where oxygen delivery does not meet metabolic demand Adult vs Pediatric Shock - Same causes/different frequencies Pediatric Shock Hypovolemia Most
NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY
 Background NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY A perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic insult may present with varying degrees of neonatal encephalopathy, neurological disorder and
Background NEONATAL HYPOXIC-ISCHAEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY (HIE) & COOLING THERAPY A perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic insult may present with varying degrees of neonatal encephalopathy, neurological disorder and
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES
 PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2)
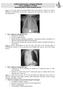 Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2) - Case 1: a 32 weeks preterm developed RDS 4 hours after delivery. Chest X-ray shows:
Arabian Gulf University Kingdom of Bahrain Year 5 Pediatrics 3 rd Week Discussion with Dr. Muna Al-Jufairi (Part 2) - Case 1: a 32 weeks preterm developed RDS 4 hours after delivery. Chest X-ray shows:
Chain of Survival. Highlights of 2010 American Heart Guidelines CPR
 Highlights of 2010 American Heart Guidelines CPR Compressions rate of at least 100/min. allow for complete chest recoil Adult CPR depth of at least 2 inches Child/Infant CPR depth of 1/3 anterior/posterior
Highlights of 2010 American Heart Guidelines CPR Compressions rate of at least 100/min. allow for complete chest recoil Adult CPR depth of at least 2 inches Child/Infant CPR depth of 1/3 anterior/posterior
It is important to point out and frequently remind learners that they are expected to complete ALL aspects of a normal assessment.
 Background The purpose of this document is to provide guidelines for faculty on various aspects of patient simulators to be emphasized to learners during orientation. We recommend that every learner be
Background The purpose of this document is to provide guidelines for faculty on various aspects of patient simulators to be emphasized to learners during orientation. We recommend that every learner be
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview 2006 Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P General Our Database is lacking in pediatrics Pediatrics are DIFFERENT than Adults not just smaller The same procedure may require
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Overview 2006 Judy Haluka BS, RCIS, EMT-P General Our Database is lacking in pediatrics Pediatrics are DIFFERENT than Adults not just smaller The same procedure may require
What is symptomatic? Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Hypoglycemia and MRI. Conflicts. What s the problem? Hypoglycemia and MRI
 Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Kristi Watterberg, MD Professor of Pediatrics, UNM What is symptomatic? Jitteriness Cyanosis Poor feeding Weak, high-pitched cry Seizures Apnea Lethargy, low
Neonatal hypoglycemia: how low can you go? Kristi Watterberg, MD Professor of Pediatrics, UNM What is symptomatic? Jitteriness Cyanosis Poor feeding Weak, high-pitched cry Seizures Apnea Lethargy, low
Lectures 4 Early fetal assessment, screening, ultrasound and treatment modalities during pregnancy. II. Asphyxia and Resuscitation (3 lectures)...
 Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Outline of a 2 year Neonatology educational course (80 lectures) PLUS 2 graduate level courses (GENETICS and BIOSTATISTICS & EPIDEMIOLOGY Approximate Percent in Examination I. Maternal-Fetal Medicine (6
Neonatal Resuscitation. Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology
 Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
Neonatal Resuscitation Dustin Coyle, M.D. Anesthesiology Recognize complications Maternal-fetal factors Maternal DM PIH Chronic HTN Previous stillbirth Rh sensitization Infection Substance abuse/certain
1st Annual Clinical Simulation Conference
 1st Annual Clinical Simulation Conference Newborns with Acute Respiratory Distress: Diagnosis and Management Ma Teresa C. Ambat, MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics
1st Annual Clinical Simulation Conference Newborns with Acute Respiratory Distress: Diagnosis and Management Ma Teresa C. Ambat, MD Assistant Professor Division of Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls
 McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls November 2, 2016 Image from: www.prweb.com Procedures www.laerdal.com www.gaumard.com www.rch.org.au www.laerdal.com ekja.org NRP Epinephrine: 0.1ml/kg
McMaster Neonatal Skills Workshop Procedure Pearls November 2, 2016 Image from: www.prweb.com Procedures www.laerdal.com www.gaumard.com www.rch.org.au www.laerdal.com ekja.org NRP Epinephrine: 0.1ml/kg
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC
 SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
SUMMARY OF MAJOR CHANGES 2010 AHA GUIDELINES FOR CPR & ECC The following is a summary of the key issues and changes in the AHA 2010 Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) and Emergency Cardiac
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Training. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Training The training module will follow the national standard curriculum as it relates to the application and use of CPAP. The proposed curriculum will closely resemble the following algorithm utilizing
Training The training module will follow the national standard curriculum as it relates to the application and use of CPAP. The proposed curriculum will closely resemble the following algorithm utilizing
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE Management, Monitoring & Documentation of a Clinically Significant Cardiopulmonary Event (CSCPE) (NUR47) DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 9/09 9/17 1 of 6 PS1094
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL TITLE: NURSING PROCEDURE Management, Monitoring & Documentation of a Clinically Significant Cardiopulmonary Event (CSCPE) (NUR47) DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 9/09 9/17 1 of 6 PS1094
ACoRN Workbook 2010 Update
 ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia www.acornprogram.net ACoRN Workbook 2010 Update Name: ACoRN Acute Care of at-risk Newborns The ACoRN
ACoRN Neonatal Society Société néonatale ACoRN A Canadian non-profit Society Vancouver, British Columbia www.acornprogram.net ACoRN Workbook 2010 Update Name: ACoRN Acute Care of at-risk Newborns The ACoRN
MICHIGAN. State Protocols. Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.
 MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
MICHIGAN State Protocols Protocol Number Protocol Name Pediatric Cardiac Table of Contents 6.1 General Pediatric Cardiac Arrest 6.2 Bradycardia 6.3 Tachycardia PEDIATRIC CARDIAC PEDIATRIC CARDIAC ARREST
Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease. Frequently Asked Questions
 Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease Frequently Asked Questions Current Recommendation: The current recommendation from the Canadian Cardiovascular
Pulse Oximetry Screening in Newborns to Enhance the Detection Of Critical Congenital Heart Disease Frequently Asked Questions Current Recommendation: The current recommendation from the Canadian Cardiovascular
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010
 PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010 DR WALEED ALAMRI PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CONSULTANT FEB 24, 2011 Pediatric Basic Life Support Change in CPR Sequence (C-A-B Rather Than A-B-C) 2010 (New): Initiate CPR for infants
PALS NEW GUIDELINES 2010 DR WALEED ALAMRI PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY CONSULTANT FEB 24, 2011 Pediatric Basic Life Support Change in CPR Sequence (C-A-B Rather Than A-B-C) 2010 (New): Initiate CPR for infants
PRACTICE GUIDELINES WOMEN S HEALTH PROGRAM
 C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
C Title: NEWBORN: HYPOGLYCEMIA IN NEONATES BORN AT 35+0 WEEKS GESTATION AND GREATER: DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT IN THE FIRST 72 HOURS Authorization Section Head, Neonatology, Program Director, Women s Health
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia
 1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
1.40 Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Purpose Audience Policy Statement: The guideline is designed to reduce the incidence of pneumonia and other acute lower respiratory tract infections. All UTMB healthcare
Delivery Room Resuscitation of Newborns with Congenital Anomalies
 Delivery Room Resuscitation of Newborns with Congenital Anomalies Anne Ades, MD, MSEd Director of Neonatal Education The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Associate Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Perelman
Delivery Room Resuscitation of Newborns with Congenital Anomalies Anne Ades, MD, MSEd Director of Neonatal Education The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Associate Professor of Clinical Pediatrics Perelman
Pediatrics. Blue Baby Syndrome (Cyanotic Newborn) and Hyperoxia Test. Definition. See online here
 Pediatrics Blue Baby Syndrome (Cyanotic Newborn) and Hyperoxia Test See online here Blue babies lack sufficient hemoglobin, resulting in the bluish discoloration of tissues, a term referred to as cyanosis.
Pediatrics Blue Baby Syndrome (Cyanotic Newborn) and Hyperoxia Test See online here Blue babies lack sufficient hemoglobin, resulting in the bluish discoloration of tissues, a term referred to as cyanosis.
Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency
 trekk.ca 1 1 Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency Emma Burns, MD, FRCPC IWK Health Centre 2 1 Objectives Critically ill neonate approach and tips Stay on time! Thanks to: Shannon MacPhee, Mike Young, Jon Cherry,
trekk.ca 1 1 Oh SCH It s a neonatal emergency Emma Burns, MD, FRCPC IWK Health Centre 2 1 Objectives Critically ill neonate approach and tips Stay on time! Thanks to: Shannon MacPhee, Mike Young, Jon Cherry,
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses
 Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
Competency Log Professional Responder Courses Check off each competency once successfully demonstrated. This log may be used as a support tool when teaching a Professional Responder course. Refer to the
CH 721 Hospital Care FINAL EXAMINATION. Semester 1, 2017
 SOLOMON ISLANDS NATIONAL UNIVERSITY School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Bachelor of Nursing: Child Health CH 721 Hospital Care FINAL EXAMINATION Semester 1, 2017 (End of semester 2 for BNCH Intake
SOLOMON ISLANDS NATIONAL UNIVERSITY School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences Bachelor of Nursing: Child Health CH 721 Hospital Care FINAL EXAMINATION Semester 1, 2017 (End of semester 2 for BNCH Intake
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Skills Checklist
 _ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
_ XXX-XX- Print Name Last 4 of SS # Date Completed Directions Please circle a value for each question to provide us and the interested facilities with an assessment of your clinical experience. These values
REMS Council Quality Improvement Committee Incident Disposition Summary FY2015 Quarter 3 (January March, 2015)
 Incident Disposition Summary FY205 Quarter 3 (January March, 205). Total number of reports filed (as reported) i : 6,488 2. Total number of reports reviewed (as reported): 3,82 3. Level of Care ii : a.
Incident Disposition Summary FY205 Quarter 3 (January March, 205). Total number of reports filed (as reported) i : 6,488 2. Total number of reports reviewed (as reported): 3,82 3. Level of Care ii : a.
Blue Babies, Twitchy Toddlers, and Kool Kids. By Beth Paton, MSN, RN, PNP, CEN, CPEN, FAEN
 Blue Babies, Twitchy Toddlers, and Kool Kids By Beth Paton, MSN, RN, PNP, CEN, CPEN, FAEN I have no disclosures OBJECTIVES By the end of this presentation, the learner will Discuss etiologies of cyanosis
Blue Babies, Twitchy Toddlers, and Kool Kids By Beth Paton, MSN, RN, PNP, CEN, CPEN, FAEN I have no disclosures OBJECTIVES By the end of this presentation, the learner will Discuss etiologies of cyanosis
PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest
 PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest 1. What is the best way to administer oxygen to a child in moderate respiratory distress? Nasal cannula Simple mask Nonrebreathing mask Bag-valve-mask device 2. A 2-year-old
PEPP Course: PEPP BLS Pretest 1. What is the best way to administer oxygen to a child in moderate respiratory distress? Nasal cannula Simple mask Nonrebreathing mask Bag-valve-mask device 2. A 2-year-old
Learning Station Competency Checklists
 Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Learning Station Competency Checklists Cardiac Arrest: Shockable Rhythm Team Dynamics Practice Demonstrates effective team dynamics (see, below) Performs manual maneuvers to open airway* Initiates assisted
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
Prehospital Care Bundles
 Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
Prehospital s The MLREMS Prehospital s have been created to provide a simple framework to help EMS providers identify the most critical elements when caring for a patient. These bundles do not replace
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General
![OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [ ] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: General](/thumbs/85/91909911.jpg) OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
OB Well Baby Nursery Admission (Term) [3040000234] For specialty focused order sets for your patient, refer to: 3040000424 Neonatal Circumcision Order Set 3040000522 Neonatal Herpes Viral Order Set 3040000524
PALS Case Scenario Testing Checklist Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction
 Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Respiratory Case Scenario 1 Upper Airway Obstruction Directs administration of 100% oxygen or supplementary oxygen as needed to support oxygenation Identifies signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services. Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual
 Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
Nassau Regional Emergency Medical Services Advanced Life Support Pediatric Protocol Manual 2014 PEDIATRIC ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT PROTOCOLS TABLE OF CONTENTS Approved Effective Newborn Resuscitation P 1
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Neurodevelopmental Risk?
 Normal Newborn During transitional hypoglycemia normal newborns have an enhanced ketogenic response to fasting. Newborn brains have enhanced capability to use ketone bodies for fuel Allows newborns to
Normal Newborn During transitional hypoglycemia normal newborns have an enhanced ketogenic response to fasting. Newborn brains have enhanced capability to use ketone bodies for fuel Allows newborns to
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 14 Practical Anesthesia Key Points 2 14.1 General Anesthesia Have a clear plan before starting anesthesia Never use an unfamiliar anesthetic technique in an emergency
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 14 Practical Anesthesia Key Points 2 14.1 General Anesthesia Have a clear plan before starting anesthesia Never use an unfamiliar anesthetic technique in an emergency
Medically Fragile Children (Chapter 2)
 Medically Fragile Children (Chapter 2) Birth to three programs classify children with delays as those who have either established risk or are at risk Established risk infants are those with Genetic disorders
Medically Fragile Children (Chapter 2) Birth to three programs classify children with delays as those who have either established risk or are at risk Established risk infants are those with Genetic disorders
ACLS Prep. Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep.
 November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
November, 2013 ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience. Please complete the ACLS Pretest and Please complete this ACLS Prep. ACLS Prep Preparation is key to a successful ACLS experience.
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate. Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA
 Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Pulmonary Problems of the Neonate Jon Palmer, VMD, DACVIM Chief, Neonatal Intensive Care Service New Bolton Center, University of Pennsylvania, USA Lower Respiratory Diseases Ventilation/Perfusion Abnormalities
Neonatal Resuscitation in What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011
 Neonatal Resuscitation in 2011- What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011 Conflicts I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this
Neonatal Resuscitation in 2011- What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011 Conflicts I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Test Taking Tips: It Is More Than Studying. Rick Zahodnic PhD RRT-NPS RPFT Program Coordinator, Macomb Community College
 Test Taking Tips: It Is More Than Studying Rick Zahodnic PhD RRT-NPS RPFT Program Coordinator, Macomb Community College OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this presentation the learner will 1. Describe how
Test Taking Tips: It Is More Than Studying Rick Zahodnic PhD RRT-NPS RPFT Program Coordinator, Macomb Community College OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this presentation the learner will 1. Describe how
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines
 table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
table of contents pediatric treatment guidelines P1 PEDIATRIC PATIENT CARE...70 P2 APPARENT LIFE-THREATENING EVENT (ALTE)...71 P3 CARDIAC ARREST INITIAL CARE AND CPR...72 73 P4 NEONATAL CARE AND RESUSCITATION...74
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview
 Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
Birth Asphyxia - Summary of the previous meeting and protocol overview Dr Ornella Lincetto, WHO Geneve Milano, 11June 2007 Vilka är Personality egenskaper med den astrologiska Tvillingarna? Objective of
Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants <34 weeks gestation.
 Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Emergency Care Progress Log
 Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
Emergency Care Progress Log For further details on the National Occupational Competencies for EMRs, please visit www.paramedic.ca. Check off each skill once successfully demonstrated the Instructor. All
