Inter-Examiner Reliability of the Manual Muscle Strength Testing
|
|
|
- Tracey Robertson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2012, TextRoad Publication ISSN Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research Inter-Examiner Reliability of the Manual Muscle Strength Testing Maryam Yahyaei-Rad University of Guilan, Iran ABSTRACT Standardized physical examination using manual muscle testing is a widely accepted method for evaluating strength. This study determines the inter-examiner reliability of manual test grades in assessing muscle strength in patients with a diagnosis of neuropathy or myopathy. Subjects were 11 patients, aged 10 to 40 years. 3 physical therapists participated in this study. 18 muscle groups in upper limb were tested bilaterally, using modification of the Medical Research council scale. Reliability of muscle strength grades obtained for individual muscle groups and individual muscle strength grades was analyzed using Cohen's weighted kappa. The reliability of grades for individual muscle groups was from 0.62 to 0.82, with the proximal muscles having the higher reliability values. The reliability of individual muscle strength grades from 0.52 to 0.88, with those in the gravity eliminated range scoring the highest. We find the MMT grades are reliable for assessing muscle strength in muscular weakness. KEYWORDS: reliability, upper limb, MMT, MRC INTRODUCTION Manual muscle testing is the most commonly used method for documenting impairments in muscle strength (17). Manual muscle tests evaluate the ability of the nervous system to adapt the muscle to meet the changing pressure of the examiner's test (13). This requires that the examiner be trained in the anatomy, physiology, and neurology of muscle function (18). The action of the muscle being tested, as well as the role of synergistic muscles, must be understood (6). Manual muscle testing is both a science and an art. To achieve accurate results, muscle tests must be performed according to a precise testing protocol (3). The appeal of the MMT is that it can be performed simply with the patient, an examiner, and a bench or table (24). This makes it ideal for the routine clinical environment where specialized equipment is unavailable and time is short (1). Manual muscle testing is a procedure for evaluating strength and function of an individual muscle or a muscle group in which the patient voluntarily contracts the muscle against gravity load or manual resistance (10,25). It is quick, efficient, and easy to learn, however, it requires total cooperation from the patient and learned response levels by the assessor (19). MMT was developed by Lovett and described by Wright in 1912 (31). This technique has been revised, advanced and promoted so that it has resulted in a range of methods from which the investigator may select the most suitable one (24). The scale proposed by the Medical Research Council (MRC) uses the numeral grades 0 5 (23). Kendall & McCreary (20) use percentages, and Daniels & Worthingham (12) use differentiation between Normal, Good, Fair, Poor, Trace and Zero. Manual grading of muscle strength is based on palpation or observation of muscle contraction, ability to move the limb through its available ROM against or without gravity, and ability to move the limb through its ROM against manual resistance by the examiner. Manual resistance is applied by the examiner using one hand with the other hand stabilizing the joint (5). Exact locations for applying resistive force are specified and must be followed exactly to obtain accurate MMT results (10).This paper will present evidence that the MMT can be a legitimate and useful evaluation tool for the assessment of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems. METHOD Subjects were 11 patients, aged 10 to 40 years, with a diagnosis of neuropathy or myopathy. Muscle strength was operationally defined by the MMT grades given. The present study was designed to clarify those results and document the reliability of the evaluation procedures. All subjects were required to be able to cooperate and perform the MMT. Muscle strength grades ranged from 0 to 5. Examiners were three physical therapists with 10 to 12 years of experience. Independently of each other, 3 examiners performed identical manual physical examinations of the maximal voluntary strength in each of the 18 muscles on both sides. Examiners were blind to other testing results. Muscle strength was assessed and individual MMT grades were assigned using a modified MRC (23)grading scale, with subtlivisions of the grades 3, 4, and 5, as follows: 5, 5-, 4+, 4, 4-, 3 +, 3, 3 -, 2, 1, 0. The modifications to the MRC scale included the addition of the grading subdivisions 5-, 3 +, and 3 -. *Corresponding Author: Maryam Yahyaei-Rad, University of Guilan, Iran myahyaei56@yahoo.com 13134
2 Yahyaei-Rad, 2012 Definitions of the individual muscle testing grades are shown in Table upper limb muscles were selected for evaluation of individual strength (Table 2). Independently of each other, 3 examiners performed identical manual physical examinations of the maximal voluntary strength in each of the 18 muscles on both sides. The criteria proposed for optimization of muscle strength testing (Danniels and Worthingham, 2002) were met. Upper limb postures were standardized for each muscle, with the part to be tested positioned with stabilization of the part proximal or adjacent to the tested part. During testing it was aimed to maximize the length of the lever arm. Each test moment was defined from the functional anatomy of the individual muscle. Table1. Modified medical research council scale Grade Grade Definition 5 Normal strength -5 Barely detectable weakness +4 Same as grade 4, but muscle holds the joint against moderate to maximal resistance 4 Muscle holds the joint against a combination of gravity and moderate resistance -4 Same as grade 4, but muscle holds the joint only against minimal resistance +3 Muscle moves the joint fully against gravity and is capable of transient resistance, but collapses abruptly 3 Muscle cannot hold the joint against resistance, but moves the joint fully against gravity -3 Muscle moves the joint against gravity, but not through full mechanical range of motion 2 Muscle moves the joint when gravity is eliminated 1 A flicker of movement is seen or felt in the muscle 0 No movement The aim was to optimize the position to facilitate the exertion of maximal strength by each muscle. A uniform placement of the hand for applying pressure was defined, and the pressure was applied directly and gradually, opposite to the line of pull of the muscle being tested. The intent to assess the peak strength as well as the ability of the individual to hold the force at a constant level during testing (endurance) demanded elements of isometric testing to be combined with an evaluation of eccentric dynamic resistance. Testing was performed up to three times. Assessment of strength in each muscle was based on a comparison of the intact contra lateral muscle or with bilaterally reduced strength in the particular muscle to other muscles of the individual in which the strength was assessed as intact (12). Data were analyzed using the weighted Kappa, as described Cohen (11) to determine the reliability of individual MMT grades and grades obtained for individual muscle groups. Kappa is a chance-corrected measure of agreement in which all disagreements are given equal weight. In contrast, the weighted Kappa takes into account the degree of disagreement among raters. Assessment of the reliability of individual muscle strength grades was made by using a modification of Cohen's Kappa, as described by Cicchetti and colleague (9). The total muscle score is determined by transforming individual muscle grades to a 10-point scale (5=10, 5- =9, 4+ =8, and so on), adding all converted scores, and using that sum for comparisons. RESULTS Table 2. Manual muscle test grades for individual muscle groups obtained using modified medical research council scale Muscle groups Weighted kappa Serratus anterior 0.82 Scapula elevation 0.73 Scapula adduction 0.76 Rhomboids 0.77 Shoulder flexion 0.78 Shoulder extension 0.79 Shoulder abduction 0.78 Shoulder horizontal abduction 0.70 Shoulder horizontal adduction 0.76 Shoulder external rotation 0.80 Shoulder internal rotation 0.80 Elbow flexion 0.75 Thumb abduction 0.73 Elbow extension 0.81 Forearm supination 0.64 Forearm pronation 0.62 Wrist flexion 0.69 wrist extension
3 Inter-examiner reliability of MMT grades obtained with the modified MRC scale for individual muscle groups, as determined by the weighted Kappa, is shown in Table 2. Grades of proximal muscle groups were more reliable than were grades of muscle groups located distally. Inter-examiner reliability of MRC grades 0 to 5, as determined by the weighted Kappa, is shown in Table 3, along with the number of assignments within each grade. The reliability varied among individual grades, with grades in the gravity-eliminated position having the highest reliability values. Table3. Inter-examiner reliability of individual muscle strength grades obtained using the modified medical research council scales Grade N Weighted kappa N=number of assignments DISCUSSION The reliability and validity of various MMT techniques have been tested in patients with poliomyelitis (18, 22, 29) and muscular dystrophy (14, 15). Barr et al. (4) assessed the reliability of an mmrc scale that uses plus and minus sub-divisions (23). Perfect agreement was seen 35.9% of the time, consistency within one consecutive strength grade was found 66.5% of the time, and within 2 consecutive steps 84.7% of the time. The agreement for measures of proximal muscle strength (r = 0.80) was found to be more consistent than that for measures of distal muscle strength (r = 0.58) (4). Other studies addressed the reliability of a composite score, weighted by a factor that assessed muscle bulk rather than assigning grades to individual muscle groups or individual grades within a particular score (18, 22, 29). Some studies that addressed inter-rater reliability used a sum score of various muscles rather than analysing reliability for individual muscle groups (14, 21). Escolar et al. (14) determined a sum score of the mmrc scale and compared the reliability of MMT and quantitative muscle testing. MMT was not as reliable and required repeated training of evaluators to bring all groups to a correlation coefficient > 0.75 (14). Kleyweg et al. (21) registered nearly perfect interobserver agreement of a sum score of various muscles tested with the MRC scale in patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. The MMT method described by Daniels & Worthingham (12) was shown to be reliable (26, 28). Brandsama et al. (7) tested the reliability of the 6-point MRC scale of intrinsic muscles of the hand. They suggested testing specific movements rather than selective muscles because it is difficult to isolate, and hence grade, most of the intrinsic muscles of the hand (7). They also introduced a mmrc scale (8), which includes the description of ROM as well as resistance into the 6-point original MRC scale. In their mmrc scale, grade 3 has to have normal ROM. In our modified scale, grade 3 has to have more than 50% of the feasible ROM and additional 3 grades (grade 2 3, 3 4 and 4 5) were included, which was assumed to represent better the clinical course of nerve regeneration. Manual muscle testing, using the MRC scale, provides reliable grades for then assessment of strength of individual muscle groups within a sample of patients with a Diagnosis of neuropathy or myopathy. Inter-examiner reliability ranged from 0.62 to The weighted Kappa values for the proximal muscles were more consistent than those for the distal muscles. Weighted Kappa values for Inter-examiner reliability varied among individual muscle groups ( ). Inter-examiner reliability varies among individual muscle grades with those in he gravityeliminated position (MRC 0-2) grading most reliably ( 0.86). This finding differs from that of Frese and Colleagues (16) who found poor. Inter-examiner reliability in grades below Fair; similarly, Beasley (5) found poor differentiation in grades below Fair. These grades were the only categories that had no subdivisions (no plus or minus designations) and were strictly defined, but Frese and colleagues also stated that "compressing the scores by eliminating pluses and minuses did not appreciably change the Inter-examiner reliability coefficients (16)
4 Yahyaei-Rad, 2012 The strength grading subdivisions in which gravity and resistance are factors in determining the MMT grade have come under much criticism (2, 27, 30) be cause they require judgments beyond assigning the original grade on the part of the examiner. The weighted Kappas for the MRC grades 4- to 5 ranged from 0.64 to These grades are less reliable than those given in positions in which the factors of gravity and resistance have been eliminated but, we believe, are still acceptable for measurement in the clinical trial setting. The reliability coefficients in our MMT study ranged from 0.63 to 0.85 in the Good to Normal range (MRC 4-5). Studies relating to the sensitivity of these methods of measurement of muscle strength are needed to determine the most useful method for documentation, as both methods appear reliable in the assessment. The lowest reliability coefficient for an individual muscle grade in this study was 0.60, with a grade of 3+. The definition of this grading subdivision in our study required considerable judgment by the examiner because this grade indicates that the muscle "is capable of transient resistance, but collapses abruptly." Controversy exists in the literature over the use of the MMT as a measurement tool in the documentation of muscle strength. Our study suggests that MMT grades obtained with the MRC scale are reliable. Some authors have suggested that MMT grades below Fair (MRC <3) are not reliable (16, 27) and that grades of Good (4) and Normal (5) are subjective." Our study suggests that we need to be most cautious of the grades Fair minus (3- ), Fair plus (3+), Good minus (4- ), Good (4), Good plus (4+) and Normal minus (5-) and that the most reliable grades are those made with the factor of gravity eliminated. The MMT is shown to yield reliable grades within individual muscle groups, but reliability varied proximal to distal within an extremity. The best agreement was shown when MMT grades for individual muscle groups were combined into a total muscle score. This finding suggests the most stable measure for documenting muscle strength in systemic diseases or with systemic interventions is a composite score. REFERENCES 1. Amundsen L. Muscle Strength Testing: Instrumented and Non-Instrumented Systems. New York: Churchill Livingstone; Andres PL, Skerry LM, Munsat TL. Measurement of strength in neuromuscular diseases. In: Munsat TI., ed. Quantification of Neurologic Deficit. Boston, Mass: Butterworth- Heinemann; 1989: Barbano RL: Handbook of Manual Muscle Testing. Neurology 2000, 54(5): Barr AE, Diamond BE, Wade CK, Harashima T, Pecorella WA, Potts CC, et al. Reliability of testing measures in Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1991; 72: Beasley WC. Quantitative muscle testing: principles and applications to research and clinical services. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1961; 42: Bohannon RW: Manual muscle testing: does it meet the standards of an adequate screening test? Clin Rehabil 2005, 19(6): Brandsama JW, Schreuders TA, Birke JA, Piefer A, Oostendorp R. Manual Muscle Strength testing: intraobserver and interobserver reliabilities for the intrinsic muscles of the hand. J Hand Ther 1995; 8: Brandsama JW, Schreuders TA. Sensible manual muscle strength testing to evaluate and monitor strength of the intrinsic muscles of the hand: a commentary. J Hand Ther 2001; 14: Cicchetti DV, Lee C, Fontana AF, Dowde A. A computer program for assessing specific category rater agreement for qualitative data. Educational and Psychological Measurement. 1978; 38: Clarkson HM. Musculoskeletal Assessment: Joint Range of Motion and Manual Muscle Strength. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Cohen J. Weighted Kappa: normal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement on partial credit. Psycho1 Bull. 1968; 70:
5 12. Daniels L, Worthingham K: Muscle Testing Techniques of Manual Examination 7th edition. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders Co; Dvir Z. Isokinetics: Muscle Testing, Interpretation and Clinical Applications. New York; Churchill Livingstone; Escolar DM, Henricson EK, Mayhew J, Florence J, Leshner R, Patel KM, Clemens PR. Clinical evaluator reliability for quantitative and manual muscle testing measures of strength in children. Muscle Nerve 2001; 24: Florence JM, Pandya S, King WM, Robison JD, Signore LC, Wentzell M, Province MA. Clinical trials in Duchenne dystrophy. Standardization and reliability of evaluation procedures. Phys Ther 1984; 64: Frese E, Brown M, Norton BJ. Clinical reliability of manual muscle testing: middle trapezius and gluteus medius muscles. Phys Ther. 1987;67: Hough CL, Lieu BK, Caldwell ES. Manual muscle strength testing of critically ill patients: feasibility and interobserver agreement. Critical care 2011; 15: Iddings DM, Smith LK, Spencer WA. Muscle testing. 2. Reliability in clinical use. Phys Ther Rev 1961; 41: Kendall F P. Manual muscle testing: there is no substitute. J Hand Ther 1991; 4: Kendall FP, McCreary EK, Provance PG: Muscles: Testing and Function Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; Kleyweg RP, van der Meché FG, Schmitz PI. Interobserver agreement in the assessment of muscle strength and functional abilities in Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Muscle Nerve 1991; 14: Lilienfeld AM, Jacobs M, Willis M. A study of the reproducibility of muscle testing and certain other aspects of muscle scoring. Phys Ther Rev 1954; 34: Medical Research Council (MRC). Aids to the investigation of peripheral nerve injuries. London: Her Majesty s Stationery Office; Mendell JR, Florence JM. Manual muscle testing. Muscle Nerve. 1990; 13:S16-S Neistadt M, Crepeau E. Willard and Spackman s Occupational Therapy. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Nitz JC, Burns YR, Jackson RV. A longitudinal physical profile assessment of skeletal muscle manifestation in myotonic dystrophy. Clin Rehabil 1999; 13: Rothstein JM. Measurement and clinical practice: theory and application. In: Rothstein JM, ed. Measurement in Physical Therapy. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone Inc; 1985: Silver M, McElroy A, Morrow L, Heafner BK. Further standardization of manual muscle test for clinical study: applied in chronic renal disease. Phys Ther. 1970; 50: Smith LK, Iddings DM, Spencer WA, Harrington PR. Muscle testing, part I: description of a numerical index for clinical research. Phys Ther Rev 1961; 41: Stuberg WA, Metcalf WK. Reliability of quantitative muscle testing in healthy children and in children with Duchenne muscular dystrophy using a hand-held dynamometer. Phys Ther. 1988; 68: Wright W. Muscle training in the treatment of infantile paralysis. Boston Med Surg J 1912; 167:
RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MEDICAL RESEARCH
 J Rehabil Med 2008; 40: 665 671 ORIGINAL REPORT RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL (MRC) SCALE AND A MODIFIED SCALE FOR testing muscle strength in PATIENTS WITH RADIAL PALSY Tatjana
J Rehabil Med 2008; 40: 665 671 ORIGINAL REPORT RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL (MRC) SCALE AND A MODIFIED SCALE FOR testing muscle strength in PATIENTS WITH RADIAL PALSY Tatjana
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS. I. Devreux
 EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
EVALUATION AND MEASUREMENTS I. Devreux To determine the extent and degree of muscular weakness resulting from disease, injury or disuse. The records obtained from these tests provide a base for planning
Comparison of three methods to assess muscular strength in individuals with spinal cord injury
 Spinal Cord (1998) 36, 716 ± 723 1998 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Comparison of three methods to assess muscular
Spinal Cord (1998) 36, 716 ± 723 1998 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 1362 ± 4393/98 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/sc Comparison of three methods to assess muscular
Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain
 Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 29 (2016) 549 555 549 DOI 10.3233/BMR-160656 IOS Press Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain Shannon M. Petersen a,,nathana.domino
Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation 29 (2016) 549 555 549 DOI 10.3233/BMR-160656 IOS Press Scapulothoracic muscle strength in individuals with neck pain Shannon M. Petersen a,,nathana.domino
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry
 37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry David A. Krause, PT, MBA, DScPT, OCS, Susan J. Schlagel,
37 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Influence of Lever Arm and Stabilization on Measures of Hip Abduction and Adduction Torque Obtained by Hand-Held Dynamometry David A. Krause, PT, MBA, DScPT, OCS, Susan J. Schlagel,
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008
 Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) test July 2008 RIHM HAPE EXTURE DENTIFICATION Instructions for administering the Rotterdam Intrinsic Hand Myometer (RIHM) A dynamometer
Inhibition Associated with somatic dysfunctions, no matter which components are impaired Implies consideration of all components in treatment planning
 Somatic Dysfunction Impaired or altered function of related components of the somatic system including the skeletal, arthrodial, myofascial structures and their related vascular, lymphatic and neural elements.
Somatic Dysfunction Impaired or altered function of related components of the somatic system including the skeletal, arthrodial, myofascial structures and their related vascular, lymphatic and neural elements.
RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University
 1 RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University 2 The scapulae lie against the thorax approximately
1 RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University 2 The scapulae lie against the thorax approximately
MMT measurements are acceptable in routine clinical practice: Results from periodic medical examinations of polio survivors
 51 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article MMT measurements are acceptable in routine clinical practice: Results from periodic medical examinations of polio survivors
51 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2017) Original Article MMT measurements are acceptable in routine clinical practice: Results from periodic medical examinations of polio survivors
Scapular Muscle Strengthening
 Original Research Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1995, 4, 244-252 O 1995 Human Kinetics Publ~shers, Inc. Scapular Muscle Strengthening Thomas Zmierski, Sam Kegerreis, and James Scarpaci The purposes
Original Research Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1995, 4, 244-252 O 1995 Human Kinetics Publ~shers, Inc. Scapular Muscle Strengthening Thomas Zmierski, Sam Kegerreis, and James Scarpaci The purposes
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 1 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL THERAPY PROCEDURES RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King Saud
1 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICAL THERAPY PROCEDURES RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King Saud
How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic
 How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic Patrick Gordon Consultant Rheumatologist / Honorary Senior Lecturer King s Health Partners Email: patrick.gordon2@nhs.net Many
How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic Patrick Gordon Consultant Rheumatologist / Honorary Senior Lecturer King s Health Partners Email: patrick.gordon2@nhs.net Many
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH
 10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
10.1515/AMB-2016-0020 PROCEDURAL OPTIONS FOR MEASURING MUSCLE STRENGTH S. Mindova, I. Karaganova and I. Stefanova Faculty of Public Health and Health Care, University of Ruse Angel Kanchev, Ruse, Bulgaria
Orthopedic Surgery and Sports Medicine FL License:
 Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol: The intent of this protocol is to provide the therapist with a guideline for the post-operative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone a Reverse Shoulder
Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol: The intent of this protocol is to provide the therapist with a guideline for the post-operative rehabilitation course of a patient that has undergone a Reverse Shoulder
G roin pain is associated with many sports and
 446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... Br J Sports Med 2004;38:446 451. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2003.004754
446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... Br J Sports Med 2004;38:446 451. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2003.004754
Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases. Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2)
 Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2) ITIS d. o. o. Ljubljana, Center for Implantable Technology
Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2) ITIS d. o. o. Ljubljana, Center for Implantable Technology
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
G roin pain is associated with many sports and
 446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... See end of article for authors affiliations...
446 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical examination of athletes with groin pain: an intraobserver and interobserver reliability study PHölmich, L R Hölmich, A M Bjerg... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS
 Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease
 Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
Dynamometry of intrinsic hand muscles in patients with Charcot Marie Tooth disease R.W. Selles, PhD; B.T.J. van Ginneken, MSc; T.A.R. Schreuders, PT, PhD; W.G.M. Janssen, MD; and H.J. Stam, MD, PhD, FRCP
Manual Muscle Strength Testing:
 ( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLES J Manual Muscle Strength Testing: Intraobserver and Interobserver Reliabilities for the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand J. Willem Brandsma, PhD Physical Therapist, National
( SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLES J Manual Muscle Strength Testing: Intraobserver and Interobserver Reliabilities for the Intrinsic Muscles of the Hand J. Willem Brandsma, PhD Physical Therapist, National
A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy
 A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy Table of Contents Introduction.. 3 Active Movement Scale 4 AMS Evaluation Form.
A Clinicians Guide To The Active Movement Scale (AMS) An Evaluative Tool For Infants With Obstetrical Brachial Plexus Palsy Table of Contents Introduction.. 3 Active Movement Scale 4 AMS Evaluation Form.
Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment?
 Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment? An important component of the clinical examination for several conditions is the assessment of muscle strength. The standard clinical evaluation and diagnostic
Do you want to improve your Clinical Assessment? An important component of the clinical examination for several conditions is the assessment of muscle strength. The standard clinical evaluation and diagnostic
*Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have
 1 *Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have more than 1 action sometimes a muscle has to neutralize
1 *Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have more than 1 action sometimes a muscle has to neutralize
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Therapy Protocol
 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Therapy Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide the therapist with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Therapy Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide the therapist with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that has
Rotator Cuff Repair Therapy Protocol
 Bart Eastwood D.O. 825 Davis st Blacksburg, VA 24060 540-951-6000 All information contained in this protocol is to be used as general guidelines only. Specific variations may be appropriate for each patient
Bart Eastwood D.O. 825 Davis st Blacksburg, VA 24060 540-951-6000 All information contained in this protocol is to be used as general guidelines only. Specific variations may be appropriate for each patient
WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments
 WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments Muscle Identification The human body consists of many muscles and muscle groups. We will focus on a select few that are most prevalent when training. The muscular system
WTC I Term 2 Notes/Assessments Muscle Identification The human body consists of many muscles and muscle groups. We will focus on a select few that are most prevalent when training. The muscular system
ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS
 ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS CURE JM STANFORD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OCTOBER 3, 2014 Minal Jain, PT, DSc, PCS Research Coordinator, Physical Therapy Section Rehabilitation
ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS CURE JM STANFORD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OCTOBER 3, 2014 Minal Jain, PT, DSc, PCS Research Coordinator, Physical Therapy Section Rehabilitation
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES
 MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES From: Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement. A systematic review and synthesized
MOON SHOULDER GROUP NONOPERATIVE TREATMENT OF ROTATOR CUFF TENDONOPATHY PHYSICAL THERAPY GUIDELINES From: Kuhn JE. Exercise in the treatment of rotator cuff impingement. A systematic review and synthesized
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer
 The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle
 AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
Avon Office 2 Simsbury Rd. Avon, CT Office: (860) Fax: (860) Arthroscopic Posterior Labral Repair
 Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Arthroscopic
Katherine J. Coyner, MD UCONN Musculoskeletal Institute Medical Arts & Research Building 263 Farmington Ave. Farmington, CT 06030 Office: (860) 679-6600 Fax: (860) 679-6649 www.drcoyner.com Arthroscopic
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device
 Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
PROM is not stretching!
 Dx: o Right o Left Shoulder Replacement/Hemiarthroplasty Rehab Date of Surgery: Patient Name: PT/OT: Please evaluate and treat. Follow attached protocol. 2-3 x per week x 6 weeks. Signature/Date: The intent
Dx: o Right o Left Shoulder Replacement/Hemiarthroplasty Rehab Date of Surgery: Patient Name: PT/OT: Please evaluate and treat. Follow attached protocol. 2-3 x per week x 6 weeks. Signature/Date: The intent
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Muscles: Testing And Function, With Posture And Pain (Kendall, Muscles) By Florence Peterson Kendall, Elizabeth Kendall McCreary READ ONLINE
 Muscles: Testing And Function, With Posture And Pain (Kendall, Muscles) By Florence Peterson Kendall, Elizabeth Kendall McCreary READ ONLINE A description for this result is not available because of this
Muscles: Testing And Function, With Posture And Pain (Kendall, Muscles) By Florence Peterson Kendall, Elizabeth Kendall McCreary READ ONLINE A description for this result is not available because of this
Type II SLAP lesions are created when the biceps anchor has pulled away from the glenoid attachment.
 Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
Arthroscopic Superior Labral (SLAP) Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the post-operative rehabilitation course of
PTA Applied Kinesiology 2
 Western Technical College 10524157 PTA Applied Kinesiology 2 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3 Applies basic principles from PTA Kinesiology
Western Technical College 10524157 PTA Applied Kinesiology 2 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3 Applies basic principles from PTA Kinesiology
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 1 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Introduction to Physical Therapy Procedures RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King
1 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Introduction to Physical Therapy Procedures RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Tel# 4693601 Department of Physical Therapy King
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles
 Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation
 Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Integrating Sensorimotor Control Into Rehabilitation BRADY L. TRIPP, PhD, LAT, ATC Florida International University Key Points As evidence accumulates, so does our appreciation of the integral roles that
Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work
 Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work RE: Baldwin ERL, Baldwin TD, Lancaster JS, et al. Neuromuscular electrical
Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work RE: Baldwin ERL, Baldwin TD, Lancaster JS, et al. Neuromuscular electrical
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears:
 Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
Arthroscopic Labral Repair Protocol-Type II, IV, and Complex Tears: The intent of this protocol is to provide the clinician with a guideline of the postoperative rehabilitation course of a patient that
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
FEASIBILITY OF EMG-BASED CONTROL OF SHOULDER MUSCLE FNS VIA ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK
 FEASIBILITY OF EMG-BASED CONTROL OF SHOULDER MUSCLE FNS VIA ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK R. F. Kirsch 1, P.P. Parikh 1, A.M. Acosta 1, F.C.T. van der Helm 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Case Western
FEASIBILITY OF EMG-BASED CONTROL OF SHOULDER MUSCLE FNS VIA ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK R. F. Kirsch 1, P.P. Parikh 1, A.M. Acosta 1, F.C.T. van der Helm 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Case Western
Station 1: Muscle Structure Table 3: Muscle Structure. Station 1: Muscle Contraction
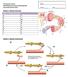 The Muscular System Name: HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Answer Sheet Period: Date: Station 1: Muscle Structure Table 3: Muscle Structure A K B L C M D N E O F P G Q H R I S J T Station
The Muscular System Name: HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Answer Sheet Period: Date: Station 1: Muscle Structure Table 3: Muscle Structure A K B L C M D N E O F P G Q H R I S J T Station
Arthroscopic SLAP Lesion Repair Rehabilitation Guideline
 Arthroscopic SLAP Lesion Repair Rehabilitation Guideline This rehabilitation program is designed to return the individual to their activities as quickly and safely as possible. It is designed for rehabilitation
Arthroscopic SLAP Lesion Repair Rehabilitation Guideline This rehabilitation program is designed to return the individual to their activities as quickly and safely as possible. It is designed for rehabilitation
After Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Intact Rotator Cuff (Distal Clavicle Resection)
 After Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Intact Rotator Cuff (Distal Clavicle Resection) Rehabilitation Protocol Phase 1: Weeks 0-4 Restrictions ROM 140 degrees of forward flexion 40 degrees of external
After Arthroscopic Subacromial Decompression Intact Rotator Cuff (Distal Clavicle Resection) Rehabilitation Protocol Phase 1: Weeks 0-4 Restrictions ROM 140 degrees of forward flexion 40 degrees of external
TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY / HEMIARTHROPLASTY
 Teodoro P. Nissen, M.D., Q.M.E. Fellowship Trained Board Certified Joseph M. Centeno, M.D. Fellowship Trained Board Certified TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY / HEMIARTHROPLASTY Protocol: The intent of this
Teodoro P. Nissen, M.D., Q.M.E. Fellowship Trained Board Certified Joseph M. Centeno, M.D. Fellowship Trained Board Certified TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY / HEMIARTHROPLASTY Protocol: The intent of this
Evidence- Based Examination of the Shoulder Presented by Eric Hegedus, PT, DPT, MHSC, OCS, CSCS Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs
 Evidence- Based Examination of the Shoulder Practice Session & Skills Check- offs Evidence- Based Examination of the Shoulder Presented by Eric Hegedus, PT, DPT, MHSC, OCS, CSCS Practice Sessions/Skill
Evidence- Based Examination of the Shoulder Practice Session & Skills Check- offs Evidence- Based Examination of the Shoulder Presented by Eric Hegedus, PT, DPT, MHSC, OCS, CSCS Practice Sessions/Skill
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS
 Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Rehab protocol. Phase I: Immediate Post-Surgical Phase: Typically 0-4 weeks; 2 PT visits. Goals:
 Reverse Total shoulder arthroplasty Rehab protocol Phase I: Immediate Post-Surgical Phase: Typically 0-4 weeks; 2 PT visits Allow healing of soft tissue Maintain integrity of replaced joint Gradually increase
Reverse Total shoulder arthroplasty Rehab protocol Phase I: Immediate Post-Surgical Phase: Typically 0-4 weeks; 2 PT visits Allow healing of soft tissue Maintain integrity of replaced joint Gradually increase
A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic Functional Strength of the Wrist for Junior Baseball Players
 Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(18), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i18/76239, August 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic
Indian Journal of Science and Technology, Vol 8(18), DOI: 10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i18/76239, August 2015 ISSN (Print) : 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 A Study on the Norm-Referenced Criteria for Isokinetic
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN
 STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
STRENGTH MEASUREMENTS IN ATHLETES WITH GROIN PAIN Written by Kristian Thorborg, Denmark INTRODUCTION Hip and groin pain is a common problem often related to physical functioning and sports activities.
Palpation Assessment
 Palpation Assessment by Joe Muscolino Never treat without an ASSESSMENT There is an old adage in the world of medicine - never treat without a diagnosis. A similar principle can be articulated in the world
Palpation Assessment by Joe Muscolino Never treat without an ASSESSMENT There is an old adage in the world of medicine - never treat without a diagnosis. A similar principle can be articulated in the world
Total Shoulder Rehab Protocol Dr. Payne
 Total Shoulder Rehab Protocol Dr. Payne Phase I Immediate Post Surgical Phase (0-4 weeks): Allow healing of soft tissue Maintain integrity of replaced joint Gradually increase passive range of motion (PROM)
Total Shoulder Rehab Protocol Dr. Payne Phase I Immediate Post Surgical Phase (0-4 weeks): Allow healing of soft tissue Maintain integrity of replaced joint Gradually increase passive range of motion (PROM)
Ton A. R. Schreuders, 1 Marij E. Roebroeck, 1 Jean-Bart Jaquet, 2 Steven E. R. Hovius 2 and Henk J. Stam 1 INTRODUCTION
 J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
J Rehabil Med 2004; 36: 273 278 LONG-TERM OUTCOME OF MUSCLE STRENGTH IN ULNAR AND MEDIAN NERVE INJURY: COMPARING MANUAL MUSCLE STRENGTH TESTING, GRIP AND PINCH STRENGTH DYNAMOMETERS AND A NEW INTRINSIC
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting)
 ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
ELBOW - 1 FLEXION: ROM (Supine / Sitting) Position (A) Patient: Place arm against side of trunk. Helper: Hold elbow to stabilize. (B) - Lift hand toward shoulder, palm up. - Keep wrist straight. Do sessions
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS
 Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Ms. Ruth A. Delaney, MB BCh BAO, MMedSc, MRCS Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder Specialist. +353 1 5262335 ruthdelaney@sportssurgeryclinic.com Modified from the protocol developed at Boston Shoulder
Scapular Protraction in Sitting
 9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM
 Throwers Shoulder Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The throwers ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing.
Throwers Shoulder Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The throwers ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing.
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL)
 ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) 1(6) ACGIH TLV for Hand Activity Level (HAL) General description and development of the method The ACGIH HAL TLV uses HAL (Hand activity level) and peak hand forces
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
NZQA Expiring unit standard 7026 version 4 Page 1 of 7. Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics
 Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Head, Neck, and Cervical Spine Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS Pre- Chapter Case Study
 Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
Pain Assessment Patient Interview (location/nature of symptoms), Body Diagram. Observation and Examination: Tests and Measures
 Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Change in muscle strength over time in spinal muscular atrophy types II and III. A long-term follow-up study
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Neuromuscular Disorders 22 (2012) 1069 1074 www.elsevier.com/locate/nmd Change in muscle strength over time in spinal muscular atrophy types II and III. A long-term
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Neuromuscular Disorders 22 (2012) 1069 1074 www.elsevier.com/locate/nmd Change in muscle strength over time in spinal muscular atrophy types II and III. A long-term
Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers
 Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Isokinetics and Exercise Science 12 (4) 91 97 91 IOS Press Intramachine and intermachine reproducibility of concentric performance: A study of the Con-Trex MJ and the Cybex Norm dynamometers C. Bardis
Verification of Immediate Effect on the Motor Function of a Plegic Upper Limb after Stroke by using UR-System 2.2
 Verification of Immediate Effect on the Motor Function of a Plegic Upper Limb after Stroke by using UR-System. Hiroki Sugiyama,a, Hitomi Hattori,b, Ryosuke Takeichi,c, Yoshifumi Morita,d, Hirofumi Tanabe,e
Verification of Immediate Effect on the Motor Function of a Plegic Upper Limb after Stroke by using UR-System. Hiroki Sugiyama,a, Hitomi Hattori,b, Ryosuke Takeichi,c, Yoshifumi Morita,d, Hirofumi Tanabe,e
Manual Muscle Testing. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides
 IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
Sterile gauze used at incision site. Check brace for rubbing or irritation. Compression garment at elbow to be used with physician s authorization
 ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION GUIDELINE Functional Outcome Measure KJOC (Appendix 1) should be completed at initial evaluation and at all identified times through guideline, Phase 1 Immediate
ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION GUIDELINE Functional Outcome Measure KJOC (Appendix 1) should be completed at initial evaluation and at all identified times through guideline, Phase 1 Immediate
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Protocol
 Adam N. Whatley, M.D. 6550 Main St., STE. 2300 Zachary, LA 70791 Phone(225)658-1808 Fax(225)658-5299 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide the
Adam N. Whatley, M.D. 6550 Main St., STE. 2300 Zachary, LA 70791 Phone(225)658-1808 Fax(225)658-5299 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty / Hemiarthroplasty Protocol The intent of this protocol is to provide the
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
Skeletal Muscles and Functions
 Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity
 THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS
 DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
APPENDIX: The Houston Astros Stretching Program
 Vol. 35, No. 4, 2007 Glenohumeral Internal Rotation Deficits 1 APPENDIX: The Houston Astros Stretching Program Our Flexibility program consists of 5 positions. Four of the 5 have 2 variations of each position.
Vol. 35, No. 4, 2007 Glenohumeral Internal Rotation Deficits 1 APPENDIX: The Houston Astros Stretching Program Our Flexibility program consists of 5 positions. Four of the 5 have 2 variations of each position.
On the reliability and validity of manual muscle testing: a literature review
 On the reliability and validity of manual muscle testing: a literature review Scott C Cuthbert 1 and George J Goodheart Jr 2 1 Chiropractic Health Center, 255 West Abriendo Avenue, Pueblo, CO 81004, USA
On the reliability and validity of manual muscle testing: a literature review Scott C Cuthbert 1 and George J Goodheart Jr 2 1 Chiropractic Health Center, 255 West Abriendo Avenue, Pueblo, CO 81004, USA
Figure 11-1: The lever-fulcrum principle is illustrated by flexion of the forearm.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1
 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
WEEKEND 2 Elbow. Elbow Range of Motion Assessment
 Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK.
 CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
CMTM10 INVESTIGATION ON UPPER LIMB AND LOWER BACK MUSCLES ACTIVITIES DURING SEDENTARY WORK. Nurhayati Mohd Nur 1, Siti Zawiah Md Dawal 2 1 University of Kuala Lumpur-MIAT, Jenderam Hulu, 43800 Dengkil,
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION USING AUTOGENOUS GRACILIS GRAFT
 Therapist POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION USING AUTOGENOUS GRACILIS GRAFT I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (0-3 weeks) Protect healing tissue
Therapist POST-OPERATIVE REHABILITATION PROTOCOL FOLLOWING ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION USING AUTOGENOUS GRACILIS GRAFT I. IMMEDIATE POST-OPERATIVE PHASE (0-3 weeks) Protect healing tissue
Anterior Labrum Repair Protocol
 Anterior Labrum Repair Protocol Stage I (0-4 weeks): Key Goals: Protect the newly repaired shoulder. Allow for decreased inflammation and healing. Maintain elbow, wrist and hand function. Maintain scapular
Anterior Labrum Repair Protocol Stage I (0-4 weeks): Key Goals: Protect the newly repaired shoulder. Allow for decreased inflammation and healing. Maintain elbow, wrist and hand function. Maintain scapular
