DO ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF THE HAND IMPACT THE HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN MEDIAN NERVE AT THE LEVEL OF THE CARPAL TUNNEL?
|
|
|
- Byron Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FOLIA MEDICA CRACOVIENSIA Vol. LII, 1 2, 2012: PL ISSN KRZYSZTOF A. TOMASZEWSKI 1, IWONA M. TOMASZEWSKA 2, WOJCIECH KURZYDŁO 3, JANUSZ SKRZAT 1, ALEKSANDRA MATUSZYK 1, MICHAŁ KŁOSIŃSKI 1, EWA MIZIA 1 DO ANTHROPOMETRIC MEASUREMENTS OF THE HAND IMPACT THE HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN MEDIAN NERVE AT THE LEVEL OF THE CARPAL TUNNEL? Abstract: Do anthropometric measurements of the hand impact the histological structure of the human median nerve at the level of the carpal tunnel? Introduction: The literature lacks data on the histological structure of the median nerve on the level of the carpal tunnel, and its possible correlations with the anthropometric measurements of the hand. A i m: The aim of this study was to assess the anthropometric measurements of human cadaver hands and their median nerves histological structure and whether a correlation existed between these two. Material & Methods: This study has been conducted using cadavers stored in a 10% solution of formaldehyde at the Department of Anatomy of the Jagiellonian University Medical College (JUMC) and cadavers from the Department of Forensic Medicine JUMC. Before dissection anthropometric measurements were carried out. After dissection the median nerves were stained with haematoxylin and eosin and histological slides were prepared. These were later photographed (16 magnification) and analysed using ImageJ software. Results: The studied group comprised 8 women and 22 men (age between years). Anthropometric measurements comparison by gender revealed statistically significantly larger CR-CU, MR-MU and TS-ID distances in men then in women. When comparing sides, the crosssectional area (CSA) of the right median nerve (0.216 ± 0.06 cm 2 ) was statistically significantly larger (p = 0.017) then the CSA of the left median nerve (0.173 ± 0.05 cm 2 ). No correlation was noted between the anthropometric and histological measurements obtained in this study. Conclusions: Anthropometric measurements of the hand do not impact the histological structure of the human median nerve at the level of the carpal tunnel. Nerve bundles of the median nerve, at the level of the carpal tunnel, display no particular type of arrangement. Key words: median nerve, nerve bundles, anthropometric measurements, carpal tunnel
2 18 INTRODUCTION The carpal tunnel, located on the palmar surface of the wrist, contains the median nerve, four tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis, four tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus, and the tendon of the flexor pollicis longus [1]. The median nerve is a mixed motor and sensory nerve [2]. It descends beneath the flexor digitorum superficialis, lying on the flexor digitorum profundus in the forearm, within 5 cm of the transverse carpal ligament and then it becomes more superficial, situated between the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and the flexor carpi radialis [3]. It lies behind and radial to the side of the palmaris longus tendon just before entering the carpal tunnel [3]. The median nerve normally divides into six branches at the distal terminus of the flexor retinaculum [1 3]. These include the recurrent motor branch innervating the opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis and the flexor pollicis brevis [2]. Since the nerve passes through the narrow carpal tunnel, which is crowded inside and outside, by a series of structures, it is therefore important for clinicians to recognize the frequency and multiplicity of the variations within the region of the wrist [4, 5]. The literature lacks data on the histological structure of the median nerve on the level of the carpal tunnel, and its possible correlations with the anthropometric measurements of the hand. This might be due to the fact that most studies focusing on the median nerve are conducted during surgery or by using ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging. The first aim of this study was to assess the anthropometric measurements of human cadaver hands and their median nerves histological structure. The second aim was to determine whether a correlation existed between these measurements. MATERIALS AND METHODS This study has been conducted using cadavers stored in a 10% solution of formaldehyde at the Department of Anatomy (Jagiellonian University Medical College) as well as cadavers from the Department of Forensic Medicine (Jagiellonian University Medical College). The studied group comprised 8 women and 22 men (age span between 23 and 92 years). A total of 60 median nerves was acquired. There were no restrictions as to gender or age concerning inclusion into the study. Exclusion criteria included extensive damage to the median nerve preventing proper sample acquisition.
3 19 The research protocol was approved by the Jagiellonian University Ethics Committee (registry KBET/209/B/2002). Anthropometric points and measurements Before dissection, anthropometric measurements of the hand were carried out, using a digital caliper (Limit, Poland). The following anthropometric points were used: Carpale radiale (CR) situated on the lateral margin of the hand, on the level of the radiocarpal joint; Carpale ulnare (CU) situated on the medial margin of the hand, on the level of the ulnocarpal joint; Metacarpale radiale (MR) situated on the lateral margin of the hand, in the place of the biggest prominence of the head of the second metacarpal; Metacarpale ulnare (MU) situated on the medial margin of the hand, in the place of the biggest prominence of the head of the fifth metacarpal. For this study, apart from the standard anthropometric points, additional points were set: The tuberculum of the scaphoid bone (TS); Interdigitalis II III (ID) situated halfway between the bases of the second and third fingers. The following measurements were made: The width of the wrist the distance between the CR and the CU; The width of the metacarpus the distance between the MR and the MU; The distance between the TS and the ID. Each measurement phase was carefully photographed using a digital camera [6]. Dissection technique The incision was made starting at the distal 1/3 of the forearm, continuing between the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis and the tendon of the palmaris longus muscle, along the thumb flexion line. After dissecting the skin and the subcutaneous tissue, the median nerve was exposed and the flexor retinaculum was cut on the ulnar side. Next the median nerve was dissected (in or above the carpal tunnel). The existing incision was closed using a running intradermal suture.
4 20 Preparing histological slides First a fragment of the main stem of the median nerve was excised (between the distal 1/3 part of the forearm to the site where the common palmar digital nerves branch out). This fragment of the median nerve was then placed in a glass container with a 10% solution of formaldehyde (ph 7.4). After 2 to 5 days a part of the main stem of the median nerve was excised (right above the motor branch). Tissues were dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 4μm and stained with hematoxylin & eosin. Micromorphometry The number of nerve bundles in the main stem of the median nerve was assessed using light microscopy (100x magnification). Next, each main stem crosssection was photographed (16x magnification) and the images were analyzed using Java ImageJ (version 1.46d) developed by Wayne Rasband (National Institute of Health) [7]. The cross-sectional area, transverse and longitudinal dimensions and the number of nerve bundles in the median nerve were calculated. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was conducted using computer software Statistica 10.0 PL by StatSoft Poland. To analyze the data, elements of descriptive statistics were used (mean, standard deviation, percentage distribution, minimum value, maximum value). To assess differences between groups the Students t-test was used. The significance level was set at p < RESULTS Anthropometric measurements The width of the wrist in the whole group varied from 4.50 cm to 6.20 cm (mean 5.43 cm). The width of the metacarpus varied from 6.30 cm to 9.10 cm (mean 7.88 cm). The distance between the TS and the ID varied from 7.40 cm to cm (mean 9.12 cm). The width of the flexor retinaculum (FR) varied from 2.10 cm to 4.20 cm (mean 2.75 cm). The distance between the TS and the point where the motor branch (MB) of the median nerve branched off the median nerve varied from 1.80 cm to 4.50 cm (mean 2.92 cm).
5 21 Anthropometric measurements comparison by gender is presented in Table 1. Anthropometric measurements comparison by side did not reveal any statistically significant differences. Anthropometric measurements comparison by gender Table 1 Measurements [cm] Women Men Mean SD Mean SD p-value CR-CU < MR-MU < TS-ID FR width TR-MB distance SD Standard deviation; CR Carpale radiale; CU Carpale ulnare; MR Metacarpale radiale; MU Metacarpale ulnare; TS Scaphoid tuberculum; ID Interdigitalis II III Histological measurements The cross-sectional area of the median nerve varied from cm 2 to 0.36 cm 2 (mean 0.19 cm 2 ). The longitudinal dimensions varied between 0.40 cm to 0.79 cm (mean 0.59 cm). The transverse dimensions varied between 0.28 cm to 0.79 cm (mean 0.40 cm). The number of nerve bundles in the stem of the median nerve varied from 13 to 38 (mean 24.97). No particular arrangement of median nerve nerve bundles was observed at the level of the carpal tunnel. Histological measurements comparison by gender did not reveal any statistically significant differences. When comparing sides, the cross-sectional area of the right median nerve (0.216 ± 0.06 cm 2 ) was statistically significantly larger (p = 0.017) then the cross-sectional area of the left median nerve (0.173 ± 0.05 cm 2 ). No correlation was noted between the anthropometric and histological measurements obtained in this study. DISCUSSION This study presents data on the subject of anthropometric measurements of the human hand and histological measurements and structure of the median nerve, and their possible correlations. To the authors knowledge this is the first study assessing such correlations.
6 22 In this study the anthropometric measurements had no impact on the histological measurements of the median nerve. When preparing this study we based on the fact that several authors showed that wrist ratio and wrist circumference can be independent risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) development [8]. Moghtaderi et al. [8] revealed that wrist ratio could be an independent risk for CTS development, while wrist circumference might have a protective effect. Boz et al. [9] showed that wrist ratio, shape index and digit index were independent risk factors in females, but failed to show statistically any significant difference between male cases and controls in these measurements. There are several other studies that have depicted wrist ratio as the prime suspect in the establishment of CTS [8 10]. The role of wrist ratio in CTS development is not fully understood but several theories pretending to explaining this exist. There may be a potential link between wrist ratio and variations in carpal stenosis in the dynamic and static relationship of structures and median nerve abnormalities [10]. Specific wrist shapes may increase the potential for CTS to develop, because of an increase in repetitive hand movements, making the subject more susceptible to CTS [11]. At the assessed level there was no particular type of nerve bundle arrangement in the median nerve or in its motor branch. This finding is consistent with other studies assessing the cross-sections of other human nerves such as the oculomotor nerve [12]. When comparing sides, the right median nerves had a significantly larger cross-sectional area (on the level of the carpal tunnel), which might be contributed to the fact that the majority of the Polish population is righthanded. The mean cross-sectional area of the median nerve obtained in our study is significantly larger (0.19 vs cm 2 ; p < ) than in the study by Yao and Gai [13]. This might relate to anatomic differences in the perceived boundary of the nerve in magnetic resonance imaging. This problem disappears when using computer-assisted histological image analysis [7]. Further studies conducted on larger sample groups, using immunohistochemistry [14, 15], should concentrate on the role of median nerve motor and sensory nerve bundles and their correlations with anthropometric measurements of the hand. CONCLUSIONS CR-CU, MR-MU and TS-ID distances are larger in men then in women. Anthropometric measurements of the hand do not impact the histological measurements and structure of the human median nerve at the level of the carpal tunnel.
7 23 The number of nerve bundles in the stem of the median nerve varied from 13 to 38. The nerve bundles of the median nerve, at the level of the carpal tunnel, display no particular type of arrangement. None declared. CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT REFERENCES 1. Mizia E., Klimek-Piotrowska W., Walocha J., Rutowski R., Wojtala R.: The median nerve in the carpal tunnel. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2011, 70(1): Mizia E., Tomaszewski K.A., Goncerz G., Kurzydło W., Walocha J.: Median nerve thenar motor branch anatomical variations. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2012, 71(3): Demircay E., Civelek E., Cansever T., Kabatas S., Yilmaz C.: Anatomic variations of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel: a brief review of the literature. Turk Neurosurg. 2011, 21(3): Budhiraja V., Rastogi R., Asthana A.K.: Variations in the formation of the median nerve and its clinical correlation. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2012, 71(1): Uzel A.P., Bulla A., Laurent-Joye M., Caix P.: Antero-medial approach to the wrist: anatomic basis and new application in cases of fracture of the lunate facet. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2011, 70(3): Skrzat J.: Enhancement of the focal depth in anatomical photography. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2011, 70(4): Mizia E., Tomaszewski K.A., Lis G.J., Goncerz G., Kurzydło W.: The use of computer-assisted image analysis in measuring the histological structure of the human median nerve. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2012, 71(2): Moghtaderi A., Izadi S., Sharafadinzadeh N.: An evaluation of gender, body mass index, wrist circumference and wrist ratio as independent risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. 2005, 112(6): Boz C., Ozmenoglu M., Altunayoglu V., Velioglu S., Alioglu Z.: Individual risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome: an evaluation of body mass index, wrist index and hand anthropometric measurements. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2004, 106(4): Kouyoumdjian J.A., Zanetta D.M., Morita M.P.: Evaluation of age, body mass index, and wrist index as risk factors for carpal tunnel syndrome severity. Muscle Nerve. 2002, 25(1): Werner R.A., Andary M.: Carpal tunnel syndrome: pathophysiology and clinical neurophysiology. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002, 113(9): Sharma S., Ray B., Bhardwaj D., Dwivedi A.K., Roy T.S.: Age changes in the human oculomotor nerve a stereological study. Ann Anat. 2009, 191(3): Yao L., Gai N.: Median nerve cross-sectional area and MRI diffusion characteristics: normative values at the carpal tunnel. Skeletal Radiol. 2009, 38(4): Wang H., Ma F., Wang F., Liu D., Li X., Du S.: Identification of motor and sensory fascicles in peripheral nerve trunk using immunohistochemistry and micro-raman spectroscopy. J Trauma. 2011, 71(5): Walocha J.A., Szczepański W., Miodoński A.J., et al.: Application of acrylic emulsion Liquitex R (Binney and Smith) for the preparation of injection specimens and immunohistochemical studies an observation. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2003, 62(2):
8 24 1 Department of Anatomy Jagiellonian University Medical College ul. Kopernika 12, Kraków, Poland Head: dr hab. n. med. Jerzy Walocha, prof. UJ 2 Department of Dental Prosthetics Institute of Dentistry Jagiellonian University Medical College ul. Montelupich 4, Kraków, Poland Head: dr hab. n. med. Grażyna Wiśniewska 3 Department of Rehabilitation Institute of Physiotherapy Jagiellonian University Medical College ul. Michałowskiego 12, Kraków, Poland Head: dr n. med. Wojciech Szwarczyk Corresponding Author: Krzysztof Tomaszewski Department of Anatomy Jagiellonian University Medical College ul. Kopernika 12, Kraków, Poland Phone/Fax: krzysztof.tomaszewski@uj.edu.pl
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Muscles of the hand Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Thenar Muscles Thenar muscles are three short muscles located at base of the thumb. All are innervated by
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Computer-assisted assessment of the histological structure of the human sural nerve
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 292 297 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0046 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Computer-assisted assessment of the histological
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 73, No. 3, pp. 292 297 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2014.0046 Copyright 2014 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Computer-assisted assessment of the histological
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7
 Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Forearm and Wrist Regions Neumann Chapter 7 REVIEW AND HIGHLIGHTS OF OSTEOLOGY & ARTHROLOGY Radius dorsal radial tubercle radial styloid process Ulna ulnar styloid process ulnar head Carpals Proximal Row
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락
 Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist & Hand Ultrasonography 대구가톨릭대학교병원재활의학과 권동락 Dorsal Wrist Evaluation (1 st Compartment) EPB APL Transverse View APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis Dorsal Wrist Evaluation
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
MEDIAN NERVE (ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS) AND CARPAL TUNEL SYNDROME REVISITED
 FOLIA MEDICA CRACOVIENSIA Vol. LIII, 4, 2013: 37 46 PL ISSN 0015-5616 37 Ewa Mizia 1, Krzysztof Tomaszewski 1, Paweł Depukat 1, Wiesława Klimek-Piotrowska 1, Artur Pasternak 1, Izabela Mróz 1, Tomasz Bonczar
FOLIA MEDICA CRACOVIENSIA Vol. LIII, 4, 2013: 37 46 PL ISSN 0015-5616 37 Ewa Mizia 1, Krzysztof Tomaszewski 1, Paweł Depukat 1, Wiesława Klimek-Piotrowska 1, Artur Pasternak 1, Izabela Mróz 1, Tomasz Bonczar
10/15/2014. Wrist. Clarification of Terms. Clarification of Terms cont
 Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
Wrist Clarification of Terms Palmar is synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Ventral is also synonymous with anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal refers to the posterior aspect
divided by the bones ( redius and ulna ) and interosseous membrane into :
 fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
fossa Cubital Has: * floor. * roof : - Skin - superficial fasica - deep fascia ( include bicipital aponeurosis ) Structures within the roof : -cephalic and basilic veins -and between them median cubital
The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. In Slide #2 there was a mistake where the doctor mentioned lateral septum twice.
 We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
We should only know: Name, action & nerve supply Layers - Skin - Superficial fascia - Deep fascia The hand is full with sweat glands, activated at times of stress. Deep fascia In Slide #2 there was a mistake
Hand and Wrist Editing file. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation
 Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Hand and Wrist Editing file Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives Describe the anatomy of the deep fascia of the wrist & hand (flexor & extensor retinacula & palmar aponeurosis).
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings
 Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Ultrasonography of the wrist - a step-by-step approach to study protocols and normal findings Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno, A. P. Pissarra,
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series 2017-2018 Anatomy -
Anatomy - Hand. Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics. Osteology. Carpal Arch. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Wrist and Hand Anatomy/Biomechanics Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT The wrist The metacarpals The Phalanges Digit 1 thumb Digit 5 digiti minimi Anatomy - Hand Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
8/25/2014. Radiocarpal Joint. Midcarpal Joint. Osteology of the Wrist
 Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Structure and Function of the Wrist 2 joints and 10 different bones Combine to create wrist motion Anatomical Terms: Wrist/Hand Palmar = anterior aspect of the wrist and hand Dorsal = posterior aspect
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
The hand. it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand**
 Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Today at 12:48 AM The hand it's the most important subject of the upper limb because it has a clinical importance. the palm of the hand** -the palmar aponeurosis located in the palm of the hand which is
Small muscles of the hand
 By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
By the name of Allah Small muscles of the hand Revision: The palmar aponeurosis is triangular in shape with apex and base. It is divided into 4 bands that radiate to the medial four fingers. Dupuytren
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]
![[[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]] [[Sally Leaning Towards Peter To Take Cold Hand]]](/thumbs/84/91174469.jpg) In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
In this lecture we will talk about the bones of the hand, and the muscles and contents of the forearm. *The hand bones are: - Carpal bones. -Metacarpals. -Phalanges. *The carpal bones (wrist bones): They
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
13 13/3/2012. Adel Muhanna
 13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
13 13/3/2012 Adel Muhanna بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The Hand Extensor retinaculum: Deep fascia of anterior compartment of the wrist is thickened to form flexor retinaculum : a bridge that have 6 structures
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Viorel Nacu. The clinical anatomy of the Hand
 Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Viorel Nacu The clinical anatomy of the Hand The distal part of the upper limb is divided in to three regions: 1. The wrist (carpus) 2. The hand (metacarpus) 3. The digits (fingers) The landmarks of this
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
 Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles
 Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
Lecture 9: Forearm bones and muscles Remember, the region between the shoulder and the elbow = brachium/arm, between elbow and wrist = antebrachium/forearm. Forearm bones : Humerus (distal ends) Radius
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 October 6, 2006 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (8 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) B C A. _pisiform B. _ulnar artery A C. _flexor carpi
The Forearm 2. Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm
 The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
The Forearm 2 Extensor & lateral Compartments of the Forearm 1-Lateral Fascial Compartment (at the lateral side of the forearm ) *Some books mention the lateral compartment contain just the Brachioradialis
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages External surfaces of ribs 3-5
 MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
MUSCLE ORIGIN INSERTION ACTION NERVE Pectoralis Major medial half of clavicle; Sternum; upper six costal cartilages Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of horizontal adduction Medial and lateral pectoral
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful
 In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
In the name of Allah, Most gracious, Most merciful This lecture includes the following: The Palmer Oponeurosis. The Carpel tunnel. The palmaris brevis muscle. The anatomical snuffbox. The Fibrous flexor
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES
 LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
LECTURE 8 HANDS: BONES AND MUSCLES WRIST AND HAND - Human hand can do power grip and precision grip - Thumb is 90 to the rest of the hand can do fine actions - Often able to do power actions o Take tools
BRACHIAL PLEXUS. DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae
 THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS DORSAL SCAPULAR NERVE (C5) supraclavicular branch innervates rhomboids (major and minor) and levator scapulae SCHEMA OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS PHRENIC NERVE supraclavicular
compartments of the forearm
 " forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
" forearm posterior compartment " compartments of the forearm Posterior Fascial compartment Muscles: ** The superficial group 1. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 2. Ex. digitorum 3. Ex. digiti minimi 4.
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
Morphological Variations in Lumbricals of Hand A Cadaveric Study
 IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
IBIMA Publishing Plastic Surgery: An International Journal http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/psij/psij.html Vol. 2013 (2013), Article ID 821692, 7 pages DOI: 10.5171/2013.821692 Morphological Variations
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk
 Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Module 7 - The Muscular System Muscles of the Arm and Trunk This Module will cover the muscle anatomy of the arms and trunk. We have already seen the muscles that move the humerus, so this module will
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON
 REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
REFERENCE DIAGRAMS OF UPPER LIMB MUSCLES: NAMES, LOCATIONS, ATTACHMENTS, FUNCTIONS MUSCLES CONNECTING THE UPPER LIMB TO THE AXIAL SKELETON A25LAB EXERCISES: UPPER LIMB MUSCLES Page 1 MUSCLES CONNECTING
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
# Anatomy. Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla. Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil. Page 0 of 16
 #10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
#10 25 Anatomy Upper Extremities Muscles and anatomy of axilla Tiba Al-Ani 9/10/2015 Nabil Page 0 of 16 Salam AWN Today s lecture is divided into two parts, the first part is the continuation of the upper
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Supplied in part by the musculocutaneous nerve. Forms the axis of rotation in movements of pronation and supination
 Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy: Upper limb (15 questions) 1. Latissimus Dorsi: Is innervated by the dorsal scapular nerve Lies above feres major muscle Medially rotates the humerus All of the above 2. Supinator muscle is: Deep
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
High-resolution Ultrasound of the Thenar Motor Branch of the Median Nerve
 High-resolution Ultrasound of the Thenar Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Poster No.: C-1727 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: F. Zaottini, J. Smith, S. Airaldi, C. Martinoli ; Genova/IT,
High-resolution Ultrasound of the Thenar Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Poster No.: C-1727 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: F. Zaottini, J. Smith, S. Airaldi, C. Martinoli ; Genova/IT,
Cubital fossa and forearm
 Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
Cubital fossa and forearm Cubital fossa is the triangular space in front of elbow joint. - The Cubital fossa has boundaries: apex, base, roof and floor and it has contents. The base: an imaginary horizontal
ULNAR NERVE, ITS TERMINATION AND SUPERFICIAL BRANCHES IN HAND: A CADAVERIC STUDY
 Original Research Article ULNAR NERVE, ITS TERMINATION AND SUPERFICIAL BRANCHES IN HAND: A CADAVERIC STUDY A Priyadarshini 1, Sudakshina Chakrabarti * 2, Gunapriya Raghunath 3. ABSTRACT International Journal
Original Research Article ULNAR NERVE, ITS TERMINATION AND SUPERFICIAL BRANCHES IN HAND: A CADAVERIC STUDY A Priyadarshini 1, Sudakshina Chakrabarti * 2, Gunapriya Raghunath 3. ABSTRACT International Journal
forearm posterior compartment
 Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Quick revision: The anterior compartment of the forearm contains of 8 muscles... -4 superficial -1 intermediate -3 deep *All supplied by median nerve except 1 and 1/2 muscle (by ulnar N.) forearm posterior
Anatomy of the Upper Limb
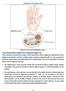 Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Anatomy of the Upper Limb Figure 53: The thenar & midpalmar spaces. The synovial (tendon) sheaths of the long flexors [Figure.54] These sheaths surround the tendons of the long flexors; flexor digitorum
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Abduction of arm until your hand rich your head. Flexion of forearm at elbow joint. Extension of arm at elbow joint. Flexion of fingers 10.
 Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Num. answer 1. Medialy With the manubrium ( sternum ), and laterally with the acromion of the scapula 2. 1. Trapezius 2. Levator scapulae 3. Rhomboids 3. 1. Pectoralis major 2. Pectoralis minor 3. Latissiumus
Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
ANATOMY. Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date :
 ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
ANATOMY Subject : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 11 Date : Median nerve Meaian nerve to Pronator teres Course: Enter cubital fossa. Pierce Pronat. teres Between to FDS, FOP Below and lateral
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report
 Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Article ID: WMC003387 ISSN 2046-1690 Variation of Superficial Palmar Arch: A Case Report Corresponding Author: Dr. Liju S Mathew, Demonstrator, Anatomy, Gulf Medical University, 4184 - United Arab Emirates
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel
 Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
Ulnar Neuropathy in the Distal Ulnar Tunnel DAVID W. SHUPE, PT, ATC' Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy A brief anatomical review of the ulnar nerve and areas of ulnar nerve entrapment is
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017
 Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Difference Between Angle You Can Bend Your Left Wrist Back vs Your Right Wrist Jenna Priest Science Department Altoona High School January 25, 2017 Background 1- The wrist joint (also known as the radiocarpal
Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with Variant Branch of Ulnar Nerve
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.22126-17.2 Received: 23.11.2017 / Accepted: 07.02.2018 Published Online: 26.02.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.22126-17.2 Received: 23.11.2017 / Accepted: 07.02.2018 Published Online: 26.02.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation Co-Innervation of Triceps Brachii Muscle with
VARIANT ARTERIAL PATTERN IN THE FOREARM WITH ITS EMBRYOLOGICAL BASIS. Vaishnavi Joshi and Dr. Shaheen Sajid Rizvi
 Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
Volume-8, Issue-3 July-Sept-2018 Coden:IJPAJX-CAS-USA, Copyrights@2018 ISSN-2231-4490 Received: 8 th June-2018 Revised: 15 th July-2018 Accepted: 16 th July-2018 DOI: 10.21276/Ijpaes http://dx.doi.org/10.21276/ijpaes
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST
 MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
MR IMAGING OF THE WRIST Wrist Instability Dissociative Pattern apparent on routine radiographs Non-dissociative Stress / positional radiographs Dynamic fluoroscopy during stress Arthrography MRI / MR arthrography
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation.
 Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Elbow, Wrist & Hand Evaluation www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Common Injuries to the Elbow, Wrist, Hand & Fingers Lateral epicondylitis tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis golfer s s elbow, little league elbow
Clinical Study Sonographic Wrist Measurements and Detection of Anatomical Features in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 2014, Article ID 657906, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/657906 Clinical Study Sonographic Wrist Measurements and Detection of Anatomical
Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 2014, Article ID 657906, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/657906 Clinical Study Sonographic Wrist Measurements and Detection of Anatomical
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Interesting Case Series. Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression
 Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Interesting Case Series Posterior Interosseous Nerve Compression Jeon Cha, BMedSci, MBBS, Blair York, MBChB, and John Tawfik, MBBS, BPharm, FRACS The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney
Anatomical landmarks for safer carpal tunnel decompression: an experimental cadaveric study
 Samarakoon et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014, 8:8 RESEARCH Open Access Anatomical landmarks for safer carpal tunnel decompression: an experimental cadaveric study Lasitha B Samarakoon 1*, Malith H
Samarakoon et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2014, 8:8 RESEARCH Open Access Anatomical landmarks for safer carpal tunnel decompression: an experimental cadaveric study Lasitha B Samarakoon 1*, Malith H
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH!
 Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH! Case the athlete FOOSH from sporting event 2 days ago C/O wrist swelling, pain, worse with movement Hmmm Wrist pain Exam of the wrist - basics Appearance Swelling, bruising,
Acute Wrist Injuries OUCH! Case the athlete FOOSH from sporting event 2 days ago C/O wrist swelling, pain, worse with movement Hmmm Wrist pain Exam of the wrist - basics Appearance Swelling, bruising,
Wrist, Elbow Hand. Surface Recording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle
 Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Clinical and Electrophysiological Study in Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
 IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2015), PP 32-37 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Electrophysiological
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-issn: 2278-3008, p-issn:2319-7676. Volume 10, Issue 3 Ver. IV (May - Jun. 2015), PP 32-37 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Electrophysiological
ANATOMY. Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date :
 ANATOMY Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date : HAND Skin ~ Thick and shovv many flexure creases (folds). ~ Flexure creases are an important landmarks. 111 Proximal palmar crease.
ANATOMY Su~,ect : Lecturer : Maher Hadidi Done by: lecture # : 1 3 Date : HAND Skin ~ Thick and shovv many flexure creases (folds). ~ Flexure creases are an important landmarks. 111 Proximal palmar crease.
Wrist movements, apart from the distal radioulnar joint, take place in two planes:
 The wrist consists of eight bones in two rows: the proximal and distal. The proximal row includes (starting from the radial bone): the scaphoid bone, the lunate bone, the triangular bone and the postulnar
The wrist consists of eight bones in two rows: the proximal and distal. The proximal row includes (starting from the radial bone): the scaphoid bone, the lunate bone, the triangular bone and the postulnar
Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial Radial Nerve and Cephalic Vein Ki Hoon Kim, MD, Eun Jin Byun, MD, Eun Hyun Oh, MD
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):52-56 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(1):52-56 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.1.52 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Ultrasonographic Findings of Superficial
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
1/13/2013. Anatomy Guy Dissection Sheet Extensor Forearm and Hand. Eastern Virginia Medical School
 Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
Dr. Craig Goodmurphy Anatomy Guy Superficial Extensor Muscles Complete skin removal if necessary then remove the antebrachial fascia starting at the extensor retinaculum and working proximally. Define
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow.
 MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
MLT Muscle(s) Patient Position Therapist position Stabilization Limb Position Picture Put biceps on slack by bending elbow. Pectoralis Minor Supine, arm at side, elbows extended, supinated Head of Table
