Laurent Itti: CS564 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 4: Experimental techniques in visual neuroscience. Reading Assignments: None!
|
|
|
- Jasmine Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CS 564 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Experimental techniques in visual neuroscience Reading Assignments: None! 1
2 Today we will briefly review - electrophysiological recording and stimulation - visual psychophysics - functional neuroimaging -positron emission tomography (PET) -single-photo emission tomography (SPECT) -functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) - optical imaging - electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG) 2
3 Electrophysiology Basic idea: record electrical activity associated with neuronal activity, using electrodes inserted in the brain of an animal. Typical setup for visual experiment: - animal is either anaesthetized or awake. - various stimuli are presented on computer screen. - activity of one neuron or a small group is recorded for a few seconds around stimulus presentation. - (optional): if awake, animal may be doing a visual task and give responses, e.g., by pressing a button. - many such trials are acquired from many different recording sites. - recordings are pooled and analyzed. 3
4 Typical Setup 4
5 Electrode setup - drill hole in cranium under anesthesia - install and seal recording chamber - allow animal to wake up and heal - because there are no pain receptors in brain, electrodes can then be inserted & moved in chamber with no discomfort to animal. 5
6 - Connect electrodes to amplifier & noise supression board. - Sample & record. - Label & store data. Recording setup Result: sampled traces of V or I as function of time. 6
7 Multi-Electrode Arrays Allow simultaneous recording from many locations. Problem: does that mean from many neurons? The answer is no. Much signal processing needed to separate sources. 7
8 Localization & source separation Main problem: we don t see the image below! With individually adjustable electrodes: slowly advance them until a clear signal is obtained. With fixed arrays: separate sources by post-processing software. 8
9 Visual Electrophysiology: Receptive Field Issue: Neurons in visual processing areas do not respond to every location in visual field. Recall: retinotopic organization. So, once a neuron is localized, we also need to localize its receptive field, that is, the region of visual space (or computer screen) in which the presentation of a stimulus will elicit a response from our neuron. Kuffler (1953): shine a spot of light at many different locations over screen and monitor cell activity. All locations where light elicits neuronal response belong to neuron s receptive field (RF). 9
10 Receptive field 10
11 RFs increase in size and complexity 11
12 Raster Displays and Histograms 12
13 Single-unit recording in humans! Kreiman & Koch,
14 Single-unit recording in humans 14
15 Visual Psychophysics Basic idea: instead of recording from individual neurons, record from the whole organism. Typical setup for visual experiment: - animal or human subject is always awake. - a stimulus appears on computer screen, and subject is asked to make a judgment about the stimulus. - subject reports judgment, e.g., by pressing a button. - experimenter monitors subject responses over many trials and modifies stimulus during experiment so that judgment becomes harder and harder to make. - from results over many trials, experimenter can compute the subject s threshold, i.e., the breaking point in the subject s ability to make the judgment. 15
16 Example: yes/no task Example of contrast discrimination using yes/no paradigm. - subject fixates cross. - subject initiates trial by pressing space bar. - stimulus appears at random location, or may not appear at all. - subject presses 1 for stimulus present or 2 for stimulus absent. - if subject keeps giving correct answers, experimenter decreases contrast of stimulus (so that it becomes harder to see). + time 16
17 Staircase procedure Staircase procedure is a method for adjusting stimulus to each observer such as to find the observer s threshold. Stimulus is parametrized, and parameter(s) are adjusted during experiment depending on responses. Typically: - start with a stimulus that is very easy to see. - 4 consecutive correct answers make stimulus more difficult to see by a fixed amount. - 2 consecutive incorrect answers make stimulus easier to see by a fixed amount. 17
18 Psychophysical threshold The threshold is the value of the stimulus parameter for which a given probability of making a correct judgment is obtained. Typically, in a yes/no task: - chance level = 50% correct. - perfect judgment every time = 100% correct. - threshold set at 75% correct. 18
19 Confusing terminology The threshold is the value of the stimulus parameter for which the threshold performance (e.g., 75% correct) is reached. This notion thus is highly task-dependent. For example: A contrast threshold may be the value of contrast for which 75% correct discrimination in the task was there a stimulus? is obtained. An orientation threshold may be the angle for which 75% correct discrimination in the task was the stimulus vertical or tilted? is obtained. and so on 19
20 Better presentation techniques: 2AFC One problem with the yes/no paradigm is that observers may develop a bias in their judgment (e.g., always answer yes when not sure). The (temporal) two-alternative forced-choice (2AFC) paradigm eliminates this problem by always showing two stimulus alternatives, one after the other, in random order, and by forcing the observer to report on the order in which those two alternatives appeared. e.g., a vertical and tilted gratings appear in random order; the observers answers was the stimulus vertical then tilted? In the spatial 2AFC, both stimulus alternatives appear simultaneously, next to each other. 20
21 Example of psychophysical data 21
22 Functional Neuroimaging Basic idea: monitor brain activity using an external, non-invasive machine, and do it simultaneously for the entire brain (at the cost of a fairly low spatial and temporal resolution). Typical setup for a visual experiment: - subject lies in scanner and views stimuli on a screen. - an image of the brain is taken at rest. - subject does a visual task. - an image of the brain is taken during or just after task. - the difference between rest and task images tells us what changed in subject brain because of task. Thus, the subject (at rest) is his/her own reference for detecting taskrelated activation. 22
23 Different imaging techniques - Nuclear medicine (PET and SPECT): inject a radioactive tracer into the subject s blood stream. Tracer will get trapped into those neurons which are active. Thus, imaging the radioactive regions in the subject s brain reveals those areas where strong neuronal activity was present during experiment. - functional MRI: most commonly, exploit the property that oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin have distinct magnetic properties; thus regions where magnetic changes are seen indicate higher consumption of oxygen, and, by inference, higher neuronal activity. - perfusion MRI: inject a paramagnetic tracer into blood stream; thus, regions where magnetic properties change are where a lot of blood arrives, presumably because of neural activity. - MR spectroscopy: different chemicals have different resonance frequencies; thus, by sweeping over those frequencies and recording resonance responses, we measure concentration of chemicals. 23
24 Single-Photon Emission Tomography Basic physics: - uses gamma-radioactive elements: those emit a gamma photon as they transition to a lower energy state. - the imaging tracer is a complex chemical, in which one element is gamma-radioactive. - gamma-ray detectors placed around the subject s head detect the gamma photons; this is done from different viewpoints (e.g., by rotating an array of detectors around the subject). - from the multiple projections of the subject s head, a 3D volume can be reconstructed by tomographic reconstruction. Typical tracers: HMPAO ( 99m Tc hexamethyl propylene amine oxime enters neurons and is metabolized and trapped); 201 Tl-based agents enter tumors; ECD ( 99m Tc ethyl cysteinate dimer) is similar to HMPAO; but also tracers to specifically image lungs, bone, specific glands and organs, etc. 24
25 Tomographic reconstruction 25
26 Example SPECT images 26
27 Positron Emission Tomography Basic physics: - some radioactive elements emit a positron (e+) as they transition to a lower energy level. - the positron (an anti-particle) soon collides with a nearby electron (e- ), yielding an annihilation. - energy is liberated during the annihilation by the emission of two gamma photons traveling in exactly opposite direction. - a ring of gamma light detectors around the subject s head captures the photons. - because we know that annihilation yields two opposed photons, the reconstruction algorithm can take this into account to eliminate scatter. Results in better resolution than SPECT. Typical tracers: radioactive labeled oxygen ( 15 O) or glucose ( 18 F FDG; fluoro-deoxy glucose). 27
28 Reconstruction using coincidence 28
29 Example PET image 29
30 Use in activation studies Show difference image between, e.g., rest and task, superimposed onto a structural scan (here MRI), possibly normalized to a standard coordinate system (here Talairach). Maguire et al.,
31 Use in activation studies 31
32 PET vs. SPECT Positron-emitting elements are to create and have very short half-life (a few minutes). PET scanners require cyclotron on premises. SPECT tracers easily created by mixing two stable reactants. Coincidence in PET yields better resolution and less scatter. SPECT tracers applicable to wider range of studies (lungs, bone, grands, etc). SPECT tracers decay more slowly so scans cannot be made as often as PET. 32
33 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basic idea: protons in brain have a magnetic moment; when placed in a magnetic field the moments align with the field and precess around it; an RF pulse can kick them out of alignment; their precession can then be picked up by sensitive coils (dynamo effect). Use in visual neuroscience: - regular MRI provides very detailed anatomical information - functional MRI for more info: 33
34 34
35 35
36 36
37 37
38 38
39 39
40 40
41 41
42 42
43 43
44 44
45 45
46 46
47 47
48 BOLD effect Blood-oxygen level-dependent effect: the presence of fresh (oxygenated) blood affects the MRI signal. no magnetic moment magnetic moment Fe Oxyhemoglobin Fe Deoxyhemoglobin The magnetic moment of deoxyhemoglobin leads to an increase of the magnetic field in the surrounding of the erythrocytes. B 48
49 BOLD contrast The magnetic properties of blood change with the amount of oxygenation resulting in small signal changes Bo with deoxygenated blood Bo with oxygenated blood 49
50 Vascular System arteries arterioles (<0.1mm) capillaries venules (<0.1mm) veins 50
51 Oxygen consumpsion O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 The exclusive source of metabolic energy of the brain is glycolysis: O O 2 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 C 6 H 12 O O 2 6 H 2 O+ 6 CO 2 O O 2 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 51
52 BOLD Contrast stimulation neuronal activation metabolic changes hemodynamic changes local susceptibility changes MR-signal changes signal detection data processing functional image 52
53 Note about BOLD effect The observed change in the MR signal indicates an increase of oxygenation in the activated areas! So, what we measure is an overshoot in the brain s vascular response to oxygen consumption. neural activity => oxygen consumption => oxygen depletion => vascular response: increase blood supply => more oxygenated blood arrives at site of activity => increased concentration of oxyhemoglobin picked by MRI BOLD measures a hemodynamic (change in blood supply) response. 53
54 Fast response & early dip 54
55 Two basic classes: Experimental paradigms - Blocked: rest for a while, do task for a while; repeat. Subtract average activity during rest from that during task. - Single-event: do a single trial of task once in a while (possibly at randomly distributed times); record activity associated with each event; re-align all recordings and compute statistics on the average. 55
56 Example of Blocked paradigm Gandhi et al.,
57 First BOLD-effect experiment Kwong and colleagues at Mass. General Hospital (Boston). Stimulus: flashing light. 57
58 Example: ball-tracking Attentional Tracking Passive Viewing 3 Targets 7 Distractors 0 Targets Ernst et al.,
59 Ball-tracking: activation Parietal (Post. PC) Dorsal CS CS Posterior z > Women 7 Men No gender differences, or lateralization MT/V5 MT/V5 Right Left 59
60 Single-event responses 60
61 Optical imaging Basic idea: reflectance properties of neurons change with activity. 61
62 Optical imaging of V1 62
63 Optical imaging of V1 63
64 V1 orientation & ocular dominance columns 64
65 Electroencephalography (EEG) Basic idea: detect electrical fields generated by neural activity, using electrodes placed at surface of skin. 65
66 EEG terminology VEP = visually-evoked potentials ERP = event-related potentials OSP = omitted-stimulus potentials are all EEGs 66
67 Magnetoencephalography (MEG) Basic idea: detect magnetic fields generated by brain activity, using an array of very sensitive coils. difficulty: magnetic field generated by the conjoint activity of 100,000 neurons is on the order of a few femtotesla (10-15 ); in comparison, earth magnetic field around 10-5 Tesla. hence: use very sensitive magnetic detectors (SQUID: Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices that work in liquid helium at 269 degrees C), and place machine in magnetically shielded room. inherent limitation: coils can only pickup the component of the magnetic fields that is perpendicular to them. 67
68 MEG machine 68
69 Raw MEG data 69
70 MEG activity in auditory cortex One trace is shown per detector. Activity is found in auditory cortex about 80ms after onset of auditory stimulus. 70
71 Mapping MEG results onto anatomy Localization of auditory activation source with respect to array of detectors. 71
72 MEG source localization A mix of activity from several sources is detected by several detectors; hence we have a source separation problem. 72
73 Combination of techniques from Rosen et al.,
74 Summary 74
75 Summary 2 75
Non-Invasive Techniques
 Non-Invasive Techniques Key: Does not hurt the organism Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the video presentation
Non-Invasive Techniques Key: Does not hurt the organism Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the video presentation
Non-Invasive Techniques
 Many Procedures Non-Invasive Techniques Key: Does not hurt the organism Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the
Many Procedures Non-Invasive Techniques Key: Does not hurt the organism Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides or view the
Outline. Biological Psychology: Research Methods. Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz
 Biological Psychology: Research Methods Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz Outline Neuroscience Methods Histology Electrophysiological Recordings Lesion Neuroimaging Neuroanatomy Histology: Brain structure
Biological Psychology: Research Methods Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz Outline Neuroscience Methods Histology Electrophysiological Recordings Lesion Neuroimaging Neuroanatomy Histology: Brain structure
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 17. Peeking Inside The Head. Part 1. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 17 Peeking Inside The Head Part 1 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Imaging The Living Brain! Computed Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 17 Peeking Inside The Head Part 1 Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Imaging The Living Brain! Computed Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional
Beyond fmri. Joe Kable Summer Workshop on Decision Neuroscience August 21, 2009
 Beyond fmri Joe Kable Summer Workshop on Decision Neuroscience August 21, 2009 What are the strengths of fmri?! Noninvasive, safe! Can be done in humans! Verified correlate of neural activity! Great spatio-temporal
Beyond fmri Joe Kable Summer Workshop on Decision Neuroscience August 21, 2009 What are the strengths of fmri?! Noninvasive, safe! Can be done in humans! Verified correlate of neural activity! Great spatio-temporal
Neuroimaging. BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT. Human Brain Mapping
 11/8/2013 Neuroimaging N i i BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT 2 Human Brain Mapping H Human m n brain br in m mapping ppin can nb
11/8/2013 Neuroimaging N i i BIE601 Advanced Biological Engineering Dr. Boonserm Kaewkamnerdpong Biological Engineering Program, KMUTT 2 Human Brain Mapping H Human m n brain br in m mapping ppin can nb
Introduction to Brain Imaging
 Introduction to Brain Imaging Human Brain Imaging NEUR 570 & BIC lecture series September 9, 2013 Petra Schweinhardt, MD PhD Montreal Neurological Institute McGill University Montreal, Canada Various techniques
Introduction to Brain Imaging Human Brain Imaging NEUR 570 & BIC lecture series September 9, 2013 Petra Schweinhardt, MD PhD Montreal Neurological Institute McGill University Montreal, Canada Various techniques
P2 Visual - Perception
 P2 Visual - Perception 2014 SOSE Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions gyula.kovacs@uni-jena.de 11/09/06 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) The very basics What is fmri? What is MRI? The
P2 Visual - Perception 2014 SOSE Neuroimaging of high-level visual functions gyula.kovacs@uni-jena.de 11/09/06 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) The very basics What is fmri? What is MRI? The
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION. Alternatives to BOLD for fmri
 PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
PHYSICS OF MRI ACQUISITION Quick Review for fmri HST-583, Fall 2002 HST.583: Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology
Neuroimaging and Assessment Methods
 Psych 2200, Lecture 5 Experimental Design and Brain Imaging Methods Tues Sept 15, 2015 Revised TA office hours (Sam), today 4-5p, and wed 11:30-1:30. I will not have office hours this thurs but you should
Psych 2200, Lecture 5 Experimental Design and Brain Imaging Methods Tues Sept 15, 2015 Revised TA office hours (Sam), today 4-5p, and wed 11:30-1:30. I will not have office hours this thurs but you should
Brain and Cognition. Cognitive Neuroscience. If the brain were simple enough to understand, we would be too stupid to understand it
 Brain and Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience If the brain were simple enough to understand, we would be too stupid to understand it 1 The Chemical Synapse 2 Chemical Neurotransmission At rest, the synapse
Brain and Cognition Cognitive Neuroscience If the brain were simple enough to understand, we would be too stupid to understand it 1 The Chemical Synapse 2 Chemical Neurotransmission At rest, the synapse
Methods for assessing the brain basis of developmental disorders
 Announcements LIGN171: Child Language Acquisition http://ling.ucsd.edu/courses/lign171 Final Exam will be a take-home exam Format similar to the short assignment (no multiple choice, etc.) Will be handed
Announcements LIGN171: Child Language Acquisition http://ling.ucsd.edu/courses/lign171 Final Exam will be a take-home exam Format similar to the short assignment (no multiple choice, etc.) Will be handed
Ways to Study Brain Structures and Functioning. Can physically trace connections. Ablation. Is the most primitive Can be done with any structures
 Ways to Study Brain Structures and Functioning Can physically trace connections Is the most primitive Can be done with any structures Ablation Can remove a piece of the brain and see what happens If the
Ways to Study Brain Structures and Functioning Can physically trace connections Is the most primitive Can be done with any structures Ablation Can remove a piece of the brain and see what happens If the
Announcements. Final Exam will be a take-home exam. Format similar to the short assignment (no multiple choice, etc.)
 Announcements Final Exam will be a take-home exam Format similar to the short assignment (no multiple choice, etc.) Will be handed out at end of last class period (Thursday June 5 th ) Due by 6 pm June
Announcements Final Exam will be a take-home exam Format similar to the short assignment (no multiple choice, etc.) Will be handed out at end of last class period (Thursday June 5 th ) Due by 6 pm June
Table 1. Summary of PET and fmri Methods. What is imaged PET fmri BOLD (T2*) Regional brain activation. Blood flow ( 15 O) Arterial spin tagging (AST)
 Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
Table 1 Summary of PET and fmri Methods What is imaged PET fmri Brain structure Regional brain activation Anatomical connectivity Receptor binding and regional chemical distribution Blood flow ( 15 O)
The Cognitive Neuroscientist s Toolkit
 The Cognitive Neuroscientist s Toolkit Jesse Rissman CS 182 Guest Lecture, 2/1/07 QuickTimeª and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. LESION PET fmri EEG/MEG TMS A little
The Cognitive Neuroscientist s Toolkit Jesse Rissman CS 182 Guest Lecture, 2/1/07 QuickTimeª and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. LESION PET fmri EEG/MEG TMS A little
Eavesdropping on the Mind. COGS 17 - Winter 2019 Andrew Shibata
 Eavesdropping on the Mind COGS 17 - Winter 2019 Andrew Shibata Announcements - Midterm I is next Tuesday! - Exam is worth 25% of your grade - Homework 1 is due at the exam (worth 2.5% of grade) - Review
Eavesdropping on the Mind COGS 17 - Winter 2019 Andrew Shibata Announcements - Midterm I is next Tuesday! - Exam is worth 25% of your grade - Homework 1 is due at the exam (worth 2.5% of grade) - Review
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits
 Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Prof. Greg Francis 1/2/19
 Brain scans PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 03 How to study the brain without killing someone. Scanning Technology provides insight into brain processes w EEG recordings w MRI w Non-invasive Maps of brain
Brain scans PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 03 How to study the brain without killing someone. Scanning Technology provides insight into brain processes w EEG recordings w MRI w Non-invasive Maps of brain
fmri: What Does It Measure?
 fmri: What Does It Measure? Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/02/2018: Lecture 02-1 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
fmri: What Does It Measure? Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/02/2018: Lecture 02-1 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Syllabus References. Resources. Video: MRI Introduction
 MRI Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.6.4.2.5 Define precessing and relate the frequency of the precessing to the composition of the nuclei and the strength of the applied external magnetic field 9.6.4.2.6
MRI Lesson Outline Syllabus References 9.6.4.2.5 Define precessing and relate the frequency of the precessing to the composition of the nuclei and the strength of the applied external magnetic field 9.6.4.2.6
Competing Streams at the Cocktail Party
 Competing Streams at the Cocktail Party A Neural and Behavioral Study of Auditory Attention Jonathan Z. Simon Neuroscience and Cognitive Sciences / Biology / Electrical & Computer Engineering University
Competing Streams at the Cocktail Party A Neural and Behavioral Study of Auditory Attention Jonathan Z. Simon Neuroscience and Cognitive Sciences / Biology / Electrical & Computer Engineering University
Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain
 Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain! Contrast X-rays! Computerized Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional MRI! Magnetoencephalography
Methods of Visualizing the Living Human Brain! Contrast X-rays! Computerized Tomography (CT)! Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)! Positron Emission Tomography (PET)! Functional MRI! Magnetoencephalography
LESSON 1.3 WORKBOOK. How can we study the behaving brain?
 LESSON 1.3 WORKBOOK How can we study the behaving brain? We are in the middle of a technological revolution when it comes to how closely we can look at the behaving brain. Scientists and doctors now have
LESSON 1.3 WORKBOOK How can we study the behaving brain? We are in the middle of a technological revolution when it comes to how closely we can look at the behaving brain. Scientists and doctors now have
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function:
 Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
Neural Correlates of Human Cognitive Function: A Comparison of Electrophysiological and Other Neuroimaging Approaches Leun J. Otten Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience & Department of Psychology University
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION
 HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
HST 583 fmri DATA ANALYSIS AND ACQUISITION Neural Signal Processing for Functional Neuroimaging Neuroscience Statistics Research Laboratory Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School/MIT Division
What is cognitive neuroscience?
 9.63 - Fall 2005 Lecture 7 Ben Balas Courtesy of Ben Balas. Used with permission. What is cognitive neuroscience? Experimental Psychology is more or less the study of subjects behavior subject to various
9.63 - Fall 2005 Lecture 7 Ben Balas Courtesy of Ben Balas. Used with permission. What is cognitive neuroscience? Experimental Psychology is more or less the study of subjects behavior subject to various
Molecular Imaging and the Brain
 Molecular imaging technologies are playing an important role in neuroimaging, a branch of medical imaging, by providing a window into the living brain. Where CT and conventional MR imaging provide important
Molecular imaging technologies are playing an important role in neuroimaging, a branch of medical imaging, by providing a window into the living brain. Where CT and conventional MR imaging provide important
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
 Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 10: Brain-Computer Interfaces Ilya Kuzovkin So Far Stimulus So Far So Far Stimulus What are the neuroimaging techniques you know about? Stimulus So Far
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience Lecture 10: Brain-Computer Interfaces Ilya Kuzovkin So Far Stimulus So Far So Far Stimulus What are the neuroimaging techniques you know about? Stimulus So Far
Introduction to Functional MRI
 Introduction to Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory University of Michigan Outline Brief overview of physiology and physics of BOLD fmri Background
Introduction to Functional MRI Douglas C. Noll Department of Biomedical Engineering Functional MRI Laboratory University of Michigan Outline Brief overview of physiology and physics of BOLD fmri Background
Physiological and Physical Basis of Functional Brain Imaging 6. EEG/MEG. Kâmil Uludağ, 20. November 2007
 Physiological and Physical Basis of Functional Brain Imaging 6. EEG/MEG Kâmil Uludağ, 20. November 2007 Course schedule 1. Overview 2. fmri (Spin dynamics, Image formation) 3. fmri (physiology) 4. fmri
Physiological and Physical Basis of Functional Brain Imaging 6. EEG/MEG Kâmil Uludağ, 20. November 2007 Course schedule 1. Overview 2. fmri (Spin dynamics, Image formation) 3. fmri (physiology) 4. fmri
A U. Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience 2/8/2016. Neat Stuff! Cognitive Psychology
 Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Neat Stuff! Optogenetics http://spie.org/newsroom/technical-articles-archive/videos/0411-boyden Stimulating the brain with light Cognitive Psychology Mental Representation
Methods of Cognitive Neuroscience Neat Stuff! Optogenetics http://spie.org/newsroom/technical-articles-archive/videos/0411-boyden Stimulating the brain with light Cognitive Psychology Mental Representation
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging. Danielle Wilson
 Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
The Tools: Imaging the Living Brain
 The Tools: Imaging the Living Brain I believe the study of neuroimaging has supported the localization of mental operations within the human brain. -Michael I. Posner, 2003 Neuroimaging methods Since Descarte
The Tools: Imaging the Living Brain I believe the study of neuroimaging has supported the localization of mental operations within the human brain. -Michael I. Posner, 2003 Neuroimaging methods Since Descarte
Intrinsic Signal Optical Imaging
 Intrinsic Signal Optical Imaging Introduction Intrinsic signal optical imaging (ISOI) is a technique used to map dynamics in single cells, brain slices and even and most importantly entire mammalian brains.
Intrinsic Signal Optical Imaging Introduction Intrinsic signal optical imaging (ISOI) is a technique used to map dynamics in single cells, brain slices and even and most importantly entire mammalian brains.
Chapter 1 Introduction. Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception
 1 Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception Introduction What do we mean by Sensation & Perception?
1 Introduction Chapter 1 Introduction Welcome to Our World Thresholds and the Dawn of Psychophysics Sensory Neuroscience and the Biology of Perception Introduction What do we mean by Sensation & Perception?
Nuclear imaging of the human brain
 Nuclear imaging of the human brain Steven Laureys Coma Science Group Cyclotron Research Centre & Neurology Dept. University of Liège, Belgium Neuroimaging structure function Neuroimaging: Modalities Structural
Nuclear imaging of the human brain Steven Laureys Coma Science Group Cyclotron Research Centre & Neurology Dept. University of Liège, Belgium Neuroimaging structure function Neuroimaging: Modalities Structural
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): 359-364 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info Investigating relative strengths and positions of electrical activity in the left and right hemispheres of the human brain
Biomedical Research 2013; 24 (3): 359-364 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info Investigating relative strengths and positions of electrical activity in the left and right hemispheres of the human brain
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
COGNITIVE NEUROSCIENCE
 HOW TO STUDY MORE EFFECTIVELY (P 187-189) Elaborate Think about the meaning of the information that you are learning Relate to what you already know Associate: link information together Generate and test
HOW TO STUDY MORE EFFECTIVELY (P 187-189) Elaborate Think about the meaning of the information that you are learning Relate to what you already know Associate: link information together Generate and test
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system
 Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
Psychophysics & a brief intro to the nervous system Jonathan Pillow Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Lec. 3 Outline for today: psychophysics Weber-Fechner Law Signal Detection
An Overview of BMIs. Luca Rossini. Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications
 An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5)
 PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
General Nuclear Medicine
 General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan. Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1
 The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
Psychology Fall Dr. Michael Diehr. Psychology Fall Dr. Michael Diehr. Contrasted Group External Empirical Criterion-keyed
 Ch. 15: New directions New directions New Theory Cognitive-behavioral New Computerized & Tools Psychophysiology Traditional Test administration Computer-Aided Interview Computer-Administered test Test
Ch. 15: New directions New directions New Theory Cognitive-behavioral New Computerized & Tools Psychophysiology Traditional Test administration Computer-Aided Interview Computer-Administered test Test
3/1/18. Overview of the Talk. Important Aspects of Neuroimaging Technology
 3/1/18 Considerations for the Use of Neuroimaging for Predicting Recovery of Speech and Language in Aphasia Linda I. Shuster, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Overview of the Talk Important aspects of neuroimaging technology
3/1/18 Considerations for the Use of Neuroimaging for Predicting Recovery of Speech and Language in Aphasia Linda I. Shuster, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Overview of the Talk Important aspects of neuroimaging technology
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques. Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology
 Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
HST.582J / 6.555J / J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.582J / 6.555J / 16.456J Biomedical Signal and Image Processing Spring 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Daniel Bulte. Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain. University of Oxford
 Daniel Bulte Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain University of Oxford Overview Signal Sources BOLD Contrast Mechanism of MR signal change FMRI Modelling Scan design details Factors
Daniel Bulte Centre for Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain University of Oxford Overview Signal Sources BOLD Contrast Mechanism of MR signal change FMRI Modelling Scan design details Factors
Methods for Seeing the Brain (http://www.pbs.org/wnet/brain/scanning/)
 Mind-Brain There are 2 broad approaches to connecting brain and cognitive activity: 1. (modern) Imaging techniques 2. (classic) Patients with brain trauma H. Jackson, A.R. Luria, O. Sacks Methods for Seeing
Mind-Brain There are 2 broad approaches to connecting brain and cognitive activity: 1. (modern) Imaging techniques 2. (classic) Patients with brain trauma H. Jackson, A.R. Luria, O. Sacks Methods for Seeing
NEUROSCIENCE. W1 Divisions of the nervous system PSYC1002 NOTES
 PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism. Outline
 BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism R. Hoge, MGH NMR Center Outline physiological events accompanying neuronal activation factors affecting BOLD signal sensitivity BOLD response dynamics
BOLD signal dependence on blood flow and metabolism R. Hoge, MGH NMR Center Outline physiological events accompanying neuronal activation factors affecting BOLD signal sensitivity BOLD response dynamics
Chapter 5 The Research Methods of Biopsychology
 Chapter 5 The Research Methods of Biopsychology Understanding What Biopsychologists Do This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any
Chapter 5 The Research Methods of Biopsychology Understanding What Biopsychologists Do This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any
Magnetic Resonance Imaging on Soft Tissue. Jiten K. Mistry Calvin Gan
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging on Soft Tissue 1 Jiten K. Mistry Calvin Gan Outline Background of Medical Imaging Introduction to MRI How MRI works MRI of Soft Tissue Benefits & Risks Recent Advances 2 The
Magnetic Resonance Imaging on Soft Tissue 1 Jiten K. Mistry Calvin Gan Outline Background of Medical Imaging Introduction to MRI How MRI works MRI of Soft Tissue Benefits & Risks Recent Advances 2 The
COMENIUS-Project: SM&CLIL Radiation & Medicine
 Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Clinically Available Optical Topography System
 Clinically Available Optical Topography System Clinically Available Optical Topography System 18 Fumio Kawaguchi Noriyoshi Ichikawa Noriyuki Fujiwara Yûichi Yamashita Shingo Kawasaki OVERVIEW: Progress
Clinically Available Optical Topography System Clinically Available Optical Topography System 18 Fumio Kawaguchi Noriyoshi Ichikawa Noriyuki Fujiwara Yûichi Yamashita Shingo Kawasaki OVERVIEW: Progress
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes
 Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Titelmaster The physics of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri)
 Titelmaster The physics of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) Outline 1.Introduction 2.The fmri experiment 2 3.The physics basis of fmri 4.Application Outline 3 1.Introduction Introduction Phrenology
Titelmaster The physics of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) Outline 1.Introduction 2.The fmri experiment 2 3.The physics basis of fmri 4.Application Outline 3 1.Introduction Introduction Phrenology
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines. Due: Friday, April 14
 CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Assignment 5: Neural mechanisms of object-based attention Due: Friday, April 14 This Assignment is a guided reading of the 2014 paper, Neural Mechanisms of Object-Based
CS/NEUR125 Brains, Minds, and Machines Assignment 5: Neural mechanisms of object-based attention Due: Friday, April 14 This Assignment is a guided reading of the 2014 paper, Neural Mechanisms of Object-Based
Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging: An Overview. Barry Horwitz Brain Imaging & Modeling Section NIDCD, NIH
 Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging: An Overview Barry Horwitz Brain Imaging & Modeling Section NIDCD, NIH Methods to Understand Neural Basis of Human Cognition 1. Brain lesions & cognitive neuropsychology
Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging: An Overview Barry Horwitz Brain Imaging & Modeling Section NIDCD, NIH Methods to Understand Neural Basis of Human Cognition 1. Brain lesions & cognitive neuropsychology
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab
 TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
Recording ac0vity in intact human brain. Recording ac0vity in intact human brain
 Recording ac0vity in intact human brain Recording ac0vity in intact human brain BIONB 4910 April 8, 2014 BIONB 4910 April 8, 2014 Objec0ves: - - review available recording methods EEG and MEG single unit
Recording ac0vity in intact human brain Recording ac0vity in intact human brain BIONB 4910 April 8, 2014 BIONB 4910 April 8, 2014 Objec0ves: - - review available recording methods EEG and MEG single unit
Primary Visual Pathways (I)
 Primary Visual Pathways (I) Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Where does visual information go from the eye? Where does
Primary Visual Pathways (I) Introduction to Computational and Biological Vision CS 202-1-5261 Computer Science Department, BGU Ohad Ben-Shahar Where does visual information go from the eye? Where does
The Biological Level of Analysis: Studying the Brain
 The Biological Level of Analysis: Studying the Brain In the past the study of the brain was limited to people suffering from head injuries and the effects of accidental damage. It was only possible to
The Biological Level of Analysis: Studying the Brain In the past the study of the brain was limited to people suffering from head injuries and the effects of accidental damage. It was only possible to
Medical Use of Radioisotopes
 Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
for Heart-Health Scanning
 Magnetocardiography for Heart-Health Scanning CardioMag Imaging, Inc. 1 Basic Principles of Magnetocardiography (MCG) The cardiac electric activity that produces a voltage difference on the body surface
Magnetocardiography for Heart-Health Scanning CardioMag Imaging, Inc. 1 Basic Principles of Magnetocardiography (MCG) The cardiac electric activity that produces a voltage difference on the body surface
The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri?
 The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri? Methods and Models in fmri, 10.11.2012 Jakob Heinzle Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institute for Biomedical Engineering (IBT) University
The physiology of the BOLD signal What do we measure with fmri? Methods and Models in fmri, 10.11.2012 Jakob Heinzle Translational Neuromodeling Unit (TNU) Institute for Biomedical Engineering (IBT) University
Functional MRI Mapping Cognition
 Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
MEDICAL REVIEW Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Acquisition to Application
 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Acquisition to Application Gail Yarmish * and Michael L. Lipton *, Departments of Radiology *, and Neuroscience Albert Einstein College of Medicine Bronx, New
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Acquisition to Application Gail Yarmish * and Michael L. Lipton *, Departments of Radiology *, and Neuroscience Albert Einstein College of Medicine Bronx, New
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
Concurrent near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) of the brain
 Motor cortex activation fmri Near-infrared imaging Concurrent near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) of the brain Sergio Fantini s group, Department of Biomedical
Motor cortex activation fmri Near-infrared imaging Concurrent near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) of the brain Sergio Fantini s group, Department of Biomedical
AdvAnced TMS. Research with PowerMAG Products and Application Booklet
 AdvAnced TMS Research with PowerMAG Products and Application Booklet Table of ConTenTs Introduction p. 04 Legend p. 06 Applications» navigated TMS p. 08» clinical Research p. 10» Multi-Modal TMS p. 12»
AdvAnced TMS Research with PowerMAG Products and Application Booklet Table of ConTenTs Introduction p. 04 Legend p. 06 Applications» navigated TMS p. 08» clinical Research p. 10» Multi-Modal TMS p. 12»
Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response
 Human Brain Mapping 6:373 377(1998) Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response Randy L. Buckner 1,2,3 * 1 Departments of Psychology, Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Radiology, Washington University,
Human Brain Mapping 6:373 377(1998) Event-Related fmri and the Hemodynamic Response Randy L. Buckner 1,2,3 * 1 Departments of Psychology, Anatomy and Neurobiology, and Radiology, Washington University,
Announcements. Exam 1. VII. Imaging techniques of the brain. Anatomical/Structural Scans. Structural Scans: CT. Structural Scans: CT 2/17/2014
 Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1. Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6%
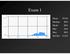 Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Psychophysiological Methods in Neuroscience
 Psychophysiological Methods in Neuroscience by Zachary Infantolino and Gregory A. Miller is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. 2014, Diener
Psychophysiological Methods in Neuroscience by Zachary Infantolino and Gregory A. Miller is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license. 2014, Diener
Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM
 Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM Patrick Dupont Laboratory for Cognitive Neurology Laboratory for Epilepsy Research Medical Imaging Research Center KU Leuven, Belgium E-mail: Patrick.Dupont@med.kuleuven.be
Imaging in epilepsy: Ictal perfusion SPECT and SISCOM Patrick Dupont Laboratory for Cognitive Neurology Laboratory for Epilepsy Research Medical Imaging Research Center KU Leuven, Belgium E-mail: Patrick.Dupont@med.kuleuven.be
Experimental design for Cognitive fmri
 Experimental design for Cognitive fmri Alexa Morcom Edinburgh SPM course 2017 Thanks to Rik Henson, Thomas Wolbers, Jody Culham, and the SPM authors for slides Overview Categorical designs Factorial designs
Experimental design for Cognitive fmri Alexa Morcom Edinburgh SPM course 2017 Thanks to Rik Henson, Thomas Wolbers, Jody Culham, and the SPM authors for slides Overview Categorical designs Factorial designs
Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE
 Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE Pioneers in lesion studies Their postmortem examination provided the basis for the linkage of the left hemisphere with language C. Wernicke
Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE Pioneers in lesion studies Their postmortem examination provided the basis for the linkage of the left hemisphere with language C. Wernicke
Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
Elekta Neuromag TRIUX State-of-the-art Magnetoencephalography. The next level in functional mapping
 Elekta Neuromag TRIUX State-of-the-art Magnetoencephalography The next level in functional mapping The Path to the Future of MEG Starts Here As the leader in MEG technology, Elekta is pleased to introduce
Elekta Neuromag TRIUX State-of-the-art Magnetoencephalography The next level in functional mapping The Path to the Future of MEG Starts Here As the leader in MEG technology, Elekta is pleased to introduce
NEUROSCIENCE. Barbora Cimrová
 NEUROSCIENCE Barbora Cimrová Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (NS) structure, organization, function of its parts and its functioning as a whole unit traditionally: branch of
NEUROSCIENCE Barbora Cimrová Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (NS) structure, organization, function of its parts and its functioning as a whole unit traditionally: branch of
Cardiac PET. John Buscombe
 Cardiac PET John Buscombe Why PET? Improved resolution-not really required in cardiology Improved sensitivity this may be important-financially as reduced acquisition time Improved attenuation correction-good
Cardiac PET John Buscombe Why PET? Improved resolution-not really required in cardiology Improved sensitivity this may be important-financially as reduced acquisition time Improved attenuation correction-good
Supplemental Information
 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Neural Correlates of Crowding-Induced Changes in Appearance Elaine J. Anderson, Steven C. Dakin, D. Samuel Schwarzkopf, Geraint Rees, and John Greenwood
Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Neural Correlates of Crowding-Induced Changes in Appearance Elaine J. Anderson, Steven C. Dakin, D. Samuel Schwarzkopf, Geraint Rees, and John Greenwood
Lecture overview. What hypothesis to test in the fly? Quantitative data collection Visual physiology conventions ( Methods )
 Lecture overview What hypothesis to test in the fly? Quantitative data collection Visual physiology conventions ( Methods ) 1 Lecture overview What hypothesis to test in the fly? Quantitative data collection
Lecture overview What hypothesis to test in the fly? Quantitative data collection Visual physiology conventions ( Methods ) 1 Lecture overview What hypothesis to test in the fly? Quantitative data collection
Molecular Imaging and Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Brain and Nervous System Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 3, Part 2
 Brain and Nervous System Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 3, Part 2 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A January 23, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Studying the Nervous System
Brain and Nervous System Gleitman et al. (2011), Chapter 3, Part 2 Mike D Zmura Department of Cognitive Sciences, UCI Psych 9A / Psy Beh 11A January 23, 2014 T. M. D'Zmura 1 Studying the Nervous System
45 Hr PET Registry Review Course
 45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM
 Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings. Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014
 Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
Analysis of in-vivo extracellular recordings Ryan Morrill Bootcamp 9/10/2014 Goals for the lecture Be able to: Conceptually understand some of the analysis and jargon encountered in a typical (sensory)
