Know Your Flow A GUIDE TO PERIODS. A special thank you to our committee who made this guide possible:
|
|
|
- Erik Kevin Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Know Your Flow A GUIDE TO PERIODS A special thank you to our committee who made this guide possible: Dr Lori Brotto Executive Director of the Women s Health Institute Jessica Bahra-Mangat Masters in Counselling Psychology, Elementary School Counsellor Renee Gregerson Sexual Health Educator Marchien Veen Illustrator Marcy Gooberman Designer 1
2 Puberty WHAT'S HAPPENING ON THE OUTSIDE? 1 YOUR BRAIN IS CHANGING, TOO Your Period WHAT IS IT? 2 HOW OFTEN DOES IT COME? WHAT S A PERIOD FOR? The Cycle THE FOUR STAGES Tracking Your Period HOW + WHY 5 7 COMMON QUESTIONS EVERYTHING YOU NEED TO KNOW PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (AKA PMS) WHAT IS IT? Premenstraul Syndrome (PMS) WHAT IS IT? Self-Care COMING UP WITH A PLAN BODY, MIND + HAPPINESS SYMPTOMS + SOLUTIONS
3 The Products PADS + TAMPONS 14 INSERTING A TAMPON WHEN DO I CHANGE THEM? PROPER DISPOSAL REUSABLE PADS PERIOD UNDERWEAR MENSTRUAL CUPS INSERTING A CUP WHAT S THE RIGHT PRODUCT FOR ME? Is Everything OK? WHEN TO SEE A DOCTOR Common Questions Period Glossary DEFINING THE TERMS
4 Puberty What s happening on the outside? When you go through puberty, lots of changes take place on the outside of your body. You ll get taller, you ll develop breasts, you ll grow hair in your armpits and around your privates, and you may notice vaginal discharge in your underwear. These are all totally normal and just mean you re growing up! Your brain is changing, too. While these changes are happening on the outside of your body, changes are happening on the inside, too. The first place these changes happen is in the brain. In the brain there is something called the Prefrontal Cortex and the Limbic System. When you re young, these systems are still developing, and they contribute to complex thinking, our emotions, and regulating our hormones. These rapidly changing and growing systems are why it s totally normal for teens to experience quick changes in mood! During puberty, the pituitary gland (also in our brains!) tells our ovaries to start producing two hormones: estrogen and progesterone. These hormones cause the physical changes we see in our bodies (like getting taller), but also cause invisible things like our emotions to change too. Along with all of these changes also comes our first period. 4
5 Your Period Getting your period is probably the biggest change you ll experience during puberty. You might hear it referred to differently by many people. But whatever the name, it s all the same. Menstruation is what we call the days of the month when you begin to shed tissue, fluid, and blood (also known as menstrual fluid or period blood) from your uterus and eventually out of your vagina. How often does it come and how long does it last? Well, that can change. Periods come on average every days, and last between 1-7 days. However, every body is different and periods can be shorter or longer from person to person. It all depends! Everyone gets their period at the time that s right for them. You might be the first of your friends to get it, or you might be the last to. The average range for most people is between the 8 and 15 years of age. Sometimes people who are very really athletic or very thin won t get their period until a bit later. This has to do with the amount of body fat we have. So whether you re early or late, just know that no period is perfect, everyone s experience is different, and your time is the right time for you! Why do we get periods? We get our first periods during puberty, which means we re transforming into adults. Being an adult (especially an adult with a uterus!) means that we have the incredible ability to create life and have children - if you want to and are ready to, that is. Every month your body goes through a cycle to prepare for this opportunity. Each cycle is built up of 4 stages. Let s take a look at those stages in depth! 5
6 Stage 1: Pre-Ovulation Inside your body there are two little sacs called ovaries that contain hundreds of thousands of tiny eggs. Each month estrogen (that s a hormone) tells your body to release one of these eggs. While this is happening, the uterus lining (also known as endometrium) starts to thicken. Stage 2: Ovulations Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from the ovary. After the egg is released, it travels along the fallopian tube to the thickening endometrium. One of two things can happen here: the egg could be fertilized by sperm, which is the male reproductive cell. If fertilization occurs, a baby develops. If there is no fertilization, no baby will develop. Throughout your cycle, you ll notice vaginal discharge that changes colour and consistency. These changes have to do with where you are in your cycle and your changing hormones! 6
7 Stage 3: Pre-Menstrual When the egg is not fertilized, it breaks down and the nutrient-rich endometrium is no longer needed. As a result, hormone levels in the body drop and peak. This causes the endometrium to shed, and can also cause people to experience a set of symptoms known as Premenstrual Syndrome (also known as PMS). Stage 4: Menstruation The endometrium leaves the body through the vagina as a fluid containing blood and tissue. This substance can be thick, watery, brown, gooey, red, or translucent. This is your period! Menstruation looks different depending on where you are in your cycle. For many people, day 1 and day 2 have the heaviest flow. That means on those days your body will expel the largest amount of fluid, whereas on day 3 many people have very little fluid. It s different for everyone, but there are ways to know what to expect and keep yourself ready! 7
8 Tracking Your Period Tracking your cycle is easy! Just fill in the information below and we ll show you what your cycle may look like. Why you should Your cycle is unique to you. It might only be 21 days, or it might be 35! To get to know your body better, it is important to track your own cycle. The more intimately you know your own body, the more easily you can recognize when something is wrong. A change in your menstrual cycle is often the first obvious symptom for several women s health issues. One late, early, or missed period isn t cause for alarm, but if the menstrual irregularity is coupled with other symptoms, you should see your doctor. The better you know your flow, the better informed you can stay about your health. The easiest way to track your cycle is to start with the first day of your last period. The first day you start bleeding is Day 1. Tracking your cycle is easy! Just fill in the information below and we ll show you what your cycle may look like. First day of bleeding? : (i.e. January 5, 2017) How many days did you bleed for? : First day of your next period? : How many days between the 2 cycles? Check the calendar! 8
9 Calendar In this example, the first day of bleeding (day 1) falls on the first day of the month. The menstruation continues for 5 days, and the full cycle in this example goes on for 30 days! On the calendars below, fill in your period. Which day does it fall on? Colour it in! (note: if the month has 30 days, just cross off the 31!) 9
10 Premenstrual Syndrome You may have noticed a section of the cycle says Premenstrual Syndrome, commonly referred to as PMS! But what is it? PMS is a set of possible physical and emotional responses to the hormone levels changing in our bodies as we approach menstruation. PMS symptoms are not the same for everyone, and can change throughout your lifetime. Which symptoms do you experience? (Challenge: Try circling the emotional symptoms in red and the physical symptoms in blue!) acne bloating constipation cramping cravings diarrhea difficulty sleeping headache irritability joint pain mood swings muscle ache tender breasts tiredness 10
11 Self-Care Your period can make your emotions feel different than they usually do, and that can be a difficult change to adjust to. Not everyone will experience these symptoms, but it does happen to many of us. Just remember that it s normal and can be managed with self-care! Self-care isn t just important during PMS and your period, it s important to practice self-care every day of your life! Try to recognize the way you re feeling throughout the month and think about why you might be feeling that way. To help take care of yourself, try making a self-care plan. To start, make a list of some things you enjoy doing things that make you feel happier or more relaxed: Unsure of what to write down? Here are some examples of common self-care practices: Exercise Do you have a favourite sport or activity that involves exercise? Exercise releases hormones called endorphins. Endorphins can help us feel less pain, feel happier, and overall have a positive effect on our bodies! Journaling Reflecting on the way you re feeling and writing it down can help sort out confusing emotions. Try writing down how you feel and why you think you feel that way. If you re feeling down, write 3 things everyday that you re grateful for! 11
12 Reading or Netflix Many PMS symptoms can make us feel upset irritated, and uncomfortable. Sometimes we just need to get away from those feelings for a little while. Try snuggling up with a favourite book or movie and getting lost in the story. It s a great way to take our minds off of the things around us. In the circles below, write in the ways you can take care of yourself and your body. Ask yourself, what can I do for my mind (meditation, deep breathing, keeping a journal)? What can I do for my body (stretch, exercise, eat healthy)? What can I do for my happiness (things you love and enjoy)? Mind Body Happiness You are real and you are important! Love your body and treat it well. It s the only body you ll ever have! It s so important to treat your body with compassion and kindness. That means accepting your body for what it is, no matter what. Try not to look at your body in comparison to others, because a lot of the bodies we see online, on TV and in magazines aren t real. 12
13 Solutions Sometimes we experience symptoms that we aren t sure how to cope with. On the next few pages we ll go over some common symptoms, reasons why they happen, and some useful tips and tricks to help cope with these new changes! Symptom + Solution Acne is caused by rising levels of the hormone progesterone. Progesterone tells our skin to produce extra sebum - that s a thick oily substance that can clog our pores and cause breakouts. Hormonal acne can only be treated from the inside, so talk to your doctor if you experience frequent acne right before your period. From the outside, you can help your skin by eating healthy and washing your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser. Constipation and other changes in bowel movements are caused by progesterone as well! Progesterone can slow down digestion in the intestines which can lead to constipation. To relieve constipation it s wise to look at your diet. Fiber is an easy way to relieve discomfort. Fibre can be found in fruits, vegetables, and whole wheat bread! Other things to help with constipation are: increased water intake, less sugar, and less salt. Cramping is caused by the contractions of the uterus as it sheds tissue. For some people cramps can be very painful and unbearable. If your cramping is severe please visit a doctor! For the average cramping, taking a painkiller such as ibuprofen is often helpful, as well as using a hot water bottle and doing pelvic stretches. 13
14 Cravings of unhealthy fatty foods, sweets and carbs during PMS are caused by peaks in our stress hormones. Indulging in these a lot can make you feel tired and sluggish. There are many possible ways to combat these cravings! Many people will eat 3 large meals during the day, which leaves a lot of room for us to be hungry and develop cravings. Having more, smaller, meals during the day can help fight cravings. Eating more fibre-rich foods, nuts, and proteins, while keeping active are all good ways to block cravings as well! Bloating right before your period is caused by our bodies retaining excess water. If you re feeling bothered by bloating, you can help to lessen the sensation by watching what you eat. Salt and salty foods will make your bloating feel worse - so try to avoid those if you often experience this PMS symptom! Many people will have trouble sleeping before they get their periods. Changing levels of the hormone estrogen are to blame for these sleepless nights. In order to get that good night s sleep, it s wise to introduce more exercise into your days, and avoid caffeine if you usually consume it (caffeine can be found in coffee, tea, some sodas, and candy bars! If you are going to have tea, try something that has valerian roof in it - it s a natural way to feel sleepy. Headaches and body pains are frequently experienced as PMS symptoms. As you might have already guessed, the reason we experience these aches and pains is because of hormones. Hormones cause headaches even when they re not from PMS! The best way to fight headaches and aches is to relax and avoid stress. Take it easy, have a bath, stay out of bright lights, drink lots of water, and take a painkiller such as ibuprofen if you need to. Mood swings can make us feel sad, angry, anxious and stable. Not feeling like you have control over your emotions can be very difficult. To help cope, take extra good care of yourself. Get extra sleep, exercise more, eat well, and do the things that you enjoy to make you feel happy and stable. 14
15 Products Everybody has a different flow. It could be light, regular, or heavy. Some days could be light, while others might be heavier. What you choose to use will depend on your unique period. Period products or menstrual hygiene products are what we call the products you use before, during, and after your period. They help absorb the flow of menstrual fluid. There is a spectrum of products to choose from, so let s take a look! Pads Pads are an external means of protection that you wear in your underwear. One side of a pad is coated in a sticky tape that helps to attach it to the inside of your underwear. The other side is soft and very absorbent. This part is worn right against the vagina and can help catch and absorb your period. There are many types of pads to choose from. First of all, pads will come in 2 varieties: with wings and without wings. Some people find that winged pads will stay in place better, as there are extra pieces to stick onto underwear. Pads also come in many different absorbencies: PANTY LINERS These are the least absorbent style of pad. They are often quite thin and used during light periods, spotting (before or after your period starts), or worn with tampons for extra protection. 15
16 REGULAR The name regular says it all! These pads are medium absorbency, medium length, medium thickness. If you re not sure how heavy your flow will be, regular is a good choices. MAXI These pads are much thicker than the previous two, and can absorb a much heavier flow. Some people enjoy wearing maxi pads overnight while they sleep due to the high absorbency. Tampons Tampons are small cotton plugs that are worn inside the vagina to help absorb period blood. They are a popular choice as they are compact, and allow for a lot of movement and activity. There are two types of tampons to consider: tampons with applicators and tampons without applicators. There is no difference between the tampons - it s just whether you prefer to insert the tampon with your finger or with an extra piece of material that works as a barrier and a guide! Just like pads, tampons come in a range of absorbencies to match your flow. Light, regular, and super are the 3 most common absorbency levels for tampons, and these correspond to your flow in the same way that pads do! 16
17 Before you try putting in your first tampon, it s good to get familiar with your body. Use a hand-mirror to look at your vulva. You ll notice three holes: your urethral opening (1), vagina (2), and your anus (3). The vagina is where menstrual fluid will be coming out of, and where you ll insert your first tampon. Inserting a Tampon Using a tampon for the first time can be tricky. Don t get discouraged if it doesn t work out the first time! It can take a few tries to get it right. WITHOUT AN APPLICATOR Pull the tampon from side to side in all directions to create a small pocket for your finger to go in. Next, use the top of the tampon to find your vaginal opening. Once it s lined up, begin to push upwards and slightly toward your lower back until the tampon is completely inserted, comfortable, and the string is hanging out. STEP 1: Choose a tampon that s right for your flow. Start with a low absorbency and only go higher if you are having leaks or changing it too often! STEP 2: Wash your hands. It s important to make sure your hands are clean and free of bacteria before and after you insert. STEP 3: Find a position that s comfortable for you. Some people find it easier to insert a tampon with a leg raised and resting on the bath ledge or toilet seat. Other people may prefer squatting slightly. STEP 4: Remove the packing of your tampon of choice. What happens next will depend on if you are using a tampon with an applicator, or one without! 17
18 WITH AN APPLICATOR Find your vaginal opening with the tip of the tampon applicator. The two tubes should be fully visible while this step takes place. Using the same slightly-toward-back angle, begin to insert the top section of the tube. Once that s in approximately inches, push the smaller tube up so it s hidden. Remove the applicator and leave the tampon string hanging out! WHEN DO I CHANGE THEM? When you change your tampons depends on your flow. Pads and tampons can hold different amounts of menstrual fluid depending on their size (light, regular, super, overnight), so it will depend on the day and heaviness of your flow. If your tampon is leaking, soaking through, or beginning to smell, it is a good time to change it. To be safe, tampons should always be changed within 4-6 hours of use. Wearing a tampon for too long can put you at risk for toxic shock syndrome (TSS). TSS is rare but it can never hurt to be safe! Just make sure that you wear tampons appropriate for your flow, take them out by 6 hours, and cut the risk even more by choosing organic. 18
19 Reusable Pads Reusable pads are worn inside the underwear in a similar way as single use pads. Reusable pads have a snap button to help attach it in place. These pads absorb menstrual fluid into the fabric (often fleece or flannel), and are washed after each use. You can buy additional inserts to put into the pad so it can last your whole cycle! Reusable pads can be washed by hand or by machine with regular detergent. We recommend pre-soaking or rinsing your pads in cold water before washing. Period Underwear These absorbent pairs of underwear can be worn throughout the day, keeping you leak free and extremely comfortable. No need for pads or tampons with these! Just like reusable pads, period underwear can be worn over and over again. They just need to be washed after each use. Period underwear are made up of absorbent material that is leak proof and odour resistant. You wear them like normal, and change them at the end of the day! To wash, rinse the underwear in cold water and then proceed to wash as usual. Just be sure not to use any fabric softener or bleach! 19
20 Menstrual Cups Menstrual cups are soft silicone cups that are worn inside of the vagina to collect menstrual fluid. They are flexible, washable, and reusable. One cup can last up to 10 years! When using a menstrual cup, you should empty it every 4-12 hours (depending on your flow), wash it in the sink, and then reinsert as needed. After your cycle is over, you should sterilize the cup by sitting it in boiling water for about 10 minutes. Menstrual cups can be folded in many different shapes to make it easy for insertion into the vagina. It should sit comfortably at the top of the vaginal canal, suctioning itself against the cervix. At the bottom of all cups is a stem, which is necessary for removal. To remove, simply pull the stem downward until you can reach the base of the cup. Pinching the base will release the seal which will allow it to come out easily! Start by folding your menstrual cup into a small, narrow, shape. Try one of these 3 popular folds! The rest of the insertion should be quite similar to inserting a tampon. The only difference is that once the cup is no longer folded it will expand open into its full cup shape! It should feel comfortable and sit like this in your body: 20
21 There are options as unique as you! This is Marta. She s just gotten her first period and isn t sure yet which product is best for her. Right now she prefers pads as they are easy to put on and take off. As a new mother, Bea s cycle is irregular again, and she is often spotting between periods. She prefers panty liners for the spotting, and reusable pads on the days where her flow is heavier. Nitya got her first period at age 15, which often happens if you re as athletic as she is! She prefers tampons as they are very comfortable during her activities. Sam was born with a uterus and identifies as a male. He prefers period underwear as he doesn t have to worry about changing them throughout the day. Karen is entering into menopause, which means that her body is no longer releasing eggs. Her period is irregular, and so she prefers panty liners and pads. 21
22 Is everything ok? Because every period is different, there isn t one normal way for a cycle to look. However, there are some experiences that are abnormal, that you should look out for and tell your doctor about. If you experience heavy bleeding for more than 7 days in a row, talk to your doctor. Heavy bleeding for a long time can make your body be low on iron, which makes you feel very tired. If you re not bleeding at all, you should also talk to your doctor. Irregular cycles are usually nothing to worry about, but they can signal a health condition, so it s good to get it checked out either way! If you experience severe cramping, you may have a condition called endometriosis and you should talk to your doctor about it. Tracking your period is a great way to look at what s normal for you and your cycle, so if you do experience something abnormal it will be easier to notice and get taken care of! Common Questions Can anyone tell I m having my period? No! Not unless you tell them, that is. Can I exercise during menstruation? Yes! It s actually recommended to. Light stretches and workouts can help reduce cramping and make you feel happier, too. Can I take a bath during my period?? Of course! Because of the water pressure, when you re in water your menstrual fluid won t actually go outside of your vagina. 22
23 Can anyone tell I m having my period? No! Not unless you tell them, that is. Can I exercise during menstruation? Yes! It s actually recommended to. Light stretches and workouts can help reduce cramping and make you feel happier, too. Can I take a bath during my period? Of course! Because of the water pressure, when you re in water your menstrual fluid won t actually go outside of your vagina. Can I go swimming during my period? Yes. When you go swimming you should be using a tampon and not a pad. Tampons will absorb your menstrual flow, not the water in the pool! Can anyone smell my period? If you change your pads and tampons regularly, nobody will be able to tell! Why s there white fluid on my underwear? What you re seeing is vaginal discharge. This is totally normal as it s our bodies natural way of cleaning the vagina. If your discharge starts to smell or change into a colour that isn t white, clear, or cloudy, then you could talk to your doctor about it. Some people will wear a pantyliner to help collect excess discharge. At what age can I use tampons? You can use them whenever you feel ready! Choose whatever product works for you. What if I can t find the string? If for some reason your tampon string is no longer sticking outside of your body, use a clean finger to feel for it inside the vagina. Can the tampon get lost or fall out? Definitely not! Your cervix blocks the tampons from travelling any further than where you inserted it. Tampons are held in place by the muscular walls of your vagina, so once it s in, it will not fall out. 23
24 Does it hurt to put in a tampon? If it s your first time using a tampon, it may feel slightly uncomfortable to put in. If you re using the right size and putting it in the right place it should feel like it s not even there! Does it hurt to wear a tampon? You will know the tampon is in fully when you can no longer feel it. If it feels uncomfortable while you are wearing it, it may not be inserted deep enough. Take out the tampon and try it again - it can take a few tries to get the hang of! Can you lose your virginity to a tampon? No! Absolutely not. Your virginity has nothing to do with using tampons and can be defined by you when you re sexually active. Am I able to pee while wearing a tampon? Yes! Urine comes out of your urethra, whereas your tampon is in your vagina. You may want to move the string out of the way before you start peeing, though. Glossary ANUS The opening where the gastrointestinal tract ends and exits the body. CERVIX The narrow passage forming the lower end of the uterus. ENDOMETRIUM The mucous membrane lining the uterus, which thickens during the menstrual cycle in preparation for possible implantation of an embryo. ESTROGEN Any of a group of steroid hormones that promote the development and maintenance of female characteristics of the body. Such hormones are also produced artificially for use in oral contraceptives or to treat menopausal and menstrual disorders. FALLOPIAN TUBES A pair of tubes in the reproductive system which allow eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. 24
25 FERTILIZATION The process of combining an egg (ovum) with sperm to create a zygote. OVUL ATION The process of an egg leaving the ovary. HORMONE A chemical substance produced in an our bodies that helps to control and regulate our cells, organs, behaviour, and mood. UTERUS This is our reproductive organ! This is the site of ovulation, menstruation, and where babies grow. IRREGULAR An abnormal variation in length of menstrual cycles. MENARCHE The first occurence of menstruation. PRE-MENSTRUAL SYNDROME The physical and emotional symptoms that some people experience in the weeks leading up to menstruation. MENSES Blood and other matter discharged from the uterus during menstruation. PUBERTY The time in which adolescents reach sexual maturity and become capable of reproduction. MENSTRUAL CYCLE The process of ovulation and menstruation that we experience repeatedly from menarche to menopause. PERIOD Another way to say menstruation. MENSTRUATION One of the stages of the menstrual cycle in which the lining and tissue of the uterus is shed through the vagina. PROGESTERONE A steroid hormone that stimulates the uterus to prepare for pregnancy. 25
26 OVARIES A part of the reproductive organ that contains and produces eggs. SPERM A reproductive cell found in the male reproductive organ. To create a baby, a sperm cell needs to fertilize an egg in the uterus. OVA / OVUM The singular and plural names for the eggs in the ovaries. They can be fertilized by sperm eventually turning into an embryo. TIME OF THE MONTH Another way to say menstruation (as many people s cycles are roughly a month long). URETHRAL OPENING The opening where the urethra (a tube) connects the bladder. This is where pee comes out of. VAGINA The muscular canal that extends from the vulva to the cervix. This is where menstrual fluid exits the body during menstruation, where sexual intercourse leading to reproduction takes place, and where babies exit the body during childbirth. VAGINAL DISCHARGE A combination of fluid and cells that are continuously shed through the vagina. Normal discharge helps keep vaginal tissues healthy, provides lubrication and protects against infection and irritation. The amount, color and consistency of normal discharge varies from whitish and sticky to clear and watery. It depends on the stage of your menstrual cycle. Abnormal discharge (having an unusual appearance or smell) may be a sign that something is wrong. VULVA The external genitals. Many people will refer to the external genitals as the vagina but that is incorrect. The vagina is the canal inside of our bodies, though it is visible as a small hole from the outside. 26
Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin.
 Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin. Puberty begins two years earlier for girls than for boys. For most girls,
Puberty is the time when a young person s body begins maturing and changing to become like an adult. At puberty, many changes begin. Puberty begins two years earlier for girls than for boys. For most girls,
LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3:
 GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
GRADE 5 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY LESSON 3 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Lesson 3 1 GRADE 5 LEARNER OUTCOME 2 W-5.3: Identify the basic components of the human reproductive system, and describe the basic functions of
Interactive Questions & Exercises
 Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Interactive Questions & Exercises To accompany I m a Girl, Hormones! for girls age 10+ Whether your daughter reads this book on her own or with you, these questions and exercises will help to make the
Taking Care of Your Sexual Health
 Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
Sexual health is an important part of overall health. Taking responsibility for caring for their sexual health will help men and women stay healthy for a lifetime. Things for Everyone to Know Staying Clean
are some questions. level and Group similar of discussion. the class. somewhere! Avoid offering 1. Is ways to make mean, it means that the a healthy
 Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
Teaching Human Sexuality Answers to Sample Questions Elementary Grade 4, 5, 6 The inquiry process is an important strategy to use for effective human sexuality classes. Here are some tips when answering
CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY
 Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Changing Bodies CHANGING BODIES: REPRODUCTIVE AND SEXUAL ANATOMY Summary Understanding medically-accurate names and functions of the reproductive system is the foundation upon which other sexuality topics
Name Class Date. Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter.
 Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 6 Study Guide STUDY TIPS Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Grade 6 Reproduction Review
 Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Grade 6 Reproduction Review Learner Outcomes W-6.3 Identify and describe the stages and factors that can affect human development from conception through birth How To Use This lesson plan is a review of
Si-Bell s USER GUIDE - ENGLISH
 Si-Bell s USER GUIDE - ENGLISH WELCOME Thank you for choosing Si-Bell, a reusable menstrual cup made of medical grade silicone. Si-Bell is hypoallergenic and without latex. Si-Bell has been designed to
Si-Bell s USER GUIDE - ENGLISH WELCOME Thank you for choosing Si-Bell, a reusable menstrual cup made of medical grade silicone. Si-Bell is hypoallergenic and without latex. Si-Bell has been designed to
Growing up. W Worksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts
 3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
3.1 W WWorksheet 3.1: Percentile growth charts Growing up From the day we are conceived, each and every one of us follows a life cycle. The human life cycle can be divided into stages such as baby, child,
Level I - Lesson 8: Know Your Body
 Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Level I - Lesson 8: Synopsis: This computer session will allow students to learn more about the human reproductive system and the changes their body will go through during puberty. Objectives: Students
Healthy Boys POWERFUL BOYS
 Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Healthy Boys are POWERFUL BOYS Your Sexual & Reproductive Health Education Booklet This book belongs to: Rise 2 Raise Mentoring Program By Robert Ingersoll 2 Introduction The more knowledge you have, the
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment
 Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Managing Symptoms after Prostate Cancer Urine Leaks after Prostate Cancer Treatment Urine leaks after surgery or radiation for prostate cancer are common. The medical term for this is incontinence (say:
Unit 8: Human Sexuality
 Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Unit 8: Human Sexuality Adolescence is the time when young people go through the, emotional, and social changes that end in adulthood. refers to the physical changes that occur during adolescence. During
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Male Reproductive System
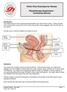
 Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that are part of the reproductive process. The following sections describe the function of each part of the male
Female Reproduction. Ova- Female reproduction cells stored in the ovaries
 Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
Reproduction Puberty stage of growth and development where males and females become capable of producing offspring. Time of physical and emotional changes. Female *occurs between ages 8 -- 15 *estrogen
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System: Words to be familiar with ESTROGEN
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
The friendly guide to fertility
 hannamfertility.com The friendly guide to fertility Written by fertility doctors, translated for everyone. Visit FERTILITY.CA for more info Get busy. Just starting? Many women get pregnant the first month
hannamfertility.com The friendly guide to fertility Written by fertility doctors, translated for everyone. Visit FERTILITY.CA for more info Get busy. Just starting? Many women get pregnant the first month
17. Preventing pregnancy
 17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
17. Preventing pregnancy Objectives By the end of this session, group members will be able to: Define contraception. List ways young people can prevent pregnancy. Background notes What is contraception?
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1)
 What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1) What is Puberty? I understand why I go through puberty and what happens to me during this time. I feel confident in dealing with the challenges puberty will bring and
What is PUBERTY? Year 5 (Lesson 1) What is Puberty? I understand why I go through puberty and what happens to me during this time. I feel confident in dealing with the challenges puberty will bring and
Bowel health and screening: carers guide. A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials
 Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents Page 3: About this booklet Page 4: What is the bowel? Page 5: Helping someone to have good bowel
Chapter 18. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Chapter 18 Vocabulary endocrine glands reproductive system ova hormones sperm uterus thyroid gland testosterone ovaries parathyroid glands testes ovulation pancreas scrotum fallopian tubes pituitary gland
Pelvic Support Problems
 AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
AP012, April 2010 ACOG publications are protected by copyright and all rights are reserved. ACOG publications may not be reproduced in any form or by any means without written permission from the copyright
All you need to know about USING A MENSTRUAL CUP
 All you need to know about USING A MENSTRUAL CUP PREPARED BY Lunette for the Benefits: why use a menstrual cup? Eco-friendly saves one shopping bag worth of plastic and fibres every cycle Saves money $8000
All you need to know about USING A MENSTRUAL CUP PREPARED BY Lunette for the Benefits: why use a menstrual cup? Eco-friendly saves one shopping bag worth of plastic and fibres every cycle Saves money $8000
b o ys Growing Up g i r l s how your body changes
 g i r l s how your body changes NHS South of Tyne and Wear b o ys Growing Up girls Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust 2 boys and girls
g i r l s how your body changes NHS South of Tyne and Wear b o ys Growing Up girls Gateshead Primary Care Trust South Tyneside Primary Care Trust Sunderland Teaching Primary Care Trust 2 boys and girls
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD
 Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
Information for Informed Consent for Insertion of a Mirena IUD What is an IUD (intrauterine Device)? An intrauterine device (IUD) is a plastic device that is placed into your uterus to prevent pregnancy.
H2O to Go! Hydration. It s easier than you think to get dehydrated. No water, no go...
 H2O to Go! Hydration You ve probably heard those narrators on the National Geographic specials say things like, Water gives life, or, Without water there could be no life. They may be overly dramatic,
H2O to Go! Hydration You ve probably heard those narrators on the National Geographic specials say things like, Water gives life, or, Without water there could be no life. They may be overly dramatic,
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Learner Outcomes. Classroom Activities & Timing
 Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Grade 7 Reproduction Learner Outcomes W-7.3 Examine the human reproductive process, and recognize misunderstandings associated with sexual development How To Use This lesson plan contains several activities
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12
 Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
Reproductive System, day 2 Grades 4-6, Lesson #12 Time Needed 40-50 minutes Student Learning Objectives To be able to... 1. Distinguish reproductive system facts from myths. 2. Distinguish among definitions
A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco
 Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
Let s Talk Tobacco A Guide to Help You Reduce and Stop Using Tobacco Congratulations for taking this first step towards a healthier you! 1-866-710-QUIT (7848) albertaquits.ca It can be hard to stop using
What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells
 What s Happening? What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells Or start to make egg cells What is Puberty?
What s Happening? What is Puberty? It is the time when our bodies change toward an adult body. Start to develop new feelings and interests Start to make sperm cells Or start to make egg cells What is Puberty?
Female and Male Reproductive Systems
 Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Female and Male Reproductive Systems Reproductive System: Organs that make possible the production of offspring. Female Reproductive System: Produces the female sex hormones Provides female reproductive
Bowel health and screening: carers guide. A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials
 Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents About this booklet Page 3: Page 4: Page 5: Page 6: Page 6: Page 7: Page 8: Page 10: Page 10:
Bowel health and screening: carers guide A booklet for carers of people who use easy read materials Contents About this booklet Page 3: Page 4: Page 5: Page 6: Page 6: Page 7: Page 8: Page 10: Page 10:
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 6th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health
 SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
SPECIAL EDITION: Men s Health 1 Heart Health If you re like most Americans, heart health might be something you don t think about very often. You should. The risk of heart disease increases with age and
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM ~::> bladder penis prostate gland scrotum seminal vesicle testicle urethra vas deferens ;:; . l0\ OJ IQ) I"- ...
 MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
MALE SEXUAL SYSTEM 8 7 7 8. l0\... OJ '" ~ IQ) I"- cr su::> >. ~::> "0 ~
Human Reproduction. Male & Female Systems & Menstration
 Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
Human Reproduction Male & Female Systems & Menstration Make a Sperm & Ovum Female Mons Pubis Labia Urethra Perineum Vagina Cervix Uterus Endometrium Fallopian tubes Ovaries Ovum Male Scrotrum Testicle
"PCOS Weight Loss and Exercise...
 "PCOS Weight Loss and Exercise... By Dr. Beverly Yates Dr. of Naturopathic Medicine, PCOS Weight Loss Expert & Best Selling Author Table of Contents Introduction... 2 If You Are Dieting Do You Need To
"PCOS Weight Loss and Exercise... By Dr. Beverly Yates Dr. of Naturopathic Medicine, PCOS Weight Loss Expert & Best Selling Author Table of Contents Introduction... 2 If You Are Dieting Do You Need To
Family Planning UNMET NEED. The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows
 Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
Family Planning UNMET NEED The Nurse Mildred Radio Talk Shows TOPIC 9: IUD/COIL Guests FP counsellor from MSU, RHU& UHMG Nurse Mildred Nurse Betty Objectives of the programme: To inform listeners about
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate
 TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
TURP - TransUrethral Resection of the Prostate To learn about a TURP, you will need to know these words: The prostate is the sexual gland that makes a fluid which helps sperm move. It surrounds the urethra
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery. Island Health Surgery Resources
 Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery Island Health Surgery Resources 1 Printing number # 9-90598 Rev05/20/2017 Surgical Services, Island Health About these materials This booklet
Getting ready for and recovering from Gynecological Surgery Island Health Surgery Resources 1 Printing number # 9-90598 Rev05/20/2017 Surgical Services, Island Health About these materials This booklet
Session 16: Manage Your Stress
 Session 16: Manage Your Stress Stress is part of life. However, you can learn better ways to take care of yourself when faced with stress. Stress is not always bad. Some stress can make life interesting
Session 16: Manage Your Stress Stress is part of life. However, you can learn better ways to take care of yourself when faced with stress. Stress is not always bad. Some stress can make life interesting
YOUR CHANGING BODY. A Catholic Booklet About Puberty For Girls
 Created in collaboration with the Lewis University College of Nursing and the Diocese of Joliet Family Life Committee 2011 Material reflects USCCB Guideline Formation in Chaste Living and Diocese of Joliet
Created in collaboration with the Lewis University College of Nursing and the Diocese of Joliet Family Life Committee 2011 Material reflects USCCB Guideline Formation in Chaste Living and Diocese of Joliet
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation
 Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
Anterior Sphincter Repair Operation How will the operation help me? The investigations that you have had indicate that your anal sphincter is damaged or very weak, and this is why you are having trouble
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM UTERUS (made up of muscular walls, a lining called the endometrium, and a cervix. The uterus is also called womb ) houses and protects embryo/fetus/baby allows nutrient & waste
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System The male sex cell is a sperm cell The whole purpose is to produce and deliver sperm to the egg Structure of a Human Sperm Cell Streamlined, built to
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas. Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N
 Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Uterine prolapse & Fistulas Raja Nursing Instructor RN, DCHN, Post RN. BSc.N 31/03/2016 Objectives 1. Review the anatomy & physiology of female reproductive system 2. Discuss the causes, pathophysiology,
Ohio Northern University HealthWise. Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018
 Women s Health Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018 Let Your Body Empower You! National Women s Health Week Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Page 2 Breast
Women s Health Authors: Alexis Dolin, Andrew Duska, Hannah Lamb, Eric Miller, Pharm D Candidates 2018 May 2018 Let Your Body Empower You! National Women s Health Week Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Page 2 Breast
Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education
 Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education Dear Parent/Guardian: Grade 6 students will be receiving 4 hours of instruction from one of our district Sexual Health Education teachers soon. The classroom
Preparing for Grade 6 Sexual Health Education Dear Parent/Guardian: Grade 6 students will be receiving 4 hours of instruction from one of our district Sexual Health Education teachers soon. The classroom
WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES?
 CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
CONTRACEPTION WHAT ARE CONTRACEPTIVES? Methods used to prevent fertilization *Also referred to as birth control methods With contraceptives, it is important to look at what works for you and your body.
THE four SEASONS. OF THE FEMALE CYCLE Susan Hart
 THE four SEASONS OF THE FEMALE CYCLE Susan Hart WEEK ONE: SPRING What to expect The start of week one is summed up in one word relief. The PMS you experienced during the past four days has completely gone.
THE four SEASONS OF THE FEMALE CYCLE Susan Hart WEEK ONE: SPRING What to expect The start of week one is summed up in one word relief. The PMS you experienced during the past four days has completely gone.
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms
 HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms WHAT SYMPTOMS ARE YOU EXPERIENCING? Follow the instructions in each of the 4 categories, count your scores, discover how to interpret your symptoms and
HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms WHAT SYMPTOMS ARE YOU EXPERIENCING? Follow the instructions in each of the 4 categories, count your scores, discover how to interpret your symptoms and
Lecture Series: Pregnancy
 Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Lecture Series: Pregnancy Stephanie Mitelman, MA, CSE Certified Sexuality Educator Teacher's Notes Information Slides Review Quiz 1 Teacher's Notes Welcome! These slides will help you teach your class
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control
 Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Contraception Effective Methods of Birth Control Abstinence Means choosing NOT to have sex It is the ONLY method that is 100% effective It is your right to be in control of your body and say NO What are
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information.
 Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
Every Starred Slide Identifies Critical Information that needs to be covered, other slides support critical information. RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manner, no name calling, and
always changing and growing up girl s guide
 always changing and growing up girl s guide Puberty Contents Puberty 1 Body Growth 7 Breast Growth 8 Skin Changes 10 Hair Changes 11 Perspiration 12 Vaginal Discharge 14 Your Period 15 Feminine Protection
always changing and growing up girl s guide Puberty Contents Puberty 1 Body Growth 7 Breast Growth 8 Skin Changes 10 Hair Changes 11 Perspiration 12 Vaginal Discharge 14 Your Period 15 Feminine Protection
Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community
 2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
2 CHAPTER Teaching Family and Friends in Your Community 9 Old people can remember when there were fewer problems with teeth and gums. Children s teeth were stronger and adults kept their teeth longer.
Uterus (Womb) Rectum. Another problem could be the sensation of something coming down at the birth canal or back passage (prolapse).
 Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Women Physiotherapy Department Continence Service Introduction This leaflet tells you how to exercise and strengthen your pelvic floor muscles. These muscles form a broad sling
METABOLIC ASSESSMENT FORM
 METABOLIC ASSESSMENT FORM Name: Age: Sex: Date: PART 1 Please list the 5 major health concerns in your order of importance: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PART 2 Please circle the appropriate number 0-3 on all questions
METABOLIC ASSESSMENT FORM Name: Age: Sex: Date: PART 1 Please list the 5 major health concerns in your order of importance: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PART 2 Please circle the appropriate number 0-3 on all questions
UNDERSTANDING PMS AND DIY ACTIVITIES FOR ITS MANAGEMENT
 UNDERSTANDING PMS AND DIY ACTIVITIES FOR ITS MANAGEMENT Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a condition that affects a woman s emotions, physical health, and behavior during certain days of the menstrual cycle,
UNDERSTANDING PMS AND DIY ACTIVITIES FOR ITS MANAGEMENT Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a condition that affects a woman s emotions, physical health, and behavior during certain days of the menstrual cycle,
Birth Control Options Chart
 Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Hormonal Methods Birth control pills also known as mini-pills 91-99% A daily pill containing hormones that stops you from ovulating. There are combination estrogen or progestin-only (mini-pill) options.
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS
 Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Body Wise. Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only
 Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
Body Wise Living, Growing, Learning Boys Only So what have we learned so far? Remember the rules This may be embarrassing and cause you to laugh but compose yourself quickly Female Reproductive System
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA
 For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
For the Patient: Trastuzumab emtansine Other names: KADCYLA Trastuzumab emtansine (tras tooz' ue mab em tan' seen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer. Trastuzumab emtansine is a clear
HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms
 HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms WHAT SYMPTOMS ARE YOU EXPERIENCING? Follow the instructions in each of the 4 categories, count your scores, discover how to interpret your symptoms and
HORMONE QUIZ Time to get clear about your symptoms WHAT SYMPTOMS ARE YOU EXPERIENCING? Follow the instructions in each of the 4 categories, count your scores, discover how to interpret your symptoms and
Health Final Exam Study Guide
 Health Final Exam Study Guide 1. The providing of accurate health information to help people make healthy choices is called. (Chp.1) 2. Refusal skills are. (Chp. 2) 3. The three categories of total health
Health Final Exam Study Guide 1. The providing of accurate health information to help people make healthy choices is called. (Chp.1) 2. Refusal skills are. (Chp. 2) 3. The three categories of total health
Human Growth and Development
 Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Human Growth and Development 5th Grade Male Click here for teacher notes Ground Rules Use proper terminology. (Do not use slang.) Participate seriously. Share today s information with your parents. (Do
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
FDA-Approved Patient Labeling Patient Information Mirena (mur-ā-nah) (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) Mirena does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections
Spring - Restore Your Liver
 Spring - Restore Your Liver Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Unfortunately we live in a stressful and toxic world but there is something you can do about it. IF YOU DO NOTHING toxins build up in your
Spring - Restore Your Liver Answers to Frequently Asked Questions Unfortunately we live in a stressful and toxic world but there is something you can do about it. IF YOU DO NOTHING toxins build up in your
Controlling Worries and Habits
 THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
THINK GOOD FEEL GOOD Controlling Worries and Habits We often have obsessional thoughts that go round and round in our heads. Sometimes these thoughts keep happening and are about worrying things like germs,
Premenstrual Syndrome
 page 1 Premenstrual Syndrome Q: What is premenstrual syndrome (PMS)? A: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a group of symptoms linked to the menstrual cycle. PMS symptoms occur in the week or two weeks before
page 1 Premenstrual Syndrome Q: What is premenstrual syndrome (PMS)? A: Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a group of symptoms linked to the menstrual cycle. PMS symptoms occur in the week or two weeks before
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA
 For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
For the Patient: Bendamustine Other names: TREANDA Bendamustine (ben'' da mus' teen) is a drug that is used to treat some types of cancer (lymphoma). It is a clear liquid that is injected into a vein.
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be
 RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
RULES: We will act in an appropriate and respectful manor, no name calling, and use appropriate language at all times. Personal stories will not be shared, please place all questions in question box if
All Play All Play All Play All Play. All Play All Play All Play All Play
 All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play All Play Role-Play Three girls and boys act out how they might share their hopes and dreams for the future
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya
 Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Reproductive system Presented by: Ms. Priya Reproductive system Female reproductive system has two functions: produce egg cells to protect and nourish the offspring (baby) until birth. Male reproductive
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
 What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
What is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)? Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a health issue found in your intestines (gut). IBS can cause symptoms such as: Belly pain. Cramping. Gas. Bloating (or swelling)
the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD the IUD your guide to
 your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
your guide to Helping you choose the method of contraception that s best for you IUD IUD the e IUD IU IUD the IUD 2 3 The intrauterine device (IUD) An IUD is a small plastic and copper device that s put
Professor Christian Phillips BSc Hons BM DM FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist
 Professor Christian Phillips BSc Hons BM DM FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a laparoscopic hysterectomy? Laparoscopic hysterectomy is an operation
Professor Christian Phillips BSc Hons BM DM FRCOG Consultant Gynaecologist and Urogynaecologist Laparoscopic Hysterectomy What is a laparoscopic hysterectomy? Laparoscopic hysterectomy is an operation
Your Own Teeth and Gums
 Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Your Own Teeth and Gums CHAPTER1 Next time you look in a mirror, look at your teeth and the skin (gums) around them. Look in your children s mouths, too. Look at both gums and teeth, because the health
Puberty and Reproduction
 Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
Puberty and Reproduction A Lesson Plan from Rights, Respect, Responsibility: A K-12 Curriculum Fostering respect and responsibility through age-appropriate sexuality education. NSES ALIGNMENT: By the end
41a Pathology: Reproductive System
 41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
41a Pathology: Reproductive System 41a Pathology: Reproductive System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active
Beat. Adrenal Fatigue Naturally!
 Beat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally! What is Adrenal Fatigue? Before we dive into adrenal fatigue, let s first start with the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are glands that sit on top of the kidneys. They
Beat Adrenal Fatigue Naturally! What is Adrenal Fatigue? Before we dive into adrenal fatigue, let s first start with the adrenal glands. The adrenal glands are glands that sit on top of the kidneys. They
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary
 X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
X-Plain Ovarian Cancer Reference Summary Introduction Ovarian cancer is fairly rare. Ovarian cancer usually occurs in women who are over 50 years old and it may sometimes be hereditary. This reference
Patient Information Leaflet
 Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
Patient Information Leaflet Haemorrhoid Operation What are haemorrhoids? Everyone has swellings in the anal canal (back passage) called anal cushions. These bulges in the lining of the anal canal act like
penis and testicles below the belt
 below the belt penis and testicles Here are some tips on taking care of and enjoying your parts if you have a penis and testicles (balls, testes). Not everyone experiences or relates to their penis and
below the belt penis and testicles Here are some tips on taking care of and enjoying your parts if you have a penis and testicles (balls, testes). Not everyone experiences or relates to their penis and
Welcome to Mirena. The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena. mirena.com. Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S.
 Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
Mirena is the #1 prescribed IUD * in the U.S. Welcome to Mirena The Mirena Handbook: A Personal Guide to Your New Mirena *Intrauterine Device Supported by 2015-2016 SHS data INDICATIONS FOR MIRENA Mirena
