Intestinal Protozoa 1- Entamoeba Histolytica
|
|
|
- Clyde Perkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Check NOTES BOXES in sheet 27, just in case 1- Trophozoite Form (Vegetative form / tissue form). 2- Cyst Form (Luminal form), small and circular, can be: a- Immature cyst, which can be either Uninucleate cyst with one nucleus, or Binucleate cyst with 2 nuclei. b- Mature cyst, (Quadri-nucleate cyst) Intestinal Protozoa 1- Entamoeba Histolytica Morphology Mode of infection The Life Cycle Notes 1- Contaminated stuff with human 1- Ingestion of the cyst stool containing mature cysts. (the infectious form). 2- Handling food through infected food handlers as cookers and waiters. 3- Flies and cockroaches. 4- Autoinfection (faeco-oral or hand to mouth infection). 5- Homosexual transmission. 2- Excystation, to produce Trophocytes. 3- The Trophocytes multiplicate to produce 4 cysts. 4- Cysts go to the site of infection. - Worldwide distributed, more common in poor sanitary conditions. - Inhabit the L. intestine. - D.H: Man - R.H: Dogs, pigs, rats and monkeys. - Causes: Amoebiasis (amoebic dysentery). 1- Trophozoite (active) - Attaches to the lining of the small intestine and colonize it. - Responsible for the signs and symptoms of giardiasis. - Heart-shaped with 4 pairs of flagella, - 2 nuclei with central karyosome and 2 axostyles - Swaying/ dancing motion 2- Cyst (inactive) - Found in stool - Ellipsoid, thick walled and highly resistant to chlorinated water. - Mature: 4 nuclei Immature: 2 nuclei 2- Giardia Lamblia Morphology Pathogenesis Transmission Life Cycle Clinical Aspects Diagnosis Treatment - Usually weak 1- Ingestion Quinacrine & pathogens. Metronidazole - Large numbers of parasites cause irritation, low-grade inflammation of the duodenal or jejunal mucosa, with acute or chronic diarrhea, associated with epithelial cell damage. - Fecal-oral route with the ingestion of cysts - Personal contact with animals like beavers, oral anal sex and man to man sex. 2- Excystation in small intestine. (cyst 2trophozoite) 3- Trophozoite undergoes binary fission. 4- Encystation. - Varies from asymptomatic carriage to severe diarrhea and malabsorption. - Stools may be watery, and foul smelling and does not contain mucous or blood. To detect Giardia antigen: 1- Immunologic enzyme-linked immunoassays (EIAs). 2- Immunefluorescence microscopy To detect Giardia: Trichrome stain of preserved stool. The cyst in nondiarrheal stool. The trophozoite in diarrheal stools. Tinidazole Furazolidone paromomycin
2 3- Cryptosporidium Morphology Pathogenesis Transmission Life Cycle Clinical Aspects Diagnosis Treatment - Small spherical structures arranged along the line of epithelial cells inhabiting the surface of villi of the lower small bowel. - Acid-fast staining - Infective stage of Cryptosporidium is called Sporulated oocyst. - Usually asymptomatic and transient. - C hominis, C parvum can infect the intestine in immunecompromised persons - Parasites of rodents, fowl (eggs/flesh of a bird), rhesus monkeys, cattle, and other herbivores. - Causes self-limited, mild gastroenteritis and diarrhea. - Contact with contaminated water and food. - Exposure to infected animals or to water contaminated by feces of infected animals. - Completes its life cycle within a host, including its asexual and sexual reproductive cycles. - They are immediately infectious. 1- Ingestion or inhalation of Sporulated oocysts. 2- Excystation. 3- Sporozoites are released and parasitize epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract or other tissues such as the respiratory tract. - Immuno-competent patients: asymptomatic infection or selflimited watery diarrhea - Immunecompromised patients: chronic, severe, non-bloody diarrhea with nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and anorexia resulting in weight loss and death - Detection of oocysts in fresh stool samples: Acid fast stain. - Stool antigen detection: Direct fluorescent antibody or EIA tests. Nitazoxanide 4- Cyclospora Life cycle Clinical Aspects Diagnosis Treatment - Similar to the Cryptosporidium and appears to involve only a single host. - Main difference is that Cyclospora oocysts are not immediately infectious when freshly passed in stools, so person to person transmission is uncommon. Causes altered mucosal architecture with shortening of intestinal villi due to diffused edema and infiltration of inflammatory cells which leads to diarrhea, anorexia, fatigue, and weight loss. Examining stools for oocysts which are acid-fast positive (reddish color). Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ).
3 5- Balantidium coli Morphology Clinical Aspects Treatment - The largest intestinal protozoa of humans. - The trophozoite stage is a ciliated oval organism. - It rotates around a long axis motion (Rotary motility). - It causes Balantidiasis (Balantidium dysentery). - Most infections are harmless. However, rarely, in acute outbreaks the trophozoites invade the large bowel and terminal ileum causing erosions and ulceration. - Some trophozoites invade the wall of the colon and multiply, leading to the presence of mucous and blood in the stool. Oxytetracycline, which may be followed by Iodoquinol or Metronidazole End on Intestinal Protozoa Sexually Transmitted Protozoa, Trichomonas General characteristics Diagnosis Treatment - Flagellated protozoa with 3-5 anterior flagella. - In most symptomatic cases, wet mount examination for motile trophozoites is enough. - Topical and systemic Metronidazole. - There is no Cyst stage within Trichomonas, so we depend on Trophozoites for diagnosis. There are three members of the genus Trichomonas that parasitize humans: - Tinidazole and Ornidazole are equally effective with fewer side effects. - These drugs belong to (Nitroimidazoles) family. 1- Trichomonas Hominis: parasitize the intestine. 2- Trichomonas Tenax: parasitize the mouth. 3- Trichomonas Vaginalis: Parasitize the Vagina in females causing low-grad inflammation limited to vulva vagina and cervix, causing vaginitis with frothy yellow or creamy discharge, while in males in parasitizes the prostate, seminal vesicle and Urethra - Trichomonas vaginalis cause trichomoniasis in humans. - It is pear- shaped with undulating membrane (which enhances motility of the parasite in a viscous fluid, such as blood ) lined with a flagellum and 4 anterior flagella. - It moves with wobbling or rotating motion - Direct contact of T-vaginalis with the squamous epithelium of the genitourinary tract results in: a) Destruction of the involved epithelial cells. b) Development of a neutrophilic inflammatory reaction. c) Petechial hemorrhages (tiny pinpoint red mark). d) Pain during urination (dysuria) or sexual intercourse. - It is a sexual transmitted disease (STD) but sometimes, nonvenereal transmission can occur (non-sexual transmission) for example babies can get infected as they move through the birth.
4 b- Leishmania American Trypanosoma a- Trypanosoma African Trypanosoma Blood and Tissue Protozoa 1- Hemoflagellates - They are invasive either in tissues or in the blood. They produce highly morbid, and lethal diseases. They usually need I.H (Vectors). - Hemoflagellates have several morphologic forms: a) Amastigote (rounded form): Found in intracellular Environments (Tissues) b) Epimastigote and Promastigote: Found in insect hosts c) Trypomastigote: Found in mammalian Bloodstream - Vector: tsetse fly (Glossina species), Which is found only in rural Africa: a) Glossina palpalis transmits Trypanosomiasis brucei gambiense. b) Glossina morsitans transmits Trypanosomiasis brucei rhodesiense. - Tsetse flies of both sexes transmit pathogenic African trypanosomes (if we compare it to malaria, only female anopheles mosquito can transmit the disease). A bite by the tsetse fly is often painful and can develop into a red sore (Chancroid) then parasitemia occurs and the infection invades the CNS. - Tsetse fly bites humans and inoculates parasites that are found in its saliva. - The infection leads to Insomnia at night, and Sleepiness during the day. - The African trypanosomes shows two morphologic forms: Trypomastigote and Epimastigote. - The African trypanosomes only attach to RBCs, without invading them, unlike malaria, which invades RBCs. - West African Trypanosomiasis causes slowly developing chronic disease, while East African Trypanosomiasis causes acute disease. - Vector: Reduviid bugs (also called Triatomine bugs, kissing bugs). Causes zoonotic disease. - It has 3 developmental stages: 1- Epimastigote, Inhabits insects. 2- Trypomastigote, Inhabits the bloodstream. 3- Amastigotes, inhabits tissues. It is usually found in heart, liver and brain, so it s a serious infection - D.H: Humans, dogs, cats and rat. - Reduviid bug defecates near wounds while taking a blood meal, then a chagoma forms (an inflammatory nodule at the bite site of the reduviid bug). - It is flagellated, obligate intracellular protozoa. - Life cycle requires two hosts: a) Vertebrate; mammalian host b) Invertebrate vector; female sand fly. - Infects primarily phagocytic cells and macrophages. - Transmission occurs through: 1. Bite of sand fly. 2. Transfusion blood and transplantation. 3. Mother to baby. 4. Direct contact; from man to man through nasal secretion.
5 Cont. Leishmaniasis is divided into clinical syndromes according to what part of the body is affected most: 1- Cutaneous Leishmaniasis it is also called (Baghdad boil, oriental sore), caused by (L. Tropica) and (Leishmania major). Leishmania major is the most common type in Jordan especially in areas near to Al Aqaba city. 2- Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis is caused by (L. Braziliensis). 3- Visceral Leishmaniasis (black fever, kala-azar), caused by (L. Donovani). 2- Plasmodium (Blood Sporozoa) - Cause malaria in their hosts. The parasite always has two hosts in its life cycle: Dipteran insect host and a vertebrate host. - The life cycle of Plasmodium can be divided into two distinct phases: 1- The asexual cycle (schizogony), in vertebrate hosts e.g. humans. 2- The sexual cycle, in insect e.g. mosquitoes. - The vector for malaria is the female anopheline mosquito. 1- P. Malaria: Types Mechanism of infection Diagnosis Treatment Causes quartan fever, recur (occur again) every 72 hours or every fourth day (at three-day intervals). Also causes classical malaria in humans 2. P. vivax: The most frequent and widely distributed cause of malaria. Cause tertian fever, recur every 48 hours or every third day (twoday intervals). 3. P. Ovalle: Relatively uncommon. Also causes tertian fever. 1. The vector mosquito takes a blood meal. 2. Sporozoites, in the saliva of the Mosquito, are discharged into the punctured wound. 3. Within an hour, infective sporozoites are carried via the blood to the liver. 4. They penetrate hepatocytes and begin to grow, initiating the pre-erythrocytic or primary exoerythrocytic cycle. The parenchyma cells of the host become infected before RBCs. Exoerythrocytic cycle: is the developmental stage of the malaria parasite in liver. To determine which type of plasmodium is causing the disease: 1- Thick and thin blood films, oil immersion fields. 2- Blood is collected using EDTA anticoagulant. 3- Giemsa stain, Wright s stain, Fluorescent nucleic acid stains, such as acridine orange are used. Or we use antigen-antibody detection. 1- Quinolines (e.g. Chloroquine): Used for all types except for P. falciparum infections due to acquired resistance, they are treated using combination therapies. 2- Primaquine Treats Hypnozoites. 3- Artemisinin. 4- Tetracycline, doxycycline, and clindamycin Cont. in next page Cont. in next page
6 4. P. Falciparum: Major species associated with deadly infections throughout the world. It causes malignant fever which recurs every 48 hours but with more severe symptoms, the temperature can reach more than 42 degrees affecting the brain and cerebral cortex. 5. P. Knowlesi: It causes malaria in monkeys and can infect human as well 5. The sporozoites become round/ oval and begin dividing repeatedly. Schizogony results in large numbers of exoerythrocytic merozoites (a small ameboid trophozoite). 6. Once these merozoites leave the liver, they invade the RBCs, this mark the end of the exoerythrocytic cycle, initiating the erythrocytic cycle (Infection of RBCs). 7. Once the RBCs and reticulocytes (immature red blood cell) have been invaded, the parasites grow and feed on hemoglobin. 8. Within the RBC, the merozoite (or young trophozoite) becomes vacuolated, ring shaped, ameboid, and uninucleate. 9. Merozoites progress into mature trophozoites. Once the nucleus begins to divide, the trophozoite is called a developing schizont (contains many merozoites, which rupture releasing merozoites into the bloodstream). 10.The excess protein and hematin present from the metabolism of hemoglobin (hemolytic anemia) combine to form malarial pigment. These drugs are classified into the following, according to the stage of malarial growth that they target: 1. Tissue schizonticides: kill tissue schizonts. 2. Blood schizonticides: kill blood schizonts. 3. Gametocytocides: kill gametocytes. 4. Sporonticides: prevent formation of sporozoites within the mosquito, inhibiting the life cycle of malarial parasite. Toxoplasma Gondii Tissue protozoa (cysts of parasites in tissues are called bradyzoites) - It is coccidian protozoa with worldwide distribution that infects wide range of animals and birds but does not appear to cause disease in them. - The only host of which the oocyst-producing sexual stage of toxoplasma can develop are strictly the cats and their relatives. - When oocysts are ingested, they either repeat their sexual life cycle in a cat, or if ingested by a human they can establish an infection in which it can reproduce asexually, where it opens and releases sporozoites to the duodenum then invade various cells especially macrophages where they form tachyzoites which spread infection to lymph nodes and other organs. - Latent infections occur with Toxoplasma. - It produces either congenital or postnatal toxoplasmosis. Congenital infections occur in non-immune mothers during pregnancy.
7 Major Points - E. Histolytica: Causes Amoebiasis - Balantidium Coli: Largest intestinal Protozoa, causes Balantidiasis and has a rotary motility. - G. Lamblia: Swaying/ Dancing motion. Infection Varies from asymptomatic carriage to severe diarrhea and mal-absorption. - Cyclospora & Cryptosporidium: Single host & Acid-Fast staining - Cryptosporidium: self-limited, mild gastroenteritis and diarrhea. - Cyclospora: Altered mucosal architecture, diarrhea, anorexia, fatigue, and weight loss. - Sexually Transmitted Protozoa: Trichomonas. - African Tryp. Tsetse fly, causes Insomnia and sleeplessness. - American Tryp. Reduviid Bugs, forms chagoma. - Trichomonas Vaginalis: Causes Trichomoniasis - Toxoplasma Gondii: Causes Toxoplasmosis - P. Malaria: Quartan fever and classical Malaria. P. Vivax: Most freq. and causes tertian fever. - P. Ovalle: Uncommon, causing tertian fever. P. Knowlesi: Malaria in monkeys. - P. Falciparum: Causes major deadly infections and malignant fever. Best Wishes Tala Saleh
Protozoal Infections. By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Protozoal Infections By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Classification of Phylum Protozoa 1- According to the organ of locomotion 1- Class Rhizopoda (Amoebae) 2- Class Ciliata (Ciliates) 3- Class Zoomastigophora
Protozoal Infections By: Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Classification of Phylum Protozoa 1- According to the organ of locomotion 1- Class Rhizopoda (Amoebae) 2- Class Ciliata (Ciliates) 3- Class Zoomastigophora
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
2.Trichomonas vaginalis
 2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
2.Trichomonas vaginalis 1. Pathogenic to human &causes vaginitis (trichomoniasis). 2. troph. Is round or pear like in shape, contains 4-6 flagella, all originating from anterior end & only one extend posteriorly.
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Learning Objectives. 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic Morphology 5. Name of diesease 6. Prevention and Control
 Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Flagellates. Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA
 Flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317242 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellates Classification of Protozoa Based on locomotive
Flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317242 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellates Classification of Protozoa Based on locomotive
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Protozoa from tissues. Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp.
 Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Morphological forms of hemoflagellates
 Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
Parasitology Lecture: 1 Hemoflagellates (blood and tissue flagellates) *Classification: - Sub-kingdom: Protozoa -Phylum: Sarcomastigophora -Sub-phylum: Mastigiphora -Class: Zoomastigophora د. رائد *Flagellates
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011
 1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2011 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate)
 Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Introduction to Medical Parasitology
 Introduction to Medical Parasitology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human Medical Parasitology Human parasitology is
Introduction to Medical Parasitology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human Medical Parasitology Human parasitology is
HAEMOFLAGELLATES. Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine
 HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
HAEMOFLAGELLATES Dr. Anuluck Junkum Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma
cytoplasm contains two 2 nuclei and two parabasal bodies (Figure 7).
 Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture one GIARDIASIS (lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture one GIARDIASIS (lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS
 TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
Parasitology. The genus Trichomonas
 Parasitology Lecture: 2 د. هيفاء The genus Trichomonas -These are common flagellates of the tropical areas,. -They exist only in trophozoite stage. -They are pear-shaped body and measures 10-12 microns
Parasitology Lecture: 2 د. هيفاء The genus Trichomonas -These are common flagellates of the tropical areas,. -They exist only in trophozoite stage. -They are pear-shaped body and measures 10-12 microns
Entamoeba histolytica
 Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Blood Smears Only 6 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control 15B-K
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 6 October 5 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology - Blood Smears Only is
Lecture 1 Dr. Jabar Etaby OTHER INTESTINAL PROTOZOA
 Lecture 1 Dr. Jabar Etaby OTHER INTESTINAL PROTOZOA Classification Higher order taxa Domain : Eukaryota, Phylum : Ciliophora, Class : Litostomatea, Order : Vestibuliferida, Family : Balantiididae, Genus
Lecture 1 Dr. Jabar Etaby OTHER INTESTINAL PROTOZOA Classification Higher order taxa Domain : Eukaryota, Phylum : Ciliophora, Class : Litostomatea, Order : Vestibuliferida, Family : Balantiididae, Genus
1. Toxoplasma gondii:
 Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Parasites affecting the central nervous system: 1. Toxoplasma gondii: It s a protozoa family member, more specifically a member of the apicomplexa just like plasmodium malaria. Causes toxoplasmosis Has
Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis)
 Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis) An acute bacterial disease involving the large and distal small intestine, caused by the bacteria of the genus shigella. Infectious agent Shigella is comprised of four
Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis) An acute bacterial disease involving the large and distal small intestine, caused by the bacteria of the genus shigella. Infectious agent Shigella is comprised of four
Introduction to Protozoa:
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Protozoa: Protozoa are mostly single-celled, animal-like organisms. Although some are colonial or form loose aggregations,
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Protozoa: Protozoa are mostly single-celled, animal-like organisms. Although some are colonial or form loose aggregations,
Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans:
 The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections
 Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged lymph nodes Anaemia Dysentery Parasites causing this clinical presentation How did the parasite produce this presentation
Common Clinical Presentations of Parasitic Infections Hepatosplenomegaly Enlarged lymph nodes Anaemia Dysentery Parasites causing this clinical presentation How did the parasite produce this presentation
Amoebas are motile by means of pseudopodia cytoplasmic extensions which allow it to crawl across surfaces.
 Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Chapter 23 Eukaryotic Parasites of Medical Importance: Protozoa and Helminths* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates
 Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
Laboratory diagnosis of Blood and tissue flagellates (Leishmania and trypanosma) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University Leishmania and trypanosma:
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين
 اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
اعداد رغداحمد رغد جمال الدين Trypanosoma Causes Trypanosomiasis West African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei gambiense Sleeping sickness East African Trypanosomiasis T.brucei rhodesiense American Trypanosomiasis
 Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Malaria parasites Malaria parasites are micro-organisms that belong to the genus Plasmodium. There are more than 100 species of Plasmodium, which can infect many animal species such as reptiles, birds,
Blood Smears Only 07 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control 12B A
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Blood Smears Only 07 February 2012 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology Blood Smears Only
Trypanosomiasis. By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy
 Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
Trypanosomiasis By Ahmed Faris Alila Ahmed Laith Al-Nuaimi Ahmed Mohammed Al-juboory Ahmed Naaif Talib Ahmed Nadhem Al-Obeidy Osama Ahmed Al-Obeidy Ahmed Faris Alila Trypanosomiasis Kingdom: Protisata
EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014
 1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
1 Name EEB 4274 Lecture Exam #1 Protozoa September 2014 Read through the exam once before you begin. Read the questions CAREFULLY; be certain to provide all of the information requested. In instances in
Amoebiasis. (Amoebic dysentery)
 Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery) Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica Amoebiasis Harbouring of protozoa E. histolytica inside the body with or without disease only 10% of infected develop disease two types
Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery) Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica Amoebiasis Harbouring of protozoa E. histolytica inside the body with or without disease only 10% of infected develop disease two types
XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c.
 XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma (2)
XIII Flagellates (2005) A. Hemoflagellates (Chapter 5) 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenazoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma (2)
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS
 FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
Kinetoplastids Handout
 Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Kinetoplastids Handout 1 Kinetoplastids widespread group of flagellated protozoa parasitize virtually all animal groups as well as plants and insects 3 distinct kinetoplastid species cause human disease
Coccidia. Eucoccidioside
 Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Modified mitochondrion near base of flagellum
 XV. The Flagellates (Chapters 5 & 6) 2011 A. Hemoflagellates 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenozoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma
XV. The Flagellates (Chapters 5 & 6) 2011 A. Hemoflagellates 1. Classification of trypanosomes a. Phylum Euglenozoa b. Subphylum Kinetoplasta * c. Class Trypanosomatida d. Important genera (1) Trypanosoma
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4.
 Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4. Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/15085/ DOI: Usage Guidelines Please refer
Ackers, JP (2003) Trichomonas. In: The Oxford Textbook of Medicine. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1:783-4. Downloaded from: http://researchonline.lshtm.ac.uk/15085/ DOI: Usage Guidelines Please refer
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
BIO Parasitology Spring C. mesnili Life Cycle. Lecture 7
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 7 C. mesnili Life Cycle 1. Transmitted by cysts in stools, thus indicate contaminated
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 7 C. mesnili Life Cycle 1. Transmitted by cysts in stools, thus indicate contaminated
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate. Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University
 Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Malaria. benign (mild) malaria
 Malaria Caused by the plasmodium protozoa. Four species of plasmodium causes human malaria: Plasmodium falciparum responsible for nearly all serious complications and deaths. P. vivax P. malariae P. ovale
Malaria Caused by the plasmodium protozoa. Four species of plasmodium causes human malaria: Plasmodium falciparum responsible for nearly all serious complications and deaths. P. vivax P. malariae P. ovale
Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear. Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006
 Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006 Pathogens detected in PS Bacteria Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae Staphylococcus sp. Bartonella
Diagnosis of Infectious Agents in the Peripheral Blood Smear Meredith Reyes, MD July 24, 2006 Pathogens detected in PS Bacteria Neisseria meningitidis Streptococcus pneumoniae Staphylococcus sp. Bartonella
Giardiasis Surveillance Protocol
 Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
Provider Responsibilities 1. Report all cases to your local health department by completing the provider section of the WVEDSS form within the timeframe indicated: Sporadic case of - should be reported
OTHER BODY SITES PATHOGENIC FLAGELLATE
 OTHER BODY SITES PATHOGENIC FLAGELLATE Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas tenax 1 Trichomonasvaginalis Pathogenic protozoan Site-specific : on the mucosal surfaces of the urogenitaltracts ofhumans, predominantly
OTHER BODY SITES PATHOGENIC FLAGELLATE Trichomonas vaginalis Trichomonas tenax 1 Trichomonasvaginalis Pathogenic protozoan Site-specific : on the mucosal surfaces of the urogenitaltracts ofhumans, predominantly
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 2 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control. 12 K (All Parasites)
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
Malaria. An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture
 Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
Malaria An Overview of Life-cycle, Morphology and Clinical Picture Malaria Malaria is the most important of all tropical parasitic disease,causes death and debility and is endemic throughout the tropics
BIO Parasitology Spring 2009
 BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
BIO 475 - Parasitology Spring 2009 Stephen M. Shuster Northern Arizona University http://www4.nau.edu/isopod Lecture 5 Discovery of the Disease In 1924 the Kala-Azar Commission noted that the distribution
CHAPTER FOUR. Intestinal Amebae
 PART II Protozoa CHAPTER FOUR Intestinal Amebae OUTLINE INTESTINAL AMEBAE Entamoeba histolytica/entamoeba dispar (EN-ta-MEE-buh HIS-toe-LIT-I-ka/EN-ta-MEEbuh DIS-par) Entamoeba hartmanni (EN-ta-MEE-buh
PART II Protozoa CHAPTER FOUR Intestinal Amebae OUTLINE INTESTINAL AMEBAE Entamoeba histolytica/entamoeba dispar (EN-ta-MEE-buh HIS-toe-LIT-I-ka/EN-ta-MEEbuh DIS-par) Entamoeba hartmanni (EN-ta-MEE-buh
Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages :
 Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
Trypanosomiasis. Introduction. Epidemiology. Global Epidemiology. Trypanosomiasis Risk in UK Travellers
 Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
Trypanosomiasis Introduction Epidemiology Risk for travellers Transmission Signs and symptoms Treatment Prevention References Reading list Links Introduction Trypanosomiasis is caused by parasitic protozoa
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27
 KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
KINGDOM PROTISTA CHAPTERS 26 & 27 CHARACTERISTICS Eukaryotic Heterotrophic & Autotrophic Mostly unicellular ; some multicellular Asexual reproduction binary fission Sexual reproduction - conjugation Plant
Giardiasis. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
Table of Contents Case Definition... Error! Bookmark not defined. Reporting Requirements... 2 Etiology... Error! Bookmark not defined. Clinical Presentation... Error! Bookmark not defined. Diagnosis...
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #14 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 37-year-old woman, who had traveled to New Guinea for several weeks, presented to the medical clinic with fever, chills, and rigors within
Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Protozoa: This is what he saw in his own stool sample. Morphology 10/14/2009. Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Anton van Leeuwenhoek Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease This is what he saw in his own stool sample 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Anton van Leeuwenhoek Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease This is what he saw in his own stool sample 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right. Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Blood and Tissue Protozoa
 Blood and Tissue Protozoa Blood and Tissue Protozoa Flagelates Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness (chr, Af) Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness (ac, Af) Trypanosoma cruzi Chagas
Blood and Tissue Protozoa Blood and Tissue Protozoa Flagelates Trypanosoma brucei gambiense sleeping sickness (chr, Af) Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness (ac, Af) Trypanosoma cruzi Chagas
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
Extra-intestinal coccidians
 Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Cryptosporidiosis. By: Nikole Stewart
 Cryptosporidiosis By: Nikole Stewart Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto"); Etiological agent- Cryptosporidium (1) Transmission: Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route when individuals ingest water or food
Cryptosporidiosis By: Nikole Stewart Cryptosporidiosis ("Crypto"); Etiological agent- Cryptosporidium (1) Transmission: Transmission occurs via the fecal-oral route when individuals ingest water or food
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM)
 HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
HELMINTHS IMAGE DISEASE STAGE SOURCE SYMPTOMS FOUND LEN TAENIA SAGINATA (BEEF) TAENIA SOLIUM (PORK) TAENIASIS (TAPEWORM) HOOKS /AND /OR/SUCKERS SCOLEX (ADULT) INGESTION OF CONTAMINATED PORK OR BEEF DIARRHEA
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program. Parasitology (General) 01 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 01 February 2011 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Malaria. Population at Risk. Infectious Disease epidemiology BMTRY 713 (Lecture 23) Epidemiology of Malaria. April 6, Selassie AW (DPHS) 1
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 23 Vector-Borne Disease (Part II) Epidemiology of Malaria Learning Objectives 1. Overview of malaria Global perspectives 2. Identify
Malaria Life Cycle Life Cycle
 Malaria Malaria Life Cycle Life Cycle Oocyst Zygote Sporogony Sporozoites Mosquito Salivary Gland Gametocytes Exoerythrocytic (hepatic) cycle Hypnozoites (for P. vivax and P. ovale) Erythrocytic Cycle
Malaria Malaria Life Cycle Life Cycle Oocyst Zygote Sporogony Sporozoites Mosquito Salivary Gland Gametocytes Exoerythrocytic (hepatic) cycle Hypnozoites (for P. vivax and P. ovale) Erythrocytic Cycle
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
Invest in the future, defeat malaria
 Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
Invest in the future, defeat malaria Malaria is caused by parasites from the genus Plasmodium, which are spread to people by infected mosquitoes. There are five species of Plasmodium that can infect humans.
American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX
 Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
Ameba has two stages of development: cyst and trophozoite
 Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Short Video. shows/monsters-inside- me/videos/toxoplasma-parasite/
 The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
KINETOPLASTIDS. Kinetoplast. Nucleus
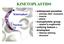 KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
KINETOPLASTIDS Kinetoplast Nucleus widespread parasites animals (fish humans) insects plants monophyletic group related to euglenoids unifying feature = kinetoplast Giemsa staining structure KINETOPLAST
Diseases: If you think about the spread of disease caused by parasites such as blindness, There are several infective causes of blindness :
 Introduction : -The parasites are usually negligible and we don't take it seriously. - They cause diseases in the world. ( morbidity ) - Parasite means الطفيلي somebody who eats at someone else's table!!!!
Introduction : -The parasites are usually negligible and we don't take it seriously. - They cause diseases in the world. ( morbidity ) - Parasite means الطفيلي somebody who eats at someone else's table!!!!
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale. Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum
 The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 1 Distribution Of Plasmodium vivax 2 Global Risk By Country-Proportionality
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 5 November 2013
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
Transmission network dynamics of Plasmodium Vivax Malaria
 Transmission network dynamics of Plasmodium Vivax Malaria P. Pongsumpun, and I.M.Tang Abstract One of the top ten killer diseases in the world is Malaria. In each year, there are between 3 to 5 million
Transmission network dynamics of Plasmodium Vivax Malaria P. Pongsumpun, and I.M.Tang Abstract One of the top ten killer diseases in the world is Malaria. In each year, there are between 3 to 5 million
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Vernon Carruthers, Ph.D., Cary Engleberg, M.D., D.T.M.&H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License:
Author(s): Vernon Carruthers, Ph.D., Cary Engleberg, M.D., D.T.M.&H., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License:
Medical Parasitology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Medical Parasitology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Definitive (final) host harbors adult or sexually reproductive stage of a parasite. Intermediate host: harbors larval or asexually reproductive stage of a parasite,
Medical Parasitology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Definitive (final) host harbors adult or sexually reproductive stage of a parasite. Intermediate host: harbors larval or asexually reproductive stage of a parasite,
DISTANCE LEARNING ANSWER SHEET Please circle the one best answer for each question.
 1 DISTANCE LEARNING ANSWER SHEET Please circle the one best answer for each question. COURSE NAME: POTENTIAL PROBLEMS WITH THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALARIA IN THE UNITED STATES COURSE # DL-002 NAME LIC. # DATE
1 DISTANCE LEARNING ANSWER SHEET Please circle the one best answer for each question. COURSE NAME: POTENTIAL PROBLEMS WITH THE DIAGNOSIS OF MALARIA IN THE UNITED STATES COURSE # DL-002 NAME LIC. # DATE
Toxoplasma gondii. Definitive Host adult forms sexual reproduction. Intermediate Host immature forms asexual reproduction
 Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
University Of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy
 PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD PharmD University of Jordan Faculty of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Microbiology (1) 1202341- Dr. Randa Haddadin PharmD-
3-Mutualism: It is a relationship between two. organisms; one called. or harmless. 2-Commensalism: It is a relationship in which one
 Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA K. C. Nayak, Rakesh Meena, *Surendra Kumar, B. K. Gupta, V. B. Singh and Varun Kulkarni Department
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF QUININE V/S ARTESUNATE IN SEVERE MALARIA PATIENTS IN NORTHWESTERN RAJASTHAN, INDIA K. C. Nayak, Rakesh Meena, *Surendra Kumar, B. K. Gupta, V. B. Singh and Varun Kulkarni Department
CONTINUED FROM PART 1
 CONTINUED FROM PART 1 1 LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 2 MALARIA
CONTINUED FROM PART 1 1 LYNNE S. GARCIA, MS, CLS, FAAM Lynnegarcia2@verizon.net CAPHLD 65 th Institute Future Challenges in Diagnostic Medical Parasitology SPONSOR: MEDICAL CHEMICAL CORPORATION 2 MALARIA
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MD (MEDICAL PARASITOLOGY) EXAMINATION JANUARY, 2001 PAPER 1
 JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
JANUARY, 2001 Date: 15 th January 2001 Time: 2.00 p.m. -500 p.m. PAPER 1 Answer all five (5) questions Answer each question in a separate book 1. Discuss the underlying principles relating to the use of
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY
 MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
MALARIA CONTROL FROM THE INDIVIDUAL TO THE COMMUNITY Calvin L. Wilson MD Clinical Professor of Family Medicine and Public Health University of Colorado Anschutz OBJECTIVES 1. Understand the unique characteristics
Brachyspira & Lawsonia
 General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
General Brachyspira & Lawsonia Gram-negative Anaerobic but with aerotolerance Colonize the large intestine of mammals and birds Infections with Brachyspira species are important in pigs Species & Disease
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
Anopheles freeborni. Courtesy
 Anopheles freeborni Courtesy Plasmodia seen with the microscope M. Lontie, MCH, Leuven, 2012 Diagnosis of malaria Thin film (better for species identification). Thick film (more sensitive). QBC (quantitative
Anopheles freeborni Courtesy Plasmodia seen with the microscope M. Lontie, MCH, Leuven, 2012 Diagnosis of malaria Thin film (better for species identification). Thick film (more sensitive). QBC (quantitative
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE. 1. Type of cell. 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIO 140 MYCOLOGY OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION TO THE KINGDOM FUNGI DOMAIN EUKARYA A. General Characteristics 1. Type of cell 2. Fungi may be unicellular or multicellular
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Giardiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
August 2011 Giardiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 39-year old male traveler developed fever and thrombocytopenia after returning from a trip to the Philippines. The parasitemia was 10,000
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY #11 (BLOOD PARASITES) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 39-year old male traveler developed fever and thrombocytopenia after returning from a trip to the Philippines. The parasitemia was 10,000
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale. Watersheds of the African Continent
 The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Global Risk By Country-Proportionality Plot P. falciparum P. vivax Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 3 million
The Malarias: Plasmodium falciparum Plasmodium vivax Plasmodium malariae Plasmodium ovale Global Risk By Country-Proportionality Plot P. falciparum P. vivax Distribution of Plasmodium falciparum 3 million
