H-Reflex Suppression and Autonomic Activation During Lucid REM Sleep: A Case Study
|
|
|
- Elvin Eaton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sleep 12(4): , Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Short Communication H-Reflex Suppression and Autonomic Activation During Lucid REM Sleep: A Case Study * Andrew Brylowski, Lynne Levitan, and Stephen LaBerge *University of Texas Medical School at Houston, Houston, Texas, and Sleep Research Center, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California, U.S.A. Summary: A single subject, a proficient lucid dreamer experienced with signaling the onset of lucidity (reflective consciousness of dreaming) by means of voluntary eye movements, spent 4 nonconsecutive nights in the sleep laboratory. The subject reported becoming lucid and signaling in 8 of the 18 rapid-eye movement (REM) periods recorded. Ten lucid dream reports were verified by polygraphic examination of signals, providing a total of 12.5 min of signalverified lucid REM. H-Reflex amplitude was recorded every 5 s, along with continuous recording of electroencephalogram, electrooculogram, electromyogram, electrocardiogram, finger pulse, and respiration. Significant findings included greater mean H-reflex suppression during lucid REM sleep than during nonlucid REM and correlations of H-reflex suppression with increased eye movement density, heart rate, and respiration rate. These results support previous studies reporting that lucid REM is not, as might be supposed, a state closer to awakening than ordinary, or nonlucid, REM; rather, lucid dreaming occurs during unequivocal REM sleep and is characteristically associated with phasic REM activation. Key Words: H-Reflex-Lucid REM sleep. Electrophysiological studies have shown that "lucid" dreams, in which persons are explicitly aware that they are dreaming while continuing to dream, occur almost exclusively in rapid-eye-movement (REM) sleep (1). Further investigations (2,3) have indicated that lucid REM sleep is characterized by higher levels of phasic activity and autonomic activation than ordinary REM sleep, and therefore that it is likely that lucidity occurs during periods of relatively great cortical activation. Contrary to some earlier suggestions that lucid dreaming might be the result of microawakenings, brief intrusions of waking consciousness, in REM periods (4), the findings that lucidity is Accepted for publication September Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. A. Brylowski at Department of Psychiatry, Southwestern Medical School at Dallas, 5323 Harry Hines Blvd., Dallas, TX , U.S.A. 374
2 H-REFLEX SUPPRESSION IN LUCID REM 375 associated with more intense, activated REM sleep suggest rather that lucid REM is a deep sleep state and not nearer to waking than ordinary REM sleep. The primary goal of this experiment was to investigate the status of H-reflex suppression in lucid dreams. Given that both human (5,6) and feline (7,8) studies have demonstrated tonic reflex inhibition during phasic REM and that lucidity is associated with phasically active REM, it was predicted that the H-reflex during lucid REM would be at least as suppressed as it is in ordinary REM. In the H-reflex analysis, the polygraph records were divided into 5-s epochs instead of the standard 30-s epochs (9), enabling correspondingly finer resolution of the state changes during REM and especially lucid REM sleep. It was possible to identify microawakenings and transitions to non-rem (NREM) sleep if any occurred during the periods of lucidity. METHODS The subject was a 25-year-old medical student, an experienced lucid dreamer who was familiar with the method of signaling from lucid dreams by means of eye movements verifiable on the polygraph record (1). His sleep was normal during an all-night polysomnogram without continuous H-reflex monitoring. On 4 nonconsecutive nights his H-reflex was measured as he slept with the intention to recognize when he was dreaming and to signal the onset of lucidity. The experimental protocol called for the subject to signal the onset of lucidity with two pairs of extreme left-right eye movements and to signal awakening with four pairs of left-right eye movements. The subject wrote reports of mental activity after each spontaneous awakening, including the times of awakening. Following previously described methodology (I), reports were scored as signal-verified lucid dreams if (a) the subject reported that he had become lucid and made the eye movement signals and (b) the corresponding section of the polygraph record showed the reported signals. A Grass model 8-18D was used to record several channels of electroencephalogram, induding the standard central positions used for sleep scoring, vertical and horizontal electrooculogram, electrocardiogram, nasal airflow, finger pulse, and H-reflex amplitude. Standard procedures for measuring H-reflex were used, modified for continuous measurement (10,11). The subject's knee was immobilized in a knee immobilizer set at 100 flexion and a O.I-ms 50-V stimulus was delivered to the right posterior tibial nerve every 5 s as the contraction of the soleus muscle was monitored. A TECA model TE42 electromyogram (EMG) machine provided the electrical stimulus and amplified the EMG signal, which was sent to the J5 external input on the Grass polygraph. The polygraph records were scored according to the standard criteria (9). The REM periods, including the 30 s pre and post REM, were subdivided into 5-s epochs, one epoch for each H-reflex sample. These 5-s epochs were again scored for sleep stages according to the standard criteria modified for 5-s epochs. An epoch was scored as Stage 2 if no change in stage had occurred between K-complexes or sleep spindles or if a K-complex or sleep spindle was present anywhere in the epoch. Also, an epoch was scored as lucid REM only if it contained an eye movement signal or lay between epochs containing signals corresponding with the subject's written report (see Fig. 1). In addition to sleep staging, several other physiological measures were collected and analyzed in 5-s epochs. These were H-reflex amplitude (millimeters of pen deflection), eye movement density (number of eye movements per epoch), heart rate (beats per
3 376 A. BR YLOWSKI ET AL. C4 A2 ~~I~ I V."""V~"'Ii.rl.~... r'~<'f\"\a~ Cz A2 ~I~~~l~~'\i'" YJ!},,j~NJtA,,,,\~f,MwJ(I!~... ~/r'"h\f\. T3 A1,~ tv~/' ~,~----~ T4 A2 ~V\f''''----V~t 01 A1 02 A2 LOC A1 ROC A2 F. Pulse EMG EKG H Reflex Resp \ \ \ ~ A. Awake B. REM Sleep ---==-----,150!l V 5 Sec FIG. 1. A: Awake, eyes closed. Two sets of eye movement signals are shown. B: REM sleep. Two sets of eye movement signals are shown, with the onset of a lucid dream at the first (arrow). Note the indications of autonomic activation [skin potential artifact in the electroencephalogram and electrocardiogram (EKG) chan nels and finger pulse amplitude suppression] and the profound H-reflex suppression accompanying lucidity. epoch converted for analysis to beats per minute), and respiration interval (measured for the breath cycle occupying >50% of the 5-s epoch and converted for analysis to breaths per minute). RESULTS Eighteen REM periods were recorded; eight included portions of lucid REM with a total of 10 lucid dreams. A total of 150 epochs (12.5 min) of lucid REM were collected across the 4 recording nights out of 2,470 REM epochs (206 min). The number of epochs oflucid REM for nights 1-4 was 18 (1.5 min), 18 (1.5 min), 48 (4 min), and 66 (5.5 min), respectively. The percentage of total sleep time spent in REM from nights 1 through 4 was 5.4% (19 min/349.5 min), 11.1% (60 min/538.5 min), 18.4% (64 min/348 min), and 29.4% (63 min/214.5 min), respectively. The increasing percentages of REM are presumably due to the subject adapting to sleeping under the difficult experimental conditions. Only the epochs within REM periods actually scored as REM were analyzed. None of the portions of lucid REM were found to contain any microawakenings or transitions to NREM. The mean H-reflex amplitude was determined for the nonlucid epochs and lucid epochs of each REM period that included lucid REM. In all eight cases, the mean H-reflex amplitude for lucid REM was lower than that for nonlucid REM (binomial test,
4 H-REFLEX SUPPRESSION IN LUCID REM 377 p = 0.(04). A one-tailed paired t test of the REM period means of lucid REM versus nonlucid also revealed lucid REM H-reflex amplitude to be significantly lower than nonlucid (t(7) = 4.43, p < 0.005). As mentioned above, previous studies have shown that the initiation Of lucidity in REM sleep is associated with autonomic activation (2,3). To examine the relationship between the onset of lucidity and H-reflex suppression, the mean values of H-reflex amplitude for the 30 s preceding and the 30 s following lucidity initiation were compared with the REM period median H-reflex amplitude. For both pre- and postlucidity periods, 8 of 10 mean amplitudes were lower than the all-rem period median amplitudes (binomial test, p = 0.05). The same type of comparison was performed on eye movement density in the 30 s pre- and postlucidity initiation. For all 10 lucid dreams, the eye movement density means were higher just before and after lucidity onset than the all-rem period medians (binomial test, p = 0.001), bearing 'Out the earlier findings on this measure of autonomic arousal. Direct comparisons of the relationship between H-reflex suppression and other autonomic variables were done with Spearman rank correlations of H-reflex amplitude with eye movement density, respiration rate, and heart rate. These tests showed highly significant (p < 0.001) negative correlations between H-reflex amplitude and all other physiological variables when the values from nights 1-4 were pooled. For the individual nights, 11 of 12 coefficients showed significant correlations (p < 0.05) (see Table O. DISCUSSION The results of the above comparisons of H-reflex amplitude during lucid and nonlucid REM sleep clearly show not only that H-reflex is suppressed during REM lucid dreams, as it is in ordinary REM sleep, but that it tends to be more suppressed during lucid than nonlucid REM. Increased H-reflex suppression was also strongly associated with phasic REM activity and autonomic activation, two factors that previous studies (2,3) have shown to also be associated with lucid REM sleep. The findings presented here demonstrate that lucid dreaming occurs during unambiguous REM sleep, without microawakenings or other arousals, and also that lucid REM sleep is associated with relatively high phasic activity, autonomic activation, and TABLE 1. Correlations of H-reflex amplitude with eye movement density, heart rate, and respiration rate for the 4 nights individually and pooled using Spearman's correlation coefficient H-Reflex amplitude with Eye movement density Heart rate Respiration rate Night 1 Night 2 Night 3 Night 4 All nights pooled " (n = 192) a (n = 981) a (n = 1,057) a (n = 970) " (n = 3,200) (n = 192) -O.3508 a (n = 980) -O.0698 b (n = I,OS9) a (n = 970) -O.3198 a (n = 3,201) -0.IS20 b (n = 191) S Q (n = 980) Q (n = I,OS6) -O.l164 Q (n == 962) " (n = 3,189) Q P < b P < O.OS.
5 378 A. BR YLOWSKI ET AL. deep reflex suppression. By showing that the H-reflex is even more suppressed during lucid REM than nonlucid REM, these analyses suggest that lucid REM is not, as might be supposed, a state closer to awakening than ordinary, or nonlucid REM. Additionally, a direct relationship is suggested between the depth of H-reflex suppression and increased phasic activation in REM sleep. Further research is indicated to confirm these findings with more subjects and to investigate in more detail the relationship between various modes of physiological activation, tonic reflex suppression, and the mental activity of the dreamer. Acknowledgment: The support of The Institute of Human Development is gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES 1. LaBerge SP, Nagel LE, Dement WC, Zarcone VP. Lucid dreaming verified by volitional communication during REM sleep. Percept Mot Skills 1981 ;52: LaBerge SP, Nagel LE, Taylor WB, Dement WC, Zarcone VP. Psychophysiological correlates of the initiation of lucid dreaming. Sleep Res 1981 ;10: LaBerge S, Levitan L, Dement WC. Lucid dreaming: physiological correlates of consciousness during REM sleep. J Mind Behav 1986;7: Schwartz BA, Lefebvre A. Contact veille/p.m.o. II. Les P.M.O. morcelles. Rev Electroencephalogr Neurophysiol Clin 1973;3: Hishikawa Y, Sumitsugu N, Matsumoto K, Kaneko Z. H-reflex and EMG of the mental and hyoid muscles during sleep, with special reference to narcolepsy. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1965;18: Hodes R, Dement WC. Depression of electrically induced reflexes ("H-reflexes") in man during low voltage EEG sleep. Electroencephala/?r Clin NeurophysioI1964;17: Pivik R, Metz J. Phasic EMG inhibition and spinal reflex modulation during synchronized sleep in the cat. Exp Neural 1975;48: Pivik R, Metz J. Spinal and lateral geniculate nucleus activity during sleep: quantitative relationships. Exp NeuroI1982;77: Rechtschaffen A, Kales A, eds. A manual of standardized terminology, techniques, and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. Los Angeles: University of California at Los Angeles, Brain Information Service/Brain Research Institute, Magladery J, McDougal G. Electrophysiologic studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. I. Identification of certain reflexes in the electromyogram and the conduction of peripheral nerve fibers. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 1950;86: Magladery J, Teasdale R, Park A. Electrophysiologic studies of nerve and reflex activity in patients with lesions of the nervous system: a comparison of spinal motorneuron excitability following afferent nerve volleys in normal persons and patients with upper motor neuron lesions. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 1952;91 :
Lucid Dreaming: Physiological Correlates of Consciousness during REM Sleep
 1986 The Institute of Mind and Behavior, Inc. 25 1 [1211 The Journal of Mind and Behavior Spring and Summer 1986, Volume 7, Numbers 2 and 3 Pages 251 [121J-258 [128] ISSN 0271-0137 ISBN 0-930195-02-7 Lucid
1986 The Institute of Mind and Behavior, Inc. 25 1 [1211 The Journal of Mind and Behavior Spring and Summer 1986, Volume 7, Numbers 2 and 3 Pages 251 [121J-258 [128] ISSN 0271-0137 ISBN 0-930195-02-7 Lucid
Physiological Mechanisms of Lucid Dreaming. Stephen LaBerge Sleep Research Center Stanford University
 Physiological Mechanisms of Lucid Dreaming Stephen LaBerge Sleep Research Center Stanford University For those of you here who aren t familiar with the general approach we have been using in our research
Physiological Mechanisms of Lucid Dreaming Stephen LaBerge Sleep Research Center Stanford University For those of you here who aren t familiar with the general approach we have been using in our research
Periodic Leg Movement, L-Dopa, 5-Hydroxytryptophan, and L-Tryptophan
 Sleep 10(4):393-397, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Short Report Periodic Leg Movement, L-Dopa, 5-Hydroxytryptophan, and L-Tryptophan C. Guilleminault, S. Mondini,
Sleep 10(4):393-397, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Short Report Periodic Leg Movement, L-Dopa, 5-Hydroxytryptophan, and L-Tryptophan C. Guilleminault, S. Mondini,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Motor Area Activation During Dreamed Hand Clenching: A Pilot Study on EEG Alpha Band
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Motor Area Activation During Dreamed Hand Clenching: A Pilot Study on EEG Alpha Band Daniel Erlacher, M.A., Michael Schredl, Ph.D., Stephen LaBerge, Ph.D. In a single participant physiological
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Motor Area Activation During Dreamed Hand Clenching: A Pilot Study on EEG Alpha Band Daniel Erlacher, M.A., Michael Schredl, Ph.D., Stephen LaBerge, Ph.D. In a single participant physiological
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness Associated with Insufficient Sleep
 Sleep, 6(4):319-325 1983 Raven Press, New York Excessive Daytime Sleepiness Associated with Insufficient Sleep T. Roehrs, F. Zorick, J. Sicklesteel, R. Wittig, and T. Roth Sleep Disorders and Research
Sleep, 6(4):319-325 1983 Raven Press, New York Excessive Daytime Sleepiness Associated with Insufficient Sleep T. Roehrs, F. Zorick, J. Sicklesteel, R. Wittig, and T. Roth Sleep Disorders and Research
Simplest method: Questionnaires. Retrospective: past week, month, year, lifetime Daily: Sleep diary What kinds of questions would you ask?
 Spencer Dawson Simplest method: Questionnaires Retrospective: past week, month, year, lifetime Daily: Sleep diary What kinds of questions would you ask? Did you nap during the day? Bed time and rise time
Spencer Dawson Simplest method: Questionnaires Retrospective: past week, month, year, lifetime Daily: Sleep diary What kinds of questions would you ask? Did you nap during the day? Bed time and rise time
EEG Arousals: Scoring Rules and Examples. A Preliminary Report from the Sleep Disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association
 EEG Arousals: Scoring Rules and Examples A Preliminary Report from the Sleep Disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association Sleep in patients with a number of sleep disorders and
EEG Arousals: Scoring Rules and Examples A Preliminary Report from the Sleep Disorders Atlas Task Force of the American Sleep Disorders Association Sleep in patients with a number of sleep disorders and
LEARNING MANUAL OF PSG CHART
 LEARNING MANUAL OF PSG CHART POLYSOMNOGRAM, SLEEP STAGE SCORING, INTERPRETATION Sleep Computing Committee, Japanese Society of Sleep Research LEARNING MANUAL OF PSG CHART POLYSOMNOGRAM, SLEEP STAGE SCORING,
LEARNING MANUAL OF PSG CHART POLYSOMNOGRAM, SLEEP STAGE SCORING, INTERPRETATION Sleep Computing Committee, Japanese Society of Sleep Research LEARNING MANUAL OF PSG CHART POLYSOMNOGRAM, SLEEP STAGE SCORING,
What Is the Moment of Sleep Onset for Insomniacs?
 Sleep, 6(1): 10-\5 1983 Raven Press, New York What Is the Moment of Sleep Onset for Insomniacs? Peter Rauri and Elaine Olmstead Dartmouth Medical School, Hanover, New Hampshire, U,S,A, Summary: Subjective
Sleep, 6(1): 10-\5 1983 Raven Press, New York What Is the Moment of Sleep Onset for Insomniacs? Peter Rauri and Elaine Olmstead Dartmouth Medical School, Hanover, New Hampshire, U,S,A, Summary: Subjective
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY
 states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
states of brain activity sleep, brain waves DR. S. GOLABI PH.D. IN MEDICAL PHYSIOLOGY introduction all of us are aware of the many different states of brain activity, including sleep, wakefulness, extreme
Relationship of Periodic Movements in Sleep (Nocturnal Myoclonus) and the Babinski Sign
 Sleep. 8(3):239-243 1985 Raven Press. New York Relationship of Periodic Movements in Sleep (Nocturnal Myoclonus) and the Babinski Sign Robert C. Smith Sleep Disorders Center. St. Louis University. St.
Sleep. 8(3):239-243 1985 Raven Press. New York Relationship of Periodic Movements in Sleep (Nocturnal Myoclonus) and the Babinski Sign Robert C. Smith Sleep Disorders Center. St. Louis University. St.
A Modified Method for Scoring Slow Wave Sleep of Older Subjects
 Sleep, 5(2):195-199 1982 Raven Press, New York A Modified Method for Scoring Slow Wave Sleep of Older Subjects Wilse B. Webb and Lewis M. Dreblow Department of Psychology, University of Florida, Gainesville,
Sleep, 5(2):195-199 1982 Raven Press, New York A Modified Method for Scoring Slow Wave Sleep of Older Subjects Wilse B. Webb and Lewis M. Dreblow Department of Psychology, University of Florida, Gainesville,
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events
 The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
Patterns of Sleepiness in Various Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence
 Sleep, 5:S165S174 1982 Raven Press, New York Patterns of Sleepiness in Various Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence F. Zorick, T. Roehrs, G. Koshorek, J. Sicklesteel, *K. Hartse, R. Wittig, and T.
Sleep, 5:S165S174 1982 Raven Press, New York Patterns of Sleepiness in Various Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence F. Zorick, T. Roehrs, G. Koshorek, J. Sicklesteel, *K. Hartse, R. Wittig, and T.
Validity Established of DreamLight Cues for Eliciting Lucid Dreaming
 [LaBerge, S. and Levitan, L. (1995). Validity Established of DreamLight Cues for Eliciting Lucid Dreaming. Dreaming, 5(3): 159-68.] Validity Established of DreamLight Cues for Eliciting Lucid Dreaming
[LaBerge, S. and Levitan, L. (1995). Validity Established of DreamLight Cues for Eliciting Lucid Dreaming. Dreaming, 5(3): 159-68.] Validity Established of DreamLight Cues for Eliciting Lucid Dreaming
Neurophysiology & EEG
 Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Ultrashort Sleep-Wake Cycle: Timing of REM Sleep. Evidence for Sleep-Dependent and Sleep-Independent Components of the REM Cycle
 Sleep 10(1):62-68, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Ultrashort Sleep-Wake Cycle: Timing of REM Sleep. Evidence for Sleep-Dependent and Sleep-Independent Components
Sleep 10(1):62-68, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Ultrashort Sleep-Wake Cycle: Timing of REM Sleep. Evidence for Sleep-Dependent and Sleep-Independent Components
MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS
 MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS CONSCIOUSNESS Awareness of yourself and your environment. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS Biological rhythms (for example, of temperature and wakefulness) that
MODULE 08: SLEEP, DREAMS, AND BODY RHYTHMS CONSCIOUSNESS CONSCIOUSNESS Awareness of yourself and your environment. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS Biological rhythms (for example, of temperature and wakefulness) that
Sleep Spindle Detection Based on Complex Demodulation Jia-bin LI, Bei WANG* and Yu ZHANG
 International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 216) Sleep Spindle Detection Based on Complex Demodulation Jia-bin LI, Bei WANG* and Yu ZHANG Department of Automation, School of
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 216) Sleep Spindle Detection Based on Complex Demodulation Jia-bin LI, Bei WANG* and Yu ZHANG Department of Automation, School of
THE EFFECT OF WHOLE-BODY VIBRATION ON HUMAN PERFORMANCE AND PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS
 Industrial Health, 1977, 15, 13. THE EFFECT OF WHOLE-BODY VIBRATION ON HUMAN PERFORMANCE AND PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS PART 1. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF VERTICAL VIBRATION ON HUMAN SLEEP Kazuhide
Industrial Health, 1977, 15, 13. THE EFFECT OF WHOLE-BODY VIBRATION ON HUMAN PERFORMANCE AND PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS PART 1. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF VERTICAL VIBRATION ON HUMAN SLEEP Kazuhide
A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation
 1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
1 A 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation The following 3 minute polysomnogram (PSG) tracing was recorded in a 74-year-old man with severe ischemic cardiomyopathy
The REM Cycle is a Sleep-Dependent Rhythm
 Sleep, 2(3):299-307 1980 Raven Press, New York The REM Cycle is a Sleep-Dependent Rhythm L. C. Johnson Naval Health Research Center, San Diego, California Summary: Two studies, using data from fragmented
Sleep, 2(3):299-307 1980 Raven Press, New York The REM Cycle is a Sleep-Dependent Rhythm L. C. Johnson Naval Health Research Center, San Diego, California Summary: Two studies, using data from fragmented
XXVIII. Recording of Achilles tendon reflex
 XXVII. Examination of reflexes in man XXVIII. Recording of Achilles tendon reflex Physiology II - practice Dep. of Physiology, Fac. of Medicine, MU, 2016 Mohamed Al-Kubati Reflexes Reflex: is an involuntary
XXVII. Examination of reflexes in man XXVIII. Recording of Achilles tendon reflex Physiology II - practice Dep. of Physiology, Fac. of Medicine, MU, 2016 Mohamed Al-Kubati Reflexes Reflex: is an involuntary
Sleep Extension in Sleepy and Alert Normals
 Sleep 2(5):449-457, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Sleep Extension in Sleepy and Alert Normals Timothy Roehrs, Victoria Timms, Ardith Zwyghuizen-Doorenbos,
Sleep 2(5):449-457, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Sleep Extension in Sleepy and Alert Normals Timothy Roehrs, Victoria Timms, Ardith Zwyghuizen-Doorenbos,
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy
 Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
Practice test 1 spring 2011 copy Student: 1. The fundamental units of the nervous system are nerve cells, called: A. axons B. glial cells C. neurons D. neurotransmitters 2. Which of the following is NOT
(Received 8 December 1966)
 J. Physiol. (1967), 189, pp. 545-550 545 With 2 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain FUSIMOTOR STIMULATION AND THE DYNAMIC SENSITIVITY OF THE SECONDARY ENDING OF THE MUSCLE SPINDLE BY M. C. BROWN, I.
J. Physiol. (1967), 189, pp. 545-550 545 With 2 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain FUSIMOTOR STIMULATION AND THE DYNAMIC SENSITIVITY OF THE SECONDARY ENDING OF THE MUSCLE SPINDLE BY M. C. BROWN, I.
Students will be able to determine what stage of sleep someone is in by analyzing their EEG.
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to engage students with the concept of the neural circuit. The lesson and unit as a whole use sleep, a behavior everyone is familiar
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL. Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program)
 SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
Daytime Alertness in Patients with Chronic Insomnia Compared with Asymptomatic Control Subjects
 Sleep I ():54-60, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 988 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Daytime Alertness in Patients with Chronic Insomnia Compared with Asymptomatic Control Subjects Edward Stepanski,
Sleep I ():54-60, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 988 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Daytime Alertness in Patients with Chronic Insomnia Compared with Asymptomatic Control Subjects Edward Stepanski,
MOVEMENT RULES. Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program)
 MOVEMENT RULES Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) 1. Scoring Periodic Limb Movement in Sleep (PLMS) A. The following rules define
MOVEMENT RULES Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) 1. Scoring Periodic Limb Movement in Sleep (PLMS) A. The following rules define
Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence: Polygraphic and Clinical Data for 100 Patients
 Sleep, 4(1):23-37 1981 Raven Press, New York Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence: Polygraphic and Clinical Data for 100 Patients Johanna van den Hoed, Helena Kraemer, Christian Guilleminault, Vincent
Sleep, 4(1):23-37 1981 Raven Press, New York Disorders of Excessive Daytime Somnolence: Polygraphic and Clinical Data for 100 Patients Johanna van den Hoed, Helena Kraemer, Christian Guilleminault, Vincent
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT.
 CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
CONSCIOUSNESS IS DEFINED AS THE AWARENESS OF OURSELVES AND OUR ENVIRONMENT. CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS are our bodies biological cycles that occur every 24 hours. Sleep, blood pressure, body temperature are just
Cerebral Anoxic Attacks in Sleep Apnea Syndrome
 Sleep 12(5):400-404, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Cerebral Anoxic Attacks in Sleep Apnea Syndrome Fabio Cirignotta, Marco Zucconi, Susanna Mondini, Roberto
Sleep 12(5):400-404, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Cerebral Anoxic Attacks in Sleep Apnea Syndrome Fabio Cirignotta, Marco Zucconi, Susanna Mondini, Roberto
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
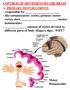 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Psychological Correlates of Electrodermal Activity During REM Sleep
 Sleep, 8(2):14fr-154 1985 Raven Press, New York Psychological Correlates of Electrodermal Activity During REM Sleep Andre Kushniruk, John Rustenburg, and Robert Ogilvie Departments of Psychology and Electronics,
Sleep, 8(2):14fr-154 1985 Raven Press, New York Psychological Correlates of Electrodermal Activity During REM Sleep Andre Kushniruk, John Rustenburg, and Robert Ogilvie Departments of Psychology and Electronics,
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man
 Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
Electrical recording with micro- and macroelectrodes from the cerebellum of man D. GRAHAM SLAUGHTER, M.D., BLAINE S. NASHOLD, Jn., M.D., AND GEORGE G. SOMJEN, M.D. The Division of Neurosurgery, and the
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to
 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
Sleep Stages and Scoring Technique
 CHAPTER 3 Sleep Stages and Scoring Technique Raman K. Malhotra Alon Y. Avidan Introduction to Sleep Stage Scoring The original Rechtschaffen and Kales sleep scoring manual of 1968, commonly known as the
CHAPTER 3 Sleep Stages and Scoring Technique Raman K. Malhotra Alon Y. Avidan Introduction to Sleep Stage Scoring The original Rechtschaffen and Kales sleep scoring manual of 1968, commonly known as the
Oxygen Consumption During Sleep: Influence of Sleep Stage and Time of Night
 Sleep 12(3):201-210, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Oxygen Consumption During Sleep: Influence of Sleep Stage and Time of Night Thomas Ryan, Stanislaw Mlynczak,
Sleep 12(3):201-210, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Oxygen Consumption During Sleep: Influence of Sleep Stage and Time of Night Thomas Ryan, Stanislaw Mlynczak,
Western Hospital System. PSG in History. SENSORS in the field of SLEEP. PSG in History continued. Remember
 SENSORS in the field of SLEEP Mrs. Gaye Cherry: Scientist in Charge Department of Sleep and Respiratory Medicine Sleep Disorders Unit Western Hospital PSG in History 1875: Discovery of brain-wave activity
SENSORS in the field of SLEEP Mrs. Gaye Cherry: Scientist in Charge Department of Sleep and Respiratory Medicine Sleep Disorders Unit Western Hospital PSG in History 1875: Discovery of brain-wave activity
Stages of Sleep * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49033 1 Stages of Sleep * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m49033 1 Stages of Sleep * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming. Elaine M. Hull
 Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
Biological Rhythms, Sleep, and Dreaming Elaine M. Hull Rhythms of Waking and Sleeping Animals generate 24 hour cycles of wakefulness and sleep. Some animals generate endogenous circannual rhythms (yearly
States of Consciousness
 States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
States of Consciousness Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Introduction Consciousness Awareness of oneself and one s environment Body Rhythms Biological Rhythms Periodic physiological fluctuations Can affect
Automated Sleep Stage Analysis Using Hybrid Rule-Based and Case-Based Reasoning
 Automated Sleep Stage Analysis Using Hybrid Rule-Based and Case-Based Reasoning ( ) 2000 8 Automated Sleep Stage Analysis Using Hybrid Rule-Based and Case-Based Reasoning Ph. D. Dissertation Automated
Automated Sleep Stage Analysis Using Hybrid Rule-Based and Case-Based Reasoning ( ) 2000 8 Automated Sleep Stage Analysis Using Hybrid Rule-Based and Case-Based Reasoning Ph. D. Dissertation Automated
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old
 Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
Physiology of Normal Sleep: From Young to Old V. Mohan Kumar Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram 1 What is sleep? As per behavioral criteria: Reduced motor
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Sleep is that golden chain that ties health and our bodies together. Thomas Dekker, English dramatist ( ).
 Sleep Sleep is that golden chain that ties health and our bodies together. Thomas Dekker, English dramatist (1572-1632). Without adequate sleep people become irritable, have lowered resistance to illness,
Sleep Sleep is that golden chain that ties health and our bodies together. Thomas Dekker, English dramatist (1572-1632). Without adequate sleep people become irritable, have lowered resistance to illness,
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to
 How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
How did you sleep last night? Were you in a deep sleep or light sleep? How many times did you wake up? What were you doing right before you went to bed? Finish presentations Homework for the weekend Interactive
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS
 37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Inter-REM Sleep Intervals Distribution in Healthy Young Subjects
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Inter-REM Sleep Intervals Distribution in Healthy Young Subjects Maria Josè Esposito, Ms.Sc.,Vincenzo Natale, M.D., Ph.D., Miranda Occhionero, M.D., Ph.D., and PierCarla Cicogna, Ph.D.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Inter-REM Sleep Intervals Distribution in Healthy Young Subjects Maria Josè Esposito, Ms.Sc.,Vincenzo Natale, M.D., Ph.D., Miranda Occhionero, M.D., Ph.D., and PierCarla Cicogna, Ph.D.
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems
 PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-7 Biopotentials- 2) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/ Electromyogram (EMG) Skeletal muscles are
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-7 Biopotentials- 2) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/ Electromyogram (EMG) Skeletal muscles are
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 24 Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Module 24: Sleep,
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 24 Sleep, Dreams, and Body Rhythms Module 24: Sleep,
Artifact Recognition and Troubleshooting
 Artifact Recognition and Troubleshooting 2017 Focus Fall Super Session The Best of the Best For Respiratory Therapists and Sleep Technologists The Doubletree Hilton Hotel Pittsburgh, PA Thursday Sept.
Artifact Recognition and Troubleshooting 2017 Focus Fall Super Session The Best of the Best For Respiratory Therapists and Sleep Technologists The Doubletree Hilton Hotel Pittsburgh, PA Thursday Sept.
Chapter 5. Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition
 Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
Chapter 5 Variations in Consciousness 8 th Edition Consciousness: Personal Awareness Awareness of Internal and External Stimuli Levels of awareness James stream of consciousness Freud unconscious Sleep/dreaming
(Received 10 April 1956)
 446 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 446-455 A COMPARISON OF FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR REFLEXES OF MUSCULAR ORIGIN BY M. G. F. FUORTES AND D. H. HUBEL From the Department ofneurophysiology, Walter Reed Army Institute
446 J. Physiol. (I956) I33, 446-455 A COMPARISON OF FLEXOR AND EXTENSOR REFLEXES OF MUSCULAR ORIGIN BY M. G. F. FUORTES AND D. H. HUBEL From the Department ofneurophysiology, Walter Reed Army Institute
Atlas, rules, and recording techniques for the scoring of cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) in human sleep
 Sleep Medicine 3 (2002) 187 199 Consensus Report Atlas, rules, and recording techniques for the scoring of cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) in human sleep Mario Giovanni Terzano a, *, Liborio Parrino a,
Sleep Medicine 3 (2002) 187 199 Consensus Report Atlas, rules, and recording techniques for the scoring of cyclic alternating pattern (CAP) in human sleep Mario Giovanni Terzano a, *, Liborio Parrino a,
An exploratory sleep laboratory study
 Lucid dream induction by visual and tactile stimulation I J o Lucid dream induction by visual and tactile stimulation: An exploratory sleep laboratory study Franc Paul 1, Melanie Schädlich 2, & aniel Erlacher
Lucid dream induction by visual and tactile stimulation I J o Lucid dream induction by visual and tactile stimulation: An exploratory sleep laboratory study Franc Paul 1, Melanie Schädlich 2, & aniel Erlacher
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
EFFICACY OF MODAFINIL IN 10 TAIWANESE PATIENTS WITH NARCOLEPSY: FINDINGS USING THE MULTIPLE SLEEP LATENCY TEST AND EPWORTH SLEEPINESS SCALE
 EFFICACY OF MODAFINIL IN 10 TAIWANESE PATIENTS WITH NARCOLEPSY: FINDINGS USING THE MULTIPLE SLEEP LATENCY TEST AND EPWORTH SLEEPINESS SCALE Shih-Bin Yeh 1 and Carlos Hugh Schenck 2,3 1 Department of Neurology
EFFICACY OF MODAFINIL IN 10 TAIWANESE PATIENTS WITH NARCOLEPSY: FINDINGS USING THE MULTIPLE SLEEP LATENCY TEST AND EPWORTH SLEEPINESS SCALE Shih-Bin Yeh 1 and Carlos Hugh Schenck 2,3 1 Department of Neurology
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
Neonatal EEG Maturation
 Neonatal EEG Maturation Cindy Jenkinson, R. EEG T., CLTM October 7, 2017 Fissure Development 3 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/develop ment-human-embryonic-brain 4 WHAT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW BEFORE I
Neonatal EEG Maturation Cindy Jenkinson, R. EEG T., CLTM October 7, 2017 Fissure Development 3 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/develop ment-human-embryonic-brain 4 WHAT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW BEFORE I
Sleep Stage Scoring. emedicine.medscape.com. emedicine Specialties > Neurology > Sleep-Related Diseases
 emedicine.medscape.com emedicine Specialties > Neurology > Sleep-Related Diseases Sleep Stage Scoring Ron A Shatzmiller, MD, MSc, Fellow in Clinical Neurophysiology, Department of Neurology, Keck School
emedicine.medscape.com emedicine Specialties > Neurology > Sleep-Related Diseases Sleep Stage Scoring Ron A Shatzmiller, MD, MSc, Fellow in Clinical Neurophysiology, Department of Neurology, Keck School
The Effects of Presleep Stress on Sleep-Onset Insomnia
 Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1981, Vol. 90, No. 6, 601-606 Copyright 1981 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0021-843X/81/9006-0601S00.75 The Effects of Presleep Stress on Sleep-Onset Insomnia
Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1981, Vol. 90, No. 6, 601-606 Copyright 1981 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0021-843X/81/9006-0601S00.75 The Effects of Presleep Stress on Sleep-Onset Insomnia
Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data
 Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Recognition of Sleep Dependent Memory Consolidation with Multi-modal Sensor Data The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
An Overview of BMIs. Luca Rossini. Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications
 An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
An Overview of BMIs Luca Rossini Workshop on Brain Machine Interfaces for Space Applications European Space Research and Technology Centre, European Space Agency Noordvijk, 30 th November 2009 Definition
CLASSIFICATION OF SLEEP STAGES IN INFANTS: A NEURO FUZZY APPROACH
 CLASSIFICATION OF SLEEP STAGES IN INFANTS: A NEURO FUZZY APPROACH J. E. Heiss, C. M. Held, P. A. Estévez, C. A. Perez, C. A. Holzmann, J. P. Pérez Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile,
CLASSIFICATION OF SLEEP STAGES IN INFANTS: A NEURO FUZZY APPROACH J. E. Heiss, C. M. Held, P. A. Estévez, C. A. Perez, C. A. Holzmann, J. P. Pérez Department of Electrical Engineering, Universidad de Chile,
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Guidelines for the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): A Standard Measure of Sleepiness *
 Sleep 9(4):519-524, Raven Press, New York 1986, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Guidelines for the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): A Standard Measure of Sleepiness * Chairman: Mary A. Carskadon
Sleep 9(4):519-524, Raven Press, New York 1986, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Guidelines for the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT): A Standard Measure of Sleepiness * Chairman: Mary A. Carskadon
Non-REM Lucid Dreaming. Joe Dane Pain Management Center University of Virginia Medical School
 Non-REM Lucid Dreaming Joe Dane Pain Management Center University of Virginia Medical School As with Pierre and others, I m not going to try to present a lot of the details of our study, nor defend what
Non-REM Lucid Dreaming Joe Dane Pain Management Center University of Virginia Medical School As with Pierre and others, I m not going to try to present a lot of the details of our study, nor defend what
March 14. Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part Dream Journal Assignment
 March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
March 14 Agenda: 1. Graphic Organizer Part 1 for Unit 5 2. Sleep episode Table of Contents: 91. March 14 & 15 92. Unit 5 Graphic Organizer part 1 93. Dream Journal Assignment Homework: 1. Test on Friday!
Dream Sources, Associative Mechanisms, and Temporal Dimension
 Sleep 10(1):78-83, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Dream Sources, Associative Mechanisms, and Temporal Dimension Corrado Cavallero Department of Psychology, University
Sleep 10(1):78-83, Raven Press, New York 1987, Association of Professional Sleep Societies Dream Sources, Associative Mechanisms, and Temporal Dimension Corrado Cavallero Department of Psychology, University
HHS Public Access Author manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 September 19.
 Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Selective optical drive of thalamic reticular nucleus generates thalamic bursts & cortical spindles Michael M. Halassa 1,2,4, Joshua H. Siegle 2,4, Jason T. Ritt 3, Jonathan T. Ting 2, Guoping Feng 2,
Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1967, 30, 233 Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt C.-B. YAP AND T. HIROTA From the Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Northwestern University Medical School,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1967, 30, 233 Sciatic nerve motor conduction velocity studyt C.-B. YAP AND T. HIROTA From the Department of Neurology and Psychiatry, Northwestern University Medical School,
Healing Through Lucid Dreams. Stephen LaBerge Stanford University & Saybrook Institute
 Healing Through Lucid Dreams Stephen LaBerge Stanford University & Saybrook Institute According to Jaffe and Bresler (1980), mental imagery mobilizes the latent, inner powers of the person, which have
Healing Through Lucid Dreams Stephen LaBerge Stanford University & Saybrook Institute According to Jaffe and Bresler (1980), mental imagery mobilizes the latent, inner powers of the person, which have
linkedin.com/in/lizziehillsleeptechservices 1
 BSS2015 Hands-On Tech Breakfast SCORING SLEEP USING AASM GUIDELINES: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION Lizzie Hill BSc RPSGT EST Specialist Respiratory Clinical Physiologist, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh
BSS2015 Hands-On Tech Breakfast SCORING SLEEP USING AASM GUIDELINES: A BRIEF INTRODUCTION Lizzie Hill BSc RPSGT EST Specialist Respiratory Clinical Physiologist, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh
Increase of Regional Cerebral Blood Volume during REM-Sleep in Man l
 Free Communications: E. Phenomenology of Sleep in Man 384 References BELL, A. 1.; STROEBEL, C. F., and PRIOR, D. D.: Interdisciplinary study. Scrotal sac and testes psychophysiological and psychological
Free Communications: E. Phenomenology of Sleep in Man 384 References BELL, A. 1.; STROEBEL, C. F., and PRIOR, D. D.: Interdisciplinary study. Scrotal sac and testes psychophysiological and psychological
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep Stage Estimation Based on Approximate Heartrate Calculated from Other Persons
 The AAAI 2017 Spring Symposium on Wellbeing AI: From Machine Learning to Subjectivity Oriented Computing Technical Report SS-17-08 Sleep Stage Estimation Based on Approximate Heartrate Calculated from
The AAAI 2017 Spring Symposium on Wellbeing AI: From Machine Learning to Subjectivity Oriented Computing Technical Report SS-17-08 Sleep Stage Estimation Based on Approximate Heartrate Calculated from
Nightcap Measurement of Sleep Quality in Self-Described Good and Poor Sleepers
 Sleep, 17(8):688-692 1994 American Sleep Disorders Association and Sleep Research Society Sleep Quality, Behavioral Scales and Sleep Scoring Nightcap Measurement of Sleep Quality in Self-Described Good
Sleep, 17(8):688-692 1994 American Sleep Disorders Association and Sleep Research Society Sleep Quality, Behavioral Scales and Sleep Scoring Nightcap Measurement of Sleep Quality in Self-Described Good
What is Consciousness?
 What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
What is Consciousness? Module 6 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind: Dual processing, Sleep and Dreams Class Objectives What is consciousness? What are the stages of sleep? How does sleep deprivation
Chapter 2 Normal Human Sleep : An Overview Mary A. Carskadon, William C. Dement Abstract
 Carskadon, M.A., & Dement, W.C. (2011). Monitoring and staging human sleep. In M.H. Kryger, T. Roth, & W.C. Dement (Eds.), Principles and practice of sleep medicine, 5th edition, (pp 16-26). St. Louis:
Carskadon, M.A., & Dement, W.C. (2011). Monitoring and staging human sleep. In M.H. Kryger, T. Roth, & W.C. Dement (Eds.), Principles and practice of sleep medicine, 5th edition, (pp 16-26). St. Louis:
I. What Is Consciousness? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you. 3 Meanings of Consciousness
 I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
I. What Is? Definition Awareness of things inside you and outside you I. What Is? is a construct What is a construct? Something that we can t directly see or measure Examples: self-esteem intelligence
Spontaneous EEG and Sleep Donders MEG/EEG Toolkit Martin Dresler
 Spontaneous EEG and Sleep Donders MEG/EEG Toolkit Martin Dresler Spontaneous EEG and Sleep Agenda Recording methods Oscillations on different time scales Examples: functions of sleep Polysomnography Electroencephalogram
Spontaneous EEG and Sleep Donders MEG/EEG Toolkit Martin Dresler Spontaneous EEG and Sleep Agenda Recording methods Oscillations on different time scales Examples: functions of sleep Polysomnography Electroencephalogram
Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man*
 X Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man* A. J. Mandell, 6. Chaffey, P. Sri 11, M. P. Mandell, J. Rodnick, R. T. Rubin and R. Sheff Biochemical Correlates Laboratory Departments
X Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man* A. J. Mandell, 6. Chaffey, P. Sri 11, M. P. Mandell, J. Rodnick, R. T. Rubin and R. Sheff Biochemical Correlates Laboratory Departments
Automobile Accidents in Patients with Sleep Disorders
 Sleep 12(6):487-494, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Automobile Accidents in Patients with Sleep Disorders Michael S. Aldrich Department of Neurology, University
Sleep 12(6):487-494, Raven Press, Ltd., New York 1989 Association of Professional Sleep Societies Automobile Accidents in Patients with Sleep Disorders Michael S. Aldrich Department of Neurology, University
Multiple Naps and the Evaluation of Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Upper Airway Sleep Apnea
 Sleep. 3(3/4):425-439 1980 Raven Press. New York, Multiple Naps and the Evaluation of Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Upper Airway Sleep Apnea T. Roth, K. M. Hartse, F. Zorick, and W. Conway Sleep
Sleep. 3(3/4):425-439 1980 Raven Press. New York, Multiple Naps and the Evaluation of Daytime Sleepiness in Patients with Upper Airway Sleep Apnea T. Roth, K. M. Hartse, F. Zorick, and W. Conway Sleep
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events
 The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events The 2007 AASM Scoring Manual vs. the AASM Scoring Manual v2.0 October 2012 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events The 2007 AASM Scoring Manual vs. the AASM Scoring Manual v2.0 October 2012 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity.
 Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Sleep is a state of altered consciousness (different levels of awareness), characterized by certain patterns of brain activity. State of awareness, including a person s feelings, sensations, ideas, and
Periodic Leg Movements in Narcolepsy
 In: Nacrolepsy: Symptoms, Causes... ISBN: 978-1-60876-645-1 Editor: Guillermo Santos, et al. 2009 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. Chapter 7 Periodic Leg Movements in Narcolepsy Ahmed Bahammam * Sleep Disorders
In: Nacrolepsy: Symptoms, Causes... ISBN: 978-1-60876-645-1 Editor: Guillermo Santos, et al. 2009 Nova Science Publishers, Inc. Chapter 7 Periodic Leg Movements in Narcolepsy Ahmed Bahammam * Sleep Disorders
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
Induction of Visual Imagery During NREM Sleep
 Sleep, 20(11 ):948-956 1997 American Sleep Disorders Association and Sleep Research Society Induction of Visual Imagery During NREM Sleep *Russell Conduit, tdorothy Bruck and :j:grahame Coleman *School
Sleep, 20(11 ):948-956 1997 American Sleep Disorders Association and Sleep Research Society Induction of Visual Imagery During NREM Sleep *Russell Conduit, tdorothy Bruck and :j:grahame Coleman *School
Neuroscience of Consciousness I
 1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness I Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 What is consciousness? 3 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive
1 C83MAB: Mind and Brain Neuroscience of Consciousness I Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 2 What is consciousness? 3 Consciousness State of consciousness - Being awake/alert/attentive/responsive
SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE
 of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
Physiology. D. Gordon E. Robertson, PhD, FCSB. Biomechanics Laboratory, School of Human Kinetics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
 Electromyography: Physiology D. Gordon E. Robertson, PhD, FCSB Biomechanics Laboratory, School of Human Kinetics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada Nervous System Central Nervous System (cerebellum,
Electromyography: Physiology D. Gordon E. Robertson, PhD, FCSB Biomechanics Laboratory, School of Human Kinetics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada Nervous System Central Nervous System (cerebellum,
