Chapter 8 teachers 1) A drug is a substance, other than food which may: a) Give us energy b) Relax us when nervous c) Change our ways of thinking
|
|
|
- Berenice Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8 teachers 1) A drug is a substance, other than food which may: a) Give us energy b) Relax us when nervous c) Change our ways of thinking 2) When one is addicted to a substance, the body: a) Requires the substance to feel normal (A) b) Requires the substance to feel high c) Requires the substance to feel happy d) Requires the substance to stay alive 3) In substance abuse, the term craving refers to: a) The subjective drive that addict s have to use the substance (A) b) Overwhelming desire to get high c) Overwhelming desire to feel happy d) Overwhelming desire to blot out reality 4) The term psychological dependence is used when: a) It is clear that the individual has changed their life to ensure continued use of the drug b) Their activities are centred on the drug and its use c) Leads to neglect of other important activities such as work, social and family commitments 5) The DSM-IV-TR criteria for substance dependence includes: a) The substance is often taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than was intended b) There is a persistent desire or unsuccessful efforts to cut down or control substance use c) A great deal of time is spent in activities necessary to obtain the substance 6) Tolerance in substance dependence is defined by which two of the following? a) A need for markedly increased amounts of the substance to achieve intoxication or desired effect (A) b) Markedly diminished effect with continued use of the same amount of the substance (A) c) A relaxed attitude towards others drug use d) A desire to socialise the act of drug taking 7) Withdrawal in substance dependence is defined by which two of the following? a) The characteristic withdrawal syndrome for the substance (A)
2 b) The same (or closely related) substance is taken to relieve or avoid withdrawal symptoms (A) c) Closet substance misuse d) Becoming socially withdrawn 8) Which of the following are characteristic of substance abuse? a) Failure to meet many normal daily obligations because of the drug b) Using the substance in ways which may be physically hazardous c) Legal-problems resulting from behaviour caused directly or indirectly by the drug 9) Which of the following is an example of a Substance use disorder (SUD)? a) Alcohol related disorders b) Caffeine related disorders c) Inhalant related disorders 10. The lifetime prevalence rate for substance dependence in the US has been calculated at? a) 5.1% (A) b) 10% c) 22.8% d) 43% 10) In the US it has been calculated that which percentage individuals aged between years had used illegal drugs, non-medical prescription drugs, or inhalants at some point in their lives? a) 51% (A) b) 80% c) 11.4% d) 5.1% 11) Which of the following is not a stimulant? a) Cocaine b) Amphetamine c) Caffeine d) Phenylalanine (A) 12) Which of the following is not a sedative? a) Opiates b) Phosphates (A) c) Barbiturates d) Analgesic 13) Which of the following is not a hallucinogenic? a) Cannabis b) MDMA c) LSD
3 d) Antibiotics (A) 14) Which statistic represents the figure in the UK of males which have sometime consumed a drink containing alcohol? a) 92% (A) b) 65% c) 21% d) 72% 15) Which statistic represents the figure in the UK of females which have sometime consumed a drink containing alcohol? a) 86% (A) b) 92% c) 45% d) 72% 16) In the UK a male hazardous drinker would consume? a) 5 or more standard drinks (A) b) 10 or more standard drinks c) 7 or more standard drinks d) 4 or more standard drinks on a typical drinking day 17) In the UK a female hazardous drinker would consume? a) 3 or more standard drinks (A) b) 5 or more standard drinks c) 7 or more standard drinks d) 10 or more standard drinks on a typical working day 18) In 2002 what percent of English school children below the age of 11years reported having consumed alcohol? a) 61% (A) b) 80% c) 25% d) 80% 19) In the UK, binge drinking in males is defined as: a) At least 8 units a day (A) b) At least 4 units a day c) At least 10 units a day
4 d) At least 15 units a day 20) In the UK, binge drinking in females is defined as: a) At least 6 units a day (A) b) At least 10 units a day c) At least 2 units a day d) At least 15 units a day 21) Which of the following percentages in the UK represents men who report binge drinking at least once a month? a) 58% (A) b) 73% c) 22% d) 96% 22) Which of the following percentages in the UK represents women who report binge drinking at least once a month? a) 34%(A) b) 65% c) 83% d) 21% 23) The main constituent of alcohol is: a) Ethyl alcohol (A) b) Lethal alcohol c) Methyal alcohol d) Benzo alcohol 24) At first, alcohol acts to relax the individual, and it does this by influencing the receptors associated with the neurotransmitter:
5 a) GABA (A) b) Acetylcholine c) Serotonin d) Dopamine 25) With alcohol, initially the drinker is reactive and happy, but later effects acts as a depressant. This course of the effect of alcoholis know as? a) Biphasic (A) b) Bipolar c) Biopic d) Binomial 26) Following withdrawal after extended heavy drinking over a number of years, the drinker may experience: a) Delirium tremens (DTs) (A) b) Saccadian Dysrhythmia c) Homeostasis d) Leptokurtic reaction 27) After extended heavy drinking over a number of years, a drinker may experience delirium tremens (DTs). Which of the following are symptoms of DTs? a) Unpleasant hallucinations b) Shaking c) Muscle tremors 28) Longer-term negative physical effects of heavy alcohol consumption include: a) Brain damage
6 b) Stomach ulcers c) Early dementia 29) The consequence of vitamin and mineral deficiencies which can lead to dementia and memory disorders in alcohol abuse, is known as: a) Korsakoff s syndrome (A) b) Smirnoff s syndrome c) Helmert syndrome d) Huynh-Feldt syndrome 30) Heavy drinking in women during pregnancy can cause foetal alcohol syndrome (FAS). Which of the following abnormalities are found in babies born with FAS? a) Heart problems b) Stunted growth c) Learning difficulties 31) Alcohol Dependence is supported specifically by evidence of tolerance effects and withdrawal symptoms that develop within: a) 4-12 hours of restricted consumption (A) b) 1-2 hours of restricted consumption c) 3-6 hours of restricted consumption d) hours of restricted consumption 32) Alcohol abuse has fewer symptoms than dependence, but can still have negative effects on daily life. Which of the following are features that may affect performance? a) After effects of drinking b) Intoxication while at work
7 c) Child care responsibilities 33) A US national survey indicated that workplace alcohol use and impairment directly affected what percentage of the US workforce? a) 15% (A) b) 65% c) 32% d) 41% 34) A US national survey indicated what percentage of the US workforce was working under the influence of alcohol? a) 1.6% (A) b) 5% c) 10.3% d) 7% 35) A US national survey indicated what percentage of the US workforce was working with a hangover? a) 9.2% (A) b) 3% c) 15.5% d) 1.6% 36) The lifetime prevalence rate for alcohol dependence and abuse is: a) 15% (A) b) 25% c) 35% d) 45%
8 37) The rate of alcohol dependence in the general population at any one time is around: a) 5% (A) b) 10% c) 15% d) 20% 38) In substance abuse the term polydrug abuse refers to: a) Abuse of more than one drug at a time (A) b) The use of artificially manufactured drugs c) The abuse of placebos d) The abuse of three or more drugs at the same time 39) In polydrug abuse, which percentage of alcohol abuse percentage are smokers? a) 80% (A) b) 20% c) 35% d) 5% 40) Alcohol dependence and abuse is frequently comorbid with a range of other psychological disorders, including: a) Mood disorders b) Anxiety disorders c) Schizophrenia 41) Which of the following represents the percentage of suicides in which alcohol appears to play an important role?
9 a) 25% (A) b) 35% c) 14% d) 5% 42) In economic terms, alcohol-related problems cost the US economy in 1998 cost around: a) $185 billion (A) b) $10 million c) $270 million d) $450 billion 43) Annual alcohol-related costs of crime and public disorder in the UK in 2003 were estimated at: a) 7.3 billion (A) b) 1.2 million c) 1.2 billion d) 7.3 million 44) Annual alcohol-related workplace costs in the UK in 2003 were: a) 6.4 billion (A) b) 6.4 million c) 1.2 billion d) 1.2 million 45) Alcohol related costs to the UK National Health Service per annum are: a) 1.7 billion (A) b) 1.7 million
10 c) 6.8 billion d) 6.8 million 46) In the UK accident and emergency attendance costs related to alcohol problems are estimated at: a) 35% (A) b) 45% c) 25% d) 15% 47) Drink driving accounts for: a) 20% (A) b) 10% c) 15% d) 30% of all road deaths on the UK 48) Norstrom & Ramstedt (2005) found that per capita alcohol consumption in a country significantly predicted: a) Mortality from liver cirrhosis and other alcohol-related diseases b) Mortality from accidents and homicide C) death from suicide 49) Nicotine has a number of physical effects, including: a) Increasing blood pressure and heart rate
11 b) Reducing self-reported stress levels c) Reducing feelings of anxiety and anger 50) Growing evidence to suggest that nicotine has its effects by: a) Releasing dopamine in the mesolimbic system of the brain (A) b) Releasing serotonin into the cerebellum c) Releasing GABA into the hypothalamus d) Releasing acetylcholine into the diencephalons 51) In substance abuse the effects of dopamine released in the mesolimbic system is to: a) Elevate mood b) Decrease appetite c) Enhance cognitive functioning 52) After alcohol, nicotine is the: a) Second (A) b) Third c) Fourth d) Fifth most widely used drug in the world
12 53) It is estimated that: a) One third (A) b) One quarter c) Two thirds d) Three quarters of the adult global population smokes 54) While the rate of smoking is gradually falling in developed nations, which of the following represents the rise per year in the developing world? a) 3.4% (A) b) 10% c) 5.8% d) 15.7% 55) Evidence suggests that around 50% of those who start smoking in their adolescent years will go on to smoke for at least a further: a) years (A) b) 5-10 years c) years d) years
13 56) Which of the following percentages represent the number of smokers who a) want to give up, but b) said it would be difficult to go without a cigarette for a day? a) 68% and 55% (A) b) 78% and 15% c) 75% and 12% d) 80% and 60% 57) Abstinence or restricted access to nicotine produces a well-defined withdrawal syndrome. Which of the following are symptoms? a) Dysphonic or depressed mood b) Insomnia c) Difficulty concentrating 58) Which pf the following percent represents the number of regular smokers meet the diagnostic criteria for nicotine dependence? a) 80-90% (A) b) 20-30% c) 30-40% d) 60-70% 59) Which of the following are additional characteristics associated with nicotine dependence?
14 a) Smoking when ill b) Smoking soon after waking c) Smoking more in the morning than the afternoon 60) Which percentage represents the co morbidity of nicotine dependence with other psychiatric disorders? a) 55-90% (A) b) 20-30% c) 30-40% d) 30-60% 61) Studies suggest that children are more likely to take up smoking when influenced by? a) Advertising (A) b) Peer pressure c) Parental behaviour d) Sibling behaviour 62) According to Wesnes & Warburton (1983), smokers will feel the post-cigarette benefit of increased concentration and better cognitive performance due to? a) CNS stimulant properties of nicotine (A) b) The behaviour reinforced ritual of smoking c) The enforced cerebral rest of a cigarette break d) Raising of Serotonin levels
15 63) Smoking a cigarette generates feelings of relaxation pleasure and improved concentration as nicotine levels increase and normal psychological functioning is restored. This suggests that: a) Mood modulation (A) b) Increased blood pressure c) Changes in levels of GABA d) The behavioural ritual is an important part of nicotine dependence 64) Parrott s (1998, 1999) model of smoking as an addictive activity attempts to explain why negative mood plays an important role in maintaining smoking because: a) Relapse during attempts to quit smoking frequently occur under conditions of high stress b) Nicotine dependence is related to number of adverse childhood experiences and the incidence of depression in young adults c) Individuals with depression or anxiety develop nicotine dependence more rapidly than others 65) Smoking is a significant risk factor in: a) Heart disease b) Cancer of the pancreas
16 c) Cancer of the kidneys 66) In the UK, what percent of patients are admitted to NHS hospitals every year due to smoking-related diseases? a) Over 300,000 (A) b) Over 200,000 c) Over d) Over 600,000 67) In the UK, the treatment of smoking-related disorders costs the NHS around: a) billion a year (A) b) million a year c) billion a year d) million a year 68) Jamrozik (2005) estimated that across the UK as a whole, passive smoking at work is likely to be responsible for: a) 617 deaths a year (A) b) 250 deaths a year c) 894 deaths a year d) 135 deaths a year
17 69) Second-hand smoke at home accounts for: a) 2700 deaths in persons aged years (A) b) 1500 deaths in persons aged years c) 5000 deaths in persons aged years d) 1350 deaths in persons aged years 70) Cocaine is a natural stimulant derived from: a) The coca plant (A) b) The cactus plant c) The cocoa plant d) Baobab plant 71) The main effects of cocaine are caused by the drug: a) Blocking the reuptake of dopamine in the brain (A) b) Blocking the reuptake of serotonin in the brain c) Blocking the reuptake of acetylcholine in the brain d) Blocking the reuptake of GABA in the brain 72) In the early years of the 20 th century, many viewed cocaine as a drug with many positive attributes. These included which if the following? a) Pain relief
18 b) To reduce depression c) Used in the original Coca-Cola recipe 73) High doses of cocaine can cause cocaine intoxication. This may produce which of the following symptoms? a) Impaired judgement b) Psychotic episodes c) Hallucinogenic episodes 74) The physical effects of cocaine intoxication may include: a) Perspiration or chills b) Nausea or vomiting c) Cardiac irregularities 75) Chronic use of cocaine may cause: a) Changes in personality b) Memory deficits c) Increased risk of stroke
19 76) Cocaine can be ingested by free-basing where a purer cocaine alkaloid is obtained. This process involves: a) Heating the processed cocaine and inhaling the smoking (A) b) Ingesting the cocaine in food c) Ingesting the cocaine through the nasal passages d) Obtaining cocaine on prescription 77) Crack cocaine is currently a popular way to ingest the drug. It consist of: a) Free-based cocaine boiled down into crystalline balls (A) b) Cocaine cut with heroine c) Cocaine mixed with Cannabis d) Synthetically produced cocaine 78) According to the World Health Organisation (WHO) the lifetime prevalence rate of cocaine use in developed countries is: a) 1-3% (A) b) 10-15% c) 5-10% d) 15-20%
20 79) Lifetime prevalence rates of Cocaine use in the USA is: a) 14.4% (A) b) 25% c) 34.4% d) 42% 80) Cocaine use by young adults aged in the UK is around: a) 4% (A) b) 10% c) 2% d) 20% 81) Cocaine dependence occurs when the individual finds it difficult to resist using the drug. Evidence from animal studies that a single exposure to cocaine induces longterm changes in? a) Dopamine neurons in the brain (A) b) Changes in Serotonin re-uptake c) Changes in Frontal lobe activity d) Changes in GABA levels in the hippocampus 82) When not taking cocaine, severe withdrawal symptoms can occur. These include: a) Hypersomnia b) Increased appetite
21 c) Negative and depressed mood 83) A long-term user of cocaine may well develop symptoms of other psychological disorders, such as: a) Major depression b) Social phobia c) Eating disorders 84) Acute intoxication is often associated with cocaine abuse, and this is characterized by: a) Rambling speech b) Headaches c) Tinnitus 85) Which of the following are characteristics of cocaine abuse? a) Paranoid ideation b) Auditory and tactile hallucinations c) Anger
22 86) In a study of 112 regular male cocaine users with an average age of 44 years: a) 30.4% (A) b) 10.4% c) 20.4% d) 40.4% showed evidence of coronary artery aneurysms 87) Which of the following are common forms are amphetamine? a) Benzedrine b) Dexedrine c) Methedrine 88) Small doses, amphetamines enable individuals to feel alert, confident and energized. However, contrary to popular belief they do not help: a) Intellectual skills (A) b) Libido c) Reaction times d) Memory
23 89) According to DSM-IV-TR the lifetime prevalence of amphetamine use disorders is around: a) 1.5% (A) b) 2.5% c) 3.5% d) 4.5% 90) The World Health Organisation estimates that the use of amphetaminetype stimulants accounts for: e) 16% (A) f) 25% g) 5% h) 30% of worldwide illicit drug abuse 91) Those dependent on methamphetamine (so-called speed freaks ), may become: a) Anxious, b) Paranoid c) Aggressive
24 92) Physical symptoms of Amphetamine intoxication include: a) Pupillary dilation b) Perspiration or chills c) Nausea or vomiting 93) Caffeine is taken in one form or another by: a) 85% (A) b) 70% c) 65% d) 95% of the population of the world 94) Caffeine intoxication can include which of the following physical and psychological effects? a) Flushed face b) Diuresis c) Muscle twitching
25 95) Symptoms of Caffeine withdrawal include which of the following? a) Depression b) Anxiety c) Fatigue 96) Which of the following are derivatives of Opium? a) Morphine b) Codeine c) Heroin 97) A synthetic form of Opium was developed by the German s during World War II. This is known as? a) Methadone (A) b) Prednisalone c) Cortisone d) Polyheroin 98) The most widely abused of the Opiates is: a) Heroin (A)
26 b) Methadone c) Morphine d) Codeine 99) Opiates have their effects by depressing the central nervous system, and the drug attaches to brain receptor sites that normally receive: a) Endorphins (A) b) Hormones c) Geons d) Neurons 100) What percent of people worldwide are estimate to take opiates? a) 13.5% (A) b) 35% c) 2.7% d) 25%
Main Questions. Why study addiction? Substance Use Disorders, Part 1 Alecia Schweinsburg, MA Abnromal Psychology, Fall Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders. A Major Problem. Defining Addiction 2/24/2009. Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 %
 Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29
 PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. RG 5c
 PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
Table of Contents VOLUME 1
 VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Understanding Addiction and Dugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN wawilson@duke.edu There is a lot of epidemiological evidence that addiction begins before brain maturity, and lately some biological
Chapter 23. Medicines and Drugs
 Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Live A Life Above The Influence!
 Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
Drug abuse: Drug misuse Dependence abuse
 Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
Drug abuse: Use of drugs for non-medical purposes Drug misuse: wrong use of drugs: Wrong choice Wrong dose & wrong duration e.g. misuse of antibiotics Dependence is associated with abuse 1 Repeated, periodic
4 CATEGORIES. Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs
 DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
The causes of misuse:
 The Drug Misuse The causes of misuse: Availability of drugs. A vulnerable personality. Adverse social environment. Regular drug taking play a role. Determining misuse and dependence, it is unclear whether
The Drug Misuse The causes of misuse: Availability of drugs. A vulnerable personality. Adverse social environment. Regular drug taking play a role. Determining misuse and dependence, it is unclear whether
ADDICTIONS. Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry
 ADDICTIONS Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Addictions-terminology drug abuse drug dependence drug addiction intoxication withdrawal tolerance
ADDICTIONS Mine Özmen, M.D. University of İstanbul Cerrahpaşa School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry Addictions-terminology drug abuse drug dependence drug addiction intoxication withdrawal tolerance
Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Substance Use Disorder This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and
Substance Use Disorders Substance Use Disorder This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars monthly to address topics related to risk adjustment documentation and
Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs
 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP
 Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
Neurobiology of Addiction JeanAnne Johnson Talbert, DHA, APRN BC, FNP, CARN AP Disclosures This speaker has no conflicts of interest to disclose Objectives Define drug abuse and addiction Identify the
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes. Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
 Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes mood, perception, memory, state of consciousness May be illegal: Heroin Cocaine Legal: Alcohol nicotine Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
Psychoactive drugs Drugs which affect mental processes mood, perception, memory, state of consciousness May be illegal: Heroin Cocaine Legal: Alcohol nicotine Legal but restricted (by prescription only)
Psychoactive Drugs. Psychoactive drug: A chemical substance that alters perceptions and mood.
 LP 5C Drugs and alcohol 1 Psychoactive Drugs Psychoactive drug: A chemical substance that alters perceptions and mood. Your textbook characterizes three broad categories of psychoactive drugs Depressants:
LP 5C Drugs and alcohol 1 Psychoactive Drugs Psychoactive drug: A chemical substance that alters perceptions and mood. Your textbook characterizes three broad categories of psychoactive drugs Depressants:
Build Science Skills. Address Misconceptions. Answer to... UNIVERSAL ACCESS. Nervous System 911
 Section 35 5 35 5 Drugs and the Nervous System 1 FOCUS Objectives 35.5.1 Name the different classes of drugs that directly affect the nervous system. 35.5.2 Describe the effect of alcohol on the body.
Section 35 5 35 5 Drugs and the Nervous System 1 FOCUS Objectives 35.5.1 Name the different classes of drugs that directly affect the nervous system. 35.5.2 Describe the effect of alcohol on the body.
*IN10 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT*
 BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
BIOPSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESSMENT 224-008B page 1 of 5 / 06-14 Please complete this questionnaire and give it to your counselor on your first visit. This information will help your clinician gain an understanding
Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE
 Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE Dr. Brian L. Bethel Child and Family Therapist Independent Trainer and Consultant LPCC-S, LCDC III, RPT-S www.brianlbethel.com INTERPLAY COUNSELING & CONSULTING
Wasted AN INTRODUCTION TO SUBSTANCE ABUSE Dr. Brian L. Bethel Child and Family Therapist Independent Trainer and Consultant LPCC-S, LCDC III, RPT-S www.brianlbethel.com INTERPLAY COUNSELING & CONSULTING
BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES
 Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
The Art of being Human
 Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450
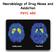 Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450 Healthy Control Drug Abuser Illicit drug use, lifetime and past year, in Canada 50 Canabis only Any drug Any of 5 drugs (without canabis) (CADUMS 2012)
Neurobiology of Drug Abuse and Addiction PSYC 450 Healthy Control Drug Abuser Illicit drug use, lifetime and past year, in Canada 50 Canabis only Any drug Any of 5 drugs (without canabis) (CADUMS 2012)
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Drugs and the School Aged Child. Objectives. Substance Abuse. Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN. n List signs of drug use in children
 Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use
 Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children. Jackie McReynolds Washington State University
 Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
TRENDS IN SUBSTANCE USE AND ASSOCIATED HEALTH PROBLEMS
 Fact Sheet N 127 August 1996 TRENDS IN SUBSTANCE USE AND ASSOCIATED HEALTH PROBLEMS Psychoactive substance use is an increasing public health concern. Problems associated with this use cover a broad spectrum
Fact Sheet N 127 August 1996 TRENDS IN SUBSTANCE USE AND ASSOCIATED HEALTH PROBLEMS Psychoactive substance use is an increasing public health concern. Problems associated with this use cover a broad spectrum
Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
 SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH
 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
Recreational Pharmaceuticals
 Recreational Pharmaceuticals Pulse Check 2013 Presenter: Doug Wildermuth Working Definition of Drug Any substance, which when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of that person. On something?
Recreational Pharmaceuticals Pulse Check 2013 Presenter: Doug Wildermuth Working Definition of Drug Any substance, which when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of that person. On something?
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Substance Misuse and Abuse
 CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders. By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP
 Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP History of Psychoactive Substances Used by people in almost all cultures since prehistoric times Produce effects in the
Mental Health Nursing: Substance-Related Disorders By Mary B. Knutson, RN, MS, FCP History of Psychoactive Substances Used by people in almost all cultures since prehistoric times Produce effects in the
Final Review. Directions: Choose the correct letter based on the given question.
 Final Review Directions: Choose the correct letter based on the given question. 1. An example of drug use: a. taking an aspirin to treat a headache b. taking a dose of cough syrup c. smoking marijuana
Final Review Directions: Choose the correct letter based on the given question. 1. An example of drug use: a. taking an aspirin to treat a headache b. taking a dose of cough syrup c. smoking marijuana
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders
 Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
4. Carlos suddenly stopped taking amphetamines after prolonged abuse of the drug. He became very ill and died. His death is an example of
 Chapter 10: Substance-Related Disorders a. substance abuse b. substance dependence c. substance use d. All of the above are equally serious. Answer: B Type: Factual Page: 297 2. Catherine has been unable
Chapter 10: Substance-Related Disorders a. substance abuse b. substance dependence c. substance use d. All of the above are equally serious. Answer: B Type: Factual Page: 297 2. Catherine has been unable
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL
 PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS CHAPTER 13 MEYERS AND DEWALL OVERVIEW What are Psychological Disorders? Anxiety Disorders, OCD, and PTSD Substance Use and Addictive Disorders Mood Disorders Schizophrenia Additional
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER:
 NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
Neurobiology of Addiction and Recovery
 and Recovery R. Dewayne Book, M.D. Medical Director Fellowship Hall Greensboro, North Carolina Addiction Drug Addiction results from adaptations in specific brain neurons caused by repeated exposure to
and Recovery R. Dewayne Book, M.D. Medical Director Fellowship Hall Greensboro, North Carolina Addiction Drug Addiction results from adaptations in specific brain neurons caused by repeated exposure to
Neurobiology of Addiction and Recovery. R. Dewayne Book, M.D. Medical Director Fellowship Hall Greensboro, North Carolina
 Neurobiology of Addiction and Recovery R. Dewayne Book, M.D. Medical Director Fellowship Hall Greensboro, North Carolina 1 Addiction Drug Addiction results from adaptations in specific brain neurons caused
Neurobiology of Addiction and Recovery R. Dewayne Book, M.D. Medical Director Fellowship Hall Greensboro, North Carolina 1 Addiction Drug Addiction results from adaptations in specific brain neurons caused
Defining Drugs. Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions
 Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Research Paper 21/08/
 Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Research Paper 21/08/18 20.35 D: 1. The nervous system. 2. The nervous system and drugs. 3. How do drugs effect the central nervous system. 4. Stimulants, hallucinogens, depressants and their effects on
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment
 Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Child Welfare and Substance Abuse. Erica Tarasovitch, MSW Central Florida Behavioral Health Network
 Child Welfare and Substance Abuse Erica Tarasovitch, MSW Central Florida Behavioral Health Network Parental Substance Use Marijuana was the most commonly used illicit drug in 2006, accounting for 72.8
Child Welfare and Substance Abuse Erica Tarasovitch, MSW Central Florida Behavioral Health Network Parental Substance Use Marijuana was the most commonly used illicit drug in 2006, accounting for 72.8
Peripheral Nervous System
 Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
Physical and Physiological Aspects of Drug Use and Abuse
 Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Classes of Neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters
 1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
1 Drugs Outline 2 Neurotransmitters Agonists and Antagonists Cocaine & other dopamine agonists Alcohol & its effects / Marijuana & its effects Synthetic & Designer Drugs: Ecstasy 1 Classes of Neurotransmitters
Adolescents And Addiction
 Adolescents And Addiction 1) According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAHMSA), over million people over the age of 12 years needed treatment for substance use in 2012.
Adolescents And Addiction 1) According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAHMSA), over million people over the age of 12 years needed treatment for substance use in 2012.
Patterns of Alcohol Use
 Alcohol and Tobacco Learning Objectives 1) Describe the patterns of alcohol use, and the health risks and social problems that can result from alcohol use, abuse, and dependence 2) Explain treatment approaches
Alcohol and Tobacco Learning Objectives 1) Describe the patterns of alcohol use, and the health risks and social problems that can result from alcohol use, abuse, and dependence 2) Explain treatment approaches
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
Dependence. Worldwide projected mortality. Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD)
 Dependence Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD) Dr. Aurelijus Veryga Kaunas university of medicine This is defined as: A cluster of behavioral,
Dependence Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD) Dr. Aurelijus Veryga Kaunas university of medicine This is defined as: A cluster of behavioral,
Lecture Outline Definitions Psychoactive Substances Epidemiology Assessment Etiological Models Treatment Stages of Change
 Substance-Related Disorders Cornelia Pinnell, Ph.D. Argosy University/Phoenix Lecture Outline Definitions Psychoactive Substances Epidemiology Assessment Etiological Models Treatment Stages of Change Substances
Substance-Related Disorders Cornelia Pinnell, Ph.D. Argosy University/Phoenix Lecture Outline Definitions Psychoactive Substances Epidemiology Assessment Etiological Models Treatment Stages of Change Substances
Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp ; 11 th pp Alcohol: The Worlds most danerious drug? The Lancet Medical Journal - 1 November, 2014
 Chapter Eight Alcohol and ending Tobacco Use (including caffeine) 12 th edition: pp. 231-261 11 th edition: pp. 227-258 Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp. 232-223; 11 th pp. 228-229 alcohol is the most widely
Chapter Eight Alcohol and ending Tobacco Use (including caffeine) 12 th edition: pp. 231-261 11 th edition: pp. 227-258 Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp. 232-223; 11 th pp. 228-229 alcohol is the most widely
EVIDENCE-BASED INTERVENTIONS TO HELP PATIENTS QUIT TOBACCO
 EVIDENCE-BASED INTERVENTIONS TO HELP PATIENTS QUIT TOBACCO Lena Matthias Gray, MSA, CTTS-M University of Michigan MHealthy Tobacco Consultation Service Overview of Tobacco Use The World Health Organization
EVIDENCE-BASED INTERVENTIONS TO HELP PATIENTS QUIT TOBACCO Lena Matthias Gray, MSA, CTTS-M University of Michigan MHealthy Tobacco Consultation Service Overview of Tobacco Use The World Health Organization
7/3/2013 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER ELEVEN CHAPTER OUTLINE. Substance Use Disorders. Oltmanns and Emery
 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern. Chapter 12
 Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
Alcohol, Tobacco, and Other Drugs: A Community Concern Chapter 12 Introduction Use, misuse, and abuse of mind-altering substances predates recorded history Chronic alcohol and other drug abuse or dependence
Initial Substance Use Assessment
 Date of Assessment: Source of Referral: Choose an item. Persons Present: Client and Provider only Transportation Assistance Needed: Yes No Member has a Primary Care Physician (PCP)? Yes No If yes PCP,
Date of Assessment: Source of Referral: Choose an item. Persons Present: Client and Provider only Transportation Assistance Needed: Yes No Member has a Primary Care Physician (PCP)? Yes No If yes PCP,
Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs
 Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Cigarettes and Other Nicotine Products
 Cigarettes and Other Nicotine Products Nicotine is one of the most heavily used addictive drugs in the United States. In 2002, 30 percent of the U.S. population 12 and older 71.5 million people used tobacco
Cigarettes and Other Nicotine Products Nicotine is one of the most heavily used addictive drugs in the United States. In 2002, 30 percent of the U.S. population 12 and older 71.5 million people used tobacco
Steve Hanson Associate Commissioner New York State Office of Alcoholism & Substance Abuse Services
 Understanding Alcohol Abuse and Addiction Steve Hanson Associate Commissioner New York State Office of Alcoholism & Substance Abuse Services Steve.hanson@oasas.state.ny.us Agenda Understanding Alcohol/Drug
Understanding Alcohol Abuse and Addiction Steve Hanson Associate Commissioner New York State Office of Alcoholism & Substance Abuse Services Steve.hanson@oasas.state.ny.us Agenda Understanding Alcohol/Drug
Psychology 210. Chemical Messengers. Types of NTs. Properties of Neurotransmitters. Cholinergic Neurons. Small molecule NTs.
 Psychology 210 Lecture 3 Kevin R Smith Chemical Messengers Neurotransmitters Act on neurons locally At one synapse Neuromodulators Act on clusters of neurons May not be in the immediate vicinity of where
Psychology 210 Lecture 3 Kevin R Smith Chemical Messengers Neurotransmitters Act on neurons locally At one synapse Neuromodulators Act on clusters of neurons May not be in the immediate vicinity of where
Welcome! Today we ll discuss some of the important relationships between mental and physical health that clinicians may encounter as they apply the
 Welcome! Today we ll discuss some of the important relationships between mental and physical health that clinicians may encounter as they apply the SBIRT process in practice. 1 We ll start by considering
Welcome! Today we ll discuss some of the important relationships between mental and physical health that clinicians may encounter as they apply the SBIRT process in practice. 1 We ll start by considering
The National Methamphetamine Symposium
 The National Methamphetamine Symposium Making Research Work in Practice 12 May 2015 Arts Centre, Melbourne Physical and psychological effects of methamphetamine use Amanda Baker PhD National Centre for
The National Methamphetamine Symposium Making Research Work in Practice 12 May 2015 Arts Centre, Melbourne Physical and psychological effects of methamphetamine use Amanda Baker PhD National Centre for
Biological Psychology. Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology
 Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
Biological Psychology Unit Two AH Mr. Cline Marshall High School Psychology Meditation As you just experienced, Guided meditation is one way that you can learn to focus your attention. Another way that
Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014
 Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014 OVERVIEW Definitions Disease concept Anatomy and neurochemistry Risk Factors Defenses, statistics, comorbidity Professionals and treatment
Jay Weiss, MD Drug Summit Little Rock, Arkansas Sep 9/10, 2014 OVERVIEW Definitions Disease concept Anatomy and neurochemistry Risk Factors Defenses, statistics, comorbidity Professionals and treatment
CHD 110 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND SUBSTANCE ABUSE
 CHD 110 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND SUBSTANCE ABUSE PRESENTED AND APPROVED: DECEMBER 7, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FALL 2013-14 Prefix & Number CHD 110 Purpose of this submission: Change course title to reflect current
CHD 110 PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY AND SUBSTANCE ABUSE PRESENTED AND APPROVED: DECEMBER 7, 2012 EFFECTIVE: FALL 2013-14 Prefix & Number CHD 110 Purpose of this submission: Change course title to reflect current
Adolescents And Addiction
 Adolescents And Addiction 1) According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAHMSA), over million people over the age of 12 years needed treatment for substance use in 2012.
Adolescents And Addiction 1) According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAHMSA), over million people over the age of 12 years needed treatment for substance use in 2012.
Scientific Facts on. Psychoactive Drugs. Tobacco, Alcohol, and Illicit Substances
 page 1/5 Scientific Facts on Psychoactive Drugs Tobacco, Alcohol, and Illicit Substances Source document: WHO (2004) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Psychoactive drugs such as tobacco, alcohol,
page 1/5 Scientific Facts on Psychoactive Drugs Tobacco, Alcohol, and Illicit Substances Source document: WHO (2004) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - Psychoactive drugs such as tobacco, alcohol,
Alcoholism has been demonstrated to have a genetic component, especially among men.
 Causes and Treatment of Substance-Related Disorders (Chapter 10) Familial and Genetic Influences Alcoholism has been demonstrated to have a genetic component, especially among men. Seems to be a common
Causes and Treatment of Substance-Related Disorders (Chapter 10) Familial and Genetic Influences Alcoholism has been demonstrated to have a genetic component, especially among men. Seems to be a common
The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin
 The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin Plant Secondary Compounds The Spice of Life Cultural Use of Spices Spice Use by Region 1 Silurian Land Plants History of Insect Damage 416-447 MYA Colonization of
The Human Animal Drugs of Plant Origin Plant Secondary Compounds The Spice of Life Cultural Use of Spices Spice Use by Region 1 Silurian Land Plants History of Insect Damage 416-447 MYA Colonization of
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Drug Use Around the World
 Special Agents U.S. DRUG ENFORCEMENT AGENCY STAFFING AND BUDGETS 1975 2000 10000 5000 Total Employees 8000 6000 4000 3000 2000 4000 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 1000 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Support
Special Agents U.S. DRUG ENFORCEMENT AGENCY STAFFING AND BUDGETS 1975 2000 10000 5000 Total Employees 8000 6000 4000 3000 2000 4000 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 1000 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Support
Session 2: Alcohol and Recovery 2-1
 Session 2: Alcohol and Recovery 2-1 Alcohol in the Brain Alcohol upsets a delicate balance between chemical systems that stimulate and chemical systems that inhibit functions of the brain and body. Matrix
Session 2: Alcohol and Recovery 2-1 Alcohol in the Brain Alcohol upsets a delicate balance between chemical systems that stimulate and chemical systems that inhibit functions of the brain and body. Matrix
Cocaine. How Is Cocaine Abused? How Does Cocaine Affect the Brain?
 Cocaine Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant drug. The powdered hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and then injected. Crack is the street name given to the form
Cocaine Cocaine is a powerfully addictive stimulant drug. The powdered hydrochloride salt form of cocaine can be snorted or dissolved in water and then injected. Crack is the street name given to the form
THE STATE OF MEDICINE IN ADDICTION RECOVERY
 OVERVIEW: Review addiction stats and trends Define addiction Explain neurobiology of addiction Review treatments of addiction Addiction Definition: A Primary, chronic, relapsing disease of brain reward,
OVERVIEW: Review addiction stats and trends Define addiction Explain neurobiology of addiction Review treatments of addiction Addiction Definition: A Primary, chronic, relapsing disease of brain reward,
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
BASIC VOLUME. Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
 BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
Industry Health & Safety Testing, Training & Prevention.
 Industry Health & Safety Testing, Training & Prevention How Drugs Affect Your Health & Safety Presentation Outline Introduction Workplace Health and Safety What are Drugs? Health Effects of Psychoactive
Industry Health & Safety Testing, Training & Prevention How Drugs Affect Your Health & Safety Presentation Outline Introduction Workplace Health and Safety What are Drugs? Health Effects of Psychoactive
Drug Free Schools and Community Act
 Drug Free Schools and Community Act Collin College supports the requirements of the Drug Free Schools and Communities Act. The College also endorses the Standards of the Commission of Colleges and Universities
Drug Free Schools and Community Act Collin College supports the requirements of the Drug Free Schools and Communities Act. The College also endorses the Standards of the Commission of Colleges and Universities
Illegal drugs. Epidemiology &Prevention
 Illegal drugs Epidemiology &Prevention Classification Legal drug abuse Substance abuse Prescription drugs Sedatives/hypnotics Alcohol Tobacco Volatile solvents Non-substance abuse Gambling addiction Internet
Illegal drugs Epidemiology &Prevention Classification Legal drug abuse Substance abuse Prescription drugs Sedatives/hypnotics Alcohol Tobacco Volatile solvents Non-substance abuse Gambling addiction Internet
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
[ ASSESSING THE BURDEN OF ILLICIT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL ABUSE:] Macomb County Office of Substance Abuse. A Focus on Heroin and Prescription Drug Abuse
![[ ASSESSING THE BURDEN OF ILLICIT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL ABUSE:] Macomb County Office of Substance Abuse. A Focus on Heroin and Prescription Drug Abuse [ ASSESSING THE BURDEN OF ILLICIT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL ABUSE:] Macomb County Office of Substance Abuse. A Focus on Heroin and Prescription Drug Abuse](/thumbs/90/102858739.jpg) 2010 Macomb County Office of Substance Abuse Planning Contracting Monitoring [ ASSESSING THE BURDEN OF ILLICIT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL ABUSE:] A Focus on Heroin and Prescription Drug Abuse 22550 Hall Road Clinton
2010 Macomb County Office of Substance Abuse Planning Contracting Monitoring [ ASSESSING THE BURDEN OF ILLICIT DRUGS AND ALCOHOL ABUSE:] A Focus on Heroin and Prescription Drug Abuse 22550 Hall Road Clinton
Asperger s Syndrome. severe difficulties interacting socially (Gillberg 2002). He named this difficulty
 Julie Burton 7.16.2012 ED 243 Paper Asperger s Syndrome History In 1944 an Austrian pediatrician named Hans Asperger wrote an article about a group of school- aged boys when he discovered that some of
Julie Burton 7.16.2012 ED 243 Paper Asperger s Syndrome History In 1944 an Austrian pediatrician named Hans Asperger wrote an article about a group of school- aged boys when he discovered that some of
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE
 DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
Unit 4 Lecture: States of Consciousness
 Unit 4 Lecture: States of Consciousness Definition is our awareness of various cognitive processes, such as sleeping, dreaming, concentrating and making decisions. William James Consciousness is continuous
Unit 4 Lecture: States of Consciousness Definition is our awareness of various cognitive processes, such as sleeping, dreaming, concentrating and making decisions. William James Consciousness is continuous
WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence Pre-Review: Cannabis plant and resin. Expert Peer Review 2
 WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence Pre-Review: Cannabis plant and resin Expert Peer Review 2 1. Comments based on the review report a. Evidence on dependence and abuse potential Dependence potential:
WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence Pre-Review: Cannabis plant and resin Expert Peer Review 2 1. Comments based on the review report a. Evidence on dependence and abuse potential Dependence potential:
Addictions in General Practice 16 th November 2017
 Addictions in General Practice 16 th November 2017 Dr Anshul Swami in Addictions Consultant Psychiatrist Priory Hospital North London, Southgate Consultant telephone: 020 8920 5616 Consultant email: SueGranger@priorygroup.com
Addictions in General Practice 16 th November 2017 Dr Anshul Swami in Addictions Consultant Psychiatrist Priory Hospital North London, Southgate Consultant telephone: 020 8920 5616 Consultant email: SueGranger@priorygroup.com
substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both?
 substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both? Stephen Strobbe, PhD, RN, PMHCNS-BC, CARN-AP Dawn Farm Education Series St. Joe s Education Center, Ypsilanti, MI Tuesday, January 27, 2015
substance use and mental disorders: one, the other, or both? Stephen Strobbe, PhD, RN, PMHCNS-BC, CARN-AP Dawn Farm Education Series St. Joe s Education Center, Ypsilanti, MI Tuesday, January 27, 2015
Activation-synthesis hypothesis. compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse consequences. Addition. Amphetamines. Barbiturates.
 Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
Activation-synthesis hypothesis Suggests that in the brain engages in a lot of neural activity that is random. Dreams make sense of this activity. Addition compulsive drug craving and use, despite adverse
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders
 SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
Drugs of abuse. CNS stimulants. Drugs of abuse: CNS Stimulants. Cocaine. Absorption of cocaine (pharmacokinetics) 28/10/2014.
 Learning outcomes Drugs of abuse Drugs of abuse: CNS Stimulants Dr B.Vahabi Identify different CNS stimulant drugs Explain the mechanism of action by which CNS stimulant drugs mediate their effects and
Learning outcomes Drugs of abuse Drugs of abuse: CNS Stimulants Dr B.Vahabi Identify different CNS stimulant drugs Explain the mechanism of action by which CNS stimulant drugs mediate their effects and
