Substance Abuse and Addiction
|
|
|
- Charity O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Substance Abuse and Addiction Course Health Science Unit V Safety and Governmental Regulations Unit XI Occupationally Specific Knowledge and Skills Essential Question What is the difference between abuse and addiction TEKS (c) 8A Prior Student Learning N/A Estimated time Approximately 4-5 class periods Rationale Throughout history, cultures have used psychoactive drugs for various purposes such as recreation, rituals, ceremonies, and medicinal purposes. A major concern for today s medical professionals is substance abuse and its effect on society. To live a healthy lifestyle throughout one s lifespan an understanding of the relationship between unsafe behavior and personal health is important. Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to: identify the most commonly abused drugs and list their effects; evaluate and explain why it is important to stay drug and alcohol-free; and develop strategies for preventing the use of tobacco, alcohol, and other addictive substances. Engage Discuss the following myths and or false statements: Marijuana is not addictive. The truth is, statistically, 1 in 10 will become addicted. Using certain drugs, even once, means you re automatically addicted. Addiction can be cured by medicine. Children should be permitted to drink in the presence of their parents because a drink or two is harmless. Discuss the following true statements: Children who start drinking in their early teen years are much more likely to develop problems with alcohol than those who wait until they are 21. Drug use and addiction is linked to at least half of the major crimes in this country, as at least half of the suspects arrested for violent crimes, such as homicide and assault, were under the influence of drugs when they were arrested. Stress is a major factor in drug use and abuse. Sadly, nearly two-thirds of people in drug abuse treatment report that they were physically or sexually abused as children. Child abuse is a major contributing factor to drug addiction.
2 Key Points I. Substance-related disorder A. Major categories of substances that are abused: 1. Alcohol 2. Amphetamine 3. Caffeine 4. Cannabis 5. Cocaine 6. Hallucinogen 7. Inhalant 8. Nicotine 9. Opioid 10. Sedative, Hypnotic, or Anxiolytic 11. Club Drugs II. Substance Dependence and Substance Abuse A. Dependence: is being unable to stop using 1. Individual s symptoms have persisted for at least 1 month 2. Individual must manifest three of the following symptoms: a. Tolerance i. need for markedly increased amounts of substance to achieve desired effect ii. Markedly diminished effect with continued use of same amount of substance b. Withdrawal c. substance is taken in larger amounts or over a longer period than was intended d. a pattern of persistent desire e. great deal of time is spent in activities necessary to obtain the substance, use the substance, or recover from its effects f. important social, occupational, or recreational activities are given up or reduced because of substance abuse g. substance use is continued despite knowledge that it is a problem B. Abuse: people making bad decisions, like having too many drinks at a bar on Saturday night 1. Pattern of substance use by one (or more) of the following: a. recurrent substance use resulting in failure to fulfill obligations at school, home, or work
3 b. recurrent substance use in situations in which it is physically hazardous c. recurrent substance-related legal problems d. continued substance use despite having persistent relationship problems caused by effects of substance III. Alcohol-Related Disorder A. Terminology 1. FAS: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome causes mental and physical abnormalities 2. DWI: driving while intoxicated 3. DUI: driving under the influence 4. BAC: Blood Alcohol Concentration 5. Alcoholism: addiction to alcohol cannot keep from drinking, cannot manage time without drinking, and cannot stop drinking once they have started 6. Cirrhosis: scarring of the liver 7. Jaundice: yellowing of the skin and eyes B. Criteria for alcohol abuse: 1. Daily use of alcohol necessary to function 2. Person unable to cut down or stop drinking 3. Binges last longer than 2 days 4. Person occasionally consumes as much as a fifth of liquor per day 5. Amnesia occurs during periods of intoxication (blackouts) 6. Inability to function at work or with friends and/or family C. Symptoms of Intoxication: 1. Slurred speech 2. Lack of coordination 3. Unsteady walking 4. Nystagmus: involuntary, rhythmic eyeball movement D. Effects of Alcohol on the organs 1. Brain decreased activity of the nervous system, thought processes are disorganized, memory and concentration are dulled, leads to brain damage resulting in loss of intellectual abilities 2. Liver inhibits the liver s ability to breakdown fats, fats accumulate leading to a fatty liver, the increased amount of fat keeps the liver cells from working and new liver cells being formed; cirrhosis no blood flow through scarred area of the liver, causes the increase in blood pressure,
4 hemorrhage, abdominal swelling, infection, jaundice 3. Blood Vessels increase heart rate and blood pressure 4. Kidneys increased urination, dehydration 5. Stomach increased flow of gastric acids, inflammation, ulceration E. Tolerance need to drink more to get the same effect F. Dependence physiologically addicted G. Withdrawal sleeplessness, sweating, tremors, and hallucinations H. Treatment for alcoholism 1. Detoxification process --takes place in hospital or rehabilitation center 2. Major treatment options frequently presented to recovering alcoholics a. aversive therapy (Disulfiram/Antabuse therapy) i. form of behavior therapy that uses learning principles to cause patient to associate thought of drinking with unpleasant stimulus ii. Motivates the patient to avoid drinking iii. Disulfiram (Antabuse) is a drug that causes metabolism of alcohol to be blocked iv. Result is buildup of toxic alcoholic byproduct called acetaldehyde v. produces unpleasant symptoms: flushing, sweating, palpitations, dyspnea, hyperventilation, tachycardia, hypotension, nausea, and vomiting vi. Useful adjunct treatment b. inpatient rehabilitation treatment program i. individual and group therapy ii. Intensive education and behavior modification to teach new coping skills to individuals who previously turned to alcohol iii. Teach patient communication skills and stress management c. Alcoholics Anonymous i. worldwide and is available in most communities
5 ii. The goal is to achieve a life of sobriety iii. Peer-support, self-help program iv. Related organizations for families of alcoholics (Al-Anon) I. Teenage Drinking 1. Reasons teens drink a. to have fun b. to relax c. to feel more self-confident d. to fit in peer pressure e. to get away with something 2. Negative social consequences difficulties with family, friends, school, and police J. Alcohol and pregnancy 1. FAS fetal alcohol syndrome, a cause of mental retardation 2. Shorter, smaller babies, slow body growth 3. Facial abnormalities 4. Poor coordination 5. Heart defects 6. Poor attention span, nervousness, hyperactivity K. Drinking and driving 1. #1 cause of death for teenagers in the US 2. Decreases the ability to judge distances, speeds, turns 3. Decreases abilities and limitations 4. Increases risk taking 5. Slows reflexes 6. Adds to forgetfulness 7. Decreases the ability to concentrate L. Stages of Alcoholism 1. Stage 1: physiological and psychological dependence, drinks regularly, may have blackouts 2. Stage 2: cannot stop drinking, defensive, denial, tolerance, performance at school/work declines 3. Stage 3: drinking is visible, uncontrollable IV. Amphetamine-Related Disorder A. Drugs included in this category: 1. Amphetamines 2. Dexedrine 3. Methamphetamine (speed) 4. Appetite Suppressants
6 B. Typical uses: 1. Used to treat obesity 2. Used by students to stay alert and study 3. Used by truck drivers to stay awake 4. Used by soldiers to decrease fatigue and increase aggression C. Symptoms of intoxication: 1. Euphoria 2. Grandiosity 3. Excessive wordiness 4. Excessive vigilance 5. Agitation 6. Dilated pupils 7. Elevated blood pressure 8. Tachycardia 9. Nausea and vomiting 10. Chills or perspiration D. Effects of Amphetamine use 1. Increase heart rate and breathing 2. Anxiety, sleeplessness 3. Tolerance, dependence 4. Methamphetamine (crank, speed, ice) cause paranoia and may increase violent tendencies E. Today s evidence suggests that amphetamine and related drugs produce both dependency and withdrawal states F. Most dangerous drugs presently available 1. Can produce toxic psychosis in mentally stable people 2. Death from over dosage (usually associated with hyperpyrexia, convulsions, and cardiovascular shock) G. Amphetamine-induced psychotic disorder clears in a matter of days or weeks following withdrawal of drug H. Withdrawal depression may reach suicidal proportions may be treated with tricyclic antidepressants V. Cannabis-Related Disorder A. Substances included in this category 1. Marijuana hemp plant Cannabis, the leaves and flowers are smoked, eaten, drunk. Over 400 chemicals present 2. Hashish dark brown resin from the tops of the cannabis plant 3. Purified delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) chemical that causes the psychoactive effect; stored in fatty tissue,
7 especially in brain cells, liver, lungs, kidneys, and reproductive organs; acts as a poison and prevents proper formation of DNA B. Marijuana is the most commonly used substance in this category 1. Widely prescribe for variety of ailments during the 19 th century coughing, fatigue, migraine, asthma, delirium tremens, etc. 2. Effects a. ability to cause euphoria b. tendency to produce sedation effects last 2 to 4 hours from smoking and 5 to 12 hours from ingestion c. sensory perception changes d. decreased body temperature, increased heart rate and blood pressure e. stimulates appetite f. decreases self-control g. mood changes can be influenced by mood and environment h. personality problems with increased use i. lack of will power and motivation ii. lack of interest iii. paranoia iv. apathy and lethargy i. psychological dependence j. memory deficits k. decreased concentration and coordination l. decreased immune system function m. decreased testosterone, decreased sperm production n. use during pregnancy causes condition in baby similar to FAS 3. Intoxication symptoms a. tachycardia b. perception of slowed time c. intensified subjective perceptions d. apathy e. elation f. dry mouth g. increased appetite
8 h. redness of eyes 4. Adverse reactions a. appear to be dose related and environment in which it is used b. rare reactions: i. anxiety states ii. panic states iii. toxic psychosis VI. Cocaine-Related Disorder A. Cocaine abuse is a problem of almost epidemic proportions in our society today B. Derived from leaves of coca plant which is indigenous to Bolivia and Peru 1. Leaves chewed by natives for many years for ceremonial highs and religious insight 2. Can be snorted, smoked, or injected 3. Rapid acting and powerful stimulant 4. Increases risk of heart attack, heart rhythm irregularities, and cardiac arrest 5. Increased risk of HIV with use of shared needles for injecting C. Intoxication Symptoms: cocaine high is similar to that of amphetamines 1. Euphoria 2. Exhilaration 3. Powerful sense of well-being and confidence 4. Agitation 5. Dilated pupils 6. Elevated blood pressure 7. Tachycardia and tachypnea 8. Nausea and vomiting 9. Chills or perspiration 10. Paranoia, hallucinations 11. Psychological and physiological dependence D. Commonly abused form of cocaine is crack 1. Inexpensive, very potent, readily available 2. Smokable form of cocaine 3. Danger or injury/death from explosion or fire 4. Causes insomnia, hallucinations, paranoia, and seizures as well as all of the common physiological symptoms like increased heart rate and blood pressure and lung damage
9 5. Extremely addictive E. crack/cocaine intoxication marked by: 1. Excitement, euphoria, restlessness, stereotyped movement, gnashing, grinding, or clenching teeth F. tolerance and physical dependency develops G. toxic psychosis with visual, auditory, and tactile hallucinations and paranoia VII. Hallucinogen-Related Disorder A. not categorized by intoxication or withdrawal instead by their ability to alter mental status B. psychedelics C. alter mood, thought, and the senses D. episodes of hallucinogenic flashbacks can occur at unpredictable times for years following termination of drug E. Includes LSD, DMT, PCP, inhalants, and mescaline 1. LSD: lysergic acid diethylamide a. increases heart rate and blood pressure b. chills, fever, loss of appetite, nausea c. panic attacks, anxiety, accidental suicide d. flashbacks 2. PCP: phencyclidine, angel dust a. distorts senses b. muscle coordination is impaired c. false sense of power and strength; results in violence and accidents d. can cause permanent psychiatric disorders e. flashbacks a recurrence of the effect of the drug, may occur at a later date 3. Inhalants sniffed, inhaled a. glue, spray paints, aerosols, gasoline b. decreases the central nervous system c. effects i. nausea, sneezing, cough, nosebleeds, fatigue, lack of coordination, loss of appetite ii. judgment is impaired iii. kidney, bone marrow, brain, and lung damage d. suffocation death VIII. Inhalant-Induced Disorder A. intoxication symptoms:
10 1. Belligerence 2. Impaired social functioning 3. Dizziness 4. Nystagmus 5. Lack of coordination 6. Slurred speech 7. Unsteady gait 8. Lethargy 9. Depressed reflexes 10. Tremor 11. Muscle weakness 12. Stupor or coma 13. Euphoria IX. Nicotine-Related Disorder A. Tobacco Terminology 1. Nicotine: addictive drug found in cigarettes 2. Stimulant: a drug that increases activity of the central nervous system and other organs 3. Tar: thick, sticky, dark fluid produced when tobacco burns 4. Carcinogen: a cancer causing substance 5. Carbon monoxide: a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas in cigarette smoke that passes through the lungs into the blood 6. Leukoplakia: thick, white, leather appearing spots in the inside of a smokeless tobacco user s mouth, it is precancerous 7. Passive smoke: cigarette, cigar, or pipe smoke inhaled by non-smokers 8. Mainstream smoke: smoke the smoker blows off 9. Sidestream smoke: smoke that comes from the burning tobacco 10. Cilia: hair like projections in the respiratory tract, keep airway clean 11. Chronic bronchitis: bronchi are irritated, cilia do not work, chronic coughing and excessive mucus 12. Emphysema: destruction of air sacs in the lungs through which oxygen is absorbed 13. Lung cancer: cancer of the lungs, one of the leading causes of death 14. Addictive: physiologically, psychological dependence 15. Physiological addiction: body has a chemical need for the
11 drug 16. Psychological addiction: person thinks they need the drug to function 17. Withdrawal: symptoms when substance that they are addicted to is withdrawn B. Cigarettes: have more than 4,000 chemicals, at least 43 known carcinogens 1. Nicotine is the addictive stimulant that increases blood pressure and heart rate 2. Tar: carcinogen, coats and penetrates the airway and lungs, paralyzes and destroys the cilia 3. Dangers of smoking a. COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease i. chronic bronchitis ii. emphysema b. lung cancer c. circulatory system i. decreased circulation ii. increased plaque buildup in the vessels iii. increased risk of myocardial infarction iv. increased blood pressure v. increased risk of stroke vi. damages the heart muscle 4. Smoking and pregnancy a. small fetal growth and low birth weight b. increased chance of miscarriage and stillbirths c. growth and development during childhood d. nicotine transfers during breast feeding e. children of cigarette smokers have increased respiratory problems, poor lung functions, and are twice as likely to develop lung cancer 5. Pipe and cigar smokers are more likely to develop lip, mouth, and throat cancer 6. Smokeless tobacco: mouth sores, leukoplakia, may turn into cancer of the mouth; also an increased chance of developing cancer of the lip, throat, damage of the teeth, gums, and digestive system a. Dangers of smokeless tobacco i. addictive ii. leukoplakia iii. bad breath, discolored teeth
12 iv. decreased smell and taste senses C. Tobacco dependence withdrawal symptoms 1. Depressed mood 2. Insomnia 3. Irritability, frustration, and anger 4. Anxiety 5. Difficulty concentrating 6. Restlessness 7. Decreased heart rate 8. Increased appetite or weight gain X. Opioid-Related disorder A. Includes opium, heroin, morphine, meriperidine (Demerol), codeine, and methadone 1. Heroin: has no medical use in the United States; depresses the central nervous system; causes coma and/or death with large doses; tolerance; withdrawal from drug is difficult and painful; and increased risk of HIV infection from contaminated needles B. The most addictive drugs abused C. Depresses areas of the brain that reduce hunger, thirst, and sex drive D. Demerol, morphine, and codeine used in healthcare facilities as painkillers E. Methadone used to treat heroin addiction F. Intoxication symptoms: 1. Euphoria 2. Drowsiness ( nodding out ) 3. Constriction of pupils (dilation if major overdose) 4. Dysphoria, apathy 5. Psychomotor retardation 6. Tachycardia 7. Fever 8. Lacrimation 9. Rhinorrhea 10. Piloerection 11. Sweating 12. Diarrhea G. Withdrawal symptoms: 1. Sweats 2. Shakes 3. Chills
13 4. Diarrhea 5. Vomiting XI. Sedative-Hypnotic-Related Disorder A. CNS depressants such as Librium, Valium, Seconal, and Serax B. Used to relieve anxiety, chill-pills produce feelings of relaxation and inhibition; decreases heart rate and respiratory rate C. This class of drugs most often abused because they create longer acting effect than alcohol D. Extremely addictive causing physiological and psychological dependence E. Intoxication symptoms cognitive confusion (memory impaired) F. Withdrawal symptoms: 1. Coarse tremors of hands, eyelids, and tongue 2. Nausea and vomiting 3. Malaise or weakness 4. Autonomic hyperactivity 5. Anxiety 6. Depressed or irritable mood G. Sudden withdrawal can cause seizures XII. Barbiturates A. This is a sedative category which relaxes the central nervous system B. Synthetic drugs made from barbituric acid C. Prescribed to treat insomnia, high blood pressure, and epilepsy D. When taken with alcohol, they tend to enhance effect E. Symptoms: 1. mood shifts 2. restlessness 3. euphoria 4. excitement 5. confusion 6. hallucinations F. Withdrawal symptoms: 1. cramps 2. nausea 3. delirium 4. convulsions G. Dependent individuals need to be withdrawn very slowly since sudden withdrawal can result in death
14 XIII. Club Drugs A. Ecstasy MDMA 1. tablet, powder, capsule 2. usually consumed orally 3. effects can last from 3-24 hours 4. causes euphoria and intoxication 5. depression, paranoia, and sometimes violent and irrational behavior 6. physical reactions : a. loss of appetite b. nausea and vomiting c. blurred vision d. increased heart rate and blood pressure e. chills f. sweating g. tremors h. insomnia i. convulsions j. heat k. exhaustion l. dehydration B. Rohypnol sedative, ten times as strong as Valium 1. taken orally 2. causes intoxication 3. can cause deep sedation, respiratory distress, blackouts can last up to 24 hours 4. short term amnesia 5. can cause aggression 6. called the date rape drug C. Anabolic Steroids synthetic derivative of male hormone testosterone 1. used illegally to increase athletic performance 2. increases aggressiveness and strength 3. side effects a. increased blood pressure, acne, liver damage, heart disease, and stroke b. males baldness, depression, aggressiveness, decreased sperm production, decreased testicular size, increase breast growth and body and facial hair c. females breast shrinkage, growth of facial hair,
15 baldness d. mood swings e. increase risk of HIV infection with shared needles XIV. Addiction it is a disease like hypertension or diabetes A. Tolerance B. Physiological and psychological dependence C. Withdrawal D. Intervention interrupting the addiction E. Recovery process that happens over time 1. counseling 2. support groups 12 step programs like AA Alcoholics Anonymous 3. Alcohol and Drug treatment centers (Costs Americans approximately $500 billion annually) F. Family disease 1. codependency being overly concerned with other people s behaviors and problems, feeling responsible to fix and control those problems 2. enabling trying to protect the person having trouble facing the consequences of their use 3. recovery from codependency a. get help from outside the family b. counselors c. support groups XV. Predisposing Factors A. Healthcare workers (high risk due to available of drugs) 1. highest addiction rate anesthesiologists B. Family history of substance abuse C. Emotional problems D. Ineffective coping mechanisms E. History of childhood physical or sexual abuse F. Addictive personalities Activity I. Write a critical analysis on an article related to substance abuse (e.g. Addiction As a Disease, Can the Addicted Brain Change Back? The Role of Biology and Addiction, Gateway Drugs. (See Materials) II. Cut out smoking advertisements and bring them to class; divide the students into small groups and have them discuss a. What message does the advertisement imply? b. What group is the advertisement targeting? c. Does the advertisement really have anything to do with smoking?
16 d. What is the purpose of the advertisement? III. Create anti-drinking and anti-drug advertisements that can be placed around the school for red ribbon week, prom week, homecoming week, etc. Assessment Successful completion of the Substance-Related Disorders Quiz Successful completion of the critical analysis of a substance abuse article Materials -- Informational site for activity. Key for Quiz Critical Analysis Rubric Art supplies: construction paper, markers, scissors, glue, poster board, etc. The Addicted Brain, Films for the Humanities & Sciences (800) #DPM1363. Excellent documentary video that examines the biochemistry of addiction and addictive behavior Accommodations for Learning Differences For reinforcement, the student will create a chart identifying substance related disorders and symptoms For enrichment, the student will research and develop charts and graphs depicting the cost of substance abuse to our society (e.g. treatment costs, law enforcement costs, etc.) National and State Education Standards National Health Science Cluster Standards HLC06.02 Safety, Health, and Environmental Health care workers will understand the fundamentals of wellness and the prevention of disease processes. They will practice preventive health behaviors among the clients. TEKS (c) 8A comply with specific industry standards related to safety and substance abuse Texas College and Career Readiness Standards English Language Arts II. B. Understand new vocabulary and concepts and use them accurately in reading writing and speaking.
17 Critical Analysis Rubric Addiction as a Disease NAME DATE PERIOD Scoring criteria 4 Excellent 3 Good 2 Needs Some Improvement 1 Needs Much Improvement N/A The critical analysis has all required parts from introduction to body to conclusion. The critical analysis is concise but complete. The critical analysis demonstrates that the writer comprehends addiction and related disorders. The critical analysis demonstrates accurate spelling, grammar, and punctuation. The overall content of critical analysis emphasizes appropriate points. The writer shows an understanding of sentence structure, paragraphing, and punctuation. The source of the critical analysis is clearly and accurately documented. The critical analysis demonstrates correct use of medical language. NOTE: N/A represents a response to the performance, which is "not appropriate."
18 Quiz Substance-Related Disorders NAME DATE PERIOD TRUE / FALSE (Circle correct answer.) 1. Individuals who are abusing alcohol might use it daily in order to function. T or F 2. Valium is a good aversive therapy for alcoholics. T or F 3. Medical supervision is necessary for alcohol detoxification. T or F 4. Amphetamines depress the central nervous system. T or F 5. Cannabis can increase appetite. T or F 6. The byproduct of cocaine that is inexpensive, and very potent is T or F derived from the hashish plant. 7. There are no adverse reactions to marijuana. T or F 8. Unpredictable hallucinogenic flashbacks can be caused by LSD. T or F 9. Withdrawal from nicotine might result in drowsiness and lethargy. T or F 10. Sedatives can depress the central nervous system, but are not addictive. T or F
19 Key: True/False Quiz Substance-Related Disorders 1. T 2. F 3. T 4. F 5. T 6. F 7. F 8. T 9. F 10. F
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
Information on Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. In most cultures, it is the most frequently used depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Ninety percent
4 CATEGORIES. Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs
 DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
DRUGS 4 CATEGORIES Medicine Tobacco Alcohol Other Illegal Drugs MEDICINE Drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions All medicines are drugs, not all drugs are medicines Drugs
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 Psychoactive Drugs Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Psychoactive drugs affect the central nervous system and can be especially damaging to the developing brain and body of a teen.
Many drugs of abuse are illegal drugs. Possessing, using, buying, or selling these drugs is illegal for people of any age.
 1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
1 Chapter 12 Section 1 Objectives List six ways illegal drug use can be dangerous. State five reasons a person might try illegal drugs. Identify the reason drug abuse is especially dangerous to teens.
Live A Life Above The Influence!
 Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Live A Life Above The Influence! Categories of Drugs 1) Inhalants 2) Stimulants 3) Depressants 4) Hallucinogens 5) Narcotics 6) Marijuana INHALANT Any substance that is inhaled glue, gas, paint thinner,
Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 8a Special Topic: Drugs and the Mind Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Substance Abuse. Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances.
 Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the use of illegal substances, as well as the misuse of legal substances. Substance Abuse Substance abuse includes the overuse, or multiple use of a drug, use of
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes.
 Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
Substance abuse is any unnecessary or improper use of chemical substances for nonmedical purposes. Illegal drugs- chemical substances that people of any age may not lawfully manufacture, possess, buy,
7th grade HEALTH- Chapter 11 9/15/2015
 Drugs and Alcohol Using Medicines Safely In this chapter, you will learn about Different types of medicines and their proper use. How alcohol affects the body. In this lesson, you will learn about Different
Drugs and Alcohol Using Medicines Safely In this chapter, you will learn about Different types of medicines and their proper use. How alcohol affects the body. In this lesson, you will learn about Different
Non-prescription Drugs. Wasted Youth
 Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Non-prescription Drugs Wasted Youth Marijuana (Cannabis) Short-Term Effects Using cannabis will probably make you feel more relaxed, free and open. If you smoke cannabis, you will probably feel the high
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information
 Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Drug and Alcohol Abuse Prevention Information A school that participates in the FSA programs must provide information to its students, faculty, and employees to prevent drug and alcohol abuse. In addition,
Specific Drugs of Abuse
 Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Specific Drugs of Abuse Alcohol In American society alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse. Use of alcohol affects judgment and decision-making abilities,
Glencoe Health. Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids
 Glencoe Health Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Three often-abused drugs that can have serious physical and mental side effects are marijuana, inhalants, and
Glencoe Health Lesson 2 Marijuana, Inhalants, and Steroids Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA Three often-abused drugs that can have serious physical and mental side effects are marijuana, inhalants, and
Drugs and the School Aged Child. Objectives. Substance Abuse. Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN. n List signs of drug use in children
 Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Drugs and the School Aged Child Janice Doyle, RN, MSN, NCSN, FNASN Objectives n List signs of drug use in children n State appropriate interventions when drug use is suspected Substance Abuse n Understanding
Defining Drugs. Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions
 Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
Defining Drugs Any substance which, when taken into the body, alters or modifies one or more body functions * Any drug, including prescription medicines and overthe-counter drugs, can be misused and abused.
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29
 PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
PSYCHOLOGY I-1 ST PER 5/29 MDMA (Ecstasy) Researchers that study the brain think that MDMA may affect neurons that use serotonin to communicate with other neurons. The serotonin system plays a direct role
Chapter 23. Medicines and Drugs
 Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
Chapter 23 Medicines and Drugs Lesson 1 The Role of Medicines 1. What are medicines? Drugs that are used to prevent disease or other conditions. 2. What are drugs? Substances other than food that change
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER:
 NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
NARCOTIC NOTES FLIPBOOK BY: PER: 1 https://www.youtube. com/watch?v=lolb21bii-a 2 Laws, Collection, & Preservation Narcotic Drugs = natural or synthetic substance that produces bodily (physiological) or
Why people abstain from tobacco?
 Why people abstain from tobacco? 1. Health a. Bad breath b. Bad odor on clothes and hair c. Poor complexion d. Discolored teeth, fingers, and fingernails e. Wrinkled skin f. Bone loss around the teeth
Why people abstain from tobacco? 1. Health a. Bad breath b. Bad odor on clothes and hair c. Poor complexion d. Discolored teeth, fingers, and fingernails e. Wrinkled skin f. Bone loss around the teeth
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use
 Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Overview of Psychoactive Drug use By Dr. Oladosu Ahmed Kayode Specialist in mental health Attending physician Dept. of psychiatry, GH Ilorin & Hopeville Psychiatric Hospital, Ilorin. Learning objectives
Table of Contents VOLUME 1
 VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
VOLUME 1 A Accidents and Injuries from Alcohol... 1 Accidents and Injuries from Drugs..... 4 Addiction: Concepts and Definitions... 7 Addictive Personality............... 12 Adolescents, Drug and Alcohol
BELL WORK. Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs.
 BELL WORK Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs. REVIEW What are the two types of medicines? Prescription and over the counter Any effect of a medicine other than the one intended
BELL WORK Write how your life would change if you were addicted to drugs. REVIEW What are the two types of medicines? Prescription and over the counter Any effect of a medicine other than the one intended
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS. RG 5c
 PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS RG 5c TODAY S GOALS Can you Explain the difference between stimulants and depressants Identify the major psychoactive drug categories (e.g., depressants, stimulants) and classify specific
Substance Use Disorders. A Major Problem. Defining Addiction 2/24/2009. Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 %
 Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Substance Use Disorders A Major Problem Lifetime rates of alcoholism estimated at 13.4 % Rates of drug abuse estimated at 6% Marijuana is most frequent Approximately 600,000 deaths each year from substance
Main Questions. Why study addiction? Substance Use Disorders, Part 1 Alecia Schweinsburg, MA Abnromal Psychology, Fall Substance Use Disorders
 Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
Substance Use Disorders Main Questions Why study addiction? What is addiction? Why do people become addicted? What do alcohol and drugs do? How do we treat substance use disorders? Why study addiction?
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT
 ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
ASSIGN ADDICTION PROJECT CLICKER SURVEY WHAT ARE DRUGS? A drug is an often illegal and sometimes addictive substance that causes changes in behavior and perception and is taken for it s effects. CATEGORIES
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES
 DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
DRUG FREE CAMPUS GUIDELINES In compliance the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for the illegal possession or distribution
Drug Abuse in America. the United States in Now days there is a lot of help to prevent drug use, like anti drug
 1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
1 Karla Campos Prof. Camille Pack English 2010 January 28, 2015 Drug Abuse in America Drugs are a major problem in American life, but not a new problem. Drugs have been a part of American history, humans
SUBSTANCE USE & ABUSE. Chapters 19-22
 SUBSTANCE USE & ABUSE Chapters 19-22 DRUGS Drugs: substances other than food that change the structure or function of the body or mind Medicines: drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other
SUBSTANCE USE & ABUSE Chapters 19-22 DRUGS Drugs: substances other than food that change the structure or function of the body or mind Medicines: drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs. Alcohol
 XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
XI. Health Risks Associated with Alcohol and Drugs Alcohol Alcohol is a legal drug. Nonetheless, it is a depressant and is the leading drug of abuse in America. Use of alcohol may affect judgment and decision-making
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders
 Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
Chapter 38 Substance Abuse and Eating Disorders Substance Abuse Introduction Variety of reasons for substance use o Depressed mood o Pain o Fear o Anxiety o Boredom Signs of problems when substance are
What is Alcohol? Produced by a fermentation process Proof is the amount of alcohol in the substance (ex. 100 proof bottle of vodka is 50% alcohol)
 ALCOHOLISM What is Alcohol? Depressant Contains intoxicating substance called ethyl alcohol or ethanol Slows down the functions of the brain and other parts of the nervous system What is Alcohol? Produced
ALCOHOLISM What is Alcohol? Depressant Contains intoxicating substance called ethyl alcohol or ethanol Slows down the functions of the brain and other parts of the nervous system What is Alcohol? Produced
Role of Medicines. Chapter 19 Lesson 1
 Role of Medicines Chapter 19 Lesson 1 Types of Medicine Medicines drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions Drugs substances other than food that change the structure or function
Role of Medicines Chapter 19 Lesson 1 Types of Medicine Medicines drugs that are used to treat or prevent diseases or other conditions Drugs substances other than food that change the structure or function
Substance Misuse and Abuse
 CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
CHAPTER 18 Substance Misuse and Abuse Lesson Objectives 1. Explain actions that can be taken to help prevent youth from abusing drugs and other substances. 2. Describe specific steps for preventing someone
Page 1 of 5. Policy Statement: II. General Policy Statement
 Page 1 of 5 Title: Drug-Free Schools Policy Statement Category: President Applies to: Staff, Faculty, Student, Department Contact: UCO Office of Legal Counsel (405) 974-3377 Purpose: I. Purpose A. The
Page 1 of 5 Title: Drug-Free Schools Policy Statement Category: President Applies to: Staff, Faculty, Student, Department Contact: UCO Office of Legal Counsel (405) 974-3377 Purpose: I. Purpose A. The
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children. Jackie McReynolds Washington State University
 Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
Understanding the Impact of Drugs on Children Jackie McReynolds Washington State University Not all drug users are addicts... Addiction develops through several well-identified phases: No use at all (abstinence)
BDJ TRUCKING CO INC. Drug and Alcohol policy & Information
 BDJ TRUCKING CO INC Drug and Alcohol policy & Information BDJ Trucking Co, Inc is committed providing a safe workplace for its contractors and the company is also committed in placing safe, professional
BDJ TRUCKING CO INC Drug and Alcohol policy & Information BDJ Trucking Co, Inc is committed providing a safe workplace for its contractors and the company is also committed in placing safe, professional
ALCOHOL. Do Now Activity. Fact or Fiction. According to the CDC Alcohol is the most used and abused drug among US youth.
 ALCOHOL Do Now Activity Fact or Fiction According to the CDC Alcohol is the most used and abused drug among US youth. According to the 2009 Monitoring the Future Survey 37% of 8 th graders have tried alcohol,
ALCOHOL Do Now Activity Fact or Fiction According to the CDC Alcohol is the most used and abused drug among US youth. According to the 2009 Monitoring the Future Survey 37% of 8 th graders have tried alcohol,
States of Consciousness Day 2
 States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
States of Consciousness Day 2 Hypnosis* l Hypnosis: involves a state of awareness characterized by deep relaxa6on, heightened sugges6bility, and focused a:en6on. l Hypno6st suggests changes in sensa6ons,
Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996)
 APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
APPENDIX 3 Federal Penalties and Sanctions for Illegal Trafficking and Possession of a Controlled Substance Federal Trafficking Penalties (As of January 1, 1996) Controlled Substances Act Schedule* 1st
Tobacco. Ms. Schafer
 Tobacco Ms. Schafer The Facts About Tobacco Tobacco is a Stimulant Tobacco is the number 1 cause of preventable death in the United States. The government requires all tobacco products to carry warning
Tobacco Ms. Schafer The Facts About Tobacco Tobacco is a Stimulant Tobacco is the number 1 cause of preventable death in the United States. The government requires all tobacco products to carry warning
Peripheral Nervous System
 Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services)
 What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) Hallucinogens are a diverse group of drugs that alter perception
What Are Hallucinogens? (National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institutes of Health; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services) Hallucinogens are a diverse group of drugs that alter perception
CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS
 CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Cannabis 101 What is cannabis? Cannabis is a product derived from the Cannabis sativa plant. Cannabis contains hundreds
CANNABIS LEGALIZATION: SUPPORT MATERIAL FOR MANITOBA PHYSICIANS 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Cannabis 101 What is cannabis? Cannabis is a product derived from the Cannabis sativa plant. Cannabis contains hundreds
DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES
 DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES In compliance with the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for
DRUG FREE CAMPUS POLICY, GUIDELINES AND DISCLOSURES In compliance with the Drug-Free Schools and Communities Act (DFSCA), the school has set forth in this guide the legal penalties under Federal law for
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS
 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS HS172A R01/10 1 SESSION XXIV DRUG COMBINATIONS Upon successfully completing this session the student will be able to: o o o o Explain the prevalence of polydrug use among
Tobacco Notes. An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums)
 Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
Tobacco Notes What is Tobacco? An agricultural crop that looks like brown cut up leaves Can be smoked (inhaled to lungs), dipped/chewed (absorbed through gums) What Products have Tobacco in them? Cigarettes,
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders
 SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
SCID-I Version 2.0 (for DSM-IV) Non-Alcohol Use Disorders *NON-ALCOHOL SUBSTANCE USE DISORDERS* (LIFETIME DEPENDENCE AND ABUSE) Now I am going to ask you about your use of drugs or medicines. SHOW DRUG
CLUB DRUGS DESIGNER DRUGS
 Club drugs are being used by young adults at all-night dance parties such as "raves" or "trances," dance clubs, and bars. MDMA (Ecstasy), GHB, Rohypnol, Ketamine, Methamphetamine, and LSD are some Of the
Club drugs are being used by young adults at all-night dance parties such as "raves" or "trances," dance clubs, and bars. MDMA (Ecstasy), GHB, Rohypnol, Ketamine, Methamphetamine, and LSD are some Of the
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders. Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder
 Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
Substance and Alcohol Related Disorders Substance use Disorder Alcoholism Gambling Disorder What is a Substance Use Disorder? According to the DSM-5, a substance use disorder describes a problematic pattern
What is a DRE. Introduction to Drugged Driving
 Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
Introduction to Drugged Driving What is a DRE DRE Training & Certification For a list of classes scheduled in 2016, click here. The DEC Program trains police officers and other approved public safety officials
Tobacco What is tobacco?
 Tobacco What is tobacco? 1891 Machine to make cigarettes was invented Until then: Rolled cigarettes/chewing tobacco 1964 Tobacco use reached its height Almost 50% of all adults in the US smoked Surgeon
Tobacco What is tobacco? 1891 Machine to make cigarettes was invented Until then: Rolled cigarettes/chewing tobacco 1964 Tobacco use reached its height Almost 50% of all adults in the US smoked Surgeon
The Art of being Human
 Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
Science - Year 6 Animals including Humans Block 6AH The Art of being Human Session 6 Resource pack Original resource copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE
 DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
DRUG AND ALCOHOL QUESTIONNAIRE Part I. Substance Abuse History Ever Used? Ever a Problem? Age of 1 st Use When last used? Alcohol Yes No Yes No Barbiturates or Yes No Yes No other sleeping pills Benzodiazepines
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1
 Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
Session 7: Opioids and Club Drugs 7-1 The Importance of Total Abstinence Abstinence from all substances that affect the brain even alcohol greatly increases the chances of a successful recovery. Matrix
Drug Free Schools and Community Act
 Drug Free Schools and Community Act Collin College supports the requirements of the Drug Free Schools and Communities Act. The College also endorses the Standards of the Commission of Colleges and Universities
Drug Free Schools and Community Act Collin College supports the requirements of the Drug Free Schools and Communities Act. The College also endorses the Standards of the Commission of Colleges and Universities
CARD TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff
 CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
CARD 1 1. TOBACCO: Cigarettes, E- Cigarettes, Cigars, Tobacco Pipe, Chewing Tobacco, Snuff 2. ALCOHOL: Beer, Wine, Liquor 3. MARIJUANA: Grass, Pot, Hashish, Hash, Hash Oil, Weed, Ganja, Marijuana Edibles
Substance Misuse. Drugs. May 2015
 S1 Substance Misuse Drugs May 2015 Lesson 1 What is a drug? TASK: Look at the list of items below. Make 3 lists to show which of these substances can be: Easily bought in shops Can only be prescribed by
S1 Substance Misuse Drugs May 2015 Lesson 1 What is a drug? TASK: Look at the list of items below. Make 3 lists to show which of these substances can be: Easily bought in shops Can only be prescribed by
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse
 Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
Understanding Alcohol And Other Drugs Of Abuse Wilkie A. Wilson, Ph.D. DukeLEARN www.dukelearn.com Duke University Medical Center 1 We teach people to respect their hearts... Exercise Eat good food Reduce
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH
 BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
BAPTIST HEALTH SCHOOL OF NURSING NSG 3036A: PSYCHIATRIC-MENTAL HEALTH THERAPEUTIC INTERVENTION AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT: SUBSTANCE RELATED DISORDERS: CO-DEPENDENCY AND THE IMPAIRED NURSE LECTURE OBJECTIVES:
Alcohol. Fits Hallucinations. Hallucinations Brain damage. Cirrhosis Gastritis. Diabetes Vomiting blood
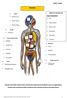 Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
Alcohol. Brain Hallucinations Brain damage. Lungs Coughing Effects of Alcohol use Fits Hallucinations Headaches. Liver and pancreas Hepatitis 4 Numbness Vomiting Swollen liver 5 5. Stomach Ulcers Cirrhosis
diii Unit #3 Review Packet Mental and Emotional Health FAS aiiabc aiiiiiiiqeiiic destiin aicoh9lism
 NAME HOUR Unit #3 Review Packet Mental and Emotional Health hapter 19 Medicines and Drugs (pgs. 522-539) hapter 20 Tobacco (pgs.540-563) hapter 21 Alcohol (pgs. 564-589) hapter 22 illegal Drugs (pgs. 590-621)
NAME HOUR Unit #3 Review Packet Mental and Emotional Health hapter 19 Medicines and Drugs (pgs. 522-539) hapter 20 Tobacco (pgs.540-563) hapter 21 Alcohol (pgs. 564-589) hapter 22 illegal Drugs (pgs. 590-621)
Chapter 14. Lessons. Bellringer
 Tobacco Tobacco Lessons Lesson 1 Tobacco Products: An Overview Lesson 2 Tobacco s Effects Lesson 3 Tobacco, Disease, and Death Lesson 4 Tobacco and Addiction Lesson 5 Quitting Lesson 6 Why People Use Tobacco
Tobacco Tobacco Lessons Lesson 1 Tobacco Products: An Overview Lesson 2 Tobacco s Effects Lesson 3 Tobacco, Disease, and Death Lesson 4 Tobacco and Addiction Lesson 5 Quitting Lesson 6 Why People Use Tobacco
Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes
 Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by drinking
Chapter 10 Section 1 Notes Alcohol Is a Drug Alcohol is the drug found in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. Intoxication includes all the physical and mental changes produced by drinking
QUESTION 1. What is a drug? ANSWER: A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel.
 What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
What is a drug? QUESTION 1 A drug is any substance that affects the way you think, act, and/or feel. QUESTION 2 What does having an addiction mean? A person addicted to a substance feels that he/she cannot
Chapter 11 Tobacco Section 1: Tobacco Use
 Chapter 11 Tobacco Section 1: T obacco Use Do Now 1. Read the article The facts behind e-cigarettes and their health risks 2. Annotate 3. Summary Key Terms Ø Nicotine Ø Carcinogen Ø Tar Ø Carbon monoxide
Chapter 11 Tobacco Section 1: T obacco Use Do Now 1. Read the article The facts behind e-cigarettes and their health risks 2. Annotate 3. Summary Key Terms Ø Nicotine Ø Carcinogen Ø Tar Ø Carbon monoxide
7/3/2013 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER ELEVEN CHAPTER OUTLINE. Substance Use Disorders. Oltmanns and Emery
 ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION Oltmanns and Emery PowerPoint Presentations Prepared by: Ashlea R. Smith, Ph.D. This multimedia and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are
Dependence. Worldwide projected mortality. Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD)
 Dependence Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD) Dr. Aurelijus Veryga Kaunas university of medicine This is defined as: A cluster of behavioral,
Dependence Youth risky behavior (substance abuse) and its relation with communicable diseases (HIV/AIDS, STD) Dr. Aurelijus Veryga Kaunas university of medicine This is defined as: A cluster of behavioral,
Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs
 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System
 The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System How do drugs work? Drugs are chemicals or substances that change the way our bodies work. Enter the body through swallowing, inhaling or injecting)
The Affects of Drugs & Alcohol on the Nervous System How do drugs work? Drugs are chemicals or substances that change the way our bodies work. Enter the body through swallowing, inhaling or injecting)
What is the difference between Vicoden, OxyContin, Percocet and Percodan
 CHAPTER 5 DRUGS NARCOTICS Narcotics are drugs that induce sleep and relieve pain. The term narcotic is used incorrectly today for example the cocaine is labeled as a narcotic but is actually a stimulant
CHAPTER 5 DRUGS NARCOTICS Narcotics are drugs that induce sleep and relieve pain. The term narcotic is used incorrectly today for example the cocaine is labeled as a narcotic but is actually a stimulant
Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies
 CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
CHAPTER 21 Poisoning and Overdose Emergencies Key Term Poison Any substance that can harm the body Four Routes of Poisoning INHALATION INJECTION Drugs Sprays Cleaning Fluid INGESTION Lye Household Cleaners
What do you need to know about CANNABIS. Answers to some of your questions.
 What do you need to know about CANNABIS Answers to some of your questions www.nwdrugtaskforce.ie Content Introduction... 1 Frequently Asked Questions... 2 How can cannabis effect my family... 4 What are
What do you need to know about CANNABIS Answers to some of your questions www.nwdrugtaskforce.ie Content Introduction... 1 Frequently Asked Questions... 2 How can cannabis effect my family... 4 What are
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment
 Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Polysubstance Use & Medication-Assisted Treatment DSM-V eliminated polysubstance disorder, instead specifying each drug of abuse and dependence. Substance-use disorder is a combination of the two DSM-IV
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs
 Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Appendix 2: The nature and addictiveness of commonly used illicit drugs Amphetamine A synthetic drug that can easily be produced on a small scale. It can be snorted, swallowed or smoked or, less frequently,
Chapter 22 Notes Lesson 1
 Chapter 22 Notes Lesson 1 The Facts About Alcohol 1) What is ethanol? The type of alcohol in alcoholic beverages 2) How is ethanol produced? Synthetically and naturally through the fermentation of fruits,
Chapter 22 Notes Lesson 1 The Facts About Alcohol 1) What is ethanol? The type of alcohol in alcoholic beverages 2) How is ethanol produced? Synthetically and naturally through the fermentation of fruits,
SUBOXONE (buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual film (CIII) IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
 SUBOXONE (buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual film (CIII) IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION What is the most important information I should know about SUBOXONE Film? Keep SUBOXONE Film in a secure place
SUBOXONE (buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual film (CIII) IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION What is the most important information I should know about SUBOXONE Film? Keep SUBOXONE Film in a secure place
SUBSTANCE ABUSE UNIT UNIT PACKET NAME: PERIOD: SCORE:
 SUBSTANCE ABUSE UNIT UNIT PACKET NAME: PERIOD: SCORE: _ \ SUBSTANCE ABUSE OVERVIEW IN-CLASS PROJECT DIRECTIONS: You will be working with your classmates to gather information about Substance Abuse. During
SUBSTANCE ABUSE UNIT UNIT PACKET NAME: PERIOD: SCORE: _ \ SUBSTANCE ABUSE OVERVIEW IN-CLASS PROJECT DIRECTIONS: You will be working with your classmates to gather information about Substance Abuse. During
Hallucinogens Marijuana
 Introduction A drug is defined as a natural or synthetic substance that is used to produce physiological or psychological effects in humans or other higher order animals. Narcotic drugs are analgesics,
Introduction A drug is defined as a natural or synthetic substance that is used to produce physiological or psychological effects in humans or other higher order animals. Narcotic drugs are analgesics,
BASIC VOLUME. Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment
 BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
BASIC VOLUME Elements of Drug Dependence Treatment BASIC VOLUME MODULE 1 Drug dependence concept and principles of drug treatment MODULE 2 Motivating clients for treatment and addressing resistance MODULE
Club Drugs. Club Drugs na'unin4. Alan I. Leshner*
 CI 14 1 ill119111 2543 Club Drugs )L-0 03/474, 59 Club Drugs na'unin4 Alan I. Leshner* Abstract : Alan I. Leshner. 2000. Club drugs. Thai J Hlth Resch 14(1): 59-63. There are detecting alarming increases
CI 14 1 ill119111 2543 Club Drugs )L-0 03/474, 59 Club Drugs na'unin4 Alan I. Leshner* Abstract : Alan I. Leshner. 2000. Club drugs. Thai J Hlth Resch 14(1): 59-63. There are detecting alarming increases
CANAM INTERVENTIONS. Addiction
 CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
CANAM INTERVENTIONS Addiction PREVENTION RESEARCH FACTS The principles listed below are the result of long-term research studies on the origins of drug abuse behaviors and the common elements of effective
Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp ; 11 th pp Alcohol: The Worlds most danerious drug? The Lancet Medical Journal - 1 November, 2014
 Chapter Eight Alcohol and ending Tobacco Use (including caffeine) 12 th edition: pp. 231-261 11 th edition: pp. 227-258 Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp. 232-223; 11 th pp. 228-229 alcohol is the most widely
Chapter Eight Alcohol and ending Tobacco Use (including caffeine) 12 th edition: pp. 231-261 11 th edition: pp. 227-258 Alcohol - an overview 12 th pp. 232-223; 11 th pp. 228-229 alcohol is the most widely
Drug and Alcohol Impairment. Alabama DRE / SFST Program
 Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
Drug and Alcohol Impairment Alabama DRE / SFST Program WHAT IS A DRUG? Working Definition of Drug : Any substance that, when taken into the human body, can impair the ability of the person to operate a
BARCLAY COLLEGE COMPLIANCE DOCUMENT STATEMENT TO EMPLOYEES AND STUDENTS REGARDING DRUG-FREE SCHOOLS AND COMMUNITIES ACT AMMENDMENTS OF 1989
 BARCLAY COLLEGE COMPLIANCE DOCUMENT STATEMENT TO EMPLOYEES AND STUDENTS REGARDING DRUG-FREE SCHOOLS AND COMMUNITIES ACT AMMENDMENTS OF 1989 March 2018 2 BARCLAY COLLEGE A DRUG FREE COMMUNITY Barclay College
BARCLAY COLLEGE COMPLIANCE DOCUMENT STATEMENT TO EMPLOYEES AND STUDENTS REGARDING DRUG-FREE SCHOOLS AND COMMUNITIES ACT AMMENDMENTS OF 1989 March 2018 2 BARCLAY COLLEGE A DRUG FREE COMMUNITY Barclay College
Richard Senysyzn, MD Psychiatry for Adults 1260 River Acres Drive New Braunfels, TX , Fax. (888)
 ADHD Evaluation Intake Form Patient Contact Information Patient Name: Date of Birth: Age: Last First MI Address: Email address: Contact phone number: Emergency Contact/Number/Relationship: Pharmacy: Primary
ADHD Evaluation Intake Form Patient Contact Information Patient Name: Date of Birth: Age: Last First MI Address: Email address: Contact phone number: Emergency Contact/Number/Relationship: Pharmacy: Primary
Chapter 23. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 23 Vocabulary medicines illicit drug use stimulants drugs overdose euphoria vaccine psychological dependence depressants analgesics physiological dependence narcotics side effects addiction hallucinogens
Chapter 23 Vocabulary medicines illicit drug use stimulants drugs overdose euphoria vaccine psychological dependence depressants analgesics physiological dependence narcotics side effects addiction hallucinogens
Facts About Alcohol. 2.1 million students between the ages of drove under the influence of alcohol last year
 Facts About Alcohol Each year, drinking by college students contributes to an estimated 1,700 student deaths, almost 600,000 injuries, almost 700,000 assaults, more than 90,000 sexual assaults, and 474,000
Facts About Alcohol Each year, drinking by college students contributes to an estimated 1,700 student deaths, almost 600,000 injuries, almost 700,000 assaults, more than 90,000 sexual assaults, and 474,000
Current Drug Trends Among Youth. Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol
 Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Current Drug Trends Among Youth Investigator J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Inv. J.J. Pedersen Nebraska State Patrol Troop C, Grand Island Investigative Services Drug Division BA 2006, C.J., UNL Joined
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2)
 Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
Alcohol/Drugs : Pleasures and Problems (part 2 of 2) Assistant Professor Cannabis Cannabis (cont d) Second only to alcohol as the most widely abused drug in India. Intoxication impaired motor coordination
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Alcohol and Substance Abuse Policy. Standards of Conduct and Enforcement
 Alcohol and Substance Abuse Policy In compliance with the United States Department of Education Drug Free Schools and Campuses Act (1989, Part 86) as a condition of receiving federal funds, or any form
Alcohol and Substance Abuse Policy In compliance with the United States Department of Education Drug Free Schools and Campuses Act (1989, Part 86) as a condition of receiving federal funds, or any form
COMPETENCY. Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel. Wednesday, January 14, 2015
 COMPETENCY Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel Wednesday, January 14, 2015 Extent of the Problem Substantial percentage of the population will be substance abusers
COMPETENCY Presented by: Hon. Candace Cooper (Ret.) Association of Corporate Counsel Wednesday, January 14, 2015 Extent of the Problem Substantial percentage of the population will be substance abusers
Tobacco Prevention ACMS SIXTH GRADE UNIT
 Tobacco Prevention ACMS SIXTH GRADE UNIT Opening Pair Share Questions ROCK WALL PARTNER: What is Tobacco? TRACK WALL PARTNER: How does tobacco affect the body and mind? A single puff of a tobacco cigarette
Tobacco Prevention ACMS SIXTH GRADE UNIT Opening Pair Share Questions ROCK WALL PARTNER: What is Tobacco? TRACK WALL PARTNER: How does tobacco affect the body and mind? A single puff of a tobacco cigarette
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e. Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst
 Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
Thinking About Psychology: The Science of Mind and Behavior 2e Charles T. Blair-Broeker Randal M. Ernst Cognitive Domain Consciousness Chapter Module 26 Drugs Module 26: Drugs Introduction Psychoactive
Vegetarianism and the environment
 Vegetarianism and the environment Vegetarians abstain from meat, poultry, fish and marine products of animal origin. Some vegetarians also eschew dairy products and eggs. Vegans add honey to the restricted
Vegetarianism and the environment Vegetarians abstain from meat, poultry, fish and marine products of animal origin. Some vegetarians also eschew dairy products and eggs. Vegans add honey to the restricted
Patterns of Alcohol Use
 Alcohol and Tobacco Learning Objectives 1) Describe the patterns of alcohol use, and the health risks and social problems that can result from alcohol use, abuse, and dependence 2) Explain treatment approaches
Alcohol and Tobacco Learning Objectives 1) Describe the patterns of alcohol use, and the health risks and social problems that can result from alcohol use, abuse, and dependence 2) Explain treatment approaches
Substance Abuse and Poisonings. Chapter 17
 Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
Substance Abuse and Poisonings Chapter 17 Identifying the Patient and the Poison Poison- any substance who s chemical reaction can damage body structures or impair body functions Poisons act by changing
