The Endocrine System
|
|
|
- Jasmin Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus and between optic chiasma and mamillary bodies Connected to the hypothalamus by infundibulum 2 1
2 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Third ventricle Median eminence Mamillary body HYPOTHALAMUS Optic chiasm Infundibulum Anterior lobe Pars tuberalis Pars distalis Pars intermedia Posterior pituitary lobe Sphenoid (sella turcica) Contains two anatomical portions that are functionally different 3 and protected by the sella tursica of the sphenoid bone! Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary gland are derived from embryonic brain tissues. The posterior pituitary gland is a down-growth of hypothalamic neural tissue The anterior pituitary gland arises from tissue in the roof of the mouth (oral mucosa). 4 2
3 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis Pituitary gland two-lobed organ that secretes nine major hormones Neuro-hypophysis : posterior lobe and contains unmyelinated axons from the hypothalamus Receives, stores, and releases hormones from the hypothalamus Adeno-hypophysis : anterior lobe, made up of glandular tissue Synthesizes and secretes a number of hormones There is no direct neural connection between APG and HT. 5 Anterior lobe ( anterior pituitary gland or APG) Also called the adeno-hypophysis Has 3 distinct regions Pars distalis Pars tuberalis Pars intermedia Contains mostly glandular tissue There is no neural connection with the HT 6 3
4 Anterior pituitary gland 6 distinct hormones are produced in the adenohypophysis The secretion of these hormones is controlled by specific releasing and inhibiting hormones produced in the HT = tropic hormones This requires an intricate network of blood vessels and capillaries to direct the hypothalamic hormones to APG cells There are thus two capillary beds connected via portal vessels! 7 Hypopheseal Portal System Optic chiasm Capillary beds MEDIAN EMINENCE Mamillary body Superior hypophyseal artery These portal vessels, which deliver hypothalamic hormones to the pituitary, are unusual in that they connect two capillary beds. ANTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY GLAND Infundibulum Portal vessels Inferior hypophyseal artery POSTERIOR LOBE OF PITUITARY GLAND This system is called the hypophyseal portal system and is fed by the superior hypophyseal artery. Endocrine cells Hypophyseal veins 8 4
5 Posterior pituitary gland or PPG Contains mostly nerves The cell bodies of the nerves are located in the hypothalamus Axons extend into the PPG Hormones are directed to the axon terminals and secreted by nerve stimuli. Thus, other names for the PPG are Pars Nervosa HYPOTHALAMUS Neuro-hypophysis an inferior hypophyseal artery and vein supply and drain the posterior lobe 9 Hormones of the posterior pituitary gland Only two hormones are released by the PPG Oxytocin Anti-diuretic Hormone (ADH) The hormones are produced by neuronal cell bodies, located in the Hypothalamus and directed via neurons of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract to the capillary bed of the PPG. (why is it called a tract? ) 10 5
6 Hormones of the posterior pituitary gland Supraoptic nuclei Paraventricular nuclei HYPOTHALAMUS Those neuronal cell bodies in the HT are : Optic chiasm Supraoptic nuclei these produce ADH Paraventricular nuclei these produce Oxytocin 11 AntiDiuretic Hormone or ADH (Vasopressin ) Physiological effect is to decrease the urine output and urine production ADH causes the kidneys to remove water from the urine that is being formed in the nephrons of the kidneys and re-direct it into the bloodstream. Since ADH promotes water return to the blood, it regulates blood volume and the state of dehydration of our body ADH production is thus of homeostatic importance and regulation is by means of negative feedback 12 6
7 Feedback Regulation of Kidneys Hypothalamic nuclei have osmo-receptors that detect changes in blood osmolarity Increased state of Dehydration means less fluid and results in increased "particles" per volume unit = osmolarity This increased blood osmolarity is sensed by the osmoreceptors in hypothalamus and results in the release of ADH from the PPG into the blood ADH travels via the blood stream to the target organ (the kidney ), where it promotes water retention. less urine production 13 Dehydration In Kidneys 14 7
8 Feedback Regulation of Kidneys Release of ADH is directly correlated to the degree of dehydration ( blood osmolarity) normal blood osmolarity = 285 mosm) above that = indicates dehydration 15 Factors that affect ADH Release Factors that release ADH Dehydration excessive sweating not enough water intake diarrhea Low blood pressure blood loss Factors that inhibit ADH release Osmolarity below 280 Osm over-hydration Alcohol inhibits ADH secretion 16 8
9 Clinical Correlation Diabetes insipidus Results from hypo-secretion of ADH or hypo-responsiveness damage to PPG or nonfunctional ADH receptors Symptoms : excretion of large amounts of urine, dehydration, thirst Normal urine volume ~ 1 to 1.5 L / day With no ADH present : urine volume ~ 24 L / day 17 Oxytocin Major function in the female, less important in the male Enhances smooth muscle contraction in the uterus during labor It is one of the few positive feedback mechanisms stretching of cervix during delivery stimulates stretch receptors in the uterine wall receptors signal HT to release more oxytocin results in more contractions and movement of baby through the birth canal, additional stretching Additional help is provided by release of local prostaglandins. 18 9
10 Oxytocin 19 Oxytocin Oxytocin Also Enhances milk ejaculation by mammary glands after childbirth ProLactin, an APG hormone, is responsible for milk production and secretion. (see later) 20 10
11 Oxytocin makes you wanna cuddle Research links oxytocin with socio-sexual behaviors Cuddle Hormone The Hormone Involved In Reproduction May Have a Role In The Maintenance Of Relationships! 21 ADH and Oxytocin are Peptide Hormones Oxytocin Cys - Tyr - Ile - Gln - Asn - Cys - Pro - Leu - Gly - NH 2 S-S ADH ( vasopressin) Cys - Tyr - Phe - Gln - Asn - Cys - Pro - Arg - Gly - NH 2 S-S Knowing this, how do these hormones work? 11
12 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Adeno-hypophesis contains mostly glandular tissue ( 75 % of APG is glandular tissue) There is no neural connection with the HT. 6 distinct hormones are produced in the adenohypophysis. All hormones are amino-acid based hormones. 23 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormones of the APG are Growth Hormone (GH) ( also called somatotropin) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) (thyrotropin) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) (corticotropin) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Prolactin (PRL) 24 12
13 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Hormone from the pars intermedia In addition, Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) has been isolated from the pituitary pars intermedia region. It functions to stimulate melanin synthesis in the epidermis It is not active in normal adults 25 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland All except Prolactin are tropic hormones they regulate the secretory activity of other endocrine glands TSH stimulates the thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands FSH and LH ( the gonadotropic hormones) stimulate the gonades GH induces the liver to secrete a growth promoting peptide hormone known as insulin like growth factor I ( IGF-I and II) Only ACTH and TSH are pure tropic hormones. The other three also regulate growth, development and metabolism
14 Direct Control by Nervous System Hypothalamus Indirect Control through Release of Regulatory Hormones Regulatory hormones are released into the hypophyseal portal system for delivery to the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland KEY TO PITUITARY HORMONES: ACTH TSH GH PRL FSH LH MSH ADH OXT Adrenocorticotropic hormone Thyroid-stimulating hormone Growth hormone Prolactin Follicle-stimulating hormone Luteinizing hormone Melanoctye-stimulating hormone Antidiuretic hormone Oxytocin Adrenal gland Adrenal medulla Adrenal cortex Anterior lobe of pituitary gland ACTH TSH GH Epinephrine and norepinephrine Thyroid gland Liver Somatomedins PRL FSH LH MSH Glucocorticoids (cortisol, corticosterone) Thyroid hormones (T 3, T 4 ) Bone, muscle, other tissues Mammary glands Inhibin Testosterone Testes of male Estrogen Ovaries of female Progesterone Melanocytes (uncertain significance in healthy adults) Inhibin 27 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Five distinct cell types within the APG produce tropic hormones Thyrotropes : endocrine cells that produce TSH Corticotropes : endocrine cells that produce ACTH Gonadotropes : endocrine cells that produce FSH and LH Somatotropes : produce GH Only PRL, exert its effect on non endocrine target cells ( breast cells); it is made in another cell type (Lactotropes ) Most of these hormones activate receptors linked to the camp mechanism 28 14
15 Hypothalamus Hormones Also called the hypophysiotropic hormones They stimulate or inhibit the Release of APG hormones They are thus referred to as Releasing Hormones or Inhibiting Hormones There are 5 releasing and 2 inhibiting hormones that originate in the HT. These regulatory hormones from the HT reach the APG by means of the blood vessels and the capillary plexi mentioned earlier. 29 Hypothalamus Hormones The hypothalamic hormones are produced by specific HT neurons and released at axon terminals. These axon terminals end in upper part of infundibilum Upper capillary bed carries hormones to the other capillary bed in the APG via portal vessels as discussed earlier
16 Hypothalamus Hormones Growth hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) stimulates secretion of GH Growth hormone Inhibiting Hormone (GHIH or somatostatin) inhibits the secretion of GH Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH) stimulates secretion of TSH Corticotropin Releasing hormone (CRH) stimulates secretion of ACTH Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) stimulates secretion of LH and FSH Prolactin Releasing Hormone (PRH) stimulates secretion of PRL Prolactin Inhibiting Hormone (PRH) inhibits secretion of PRL All are small peptide hormones 31 Hypothalamus Hormones The releasing and inhibiting hormones from the hypothalamus regulate secretion by negative feedback mechanisms. Short- and long-loop feedback relationships between hypothalamic, pituitary, and thirdgland hormones are shown in the diagram. It demonstrates the importance of homeostatic regulation of hormone synthesis and secretion
17 Figure 18-8a Feedback Control of Endocrine Secretion Hypothalamus Releasing hormone (RH) Hormone 1 (from pituitary) Endocrine target organ Hormone 2 (from target organ) RH TRH TSH Thyroid gland Thyroid hormones Pituitary gland CRH ACTH Adrenal cortex Glucocorticoids Anterior lobe Hormone 1 GnRH FSH LH Testes Ovaries Ovaries Testes Inhibin Inhibin Estrogens Progestins Estrogens Androgens Endocrine organ Hormone 2 Negative feedback KEY Stimulation Inhibition Target cells 33 Function and Action of PROLACTIN (PRL) Is important in production of milk in mammary glands Target cells are the milk producing alveolar cells of the breasts Suckling by the baby results in a 10-fold rise in plasma PRL in the mother Oxytocin is important for milk ejaculation ( smooth muscle control milk ducts), while prolactin is important for milk production by the alveolar cells
18 PROLACTIN (PRL) Suckling, child s cry results in stimulation of oxytocin release and inhibition of Prolactin Inhibiting and Hormone Nursing and suckling thus results in parallel increases in blood plasma levels for PRL and Oxytocin 35 Effect of the PTH2R antagonist (blocks the prolactin receptor) on the suckling-induced prolactin release. Cservenák M et al. Endocrinology 2010;151:
19 PROLACTIN (PRL) Pre-childbirth HT + Childbirth HT PIH - + Oxytocin PPG APG PPG PIH + APG PRH PRL Breast Alveolar cells PRL + Breast Alveolar cells Thyroid Gland and Thyroid Hormones The thyroid gland straddles the windpipe, just below the voicebox in the neck. The thyroid consists of two lobes connected by narrow isthmus. The thyroid is made from many thyroid follicles, each made from follicular cells. They work interactively to form and package the thyroid hormones. Isthmus of thyroid gland 38 19
20 Thyroid Gland and Hormones Thyroid follicles Are hollow spheres lined by cuboidal epithelium The cuboidal cells (follicular cells) surround follicle cavity that contains a viscous colloid Surrounded by network of capillaries that Deliver nutrients and regulatory hormone Accept secretory products and metabolic wastes In-between the thyroid follicles are other cells called the para-follicular cells (also called the C-cells) They produce the calcitonin hormone. 39 Thyroid Gland and Hormones Follicular cells Para follicular cells (called C-cells) Follicle Colloid 40 20
21 Thyroid Gland and Hormones Capillary Capsule C cell Thyroid follicle Follicle cavities Cuboidal epithelium of follicle Thyroglobulin stored in colloid of follicle Thyroid follicle C cell Follicles of the thyroid gland LM 260 Histological details of the thyroid gland showing thyroid follicles and both of the cell types in the follicular epithelium ATLAS: Plate 18c 41 Thyroid Hormones Synthesis Thyroid hormones are synthesized in the colloid. Ingredients for synthesis are collected from the blood stream into the follicular cells Tyrosine synthesized in sufficient amounts by the body taken up in the Follicular cells assembled into a larger protein molecule called Thyroglobulin (via ER and Golgi) Iodide we need about 1mg /week taken up in the Follicular cells as Iodide by powerful pumps ( called iodide traps) concentration within follicular cells is 30 x higher than blood within the follicular cells, it becomes oxidized to iodine (I 2 ) 42 21
22 Thyroid Hormone Synthesis Thyroglobulin and iodine are moved into the colloid Thyroglobulin is a very large protein of about 335,000 MW and contains 70 tyrosine a.a. Iodine binds to the tyrosines of the Thyroglobulin in a specific manner = iodination I 2 + Tyrosine 2I 2 + Tyrosine Mono-iodo-tyrosine (MIT) Di-iodo-tyrosine (DIT) MIT + DIT Tri-iodo-tyrosine (T 3 ) MIT + DIT Tetra-iodo-tyrosine or Thyroxine (T 4 ) 43 Thyroid Hormone Synthesis 44 22
23 Thyroid Hormones The thyroglobulin enters back into the follicular cells via endocytosis The vesicles fuse with lysosomes and the thyroglobulin is broken down, releasing T 3 and T 4. T 3 and T 4 are the active Thyroid hormones Since T 3 and T 4 are hydrophobic, they diffuse right through the cell membranes into the bloodstream In plasma, they bind to Tyroxine-binding protein,produced by the liver, and which functions as a carrier protein. 45 Thyroid Hormones More T4 is secreted than T3 but T3 is more potent T4 is converted to T3 after passage through liver and kidney Enough iodinated Thyroglobulin is stored to last for months Thyroid problems may thus go un-noticed for months 46 23
24 Thyroid follicle cell Capillary 1 Thyroglobulin is synthesized and discharged into the follicle lumen Colloid Golgi apparatus Rough ER Colloid in lumen of follicle 3b Iodine is attached to tyrosine in colloid, forming DIT and MIT Iodine Iodide (I ) 2 Iodide (I ) 3a Iodide is is trapped oxidized (actively transported in) to iodine DIT (T 2 ) MIT (T 1 ) Thyroglobulin colloid T 3 T 4 T 3 T 4 Lysosome T 4 T 3 4 Iodinated tyrosines are linked together to form T 3 and T 4 To peripheral tissues T 4 T 3 6 Lysosomal enzymes cleave T 4 and T 3 from thyroglobulin colloid and hormones diffuse from follicle cell into bloodstream T 4 T 3 5 Thyroglobulin colloid is endocytosed and combined with a lysosome Thyroid Hormone Action Thyroid Hormones Enter target cells by transport systems Affect most cells in body Bind to receptors in: 1. Cytoplasm 2. Surfaces of mitochondria 3. Nucleus In children, essential to normal development of: Skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems 48 24
25 Increases metabolic rate stimulate protein synthesis increase lipolysis (fat break down) increase glucose use increases overall metabolic rate increased O 2 uptake and energy expenditure increased heat production = calorigenic effect Effect on Cardiovascular system Thyroid Hormone Action increased metabolism and O 2 usage causes vasodilation and increased blood flow increases heart responsiveness to catecholamines due to upregulation of beta receptors increased heart rate, contractile force 49 Thyroid Hormone Action Effect on growth and nervous system Thyroid hormones are important for normal growth thyroid hormones stimulate growth hormone release Thyroid hormones are important for normal development of nervous system ( myelination etc. ) Effect on muscular system Makes muscle contract with vigor too much results in muscle tremors not enough results in sluggish muscles 50 25
26 Control of Thyroid Hormones TSH or Thyrotropin ( from APG) Works on Thyroid gland Stimulates growth of follicles Stimulates all aspects of hormone formation Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone ( from HT) Works on Thyrotrope cells of APG Induces the release of TSH Negative feedback by Thyroid Hormones Too much T3, T4 in blood inhibits TSH release and a minor effect on inhibition of TRH Not enough takes away the inhibition and TSH starts working again 51 Control of Thyroid Hormones Thus TRH turns on the output of Thyroid Hormone via TSH, while the output itself, the Thyroid Hormones, turn off the ouput. The Hypothalamic-pituitary-Thyroid axis represents a typical negative feedback system. Thyroid hormone output is as such neatly regulated and wide swings in hormone level rarely occur A typical trigger for additional hormone output is exposure to cold pregnancy hypoglycemia 52 26
27 Abnormalities in Thyroid Hormones Hyposecretion of TH during fetal life or infancy results in cretinism child exhibits dwarfism (skeleton fails to grow) mentally retarded (fewer neurons, defective myelination) retarded sexual development can be prevented by oral thyroid replacement therapy Hypothyroidism in adults results in the syndrome of Myxedema edema with swollen facial tissue diminished Basal Metabolic rate (BMR) (sensitive to cold) slow HeartRate, muscular weakness no mental retardation but less alert (more common in females) may result from thyroid gland defect inadequate TRH, TSH release 53 or due to a thyroid removal Abnormalities in Thyroid Hormones Myxedema can results from an absence of iodine follicle cells produce colloid but cannot make functional hormones APG keeps making TSH to stimulate thyroid gland to make more hormone This constant stimulation cause the thyroid gland to enlarges ( goiter) Hashimoto s disease auto-immune disease where antibodies attack and destroy the thyroid gland Occurs around year olds and more in women than men 54 27
28 Abnormalities in Thyroid Hormones Hypersecretion of Thyroid hormones increases oxygen use by tissues elevated heat production wasting of energy, resulting in thinning increased food intake sweating, nervousness Most common form is an autoimmune disorder where antibodies mimics the action of TSH without the regulating feedback action Results in a continuous stimulation of thyroid gland to secrete and grow (goiter) = Graves Disease 55 Abnormalities in Thyroid Hormones Goiter at advanced stage Exophthalmos (Graves disease) 56 28
The Endocrine System
 Collin College! BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Adeno-hypophesis contains mostly glandular tissue ( 75 % of APG is glandular tissue)
Collin College! BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gland Adeno-hypophesis contains mostly glandular tissue ( 75 % of APG is glandular tissue)
The Endocrine System
 Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
Collin College BIOL 2402 Anatomy/Physiology 2 Chapter 18 The Endocrine System 1 Pituitary Gland or Hypophysis The Pituitary Gland Also called hypophysis Lies within sella turcica Hangs inferior to hypothalamus
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 3 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland or Hyp op hysis TextBook Readings Pages 612 through 624. Make use of the figures in your textbook ; a picture
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture. Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
BIOLOGY 2402 Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Chapter 18 ENDOCRINE GLANDS 1 ENDOCRINE GLANDS Homeostasis depends on the precise regulation of the organs and organ systems of the body. Together the nervous
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
Endocrine Glands. Endocrine glands
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
ENDOCRINOLOGY Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands Produce substances called hormones. Ductless glands, i.e., they release hormones directly into the bloodstream Hormones only act at their target tissue where
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Art labeling Activity: Figure 16.1
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine Sy... Assignment 6 part I: The Endocrine System, Chapter 16 Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 4, 2013 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 11, 2017 Control Mechanisms 2: Endocrine Control Hormones are chemical messengers that are secreted into the blood by endocrine cells or specialized neurons.
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Activity of the Adenophypophysis The tropic hormones (effect endocrine glands) that are released are: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Activity of the Adenophypophysis The tropic hormones (effect endocrine glands) that are released are: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
NEUROENDOCRINOLOGY Danil Hammoudi.MD The hypothalamus and pituitary gland are key regulators of the hormone system. Sensory and endocrine information is processed and integrated t in the brain and hormone
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
The reproductive system
 The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
The reproductive system THE OVARIAN CYCLE HORMONAL REGULATION OF OOGENSIS AND OVULATION hypothalamic-pituitary-ovary axis Overview of the structures of the endocrine system Principal functions of the
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
Reproductive System (Hormone Function) Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara 1 Endocrine Control: Three Levels of Integration Hormones of the hypothalamic-anterior pituitary
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
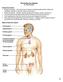 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
HIHIM 409. Endocrine system. Differences between systems. Hormone effects. Similarities. Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system
 The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
The Endocrine System Interrelationship between nervous and endocrine system Nervous system short term/ fast Endocrine system long term/slow Differences between systems Endocrine system good for gradual
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine system. General principle of endocrinology. Mode of hormone delivery to target. Mode of hormone delivery to target
 Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Endocrine system General principle of endocrinology Co-ordinating system to regulate and integrate function of different cells - Nervous system -Endocrine system Neuro-endocrine system Hormone Molecules
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
The Endocrine System: An Overview
 C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
C H A P T E R 17 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System: An Overview A system of ductless glands Secrete messenger molecules called hormones Hormones travel to distant body cells and signal characteristic
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]
![BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ] BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION. [ Academic Script ]](/thumbs/87/96904971.jpg) BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
BASIC CONCEPTS OF NEURAL AND ENDOCRINE REGULATION [ Academic Script ] Course : Zoology Name : B.Sc. 2nd Year Paper No. : Z-203B & Title : Vertebrate Endocrinology And Reproductive Biology Topic No. : 1
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland
 Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
Hypothalamus & pituitary gland Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C541, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208292 Outline Hypothalamus Relationship between the hypothalamus
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Hypothalamus. Small, central, & essential.
 Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Hypothalamus Small, central, & essential. Summary: You can t live without a hypothalamus. Located at the junction between the brain stem and the forebrain Medial hypothalamus: interface between the brain
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Endocrine System. Always willing to lend a helping gland
 Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
Endocrine System Always willing to lend a helping gland Functions of the Endocrine System Regulates metabolic activities through hormones Controls reproduction, growth and development, cellular metabolism,
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
8/26/13. Announcements
 Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 10. The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 10 The Endocrine System Chapter 10 Learning Outcomes 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-4 10-5 Explain the role of intercellular
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 10 The Endocrine System Chapter 10 Learning Outcomes 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-4 10-5 Explain the role of intercellular
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
The Endocrine System PART A
 9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
9 The Endocrine System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Endocrine System
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline. Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
ENDOCRINOLOGY Cross setion of discipline Zdeněk Fryšák, III. interní klinika, nefrologie, revmatologie a endokrinologie FN a LF Olomouc Coordination of systems involve Nervous System» Rapid response» Short
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Eleventh Edition Chapter 18 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett, Parkland College Learning outcomes 18-1 Explain the importance of intercellular
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Eleventh Edition Chapter 18 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Lori Garrett, Parkland College Learning outcomes 18-1 Explain the importance of intercellular
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
3/12/2012. Pituitary Gland (hypophysis) Anterior Pituitary. Anterior Pituitary. Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus & Pituitary Glands Hypothalamus (Master Gland) 8 hormones produced in hypothalamus 6 regulate anterior pituitary e.g., TRH, GnRH, GHRH E.g., PIH, Somatastatin (GH TSH) Hypothalamus
-Ahmad Rawajbeh. -Dania alkouz. -Saleem Khresha. 1 P a g e
 -2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
-2 -Ahmad Rawajbeh -Dania alkouz -Saleem Khresha 1 P a g e The information marked with "(+)" has not been mentioned during the lectures. I added them to clarify and explain. The pituitary gland (+) From
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland
 Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
Hypophysis or Pituitary Gland It is also called master gland because it not only secretes hormones for physiological effects, it also controls the development and functions of other endocrine glands whereas
