Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats
|
|
|
- Clementine Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats M.L. Molchanov and F.S. Guimarães Departamento de Farmacologia, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brasil Correspondence F.S. Guimarães Departamento de Farmacologia Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto, USP 19-9 Ribeirão Preto, SP Brasil Fax: fsguimar@fmrp.usp.br Presented at the International Neurobiology Course, Faculdade de Odontologia de Ribeirão Preto, Universidade de São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, SP, Brasil, May -7, 199. Research supported by CAPES, CNPq and FAPESP (No. 9/139-7). Abstract The behavioral effects of trans-(±)-1-amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid (), a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mglur) agonist, or.9% (w/v) saline, injected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray (DPAG), was investigated. Male Wistar rats showed defense reactions characterized by jumps toward the top edges of the cages (saline = vs =., medians P<.5) and gallops (saline = vs = 1., medians P<.5) during the -s period after the beginning of the injection. In another experiment animals were placed inside an open arena for 5 min immediately after injection. Their behavior was recorded by a video camera and a computer program analyzed the videotapes. Eleven of fifteen rats injected with showed a short-lasting (about 1 min) flight reaction. No saline-treated animal showed this reaction (P<.5, chi-square test). The drug induced an increase in turning behavior (P =., MANOVA) and a decrease in the number of rearings (P<.1, MANOVA) and grooming episodes (P<.1, MANOVA). These results suggest that mglurs play a role in the control of defense reactions in the DPAG. Key words Periaqueductal gray Metabotropic glutamate receptors Defense behavior Open-field Rats Received December 9, 199 Accepted September 1, 1999 It has been well established that the periaqueductal gray (PAG) matter is implicated in the control of vocalizations, nociception and defensive behavior (1). Considerable evidence suggests that excitatory amino acids (EAA) play a critical role in integrating somatic and autonomic reactions in the PAG (). L-Glutamic acid is the principal EAA neurotransmitter in the mammalian nervous system, acting on multiple receptor types classified as ionotropic and metabotropic receptors (3). Most of these receptor subtypes are found in the dorsolateral subdivision of the PAG (). The metabotropic receptor family is linked by G-proteins to various second messenger systems. Eight subtypes have been cloned so far and they can be divided into three groups based on sequence homology, signal transduction system and pharmacology (5). Many studies have been performed to investigate the effects of agonists, antagonists or modulators of glutamatergic ionotropic receptors on defensive reactions (,7). Only recently has the role of mglur in these reactions begun to be investigated (). The objective of this study was to examine the behavioral effects of trans-(±)- 1-amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid
2 153 M.L. Molchanov and F.S. Guimarães Figure 1 - Behavioral effects of saline (N = ) or trans-(±)-1- amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid (; 3 nmol; N = 5) microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats. The number of jumps (upper panel) and gallops (lower panel) was recorded for 1 min from the beginning of the injection period. The columns represent the medians and the vertical bars the interquartile intervals. P<.5 compared to control (Mann- Whitney U-test). (), a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mglur) (class I or II) agonist (5), microinjected into the dorsolateral PAG (DPAG) of rats. Male Wistar rats weighing -5 g were housed in pairs, with free access to food and water in a temperature-controlled room ( ± 1 o C) under a 1/1-h light/dark cycle (lights on at 7: a.m.) throughout the experiment. The rats were anesthetized with.5%,,-tribromoethanol (1 ml/kg, ip) and submitted to stereotaxic surgery to implant a stainless steel guide cannula (.7 mm O.D.) aimed at the DPAG (coordinates: 1.9 lateral to the lambda and. mm below the surface of the skull at an angle of 1 o with the sagittal plane). The cannula was attached to the bone with stainless steel screws and acrylic cement, and a stylet was introduced into it to prevent obstruction. Seven days after surgery, unrestrained animals housed in a Plexiglas cage (9 x 19 x 3 cm) received microinjections of saline (.3 µl) or (3 nmol/.3 µl). The dose employed (3 nmol) was based on a report by Leyva et al. (9) and on a pilot study from our laboratory showing no effect of a Jumps Gallops nmol dose. was dissolved in.1 M NaOH and the ph adjusted to 7. by adding.1 N HCl. Animals were microinjected with a thin dental needle (.3 mm O.D.) which extended 1 mm below the cannula tip. A volume of.3 µl was injected over 3 s using a Hamilton microsyringe controlled by an infusion pump (model, kdscientific, Boston, MA, USA). After the experimental session, the rats were sacrificed and the injection sites were determined histologically according to the atlas of Paxinos and Watson (1). Only data from animals that received the injections inside the DPAG were used for analysis. Animal behavior was videotaped for 1 min from the beginning of the injection and the number of jumps toward the top edges of the cage and gallops (short and frantic runs) was recorded. The results were analyzed by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U-test. induced a short-lasting (about 1 min) spontaneous defense reaction with exophthalmia, piloerection, escape attempts and runnings. There was a significant increase in the number of jumps and gallops (P<.5, Mann-Whitney U-test, Figure 1). No animal showed any sign of seizure activity. In a second experiment, animals received the same microinjections as described above. They were, however, hand-held during all the injection period. The injection needle remained in place for an additional -3 s to prevent reflux. Immediately after the end of this period, the rats were placed inside the open arena and the behavior was recorded with a videocamera (VHS movie, HNS-15B, Sony) placed 3.5 m above the arena for 5 min. The open circular arena (7 cm in diameter with 5-cm high transparent walls) was located in a sound-attenuated room illuminated with an indirect fluorescent light. Before each trial the floor was cleaned with an alcohol-water solution (7:3). Histological verification of the injection sites was performed as described above.
3 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG 1535 Videotapes were later examined on a video (VR75/7, Philips) connected to a microcomputer and the distance traveled by the animal was determined by the Ethovision software (version 1.9; Noldus, Wageningen, The Netherlands). Other behaviors, including frequency of grooming, rearings, turnings (3 o circles), or number of defecation boli, were recorded manually by the operator. The presence of an escape reaction during the injection was analyzed by a chisquare test and the number of defecation boli by a Student t-test. The remaining data were analyzed by repeated measures multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA), using time (1 to 5 min) as a within-subjects factor and drug (saline or ) as a between-subjects factor. Differences between treatments during a given one-minute period were analyzed by the t-test for independent observations. Microinjection of saline elicited no noticeable behavioral effect. On the other hand, 11 of 15 rats that received into the DPAG showed an immediate defense reaction, which started during the 3-s injection and lasted for at least 1 min (P<.5, chisquare test). After this brief behavioral activation, the animals showed a decrease in grooming (F 1,5 = 13., P<.1) and rearing (F 1,5 = 15.1, P<.1) frequency, and an increase in turnings (F 1,5 = 11.9, P =., Figure ). No main effect was found in the distance traveled or in the number of defecation boli (P>.5; data not shown). There was a main effect of time on rearing (F, = 15.9, P<.1), distance traveled (F, = 1.33, P<.1) and grooming (F, = 3.57, P =.). A large body of evidence has shown that ionotropic glutamate receptors are involved in the control of defense reactions in the DPAG (11). However, few studies have investigated the behavioral effects of mglur agonists. In a previous study, t-ada, a proposed selective class I mglur agonist, showed only minor effects on rat behavior in an open arena (1). However, this study employed icv administration, preventing Grooming Distance traveled (cm) A C Rearings Turnings B D Figure - Behavioral effects of saline (N = 1) or trans-(±)-1- amino-1,3-cyclopentanedicarboxylic acid (; 3 nmol; N = 15) microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats placed in an open arena. The number of grooming episodes (A), rearings (B), distance traveled in cm (C), and turnings (D) was recorded for 5 min. The points represent the means, and vertical bars the SEM. P<.5, P<.1 compared to control (Student t-test).
4 153 M.L. Molchanov and F.S. Guimarães References comparison with our data. The present data show that, an mglur agonist, induced a short-lasting flight reaction similar to that obtained with EEA or electrical stimulation (,13). This defense response was followed by behavioral changes such as an increase in the number of turnings and a decrease in the number of rearings and grooming episodes. Aversive stimuli such as an electric footshock can induce rotational behavior in rats (1) and it has been suggested that turnings may be part of the defensive repertoire of these animals (15). Rearings are often used to evaluate exploratory activity (1) and a decrease in exploratory drive has been observed in rats submitted to stressful events (17). Many studies suggest that grooming behavior is increased by a mild aversive stimulus; however, the response varies with the degree of fear and the habituation to the stressful situation (1). The decrease in the number of rearings and grooming probably does not reflect any locomotor deficit since there was no difference in the distance traveled by the groups. These behavioral changes, therefore, may be reflecting an anxiogenic effect of. Leyva et al. (9) showed that mglur activation by (3 nmol) injection into the DPAG of rats had a depressor effect on blood pressure in anesthetized animals. Although we have not measured cardiovascular parameters in our study, defense reactions are usually accompanied by increases in blood pressure (,). It is possible that these apparent contradictory results are due to preferential actions of on various types of mglur. In a recent report by the same group (19), a selective mglur I agonist injection into the DPAG of mice increased the latency of the nociceptive reaction in the hot plate test while mglur II and III agonists caused hyperalgesia. Anesthetic utilization may also have interfered with the response obtained by Leyva et al. (9). Toxic effects of microinjected directly into the cerebral ventricle have been previously reported (). However, Maione et al. (19) employed a higher dose than ours in the DPAG of mice without reporting any neurotoxic effects. Moreover, rats in which (3 nmol/.3 µl) injection produced a defensive response received another microinjection of the same compound h later, showing similar effects (data not shown). The reproducibility of the behavioral effects suggests that the drug did not produce significant neurotoxicity, at least within this period. In conclusion, our results suggest that mglurs play a role in the control of defense reactions. Further analyses, with subtype selective agonists or antagonists, are needed to clarify the involvement of different mglur subtypes in defense reactions mediated by the DPAG. Acknowledgments We thank J.C. de Aguiar for excellent technical support. 1. Behbehani MM (1995). Functional characteristics of the midbrain periaqueductal gray. Progress in Neurobiology, : Bandler R & Carrive P (19). Integrated defence reaction elicited by excitatory amino acid microinjection in the midbrain periaqueductal grey region of the unrestrained cat. Brain Research, 39: Ozawa S, Kamiya H & Tsuzuki K (199). Glutamate receptors in the mammalian nervous system. Progress in Neurobiology, 5: Albin RL, Makowiec RL, Hollingworth Z, Dure IV LS, Penney JB & Young AB (199). Excitatory amino acid binding sites in the periaqueductal gray of the rat. Neuroscience Letters, 11: Pin J-P & Duvoisin R (1995). Review: neurotransmitter receptors I. The metabotropic glutamate receptors: structure and functions. Neuropharmacology, 3: 1-.. Krieger JE & Graeff FG (195). Defensive behavior and hypertension induced by glutamate in the midbrain central gray of the rat. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 1: Guimarães FS, Carobrez AP, De Aguiar JC & Graeff FG (1991). Anxiolytic effect in the elevated plus-maze of the NMDA receptor antagonist AP7 microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal grey. Psychopharmacology, 13: 91-9.
5 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG Chojnacka-Wójcik E, Tatarczyñska E & Pilc A (1997). The anxiolytic-like effect of metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists after intrahippocampal injection in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 319: Leyva J, Maione S, Pallotta M, Berrino L & Rossi F (1995). Metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate opposite effects on periaqueductal gray matter. European Journal of Pharmacology, 5: Paxinos G & Watson C (1997). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 3rd edn. Academic Press, San Diego. 11. Matheus MG & Guimarães FS (1997). Antagonism of non-nmda receptors in the dorsal periaqueductal grey induces anxiolytic effect in the elevated plus-maze. Psychopharmacology, 13: Wetzel W, Wagner T, Reymann KG & Riedel G (1995). Open field behaviour in rats: role of metabotropic glutamate receptors. NeuroReport, : Graeff FG, Silveira MC, Nogueira RL, Audi EA & Oliveira RM (1993). Role of the amygdala and periaqueductal gray in anxiety and panic. Behavioural Brain Research, 5: Kaplan R, Glick ST & Goldfarb J (19). Footshock-induced rotation: lack of effects of haloperidol and AMPT. European Journal of Pharmacology, 1: Cardoso SH, Coimbra NC & Brandão ML (199). Defensive reactions evoked by activation of NMDA receptors in distinct sites of the inferior colliculus. Behavioural Brain Research, 3: Maier SE, Vandenhoff P & Crowne DP (19). Multivariate analysis of putative measures of activity, exploration, emotionality, and spatial behavior in the hooded rat (Rattus norvegicus). Journal of Comparative Psychology, 1: Guimarães FS, Del Bel EA, Padovan CM, Netto SM & de Almeida RT (1993). Hippocampal 5-HT receptors and consolidation of stressful memories. Behavioural Brain Research, 5: File SE, Mabbutt PS & Walker JH (19). Comparison of adaptive responses in familiar and novel environments: Modulatory factors. Annals of the New York A- cademy of Sciences, 55: Maione S, Marabese I, Leyva J, Palazzo E, de Novellis V & Rossi F (199). Characterisation of mglurs which modulate nociception in the PAG of the mouse. Neuropharmacology, 37: Manahan-Vaughan D, Behnisch T & Reymann KG (1999). ACPD-mediated slow-onset potentiation is associated with cell death in the rat CA1 region in vivo. Neuropharmacology, 3: 7-9.
Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not the expression, of step-down inhibitory avoidance
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Thigmotactic responses in an open-field
 Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
The brain decade in debate: II. Panic or anxiety? From animal models to a neurobiological basis
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2001) 34: 145-154 Panic or anxiety? ISSN 0100-879X 145 The brain decade in debate: II. Panic or anxiety? From animal models to a neurobiological basis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2001) 34: 145-154 Panic or anxiety? ISSN 0100-879X 145 The brain decade in debate: II. Panic or anxiety? From animal models to a neurobiological basis
Abstract. R. Roesler 1, J. Quevedo 1, C. Rodrigues 1, M. Madruga 1, M.R.M. Vianna 1 and M.B.C. Ferreira 2
 Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Routine post-weaning handling of rats prevents isolation rearing-induced deficit in prepulse inhibition
 Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) Laboratório de Psicologia Comparada, Universidade Estácio de Sá, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil b
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 243 247 Microinfusion of nefazodone into the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala enhances defensive behavior induced by NMDA stimulation of the inferior colliculus S. Maisonnette
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 243 247 Microinfusion of nefazodone into the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala enhances defensive behavior induced by NMDA stimulation of the inferior colliculus S. Maisonnette
Panic-like behaviors in Carioca High-and Low-conditioned Freezing rats
 PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2011, 4, 2, 205-210 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2011.2.005 Panic-like behaviors in Carioca High-and Low-conditioned Freezing rats Bruno de Oliveira Galvão 1,
PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2011, 4, 2, 205-210 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2011.2.005 Panic-like behaviors in Carioca High-and Low-conditioned Freezing rats Bruno de Oliveira Galvão 1,
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
USO ACADEMICO PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE
 PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2010, 3, 1, 67-72 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2010.1.008 Effects of contextual fear conditioning and pentylenetetrazol on panic-like reactions induced by dorsal
PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 2010, 3, 1, 67-72 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2010.1.008 Effects of contextual fear conditioning and pentylenetetrazol on panic-like reactions induced by dorsal
The relationship between anxiety and depression in animal models: a study using the forced swimming test and elevated plus-maze
 Brazilian Correlation Journal between of Medical plus-maze and and Biological forced Research swimming (1999) behaviors 32: 1121-1126 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1121 The relationship between anxiety
Brazilian Correlation Journal between of Medical plus-maze and and Biological forced Research swimming (1999) behaviors 32: 1121-1126 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1121 The relationship between anxiety
Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats
 Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Abstract. Introduction. R.N. Takahashi 1, O. Berton 2,3, P. Mormède 2 and F. Chaouloff 2
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Supplementary Information. Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease. Supplementary Figures S1-10
 Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Supplementary Information Staged decline of neuronal function in vivo in an animal model of Alzheimer s Disease Christine Grienberger 1 *, Nathalie L. Rochefort 1 *, Helmuth Adelsberger 1, Horst A. Henning
Maria Cecília Zanoto de Luca a, Marcus Lira Brandão a, Vítor Augusto Motta b, J. Landeira-Fernandez c,d, *
 Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 75 (2003) 459 466 www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Antinociception induced by stimulation of ventrolateral periaqueductal gray at the freezing threshold is
Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior 75 (2003) 459 466 www.elsevier.com/locate/pharmbiochembeh Antinociception induced by stimulation of ventrolateral periaqueductal gray at the freezing threshold is
Anxiolytic effect of spermine microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal grey in rats
 Anxiolytic effect of spermine microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal grey in rats José Geraldo Pereira da Cruz 1 e Antônio de Pádua Carobrez 2 1 Departamento de Ciências Naturais, Centro de Ciências
Anxiolytic effect of spermine microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal grey in rats José Geraldo Pereira da Cruz 1 e Antônio de Pádua Carobrez 2 1 Departamento de Ciências Naturais, Centro de Ciências
enhances nociceptive responses in rats
 Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Title. CitationInternational journal of urology, 23(7): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights. Type. File Information
 Title Differences in neurotransmitter systems of ventrolat nociceptive regulation : An in vivo microdialysis st Kitta, Takeya; Mitsui, Takahiko; Kanno, Yukiko; Chib Author(s) Nobuo CitationInternational
Title Differences in neurotransmitter systems of ventrolat nociceptive regulation : An in vivo microdialysis st Kitta, Takeya; Mitsui, Takahiko; Kanno, Yukiko; Chib Author(s) Nobuo CitationInternational
Different patterns of freezing behavior organized in the periaqueductal gray of rats: Association with different types of anxiety
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Behavioural Brain Research 188 (2008) 1 13 Review Different patterns of freezing behavior organized in the periaqueductal gray of rats: Association with different
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Behavioural Brain Research 188 (2008) 1 13 Review Different patterns of freezing behavior organized in the periaqueductal gray of rats: Association with different
Contrasting effects of acute and chronic treatments with ketamine on inhibitory avoidance and escape latency in the elevated-t-maze
 Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(6): 2387-2394, December 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
Available online at http://ajol.info/index.php/ijbcs Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 8(6): 2387-2394, December 2014 ISSN 1997-342X (Online), ISSN 1991-8631 (Print) Original Paper http://indexmedicus.afro.who.int
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test.
 Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Physiology & Behavior 85 (2005) Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze
 Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the
 Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Supplementary Figure 1. GABA depolarizes the majority of immature neurons in the upper cortical layers at P3 4 in vivo. (a b) Cell-attached current-clamp recordings illustrate responses to puff-applied
Abstract. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 2011, 1, 181-187 doi:10.4236/jbbs.2011.13024 Published Online August 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbbs) Anxiety-Behavior Modulated by Ventral Medial Prefrontal
Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science, 2011, 1, 181-187 doi:10.4236/jbbs.2011.13024 Published Online August 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbbs) Anxiety-Behavior Modulated by Ventral Medial Prefrontal
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Evaluation of electromyographic activity and heart rate responses to isometric exercise. The role played by muscular mass and type
 Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
Brazilian Electromyography Journal of and Medical heart and rate Biological responses Research to isometric (1999) exercise 32: 115-120 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 115 Evaluation of electromyographic
JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning
 JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning 8 6 4 Cond1 Cond2 Test VEH ANI Session Supplementary Fig. 1. Protein synthesis inhibition after a second contextual
JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning 8 6 4 Cond1 Cond2 Test VEH ANI Session Supplementary Fig. 1. Protein synthesis inhibition after a second contextual
Cannabinoid modulation of predator fear: involvement of the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (1), 17, 1193 1. CINP 1 doi:1.117/s1117131788 Cannabinoid modulation of predator fear: involvement of the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray ARTICLE S. F.
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (1), 17, 1193 1. CINP 1 doi:1.117/s1117131788 Cannabinoid modulation of predator fear: involvement of the dorsolateral periaqueductal gray ARTICLE S. F.
Carolina Irurita Ballesteros, Bruno de Oliveira Galvão, Silvia Maisonette, J. Landeira-Fernandez* Abstract. Introduction
 Effect of Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampal Lesions on Contextual Fear Conditioning and Unconditioned Defensive Behavior Induced by Electrical Stimulation of the Dorsal Periaqueductal Gray Carolina Irurita
Effect of Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampal Lesions on Contextual Fear Conditioning and Unconditioned Defensive Behavior Induced by Electrical Stimulation of the Dorsal Periaqueductal Gray Carolina Irurita
A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred for differential 5-HT 1A receptor function
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (3) 36: 63-67 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines ISSN 1-879X 63 A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (3) 36: 63-67 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines ISSN 1-879X 63 A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred
LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place
 Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
"One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic state?
 Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Chlorpheniramine facilitates inhibitory avoidance in teleosts submitted to telencephalic ablation
 398 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 398-402 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication Chlorpheniramine facilitates inhibitory avoidance in teleosts submitted to telencephalic ablation
398 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 398-402 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication Chlorpheniramine facilitates inhibitory avoidance in teleosts submitted to telencephalic ablation
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters. Paul Glue
 Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters Paul Glue Objectives Review: Relative abundance of AAs vs monoamines Pharmacology of glutamate, GABA Postulated role of glutamate, GABA dysfunction in neuropsych disorders
Supplemental Figure 1
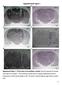 A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa
 Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
The compulsive-like aspect of the head dipping emission in rats with chronic electrolytic lesion in the area of the median raphe nucleus
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 245-250 Head dipping and the median raphe nucleus ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 245 The compulsive-like aspect of the head dipping emission
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2004) 37: 245-250 Head dipping and the median raphe nucleus ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 245 The compulsive-like aspect of the head dipping emission
PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION
 PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION Lisa A. Teather 1,2 & Richard J. Wurtman 1 1 Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
PLATELET-ACTIVATING FACTOR AFFECTS NOCICEPTION IN RATS AT CEREBRAL SITES OF ACTION Lisa A. Teather 1,2 & Richard J. Wurtman 1 1 Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Conditioned Stimulus Familiarity Determines Effects of MK-801 on Fear Extinction
 Behavioral Neuroscience 2009 American Psychological Association 2009, Vol. 123, No. 2, 303 314 0735-7044/09/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0014988 Conditioned Stimulus Familiarity Determines Effects of MK-801 on
Behavioral Neuroscience 2009 American Psychological Association 2009, Vol. 123, No. 2, 303 314 0735-7044/09/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/a0014988 Conditioned Stimulus Familiarity Determines Effects of MK-801 on
Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina mulungu on anxiety-related responses in rats
 Brazilian Erythrina Journal mulungu of and Medical anxiety and Biological Research () 35: 473-477 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 473 Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina
Brazilian Erythrina Journal mulungu of and Medical anxiety and Biological Research () 35: 473-477 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 473 Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina
AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
Cannabinoid Receptor Activation in the Basolateral Amygdala Blocks the Effects of Stress on the Conditioning and Extinction of Inhibitory Avoidance
 11078 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 9, 2009 29(36):11078 11088 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Cannabinoid Receptor Activation in the Basolateral Amygdala Blocks the Effects of Stress on the Conditioning
11078 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 9, 2009 29(36):11078 11088 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Cannabinoid Receptor Activation in the Basolateral Amygdala Blocks the Effects of Stress on the Conditioning
Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors in Male Syrian Hamsters
 Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Neuroscience Honors Theses Neuroscience Institute Spring 5-5-2017 Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors
Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Neuroscience Honors Theses Neuroscience Institute Spring 5-5-2017 Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors
ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS: EFEITOS DE DESNUTRIÇÃO E ESTIMULAÇÃO TÁTIL DOS FILHORES*
 REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o.2, 150-156. ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS:
REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o.2, 150-156. ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS:
EFFECT OF ILLUMINATION CONDITION ON RISK ASSESSMENT BEHAVIORS OF MICE
 The Psychological Record, 1997,47, 167-174 EFFECT OF ILLUMINATION CONDITION ON RISK ASSESSMENT BEHAVIORS OF MICE ERNEST D. KEMBLE and MICHAEL J. GOBLIRSCH University of Minnesota-Morris Levels of risk
The Psychological Record, 1997,47, 167-174 EFFECT OF ILLUMINATION CONDITION ON RISK ASSESSMENT BEHAVIORS OF MICE ERNEST D. KEMBLE and MICHAEL J. GOBLIRSCH University of Minnesota-Morris Levels of risk
SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY IN THE PLUS-MAZE TEST IN MICE
 Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Copyright 2004 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Polish Journal of Pharmacology Pol. J. Pharmacol., 2004, 56, 353 357 ISSN 1230-6002 SHORT COMMUNICATION EFFECT OF SILDENAFIL ON ANXIETY
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Tracking Multiple Animals per Arena. Advanced EthoVision XT. Summary Tracking multiple animals per arena. Advanced detection settings
 Advanced EthoVision XT Tutorial Fabrizio Grieco 27 August 2010 Summary Tracking multiple animals per arena Advanced detection settings Analysis of social interaction tests New detection method: Differencing
Advanced EthoVision XT Tutorial Fabrizio Grieco 27 August 2010 Summary Tracking multiple animals per arena Advanced detection settings Analysis of social interaction tests New detection method: Differencing
Effects of tryptophan depletion on anxiety induced by simulated public speaking
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2000) 33: 581-587 Tryptophan depletion in public speaking ISSN 0100-879X 581 Effects of tryptophan depletion on anxiety induced by simulated public
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2000) 33: 581-587 Tryptophan depletion in public speaking ISSN 0100-879X 581 Effects of tryptophan depletion on anxiety induced by simulated public
Nucleus accumbens lesions impair context, but not cue, conditioning in rats
 Learning and Memory PREVIOUS work has provided evidence of a role for the hippocampal formation in contextual as opposed to cue conditioning. Similar deficits have been observed after transection of the
Learning and Memory PREVIOUS work has provided evidence of a role for the hippocampal formation in contextual as opposed to cue conditioning. Similar deficits have been observed after transection of the
EFFECTS OF NITRIC OXIDE SYNTHASE INHIBITOR N G -NITRO-L-ARGININE METHYL ESTER ON SPATIAL AND CUED LEANING
 Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Pergamon Neuroscience Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 837 841, 1998 Copyright 1998 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd Printed in Great Britain. All rights reserved PII: S0306-4522(97)00457-0 0306 4522/98 $19.00+0.00
Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements
 Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Y. Isomura et al. 1 Microcircuitry coordination of cortical motor information in self-initiation of voluntary movements Yoshikazu Isomura, Rie Harukuni, Takashi Takekawa, Hidenori Aizawa & Tomoki Fukai
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/330/6009/1408/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paradoxical False Memory for Objects After Brain Damage Stephanie M. McTighe, Rosemary A. Cowell, Boyer D. Winters,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/330/6009/1408/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Paradoxical False Memory for Objects After Brain Damage Stephanie M. McTighe, Rosemary A. Cowell, Boyer D. Winters,
The Dorsolateral Periaqueductal Gray and Its Role in Mediating Fear Learning to Life Threatening Events
 The Dorsolateral Periaqueductal Gray and Its Role in Mediating Fear Learning to Life Threatening Events Grasielle C. Kincheski 1, Sandra R. Mota-Ortiz 2, Eloisa Pavesi 1, Newton S. Canteras 3, Antônio
The Dorsolateral Periaqueductal Gray and Its Role in Mediating Fear Learning to Life Threatening Events Grasielle C. Kincheski 1, Sandra R. Mota-Ortiz 2, Eloisa Pavesi 1, Newton S. Canteras 3, Antônio
Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: Fear
 Historical views that thought and emotion were processed separately in the brain Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: So far, fear is the best understood What is fear? Dictionary: A feeling of agitation and
Historical views that thought and emotion were processed separately in the brain Prof. Anagnostaras, Lecture 7: So far, fear is the best understood What is fear? Dictionary: A feeling of agitation and
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION. Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition. A Senior Honors Thesis
 Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Running head: EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL ON OBJECT RECOGNITION Alcohol on Object Recognition 1 Impairing Effects of Alcohol on Object Recognition A Senior Honors Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the
Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism
 Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
VENTRAL TEGMENTAL AREA LESIONS DIFFERENTIALLY AFFECT RESPONSES CONTROLLED BY CS-US CONTIGUITY AND RESPONSE-REINFORCER CONTINGENCY IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1987, 47: 83-91 VENTRAL TEGMENTAL AREA LESIONS DIFFERENTIALLY AFFECT RESPONSES CONTROLLED BY CS-US CONTIGUITY AND RESPONSE-REINFORCER CONTINGENCY IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Ericka
ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1987, 47: 83-91 VENTRAL TEGMENTAL AREA LESIONS DIFFERENTIALLY AFFECT RESPONSES CONTROLLED BY CS-US CONTIGUITY AND RESPONSE-REINFORCER CONTINGENCY IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Ericka
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS
 SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
SURGICAL PROCEDURE DESCRIPTIONS GONADECTOMY: CASTRATION USING SCROTAL METHOD 1. The animal is anesthetized and placed in dorsal recumbency with the tail toward the surgeon. 2. The abdominal and scrotal
Differential response to gepirone but not to chlordiazepoxide in malnourished rats subjected to learned helplessness
 54 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 54-59 ISSN 0100-879X L.M.M. Camargo et al. Differential response to gepirone but not to chlordiazepoxide in malnourished rats subjected
54 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 54-59 ISSN 0100-879X L.M.M. Camargo et al. Differential response to gepirone but not to chlordiazepoxide in malnourished rats subjected
Basic Neuroscience. Sally Curtis
 The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats
 Exp Brain Res (2001) 139:39 52 DOI 10.1007/s002210100746 RESEARCH ARTICLE Tobias Bast Wei-Ning Zhang Joram Feldon The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats Different anterograde amnesias of
Exp Brain Res (2001) 139:39 52 DOI 10.1007/s002210100746 RESEARCH ARTICLE Tobias Bast Wei-Ning Zhang Joram Feldon The ventral hippocampus and fear conditioning in rats Different anterograde amnesias of
Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight, preweaning mortality and rat behavior
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1229-1237 Prenatal chronic stress and behavior ISSN 1-879X 1229 Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1229-1237 Prenatal chronic stress and behavior ISSN 1-879X 1229 Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight,
Dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 1465-147 Grooming, dopamine receptors and pregnancy ISSN -879X 1465 Dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 1465-147 Grooming, dopamine receptors and pregnancy ISSN -879X 1465 Dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats
Chapter 3 Emotion and cognition in high and low stress susceptible mouse strains: a combined neuroendocrine and behavioural study
 Chapter 3 Emotion and cognition in high and low stress susceptible mouse strains: a combined neuroendocrine and behavioural study Brinks V, van der Mark MH, de Kloet ER, Oitzl MS Gorlaeus Lab, LACDR/LUMC,
Chapter 3 Emotion and cognition in high and low stress susceptible mouse strains: a combined neuroendocrine and behavioural study Brinks V, van der Mark MH, de Kloet ER, Oitzl MS Gorlaeus Lab, LACDR/LUMC,
Involvement of the Periaqueductal Gray in the Descending Antinociceptive Effect Induced by the Central Nucleus of Amygdala
 Physiol. Res. 67: 647-655, 2018 Involvement of the Periaqueductal Gray in the Descending Antinociceptive Effect Induced by the Central Nucleus of Amygdala N. BOURBIA 1,2, A. PERTOVAARA 1 1 Department of
Physiol. Res. 67: 647-655, 2018 Involvement of the Periaqueductal Gray in the Descending Antinociceptive Effect Induced by the Central Nucleus of Amygdala N. BOURBIA 1,2, A. PERTOVAARA 1 1 Department of
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters. motor- and cue- dependent behaviors
 Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lack of GPR88 enhances medium spiny neuron activity and alters motor- and cue- dependent behaviors Albert Quintana, Elisenda Sanz, Wengang Wang, Granville P. Storey, Ali D. Güler Matthew J. Wanat, Bryan
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Hippocampus and Two-Way Active Avoidance Conditioning: Contrasting Effects of Cytotoxic Lesion and Temporary Inactivation
 HIPPOCAMPUS 25:1517 1531 (2015) and Two-Way Active Avoidance Conditioning: Contrasting Effects of Cytotoxic Lesion and Temporary Inactivation Jia Wang, 1 Tobias Bast, 2 * Yu-Cong Wang, 1 and Wei-Ning Zhang
HIPPOCAMPUS 25:1517 1531 (2015) and Two-Way Active Avoidance Conditioning: Contrasting Effects of Cytotoxic Lesion and Temporary Inactivation Jia Wang, 1 Tobias Bast, 2 * Yu-Cong Wang, 1 and Wei-Ning Zhang
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology
 Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
Advanced Receptor Psychopharmacology Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD February 2017 Lundbeck,
Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις
 Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Biomedical Imaging & Applied Optics University of Cyprus Νευροφυσιολογία και Αισθήσεις Διάλεξη 19 Ψυχασθένειες (Mental Illness) Introduction Neurology Branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and
Anxiolytic-like effects of 4-phenyl-2- trichloromethyl-3h-1,5-benzodiazepine hydrogen sulfate in mice
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 169-173 Anxiolytic effects of a new benzodiazepine ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 169 Anxiolytic-like effects of 4-phenyl-2- trichloromethyl-3h-1,5-benzodiazepine
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 169-173 Anxiolytic effects of a new benzodiazepine ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 169 Anxiolytic-like effects of 4-phenyl-2- trichloromethyl-3h-1,5-benzodiazepine
Neuroscience Letters
 Neuroscience Letters 587 (2015) 11 16 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuroscience Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neulet Research article Dorsal hippocampal microinjection
Neuroscience Letters 587 (2015) 11 16 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Neuroscience Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/neulet Research article Dorsal hippocampal microinjection
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Brain Infusion Kit mm
 Brain Infusion Kit 1 3-5 mm 0004760 STERILE MATERIALS FOR TEN BRAIN INFUSIONS REFER TO ENCLOSED SPECIFICATIONS 7147600-5 2006 DURECT Corporation Printed in U.S.A. April 2006 CONTENTS: Ten brain infusion
Brain Infusion Kit 1 3-5 mm 0004760 STERILE MATERIALS FOR TEN BRAIN INFUSIONS REFER TO ENCLOSED SPECIFICATIONS 7147600-5 2006 DURECT Corporation Printed in U.S.A. April 2006 CONTENTS: Ten brain infusion
Both a 1 - and b 1 -adrenoceptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis are involved in the expression of conditioned contextual fear
 207..221 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01985.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1985 Both a 1 - and b 1 -adrenoceptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis are
207..221 British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01985.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1985 Both a 1 - and b 1 -adrenoceptors in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis are
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Opioid Receptors Regulate the Extinction of Pavlovian Fear Conditioning
 Behavioral Neuroscience Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2003, Vol. 117, No. 6, 1292 1301 0735-7044/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.117.6.1292 Opioid Receptors Regulate the
Behavioral Neuroscience Copyright 2003 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2003, Vol. 117, No. 6, 1292 1301 0735-7044/03/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.117.6.1292 Opioid Receptors Regulate the
THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY
 THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY By XIAOMENG YUAN A MASTER THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
THE ROLE OF ANXIETY IN A RAT MODEL OF SELF-INJURY By XIAOMENG YUAN A MASTER THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE
Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety
 C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
C82NAB Neuroscience and Behaviour Emotion I: General concepts, fear and anxiety Tobias Bast, School of Psychology, University of Nottingham 1 Outline Emotion I (first part) Studying brain substrates of
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
Session ID: 1001 June 14, 2012
 It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
It s Not Just Serotonin: Neurosignaling in Mental Illness Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Professor of Nursing Linfield College Learning Outcomes Distinguish between metabotropic and ionotropic neuroreceptors
EFEITOS DEDIFERENTES NÍVEIS DE PROTEÍNA E ESTIMULAÇÃO AMBIENTAL SOBRE O COMPORTAMENTO DE RATOS JOVENS TESTADOS NO LABIRINTO EM CRUZ ELEVADO*
 REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o. 2, 129-135. EFEITOS DEDIFERENTES NÍVEIS DE PROTEÍNA E ESTIMULAÇÃO AMBIENTAL SOBRE O COMPORTAMENTO
REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o. 2, 129-135. EFEITOS DEDIFERENTES NÍVEIS DE PROTEÍNA E ESTIMULAÇÃO AMBIENTAL SOBRE O COMPORTAMENTO
Enhancement of Latent Inhibition in Rats With Electrolytic Lesions of the Hippocampus
 Behavioral Neuroscience 1995. Vol. 109, No. 2, 366-370 Copyright 1995 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0735-7044/95/$3.00 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Enhancement of Latent Inhibition in Rats With
Behavioral Neuroscience 1995. Vol. 109, No. 2, 366-370 Copyright 1995 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 0735-7044/95/$3.00 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Enhancement of Latent Inhibition in Rats With
Physiological Society Symposium Nociceptors as Homeostatic Afferents: Central Processing
 Physiological Society Symposium Nociceptors as Homeostatic Afferents: Central Processing Distinct central representations of inescapable and escapable pain: observations and speculation Kevin A. Keay *
Physiological Society Symposium Nociceptors as Homeostatic Afferents: Central Processing Distinct central representations of inescapable and escapable pain: observations and speculation Kevin A. Keay *
Enterprise Interest None
 Enterprise Interest None EUROPEAN SOCIETY of PATHOLOGY AMSTERDAM 29th CONGRESS Parkinson s disease: myenteric gliosis in an experimental rat model Lina Carvalho 1, Ana Lúcia Silva 2, Sofia Viana 2,3, Inês
Enterprise Interest None EUROPEAN SOCIETY of PATHOLOGY AMSTERDAM 29th CONGRESS Parkinson s disease: myenteric gliosis in an experimental rat model Lina Carvalho 1, Ana Lúcia Silva 2, Sofia Viana 2,3, Inês
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY]](/thumbs/86/94924826.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 7 NEUROPHYSIOLOGY [THE SYNAPSE AND PHARMACOLOGY] Learning Objectives: Explain how neurons communicate stimulus intensity Explain how action potentials are conducted along
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
