Dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats
|
|
|
- Scott Blankenship
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: Grooming, dopamine receptors and pregnancy ISSN -879X 1465 Dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats A.P. Serafim and L.F. Felicio Departamento de Patologia, Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brasil Correspondence L.F. Felicio Departamento de Patologia Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária Universidade de São Paulo Av. Orlando Marques Paiva, São Paulo, SP Brasil Fax: Research supported by FAPESP (No. 96/4193-) and CNPq (No /96) grants to L.F. Felicio. A.P. Serafim was the recipient of FAPESP and CNPq fellowships. Received May 7, 21 Accepted September 4, 21 Abstract Dopamine receptors are involved in the expression of grooming behavior. The pregnancy-induced increase in self-licking observed in rats is important for mammary gland development and lactation. This study focuses on the role of dopamine receptor subtypes in grooming behavior of virgin and pregnant female rats. General and mammary gland grooming were measured in virgin rats treated with.25 mg/kg of the D1-like agonist SKF and antagonist SKF and the D2-like agonist lisuride and antagonist sulpiride. The effects of.1 and.25 mg/kg doses of the same agonists and antagonists were evaluated in pregnant rats as well. In virgin animals both SKF and sulpiride treatments significantly reduced the time spent in general grooming, while none of the dopamine agonists was able to significantly change any parameter of general grooming. Time spent in grooming directed at the mammary glands was not affected significantly by any of the drug treatments in virgin rats. All drugs tested significantly decreased the frequency of and the time spent with general grooming, while SKF treatment alone did not significantly reduce the duration of mammary gland grooming in pregnant rats. These data show that in female rats the behavioral effects of D1- like and D2-like dopamine receptor stimulation and blockade differ according to physiological state. The results suggest that dopamine receptors may play specific roles modulating grooming behavior in pregnant rats. Since grooming of the mammary gland during pregnancy may influence lactation, this aspect is relevant for studies regarding the perinatal use of dopamine-related drugs. Key words Self-licking Lisuride SKF SKF Sulpiride Prolactin Dopamine Introduction Almost all animal species spend a significant part of their time in grooming behavior (1). Although various neurotransmitters can modulate the expression of this behavior (2,3), dopamine is particularly involved (4,5). Lesions in brain regions rich in dopaminergic inputs influence the implementation of grooming syntax (6). Moreover, in rodents grooming behavior is differently modulated by stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptor subtypes (5,7-9), sex () and reproductive state (11). Grooming behavior is under the influence of the endocrine milieu (4,12). During pregnancy female rats change their grooming patterns, tending to lick their mammary glands more than prior to pregnancy (11,13). This in turn has been shown to be important for mammary gland development and lactation (14). Researchers have shown that dopamine is involved in both the
2 1466 A.P. Serafim and L.F. Felicio onset and maintenance of maternal care (15,16). There are two pharmacologically distinct dopamine receptor families, D1-like and D2-like (17). These receptors are represented by at least five different proteins; D 1 and D 5 are subtypes of D1-like receptors, while D 2, D 3 and D 4 are subtypes of D2-like receptors (18). While it is possible to differentiate between the two dopamine receptor subfamilies, the different members within each subfamily cannot be distinguished by pharmaceutical means. Pharmacological manipulations of the dopaminergic systems during pregnancy can influence both maternal (15,16) and offspring behavior (19-24). The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptor families in grooming behavior of virgin and pregnant rats. Our working hypothesis was that in female rats the modulatory role of each of these receptor families in grooming behavior changes according to reproductive state. Since frequently small and large doses of dopamine-related drugs have different effects, pregnant rats were challenged with two doses. Material and Methods Animals At least one month before the behavioral tests, adult virgin female Wistar rats from our own colony weighing g at the beginning of the experiments were individually housed in polypropylene cages (45 x 25 x 2 cm) on a controlled light-dark cycle (lights on from 6: to 18:) at a temperature of 22 ± 3ºC. Water and food were available ad libitum. Rats were kept virgin for experiment 1 or were mated with males (experiment 2). The day sperm was observed in the vaginal lavage was designated day 1 of pregnancy. The animals used in this study were maintained in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee on Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Resources, National Research Council, USA. Drugs Drugs were the D1-like agonist SKF and antagonist SKF and the D2-like agonist lisuride and antagonist sulpiride, all obtained from RBI (Natick, MA, USA). They were diluted in saline and administered subcutaneusly (sc) in a volume of 1. ml/kg. Measurements and observations Grooming behavior was videotaped during 3-min test sessions on days 7, 8 and 9 of pregnancy. Virgin animals were observed on each testing day as well. To minimize possible circadian influences, observations of animals from different groups were intermixed; observations began at 8: am and animals were placed in the same order every day. Each rat was videotaped under room light in her own cage with a glass cover. Two habituation sessions were held on the days preceding the day of the first testing session. Each pregnant animal was tested three times, being injected with a different dose of the drug each time. The days of each drug dose were randomly assigned to each animal. Each drug dose was tested on at least six animals. Self-licking was recorded according to the body region to which it was confined. Head, forepaws, shoulders and upper back were recorded as general grooming, while nipple lines, genital and pelvic regions were considered as mammary gland grooming. The frequency and duration in seconds of each of these behavioral categories were recorded during individual 3-min sessions. Experiment 1. Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptors on grooming behavior of virgin female rats Virgin rats were injected sc with saline or.25 mg/kg of SKF-81297, SKF-83566,
3 Grooming, dopamine receptors and pregnancy 1467 lisuride or sulpiride and tested for grooming behavior for 3 min starting min after drug injection. Experiment 2. Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptors on grooming behavior of pregnant female rats Pregnant rats were injected sc with saline,.1 or.25 mg/kg of SKF-81297, SKF , lisuride or sulpiride and tested for grooming behavior for 3 min starting min after drug injection. Statistical analysis Statistical comparisons between two groups were made using the Student t-test (Experiment 1). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey- Kramer test was used to compare grooming behavioral data when various doses were used (Experiment 2). A probability of P<.5 was considered significant for all comparisons made. Results Only the dopamine receptor antagonists SKF and sulpiride significantly reduced the time spent in general grooming by virgin rats (P<.5; Table 1), while none of the dopamine receptor agonists or antagonists significantly influenced the time spent in mammary grooming by virgins (Table 1). General grooming displayed by pregnant rats was significantly reduced by previous treatment with the lower dose (.1 mg/kg) of SKF (F(2,62) = 15.7; P<.5). Both the.1 and.25 mg/kg doses of lisuride (F(2,54) = 41.; P<.5), SKF (F(2,62) = 38.2; P<.5) and sulpiride (F(2,62) = 28.1; P<.5) significantly reduced the time for general grooming in pregnant rats (Table 2). Both doses of the D1-like antagonist SKF (F(2,62) = 9.5; P<.5; Figure 1), the D2-like agonist lisuride (F(2,54) = 11.3; P<.5) and the D2-like antagonist sulpiride (F(2,62) = 6.4; P<.5) significantly reduced the time spent in mammary gland grooming by pregnant rats (Figures 1 and 2). None of the treatments with the D1-like agonist SKF significantly influenced the time spent in mammary gland grooming by pregnant rats (Figure 1). The frequency of grooming was not significantly affected by any drug treatment in virgin rats (Table 3). Both the.1 and.25 mg/kg doses of SKF (F(2,62) = 12.3; Table 1. Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptors on time (seconds) spent in grooming behavior by virgin rats. General grooming grooming Saline (24) 58±3.7 8±2.7 SKF (6) 5±5.8 5±2.2 SKF (6) 32±6.6 9±1.7 Lisuride (6) 5±5.8 7±3.1 Sulpiride (6) 4±6.9 5±2.5 Animals were treated with saline or.25 mg/kg sc of one of the drugs and observed for 3 min for grooming behavior. Data are reported as means ± SEM. The number of animals is given in parentheses. P<.5 compared to the saline group (Student t-test). Table 2. Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptors on time spent in general grooming behavior by pregnant rats Saline 2±4 - - SKF ± ±7.4 SKF ±8.2 49±6.6 Lisuride - 29±.3 ±. Sulpiride - 9± ±4.8 Data are reported as means ± SEM. N = 45 for the saline group and N = for all other groups. P<.5 compared to the saline group (ANOVA followed by the Tukey-Kramer test).
4 1468 A.P. Serafim and L.F. Felicio Figure 1. Effects of acute sc treatment with the D1-like receptor agonist SKF (A) and antagonist SKF (B) on the duration of self-grooming of the mammary glands in 7-9-day pregnant rats. P<.5 compared to the saline-treated group (ANOVA followed by the Tukey- Kramer test). Figure 2. Effects of acute sc treatment with the D2-like receptor agonist lisuride (A) and antagonist sulpiride (B) on the duration of self-grooming of the mammary glands in 7-9-day pregnant rats. P<.5 compared to the saline-treated group (ANOVA followed by the Tukey- Kramer test). P<.5), lisuride (F(2,54) = 29.75; P<.5), SKF (F(2,62) = 12.16; P<.5) and sulpiride (F(2,62) = 2.17; P<.5) significantly reduced the frequency of general groom Saline A B A B SKF Saline SKF Saline Lisuride Saline Sulpiride ing displayed by pregnant rats (Table 3). Discussion The patterns of grooming behavior are not the same in virgin and pregnant rats. Our data confirm this finding and suggest that dopaminergic modulation of grooming differs according to reproductive physiological state as well. The fact that the effects of pharmacological manipulations of dopaminergic systems on grooming behavior were more frequent in pregnant than in virgin rats suggests that grooming displayed by females during pregnancy is more sensitive to dopaminergic modulation. This may also suggest that dopaminergic-mediated neurotransmission plays a more marked role in grooming in pregnant than in non-pregnant rats. Female reproductive state can influence dopamine-related hormones (25,26), behavior (27,28) and cognition (29,3). The fact that only the dopamine receptor antagonists influenced the general grooming displayed by virgin rats suggests that 1) dopaminergic neurotransmission is important for the expression of grooming behavior, and 2) dopaminergic overstimulation does not affect grooming in virgin rats. Neither dopamine receptor agonist-induced overstimulation nor dopamine receptor antagonist-induced disruption of neurotransmission was able to induce mammary gland grooming in virgin rats, suggesting that this specific kind of grooming is not under dopaminergic control in virgin rats. Alternatively, since mammary gland grooming expression is robust only during pregnancy (11,14) a possible role for dopaminergic neurotransmission in this behavior can be investigated only during the physiological state in which the behavior is being expressed. Low and high doses of the dopamine agonists and antagonists usually produce opposite behavioral effects. This was not observed for mammary gland grooming. Changes in motor activity (exploratory be-
5 Grooming, dopamine receptors and pregnancy 1469 Table 3. Effects of stimulation and blockade of dopamine receptors on frequency of grooming behavior in virgin and pregnant rats. Drug (mg/kg) General Virgin Pregnant Virgin Pregnant Saline 4 ± 1. (24) 6 ±.3 (45) 1 ±.3 (24) 2 ±.2 (45) SKF ±.2 () - 2 ±.3 ().25 3 ±.6 (6) 4 ±.3 () 1 ±.2 (6) 2 ±.2 () Lisuride.1-2 ±.4 () - ±.2 ().25 4 ± 11 (6) ±. () 1 ±.2 (6) ±. () SKF ±.5 () - 2 ±.2 ().25 3 ±.9 (6) 3 ±.4 () 1 ±.4 (6) 1 ±.2 () Sulpiride.1-3 ±.5 () - 2 ±.2 ().25 3 ±.7 (6) 2 ±.3 () 1 ±.3 (6) 2 ±.2 () Data are reported as means ± SEM. The number of animals is given in parentheses. P<.5 compared to the respective saline group (ANOVA followed by the Tukey-Kramer test). havior) induced by the drugs may have interfered with these results. Alternatively, since during lactation possibly the expression of mammary gland grooming achieves its physiological highest, any pharmacological challenge would only induce inhibitory effects on this behavior. Differently from virgin animals, in pregnant rats all pharmacological dopaminergic manipulations induced decreases in the time spent in general grooming. Nevertheless, the drug-induced decrease varied according to the dose. The D1-like agonist SKF reduced the time spent in general grooming only at the lowest dose. The optimum behavioral effect of both dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists can be induced by small or presynaptic doses (31). Both high and low doses of dopamine receptor agonists and antagonists can be behaviorally effective (31,32). Differently from what occurred with the expression of general grooming, these behaviors may have competed with and eventually prevailed over mammary gland grooming in pregnant animals. Future studies will focus on a possible dopaminergic modulation of grooming behavior in other physiological states such as lactation or reproductive senility. The present results show that pharmacological manipulations of dopaminergic neurotransmission modulate the expression of grooming behaviors in both virgin and pregnant rats. Concerning pregnant rats, these data may have implications for studies involving perinatal pharmacology and toxicology in which dopaminergic transmission is altered during pregnancy.
6 147 A.P. Serafim and L.F. Felicio References 1. MacFarland CG & Reeder WG (1974). Cleaning symbiosis involving Galapagos tortoises and two species of Darwin s finches. Zeitschrift für Tierpsychologie, 34: Moody TW, Merali Z & Crawley JN (1988). The effects of anxiolytics and other agents on rat grooming behavior. In: Colbern DL & Gispen WH (Editors), Neural Mechanisms and Biological Significance of Grooming Behavior. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 525: Traber J, Spencer DG, Glaser T & Gispen WH (1988). Actions of psychoactive drugs on ACTH- and novelty-induced behavior in the rat. In: Colbern DL & Gispen WH (Editors), Neural Mechanisms and Biological Significance of Grooming Behavior. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 525: Cools AR, Spruijt BM & Ellenbroek BA (1988). Role of central dopamine in ACTHinduced grooming behavior in rats. In: Colbern DL & Gispen WH (Editors), Neural Mechanisms and Biological Significance of Grooming Behavior. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 525: Drago F, Contarino A & Busa L (1999). The expression of neuropeptide-induced excessive grooming behavior in dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-deficient mice. European Journal of Pharmacology, 365: Cromwell HC & Berridge KC (1996). Implementation of action sequences by a neostriatal site: a lesion mapping study of grooming syntax. Journal of Neuroscience, 16: Starr BS & Starr MS (1987). Behavioural interactions involving D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in non-habituated mice. Neuropharmacology, 26: Starr BS & Starr MS (1986). Differential effects of dopamine D1 and D2 agonists and antagonists on velocity of movement, rearing and grooming in the mouse. Implications for the roles of D1 and D2 receptors. Neuropharmacology, 25: Starr BS & Starr MS (1986). Grooming in the mouse is stimulated by the dopamine D1 agonist SKF and by low doses of the D1 antagonist SCH 2339, but is inhibited by dopamine D2 agonists, D2 antagonists and high doses of SCH Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 24: Diaz-Veliz G, Butron S, Benavides M, Dussaubat N & Mora S (2). Gender, estrous cycle, ovariectomy, and ovarian hormones influence the effects of diazepam on avoidance conditioning in rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 66: Roth LL & Rosenblatt JS (1966). Mammary glands of pregnant rats: development stimulated by licking. Science, 151: Drago F & Lissandrello CO (2). The low-dose concept and the paradoxical effects of prolactin on grooming and sexual behavior. European Journal of Pharmacology, 45: Roth LL & Rosenblatt JS (1967). Changes in self-licking during pregnancy in the rat. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 63: Roth LL & Rosenblatt JS (1968). Self-licking and mammary development during pregnancy in the rat. Journal of Endocrinology, 42: Kinsley CH, Turco D, Bauer A, Beverly M, Wellman J & Graham AL (1994). Cocaine alters the onset and maintenance of maternal behavior in lactating rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 47: Silva MRP, Bernardi MM & Felicio LF (21). Effects of dopamine receptor antagonists on ongoing maternal behavior in rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 68: Seeman P (198). Brain dopamine receptors. Pharmacological Reviews, 32: Sokoloff P & Schwartz JC (1995). Novel dopamine receptors half a decade later. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 16: Nasello AG & Ramirez OA (1978). Openfield and Lashley III maze behaviour of the offspring of amphetamine-treated rats. Psychopharmacology, 58: Cuomo V, Cagiano R, Mocchetti I, Coen E, Cattabeni F & Racagni G (1983). Behavioural and biochemical effects in the adult rat after prolonged postnatal administration of clozapine. Psychopharmacology, 81: Hull EM, Nishita JK & Bitran D (1984). Perinatal dopamine related drugs demasculinize rats. Science, 224: Felicio LF, Palermo-Neto J & Nasello AG (1989). Perinatal bromopride treatment: Effects on sexual behavior of male and female rats. Behavioral and Neural Biology, 52: Felicio LF, Palermo-Neto J & Nasello AG (1989). Perinatal bromopride treatment: Effects on motor activity and stereotyped behavior of offspring. Physiology and Behavior, 45: Nasello AG & Felicio LF (199). Avoidance behavior, prolactin, HVA and DOPAC in offspring of bromopride treated rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 37: Bridges RS, Felicio LF, Pellerin LJ, Stuer AM & Mann PE (1993). Prior parity reduces post-coital diurnal and nocturnal prolactin surges in rats. Life Sciences, 53: Felicio LF, Florio JC, Sider LH, Cruz- Casallas PE & Bridges RS (1996). Reproductive experience increases striatal and hypothalamic dopamine levels in pregnant rats. Brain Research Bulletin, 4: Silva MRP, Bernardi MM, Nasello AG & Felicio LF (1997). Influence of lactation on motor activity and elevated plus maze behavior. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 3: Kinsley CH, Madonia L, Gifford GW, Tureski K, Griffin GR, Lowry C, Williams J, Collins J, McLearie H & Lambert KG (1999). Motherhood improves learning and memory. Nature, 42: Liu D, Diorio J, Day JC, Francis DD & Meaney MJ (2). Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nature Neuroscience, 3: Maestripieri D & Megna NL (2). Hormones and behavior in rhesus macaque abusive and nonabusive mothers. 1. Social interactions during late pregnancy and early lactation. Physiology and Behavior, 71: Nasello AG, Tieppo CA & Felicio LF (1995). Apomorphine-induced yawning in the rat: influence of fasting and day time. Physiology and Behavior, 57: Felicio LF, Nasello AG & Palermo-Neto J (1987). Dopaminergic supersensitivity after long-term bromopride treatment. Physiology and Behavior, 41:
Dynamics of mother-pup interactions: tradeoff between environment and physiology
 Psychology & Neuroscience, 2012, 5, 2, 215-219 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2012.2.12 Dynamics of mother-pup interactions: tradeoff between environment and physiology Renata Gonçalves Vasconcelos, Marianne Orlandini
Psychology & Neuroscience, 2012, 5, 2, 215-219 DOI: 10.3922/j.psns.2012.2.12 Dynamics of mother-pup interactions: tradeoff between environment and physiology Renata Gonçalves Vasconcelos, Marianne Orlandini
Thigmotactic responses in an open-field
 Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Brazilian Thigmotaxis Journal in the of open-field Medical and Biological Research (2008) 41: 135-140 ISSN 0100-879X 135 Thigmotactic responses in an open-field M.R. Lamprea 1, F.P. Cardenas 2, J. Setem
Abstract. Introduction. R.N. Takahashi 1, O. Berton 2,3, P. Mormède 2 and F. Chaouloff 2
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS
 5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril on sodium appetite of hypothyroid rats. Influence of aldosterone treatment
 Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Brazilian Sodium appetite Journal of in Medical hypothyroid and rats Biological Research (21) 34: 47-411 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 47 Effect of chronic oral administration of a low dose of captopril
Dose-related effects of propericiazine in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 227-231 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 227 Dose-related effects of propericiazine in rats E.M. Cechin 1, J. Quevedo 2, T. Barichello
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2003) 36: 227-231 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 227 Dose-related effects of propericiazine in rats E.M. Cechin 1, J. Quevedo 2, T. Barichello
Routine post-weaning handling of rats prevents isolation rearing-induced deficit in prepulse inhibition
 Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Routine Brazilian handling Journal of prevents Medical PPI and deficit Biological in isolated Research rats (2005) 38: 1691-1696 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1691 Routine post-weaning handling of
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test.
 Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Evaluation of Anxiolytic Effect of XXX in Guinea Pig Maternal Separation Test. DATE This study was conducted under terms of a Services Agreement between NeuroDetective Inc. and CLIENT, entitled TITLE OF
Cognitive Function Test. NOR & spatial NOR task. Introduction. Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Estrogen Receptor (ER) in Brain
 Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Cognitive Function Test Human Rodent Sutcliffe JS, Marshall KM, Neill JC. Behavioral Brain Research 177(2007) 117-125. Radial Arm maze Morris Water maze Siriporn Vongsaiyat 16 th Feb 2007 Novel Object
Adolescent Prozac Exposure Enhances Sensitivity to Cocaine in Adulthood INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 10-2009 The receptor mechanisms underlying the
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Faculty Publications, Department of Psychology Psychology, Department of 10-2009 The receptor mechanisms underlying the
Key words: apomorphine; dopamine; prepulse inhibition; schizophrenia; startle; strain
 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2000, 20(11):4325 4336 Toward Understanding the Biology of a Complex Phenotype: Rat Strain and Substrain Differences in the Sensorimotor Gating- Disruptive Effects
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2000, 20(11):4325 4336 Toward Understanding the Biology of a Complex Phenotype: Rat Strain and Substrain Differences in the Sensorimotor Gating- Disruptive Effects
Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Super-Stereotypy I: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Systemic Dopamine D1 Agonists
 SYNAPSE 37:194 204 (2000) Super-Stereotypy I: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Systemic Dopamine D1 Agonists KENT C. BERRIDGE 1 * AND J. WAYNE ALDRIDGE 1,2 1 Department of Psychology, University
SYNAPSE 37:194 204 (2000) Super-Stereotypy I: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Systemic Dopamine D1 Agonists KENT C. BERRIDGE 1 * AND J. WAYNE ALDRIDGE 1,2 1 Department of Psychology, University
ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS: EFEITOS DE DESNUTRIÇÃO E ESTIMULAÇÃO TÁTIL DOS FILHORES*
 REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o.2, 150-156. ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS:
REVISTA BRASILEIRA DE ANÁLISE DO COMPORTAMENTO / BRAZILIAN JOURNAL OF BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS, 2014, Vol. 10, N o.2, 150-156. ANÁLISE ETOLÓGICA DE INTERAÇÕES MÃE-FILHOTE E OUTRAS REAÇÕES COMPORTAMENTAIS EM RÁTOS:
Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1277-1283 Antagonism of tetanic fade induced by NO ISSN 0-879X 1277 Atropine and ODQ antagonize tetanic fade induced by L-arginine in cats
Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research () 33: 755-76 ACE activity in rat tissue samples ISSN -879X 755 Standardization of a fluorimetric assay for the determination of tissue angiotensin-converting
The Long-Term Effects of Maternal Deprivation Depend on the Genetic Background B.A. Ellenbroek, Ph.D., and A.R. Cools, Ph.D.
 The Long-Term Effects of Maternal Deprivation Depend on the Genetic Background B.A. Ellenbroek, Ph.D., and A.R. Cools, Ph.D. The neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia has led to a series of new
The Long-Term Effects of Maternal Deprivation Depend on the Genetic Background B.A. Ellenbroek, Ph.D., and A.R. Cools, Ph.D. The neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia has led to a series of new
Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats
 Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats Ryszard ~rusl, Ryszard szkilnik1 and Richard M. ~ostrzewa~ '~e~artment of Pharmacology, Silesian Academy of Medicine,
Nitric oxide (NO) and central dopamine (DA) D3 receptor reactivity to quinpirole in rats Ryszard ~rusl, Ryszard szkilnik1 and Richard M. ~ostrzewa~ '~e~artment of Pharmacology, Silesian Academy of Medicine,
Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic area increases prolactin secretion
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1161-1165 NPY-Y 1 receptors in the MPOA and PRL secretion ISSN 0100-879X 1161 Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1161-1165 NPY-Y 1 receptors in the MPOA and PRL secretion ISSN 0100-879X 1161 Antisense mrna for NPY-Y 1 receptor in the medial preoptic
How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen.
 An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome How to measure rodent behavior and perform a neurological screen. Fiona Harrison, PhD Department of Medicine Vanderbilt University
Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight, preweaning mortality and rat behavior
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1229-1237 Prenatal chronic stress and behavior ISSN 1-879X 1229 Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1229-1237 Prenatal chronic stress and behavior ISSN 1-879X 1229 Effects of prenatal exposure to a mild chronic variable stress on body weight,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2006 September 5.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2006 August ; 9(8): 1004 1006. Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Neurosci. 2006 August ; 9(8): 1004 1006. Maternal presence serves as a switch between learning fear and attraction in infancy
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place
 Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
Mk-801 Administration in Adolescent Male Rats and Cocaine Conditioned Place Preference Stephanie Willis, Jonnique Adjmul, Shabaaz Sandhu, Antoniette M. Maldonado-Devincci, Cheryl Kirsten ABSTRACT The present
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
Female Reproductive System. Justin D. Vidal
 Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Schizophrenic twin. Normal twin
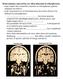 Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Brain anatomy and activity are often abnormal in schizophrenics - many studies have found the ventricles in schizophrenic patients enlarged (see below). - at the structural level, several brain areas have
Actigraphy-based sleep parameters during the reinstatement of methamphetamine self-administration in rhesus monkeys.
 Actigraphy-based sleep parameters during the reinstatement of methamphetamine self-administration in rhesus monkeys. Laís F. Berro, Emory University Monica L. Andersen, Universidade Federal de São Paulo
Actigraphy-based sleep parameters during the reinstatement of methamphetamine self-administration in rhesus monkeys. Laís F. Berro, Emory University Monica L. Andersen, Universidade Federal de São Paulo
Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female Mice of Two Strains
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works School of Arts & Sciences Theses Hunter College Summer 8-10-2017 Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works School of Arts & Sciences Theses Hunter College Summer 8-10-2017 Methamphetamine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference In Adolescent Male and Female
Abstract. S.L.D. Dalle Lucca 1, J.J. Dalle Lucca 1, A.C.R. Borges 1, S.S.M. Ihara 2 and T.B. Paiva 1
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2000) 33: 919-927 Abnormal proliferative response of the SHR ISSN 0100-879X 919 Abnormal proliferative response of the carotid artery of spontaneously
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2000) 33: 919-927 Abnormal proliferative response of the SHR ISSN 0100-879X 919 Abnormal proliferative response of the carotid artery of spontaneously
The brain decade in debate: VIII. Peptide hormones and behavior: cholecystokinin and prolactin
 Peptide Brazilian hormones Journal of and Medical behavior and Biological Research (2001) 34: 1369-1377 ISSN 0100-879X Virtual Symposium 1369 The brain decade in debate: VIII. Peptide hormones and behavior:
Peptide Brazilian hormones Journal of and Medical behavior and Biological Research (2001) 34: 1369-1377 ISSN 0100-879X Virtual Symposium 1369 The brain decade in debate: VIII. Peptide hormones and behavior:
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders
 The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
The Neurobiology of Psychiatric Disorders Vikaas S. Sohal, MD PhD Department of Psychiatry Center for Integrative Neuroscience Sloan Swartz Center for Theoretical Neurobiology Overview 1. Classification
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Open field behavior and intra-nucleus accumbens dopamine release in vivo in virgin and lactating rats
 PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 211, 4, 1, 115-121 DOI: 1.3922/j.psns.211.1.13 Open field behavior and intra-nucleus accumbens dopamine release in vivo in virgin and lactating rats Soraya
PSYCHOLOGY NEUROSCIENCE Psychology & Neuroscience, 211, 4, 1, 115-121 DOI: 1.3922/j.psns.211.1.13 Open field behavior and intra-nucleus accumbens dopamine release in vivo in virgin and lactating rats Soraya
Abstract. R. Roesler 1, J. Quevedo 1, C. Rodrigues 1, M. Madruga 1, M.R.M. Vianna 1 and M.B.C. Ferreira 2
 Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Brazilian Amygdaloid Journal non-nmda of Medical receptors and Biological and memory Research expression (1999) 32: 349-353 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 349 Increased training prevents the impairing
Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine with the combination of a dopamine Dl and D2 antagonist
 Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine with the combination of a dopamine Dl and D2 antagonist Theo F. Meert, Patrick De Haes, Nancy Aerts and Gilbert Clincke Department of Neuropsychopharmacology,
Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine with the combination of a dopamine Dl and D2 antagonist Theo F. Meert, Patrick De Haes, Nancy Aerts and Gilbert Clincke Department of Neuropsychopharmacology,
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Esposizione a livelli ambientali di xenoestrogeni: modelli di studio nel ratto in vivo e rilevanza degli effetti
 Esposizione a livelli ambientali di xenoestrogeni: modelli di studio nel ratto in vivo e rilevanza degli effetti Francesca Farabollini (a), Leonida Fusani (c), Daniele Della Seta (a), Francesco Dessì-Fulgheri
Esposizione a livelli ambientali di xenoestrogeni: modelli di studio nel ratto in vivo e rilevanza degli effetti Francesca Farabollini (a), Leonida Fusani (c), Daniele Della Seta (a), Francesco Dessì-Fulgheri
J. Afr. Ass. Physiol. Sci. 3 (1): 36-40, July 2015.
 J. Afr. Ass. Physiol. Sci. 3 (1): 36-40, July 2015. Journal of African Association of Physiological Sciences Official Publication of the African Association of Physiological Sciences http://www.jaaps.aapsnet.org
J. Afr. Ass. Physiol. Sci. 3 (1): 36-40, July 2015. Journal of African Association of Physiological Sciences Official Publication of the African Association of Physiological Sciences http://www.jaaps.aapsnet.org
breeders really don t want to miss!!!
 Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
Fertility and early embryonic development. Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012
 Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
"One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic state?
 Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Psychopharmacology (1993) 11:24-244 Psychopharmacology Springer-Verlag 1993 "One-trial tolerance" to the anxiolytic actions of benzodiazepines in the elevated plus-maze, or the development of a phobic
Food restriction: enhancing effects on drug reward and striatal cell signaling
 Food restriction: enhancing effects on drug reward and striatal cell signaling K.D. Carr Departments of Psychiatry & Pharmacology NYU School of Medicine Common Neural Substrates for Incentive-Motivating
Food restriction: enhancing effects on drug reward and striatal cell signaling K.D. Carr Departments of Psychiatry & Pharmacology NYU School of Medicine Common Neural Substrates for Incentive-Motivating
Oxytocin and Early Experience. Sue Carter The Brain Body Center Department of Psychiatry University of Illinois at Chicago
 Oxytocin and Early Experience Sue Carter The Brain Body Center Department of Psychiatry University of Illinois at Chicago At the center of the neuroendocrine mechanisms for parental behavior (both sexes)
Oxytocin and Early Experience Sue Carter The Brain Body Center Department of Psychiatry University of Illinois at Chicago At the center of the neuroendocrine mechanisms for parental behavior (both sexes)
Epigenetics and trauma
 Epigenetics and trauma Influence of trauma on mental health Patrick McGowan, PhD Biological Sciences, UTSC Cell and Systems Biology, Psychology University of Toronto patrick.mcgowan@utoronto.ca Leuven,
Epigenetics and trauma Influence of trauma on mental health Patrick McGowan, PhD Biological Sciences, UTSC Cell and Systems Biology, Psychology University of Toronto patrick.mcgowan@utoronto.ca Leuven,
Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not the expression, of step-down inhibitory avoidance
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2) 33: 829-834 Amygdaloid NMDA receptors and fear memory ISSN 1-879X 829 Infusions of AP5 into the basolateral amygdala impair the formation, but not
EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC ACID ON LEARNING AND MEMORY IN RATS
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 12, Suppl. 1, pp 132-136, 2014 Copyright 2014 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) EFFECTS OF CHLOROGENIC
GABAergic Influences Increase Ingestion across All Taste Categories. Liz Miller. Molly McGinnis. Lindsey Richardson
 GABAergic Influences Increase Ingestion across All Taste Categories Liz Miller Molly McGinnis Lindsey Richardson A research thesis submitted in partial completion of PSY451 senior research thesis, at Wofford
GABAergic Influences Increase Ingestion across All Taste Categories Liz Miller Molly McGinnis Lindsey Richardson A research thesis submitted in partial completion of PSY451 senior research thesis, at Wofford
Understanding Addiction and Its Impact on the Brain. SDSMA Webinar Matthew Stanley, DO
 Understanding Addiction and Its Impact on the Brain SDSMA Webinar Matthew Stanley, DO Estimated Economic Cost to Society Due to Substance Abuse and Addiction: Illegal drugs: Alcohol: Tobacco: $181 billion/year
Understanding Addiction and Its Impact on the Brain SDSMA Webinar Matthew Stanley, DO Estimated Economic Cost to Society Due to Substance Abuse and Addiction: Illegal drugs: Alcohol: Tobacco: $181 billion/year
Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development. Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University
 Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University Prenatal & Postnatal Experiences Individual differences in brain
Epigenetic Pathways Linking Parental Effects to Offspring Development Dr. Frances A. Champagne Department of Psychology, Columbia University Prenatal & Postnatal Experiences Individual differences in brain
Puberty onset in the female offspring of rats submitted to protein or energy restricted diet during lactation
 Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 15 (2004) 123 127 Puberty onset in the female offspring of rats submitted to protein or energy restricted diet during lactation Tatiane da Silva Faria, Cristiane da
Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 15 (2004) 123 127 Puberty onset in the female offspring of rats submitted to protein or energy restricted diet during lactation Tatiane da Silva Faria, Cristiane da
The Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor on Anxiety Induced by Maternal Care. Emily Lowry
 Running head: FGF2, ANXIETY, AND MATERNAL CARE The Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor on Anxiety Induced by Maternal Care By Emily Lowry A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences in
Running head: FGF2, ANXIETY, AND MATERNAL CARE The Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor on Anxiety Induced by Maternal Care By Emily Lowry A thesis submitted to the Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences in
FSANZ Response to Studies Cited as Evidence that BPA may cause Adverse Effects in Humans
 Annex 1 FSANZ Response to Studies Cited as Evidence that BPA may cause Adverse Effects in Humans STUDY KEY FINDINGS/CLAIMS FSANZ RESPONSE Relative binding affinity-serum modified access (RBA-SMA) assay
Annex 1 FSANZ Response to Studies Cited as Evidence that BPA may cause Adverse Effects in Humans STUDY KEY FINDINGS/CLAIMS FSANZ RESPONSE Relative binding affinity-serum modified access (RBA-SMA) assay
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis - comparison of the effects of dexamethasone and Mesna
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE
 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
SHORT COMMUNICATION ANTAGONISM OF APOMORPHINE-INDUCED CAGE CLIMBING BEHAVIOUR AND METHAMPHETAMINE STEREOTYPY BY FENFLURAMINE IN MICE V. P. GADA. V. V. JOSHI. J. J. BALSARA AND A. G. CHANDORKAR Department
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Effects of Caffeine on Memory in Rats
 Western University Scholarship@Western 2015 Undergraduate Awards The Undergraduate Awards 2015 Effects of Caffeine on Memory in Rats Cisse Nakeyar Western University, cnakeyar@uwo.ca Follow this and additional
Western University Scholarship@Western 2015 Undergraduate Awards The Undergraduate Awards 2015 Effects of Caffeine on Memory in Rats Cisse Nakeyar Western University, cnakeyar@uwo.ca Follow this and additional
Effect of SX-3228, a selective ligand for the BZ 1 receptor, on sleep and waking during the light-dark cycle in the rat
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 17-114 Effect of SX-38 on sleep and waking ISSN 1-879X 17 Effect of SX-38, a selective ligand for the BZ 1 receptor, on sleep and waking during
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 17-114 Effect of SX-38 on sleep and waking ISSN 1-879X 17 Effect of SX-38, a selective ligand for the BZ 1 receptor, on sleep and waking during
SAB Report to the Board of the Glass Packaging Institute
 SAB Report to the Board of the Glass Packaging Institute A Brief Overview of Significant Studies on BPA During 2013 November, 2013 Glass is ENDLESSLY Recyclable Introduction Number and diversity of studies
SAB Report to the Board of the Glass Packaging Institute A Brief Overview of Significant Studies on BPA During 2013 November, 2013 Glass is ENDLESSLY Recyclable Introduction Number and diversity of studies
Physiology & Behavior 85 (2005) Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze
 Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Physiology & Behavior 85 (25) 265 27 Abstract Effect of different illumination levels on rat behavior in the elevated plus-maze Andrea Milena Becerra Garcia, Fernando Parra Cardenas, Silvio Morato Faculdade
Vulnerability in early life to changes in the rearing environment plays a crucial role in the aetiopathology of psychiatric disorders
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (211), 14, 459 477. f CINP 21 doi:1.117/s1461145711239 Vulnerability in early life to changes in the rearing environment plays a crucial role in the aetiopathology
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (211), 14, 459 477. f CINP 21 doi:1.117/s1461145711239 Vulnerability in early life to changes in the rearing environment plays a crucial role in the aetiopathology
Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 777-781 Postprandial bradykinin release ISSN 0100-879X 777 Role of bradykinin in postprandial hypotension in humans S. Tumilero 1, L. Gallo
Maternal behavior in a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy
 Research paper Acta Neurobiol Exp 2008, 68: 502 508 Maternal behavior in a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy Yulia V. Dobryakova 1 *, Vyacheslav A. Dubynin 1, and Gilles van Luijtelaar 2 1 Biological
Research paper Acta Neurobiol Exp 2008, 68: 502 508 Maternal behavior in a genetic animal model of absence epilepsy Yulia V. Dobryakova 1 *, Vyacheslav A. Dubynin 1, and Gilles van Luijtelaar 2 1 Biological
FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT
 FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT B. M. BINDON Department of Veterinary Physiology, University of Sydney, Sydney 2006, Australia (Received
FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE CONTENT OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BEFORE IMPLANTATION IN THE MOUSE AND RAT B. M. BINDON Department of Veterinary Physiology, University of Sydney, Sydney 2006, Australia (Received
Mice Breeding Protocol
 UNIVERSIDAD CENTRAL DEL CARIBE Animal Resource Center Mice Breeding Protocol 1- Timeframe for reaching sexual maturity: 40 to 60 of age Although mice can reproduce well beyond one year of age, their reproductive
UNIVERSIDAD CENTRAL DEL CARIBE Animal Resource Center Mice Breeding Protocol 1- Timeframe for reaching sexual maturity: 40 to 60 of age Although mice can reproduce well beyond one year of age, their reproductive
Association of acanthosis nigricans with race and metabolic disturbances in obese women
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2002) 35: 59-64 Acanthosis nigricans, race and metabolic disturbances ISSN 0100-879X 59 Association of acanthosis nigricans with race and metabolic
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (2002) 35: 59-64 Acanthosis nigricans, race and metabolic disturbances ISSN 0100-879X 59 Association of acanthosis nigricans with race and metabolic
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
The anxiolitic effects of BTG1640 and BTG1675A on ultrasonic isolation calls and locomotor activity of rat pups
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4980-4984 The anxiolitic effects of BTG1640 and BTG1675A on ultrasonic isolation calls and locomotor activity of rat pups M. NICULESCU
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4980-4984 The anxiolitic effects of BTG1640 and BTG1675A on ultrasonic isolation calls and locomotor activity of rat pups M. NICULESCU
The Effects of Apomorphine on Sexual Behavior and Aggression in Male Golden Hamsters
 Bucknell University Bucknell Digital Commons Master s Theses Student Theses 2011 The Effects of Apomorphine on Sexual Behavior and Aggression in Male Golden Hamsters Molly Hyer Bucknell University Follow
Bucknell University Bucknell Digital Commons Master s Theses Student Theses 2011 The Effects of Apomorphine on Sexual Behavior and Aggression in Male Golden Hamsters Molly Hyer Bucknell University Follow
Super-Stereotypy II: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Intraventricular Dopamine D1 Agonists
 SYNAPSE 37:205 215 (2000) Super-Stereotypy II: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Intraventricular Dopamine D1 Agonists KENT C. BERRIDGE 1 * AND J. WAYNE ALDRIDGE 1,2 1 Departments of Psychology,
SYNAPSE 37:205 215 (2000) Super-Stereotypy II: Enhancement of a Complex Movement Sequence by Intraventricular Dopamine D1 Agonists KENT C. BERRIDGE 1 * AND J. WAYNE ALDRIDGE 1,2 1 Departments of Psychology,
The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological
 SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Material and Methods The individual animals, the basic design of the experiments and the electrophysiological techniques for extracellularly recording from dopamine neurons were
Recent Advances in Energy, Environment, Biology and Ecology
 Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Acute and long-term effects elicited by psychoactive drugs on 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations in rats: development of a new experimental tool for the study of drug-mediated reward NICOLA SIMOLA Department
Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced fever
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) 3: 38-387 Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and thermoregulation ISSN 000-879X 38 Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (999) 3: 38-387 Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and thermoregulation ISSN 000-879X 38 Effects of a neuronal nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on lipopolysaccharide-induced
AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
ORIGINAL ARTICLES AN EXPERIMENTAL MODEL OF ALCOHOL-INDUCED ANXIETY AND DEPRESSIVE BEHAVIOUR IN RATS Stefka Valcheva-Kuzmanova 1, Miroslav Eftimov 1, Krasimir Kuzmanov 2 ABSTRACT 1 Department of Preclinical
Animal Reproduction. Review for test #3. # lectures for cumulative test # 03 book
 Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 27 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture slides:
Animal Reproduction JP Advis DVM, Ph.D. Bartlett Hall, Animal Sciences, Cook, (732) 932-9240, advis@aesop.rutgers.edu 27 Course website: rci.rutgers.edu/~advis Material to be covered: About lecture slides:
Follicle profile and plasma gonadotropin concentration in pubertal female ponies
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (0) 37: 913-9 Puberty in female pony ISSN 00-79X 913 Follicle profile and plasma gonadotropin concentration in pubertal female ponies Departamento de
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (0) 37: 913-9 Puberty in female pony ISSN 00-79X 913 Follicle profile and plasma gonadotropin concentration in pubertal female ponies Departamento de
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Dev Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 June 15.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Dev Neurosci. 1998 ; 20(6): 525 532. Dose-Dependent Effects of Multiple Acute Cocaine Injections on Maternal Behavior and Aggression
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Dev Neurosci. 1998 ; 20(6): 525 532. Dose-Dependent Effects of Multiple Acute Cocaine Injections on Maternal Behavior and Aggression
OXYTOCIN SOCIAL BONDING, AUTISM, AND WOMEN S HEALTH
 OXYTOCIN SOCIAL BONDING, AUTISM, AND WOMEN S HEALTH Karen L. Bales, Department of Psychology and California National Primate Research Center, University of California, Davis The Prairie Vole Story Clinical
OXYTOCIN SOCIAL BONDING, AUTISM, AND WOMEN S HEALTH Karen L. Bales, Department of Psychology and California National Primate Research Center, University of California, Davis The Prairie Vole Story Clinical
Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder
 Research Article Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder Shaily Chaudhary* 1,2 Akash Yadav 3 Nikunjana Patel 4 Indrajeet Singhvi 1 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pacific
Research Article Study of Agomelatine for the Reduction of Marble Buying Behavior in Brain Disorder Shaily Chaudhary* 1,2 Akash Yadav 3 Nikunjana Patel 4 Indrajeet Singhvi 1 1Faculty of Pharmacy, Pacific
Protection against Neurobehavioral Changes Induced by Bisphenol A during Development in Rats
 Protection against Neurobehavioral Changes Induced by Bisphenol A during Development in Rats Azza A Ali 1, Engy M El Morsy 2, Gehad A Abdel-Jaleel 3, Hemat A Elariny 1 and Marwa Shamseldeen 1 1 Department
Protection against Neurobehavioral Changes Induced by Bisphenol A during Development in Rats Azza A Ali 1, Engy M El Morsy 2, Gehad A Abdel-Jaleel 3, Hemat A Elariny 1 and Marwa Shamseldeen 1 1 Department
Paradoxical reactions to cocaine
 Paradoxical reactions to cocaine Jan 18, 2006. Abstract. Quantitative and conventional microdialysis were used to investigate the effects of constitutive deletion of the prodynorphin gene on basal dopamine
Paradoxical reactions to cocaine Jan 18, 2006. Abstract. Quantitative and conventional microdialysis were used to investigate the effects of constitutive deletion of the prodynorphin gene on basal dopamine
Prolactin and Paternal Behavior in the Biparental California Mouse, Peromyscus californicus
 HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 23, 203-210 (1989) Prolactin and Paternal Behavior in the Biparental California Mouse, Peromyscus californicus DAVID J. GUBERNICK* AND RANDY J. NELsoNt *Department of Psychology,
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 23, 203-210 (1989) Prolactin and Paternal Behavior in the Biparental California Mouse, Peromyscus californicus DAVID J. GUBERNICK* AND RANDY J. NELsoNt *Department of Psychology,
Epigenetic and Neurodevelopmental Perspectives on Variation in Parenting Behavior
 Parenting Science and Practice ISSN: 1529-5192 (Print) 1532-7922 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/hpar20 Epigenetic and Neurodevelopmental Perspectives on Variation in Parenting
Parenting Science and Practice ISSN: 1529-5192 (Print) 1532-7922 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/hpar20 Epigenetic and Neurodevelopmental Perspectives on Variation in Parenting
PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE
 PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE Depression is a most common mood disorders characterised by a feeling of worthlessness, sadness and suicidal thoughts. Affects more than 10-15% of the
PRESENTER: DR. DEEPA JJM MEDICAL COLLEGE DAVANGERE Depression is a most common mood disorders characterised by a feeling of worthlessness, sadness and suicidal thoughts. Affects more than 10-15% of the
COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS
 The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/300/97-FINAL November 1997 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAPERONE SUMMARY REPORT
The European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products Veterinary Medicines Evaluation Unit EMEA/MRL/300/97-FINAL November 1997 COMMITTEE FOR VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCTS AZAPERONE SUMMARY REPORT
Africanized honey bees are efficient at detecting, uncapping and removing dead brood
 Africanized honey bees are efficient at detecting, uncapping and removing dead brood M.M. Morais 1, T.M. Francoy 2, R.A. Pereira 1, D. De Jong 2 and L.S. Gonçalves 1 1 Departamento de Biologia, Faculdade
Africanized honey bees are efficient at detecting, uncapping and removing dead brood M.M. Morais 1, T.M. Francoy 2, R.A. Pereira 1, D. De Jong 2 and L.S. Gonçalves 1 1 Departamento de Biologia, Faculdade
Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina mulungu on anxiety-related responses in rats
 Brazilian Erythrina Journal mulungu of and Medical anxiety and Biological Research () 35: 473-477 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 473 Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina
Brazilian Erythrina Journal mulungu of and Medical anxiety and Biological Research () 35: 473-477 ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 473 Effect of acute treatment with a water-alcohol extract of Erythrina
The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model of schizophrenia
 East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model
East Tennessee State University Digital Commons @ East Tennessee State University Undergraduate Honors Theses 5-2014 The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine sensitization in a rodent model
Effects of quinpirole on operant conditioning: perseveration of behavioral components
 Behavioural Brain Research 155 (24) 117 124 Research report Effects of quinpirole on operant conditioning: perseveration of behavioral components Daniel D. Kurylo Department of Psychology, Brooklyn College
Behavioural Brain Research 155 (24) 117 124 Research report Effects of quinpirole on operant conditioning: perseveration of behavioral components Daniel D. Kurylo Department of Psychology, Brooklyn College
Journal of Ethnopharmacology
 Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137 (2011) 1318 1322 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Ethnopharmacology jo ur nal homep age : www.elsevier.com/locate/jethpharm Nepeta cataria L. var. citriodora
Journal of Ethnopharmacology 137 (2011) 1318 1322 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Ethnopharmacology jo ur nal homep age : www.elsevier.com/locate/jethpharm Nepeta cataria L. var. citriodora
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho. REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5
 Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE. The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in
 1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
The role of beta-endorphin in the acute motor stimulatory and rewarding actions of cocaine in mice
 Psychopharmacology (2008) 197:443 448 DOI 10.1007/s00213-007-1053-z ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION The role of beta-endorphin in the acute motor stimulatory and rewarding actions of cocaine in mice Paul Marquez
Psychopharmacology (2008) 197:443 448 DOI 10.1007/s00213-007-1053-z ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION The role of beta-endorphin in the acute motor stimulatory and rewarding actions of cocaine in mice Paul Marquez
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
different ratios of PMSG and HCG on the occurrence of follicular haemorrhage THE induction of ovulation with PMSG and HCG in the rat has been studied
 Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
Q. Jl exp. Physiol. (1968) 53, 129-135 THE INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN IMMATURE RATS TREATED WITH PREGNANT MARE'S SERUM GONADOTROPHIN AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPHIN. By S. F. LUNN and E. T. BELL. From
EFFECTS OF GENETIC SELECTION AND FOOD RESTRICTION ON OVARIAN FUNCTION IN POULTRY. Roslin Institute (Edinburgh), Roslin, Midlothian, EH25 9PS, UK.
 EFFECTS OF GENETIC SELECTION AND FOOD RESTRICTION ON OVARIAN FUNCTION IN POULTRY P.M. Hocking Roslin Institute (Edinburgh), Roslin, Midlothian, EH25 9PS, UK. Abstract The prevalence of multiple ovulation
EFFECTS OF GENETIC SELECTION AND FOOD RESTRICTION ON OVARIAN FUNCTION IN POULTRY P.M. Hocking Roslin Institute (Edinburgh), Roslin, Midlothian, EH25 9PS, UK. Abstract The prevalence of multiple ovulation
5.2 ATRAZINE TOXICOLOGY
 . 5.2 ATRAZINE TOXICOLOGY Atrazine, 6-chloro-N 2 -ethyl-n 4 -isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC) (CAS No. 1912-24-9), is a selective systemic
. 5.2 ATRAZINE TOXICOLOGY Atrazine, 6-chloro-N 2 -ethyl-n 4 -isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry, IUPAC) (CAS No. 1912-24-9), is a selective systemic
Alcohol dependence induced in rats by semivoluntary intermittent intake
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 3: 117-1111 Alcohol dependence in rats ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 117 Alcohol dependence induced in rats by semivoluntary intermittent intake
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 3: 117-1111 Alcohol dependence in rats ISSN 1-879X Short Communication 117 Alcohol dependence induced in rats by semivoluntary intermittent intake
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
