A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred for differential 5-HT 1A receptor function
|
|
|
- Annabel Clare Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (3) 36: Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines ISSN 1-879X 63 A brain microdialysis study on 5-HT release in freely moving rat lines selectively bred for differential 5-HT 1A receptor function L.E. Gonzalez 1, M.A. Parada 1, S. Tucci 1, L. Teneud 1, D.H. Overstreet and L. Hernandez 1 1 Departamento de Fisiologia, Universidad de Los Andes, Mérida, Venezuela Bowles Center for Alcohol Studies, School of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA Correspondence L.E. Gonzalez Apartado, 19 Merida 511-A Venezuela Fax: gorey@ing.ula.ve Research supported by CONICIT (No. G-978) and CDCHT-ULA (No. M A). Received August, Accepted November 18, Abstract Breeding for high and low hypothermic responses to systemic administration of a serotonin 1A (5-HT 1A ) receptor agonist (8-hydroxy--(din-propylamino)tetralin, 8-OH-DPAT) has resulted in high DPATsensitive (HDS) and low DPAT-sensitive (LDS) lines of rats, respectively. These lines also differ in several behavioral measures associated with stress. In the present microdialysis study we observed that basal 5-HT concentrations in the prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus did not differ significantly between HDS and LDS rats. Thus, behavioral differences between the HDS and LDS lines might not be attributed to differences in basal 5-HT release. However, both lines had lower basal levels of 5-HT release than their randomly bred control group (random DPAT-sensitive, RDS) in the prefrontal cortex (mean ± SEM, pg/ µl, was 3. ±.4 for LDS, 3.8 ±.3 for HDS and 6.4 ±.6 for RDS; F(,59) = 5.8, P<.5). The administration of (±)- fenfluramine (1 mg/kg) induced a greater increase in hippocampal 5- HT levels in HDS rats (5%) as compared with LDS (48%) or RDS (43%) rats (P<.1). There were no significant differences in the prefrontal cortex among lines, with a fenfluramine-induced 5-HT increase of about 9% in the three groups. This differential response to fenfluramine may be due to functional alterations of hippocampal 5-HT reuptake sites in the HDS line. Key words Brain microdialysis Serotonin 5-HT 1A rat lines Fenfluramine 8-OH-DPAT Introduction The prototypical serotonin 1A (5-HT 1A ) receptor agonist 8-hydroxy--(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) induces hypothermic responses in the rat. Selective breeding for high and low 8-OH-DPAT sensitivity to this hypothermic response has led to the establishment of the high DPAT-sensitive (HDS) and low DPAT-sensitive (LDS) lines of rats. HDS rats exhibit greater immobility in the forced swim test than either the LDS rats or the randomly bred control (random DPAT-sensitive, RDS) (1,). HDS rats consistently exhibit lower social investigation than LDS rats, whereas these lines do not differ in locomotor activity (3). Furthermore, after 14 days of daily handling and injections, the HDS line showed lower exploration of open arms in the elevated plus-maze
2 64 L.E. Gonzalez et al. than the LDS line but, again, there was no difference in locomotor activity (4). Overall, these studies suggest that these lines respond differently to stress. It is remarkable that the HDS line is more stressed or anxious and also exhibits greater susceptibility to behavioral despair compared to the LDS line (1-4). Autoradiographic studies of the medial prefrontal and cingulated cortices have revealed that HDS rats had more 5-HT 1A binding sites than LDS rats (1). Administration of 8-OH- DPAT into the dorsal hippocampus decreased social interaction in the LDS line but not the HDS line, suggesting functional differences in the dorsal hippocampal 5-HT system. However, intrahippocampal administration of the 5-HT 1A receptor antagonist, WAY 1,635, had no effect in either line (3). Although these data suggest no line difference in 5-HT release in the hippocampus, the actual measurement of 5-HT levels in the hippocampus is essential to confirm such a notion. Based on these behavioral and neurochemical findings, it was considered of interest to measure basal 5-HT levels in each of these lines and to explore whether the serotonergic systems of HDS and LDS lines react differently to a serotonergic drug challenge. Fenfluramine was chosen because it releases 5-HT from nerve endings by blocking its uptake and by an exocytotic-like mechanism (5,6). Using a brain microdialysis technique in freely moving animals, basal concentrations of 5-HT and changes in its levels induced by systemic injections of fenfluramine (1 mg/kg) were studied in two 5-HT terminal areas, the medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus, of these rat lines. Material and Methods The HDS and LDS rat lines (1th and 13th generations) and their randomly bred control (RDS) came from the breeding colony at the University of North Carolina Center for Alcohol Studies (). The animals, weighing 7-35 g, were housed in groups of four and allowed weeks to recover from shipping before surgery. Food and water were freely available and room temperature was maintained at -5ºC. Lights were on from 7 pm to 7 am. Rats were anesthetized by ip co-administration of ketamine hydrochloride (11 mg/kg) and pentothal (15 mg/kg). A 1- mm long, 1-gauge stainless steel tube was implanted.6 mm anterior,.5 mm lateral and 1.5 mm ventral (for the prefrontal cortex) and 4.1 mm anterior,.4 mm lateral and 1. mm ventral (for the dorsal hippocampus) to the bregma, the midsagittal suture and the skull surface, respectively. The guide shaft was attached to the skull with stainless steel screws and acrylic cement. Microdialysis was performed after 7 days of postoperative recovery. On the experimental day, the rats were transferred from their home cage to a novel arena for the microdialysis procedure. The arena consisted of a Perspex cage (37 x 37 x 35 cm) with sawdust on the floor. Food and water were freely available during the experiment. Because 5-HT basal levels are near detection limits (.-.5 pg/ µl for our HPLC-EC instrument) and it has been previously shown that 5-HT levels are higher during the dark period on a regular 1-h/1- h light-dark cycle (7), dialysis was performed during the dark period. Laboratory-made microdialysis probes (8) protruded 5 mm out of the tip of the guide shaft. The effective lengths of the cellulose fiber were and 4 mm for the dorsal hippocampus and frontal cortex, respectively. Artificial cerebrospinal fluid (135 mm NaCl, 3.7 mm KCl, 1. mm CaCl, 1. mm MgCl, and 1 mm NaHCO 3, ph 7.4) was injected into the probe with a syringe pump at a flow rate of 1 µl/min. The HPLC system was a double-piston Water model 51 HPLC pump (Millipore, Waters, CA, USA) with a standard head and a model 715 valve (Rheodyne Co., Cotati, CA, USA) equipped with a -µl loop. Separations were made using a 1-cm long, 3.- mm bore, ODS Brownlee column containing
3 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines 65 3-µm particles (Perkin Elmer, Applied Biosystems, Woburn, MA, USA). The mobile phase was.116 M sodium acetate buffer with 1 µm EDTA, 1 mm octanesulfonic acid and 3% acetonitrile (v/v), ph.9. 5-HT was detected with a Water model 464 electrochemical detector (Millipore) equipped with a glass carbon electrode, a stainless steel auxiliary electrode and an Ag- AgCl reference electrode. The chemicals were oxidized at 6 mv applied between the working and the reference electrode. The analytes were measured by comparing the peak heights of the samples with standard solutions. Dialysis perfusion was started during the dark period of the cycle between 8 and 9 am. Samples were taken between 11 am and 4 pm every min and immediately analyzed for 5-HT. After collecting four consecutive samples that showed a stable 5-HT baseline, an ip injection of 1 mg/kg (±)- fenfluramine hydrochloride (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was given to the rat and four further consecutive samples were collected thereafter. Basal data were calculated as relative to the 5-HT ( pg/ µl) standard peak height. Four basal measurements for each rat were subjected to one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Newman-Keuls multiple comparison test. Because basal values differed among groups, all data following injections of fenfluramine were normalized to percentage of the mean basal concentrations. To compare changes in 5-HT levels between lines after fenfluramine injection, all normalized data from the three lines were subjected to mixed two-way ANOVA, with time and rat line as the repeated measures and independent factors, respectively. Concentrations at specific time points were compared by the Tukey post hoc test. At the end of the experiment, the tracks of the probes were localized by birefringence on unstained wet brain sections according to the Paxinos and Watson (9) rat brain stereotaxic atlas. Only data from animals with the probe track in the correct position were included in the study (animals/ group for the frontal cortex, HDS = 6, LDS = 5, RDS = 5, and for the dorsal hippocampus, HDS = 5, LDS = 5, RDS = 5). Results The means ± SEM of 5-HT basal concentrations (pg/ µl) for the rat lines are shown in Figure 1. One-way ANOVA showed that overall differences between lines for basal concentrations were highly significant for both prefrontal cortex [F(,63) = 18., P<.1] and dorsal hippocampus [F(,59) = 5.8, P<.5]. Multiple comparison tests showed that basal levels for the prefrontal Basal 5-HT (pg/ µl) Basal 5-HT (pg/ µl) % Basal 5-HT % Basal 5-HT A B A RDS LDS HDS Time (min) B Time (min) RDS LDS HDS LDS HDS RDS Figure 1. Basal serotonin (5-HT) concentrations. Basal 5-HT concentrations (mean ± SEM, pg/ µl) of the high DPAT-sensitive (HDS), low DPAT-sensitive (LDS) and random DPAT-sensitive (RDS) lines in dialysates from the prefrontal cortex (A) and dorsal hippocampus (B) obtained during the dark period for 5-6 animals/group. P<.5, compared with RDS (Newman-Keuls test). Figure. The fenfluramine test. Effect of fenfluramine (1 mg/ kg, ip, arrow) on serotonin (5- HT) concentration in dialysates obtained during the dark period from the prefrontal cortex (A) and dorsal hippocampus (B) of rats selectively bred for high (HDS), low (LDS) and random (RDS) 8-OH-DPAT sensitivity. Data are reported as percentage (mean ± SEM) of basal concentration for 5-6 animals/group. P<.5, HDS compared with either LDS or RDS groups (Tukey test).
4 66 L.E. Gonzalez et al. cortex did not differ between HDS and LDS, whereas both lines had lower levels than RDS rats (Figure 1A). In contrast, basal concentrations in the dorsal hippocampus only differed between the LDS and the RDS lines (Figure 1B). Fenfluramine significantly increased extracellular concentrations of 5-HT in both the prefrontal cortex [HDS, F(7,4) = 5.6, P<.1; LDS, F(7,35) = 4.7, P<.1; RDS, F(7,35) = 33.9, P<.1] and dorsal hippocampus [HDS, F(7,35) = 16.3, P<.1; LDS, F(7,35) = 4.8, P<.1; RDS, F(7,35) = 9.8, P<.1]. The largest increase was observed in sample 5 (first sample after fenfluramine injection) when compared with the four basal samples (post hoc test, P<.5). In the dorsal hippocampus, the lines differed in their response to fenfluramine [time x line factor, F(14,84) = 7., P<.1; line factor, F(,1) =.9, P<.1] and the post hoc test revealed that the HDS group had higher hippocampal 5-HT concentrations than either the LDS or RDS rats in three consecutive post-injection samples (see Figure ). In contrast, in the frontal cortex, the repeated measures test did not show significant line differences in response to fenfluramine [time x line factor, F(14,91) = 1., NS; line factor, F(,13) =.9, NS]. Discussion The fact that basal 5-HT levels were lower in both selectively bred lines (HDS and LDS) compared with the RDS rats indicates that selection for either high or low 8-OH-DPAT sensitivity leads to decreased basal 5-HT levels in the hippocampus and frontal cortex. The basis for this lowered basal 5-HT release in both lines is not known, but might be related to the fact that both lines are more immobile than the RDS rats in the forced swim test (). The lowered 5-HT levels cannot be related to 5-HT 1A receptors or responses to 8-OH-DPAT because HDS rats have greater cortical 5-HT 1A binding and greater hypothermic responses to 8-OH- DPAT than LDS rats (1,). The present finding of regional differences in fenfluramine-induced release of 5-HT supports previous reports. It has been proposed that there are two anatomically and functionally distinct sets of serotonergic neurons projecting to the forebrain. These systems originate from separate nuclei in the brainstem, the dorsal (DRN) and median (MRN) raphe nuclei and project preferentially to the prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus, respectively (1). There is evidence that these two systems differ in their pharmacological properties such as the vulnerability to the toxic actions of amphetamine derivatives (11). Furthermore, it has been suggested that fenfluramine has a greater acute effect on DRN than MRN terminals. Systemic administration of fenfluramine increased 5-HT concentrations in dialysates collected from the amygdala (a DRN terminal area) but not from the dorsal hippocampus (an MRN terminal area) (1). The increase in 5-HT observed in the three lines (HDS, LDS and RDS) following the fenfluramine challenge was less in the dorsal hippocampus (about 35%) than in the prefrontal cortex (about 9%). Thus, the present findings are consistent with the hypothesis that fenfluramine has a greater action on DRN than on MRN terminal areas. Pharmacological studies have shown that fenfluramine releases 5-HT from nerve endings by blocking its uptake and by an exocytotic-like mechanism (5,6). Because 8-OH- DPAT, the agent used to select the lines, has been found to have in vivo 5-HT uptake blocking properties in the hippocampus (13), numerical and functional differences in 5-HT reuptake sites may underlie the line differences in response to the fenfluramine challenge. Further binding studies are needed to clarify this point. Interestingly, the HDS rats had a comparatively greater increase in 5-HT levels following fenfluramine injection into the dorsal hippocampus (5%)
5 Serotonin and 5-HT 1A rat lines 67 than either LDS (48%) or RDS rats (43%). Therefore, it is possible that HDS rats have functional alterations of 5-HT reuptake sites in the hippocampus. The HDS rats have been reported to exhibit an abnormal response to 8-OH-DPAT following intrahippocampal administration. Unlike the LDS rats, which exhibit a typical anxiogenic response in the social interaction test, the HDS rats do not (3). Thus, taken together, these results indicate that HDS rats exhibit abnormal responses following intrahippocampal administration of either 8-OH-DPAT or fenfluramine due to functional alterations of 5-HT reuptake sites. References 1. Knapp DJ, Overstreet DH & Crews FT (1998). Brain 5-HT1A receptor autoradiography and hypothermic responses in rats bred for differences in 8-OH-DPAT sensitivity. Brain Research, 78: Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Knapp DJ, Crews FT & Janowsky DS (1996). Further selection of rat lines differing in 5-HT-1A receptor sensitivity: behavioral and functional correlates. Psychiatric Genetics, 6: Gonzalez LE, File SE & Overstreet DH (1998). Selectively bred lines of rats differ in social interaction and hippocampal 5-HT1A receptor function: a link between anxiety and depression. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 59: File SE, Ouagazzal A-M, Gonzalez LE & Overstreet DH (1999). Chronic fluoxetine in tests of anxiety in rat lines selectively bred for differential 5-HT 1A receptor function. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 6: Berger UV, Gu XF & Azmitia EC (199). The substituted amphetamines 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, methamphetamine, p-chloroamphetamine and fenfluramine induce 5-hydroxytryptamine release via a common mechanism blocked by fluoxetine and cocaine. European Journal of Pharmacology, 15: Bonanno G, Fassio A, Severi P, Ruelle A & Raiteri M (1994). Fenfluramine releases serotonin from human brain nerve endings by a dual mechanism. Journal of Neurochemistry, 63: Poncet L, Denoroy L & Jouvet M (1993). Daily variations in in vivo tryptophan hydroxylation and in the contents of serotonin and 5- hydroxyindoleacetic acid in discrete brain areas of the rat. Journal of Neural Transmission. General Section, 9: Hernandez L, Stanley BG & Hoebel BG (1986). A small, removable microdialysis probe. Life Sciences, 39: Paxinos G & Watson CH (1986). The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA. 1. Azmitia EC & Segal M (1978). An autoradiographic analysis of the differential ascending projections of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in the rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 179: Mamounas LA, Mullen CA, O Hearn E & Molliver ME (1991). Dual serotoninergic projections to forebrain in the rat: morphologically distinct 5-HT axon terminals exhibit differential vulnerability to neurotoxic amphetamine derivatives. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 314: Viana MB, Silveira R & Graeff FG (1996). D-fenfluramine selectively releases 5-HT from dorsal raphe terminals. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 9: Assie MB & Koek W (1996). Possible in vivo 5-HT reuptake blocking properties of 8-OH-DPAT assessed by measuring hippocampal extracellular 5-HT using microdialysis in rats. British Journal of Pharmacology, 119:
Interactions between serotonin and dopamine in the striatum are not mediated by striatal 5-HT 1B receptors
 43 CHAPTER 4 Interactions between serotonin and dopamine in the striatum are not mediated by striatal 5-HT 1B receptors Lotte de Groote, Berend Olivier, Herman G.M. Westenberg submitted Abstract In vivo
43 CHAPTER 4 Interactions between serotonin and dopamine in the striatum are not mediated by striatal 5-HT 1B receptors Lotte de Groote, Berend Olivier, Herman G.M. Westenberg submitted Abstract In vivo
Effects of chronic paroxetine treatment on dialysate serotonin in 5-HT 1B receptor knockout mice
 Journal of Neurochemistry, 2003, 86, 13 24 doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01827.x Effects of chronic paroxetine treatment on dialysate serotonin in 5-HT 1B receptor knockout mice A. M. Gardier,* D. J. David,*,
Journal of Neurochemistry, 2003, 86, 13 24 doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01827.x Effects of chronic paroxetine treatment on dialysate serotonin in 5-HT 1B receptor knockout mice A. M. Gardier,* D. J. David,*,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Methods
 1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
1 Supplementary Methods Social Preference Test Subjects Seventy-four Long-Evans, male rats served as subjects (S-rats) in the foodpreference test, with 40 assigned to the CXT-Same (CXT-S) Condition and
A Rapid UHPLC Method for the Analysis of Biogenic Amines and Metabolites in Microdialysis Samples
 A Rapid UHPLC Method for the Analysis of Biogenic Aes and Metabolites in Microdialysis Samples Bruce Bailey and Ian Acworth; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Chelmsford, MA Overview Purpose: To develop an Ultra
A Rapid UHPLC Method for the Analysis of Biogenic Aes and Metabolites in Microdialysis Samples Bruce Bailey and Ian Acworth; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Chelmsford, MA Overview Purpose: To develop an Ultra
An evaluation of the effect of NAS-181, a new selective 5-HT 1B receptor antagonist, on extracellular 5-HT levels in rat frontal cortex
 57 CHAPTER 5 An evaluation of the effect of NAS-181, a new selective 5-HT 1B receptor antagonist, on extracellular 5-HT levels in rat frontal cortex Lotte de Groote, André A. Klompmakers, Berend Olivier,
57 CHAPTER 5 An evaluation of the effect of NAS-181, a new selective 5-HT 1B receptor antagonist, on extracellular 5-HT levels in rat frontal cortex Lotte de Groote, André A. Klompmakers, Berend Olivier,
Supplemental Information. Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons. Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses
 Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Cell Reports, Volume 26 Supplemental Information Dorsal Raphe Dual Serotonin-Glutamate Neurons Drive Reward by Establishing Excitatory Synapses on VTA Mesoaccumbens Dopamine Neurons Hui-Ling Wang, Shiliang
Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia
 Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia Denoroy L, Orset C, Parrot S, Berod A, Sauvinet V, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM. Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France Striatum vulnerable to hypoxia ischemia necrotic
Brain dopamine and mild hypoxia Denoroy L, Orset C, Parrot S, Berod A, Sauvinet V, Cottet-Emard JM, Pequignot JM. Université Claude Bernard, Lyon, France Striatum vulnerable to hypoxia ischemia necrotic
Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism
 Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Research article Related Commentary, page 2697 Deficits in amygdaloid camp-responsive element binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism Subhash C. Pandey,
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN
 Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Pak. J. Bot., 38(1): 131-138, 26. ATTENUATION OF STRESS-INDUCED BEHAVIORAL DEFICITS BY AZADIRACHTA INDICA (NEEM): ROLE OF SEROTONIN NOREEN SAMAD, TAHIRA PARVEEN, SAIDA HAIDER AND DARAKHSHAN JABEEN HALEEM
Suven Microdialysis Services
 Suven Microdialysis Services In-Vivo Brain Microdialysis Studies in Rodents for Monitoring Changes in Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Histamine and Metabolite GABA and Glutamate Monoamines (NE, DA, 5HT
Suven Microdialysis Services In-Vivo Brain Microdialysis Studies in Rodents for Monitoring Changes in Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Histamine and Metabolite GABA and Glutamate Monoamines (NE, DA, 5HT
Abstract. Introduction. R.N. Takahashi 1, O. Berton 2,3, P. Mormède 2 and F. Chaouloff 2
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (21) 34: 675-682 Effects of diazepam and SB 26553 in SHR and Lewis rats ISSN 1-879X 675 Strain-dependent effects of diazepam and the 5-HT 2B/2C receptor
Simultaneous Analysis of Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Serotonin in 15 Minutes
 pplication Guide Simultaneous nalysis of Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Serotonin in 15 Minutes 1. Introduction Our customers have been seeking a separation method for norepinephrine (, noradrenalin), dopamine
pplication Guide Simultaneous nalysis of Norepinephrine, Dopamine and Serotonin in 15 Minutes 1. Introduction Our customers have been seeking a separation method for norepinephrine (, noradrenalin), dopamine
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/328/5983/1288/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Induction of Fear Extinction with Hippocampal-Infralimbic BDNF Jamie Peters, Laura M. Dieppa-Perea, Loyda M. Melendez,
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors
 Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 2: Serotonin and Histamine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Indolamines: Serotonin Basic Neurochemistry. FIGURE 15-1: Chemical structure of
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 2: Serotonin and Histamine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Indolamines: Serotonin Basic Neurochemistry. FIGURE 15-1: Chemical structure of
The relationship between anxiety and depression in animal models: a study using the forced swimming test and elevated plus-maze
 Brazilian Correlation Journal between of Medical plus-maze and and Biological forced Research swimming (1999) behaviors 32: 1121-1126 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1121 The relationship between anxiety
Brazilian Correlation Journal between of Medical plus-maze and and Biological forced Research swimming (1999) behaviors 32: 1121-1126 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1121 The relationship between anxiety
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice.
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of stress during withdrawal on expression of sensitization to repeated cocaine exposure in WT and D2R / mice. The time course of locomotor activity for WT (a, b) or D2R
 PSY 302 Lecture 6: The Neurotransmitters (continued) September 12, 2017 Notes by: Desiree Acetylcholine (ACh) CoA + Acetate Acetyl-CoA (mitochondria) (food, vinegar) + Choline ChAT CoA + ACh (lipids, foods)
PSY 302 Lecture 6: The Neurotransmitters (continued) September 12, 2017 Notes by: Desiree Acetylcholine (ACh) CoA + Acetate Acetyl-CoA (mitochondria) (food, vinegar) + Choline ChAT CoA + ACh (lipids, foods)
CMA Rev 1.0. System For Freely Moving Animals
 CMA 120 9408000Rev 1.0 System For Freely Moving Animals CMA 120 SYSTEM FOR FREELY MOVING ANIMAL, USER S MANUAL CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION.3 2. UNPACKING & ASSEMBLY 4 2.1 Packing List.. 4 3. DESCRIPTION 5
CMA 120 9408000Rev 1.0 System For Freely Moving Animals CMA 120 SYSTEM FOR FREELY MOVING ANIMAL, USER S MANUAL CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION.3 2. UNPACKING & ASSEMBLY 4 2.1 Packing List.. 4 3. DESCRIPTION 5
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa
 Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
Extended therapeutic validation of an anti-mc4 receptor antibody in an animal model of anorexia nervosa (project no. 04-12B) Authors Guus Akkermans, Martien Kas Preliminary data report Introduction In
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration.
 Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
Implanting an Adult Rat with the Single-Channel Epoch Transmitter for Recording Electrocardiogram in the Type II electrode configuration. Recommended Surgical Tools A. Scalpel handle B. Scalpel blade (#15)
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
SAMPLE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS PLEASE NOTE, THE QUESTIONS BELOW SAMPLE THE ENTIRE LECTURE COURSE AND THEREORE INCLUDE QUESTIONS ABOUT TOPICS THAT WE HAVE NOT YET COVERED IN CLASS. 1. Which of the following
JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning
 JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning 8 6 4 Cond1 Cond2 Test VEH ANI Session Supplementary Fig. 1. Protein synthesis inhibition after a second contextual
JLC Lee: Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning 8 6 4 Cond1 Cond2 Test VEH ANI Session Supplementary Fig. 1. Protein synthesis inhibition after a second contextual
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Interest of using genetically manipulated mice as models of depression to evaluate antidepressant drugs activity: a review
 doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00640.x REVIEW ARTICLE Interest of using genetically manipulated mice as models of depression to evaluate antidepressant drugs activity: a review Alain M. Gardier*, Bruno
doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00640.x REVIEW ARTICLE Interest of using genetically manipulated mice as models of depression to evaluate antidepressant drugs activity: a review Alain M. Gardier*, Bruno
Serotonergic neurons in the caudal raphe nuclei discharge in association with activity of masticatory muscles
 Serotonergic Brazilian Journal activity of Medical and masticatory and Biological muscle Research activity (1997) 30: 79-83 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 79 Serotonergic neurons in the caudal raphe
Serotonergic Brazilian Journal activity of Medical and masticatory and Biological muscle Research activity (1997) 30: 79-83 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 79 Serotonergic neurons in the caudal raphe
HTEC-500 and 700 Series Related
 HTEC-500 and 700 Series Related Columns and Reagents 681.407.00 P3-AC -PC Prepacked AC Precolumn (3pcs/pkg) 450.00 3mm 681.406.00 P3-CH-PC Prepacked CH Precolumn (3 pcs/pkg) 450.00 3mm 681.405.00 P3-CA-PC
HTEC-500 and 700 Series Related Columns and Reagents 681.407.00 P3-AC -PC Prepacked AC Precolumn (3pcs/pkg) 450.00 3mm 681.406.00 P3-CH-PC Prepacked CH Precolumn (3 pcs/pkg) 450.00 3mm 681.405.00 P3-CA-PC
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works
 UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title Differential interactions of desipramine with amphetamine and methamphetamine: Evidence that amphetamine releases dopamine from noradrenergic neurons in the medial
UCLA UCLA Previously Published Works Title Differential interactions of desipramine with amphetamine and methamphetamine: Evidence that amphetamine releases dopamine from noradrenergic neurons in the medial
Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 67 80 Effects of baseline anxiety on response to kindling of the right medial amygdala Robert Adamec, Tanya Shallow Dept. of Psychology, Memorial University, St. John s,
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) Laboratório de Psicologia Comparada, Universidade Estácio de Sá, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil b
 Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 243 247 Microinfusion of nefazodone into the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala enhances defensive behavior induced by NMDA stimulation of the inferior colliculus S. Maisonnette
Physiology & Behavior 70 (2000) 243 247 Microinfusion of nefazodone into the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala enhances defensive behavior induced by NMDA stimulation of the inferior colliculus S. Maisonnette
Gretchen N. Neigh, H. Moore Arnold, Martin Sarter, John P. Bruno* Short communication
 Brain Research 894 (2001) 354 358 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ bres Short communication Dissociations between the effects of intra-accumbens administration of amphetamine and exposure to a novel environment
Brain Research 894 (2001) 354 358 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ bres Short communication Dissociations between the effects of intra-accumbens administration of amphetamine and exposure to a novel environment
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
ALEXYS Neurotransmitter Analyzer for On-line Microdialysis Sampling
 Application Note Neuroscience ALEXYS Analyzer for Highest Sensitivity in Neurotransmitter Analysis Monoamines and Metabolites Noradrenaline Dopamine Serotonin 5-hydroxyindole aceticacid (5-HIAA) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylaceticacid
Application Note Neuroscience ALEXYS Analyzer for Highest Sensitivity in Neurotransmitter Analysis Monoamines and Metabolites Noradrenaline Dopamine Serotonin 5-hydroxyindole aceticacid (5-HIAA) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylaceticacid
Adolescent Prozac Exposure Enhances Sensitivity to Cocaine in Adulthood INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
INTRODUCTION Epidemiologic reports indicate that mood disorders in children and adolescents are quite common, with up to 70% of depressed children and adolescents experiencing a recurrence within 5 years
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
The Acute Effects of Amphetamine Derivatives on Extracellular Serotonin and Dopamine Levels in Rat Nucleus Accumbens
 PII S0091-3057(97)00527-3 Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Vol. 59, No. 4, pp. 1003 1009, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0091-3057/98 $19.00.00 The Acute
PII S0091-3057(97)00527-3 Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Vol. 59, No. 4, pp. 1003 1009, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0091-3057/98 $19.00.00 The Acute
INHJBITION OF RESTRAINT-INDUCED ANOREXIA BY INJECTED TRYPTOPHAN
 ELSEVIER PII SOO24-3205(98)00391-9 Life Sciences. Vol. 63, No. 14, pp. PI. 205-212, 1998 Copyrights 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in Ihe LISA. All rights resewed CKI24-3205/98 $19.00 +.oo PHARMACOLOGY
ELSEVIER PII SOO24-3205(98)00391-9 Life Sciences. Vol. 63, No. 14, pp. PI. 205-212, 1998 Copyrights 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in Ihe LISA. All rights resewed CKI24-3205/98 $19.00 +.oo PHARMACOLOGY
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Fast UHPLC Methods for Analysis of Amino Acids
 Fast UHPLC Methods for Analysis of Ao Acids Qi Zhang, Bruce Bailey, Marc Plante, David Thomas, and Ian Acworth Thermo Fisher Scientific, Chelmsford, MA, USA Overview Purpose: Methods that offer both rapid
Fast UHPLC Methods for Analysis of Ao Acids Qi Zhang, Bruce Bailey, Marc Plante, David Thomas, and Ian Acworth Thermo Fisher Scientific, Chelmsford, MA, USA Overview Purpose: Methods that offer both rapid
A neurotoxic regimen of MDMA suppresses behavioral, thermal and neurochemical responses to subsequent MDMA administration
 Psychopharmacology (1999) 147:66 72 Springer-Verlag 1999 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Mahalakshmi Shankaran Gary A. Gudelsky A neurotoxic regimen of MDMA suppresses behavioral, thermal and neurochemical responses
Psychopharmacology (1999) 147:66 72 Springer-Verlag 1999 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Mahalakshmi Shankaran Gary A. Gudelsky A neurotoxic regimen of MDMA suppresses behavioral, thermal and neurochemical responses
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST)
 Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurons of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis (BNST) Electrophysiological Properties and Their Response to Serotonin DONALD G. RAINNIE a Harvard Medical School and Department of Psychiatry, Brockton
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
ACTA NEUROBIOL: EXP. 1988, 48: 117-121 Short communication LESIONS OF THE MESOLIMBIC DOPAMINE SYSTEM DISRUPT SIGNALLED ESCAPE RESPONSES IN THE RAT W. Jeffrey WILSON and Jennifer C. HALL Department of Psychological
Medial prefrontal transection enhances social interaction II: Neurochemical studies
 Brain Research 887 (2000) 259 265 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ bres Research report Medial prefrontal transection enhances social interaction II: Neurochemical studies * Sonia Tucci, Quilianio Contreras,
Brain Research 887 (2000) 259 265 www.elsevier.com/ locate/ bres Research report Medial prefrontal transection enhances social interaction II: Neurochemical studies * Sonia Tucci, Quilianio Contreras,
Preliminary Study of the Effects of Melatonin Administration on the Release of Endogenous 5-HT and Its Metabolite in Rat SCN
 Preliminary Study of the Effects of Melatonin Administration on the Release of Endogenous 5-HT and Its Metabolite in Rat SCN Kazuaki Yoshioka*, Fuming Xie, James F. Gitzen, Candice B. Kissinger, and Peter
Preliminary Study of the Effects of Melatonin Administration on the Release of Endogenous 5-HT and Its Metabolite in Rat SCN Kazuaki Yoshioka*, Fuming Xie, James F. Gitzen, Candice B. Kissinger, and Peter
Serotonin-1A Autoreceptors Are Necessary and Sufficient for the Normal Formation of Circuits Underlying Innate Anxiety
 68 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 2, 211 31(16):68 618 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Serotonin-1A Autoreceptors Are Necessary and Sufficient for the Normal Formation of Circuits Underlying Innate Anxiety
68 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 2, 211 31(16):68 618 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Serotonin-1A Autoreceptors Are Necessary and Sufficient for the Normal Formation of Circuits Underlying Innate Anxiety
Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon?
 Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Supplementary information to: Is action potential threshold lowest in the axon? Maarten H. P. Kole & Greg J. Stuart Supplementary Fig. 1 Analysis of action potential (AP) threshold criteria. (a) Example
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG
 Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response
 A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
A concurrent excitation and inhibition of dopaminergic subpopulations in response to nicotine Raphaël Eddine PhD 1, Sebastien Valverde MSc 1, Stefania Tolu PhD 1, Daniel Dautan MSc 1, Audrey Hay MSc 1,
processes in the central nervous system (CNS), affecting many of the during the course of ethanol treatment. Ethanol stimulates the release of
 INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION Neuroscience research is essential for understanding the biological basis of ethanol-related brain alterations and for identifying the molecular targets for therapeutic compounds
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003
 Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors in Male Syrian Hamsters
 Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Neuroscience Honors Theses Neuroscience Institute Spring 5-5-2017 Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors
Georgia State University ScholarWorks @ Georgia State University Neuroscience Honors Theses Neuroscience Institute Spring 5-5-2017 Effects of Systemic Administration of 8-OH-DPAT on Agonistic Social Behaviors
Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview
 Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview 13 Introduction This experiment will investigate how cocaine acts on dopamine neurons in the brain. Cocaine is a drug of abuse that increases
Book 3: Lab Procedures Book 3: Ch. 1: The Hypothesis and Overview 13 Introduction This experiment will investigate how cocaine acts on dopamine neurons in the brain. Cocaine is a drug of abuse that increases
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder
 Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Neurotransmitter Functioning In Major Depressive Disorder Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc. 2017 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rockville, MD January
Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist microinjected into the dorsal periaqueductal gray of rats
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 3: 1533-1537 Behavioral effects of injected into PAG ISSN 1-79X Short Communication 1533 Defense reaction induced by a metabotropic glutamate
Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological
 Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production
 Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
Chapter V. Evaluation of the Effects of d-fenfluramine on the Cutaneous Vasculature and Total Metabolic Heat Production Experiments presented in this chapter were designed to investigate the possible mechanisms
Title Revision n date
 A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
A. THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE (TLC) 1. SCOPE The method describes the identification of hydrocortisone acetate, dexamethasone, betamethasone, betamethasone 17-valerate and triamcinolone acetonide
The Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor in the Median Raphe Nucleus in Relapse to Alcohol
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 15, 2002, 22(18):7844 7849 Brief Communication The Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor in the Median Raphe Nucleus in Relapse to Alcohol A. D. Lê, 1,2,3 S. Harding,
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 15, 2002, 22(18):7844 7849 Brief Communication The Role of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor in the Median Raphe Nucleus in Relapse to Alcohol A. D. Lê, 1,2,3 S. Harding,
Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF
 Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF Application Note 219 Joan Stevens, PhD; Luke Roenneburg; Kevin Fawcett (Gilson,
Analysis of Peptides via Capillary HPLC and Fraction Collection Directly onto a MALDI Plate for Off-line Analysis by MALDI-TOF Application Note 219 Joan Stevens, PhD; Luke Roenneburg; Kevin Fawcett (Gilson,
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
University of Groningen. Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan
 University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Effect of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) on Hippocampal Dopamine and Serotonin
 PII S0091-3057(98)00103-8 Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 361 366, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0091-3057/98 $19.00.00 Effect of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
PII S0091-3057(98)00103-8 Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 361 366, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0091-3057/98 $19.00.00 Effect of 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine
A Functional Tph2 C1473G Polymorphism Causes an Anxiety Phenotype via Compensatory Changes in the Serotonergic System
 (2012), 1 13 & 2012 American College of. www.neuropsychopharmacology.org All rights reserved 0893-133X/12 A Functional Tph2 C1473G Polymorphism Causes an Anxiety Phenotype via Compensatory Changes in the
(2012), 1 13 & 2012 American College of. www.neuropsychopharmacology.org All rights reserved 0893-133X/12 A Functional Tph2 C1473G Polymorphism Causes an Anxiety Phenotype via Compensatory Changes in the
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis
 Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
Product Guide for LudgerSep TM R1 HPLC Column for DMB labelled Sialic Acid Analysis Product # LS-R1-4.6x150 Ludger Document # LS-R1-DMB-Guide-v5.1 Ludger Ltd Culham Science Centre Oxford OX14 3EB United
Supplemental Information. A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit. for Place Navigation
 Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Neuron, Volume 99 Supplemental Information A Visual-Cue-Dependent Memory Circuit for Place Navigation Han Qin, Ling Fu, Bo Hu, Xiang Liao, Jian Lu, Wenjing He, Shanshan Liang, Kuan Zhang, Ruijie Li, Jiwei
Changes in adult brain and behavior caused by neonatal limbic damage: implications for the etiology of schizophrenia
 Behavioural Brain Research 107 (2000) 71 83 www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report Changes in adult brain and behavior caused by neonatal limbic damage: implications for the etiology of schizophrenia
Behavioural Brain Research 107 (2000) 71 83 www.elsevier.com/locate/bbr Research report Changes in adult brain and behavior caused by neonatal limbic damage: implications for the etiology of schizophrenia
Available online at Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (3):157-161 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2015, 7 (3):157-161 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Supplemental Figure 1
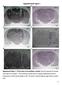 A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
A C E Supplemental Figure 1 AP 1mm A+C 1mm Apo 1mm B D 1mm CGS F 1mm All 1mm Supplemental Figure 1. The locations of microinfusion cannulae. Each dot represents the cannula tip of a given rat in Figure.
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2003 Activity-Based Anorexia in Female Rats Deann Dixon Follow this and additional works at the FSU
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2003 Activity-Based Anorexia in Female Rats Deann Dixon Follow this and additional works at the FSU
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
1 Presynaptic adaptive responses to constitutive versus adult pharmacologic inhibition of serotonin uptake
 beth a. luellen, tracy l. gilman and anne milasincic andrews 1 Presynaptic adaptive responses to constitutive versus adult pharmacologic inhibition of serotonin uptake abstract Many antidepressants are
beth a. luellen, tracy l. gilman and anne milasincic andrews 1 Presynaptic adaptive responses to constitutive versus adult pharmacologic inhibition of serotonin uptake abstract Many antidepressants are
Effects of limbic corticostriatal lesions on a u t o shaping performance in rats
 Effects of limbic corticostriatal lesions on a u t o shaping performance in rats BJ Everitt, JA Parkinson, G Lachenal, KM Halkerston, N Rudarakanchana, RN Cardinal, J Hall, CH Morrison, JW Dalley, SR Howes,
Effects of limbic corticostriatal lesions on a u t o shaping performance in rats BJ Everitt, JA Parkinson, G Lachenal, KM Halkerston, N Rudarakanchana, RN Cardinal, J Hall, CH Morrison, JW Dalley, SR Howes,
Recovery of Presynaptic Dopaminergic Functioning in Rats Treated with Neurotoxic Doses of Methamphetamine
 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 1999, 19(17):7653 7660 Recovery of Presynaptic Dopaminergic Functioning in Rats Treated with Neurotoxic Doses of Methamphetamine Wayne A. Cass and Michael W. Manning
The Journal of Neuroscience, September 1, 1999, 19(17):7653 7660 Recovery of Presynaptic Dopaminergic Functioning in Rats Treated with Neurotoxic Doses of Methamphetamine Wayne A. Cass and Michael W. Manning
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Neuropharmacological Characterization of Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Stimulated Cataplexy in Narcoleptic Canines
 EXPERIMENTAL NEUROLOGY 151, 89 104 (1998) ARTICLE NO. EN986787 Neuropharmacological Characterization of Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Stimulated Cataplexy in Narcoleptic Canines Malcolm S. Reid,* Seiji Nishino,
EXPERIMENTAL NEUROLOGY 151, 89 104 (1998) ARTICLE NO. EN986787 Neuropharmacological Characterization of Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Stimulated Cataplexy in Narcoleptic Canines Malcolm S. Reid,* Seiji Nishino,
Alexys Neurotransmitter Analyzer for Monoamines and Metabolites
 Application Note Neuroscience ALEXYS Analyzer for Highest Sensitivity in Neurotransmitter Analysis Monoamines and Metabolites Noradrenaline Dopamine Serotonin 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic
Application Note Neuroscience ALEXYS Analyzer for Highest Sensitivity in Neurotransmitter Analysis Monoamines and Metabolites Noradrenaline Dopamine Serotonin 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016.
 Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Aspartame This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive
Residue Monograph prepared by the meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), 82 nd meeting 2016 Aspartame This monograph was also published in: Compendium of Food Additive
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
DISSOCIATING SPACE AND TRACE IN DORSAL AND VENTRAL HIPPOCAMPUS. Jennifer Lee Czerniawski. A thesis submitted to the. Graduate School-New Brunswick
 DISSOCIATING SPACE AND TRACE IN DORSAL AND VENTRAL HIPPOCAMPUS By Jennifer Lee Czerniawski A thesis submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey in partial
DISSOCIATING SPACE AND TRACE IN DORSAL AND VENTRAL HIPPOCAMPUS By Jennifer Lee Czerniawski A thesis submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey in partial
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Increased anxiety in corticotropin-releasing factor type 2 receptor-null mice requires recent acute stress exposure and is associated with dysregulated serotonergic activity
Edinburgh Research Explorer Increased anxiety in corticotropin-releasing factor type 2 receptor-null mice requires recent acute stress exposure and is associated with dysregulated serotonergic activity
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology
 1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
1 Relevance of sleep neurobiology for cognitive neuroscience and anesthesiology Giancarlo Vanini, MD, Helen A. Baghdoyan, PhD, and Ralph Lydic, PhD Introduction Although general anesthetics are used for
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
Serotonin and Stress Francis Chaouloff, Ph.D., Olivier Berton, Ph.D., and Pierre Mormède, Ph.D.
 Serotonin and Stress Francis Chaouloff, Ph.D., Olivier Berton, Ph.D., and Pierre Mormède, Ph.D. Forty-five years after its discovery, brain serotonin (5-HT) is still the subject of intense research aimed
Serotonin and Stress Francis Chaouloff, Ph.D., Olivier Berton, Ph.D., and Pierre Mormède, Ph.D. Forty-five years after its discovery, brain serotonin (5-HT) is still the subject of intense research aimed
iii products for MICRODIALYSIS research
 products for MICRODIALYSIS research iii i products for MICRODIALYSIS research Copyright. All rights reserved. Harvard Apparatus / CMA Microdialysis 2011-12. ii Table of Contents iii Introduction 1-3 Introduction
products for MICRODIALYSIS research iii i products for MICRODIALYSIS research Copyright. All rights reserved. Harvard Apparatus / CMA Microdialysis 2011-12. ii Table of Contents iii Introduction 1-3 Introduction
*,1 M.I. Colado, 1 E. O'Shea, 1 R. Granados, 1 B. Esteban, 1 A.B. MartõÂ n& 2 A.R. Green. Introduction
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 911 ± 924 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Studies on the role of dopamine in the degeneration
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 126, 911 ± 924 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Studies on the role of dopamine in the degeneration
EASIMIP TM PATULIN Product Code: P250 / P250B
 EASIMIP TM PATULIN Product Code: P250 / P250B Molecularly imprinted polymer columns for use in conjunction with HPLC. For in vitro use only. P250B/V5/03.09.18 www.r-biopharm.com Contents Page Test Principle...
EASIMIP TM PATULIN Product Code: P250 / P250B Molecularly imprinted polymer columns for use in conjunction with HPLC. For in vitro use only. P250B/V5/03.09.18 www.r-biopharm.com Contents Page Test Principle...
Methods and Strategies of Research
 Methods and Strategies of Research 1 Destroying part of the brain and evaluating the animal s subsequent behavior. Lesion studies. Example: If after part of the brain is destroyed, an animal can no longer
Methods and Strategies of Research 1 Destroying part of the brain and evaluating the animal s subsequent behavior. Lesion studies. Example: If after part of the brain is destroyed, an animal can no longer
DAILY BINGEING ON SUGAR REPEATEDLY RELEASES DOPAMINE IN THE ACCUMBENS SHELL
 Neuroscience 134 (2005) 737 744 DAILY BINGEING ON SUGAR REPEATEDLY RELEASES DOPAMINE IN THE ACCUMBENS SHELL P. RADA, a,b N. M. AVENA a AND B. G. HOEBEL a * a Psychology Department, Green Hall, Princeton
Neuroscience 134 (2005) 737 744 DAILY BINGEING ON SUGAR REPEATEDLY RELEASES DOPAMINE IN THE ACCUMBENS SHELL P. RADA, a,b N. M. AVENA a AND B. G. HOEBEL a * a Psychology Department, Green Hall, Princeton
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11436 Supplementary Figure 1. CRF peptide is localized cholinergic interneurons throughout the nucleus accumbens. Immunofluorescent images demonstrating localization of CRF peptide, tyrosine
doi:10.1038/nature11436 Supplementary Figure 1. CRF peptide is localized cholinergic interneurons throughout the nucleus accumbens. Immunofluorescent images demonstrating localization of CRF peptide, tyrosine
1.0. FSL NMDAR-fEPSP 0.8. amplitude (mv) Intensity (µa) 2.0 SD FSL Time (ms)
 a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
a 2.5 1. AMPAR-fEPSP slope (mv/ms) 2. 1. NMDAR-fEPSP amplitude (mv).8.6.4.5.2. 2 4 6 8. 1 2 3 4 5 Intensity (µa) Intensity (µa) b 2. PPF Ratio (fepsp2/fepsp1) 1..5. 5 1 2 5 Time (ms) Supplementary Figure
Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration
 Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Linfield College School of Nursing Portland DBT Program AGENDA Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology review
Thinking Outside the Box: Prescribing by Synthesis & Integration Barbara J. Limandri, DNSc, APRN, BC Linfield College School of Nursing Portland DBT Program AGENDA Neuroanatomy and neurophysiology review
