Test of visual pathway function
|
|
|
- Briana Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The visual system
2 Test of visual pathway function Suppose you have a patient who may have some damage to the visual pathways leading to visual cortex, for example from multiple sclerosis. How could you non-invasively investigate where such damage might be? You could use an EEG (electroencephalogram). What kind of visual stimulus should you use to activate as many cells as possible?
3 Test of visual pathway function
4 Test of visual pathway function
5 Test of visual pathway function Reversing checkerboard is a good stimulus for several reasons: The pattern has lots of edges. The pattern changes with time.
6 0.5 mm thick The photosensors (the rods and cones) lie outermost in the retina against the pigment epithelium and choroid. Interneurons Ganglion cells (the output neurons of the retina) lie innermost in the retina closest to the lens and front of the eye. The retina
7 Rods and cones
8 It s important to know how the photoreceptors work, because modern methods are becoming available to compensate for malfunctions in many parts of the phototransduction pathway. Phototransduction Dark Na + Ca ++ Na + Light
9 In the dark, lots of positive charge enters the photoreceptors and leads to transmitter release. Light reduces the charge influx and transmitter release. Phototransduction Dark Na + Ca ++ Na + Light
10 Phototransduction The discs in the outer segment of rods contain rhodopsin molecules in their membranes (up to 100 billion molecules per photoreceptor!). The rods also contain special cation channels (CNG channels) in their outer membranes. (Cyclic nucleotidegated ion channel) High levels of cgmp are present in the dark and keep these channels OPEN. rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp
11 Phototransduction Positive charge enters the rod. This positive charge moves into the inner segment, where it leads to transmitter release. Dark rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp Na + Ca ++ Na
12 How does light shut down transmitter release? Phototransduction rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp +
13 How does light shut down transmitter release? Light activates rhodopsin. Phototransduction rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp * +
14 Phototransduction How does light shut down transmitter release? Light activates rhodopsin. Activated rhodopsin activates a G-protein (transducin). rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp transducin * * +
15 Phototransduction How does light shut down transmitter release? Light activates rhodopsin. Activated rhodopsin activates a G-protein (transducin). Transducin activates cgmp phosphodiesterase (PDE). rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp transducin PDE * * * +
16 Phototransduction How does light shut down transmitter release? Light activates rhodopsin. Activated rhodopsin activates a G-protein (transducin). Transducin activates cgmp phosphodiesterase (PDE). rhodopsin CNG channel (open) cgmp transducin PDE PDE hydrolyzes cgmp. + * * *
17 Phototransduction How does light shut down transmitter release? Light activates rhodopsin. Activated rhodopsin activates a G-protein (transducin). Transducin activates cgmp phosphodiesterase (PDE). PDE hydrolyzes cgmp. The external channels close and less current enters. rhodopsin CNG channel (closed) cgmp transducin PDE * * *
18 More light means that fewer channels are open. The rod HYPERpolarizes! It releases less transmitter as light levels increase. Phototransduction Dark Na + Ca ++ Na + Light
19 Cones work essentially the same way, but they have cone opsins instead of rhodopsin. Phototransduction Dark Na + Ca ++ Na + Light + +
20 Rods vs. cones 110,000,000 to 125,000,000 rods/retina Rods function under dim conditions but not bright conditions 6,400,000 cones/retina Cones will not function in very dimly lit conditions Cones mediate color vision
21 Color vision There are three kinds of cones, with maximum sensitivities to different wavelengths of light. blue: (short wavelength) green: (medium wavelength) red: (long wavelength)
22 The fovea It lies in the center of the macula. The central region contains only cones. The overlying retinal layers are displaced.
23 light
24 Cones are concentrated in the fovea The fovea is especially sensitive to color and detail but functions poorly in badly lit conditions. When you want to look at something, you move your eye so that the image of the object falls on the fovea.
25 The rods are concentrated in the periphery The periphery has high sensitivity under dimly-lit conditions. The periphery has poor resolution of small objects.
26 A family of hereditary diseases of the retina. Caused by at least 25 different mutations in the rod phototransduction cascade. Retinitis Pigmentosa
27 Leads to loss of peripheral vision and can progress to total blindness. A successful gene therapy to replace a faulty rhodopsin gene in one variant was announced in October. Retinitis Pigmentosa
28 Retinal interneurons Photoreceptors synapse onto many postsynaptic interneurons. The interneurons synapse onto one another and onto ganglion cells.
29 Ganglion cells There are about a million ganglion cells. There are at least 18 different types of ganglion cell in the human retina.
30 Ganglion cells Some features of ganglion cells are the same at all regions of the retina but some are very different in the fovea vs. the periphery. Understanding these differences helps to explain the consequences of disorders that affect different parts of the retina. Most of them have properties that convey information about spatial and temporal contrasts Where are there changes in brightness and color? When is the pattern of light changing?
31 Visual field vs. receptive field The term visual field refers to the whole area seen by the eye. The term visual receptive field refers to the part of the visual field where a visual stimulus affects a particular visual system neuron.
32 Ganglion cells Most ganglion cells have center-surround receptive fields. About 50% of those are ON-center OFF-surround. No light Light in center Light in surround
33 ON-center OFF-surround ganglion cells + This ganglion cell responds best (fires fastest) if there is a small spot of light centered in the receptive field.
34 ON-center OFF-surround ganglion cells + This ganglion cell responds best (fires fastest) if there is a small spot of light centered in the receptive field. It responds less to a larger spot of light because a larger spot activates inhibitory inputs to the ganglion cell as well as excitatory. vs
35 Ganglion cells Most ganglion cells have center-surround receptive fields. About 50% of those are ON-center OFF-surround. About 50% of those are OFF-center ON-surround.
36 Ganglion cells The other 50% of the center-surround cells are OFF-center ON-surround. No light Light in center Light only in surround
37 OFF-center ON-surround ganglion cells + These cells respond best to a small dark spot on a bright background. Neither type responds well to an all-bright or alldark field.
38 Sustained vs. transient responses Some respond transiently; some give sustained responses. Some ON-center cells are transient-type; others are sustained. Some OFF-center cells are transient-type; others are sustained. transient cell sustained cell
39 Other types of ganglion cells Some ganglion cells don't have center-surround receptive fields. Some project to superior colliculus and are involved in eye movement control. Some project to the suprachiasmatic nucleus, a region that controls circadian rhythms. Intrinsically photosensitive Contain the photopigment melanopsin (mainly bluesensitive)
40 Receptive field size Ganglion cell centers in the fovea are as small as a fraction of a degree. (The moon is about 0.5.) Ganglion cell centers in the periphery can be up to 5 degrees in diameter.
41 Receptive field size What makes some receptive fields small and others large? Different amounts of convergence determine different receptive field sizes. photoreceptors (thousands) interneurons (bipolars) (hundreds) ganglion cells FOVEA PERIPHERY
42 Receptive field size What is the advantage of having lots of convergence in the rod pathway? Spatial resolution is degraded (objects look fuzzy) but sensitivity to low levels of light is improved. photoreceptors (thousands) interneurons (bipolars) (hundreds) ganglion cells FOVEA PERIPHERY
43 Color vision Red/green centersurround organization is very common. Green ON Red OFF red ON/green OFF red OFF/green ON green ON/red OFF green OFF/red ON
44 Color vision Red/green centersurround organization is very common. Other color-coding cells use blue-yellow contrast. red ON/green OFF red OFF/green ON green ON/red OFF green OFF/red ON
45 Color vision Why is red-green color-blindness so common in males? The opsins for the red and green cones are coded by adjacent regions on the X chromosome and are very similar. They are prone to recombination errors.
46 Foveal vs. peripheral ganglion cells typical cell in fovea sustained color-selective small receptive field some ON-center, some OFF-center typical cell in periphery transient broad-band large receptive field some ON-center, some OFF-center
47
48 Regenerating optic pathways from the eye to the brain Bireswar Laha, Ben K. Stafford and Andrew D. Huberman (June 8, 2017) Science 356 (6342),
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
Construction of the Visual Image
 Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
Construction of the Visual Image Anne L. van de Ven 8 Sept 2003 BioE 492/592 Sensory Neuroengineering Lecture 3 Visual Perception Light Photoreceptors Interneurons Visual Processing Ganglion Neurons Optic
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
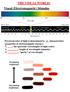 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
Image Formation and Phototransduction. By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology
 Image Formation and Phototransduction By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Vision Vision is a complex process through which an image of the external environment is formed on the photosensitive
Image Formation and Phototransduction By Dr. Abdelaziz Hussein Lecturer of Physiology Vision Vision is a complex process through which an image of the external environment is formed on the photosensitive
The Visual System. Retinal Anatomy Dr. Casagrande February 2, Phone: Office: T2302 MCN
 The Visual System Retinal Anatomy Dr. Casagrande February 2, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN Reading assignments and Good Web Sites Chapter 2 in Tovée,
The Visual System Retinal Anatomy Dr. Casagrande February 2, 2004 Phone: 343-4538 Email: vivien.casagrande@mcmail.vanderbilt.edu Office: T2302 MCN Reading assignments and Good Web Sites Chapter 2 in Tovée,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision
 Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Carlson (7e) PowerPoint Lecture Outline Chapter 6: Vision This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display,
Biological Bases of Behavior. 6: Vision
 Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Biological Bases of Behavior 6: Vision Sensory Systems The brain detects events in the external environment and directs the contractions of the muscles Afferent neurons carry sensory messages to brain
Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy. (the part that s visible to us!)
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Vision Phototransduction of light By. Prof/Faten zakareia Physiology Dept College of Medicine King Saud University
 Vision Phototransduction of light By Prof/Faten zakareia Physiology Dept College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives: -List and compare functional properties of rods and cones in scotopic and photopic
Vision Phototransduction of light By Prof/Faten zakareia Physiology Dept College of Medicine King Saud University Objectives: -List and compare functional properties of rods and cones in scotopic and photopic
What do we perceive?
 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina
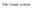 The visual system Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina 0.5 mm thick The retina 0.5 mm thick The photosensors
The visual system Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina 0.5 mm thick The retina 0.5 mm thick The photosensors
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
The Visual System. Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems
 The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
The Visual System Basic anatomy of the eye The retina Organization of cell types Rod and cone photoreceptor systems Phototransduction Conversion of energy of light into changes in V m Adaptation and expansion
Introduction to Physiological Psychology
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html This class n Sensation vs. Perception n How light is translated into what we see n Structure
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing
 Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Lecture 3 Vision 2 The Retina
 Lecture 3 Vision 2 The Retina All lecture material from the following two links: 1) http://hubel.med.harvard.edu/book/bcontex.htm 2) http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~redneu/2013/books/principles%20of%20neural%20science%20%20kandel/gateway.ut.ovid.com/gw2/ovidweb.cgisidnjhkoalgmeho00dbookimagebookdb_7c_2fc~32.htm
Lecture 3 Vision 2 The Retina All lecture material from the following two links: 1) http://hubel.med.harvard.edu/book/bcontex.htm 2) http://www.ib.cnea.gov.ar/~redneu/2013/books/principles%20of%20neural%20science%20%20kandel/gateway.ut.ovid.com/gw2/ovidweb.cgisidnjhkoalgmeho00dbookimagebookdb_7c_2fc~32.htm
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience. Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3
 Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
2/3/17. Visual System I. I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex
 1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
Vision I. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
PSY 214 Lecture 5 (09/19/2010) (Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 5 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 55-71
 Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Vision. The Eye External View. The Eye in Cross-Section
 Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
let's continue talking about the eye,
 Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Eye is mainly composed of 3 layers: External layer, which called The Sclera which is a hard connective tissue that gives the eye its round shape. Extension of the sclera into the front is the cornea, which
Eye physiology and phototransduction. Zoran Đogaš
 Eye physiology and phototransduction Zoran Đogaš Eye geometry Nervus opticus Pupillary reflex and accommodation Clinical Sy Myopia Hypermetropia Photoreceptors ROD CONE Photoreceptors The photoreceptor
Eye physiology and phototransduction Zoran Đogaš Eye geometry Nervus opticus Pupillary reflex and accommodation Clinical Sy Myopia Hypermetropia Photoreceptors ROD CONE Photoreceptors The photoreceptor
postsynaptic), and each plasma membrane has a hemichannel, sometimes called a connexon)
 The Retina The retina is the part of the CNS that sends visual information from the eye to the brain. It very efficient at capturing and relaying as much visual information as possible, under a great range
The Retina The retina is the part of the CNS that sends visual information from the eye to the brain. It very efficient at capturing and relaying as much visual information as possible, under a great range
ASSUMPTION OF COGNITIVE UNIFORMITY
 The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!!
 BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!!
 BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
BI 358 Lecture 18 Annette Sims, MD, Ophthalmologist next Tuesday! Hooray!! I. Announcements Quiz 5 returned at end of lecture. Eye Dissection & Vision lab next Tuesday > Lecture by Dr. Sims! Final Quiz
Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV
 Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV 1) The brain and spinal cord comprise the. (a) autonomic nervous system (b) peripheral nervous system (c) central nervous system (d) efferent nervous system (e) afferent nervous
Will s Pre-Test for Exam IV 1) The brain and spinal cord comprise the. (a) autonomic nervous system (b) peripheral nervous system (c) central nervous system (d) efferent nervous system (e) afferent nervous
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 05. Rods and cones
 Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Chapter 17, Part 1! The Special Senses! SECTION 17-1! Olfaction, the sense of smell, involves olfactory receptors responding to chemical stimuli!
 Chapter 17, Part 1! The Special Senses! SECTION 17-1! Olfaction, the sense of smell, involves olfactory receptors responding to chemical stimuli! 2! 1! Olfaction A Chemical Sensation! Olfactory epithelium!
Chapter 17, Part 1! The Special Senses! SECTION 17-1! Olfaction, the sense of smell, involves olfactory receptors responding to chemical stimuli! 2! 1! Olfaction A Chemical Sensation! Olfactory epithelium!
Visual Physiology. Perception and Attention. Graham Hole. Problems confronting the visual system: Solutions: The primary visual pathways: The eye:
 Problems confronting the visual system: Visual Physiology image contains a huge amount of information which must be processed quickly. image is dim, blurry and distorted. Light levels vary enormously.
Problems confronting the visual system: Visual Physiology image contains a huge amount of information which must be processed quickly. image is dim, blurry and distorted. Light levels vary enormously.
Senses are transducers. Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What?
 1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System
 CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System Lecturer: Jitendra Malik Scribe: Ryan White (Slide: layout of the brain) Facts about the brain:
CS294-6 (Fall 2004) Recognizing People, Objects and Actions Lecture: January 27, 2004 Human Visual System Lecturer: Jitendra Malik Scribe: Ryan White (Slide: layout of the brain) Facts about the brain:
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Reading Assignments: Lecture 5: Introduction to Vision. None. Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence
 Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Brain Theory and Artificial Intelligence Lecture 5:. Reading Assignments: None 1 Projection 2 Projection 3 Convention: Visual Angle Rather than reporting two numbers (size of object and distance to observer),
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
The ON and OFF Channels
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The ON and OFF Channels Questions: 1. How are the ON and OFF channels created for the cones? 2. How are the ON and OFF channels created for
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The ON and OFF Channels Questions: 1. How are the ON and OFF channels created for the cones? 2. How are the ON and OFF channels created for
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name
 Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name Multiple Choice: 1. are responsible for phosphorylation of receptor proteins, whereas are responsible for dephosphorylation of receptor proteins. a) Kinases; phosphatases*
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2 Spring, 2006 Name Multiple Choice: 1. are responsible for phosphorylation of receptor proteins, whereas are responsible for dephosphorylation of receptor proteins. a) Kinases; phosphatases*
Sense system. Introduction The visual system Hearing. Introduction to sensory mechanisms
 Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
Sense system Introduction The visual system Hearing Introduction to sensory mechanisms Sensory receptors & sense organs Sensory neurons & Receptor cells Adequate stimulus threshold Transduction Receptor
Vision. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
Vision Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Vision is the ability to detect light patterns from the outside environment and interpret them into images. Animals are bombarded with sensory information, and the sheer volume
Neuroanatomy, Text and Atlas (J. H. Martin), 3 rd Edition Chapter 7, The Visual System, pp ,
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: RETINA and CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Friday, 20
Visual System. By: Jordan Koehling
 Visual System By: Jordan Koehling What is the Visual System Photoreceptors are the type of sensory neuron involved in sight. It is part of the CNS and allows us to see our surroundings using visual light
Visual System By: Jordan Koehling What is the Visual System Photoreceptors are the type of sensory neuron involved in sight. It is part of the CNS and allows us to see our surroundings using visual light
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Eye. Cognitive Neuroscience of Language. Today s goals. 5 From eye to brain. Today s reading
 Cognitive Neuroscience of Language 5 From eye to brain Today s goals Look at the pathways that conduct the visual information from the eye to the visual cortex Marielle Lange http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/mlange/teaching/cnl/
Cognitive Neuroscience of Language 5 From eye to brain Today s goals Look at the pathways that conduct the visual information from the eye to the visual cortex Marielle Lange http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/mlange/teaching/cnl/
LIGHT DETECTION IN THE
 1 Lecture 1 October 31, 2005 Richard Masland LIGHT DETECTION IN THE RETINA INTRODUCTION Vision is an important topic in neurobiology, for both intellectual and practical reasons. Primates are peculiarly
1 Lecture 1 October 31, 2005 Richard Masland LIGHT DETECTION IN THE RETINA INTRODUCTION Vision is an important topic in neurobiology, for both intellectual and practical reasons. Primates are peculiarly
Prof. Greg Francis 7/31/15
 s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
Figure 4-1. Layers of the Neural Retina.
 Chapter 4. The Neural Retina Basic Organization At one level the retina works like film in a camera: it records the optical image that is focused onto it by the cornea and lens, and relays this information
Chapter 4. The Neural Retina Basic Organization At one level the retina works like film in a camera: it records the optical image that is focused onto it by the cornea and lens, and relays this information
UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES
 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR MBBS III BIOCHEMISTRY OF VISION: An
UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES Division of Basic Medical Sciences Discipline of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology PBL SEMINAR MBBS III BIOCHEMISTRY OF VISION: An
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction
 Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Dan Tollin, PhD
 Nervous System Block Visual System - September 19-20, 2016 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Dan, PhD The visual system can detect the detailed form of objects, slight movement of objects, can work effectively in very
Nervous System Block Visual System - September 19-20, 2016 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Dan, PhD The visual system can detect the detailed form of objects, slight movement of objects, can work effectively in very
M Cells. Why parallel pathways? P Cells. Where from the retina? Cortical visual processing. Announcements. Main visual pathway from retina to V1
 Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
Biology Animal Physiology Fall Midterm 1
 Name: Biology 449 - Animal Physiology Fall 2010 Fill in your scantron form as follows: Midterm 1 Write and bubble in your name in the upper left (last name first). Sign your form on the upper right. By
Name: Biology 449 - Animal Physiology Fall 2010 Fill in your scantron form as follows: Midterm 1 Write and bubble in your name in the upper left (last name first). Sign your form on the upper right. By
ACTIVITIES. Complete Diagrams PNS 18 and 19 Complete PNS 23 Worksheet 3 #1 only Complete PNS 24 Practice Quiz
 ACTIVITIES Complete Diagrams PNS 18 and 19 Complete PNS 23 Worksheet 3 #1 only Complete PNS 24 Practice Quiz THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable
ACTIVITIES Complete Diagrams PNS 18 and 19 Complete PNS 23 Worksheet 3 #1 only Complete PNS 24 Practice Quiz THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision. Vision. Vision. Chem Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6. Rod cells. E = hν = hc λ
 Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6 Question of the Day: Who has better color vision, a human or a mantis shrimp? involves the transduction of light energy to an nerve signal.
Chem 452 - Lecture 10 Signal Transduction & Sensory Systems Part 6 Question of the Day: Who has better color vision, a human or a mantis shrimp? involves the transduction of light energy to an nerve signal.
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Vision and Audition. This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems.
 Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
Vision and Audition Vision and Audition This section concerns the anatomy of two important sensory systems, the visual and the auditory systems. The description of the organization of each begins with
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect. absolute threshold. Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information.
 absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
absolute threshold The lowest level of stimulation that a person can detect accommodation Adapting one's current understandings to incorporate new information. acuity Sharp perception or vision audition
Fundus Autofluorescence. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Fundus Autofluorescence Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) has many important functions including phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments Cone Rod
Foundations. 1. Introduction 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina
 Foundations 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina Overview Central and peripheral retina compared Muller Glial Cells Foveal Structure Macula Lutea Blood supply to the retina Degenerative
Foundations 2. Gross Anatomy of the Eye 3. Simple Anatomy of the Retina Overview Central and peripheral retina compared Muller Glial Cells Foveal Structure Macula Lutea Blood supply to the retina Degenerative
Special Senses: The Eye
 Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
The Midget and Parasol Channels
 The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The Midget and Parasol Channels MIDGET SYSTEM PARASOL SYSTEM or Neuronal response profile ON OFF ON OFF time Midget system cones ON OFF ON
The visual and oculomotor systems Peter H. Schiller, year 2006 The Midget and Parasol Channels MIDGET SYSTEM PARASOL SYSTEM or Neuronal response profile ON OFF ON OFF time Midget system cones ON OFF ON
Photoreceptors Rods. Cones
 Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
Photoreceptors Rods Cones 120 000 000 Dim light Prefer wavelength of 505 nm Monochromatic Mainly in periphery of the eye 6 000 000 More light Different spectral sensitivities!long-wave receptors (558 nm)
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
3.4 Photoisomerization reactions
 3.4 Photoisomerization reactions A photoisomerization is the conversion of one isomer into another isomer by light. The examples we will look at involve exclusively the conversion between two geometric
3.4 Photoisomerization reactions A photoisomerization is the conversion of one isomer into another isomer by light. The examples we will look at involve exclusively the conversion between two geometric
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I
 OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Mechanisms of Color Processing . Neural Mechanisms of Color Processing A. Parallel processing - M- & P- pathways B. Second
OPTO 5320 VISION SCIENCE I Monocular Sensory Processes of Vision: Color Vision Mechanisms of Color Processing . Neural Mechanisms of Color Processing A. Parallel processing - M- & P- pathways B. Second
Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources)
 Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
Sensitivity and Adaptation in the Retina
 Sensitivity and Adaptation in the Retina Visual transduction single photon sensitivity dark current rhodopsin Ca ++ vs cgmp as the messenger amplification Operating range of vision saturation, threshold,
Sensitivity and Adaptation in the Retina Visual transduction single photon sensitivity dark current rhodopsin Ca ++ vs cgmp as the messenger amplification Operating range of vision saturation, threshold,
4/22/16. Eye. External Anatomy of Eye. Accessory Structures. Bio 40B Dr. Kandula
 Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
7. Sharp perception or vision 8. The process of transferring genetic material from one cell to another by a plasmid or bacteriophage
 1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
1. A particular shade of a given color 2. How many wave peaks pass a certain point per given time 3. Process in which the sense organs' receptor cells are stimulated and relay initial information to higher
CNS-2: Physiology: Vision
 CNS-2: Physiology: Vision The eyes are the windows to the soul This is the 3rd lecture in CNS-2 Physiology. In this lecture we will talk about one of our special senses, and that is the Vision. Hopefully
CNS-2: Physiology: Vision The eyes are the windows to the soul This is the 3rd lecture in CNS-2 Physiology. In this lecture we will talk about one of our special senses, and that is the Vision. Hopefully
Vision is the most dominant sense, about 70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes Accessory Structures of the eye : Eyelashes :
 Sight By Jess Kapp Vision is the most dominant sense, about 70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes Accessory Structures of the eye : Eyelashes : Protect eye from debris and bacteria Eyebrows
Sight By Jess Kapp Vision is the most dominant sense, about 70% of all sensory receptors in the body are in the eyes Accessory Structures of the eye : Eyelashes : Protect eye from debris and bacteria Eyebrows
INTRODUCTION: ****************************************************************************************************
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY **************************************************************************************************** EYES AND VISION ****************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY **************************************************************************************************** EYES AND VISION ****************************************************************************************************
4/17/2019. Special Senses. Special sensory receptors. Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium
 Special Senses Special sensory receptors Distinct, localized receptor cells in head Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Accessory Structures The
Special Senses Special sensory receptors Distinct, localized receptor cells in head Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Accessory Structures The
eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3
 eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3 retinal specialization fovea: highest density of photoreceptors, aimed at where you are looking -> highest acuity optic disk: cell-free area, where
eye as a camera Kandel, Schwartz & Jessel (KSJ), Fig 27-3 retinal specialization fovea: highest density of photoreceptors, aimed at where you are looking -> highest acuity optic disk: cell-free area, where
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing
 20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development
 Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
COURSE: OPTO 328 Physiology of Vision I
 COURSE: OPTO 328 Physiology of Vision I UNITS: 2 + 0 = 2. TUTOR: Dr. Ali A Abusharha RECOMMENDED TEXTS: 1) Visual Perception by Cornsweet. 2) Physiology of the Eye by Hugh Davson. 3) OPTOMETRY by Keith
COURSE: OPTO 328 Physiology of Vision I UNITS: 2 + 0 = 2. TUTOR: Dr. Ali A Abusharha RECOMMENDED TEXTS: 1) Visual Perception by Cornsweet. 2) Physiology of the Eye by Hugh Davson. 3) OPTOMETRY by Keith
The Visual System. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina
 Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
Dark and light adaptation: a job that is accomplished mainly in the retina Dark adaptation: recovery in darkness (of sensitivity) and photoreceptor pigment. Light adaptation: The ability of the visual
THE SPECIAL SENSES. Introduction Vision
 THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable complexity RECEPTORS: GENERAL PROPERTIES Transducers Receptor Potential Generator Potential RECEPTORS
THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable complexity RECEPTORS: GENERAL PROPERTIES Transducers Receptor Potential Generator Potential RECEPTORS
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms. Reading: BCP Chapter 19
 Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
Sleep-Wake Cycle I Brain Rhythms Reading: BCP Chapter 19 Brain Rhythms and Sleep Earth has a rhythmic environment. For example, day and night cycle back and forth, tides ebb and flow and temperature varies
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity. Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air
 Special Senses I. Olfaction II. Gustation A. Anatomy and general info The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air Olfactory glands
Special Senses I. Olfaction II. Gustation A. Anatomy and general info The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air Olfactory glands
XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University
 SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
SENSE ORGAN XUE HUI Department of Histology& Embryology, Basic Medicine College of Jilin University EYE fibrous globe lens photosensitive cells a system of cells and nerves concentric layers the sclera
FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2011 BILD2
 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2011 BILD2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 6 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
FIRST MIDTERM EXAM October 18, 2011 BILD2 WRITE YOUR NAME ON ALL 6 PAGES. ANSWER ALL 10 QUESTIONS (100 POINTS). CONFINE YOUR ANSWERS TO THE SPACE ALLOWED. If you would like to write on the back of the
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II
 Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
September 9, 2013: The layout of the visual system, the retina and the lateral geniculate nucleus
 September 9, 2013: The layout of the visual system, the retina and the lateral geniculate nucleus 1 Basic Wiring of the Visual System 2 The world seen by the two eyes Seen by both eyes Seen by both eyes
September 9, 2013: The layout of the visual system, the retina and the lateral geniculate nucleus 1 Basic Wiring of the Visual System 2 The world seen by the two eyes Seen by both eyes Seen by both eyes
Outline 2/19/2013. Please see me after class: Sarah Pagliero Ryan Paul Demetrius Prowell-Reed Ashley Rehm Giovanni Reynel Patricia Rochin
 Outline 2/19/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 8: Sensation and Perception 1 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Outline 2/19/2013 PSYC 120 General Psychology Spring 2013 Lecture 8: Sensation and Perception 1 Dr. Bart Moore bamoore@napavalley.edu Office hours Tuesdays 11:00-1:00 How we sense and perceive the world
Sensation & Perception The Visual System. Subjectivity of Perception. Sensation vs. Perception 1/9/11
 Sensation & Perception The Visual System Subjectivity of Perception We do not perceive the world directly Perception depends on brain stimulation Distinction between sensation and perception Sensation
Sensation & Perception The Visual System Subjectivity of Perception We do not perceive the world directly Perception depends on brain stimulation Distinction between sensation and perception Sensation
25/09/2012. Capgras Syndrome. Chapter 2. Capgras Syndrome - 2. The Neural Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
