HveC (nectin-1) is expressed at high levels in sensory neurons, but not in motor neurons, of the rat peripheral nervous system
|
|
|
- August Kelly
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of NeuroVirology, 7: 476± 480, 2001 c 2001 Taylor & Francis ISSN 1355± 0284/01 $ Short Communication HveC (nectin-1) is expressed at high levels in sensory neurons, but not in motor neurons, of the rat peripheral nervous system Marina Mata, Mindi Zhang, XiaoPing Hu, and David J Fink Departments of Neurology, Molecular Genetics and Biochemistry, University of Pittsburgh; and GRECC, VA Pittsburgh Healthcare System, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA The entry of herpes simplex virus (HSV)-1 into cells is a complex process mediated in part by the binding of the HSV glycoprotein D (gd) to a speci c cellular receptor identi ed as HveC, or nectin-1. We examined the distribution of HveC in sensory and motor neurons of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by immunocytochemistry. HveC is expressed at high levels in sensory neurons of dorsal root ganglion and their peripheral axons, at lower levels in motor neurons of spinal cord, and without detectable expression in motor nerve terminals at the neuromuscular junction. These results have implications regarding the tropism of HSV to speci c neuronal populations, and for the construction of HSV-based vectors for the peripheral nervous system. Journal of NeuroVirology (2001) 7, Keywords: herpesvirus 1; receptor; nectin; neurons The entry of herpes simplex virus into mammalian cells requires the participation of several viral envelope glycoproteins. The initial attachment of the virus to cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans is mediated by the glycoprotein C (gc) and/or gb (Herold et al, 1994; Herold et al, 1991). Viral penetration requires the fusion of the virion envelope with the cell plasma membrane, a process mediated by the viral glycoproteins gc, gb, and gh-gl acting in concert on cell surface receptors (Handler et al, 1996a; Handler et al, 1996b). Targeting of HSV to cells is achieved by several cell membrane proteins, originally identi- ed as HSV entry (Hve) mediators. HveA, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, is the principal receptor responsible for entry of HSV into human lymphoid cells but not into other cell types (Montgomery et al, 1996). HveB, also known as the poliovirus receptor-related protein 2 (PRR2), mediates the entry of HSV-2, pseudorabies virus, and the HSV-1 mutants rid1, rid2, and ANG, but does not me- Address correspondence to David Fink, S-520 Biomedical Science Tower, 200 Lothrop Street, Pittsburgh, PA 15213, USA. d nk@pitt.edu Received 7 February 2001; revised 18 April 2001; accepted 7 June diate the entry of wild-type HSV-1 into cells (Shukla et al, 1999). Neither HveA nor HveB ful ll the requirements for a coreceptor that can mediate the entry of HSV-1 into epithelial cells at the initial site of infection and into neurons for the establishment of latent infection. The principal entry mediator of HSV-1 has been identi ed as HveC (Geraghty et al, 1998), a-518 amino acid type I membrane glycoprotein that is widely expressed in cells of epithelial and neuronal origin, and is nearly identical in sequence to nectin-1 (Shukla et al, 2000). The extracellular portion consists of three immunoglobulin-like domains (V-C2- C2, from the N-terminal to the membrane proximal domain) that contain seven potential glycosylation sites (Lopez et al, 1995). This family of proteins with similar structure, which in addition to HveB, HveC, and HveD include the poliovirus receptor (PVR or CD155), function in development as homophilic cell adhesion molecules. The intracellular carboxy terminal of HveC interacts with the PDZ domain of afadin, an f-actin binding protein, linking the extracellular action to the actin cytoskeleton (Takahashi et al, 1999). Because our experiments were carried out to investigate the role of this molecule in herpes entry, we have used the term HveC in this communication. HveC mrna has been detected in a number of
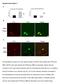
2 M Mata et al 477 Figure 1 Western blot of rat brain protein. 20 ¹g of mouse (left) and rat (right) cortex was homogenizedin lysis buffer, separated on a 4 15% SDS gel, transferred to a membrane, incubated with the anti-hvec antibody 1:1000 at 4 ± C overnight and then with a goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP conjugate (1:10,000, BioRad) for 1 h. The immunoreactive band was detected by chemiluminescence (Super- Signal A, Pierce) with a 1-min exposure to X-ray lm, and the resulting image digitized. Only a single major immunoreactive band was found, and was identical in the mouse and rat. human cell lines including NT2 teratocarcinoma, SH-SY5Y, and the IMR-5 neuroblastoma, as well as primary cell cultures of broblast and skin keratinocytes (Geraghty et al, 1998). HveC is recognized by HSV gd independent of N-linked glycosylation, in a process that appears to involve one or two molecules of gd for each molecule of HveC. The sequences of gd involved in this interaction have been identi ed, and are conserved among all the alpha herpesviruses (Krummenacher et al, 1998, 1999, 2000). In wild-type infection, HSV is spread by epithelial contact, and progeny virions are taken up by sensory neurons innervating the area of the primary infection. In studies aimed at developing HSV-based vectors for therapeutic applications for the nervous system, we found that uptake of nonreplicating HSV recombinants into motor neurons from peripheral inoculation is substantially less than that into sensory neurons. This mimics the natural distribution of infection by wild-type virus. Although that distribution might result directly form the portal of entry, it prompted us to examine the distribution of HveC in the peripheral nervous system of mature rats. The studies were performed with a polyclonal antibody (R154) raised against human HveC (Krummenacher et al, 2000) (a gift of Dr Gary Cohen) that has been previously characterized (Krummenacher et al, 1998, 2000). Mouse nectin has been cloned and is very similar to the human form (Shukla et al, 2000), but the rat isoform has not yet been cloned. Therefore, the speci city of antibody R154 for rat HveC was con rmed by comparing Figure 2 Immunostaining of DRG with anti-hvec demonstrates a high level of immunoreactivity in the sensory neuron cell bodies (black arrows, A). The nuclei are unstained. A control section, immunostained in a similar manner but with omission of the primary antibody shows no immunoreactivity in sensory neurons (black arrows, B). Immunostaining of ventral spinal cord with anti-hvec demonstrates only very faint immunoreactivity in motor neuron perikaryon (black arrows, C). A control spinal cord is shown in D.
3 478 M Mata et al Western blot of proteins from rat and mouse cortex, which demonstrated a single major immunoreactive band with an apparent MW of kd, similar in size to the glycosylated human protein (Cocchi et al, 1998), that was identical in mouse and rat brain (Figure 1). To examine the distribution of HveC in the rat peripheral nervous system, we performed an immunocytochemical study. Male Sprague Dawley rats were perfused with saline followed by 10% formalin, and DRG and spinal cord removed, post xed, and embedded in paraf n. Then, 4-¹m sections were immunostained with the primary antibody (1:1000) followed by a biotinylated anti-rabbit IgG (1:200, Vector) and developed with diaminobenzidine (Vector Elite Kit, Vector laboratories). High levels of HveC immunoreactivity was found in neurons of the DRG (Figure 2), while less immunostaining was seen in motor neurons of the ventral horn of spinal cord (Figure 2). The distribution HveC in sensory nerve terminals was examined in the footpads and digits. Fresh tissues were removed, xed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin at 4 ± C overnight, and post xed in 30% sucrose at 4 ± C for 2 days. 30-¹m sections were washed with PBS blocked with 5% NHS in PBS-T for 30 minutes, then incubated with primary antibodies, anti-tuj1 mouse monoclonal (1:250, Promega) and the anti-hvec rabbit polyclonal (1:1000), at 4 ± C overnight. After washing with PBS, the sections were incubated with anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to Cy2 (1:6000, Jackson Laboratories) and anti-mouse IgG conjugated to Cy3 (1:4000, Sigma) for 1 h at room temperature and following washing with PBS the mounted sections were examined with epi uorescence microscopy. HveC colocalized extensively with the axonal marker TUJ-1 in sensory nerves (Figure 3, left panels) and in the terminal branches in the subcutaneous tissue (Figure 3, A D). HveC immunoreactivity alone is also seen in a distribution consistent with epithelial cells and fat cells that express relatively high levels of the protein. To examine the distribution of HveC in motor nerve terminals, we studied the diaphragm, because the neuromuscular junctions are easily identi able along the midportion of that muscle. The fresh diaphragm was removed, frozen in OCT at 90 ± C, and 10-¹m sections washed with PBS, blocked with 5% NHS in PBS-T for 30 minutes, and then incubated with the Figure 3 A sensory nerve branch in the foot, cut in cross section (white arrows) is shown immunostained for HveC, the axonal marker TUJ-1, and in a fused image. The extensive overlap of HveC and TUJ-1 in the nerve bers is apparent. Sections of digits and footpad from the rat stained with antibodies against HveC and TUJ-1 (fusion image) shows extensive overlap of the two antigens (arrowheads, A D). A and B show digits, cut in cross section; the extensive staining of epithelial cells with the HveC antibody outlines the digit, and the nerve bers are seen within. C and D show footpads cut in cross section, with the dense plexus of nerve bers characterized by the double immunostaining seen in this fused image. HveC immunoreactivity alone is also seen in a distribution consistent with epithelial cells and fat cells which express relatively high levels of the protein.
4 M Mata et al 479 Figure 4 A motor endplate from the diaphragm, identi ed by bungarotoxin binding (top), shows no immunostaining with HveC (left panels). Motor nerve terminals present in this region can be identi ed with the antibody TUJ-1 (right panels) and overlap at their terminal portion with the motor endplate (fusion, right). primary antibody (TUJ-1 mouse monoclonal or anti HveC rat polyclonal) at 4 ± C overnight. After washing with PBS the bound antibody was localized with the same anti-mouse IgG conjugated to Cy2 (1:4000, Jackson Laboratories) that had been used in the studies of skin. No immunostaining of nerve bers was detected (Figure 4). To con rm that the terminal motor branches innervating the neuromuscular junction had been included, the sections were also incubated with uorescently labeled -bungarotoxin-tr (1:600, Molecular Probes) for 2 h at room temperature. As shown in Figure 4, the overlap of TUJ-1 with bungarotoxin binding con rms the localization of the motor nerve twigs, but no immunostaining against HveC is seen in these sections. These studies demonstrate that the HSV entry mediator HveC is expressed to high levels in sensory neurons, where it is naturally transported from the terminal regions of axons of those cells. In contrast, motor neurons in spinal cord express low levels of HveC, and no detectable protein is found in the nerve terminals at the neuromuscular junction. Because HveC plays an important role in mediating the entry of HSV into cells, this data may shed some light on the tropism of HSV for sensory as opposed to motor neurons, and has important implications for the design of gene transfer vectors based on HSV. Acknowledgements This work was supported by grants from the ALS Association (DJF), the Families of SMA (DJF), the Department of Veterans Affairs (MM and DJF), and the NIH (DJF). We thank Dr Gary Cohen for generously providing the antibody to nectin. References Cocchi F, Menotti L, Mirandola P, Lopez M, Campadelli- Fiume G (1998). The ectodomain of a novel member of the immunoglobulin subfamily related to the poliovirus receptor has the attributes of a bona de receptor for herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in human cells. J Virol 72(12): Geraghty RJ, Krummenacher C, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ, Spear PG (1998). Entry of alphaherpesviruses mediated
5 480 M Mata et al by poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 and poliovirus receptor. Science 280: Handler CG, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ (1996a). Cross-linking of glycoprotein oligomers during herpes simplex virus type 1 entry. J Virol 70(9): Handler CG, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH (1996b). Oligomeric structure of glycoproteins in herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol 70(9): Herold BC, Visalli RJ, Susmarski N, Brandt CR, Spear PG (1994). Glycoprotein C-independent binding of herpes simplex virus to cells requires cell surface heparan sulphate and glycoprotein B. J Gen Virol 75: Herold BC, WuDunn D, Soltys N, Spear PG (1991). Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1 plays a principal role in the adsorption of virus to cells and in infectivity. J Virol 65(3): Krummenacher C, Baribaud I, Ponce De Leon M, Whitbeck JC, Lou H, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ (2000). Localization of a binding site for herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D on herpesvirus entry mediator C by using antireceptor monoclonal antibodies. J Virol 74(23): Krummenacher C, Nicola, AV, Whitbeck JC, Lou H, Hou W, Lambris JD, Geraghty RJ, Spear PG, Cohen GH, Eisenberg RJ (1998). Herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D can bind to poliovirus receptor-related protein 1 or herpesvirus entry mediator, two structurally unrelated mediators of virus entry. J Virol 72: Krummenacher C, Rux AH, Whitbeck JC, Ponce-de-Leon M, Lou H, Baribaud I, Hou W, Zou C, Geraghty RJ, Spear PG, Eisenberg RJ, Cohen GH (1999). The rst immunoglobulin-like domain of HveC is suf cient to bind herpes simplex virus gd with full af nity, while the third domain is involved in oligomerization of HveC. J Virol 73(10): Lopez M, Eberle F, Mattei MG, Gabert J, Birg F, Bardin F, Maroc C, Dubreuil P (1995). Complementary DNA characterization and chromosomal localization of a human gene related to the poliovirus receptor-encoding gene. Gene 155(2): Montgomery RI, Warner MS, Lum BJ, Spear PG (1996). Herpes simplex virus-1 entry into cells mediated by a novel member of the TNF/NGF receptor family. Cell 87(3): Shukla D, Dal Canto MC, Rowe CL, Spear PG (2000). Striking similarity of murine nectin-1alpha to human nectin-1alpha (HveC) in sequence and activity as a glycoprotein D receptor for alphaherpesvirus entry. J Virol 74(24): Shukla D, Rowe CL, Dong Y, Racaniello VR, Spear PG (1999). The murine homolog (Mph) of human herpesvirus entry protein B (HveB) mediates entry of pseudorabies virus but not herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol 73(5): Takahashi K, Nakanishi H, Miyahara M, Mandai K, Satoh K, Satoh A, Nishioka H, Aoki J, Nomoto A, Mizoguchi A, Takai Y (1999). Nectin/PRR: An immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule recruited to cadherin-based adherens junctions through interaction with Afadin, a PDZ domain-containing protein. J Cell Biol 145(3):
A role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus type 1
 Journal of General Virology (2004), 85, 805 809 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.19641-0 Short Communication Correspondence Deepak Shukla dshukla@uic.edu A role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in cell fusion induced
Journal of General Virology (2004), 85, 805 809 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.19641-0 Short Communication Correspondence Deepak Shukla dshukla@uic.edu A role for 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate in cell fusion induced
FRANCESCA COCCHI, 1 LAURA MENOTTI, 1 PATRICE DUBREUIL, 2 MARC LOPEZ, 2
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2000, p. 3909 3917 Vol. 74, No. 8 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell-to-Cell Spread of Wild-Type Herpes Simplex
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2000, p. 3909 3917 Vol. 74, No. 8 0022-538X/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell-to-Cell Spread of Wild-Type Herpes Simplex
Soluble 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate can trigger herpes simplex virus type 1 entry into resistant Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells
 Journal of General Virology (2007), 88, 1075 1079 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.82476-0 Short Communication Correspondence Deepak Shukla dshukla@uic.edu Soluble 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate can trigger herpes simplex
Journal of General Virology (2007), 88, 1075 1079 DOI 10.1099/vir.0.82476-0 Short Communication Correspondence Deepak Shukla dshukla@uic.edu Soluble 3-O-sulfated heparan sulfate can trigger herpes simplex
Herpes Simplex Virus with Highly Reduced gd Levels Can Efficiently Enter and Spread between Human Keratinocytes
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2001, p. 10309 10318 Vol. 75, No. 21 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.21.10309 10318.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2001, p. 10309 10318 Vol. 75, No. 21 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.21.10309 10318.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes
Received 23 January 2001/Accepted 18 March 2001
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2001, p. 5684 5691 Vol. 75, No. 12 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5684 5691.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Novel, Soluble
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, June 2001, p. 5684 5691 Vol. 75, No. 12 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.12.5684 5691.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Novel, Soluble
Herpesvirus Entry Mediator HVEM Mediates Cell-Cell Spread in BHK(TK ) Cell Clones
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 1998, p. 1411 1417 Vol. 72, No. 2 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Herpesvirus Entry Mediator HVEM Mediates Cell-Cell Spread in BHK(TK )
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 1998, p. 1411 1417 Vol. 72, No. 2 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology Herpesvirus Entry Mediator HVEM Mediates Cell-Cell Spread in BHK(TK )
Roles for Endocytosis and Low ph in Herpes Simplex Virus Entry into HeLa and Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2003, p. 5324 5332 Vol. 77, No. 9 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.9.5324 5332.2003 Roles for Endocytosis and Low ph in Herpes Simplex Virus Entry into HeLa and Chinese
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2003, p. 5324 5332 Vol. 77, No. 9 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.9.5324 5332.2003 Roles for Endocytosis and Low ph in Herpes Simplex Virus Entry into HeLa and Chinese
Role of AF6 protein in cell-to-cell spread of Herpes simplex virus 1
 Role of AF6 protein in cell-to-cell spread of Herpes simplex virus 1 Johanna Keyser 1,2, Mihaela Lorger 2,3, Jovan Pavlovic, Gerald Radziwill, Karin Moelling * Institute of Medical Virology, University
Role of AF6 protein in cell-to-cell spread of Herpes simplex virus 1 Johanna Keyser 1,2, Mihaela Lorger 2,3, Jovan Pavlovic, Gerald Radziwill, Karin Moelling * Institute of Medical Virology, University
The soluble ectodomain of herpes simplex virus gd contains a membrane-proximal pro-fusion domain and suffices to mediate virus entry
 The soluble ectodomain of herpes simplex virus gd contains a membrane-proximal pro-fusion domain and suffices to mediate virus entry Francesca Cocchi*, Daniela Fusco*, Laura Menotti*, Tatiana Gianni*,
The soluble ectodomain of herpes simplex virus gd contains a membrane-proximal pro-fusion domain and suffices to mediate virus entry Francesca Cocchi*, Daniela Fusco*, Laura Menotti*, Tatiana Gianni*,
Qing Fan, 1 Erick Lin, 1 Takeshi Satoh, 2 Hisashi Arase, 2 and Patricia G. Spear 1 *
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2009, p. 7384 7390 Vol. 83, No. 15 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00087-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Differential Effects
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Aug. 2009, p. 7384 7390 Vol. 83, No. 15 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00087-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Differential Effects
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
HIV-Associated Disruption of Tight and Adherens Junctions of Oral Epithelial Cells Facilitates HSV-1 Infection and Spread
 HIV-Associated Disruption of Tight and Adherens Junctions of Oral Epithelial Cells Facilitates HSV-1 Infection and Spread Irna Sufiawati 1, Sharof M. Tugizov 1,2 * 1 Department of Medicine, University
HIV-Associated Disruption of Tight and Adherens Junctions of Oral Epithelial Cells Facilitates HSV-1 Infection and Spread Irna Sufiawati 1, Sharof M. Tugizov 1,2 * 1 Department of Medicine, University
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Generation of HVEM-restricted HSV-1 mutant viruses: Resistance of. HVEM-expressing cells and identification of mutations that rescue nectin-1
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 January 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01449-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 7 January 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01449-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 1998, p Vol. 72, No. 10. Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 1998, p. 8374 8379 Vol. 72, No. 10 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell Surface Proteoglycans Are Necessary for A27L
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 1998, p. 8374 8379 Vol. 72, No. 10 0022-538X/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Cell Surface Proteoglycans Are Necessary for A27L
Received 7 August 2003/Accepted 24 January 2004
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2004, p. 4720 4729 Vol. 78, No. 9 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.9.4720 4729.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Herpes
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 2004, p. 4720 4729 Vol. 78, No. 9 0022-538X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.9.4720 4729.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. The Herpes
Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies
 Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies DC-SIGN (DC Specific, ICAM-3 Grabbing, Nonintegrin) / CD209 and L-SIGN (liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin CD299/ DC-SIGNR (DC-SIGN-related
Anti-DC-SIGN/CD209 murine monoclonal antibodies DC-SIGN (DC Specific, ICAM-3 Grabbing, Nonintegrin) / CD209 and L-SIGN (liver/lymph node-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin CD299/ DC-SIGNR (DC-SIGN-related
Members of 3-O-Sulfotransferases (3-OST) Family: A Valuable Tool from Zebrafish to Humans for Understanding Herpes Simplex Virus Entry
 Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Virology Journal, 2013, 7, 5-11 5 Open Access Members of 3-O-Sulfotransferases (3-OST) Family: A Valuable Tool from Zebrafish to Humans for Understanding
Send Orders of Reprints at bspsaif@emirates.net.ae The Open Virology Journal, 2013, 7, 5-11 5 Open Access Members of 3-O-Sulfotransferases (3-OST) Family: A Valuable Tool from Zebrafish to Humans for Understanding
Examination of herpesvirus entry glycoprotein interactions using proximity biotinylation
 Via Sapientiae: The Institutional Repository at DePaul University College of Science and Health Theses and Dissertations College of Science and Health 8-22-2014 Examination of herpesvirus entry glycoprotein
Via Sapientiae: The Institutional Repository at DePaul University College of Science and Health Theses and Dissertations College of Science and Health 8-22-2014 Examination of herpesvirus entry glycoprotein
Herpes Simplex Virus Entry Is Associated with Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cellular Proteins
 Virology 256, 220 227 (1999) Article ID viro.1999.9673, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Herpes Simplex Virus Entry Is Associated with Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cellular Proteins Lixin
Virology 256, 220 227 (1999) Article ID viro.1999.9673, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Herpes Simplex Virus Entry Is Associated with Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Cellular Proteins Lixin
Synapse Formation. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Received 10 July 2008/Accepted 30 December 2008
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2009, p. 2951 2961 Vol. 83, No. 7 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01449-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Generation of Herpesvirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2009, p. 2951 2961 Vol. 83, No. 7 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01449-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Generation of Herpesvirus
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells are highly sensitive to infection by herpes simplex virus-1 via herpesvirus-entry-mediator A
 (2000) 7, 1210 1216 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0969-7128/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/gt VIRAL TRANSFER TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ARTICLE Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells are highly sensitive
(2000) 7, 1210 1216 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0969-7128/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/gt VIRAL TRANSFER TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ARTICLE Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells are highly sensitive
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance
 Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
In Rat Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurons, Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Tegument Forms in the Cytoplasm of the Cell Body
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2002, p. 9934 9951 Vol. 76, No. 19 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.19.9934 9951.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Rat Dorsal
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Oct. 2002, p. 9934 9951 Vol. 76, No. 19 0022-538X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.76.19.9934 9951.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. In Rat Dorsal
Fusion between perinuclear virions and the outer nuclear membrane. requires the fusogenic activity of herpes simplex virus gb
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 September 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 September 2009 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.01397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Modified FGF4 Signal Peptide Inhibits Entry of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2001, p. 2634 2645 Vol. 75, No. 6 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.6.2634 2645.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Modified FGF4
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2001, p. 2634 2645 Vol. 75, No. 6 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.6.2634 2645.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Modified FGF4
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
JERG SCHMIDT, 1 VOLKER GERDTS, 1 JÖRG BEYER, 2 BARBARA G. KLUPP, 1
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2001, p. 10054 10064 Vol. 75, No. 21 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.21.10054 10064.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Glycoprotein
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2001, p. 10054 10064 Vol. 75, No. 21 0022-538X/01/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.21.10054 10064.2001 Copyright 2001, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins E and I Facilitate Neuron-to-Neuron Spread of Herpes Simplex Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1995, p. 7087 7098 Vol. 69, No. 11 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Glycoproteins E and I Facilitate Neuron-to-Neuron Spread of Herpes Simplex
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1995, p. 7087 7098 Vol. 69, No. 11 0022-538X/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Glycoproteins E and I Facilitate Neuron-to-Neuron Spread of Herpes Simplex
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
SHORT COMMUNICATION. Human Papillomavirus Type 11 E1 Ú E4 and L1 Proteins Colocalize in the Mouse Xenograft System at Multiple Time Points
 VIROLOGY 214, 259 263 (1995) SHORT COMMUNICATION Human Papillomavirus Type 11 E1 Ú E4 and L1 Proteins Colocalize in the Mouse Xenograft System at Multiple Time Points DARRON R. BROWN,*,,1 JANINE T. BRYAN,
VIROLOGY 214, 259 263 (1995) SHORT COMMUNICATION Human Papillomavirus Type 11 E1 Ú E4 and L1 Proteins Colocalize in the Mouse Xenograft System at Multiple Time Points DARRON R. BROWN,*,,1 JANINE T. BRYAN,
Structural Rearrangement within an Enveloped Virus upon Binding to the Host Cell
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 10429 10435 Vol. 82, No. 21 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01223-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structural Rearrangement
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 10429 10435 Vol. 82, No. 21 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01223-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Structural Rearrangement
Herpes simplex virus as a model vector system for gene therapy in renal disease
 Kidney International, Vol. 61, Syposium 1 (2002), pp. S3 S8 Herpes simplex virus as a model vector system for gene therapy in renal disease BETSY C. HEROLD, DANIEL MARCELLINO, GLENDIE MARCELIN, PATRICIA
Kidney International, Vol. 61, Syposium 1 (2002), pp. S3 S8 Herpes simplex virus as a model vector system for gene therapy in renal disease BETSY C. HEROLD, DANIEL MARCELLINO, GLENDIE MARCELIN, PATRICIA
Adam L. Vanarsdall, Marie C. Chase, and David C. Johnson*
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2011, p. 11638 11645 Vol. 85, No. 22 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.05659-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2011, p. 11638 11645 Vol. 85, No. 22 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.05659-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
Medical Virology Pathogenesis of viral infection
 Medical Virology Pathogenesis of viral infection Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Pathogenesis of viral infection Viral
Medical Virology Pathogenesis of viral infection Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Pathogenesis of viral infection Viral
Site-Specific Proteolytic Cleavage of the Amino Terminus of Herpes Simplex Virus Glycoprotein K on Virion Particles Inhibits Virus Entry
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 12910 12918 Vol. 85, No. 24 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.06268-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Site-Specific Proteolytic
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2011, p. 12910 12918 Vol. 85, No. 24 0022-538X/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/jvi.06268-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Site-Specific Proteolytic
Analysis of Epstein-Barr Virus Glycoprotein B Functional Domains via Linker Insertion Mutagenesis
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2009, p. 734 747 Vol. 83, No. 2 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01817-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of Epstein-Barr
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2009, p. 734 747 Vol. 83, No. 2 0022-538X/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01817-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Analysis of Epstein-Barr
BBS2711 Virology. Central Nervous System (CNS) Viruses. Dr Paul Young, Department of Microbiology & Parasitology.
 BBS2711 Virology Central Nervous System (CNS) Viruses Dr Paul Young, Department of Microbiology & Parasitology. p.young@mailbox.uq.edu.au Viruses of the CNS Many human pathogenic viruses are capable of
BBS2711 Virology Central Nervous System (CNS) Viruses Dr Paul Young, Department of Microbiology & Parasitology. p.young@mailbox.uq.edu.au Viruses of the CNS Many human pathogenic viruses are capable of
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Advances in gene encoding proteins of human herpesvirus 6
 2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 165 6 1, 2 1., 241000; 2., 210029 : 6 ( HHV-6) DNA, HHV-6 80 100, ( IE) DNA DNA HHV-6 : 6 ; ; Advances in gene encoding proteins
2009 9 4 3 Journal of Microbes and Infection, September 2009, Vol. 4, No. 3 165 6 1, 2 1., 241000; 2., 210029 : 6 ( HHV-6) DNA, HHV-6 80 100, ( IE) DNA DNA HHV-6 : 6 ; ; Advances in gene encoding proteins
Incorporation of CD4 into Virions by a Recombinant Herpes Simplex Virus
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 1993, p. 189-195 0022-538X/93/010189-07$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 67, No. 1 Incorporation of CD4 into Virions by a Recombinant Herpes Simplex
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 1993, p. 189-195 0022-538X/93/010189-07$02.00/0 Copyright X) 1993, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 67, No. 1 Incorporation of CD4 into Virions by a Recombinant Herpes Simplex
Downloaded by on April 28, 2018 https://pubs.acs.org Publication Date: April 24, 1984 doi: /bk
 1 Virus-Receptor Interactions BERNARD N. FIELDS Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Harvard Medical School, and Department of Medicine (Infectious Disease), Brigham and Women's Hospital,
1 Virus-Receptor Interactions BERNARD N. FIELDS Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, Harvard Medical School, and Department of Medicine (Infectious Disease), Brigham and Women's Hospital,
Human Cytomegalovirus Entry into Epithelial and Endothelial Cells Depends on Genes UL128 to UL150 and Occurs by Endocytosis and Low-pH Fusion
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2006, p. 710 722 Vol. 80, No. 2 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.2.710 722.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Jan. 2006, p. 710 722 Vol. 80, No. 2 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.2.710 722.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Alpha E- and Alpha N-catenin Expression in Dorsal Root
Kobe University Repository : Kernel タイトル Title 著者 Author(s) 掲載誌 巻号 ページ Citation 刊行日 Issue date 資源タイプ Resource Type 版区分 Resource Version 権利 Rights DOI Alpha E- and Alpha N-catenin Expression in Dorsal Root
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein E Is Required for Axonal Localization of Capsid, Tegument, and Membrane Glycoproteins
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2005, p. 13362 13372 Vol. 79, No. 21 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.21.13362 13372.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2005, p. 13362 13372 Vol. 79, No. 21 0022-538X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.79.21.13362 13372.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
 Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
HCMV gh/gl/ul interferes with virus entry into epithelial cells: Evidence for cell type-specific receptors
 HCMV gh/gl/ul128 131 interferes with virus entry into epithelial cells: Evidence for cell type-specific receptors Brent J. Ryckman*, Marie C. Chase, and David C. Johnson Department of Molecular Microbiology
HCMV gh/gl/ul128 131 interferes with virus entry into epithelial cells: Evidence for cell type-specific receptors Brent J. Ryckman*, Marie C. Chase, and David C. Johnson Department of Molecular Microbiology
Two Viral Kinases are Required for Sustained Long Distance Axon Transport of a Neuroinvasive Herpesvirus
 Traffic 2008; 9: 1458 1470 Blackwell Munksgaard # 2008 The Authors Journal compilation # 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00782.x Two Viral Kinases are Required for Sustained Long
Traffic 2008; 9: 1458 1470 Blackwell Munksgaard # 2008 The Authors Journal compilation # 2008 Blackwell Munksgaard doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00782.x Two Viral Kinases are Required for Sustained Long
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA
 THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF THE NEURON AND THE NEUROGLIA DEFINITION OF A NEURON Neuron is the name given to the nerve cell and all its processes. Neurons are excitable cells that are specialized for the reception
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Introduction to viruses. BIO 370 Ramos
 Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system
 Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Systems Neuroscience November 21, 2017 The autonomic nervous system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html How is the organization of the autonomic nervous
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Herpes Simplex Virus ge/gi and US9 Proteins Promote Transport of both Capsids and Virion Glycoproteins in Neuronal Axons
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 10613 10624 Vol. 82, No. 21 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01241-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex Virus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 2008, p. 10613 10624 Vol. 82, No. 21 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01241-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex Virus
Acute neurological syndromes
 Acute neurological syndromes Assoc.Prof. Murat Sayan Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Rutin PCR Lab. Sorumlu Öğt.Üyesi Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi, DESAM Kurucu Öğrt. Üyesi sayanmurat@hotmail.com 0533 6479020 Medical
Acute neurological syndromes Assoc.Prof. Murat Sayan Kocaeli Üniversitesi, Rutin PCR Lab. Sorumlu Öğt.Üyesi Yakın Doğu Üniversitesi, DESAM Kurucu Öğrt. Üyesi sayanmurat@hotmail.com 0533 6479020 Medical
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/4/117/117ra8/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Notch4 Normalization Reduces Blood Vessel Size in Arteriovenous Malformations Patrick A. Murphy, Tyson
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoproteins gb and gh/gl Mediate Epithelial Cell-Cell Fusion When Expressed either in cis or in trans
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2008, p. 11837 11850 Vol. 82, No. 23 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01623-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Dec. 2008, p. 11837 11850 Vol. 82, No. 23 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.01623-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Human Cytomegalovirus
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Supplemental Figure 1 A S100A4: SFLGKRTDEAAFQKLMSNLDSNRDNEVDFQEYCVFLSCIAMMCNEFFEGFPDK Overlap: SF G DE KLM LD N D VDFQEY VFL I M N FF G PD S100A2: SFVGEKVDEEGLKKLMGSLDENSDQQVDFQEYAVFLALITVMCNDFFQGCPDR
Chapter 25. 바이러스 (The Viruses)
 Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
A Role for Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein E in Induction of Cell Fusion
 J. gen. Virol. (1989), 70, 2157-2162. Printed in Great Britain 2157 Key words: HS V-1/glycoprotein E/fusion A Role for Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein E in Induction of Cell Fusion By S. CHATTERJEE,*
J. gen. Virol. (1989), 70, 2157-2162. Printed in Great Britain 2157 Key words: HS V-1/glycoprotein E/fusion A Role for Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Glycoprotein E in Induction of Cell Fusion By S. CHATTERJEE,*
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of Crb3 in mouse sciatic nerve: biochemical analysis (a) Schematic of Crb3 isoforms, ERLI and CLPI, indicating the location of the transmembrane (TM), FRM binding (FB)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction
 Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction (slides 16, 17 and 18 have been slightly modified for clarity) MCP Lecture 2-3 9.013/7.68 04 Neuromuscular Junction Development 1. Muscle
Activity Dependent Changes At the Developing Neuromuscular Junction (slides 16, 17 and 18 have been slightly modified for clarity) MCP Lecture 2-3 9.013/7.68 04 Neuromuscular Junction Development 1. Muscle
Role of Filopodia in HSV-1 Entry into Zebrafish 3-O-Sulfotransferase-3- Expressing Cells
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Virology Journal, 2013, 7, 41-48 41 Open Access Role of Filopodia in HSV-1 Entry into Zebrafish 3-O-Sulfotransferase-3- Expressing Cells
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Virology Journal, 2013, 7, 41-48 41 Open Access Role of Filopodia in HSV-1 Entry into Zebrafish 3-O-Sulfotransferase-3- Expressing Cells
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1
 Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) 2018 450 MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1 Learning Outcomes The pathogenesis of viral infection The viral disease pattern Specific
Lab 3: Pathogenesis of Virus Infections & Pattern 450 MIC PRACTICAL PART SECTION (30397) 2018 450 MIC AMAL ALGHAMDI 1 Learning Outcomes The pathogenesis of viral infection The viral disease pattern Specific
ab E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit
 ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementary figure 1 (A) Quantitative analysis of F-actin signal intensity in NIH3T3 cells treated with PTD4-myc- RBD. NIH3T3 cells were treated with PTD4-myc-RBD as described. Please note the increase
Supplementary figure 1 (A) Quantitative analysis of F-actin signal intensity in NIH3T3 cells treated with PTD4-myc- RBD. NIH3T3 cells were treated with PTD4-myc-RBD as described. Please note the increase
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Product Datasheet. CD133 Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg
 Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Molecular Biology of Pseudorabies Virus: Impact on Neurovirology and Veterinary Medicine
 MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Sept. 2005, p. 462 500 Vol. 69, No. 3 1092-2172/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.69.3.462 500.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
MICROBIOLOGY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY REVIEWS, Sept. 2005, p. 462 500 Vol. 69, No. 3 1092-2172/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/mmbr.69.3.462 500.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Susceptibility of human iris stromal cells to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) entry
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 January 2013 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.03235-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 Susceptibility of human
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 23 January 2013 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.03235-12 Copyright 2013, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 Susceptibility of human
LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role in Alzheimer s disease
 Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
Brodeur et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2012, 7:31 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access LDLR-related protein 10 (LRP10) regulates amyloid precursor protein (APP) trafficking and processing: evidence for a role
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system)
 Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Nervous system Overview ( The master communication system) Neuron process Cell body nucleus Neuroglia Nerve Tissue COMPOSITION OF NERVE TISSUE Two principal types of cells, neurons and supporting cells
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Latency
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2003, p. 79 95 Vol. 16, No. 1 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.1.79 95.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Jan. 2003, p. 79 95 Vol. 16, No. 1 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.1.79 95.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Herpes Simplex
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Identification of Functional Domains in Herpes Simplex Virus 2 Glycoprotein B
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 3792 3800 Vol. 80, No. 8 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.8.3792 3800.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 3792 3800 Vol. 80, No. 8 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.8.3792 3800.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
HSV-1 gm and the gk/pul20 Complex Are Important for the Localization of gd and gh/l to Viral Assembly Sites
 Viruses 2015, 7, 915-938; doi:10.3390/v7030915 Article OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses HSV-1 gm and the gk/pul20 Complex Are Important for the Localization of gd and gh/l
Viruses 2015, 7, 915-938; doi:10.3390/v7030915 Article OPEN ACCESS viruses ISSN 1999-4915 www.mdpi.com/journal/viruses HSV-1 gm and the gk/pul20 Complex Are Important for the Localization of gd and gh/l
