Acute necrotizing pneumonia combined with parapneumonic effusion caused by Mycobacterium lentiflavum: a case report
|
|
|
- Muriel Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lee et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2015) 15:354 DOI /s z CASE REPORT Open Access Acute necrotizing pneumonia combined with parapneumonic effusion caused by Mycobacterium lentiflavum: a case report Yong Chul Lee *, Seung Bum Kim, Su Jin Gang, Seung Yong Park and So Ri Kim * Abstract Background: Mycobacterium lentiflavum (M. lentiflavum), a slow growing nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM), has recently been described as an emerging human pathogen regardless of the immune status of the host. Previous reports have demonstrated that cervical lymphadenitis of children is the most frequent pathology of M. lentiflavum. However, there are little reports regarding pulmonary diseases by M. lentiflavum specifically in immunocompetent patients. Case presentation: A 60-year-old man having prolonged productive cough and dyspnea with fever was initially diagnosed as pneumonia with parapneumonic effusion. Imaging studies showed that the radiologic abnormality was acute bronchopneumonic infiltration with abscess formation in the left lower lobe and parapneumonic pleural effusion. M. lentiflavum was identified in the cultured pleural tissues. On the basis of these findings, he was diagnosed as pulmonary infection and pleurisy caused by M. lentiflavum, which was treated with a combination of antibiotics covering NTM. His clinical manifestations were dramatically improved by the treatment targeting NTM, while those were refractory to empirical antibiotic therapy. Conclusion: In this report, we introduce the isolation of M. lentiflavum from pleural tissues associated with acute necrotizing pneumonia combined with parapneumonic effusion in an immunocompetent host, suggesting that the M. lentiflavum can be a human pathogen invovled in pulmonary infectious diseases and pleurisy with poor response to empirical antibiotic treatment. Keywords: Mycobacterium lentiflavum, Nontuberculous mycobacterium, Pleural effusion, Necrotizing pneumonia Background Mycobacterium lentiflavum (M. lentiflavum), one of slowly growing nontuberculous mycobacterium (NTM), was first identified in 1996 as a distinct strain [1]. This strain is characterized by slow growth of tiny yellow colonies and has biochemical characteristics identical to the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). In addition, mycolic acid and fatty acid chromatography patterns are very similar to those of Mycobacterium simiae [1]. Thus, the identification of M. lentiflavum is usually confirmed * Correspondence: leeyc@jbnu.ac.kr; sori@jbnu.ac.kr Equal contributors Department of Internal Medicine, Research Center for Pulmonary Disorders, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, South Korea through genetic analysis. Because like other NTM, M. lentiflavum is often isolated fortuitously, the clinical significance must be carefully considered. Recently several cases of human diseases caused by M. lentiflavum have been reported, including cervical lymphadenitis, fatal disseminated infection, ascites, soft tissue, liver abscess, and pulmonary infection in immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients [2 12]. However, there are few reports on M. lentiflavum as a cause of pulmonary disease and to date it has rarely been described in immunocompetent patients. Herein,wepresentacaseofacutenecrotizingpneumonia combined with parapneumonic effusion caused by M. lentiflavum in an immunocompetent patient Lee et al. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
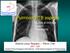
2 Lee et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2015) 15:354 Case presentation A 60-year-old man was admitted to our hospital with fever, chills, productive cough, and dyspnea for last two weeks, which had exacerbated for preceding three days despite taking oral antibiotics for about 10 days. Since he had been diagnosed to have bronchial asthma three years ago, he had taken the combined inhaled medicine of corticosteroid and a long-acting β2 agonist. However, he had no previous history of structural lung diseases including pulmonary tuberculosis and immunocompromised disorders such as HIV infection. He was an ex-smoker with 20 pack/year smoking history and his occupation was a farmer. On physical examination, inspiratory crackles were heard mainly on Page 2 of 5 the left middle and lower lung fields. Chest radiography showed pulmonary consolidation with air bronchogram in the left lower lobe, which also showed fluid shifting sign (Fig. 1a and b). Chest computed tomography (CT) scan revealed bronchopneumonic infiltration with abscess formation in the left lower lobe, accompanying left pleural effusion (Fig. 1c and d). Bacteriologic examinations including Gram stain with sputum, pleural fluids, and bronchial washing fluids revealed no definitive causative organisms. Pleural tissues were also obtained through needle biopsy, in which the acute suppurative pleural inflammatory reaction was found and some tissues were cultured to examine any bacterial or fungal growth. As a result, there was no Fig. 1 Chest X-ray and chest computed tomography (CT) findings in M. lentiflavum-infected patient. Chest Radiography (a; posteroanterior view, b; left decubitus view) shows consolidative lesion in the left lower lobe with fluid shifting sign. Chest CT scan revealed that solid consolidative lesion occupied the left lower lobe with air-bronchogram (c and d). Despite of the antibiotics therapy, the radiologic features were aggravated showing abscess formation in the left lower lobe, accompanying left pleural effusion and newly developed pneumonic infiltrative lesion on the right middle lobe (e and f)
3 Lee et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2015) 15:354 Page 3 of 5 evidence of growth of bacteria or fungi for seven days they had been cultured. Firstly, levofloxacin was prescribed as a single intravenous regimen. Up to hospital day 3, however, his clinical manifestation did not respond to the antibiotic therapy and even worsened (Fig. 1e and f). We decided to change the antibiotic regimen to aztreonam and metronidazole as a combination regimen. On hospital day 7, his symptoms including fever started to be resolved and then followed by radiologic improvement on chest radiography. After his discharge, we got a final bacteriologic report describing that M. lentiflavum was isolated from pleural specimen biopsied. The antibiotic regimen covering NTM (etambutol, ciprofloxacin, rifabutin, and clarithromycin) was prescribed to him in out-patient department, and his remnant lesions kept being improved (Fig. 2a-c), showing bronchiectasis and multiple smaller nodules of a tree-in-bud pattern in the left lingular segment and the left lower lobe (Fig. 2d and e). Discussion In 1959, Runyon proposed the first classification system of mycobacteria in which, based on growth rates, colony morphology, and pigmentation in the presence and absence of light, mycobacteria were divided into four groups of human pathogens; M. tuberculosis complex, M. leprae, slowly growing NTM, and rapidly growing NTM [13]. The NTM are usually acquired from environmental sources such as surface water, tap water, soil, domestic and wild animals, milk, and food products. Though most species are less pathogenic or sporadic, they can, in broad terms, induce four distinct clinical syndromes [14]; 1) Progressive pulmonary disease, especially in older persons with or without underlying lung disease. 2) Superficial lymphadenitis, especially cervical lymphadenitis. 3) Disseminated disease in severely immunocompromised patients. 4) Skin and soft tissue infection usually as a consequence of direct inoculation. Recently, with the availability of 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing and high-performance liquid chromatography, and polymerase chain reaction-restriction length polymorphism analysis, the number of new species of NTM including M. lentiflavum has risen dramatically [14, 15]. In fact, M. lentiflavum, one of slowly growing NTM, was first identified in a cluster of 22 isolates [1]. Among them, only one isolate from a vertebral disk in an elderly patient suffering from spondilodiscitis was clinically significant. Since then, several cases of isolates from cervical lymphadenitis of very young children have been reported [2 8]. Other infected sites including pulmonary infection are less frequent [1, 4, 6 12]. Typically, pulmonary disease by NTM is characterized as chronic progressive infectious one which develops both in healthy persons and in those with underlying pulmonary disorders or immunosuppressive conditions. The clinical features may resemble slowly progressive pulmonary tuberculosis, which is often the initial diagnosis in patients with positive results on acid fast bacilli (AFB) staining. Radiologic manifestations of pulmonary infection with NTM are various, to some degree, non-specific including the formation of solitary or multiple nodules, chronic pneumonitis, Fig. 2 Serial chest imaging findings in M. lentiflavum-infected patient. At 12 month follow-up, chest imaging studies revealed that the previous lesions in both lungs were improved remarkably (a-c). In addition, serial chest CT scans showed the distinct bronchiectasis and multiple small nodular lesions with a tree-in-bud pattern were scattered in the left lingular segment and the left lower lobe (d and e)
4 Lee et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2015) 15:354 Page 4 of 5 bronchiectasis, cavitary formation, or a combination of these features. Altogether, the diagnosis of pulmonary infection with NTM is extremely difficult due to several factors involved; these are various clinical and radiologic manifestations, the frequent presence of significant prior pulmonary disease, and harmless colonization of NTM in the lower respiratory tracts. According to American Thoracic Society (ATS)/ Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines, the diagnosis should be based on specific, validated criteria that emphasize a compatible clinical syndrome, characteristic findings on chest X-ray or CT, and repeated isolation of NTM from the sputum or growth of NTM from a lung biopsy [16]. Thus, in cases with these typical radiologic findings but with negative results of routine sputum cultures for mycobacteria, physicians have been subsequently recommended to perform bronchoscopy and transbronchial biopsy. To our knowledge, this report is the first case of acute necrotizing pneumonia with pleurisy by M. lentiflavum in an immunocompetent patient without underlying pulmonary structural disorders. In our case, a 60-year-old man having prolonged productive cough and dyspnea with fever was initially diagnosed as pneumonia with parapneumonic effusion. Imaging studies showed that the radiologic abnormality was acute bronchopneumonic infiltration with abscess formation in the left lower lobe and parapneumonic pleural effusion. Bacteriologic examinations with sputum, pleural fluids, and bronchial washing fluids, however, revealed no definitive causative organisms. Fortunately, we could confirm that the etiologic organism was M. lentiflavum found in the cultured pleural tissues, although there is still a possibility of co-infection with other bacteria such as anaerobes because it is difficult to culture or isolate anaerobes in several respiratory samples and the patient was pre-treated with the antibiotics that would have negated bacterial cultures or have activity against co-infected bacteria. On the basis of these findings, he was diagnosed as pulmonary infection and pleurisy caused by M. Lentiflavum as at least one of etiological pathogens, which was treated with a combination of antibiotics covering NTM. Conclusions In light of general information of NTM, this case report describes several interesting points as follows; the acute progress of NTM pulmonary diseases, pleural disease by NTM infection, and occurence of pulmonary infection by M. lentiflavum in immunocompetent subject. Thus, we suggest that clinicians should consider the M. lentiflavum as a human pathogen invovled in lung and pleura regardless of immune status. In addition, M. lentiflavum can be an infectious cause of acute pulmonary disease as well as chronic pulmonary disease. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report. Copies of the written consents are available for review by the editor of this journal. Abbreviations MAC: Mycobacterium avium complex; NTM: Nontuberculous mycobacterium. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions YCL and SRK designed the study. YCL and SRK drafted the manuscript. YCL, SRK, SBK, and SYP contributed to the diagnosis and treatment. SBK contributed to the analysis and identification of M. lentiflavum. SJG reviewed and edited the manuscript. YCL and SRK reviewed and supervised the manuscript. All the authors approved the final version of the manuscript. Acknowledgments We thank Professor Mie-Jae Im (Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, South Korea) for critical readings of the manuscript. This study was supported by the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant A121931), by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and future Planning (NRF- 2014R1A2A1A ), and by the fund of Biomedical Research Institute, Chonbuk National University Hospital. Received: 20 January 2015 Accepted: 10 August 2015 References 1. Springer B, Wu WK, Bodmer T, Haase G, Pfyffer GE, Kroppenstedt RM, et al. Isolation and characterization of a unique group of slowly growing mycobacteria: description of Mycobacterium lentiflavum sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34: Cabria F, Torres MV, Garcia-Cia JI, Dominguez-Garrido MN, Esteban J, Jimenez MS. Cervical lymphadenitis caused by Mycobacterium lentiflavum. Pediatr Infect Dis. 2002;21: Haase G, Kentrup H, Skopnik H, Springer B, Böttger C. Mycobacterium lentiflavum: an etiological agent of cervical lymphadenitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25: Tortoli E, Bartoloni A, Erba ML, Levrè E, Lombardi N, Mantella A, et al. Human infections due to Mycobacterium lentiflavum. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;40: Uria MJ, Garcia J, Menendez JJ, Jimenez MS. Mycobacterium lentiflavum infection: case history and review of the medical literature. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2003;21: Ibanez R, Serrano-Heranz R, Jimenez-Palop M, Roman C, Corteguera M, Jimenez S. Disseminated infection caused by slowgrowing Mycobacterium lentiflavum. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002;21: Niobe SN, Bebear CM, Clerc M, Pellegrin JL, Bebear C, Maugein J. Disseminated Mycobacterium lentiflavum infection in a human immunodeficiency virus-infected patient. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39: Galarraga MC, Torreblanca A, Jimenez MS. Isolation of Mycobacterium lentiflavum in a case of suspected lung cancer. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2002;20: Molteni C, Gazzola L, Cesari M, Lombardi A, Salerno F, Tortoli E, et al. Mycobacterium lentiflavum infection in immunocompetent patient. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11: Tortoli E, Mattei R, Russo C, Scarparo C. Mycobacterium lentiflavum, an emerging pathogen? J Infect. 2006;52: Shin S, Yoon JH, Song SH, Kim EC. Isolation of Mycobacterium lentiflavum from a patient with a lung destroyed by tuberculosis. Korean J Lab Med. 2007;27: Shamaei M, Marjani M, Farnia P, Tabarsi P, Mansouri D. Human infections due to Mycobacterium lentiflavum; first report in Iran. IRAN J Microbiol. 2010;2:29 31.
5 Lee et al. BMC Infectious Diseases (2015) 15:354 Page 5 of Runyon EH. Anonymous mycobacteria in pulmonary disease. Med Clin North Am. 1959;43: Wolinsky E. Nontuberculous mycobacteria and associated diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979;119: Brown-Elliott BA, Griffith DE, Wallace Jr RJ. Newly described or emerging human species of nontuverculous mycobacteria. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2002;16: Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliott BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, et al. ATS Mycobacterial Diseases Subcommittee; American Thoracic Society; Infectious Disease Society of America. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 28 4, 373 377, December 2016 Case Report Clarithromycin-resistant Mycobacterium Shinjukuense Lung Disease: Case Report and Literature Review Makoto HAYASHI 1, Satoshi MATSUKURA 1,
Implication of species change of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria during or after treatment
 Lee et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:213 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0539-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Implication of species change of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria during or after Jong Sik Lee 1, Jong
Lee et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:213 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0539-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Implication of species change of Nontuberculous Mycobacteria during or after Jong Sik Lee 1, Jong
2018 Vindico Medical Education. Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria: Circumventing Difficulties in Diagnosis and Treatment
 Activity presentations are considered intellectual property. These slides may not be published or posted online without permission from Vindico Medical Education (cme@vindicocme.com). Please be respectful
Activity presentations are considered intellectual property. These slides may not be published or posted online without permission from Vindico Medical Education (cme@vindicocme.com). Please be respectful
Disseminated Mycobacterium lentiflavum in a heart-transplanted man responsible for. hemophagocytic lymphohistocytosis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 May 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00758-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Disseminated Mycobacterium
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 28 May 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00758-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Disseminated Mycobacterium
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
 Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis
 Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Diagnostic Evaluation of NTM and Bronchiectasis Ashwin Basavaraj, MD, FCCP NTM patient education program November 9, 2016 Involves a combination
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated during the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
 Respiratory Medicine (2009) 103, 1936e1940 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated during the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
Respiratory Medicine (2009) 103, 1936e1940 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed Nontuberculous mycobacteria isolated during the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
ACCME/Disclosures. Two Patients and a Caveat 4/13/2016. Patient #1: 13 y/o boy with IPEX syndrome; s/p BMT
 Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
DOWNLOAD OR READ : NONTUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIA NTM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : NONTUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIA NTM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm pdf nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm patients and those
DOWNLOAD OR READ : NONTUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIA NTM PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm pdf nontuberculous mycobacteria ntm patients and those
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM)
 Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) Bacteria, like plants and animals, have been classified into similar groups. The groups are called "families." One such family of bacteria is known as the Mycobacteriaceae.
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) Bacteria, like plants and animals, have been classified into similar groups. The groups are called "families." One such family of bacteria is known as the Mycobacteriaceae.
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Research Article Computed Tomography Findings of Pulmonary Mycobacterium simiae Infection
 Hindawi Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2017, Article ID 6913564, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6913564 Research Article Computed Tomography Findings of Pulmonary Mycobacterium simiae Infection
Hindawi Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2017, Article ID 6913564, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6913564 Research Article Computed Tomography Findings of Pulmonary Mycobacterium simiae Infection
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Mycobacterium szulgai: a rare pathogen. Description of the first pulmonary case reported in Argentina ACCEPTED
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00148-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 27 June 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00148-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Standardized Case Definition for Extrapulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections
 Operational Guidance for Position Statement 17 ID 07: Standardized Case Definition for Extrapulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections Submission Date: April 28, 2017 Committee: Infectious Disease
Operational Guidance for Position Statement 17 ID 07: Standardized Case Definition for Extrapulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections Submission Date: April 28, 2017 Committee: Infectious Disease
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease in a Patient with Kartagener Syndrome
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.3.136 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:136-140 Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease in a Patient with Kartagener Syndrome
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.3.136 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:136-140 Mycobacterium abscessus Lung Disease in a Patient with Kartagener Syndrome
Bilateral multiple choroidal granulomas and systemic vasculitis as presenting features of tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
 Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Kumar et al. Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection (2016) 6:40 DOI 10.1186/s12348-016-0109-9 Journal of Ophthalmic Inflammation and Infection BRIEF REPORT Open Access Bilateral multiple choroidal
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Slowly Growing Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections
 Slowly Growing Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections Charles L. Daley, MD National Jewish Health University of Colorado, Denver Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero
Slowly Growing Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections Charles L. Daley, MD National Jewish Health University of Colorado, Denver Disclosures Advisory Board Horizon, Johnson and Johnson, Otsuka and Spero
Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2010; 44: 56-62 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.56 Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Hye-Jong Song Jung Suk
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2010; 44: 56-62 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2010.44.1.56 Pathologic Findings of Surgically Resected Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Hye-Jong Song Jung Suk
MYCOBACTERIA. Pulmonary T.B. (infect bird)
 MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
MYCOBACTERIA SPP. Reservoir Clinical Manifestation Mycobacterium tuberculosis Human Pulmonary and dissem. T.B. M. lepra Human Leprosy M. bovis Human & cattle T.B. like infection M. avium Soil, water, birds,
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/cystic-fibrosis-in-focus/nontuberculous-mycobacteria-ntm-in-patientswith-cystic-fibrosis/8337/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/cystic-fibrosis-in-focus/nontuberculous-mycobacteria-ntm-in-patientswith-cystic-fibrosis/8337/
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Philippine General Hospital
 Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Ryo Takahashi 1,2,3, Taiki Fujiwara 1,2, Hisami Yamakawa 1,2. Introduction
 Case Report Completion pneumonectomy after fenestration for empyema due to nontuberculous mycobacteriosis associated with destroyed lung as a result of cancer surgery Ryo Takahashi 1,2,3, Taiki Fujiwara
Case Report Completion pneumonectomy after fenestration for empyema due to nontuberculous mycobacteriosis associated with destroyed lung as a result of cancer surgery Ryo Takahashi 1,2,3, Taiki Fujiwara
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
Tuberculosis. Impact of TB. Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH)
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS
 CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
CHAPTER 3: DEFINITION OF TERMS NOTE: TB bacteria is used in place of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in most of the definitions presented here. 3.1 Acid-fast bacteria
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Appendix C. Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997)
 Appendix C Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Appendix C Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Isolation of non-tuberculous mycobacteria at three rural settings in Zambia; a pilot study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Isolation of non-tuberculous mycobacteria at three rural settings in Zambia; a pilot study P. C. A. M. Buijtels 1,2, M. A. B. van der Sande 3, S. Parkinson 4, H. A. Verbrugh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE BACTERIOLOGY Isolation of non-tuberculous mycobacteria at three rural settings in Zambia; a pilot study P. C. A. M. Buijtels 1,2, M. A. B. van der Sande 3, S. Parkinson 4, H. A. Verbrugh
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Case Report Pulmonary Nocardiosis in the Immunocompetent Host: Case Series
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2015, Article ID 314831, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/314831 Case Report Pulmonary Nocardiosis in the Immunocompetent Host: Case
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2015, Article ID 314831, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/314831 Case Report Pulmonary Nocardiosis in the Immunocompetent Host: Case
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining
 Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Cardiovascular Center Grand Rounds. December 15, 2016
 Cardiovascular Center Grand Rounds December 15, 2016 Agenda Overview of Heater-Cooler Device Issue NTM Infection Incidence Chronology of Events and Communications Risk Management Implications Q&A NTM Grand
Cardiovascular Center Grand Rounds December 15, 2016 Agenda Overview of Heater-Cooler Device Issue NTM Infection Incidence Chronology of Events and Communications Risk Management Implications Q&A NTM Grand
Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection Presenting as an Endobronchial Mass in a Patient with Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
 The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:215-219, 2007 Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection Presenting as an Endobronchial Mass in a Patient with Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Ho Cheol Kim,
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine : 22:215-219, 2007 Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection Presenting as an Endobronchial Mass in a Patient with Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Ho Cheol Kim,
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference
 Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas December 1-3, 2010 TB Pathogenesis and Transmission Lynn Horvath, MD; TCID December 1, 2010 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn L. Horvath, MD, FACP, FIDSA Associate Professor
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case Report of Serial Computed Tomographic Findings in a Young Male Patient
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Diseases
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Diseases Jae Joon Yim, M.D. Sung Koo Han, M.D. Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National
Diagnosis and Treatment of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Diseases Jae Joon Yim, M.D. Sung Koo Han, M.D. Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Department of Internal Medicine Seoul National
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease in Korea
 REVIEW http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.1.1 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:1-5 Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
REVIEW http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.77.1.1 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;77:1-5 Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE:
 HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE: MYCOBACTERIUM ON THE ROUTINE BENCH Christina Partington MT(ASCP) ACL Laboratory 1 Introduction The importance of the possibility of AFB appearing in a routine culture. How to recognize
HIDDEN IN PLAIN SITE: MYCOBACTERIUM ON THE ROUTINE BENCH Christina Partington MT(ASCP) ACL Laboratory 1 Introduction The importance of the possibility of AFB appearing in a routine culture. How to recognize
Communicable Disease Control Manual Chapter 4: Tuberculosis
 Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Provincial TB Services 655 West 12th Avenue Vancouver, BC V5Z 4R4 www.bccdc.ca Communicable Disease Control Manual Definitions Page 1 2.0 DEFINITIONS Many of the definitions that follow are taken from
Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Atypical Pleural Fluid Profiles in Tuberculous Pleural Effusion: Sequential Changes Compared with Parapneumonic and Malignant Pleural Effusions Chang Ho Kim, So Yeon Lee, Yong Dae Lee,
Refractory Bacteremia and Osteomyelitis Resulting in Fatal. Bacteremic Pneumonia with Multiorgan Failure Caused by
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 September 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00627-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 September 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00627-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Critical Care Nursing Theory. Pneumonia. - Pneumonia is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma
 - is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
- is an acute infection of the pulmonary parenchyma - is a common infection encountered by critical care nurses when it complicates the course of a serious illness or leads to acute respiratory distress.
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis
 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011
 Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Diagnosis of TB Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberculosis, 2011 Alfred Lardizabal, MD NJMS Global Tuberculosis Institute Diagnosis of TB, 2011 Diagnosis follows Suspicion When should we Think TB? Who is
Bacterial pneumonia with associated pleural empyema pleural effusion
 EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell lymphocyte proliferative disease
 Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
 Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Epidemiology and Clinical Management Kevin L. Winthrop, MD, MPH Associate Professor, Divisions of Infectious Diseases, Public Health and Preventive Medicine Oregon Health &
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Epidemiology and Clinical Management Kevin L. Winthrop, MD, MPH Associate Professor, Divisions of Infectious Diseases, Public Health and Preventive Medicine Oregon Health &
Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis
 Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis Amit S. Chitnis, MD, MPH; Pennan M. Barry, MD, MPH; Jennifer M. Flood, MD, MPH. California Tuberculosis Controllers
Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis Amit S. Chitnis, MD, MPH; Pennan M. Barry, MD, MPH; Jennifer M. Flood, MD, MPH. California Tuberculosis Controllers
Consolidations in Nodular Bronchiectatic Mycobacterium Avium Complex Lung Disease: Mycobacterium Avium Complex or Other Infection?
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.546 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):546-551, 2010 Consolidations in Nodular Bronchiectatic Mycobacterium Avium Complex Lung Disease: Mycobacterium
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.546 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):546-551, 2010 Consolidations in Nodular Bronchiectatic Mycobacterium Avium Complex Lung Disease: Mycobacterium
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease. Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015
 Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Diagnosis & Medical Case Management of TB Disease Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD October 22, 2015 Comprehensive Care of Patients with Tuberculosis and Their Contacts October 19 22, 2015 Wichita, KS EXCELLENCE
Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation
 Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
Original Article Different characteristics of tuberculous pleural effusion according to pleural fluid cellular predominance and loculation Jaehee Lee 1, Jae Kwang Lim 2, Seung Soo Yoo 1, Shin Yup Lee 1,
Pulmonary TB aspects
 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Appendix B. Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997)
 Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
Appendix B Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases (Revised July 1997) Since publication of the Recommendations for Counting Reported Tuberculosis Cases 1 in January 1977, numerous changes
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012
 TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 Nontuberculosis Mycobacterial Lung Disease David Griffith, MD August 8, 2012 David Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
TB Intensive San Antonio, Texas August 7-10, 2012 Nontuberculosis Mycobacterial Lung Disease David Griffith, MD August 8, 2012 David Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests
PNEUMONIA. I. Background 6 th most common cause of death in U.S. Most common cause of infection related mortality
 Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium simiae in Iran s national referral center for tuberculosis
 Original Article Pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium simiae in Iran s national referral center for tuberculosis Parvaneh Baghaei 1, Payam Tabarsi 1, Parissa Farnia 2, Majid Marjani 1, Fatemeh-Maryam
Original Article Pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium simiae in Iran s national referral center for tuberculosis Parvaneh Baghaei 1, Payam Tabarsi 1, Parissa Farnia 2, Majid Marjani 1, Fatemeh-Maryam
NON-TUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIAL (NTM) INFECTIONS ISOLATED FROM BIRMINGHAM HEARTLANDS HOSPITAL: A CASE NOTES REVIEW.
 NON-TUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIAL (NTM) INFECTIONS ISOLATED FROM BIRMINGHAM HEARTLANDS HOSPITAL: A CASE NOTES REVIEW. K. Clay 1, K. Bhatt 1, D. Burns 1, J. Evans 2, S. Gardiner 2, EG. Smith 2, P. Hawkey 2,
NON-TUBERCULOUS MYCOBACTERIAL (NTM) INFECTIONS ISOLATED FROM BIRMINGHAM HEARTLANDS HOSPITAL: A CASE NOTES REVIEW. K. Clay 1, K. Bhatt 1, D. Burns 1, J. Evans 2, S. Gardiner 2, EG. Smith 2, P. Hawkey 2,
Case Study 2016 Wisconsin Mycobacteriology Laboratory Network Annual Conference November 17, 2016
 Case Study 2016 Wisconsin Mycobacteriology Laboratory Network Annual Conference November 17, 2016 Raymond P. Podzorski, Ph.D, D(ABMM) St. Mary s Hospital Laboratory and Wisconsin Region SSMHealth 608-258-6393
Case Study 2016 Wisconsin Mycobacteriology Laboratory Network Annual Conference November 17, 2016 Raymond P. Podzorski, Ph.D, D(ABMM) St. Mary s Hospital Laboratory and Wisconsin Region SSMHealth 608-258-6393
Peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis secondary to Mycobacterium fortuitum
 Case Reports Peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis secondary to Mycobacterium fortuitum Paula McKenzie MD, David Sotello MD, Kunal Parekh MD, Kristen Fuhrmann PharmD, Richard Winn MD Abstract We report
Case Reports Peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis secondary to Mycobacterium fortuitum Paula McKenzie MD, David Sotello MD, Kunal Parekh MD, Kristen Fuhrmann PharmD, Richard Winn MD Abstract We report
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting
 Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting Professor Retno Wahyuningsih Professor of Medical Mycology Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis diagnosis and management in resource-limited setting Professor Retno Wahyuningsih Professor of Medical Mycology Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Universitas
How To Assess Severity and Prognosis
 How To Assess Severity and Prognosis Gregory Tino, M.D. Chief, Department of Medicine Penn Presbyterian Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
How To Assess Severity and Prognosis Gregory Tino, M.D. Chief, Department of Medicine Penn Presbyterian Medical Center Associate Professor of Medicine Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
Hyun Su Kim, MD Kyung Soo Lee, MD Won-Jung Koh, MD Kyeongman Jeon, MD Eun Ju Lee, MD Hee Kang, MD Joonghyun Ahn, PhD. Purpose: Materials and Methods:
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
 Held et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:355 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
Held et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2012, 12:355 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic aid to rule out pneumonia in adults with cough and feeling of fever. A validation study in the primary care setting
Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. Round Pneumonia. Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Problem Based Learning Session. Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days.
 Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
Problem Based Learning Session Mr Robinson is a 67 year old man. He visits the GP as he has had a cough and fever for 5 days. The GP takes a history from him and examines his chest. Over the left base
NTM Plus Case Studies
 NTM Plus Case Studies Youngmi Kim, Sr. Microbiologist MS, M(ASCP) Case 1 Referred Culture for ID & appropriate susceptibility Case 1 7/7/15: MGIT broth received DOC: 5-30-15 Source: FNA Mesenteric Mass,
NTM Plus Case Studies Youngmi Kim, Sr. Microbiologist MS, M(ASCP) Case 1 Referred Culture for ID & appropriate susceptibility Case 1 7/7/15: MGIT broth received DOC: 5-30-15 Source: FNA Mesenteric Mass,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Case Report Mycobacterium interjectum Lung Infection
 Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2013, Article ID 193830, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/193830 Case Report Mycobacterium interjectum Lung Infection M. C. Mirant-Borde, 1 S. Alvarez, 2 and M.
Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2013, Article ID 193830, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/193830 Case Report Mycobacterium interjectum Lung Infection M. C. Mirant-Borde, 1 S. Alvarez, 2 and M.
Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center
 CA-MRSA Pneumonia Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine Weill Cornell
CA-MRSA Pneumonia Michael S. Niederman, M.D. Clinical Director Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine New York Presbyterian Hospital Weill Cornell Medical Center Professor of Clinical Medicine Weill Cornell
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE
 DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
DIAGNOSIS AND MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF TB DISEASE Annie Kizilbash MD, MPH Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center Staff Physician, Texas Center for Infectious Diseases TB Nurse Case
Cavitary Pulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Infection in an Adult Patient with Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY and CARDIAC SURGERY VOL. 25 NO. 1 (56 60) 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Cavitary Pulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Infection in an Adult Patient with Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY and CARDIAC SURGERY VOL. 25 NO. 1 (56 60) 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 Cavitary Pulmonary Nontuberculous Mycobacterium Infection in an Adult Patient with Cyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
Scrofula Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Scrofula Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/20/2012 History 4 year old male with refractory cervical adenopathy Diagnosis Scrofula Additional Clinical Positive PPD skin test. Discussion Scrofula refers to tuberculous
Scrofula Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/20/2012 History 4 year old male with refractory cervical adenopathy Diagnosis Scrofula Additional Clinical Positive PPD skin test. Discussion Scrofula refers to tuberculous
General History. 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : ~ Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious 5 minutes in the morning.
 General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
